Abstract
Alpha2-plasmin inhibitor (α2PI) has a heterogeneous structure due to proteolytic cleavages in the circulation. The C-terminally cleaved form loses the plasminogen binding site and is, therefore, a slow plasmin inhibitor (NPB-α2PI). As FXIII primarily crosslinks the plasminogen-binding intact form (PB-α2PI) to fibrin, the effect of NPB-α2PI on fibrinolysis has been less studied. Herein, we investigated the effect of C-terminal truncation. Total-, PB-, and NPB-α2PI antigen levels and α2PI incorporation were measured by ELISAs from samples of 80 healthy individuals. Clot lysis parameters of the same subjects were investigated using an in vitro clot lysis assay. α2PI incorporation into the clot was demonstrated by Western blotting. Clot lysis and clot structure were also analyzed using an α2PI-deficient plasma substituted with recombinant PB- and NPB-α2PI. Both plasma and clot-bound levels of total- and NPB-α2PI showed a significant positive correlation with clot lysis parameters. NPB-α2PI was detected in the clot due to non-covalent binding. Regardless of the type of binding, both forms affected the clot structure by increasing the thickness of the fibrin fibers and reducing the pore size. In conclusion, we found that NPB-α2PI can bind non-covalently to fibrin, and this binding contributes to changes in clot structure and inhibition of fibrinolysis.
1. Introduction
Alpha2-plasmin inhibitor (α2PI, also named as α2-antiplasmin), the major physiological inhibitor of plasmin, has an important role in the fibrinolytic system by controlling plasmin activity [1]. Congenital deficiency of α2PI leads to severe hemorrhagic disorder due to increased predisposition to fibrinolysis [2]. Elevated fibrinogen and reduced fibrinolysis were demonstrated as risk factors for venous and arterial thrombotic events in clinical studies [3,4,5,6,7].
α2PI is a ≈67 kDa single-chain glycoprotein consisting of 464 amino acids, primarily synthesized by the liver. The human plasma concentration was estimated to be 1 µM [8]. It belongs to the serine protease inhibitor family (serpin) and has a dual function in plasmin inhibition. By forming an irreversible, plasmin–α2–antiplasmin complex (PAP-complex), the function of plasmin is inhibited, and therefore, the dissolution of the fibrin clot becomes slower. This process goes in two steps. First, the C-terminus of α2PI reversibly interacts with the plasmin(ogen) Lys-binding sites. In the second step, a covalent bond is formed between the reactive site of α2PI and the active site of plasmin [9]. Another method of clot stabilization is achieved by FXIII-mediated covalent binding of α2PI to fibrin Aα chains in the formation of fibrin mesh [10]. This cross-linking is responsible for the antifibrinolytic effect of FXIII, not the cross-linking of γ-chains [11]. It has been shown that α2PI can also bind to fibrin noncovalently, which may contribute to the formation of crosslinking by the proper orientation of the crosslinking sites [12].
Alpha2-plasmin inhibitor in the plasma undergoes proteolytic cleavages, resulting in four plasmatic forms. The full-length form (Met-α2PI) is truncated on the N-terminus between Pro12 and Asn13 amino acids by the fibroblast activation protein (sFAP, also called antiplasmin cleaving enzyme (APCE)), resulting in a 452 amino acid variant (Asn-α2PI) [13,14], which accounts for approximately 70% of α2PI in the normal human plasma [15]. Asn-α2PI is a better substrate for the active FXIII. Thus, it is cross-linked 13 times faster to fibrin than the full-length form (Met1-α2PI) [13]. In contrast to other serpins, α2PI has a C-terminal extension, which contains a number of Lys residues and binds to Lys-binding kringles of plasmin(ogen), increasing the inhibitory efficiency of α2PI [16,17]. In the circulation, α2PI could also be modified on the C-terminus. The C-terminally intact form can bind with plasmin(ogen) (PB-α2PI, plasminogen binding variant), while the truncated form loses the plasminogen binding site (NPB-α2PI, non-plasminogen binding variant). NPB-α2PI is a much less potent inhibitor of plasmin, and the binding of α2PI to fibrin by activated FXIII primarily involves the PB form [18,19,20]. A C-terminal cleavage site was demonstrated at Gln421-Asp422, but other potential cleavage sites were also suggested. The protease(s) responsible for C-terminal modification have not yet been determined. The amount of NPB-α2PI in the plasma of healthy controls was reported to be ≈35% [21]. There is a limited amount of information available on the C-terminal proteolytic variations of α2PI in different pathological conditions. A decreased level of full-length and unaltered C-terminally truncated percentage of α2PI was reported in male myocardial infarction survivors at least two months after the acute event [22]. In our previous study, total-α2PI levels proved to be elevated in patients with venous thromboembolism, and the elevation is caused by the elevation of NPB-α2PI levels with no significant change in PB-α2PI levels, compared to healthy controls. Elevated NPB-α2PI levels are independently associated with VTE risk (OR: 9.868; CI: 4.095- 23.783) [5].
During blood clot formation, several proteins, apart from α2PI, can bind to fibrin and affect the structure of the fibrin network, such as actin, albumin, α1-antitrypsin, carboxypeptidase N, coagulation factor XIII, lipoprotein(a), fibronectin, plasminogen, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI), thrombospondin, and tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) [23], and the final network structure is highly responsive to the presence of these proteins [24].
The present study aimed to investigate the consequence of C-terminal truncation on the incorporation of α2PI into the fibrin clot and its association with clot lysis and clot structure. We measured total, PB-, and NPB-α2PI levels in the plasmas of healthy individuals and in clots prepared from the same plasmas. The correlation between the measured α2PI levels and the lysis time of the clots prepared from the plasmas was also examined. The clot lysis and clot structure were also analyzed using an α2PI-deficient plasma substituted with recombinant PB- and NPB-α2PI.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Total-α2PI from human plasma was purified by affinity chromatography using the same monoclonal anti-α2PI antibody that was used in the total-α2PI ELISA. PB-α2PI was extracted from the total α2PI preparation by plasminogen sepharose affinity chromatography to obtain NPB-α2PI. Recombinant proteins were purchased from Sino Biological (Beijing, China): the full-length form of Human Serpin F2 Protein (Full-length α2PI (PB-α2PI)1-464 aa) and the C terminally truncated Human Serpin F2 Protein (1-437 aa). Alpha-2-Antiplasmin Deficient Plasma was purchased from Affinity Biologicals (Affinity Biologicals, ON, Canada). Thrombin from human plasma was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Innovin (Siemens, Marburg, Germany) was used as a human tissue factor, and Actilyse (Boehringer Ingelheim International, Germany) as rt-PA. For measuring clot lysis time, samples were added to Greiner 96-well half-area microtiter plates (Greiner Bio-one, Kremsmünster, Austria). Absorbance was measured by a Tecan Infinite 200 spectrophotometer (TECAN Trading AG, Männedorf, Switzerland). Investigation of clot structure was performed in an Ibidi µ-Slide VI slide (ibidi GmbH, Gräfelfing, Germany). Fibrinogen from human plasma (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was labeled with an Alexa-Fluor 647 (AF647) (Life Technologies, Waltham, MA, USA) in our laboratory.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Samples
Eighty plasma samples from healthy individuals were randomly selected from the sample pool of our previous study on the effect of α2-plasmin inhibitor heterogeneity on the risk of venous thromboembolism [5]. All chronic diseases except for moderate hypertension (blood pressure between 145/90 and 165/95 mmHg) and any acute illness in the previous 3 weeks were considered as exclusion criteria for healthy controls. Blood was taken from the antecubital vein into vacutainer tubes (Beckton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) containing 1/10 volume of 0.109 M citrate between 8 am and 11 am. Plasma was separated by centrifugation at 1500× g for 20 min, and aliquots were stored at −70 °C until measurements. All enrolled individuals gave written informed consent. The study fully complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was obtained from the Regional Ethics Committee at the University of Debrecen, Hungary (ETT TUKEB: 54005-3/2016/EKU).
2.2.2. α2PI Measurements
The total-α2PI antigen concentration was measured by an in-house sandwich ELISA, as previously described [25]. This assay measures all plasmatic forms of α2PI and is not influenced by the presence of plasmin–antiplasmin complexes (reference range of plasma α2PI: 48–85 mg/L). PB-α2PI concentration was measured by an in-house sandwich ELISA, as previously described [5]. NPB-α2PI was calculated by subtraction of PB-α2PI from the total-α2PI.
2.2.3. Investigation of α2PI Incorporation into the Plasma Clot
Healthy plasma samples (n = 80) were clotted by adding 2 U/mL thrombin and 20 mM CaCl2. After incubation at 37 °C for 30 min, serum samples, derived from the extrusion of fluid after plasma clotting, were separated by centrifugation (16,100× g, 5 min). Total-, PB-, and NPB-α2PI antigen levels were measured from the original plasma samples and from the obtained serum samples using the ELISA assays as described above. Values measured in the serum were multiplied by the dilution factor (1.11) caused by the addition of the coagulation activation mix. Incorporated α2PI forms were calculated by subtracting the amount of α2PI measured in the serum from the corresponding value measured in the plasma.
α2PI incorporation into the clot was also investigated by Western blot. Three randomly selected samples were clotted as above in the presence or absence of 2 mM iodoacetamide (IAA). After intensive washing with 20 × 500 μL PBS, pH 7.2, containing 3 mg/mL IAA, clots were dissolved in Laemmli buffer containing 5% mercaptoethanol and 8 M urea at room temperature for 20 h and analyzed by SDS-PAGE on 7.5% polyacrylamide gels. Proteins transferred to the PVDF membrane (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) were immunostained with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled polyclonal anti-α2PI antibody (GA2AP-AP, Affinity Biologicals, ON, Canada) or monoclonal anti-PB-α2PI antibody (Monoclonal-anti-α2AP 3AP antibody, Technoclone, Vienna, Austria), followed with anti-mouse IgG-HRPO (Southern Biotech, Birmingham, AL, USA) and ECL chemiluminescent reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used for detection.
2.2.4. Clot Lysis Assays (CLA)
An in vitro clot lysis assay was performed on 80 normal plasma samples, as previously described [26]. The time needed to reach 50% clot lysis (CLT50) was defined as the time from the midpoint of the clear-to-maximum-turbid transition, which represents clot formation, to the midpoint of the maximum-turbid-to-clear transition, representing the clot lysis.
To investigate the effect of recombinant full-length and C-terminally truncated α2PI on clot lysis, a modified clot lysis assay was performed. Alpha-2-antiplasmin-deficient plasma was substituted with different recombinant α2PI proteins. The activation mix for clot formation contained 1 U/mL thrombin and 1 mM CaCl2 in HEPES buffer (10 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween 20, pH 7.4). Plasma mix contained 1.3 times diluted plasma, 100 × diluted Innovin, and 130 ng/mL rt-PA (in HEPES buffer). 50 µL/well plasma mix and 25 µL/well activator mix were pipetted into 96-well microtiter plates. Absorbance was measured by a Tecan Infinite 200 spectrophotometer immediately after mixing at 340 nm, every 1 min, for 72 min at 37 °C. Shiny App software (Simple clot lysis analysis app version 0.3.1) was used to fit the turbidimetry curves of fibrin formation and lysis and determine different parameters of the curve, such as the maximum clot amplitude/absorbance (MaxAbs), 50% clot lysis time (CLT50, time from 50% maximum absorbance to 50% lysis), and area under the curve (AUC).
2.2.5. Clot Structure Analysis with Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
Alpha-2-antiplasmin-deficient plasma supplemented with different recombinant α2PI forms was also substituted with AF647-labeled fibrinogen to obtain a 2% labeled fibrinogen fraction. Clot formation was induced by adding 50 µL activation mix containing 0.5 U/mL thrombin and 10 mM CaCl2 in TRIS/HCl buffer (0.05M TRIS, 0.1 M NaCl, pH 7.5) to 50 µL plasma. Forty µL samples were loaded immediately into channels of an Ibidi µ-Slide VI and incubated in the dark for two hours at room temperature in a wet chamber. Wells on both sides of the channel were filled with TRIS/HCl buffer. On one side, a 2.5 mL syringe was plugged into the well and filled up with TRIS/HCl buffer to 2 mL. Clots were washed for 2 h and investigated with an Olympus FluoView 3000 confocal microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan, objective lens (UPLFLN 40× dry (refractive index = 1.0, working distance = 0.51 mm, numerical aperture (NA) was 0.75 and pinhole was 280 µm))). The total thickness of the Z-stack measured 42 µm, with a Z-stack size of 2.0 µm, resulting in a total of 22 Z-slices. For confocal image analysis of the clot structures, an open-source software, Fiji (version 2.3) (Fiji Is Just ImageJ), was used. To determine the pore size of the clots, the average radius of bubbles that can fit into the 2D pores and produce maximum coverage of the entire 2D image was calculated; the procedure employed was based on the source code developed by Münster et al. [27]. The fiber width was calculated using a MATLAB (R2019a) GUI called CT-FIRE v3.0 beta (Curvelet Transform—Fiber Extraction) [28]. Twenty-two images (1024 × 1024 pixels) of each slide were recorded in the same positions in a Z-stack. Different parameters (% area covered, pore-size (average radius of bubbles), fiber width) were calculated from the 22 evaluated images and expressed as mean ± SD [29,30].
2.2.6. Other Laboratory Methods
FXIII activity was measured by an ammonia release assay [31] using the Technochrom FXIII chromogenic assay (Technoclone, Vienna, Austria). FXIII-A2B2 antigen was determined by sandwich ELISA, as described earlier [32]. Fibrinogen concentration was measured using the Clauss method. Plasminogen was measured using the Berichrom Plasminogen assay (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics GmbH, Marburg, Germany) on the BCS XP Coagulation System.
2.3. Statistical Methods
A correlation sample size calculator was used to calculate the required sample size. The required sample size is N = 80 to establish a statistically significant correlation of r > 0.300 at alpha = 0.05 and beta = 0.2. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used for the distribution of the data. Data are presented as mean ± SD or median (interquartile range) depending on the distribution. To investigate the correlation of α2PI levels with the incorporation of different α2PI forms into the plasma clot and different clot lysis parameters, bivariate (Pearson) correlation analyses were performed. For this analysis, non-normally distributed variables were naturally log-transformed to achieve normal distribution. An independent sample t-test was used to test differences in means of different clot lysis and clot structure parameters of plasma samples supplemented with recombinant α2PI. The level of significance was 95% (p < 0.05). Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (SPSS 28.0 for Macintosh, Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Levels of Different Parameters in the Study Population
The role of NPB-α2PI in the regulation of fibrinolysis has not been previously investigated thoroughly. In this study, we intend to investigate how different α2PI forms influence clot lysis and clot structure. We randomly selected 80 plasmas from the healthy volunteers’ sample pool of our previous study [5] for the investigations. Characteristics of the study population are presented in Table 1. Each of the examined plasma parameters was in the reference range.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the study population (n = 80).
We found a robust correlation (r = 0.928, p < 0.001) between FXIII activity and antigen values (Supplementary Figure S1) and a strong correlation between α2PI activity and PB-α2PI antigen levels (r = 0.750, p < 0.001), as well as total-α2PI antigen levels (r = 0.691, p < 0.001). However, the correlation between α2PI activity and NPB-α2PI antigen levels was moderate (r = 0.325, p = 0.005) (Supplementary Figure S2).
3.2. Incorporation of α2PI Forms into the Plasma Clot
After clotting the plasma samples, we determined the clot-bound amounts of total-, PB-, and NPB-α2PI. Results are shown in Table 2. According to our calculation, 44.33 ± 6.3 percent of total-α2PI remained in the clot after centrifugation of the extruded serum, 57,8% of which was PB-α2PI. Compared to its original plasma level, a higher amount of NPB-α2PI was incorporated into the clot than PB-α2PI (58,07% vs. 37.62%, respectively). The incorporation of PB-α2PI showed a significant correlation with FXIII activity (r = 0.540, p < 0.001), fibrinogen level (r = 0.387, p < 0.001), and plasminogen level (r = 0.407, p < 0.001). The incorporation of NPB-α2PI did not show significant correlation with FXIII activity (r = 0.110, p = 0.331) and fibrinogen level (r = 0.086, p = 0.446), but correlated with plasminogen level (r = 0.322, p = 0.004).

Table 2.
α2PI amounts incorporated into the plasma clot and clot lysis parameters (n = 80).
3.3. Correlation of Different Parameters with Clot Lysis
The same plasma samples were also analyzed using a clot lysis assay, and clot formation and lysis were characterized based on CLT50, MaxAbs, and AUC values calculated during the analysis of turbidimetric curves. Correlations between parameters with a potential modifying effect on clot lysis (FXIII antigen and activity, fibrinogen, plasminogen, different forms of α2PI, and incorporated amount of α2PI forms) and parameters of clot lysis are shown in Table 3. The elevation of FXIII antigen and activity had a positive effect on MaxAbs and AUC, while they did not affect CLT50. The fibrinogen level only correlated with MaxAbs. The total-α2PI plasma level showed a statistically significant, positive correlation with all three lysis curve parameters. However, among the α2PI C terminal forms, this relationship was only observed in the case of NPB-α2PI. The plasma PB-α2PI/NPB-α2PI ratio showed a significant negative correlation with CLT50 and AUC (Supplementary Figure S3).

Table 3.
Correlation of FXIII activity, FXIII antigen, fibrinogen, plasminogen, different forms of α2PI in plasma, and clot-bound α2PI forms with clot lysis curve parameters (CLT50, MaxAbs, and AUC) (n = 80).
Interestingly, both plasma NPB-α2PI and incorporated NPB-α2PI antigen levels showed a statistically significant, positive correlation with CLT50, MaxAbs, and AUC, while for PB-α2PI, only the incorporated form correlated with MaxAbs (Figure 1A–C, Supplementary Figure S4).
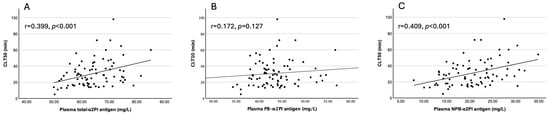
Figure 1.
Correlation of plasma (A) total-α2PI, (B) PB-α2PI, and (C) NPB-α2PI levels with CLT50 (n = 80).
3.4. Investigation of α2PI Incorporation into the Clot by Western Blot
To investigate how α2PI forms incorporate into the clot, normal plasma samples (N = 3) were clotted and analyzed as described in Section 2.2.3. Polyclonal anti-α2PI antibody was used to detect all α2PI forms incorporated into the clot (Figure 2A). To localize the PB-α2PI form, a monoclonal antibody specific to PB-α2PI was used (Figure 2B). The α2PI crosslinked to the fibrin α-chain and α-polymers can be seen after both stainings, while the reaction corresponding to the monomer α2PI (noncovalently attached) can be seen only if the polyclonal antibody was used for detection. In the presence of IAA, FXIII was inhibited. Therefore, the covalent binding did not occur, and only the monomer α2PI could be detected. This noncovalently bound α2PI is supposedly the NPB-α2PI form, as it did not react with the PB-α2PI-specific antibody.
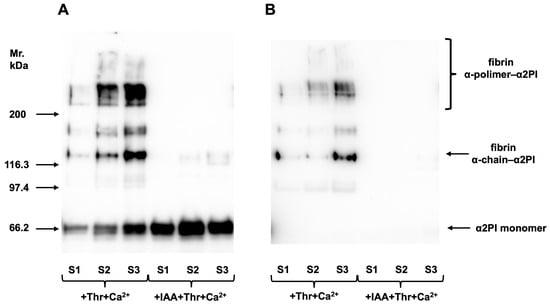
Figure 2.
Three randomly selected control samples (S1–3) were clotted by adding thrombin and Ca2+, and after intensive washing, α2PI incorporated into the clot was investigated by Western blot. Polyclonal anti-α2PI antibody was used to detect all forms of bound α2PI (A), and a monoclonal anti-PB-α2PI specific antibody to detect the localization of the PB-α2PI form (B). Covalent binding of α2PI to fibrin α-chain and α-polymers can be seen after both staining, while the reaction corresponding to the monomer α2PI (noncovalently attached) can be seen only if the polyclonal antibody was used. In the presence of iodoacetamide, FXIII was inhibited. Therefore, the covalent binding did not occur, and only the monomer α2PI could be detected. Original images can be found in Supplementary Materials.
3.5. Investigation of Clot Lysis and Fibrin Structure Using Artificial Plasma Samples
Our results showed that the PB-α2PI and NPB-α2PI levels correlated with the clot lysis parameters and both could be incorporated into the clot, albeit in different ways (Table 2, Figure 2). However, the heterogeneity of the N-terminal end of α2PI and variations in other influencing factors in real plasma samples make it difficult to detect true differences due to the C terminal truncation of α2PI. Therefore, next, we prepared plasma samples that differed only in the amount/ratio of the C-terminal forms of α2PI. α2PI-deficient plasma was supplemented with recombinant Met-PB- and/or Met-NPB-α2PI in different amounts, and a clot lysis assay was performed. Lysis time increased in the presence of both plasminogen-binding and non-binding forms of α2PI compared to the deficient plasma. Representative lysis curves are shown in Figure 3A. CLT50 was increased by 80% in the presence of 100% PB form (65 mg/L) and by 30% in the presence of 100% NPB-α2PI form (65 mg/L) compared to the α2PI-deficient plasma (Figure 3B). Next, we examined the effect of increasing NPB-α2PI on the lysis time while maintaining a constant amount of PB-α2PI form correspondingly close to the average normal plasma concentration (Figure 4). In parallel with the increase in the proportion of NPB-α2PI form, the lysis time increased, albeit slightly, but was statistically significantly (Figure 4). The highest amount of NPB-α2PI (when the PB-α2PI: NPB-α2PI ratio was 46:54%) caused a 21% elevation of CLT50 compared to the PB-α2PI: NPB-α2PI ratio of 73:27.
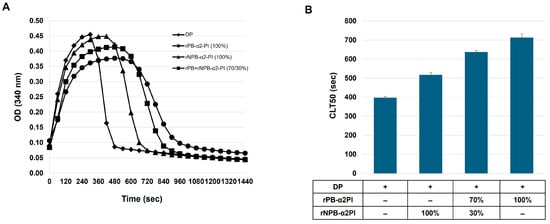
Figure 3.
Effect of α2PI forms on clot lysis time. α2PI-deficient plasma was supplemented with recombinant PB- and/or NPB-α2PI; 100% corresponded to the estimated normal plasma concentration of α2PI (65 mg/L). (A) Clot lysis curves; (B) CLT50 values presented as mean ± SD values of 3 parallel measurements.
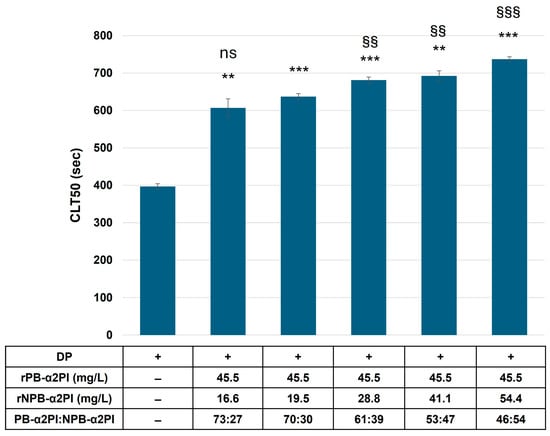
Figure 4.
Effect of elevated NPB-α2PI on clot lysis time. α2PI-deficient plasma was substituted with an equal amount of recombinant PB-α2PI and an increasing amount of recombinant NPB-α2PI. CLT50 values are presented as mean ± SD values of 3 parallel measurements. ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 comparing to α2PI deficient plasma; ns non-significant, §§ p < 0.01 and §§§ p < 0.001 comparing to 70:30 PB-α2PI:NPB-α2PI ratio.
Next, we clotted α2PI-deficient plasma supplemented with AF647-labeled fibrinogen and recombinant Met-PB- and/or Met-NPB-α2PI in different amounts, and the structural architecture of the clot was analyzed with confocal laser scanning microscopy. Figure 5A demonstrates the effect of different ratios of α2PI forms on the fibrin structure in the clot. For quantitative analysis, we determined the percentage of area coverage, pore size, and width of the fibrin fibers (the original images (n = 22) from each channel are shown in Supplementary Figure S5a–d).
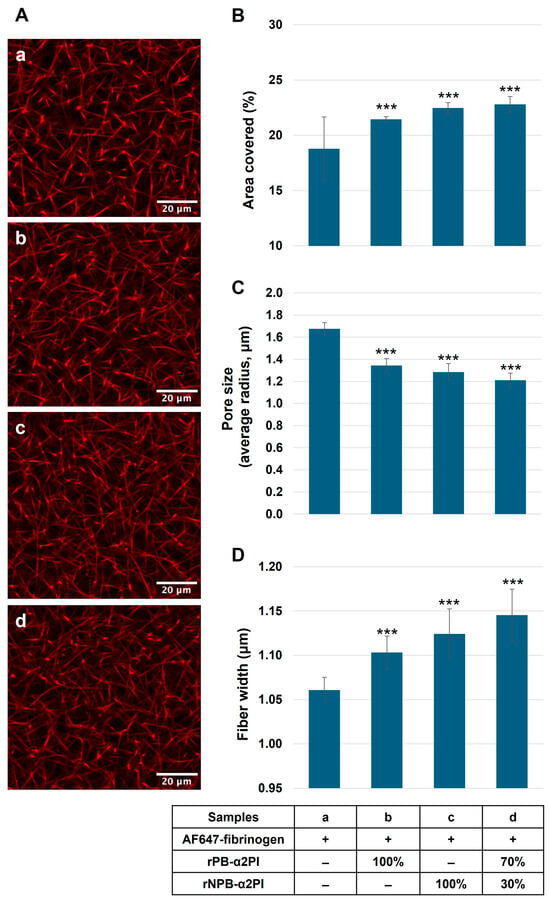
Figure 5.
α2PI-deficient plasma supplemented with AF647-labelled fibrinogen, and different amounts of recombinant PB- and/or NPB-α2PI forms were clotted (samples a–d). And the washed clot was analyzed with confocal laser scanning microscopy (A). The percentage of area coverage was determined by Fiji software; pore size and the width of the fibrin fibers were calculated using a MATLAB (R2019a) GUI called CT-FIRE v3.0 beta (curvelet transform–fiber extraction). In the presence of PB and/or NPB forms, area coverage was significantly increased (B), pore size decreased (C), and thicker fibrin fibers evolved (D), therefore becoming a denser fibrin network in clots supplemented with rα2PI compared to the α2PI-deficient clot. 100% α2PI = 65 mg/L *** p < 0.001 comparing to α2PI deficient plasma, n = 22.
The covered area significantly increased in the presence of PB and/or NPB forms (Figure 5B). The pore size decreased (Figure 5C), and thicker fibrin fibers evolved (Figure 5D) in clots supplemented with rα2PI compared to the α2PI-deficient clot. The greatest difference compared to deficient plasma resulted when both forms were present in proportions like those described in normal plasma.
4. Discussion
α2PI undergoes proteolytic cleavages in the circulation, which have functional consequences. N-terminal cleavage by sFAP, which results in faster cross-linking to fibrin by FXIII, has been studied extensively. However, the extent and impact of C-terminal cleavage are less well-understood. C-terminal cleavage may affect the efficiency of plasmin inhibition, the degree and type of α2PI incorporation into the clot, and the structure of the clot. In this study, we provided new data on the effect of plasma levels and relative ratios of C terminally intact and truncated α2PI forms on their incorporation into clots, their influence on clot structure, and clot lysis. By measuring α2PI activity and antigen levels in parallel, we confirmed the previous assumption that activity measurement only shows a strong correlation with the concentration of the PB-α2PI form and is weakly influenced by the amount of the NPB form and is not influenced by the relative ratio of the two forms in the plasma (Supplementary Figure S2) [5,22]. Previously reported results on α2PI incorporation into plasma clots were largely influenced by the methodologies used. A Laurell assay showed a reduction of 18 ± 9% (n = 12) in total-α2PI antigen in serum compared to plasma, while the immediate plasmin inhibition test revealed a 35 ± 6% reduction in inhibition [19]. By measuring the α2PI activity, a 32.3% difference was reported between the plasma and serum levels of 65 blood donors [33]. By using an ELISA method to measure the total-α2PI in 6M urea solubilized clots, only a small fraction of α2PI, 1.35 ± 0.18 mg/L out of 83.2 ± 15.4 mg/L, was detected as a clot-bound fraction [34]. The method developed by Uitte de Willige et al. that measured the ratio of fluorescently labeled α2PI-specific antibody incorporation into the plasma clot amounted to 39 ± 4.9% crosslinking in clots prepared from citrated plasma from five healthy donors. They assumed that 90% of this amount was cross-linked, as they could only detect 3.9 ± 0.5% in the presence of FXIII inhibitor [35]. These results indicate that no method has been developed to date that can accurately detect the amount of cross-linked and non-covalently bound α2PI, as well as their ratio, in the clot. In our study, we determined the total-, PB-, and NPB-α2PI antigen levels parallel in plasma and serum samples of 80 healthy individuals, and incorporated amounts were calculated from the respective plasma and serum samples. The PB: NPB ratio in the plasma was 2.1 (1.75–2.57), which is in good agreement with the ratio of 2.2 (1.8–2.7) determined using the crossed immunoelectrophoresis technique with the addition of Lys-plasminogen to the first dimension gel [36]. Our results showed that 44.3 ± 6.3% of the total α2PI remained in the clot after serum removal, which is higher than the generally cited value of approximately 30%. The PB: NPB ratio in the clot was 1.37, which shows that a significant amount of NPB is bound to the clot, in a higher proportion than the PB form when compared to their original plasma levels. Western blot analysis of the extensively washed clots showed that FXIII crosslinks the PB form to fibrin, and this form cannot be detected in the clot in a non-covalently bound form. This confirms the previous results of Kluft et al. [19]. Non-crosslinked α2PI monomer was also visible on the blot when FXIII activity was inhibited. This form is presumably the NPB form, as the PB-specific antibody did not react with it (Figure 2). Consistent with this result, plasma FXIII levels showed a significant correlation with the incorporation of the PB form (Table 3) and not with the NPB form. It has previously been shown that the cross-linking of the PB form by FXIII is essential for preventing premature clot dissolution. Therefore, it was surprising to us that neither the plasma levels of FXIII nor the PB-form showed a significant correlation with the lysis time, but they did show a positive correlation with the MaxAbs. In contrast, both the plasma level and the incorporated amount of NPB form, which is a slow plasmin inhibitor, showed a significant correlation with all three clot lysis parameters. To further investigate this effect, we supplemented α2PI-deficient plasma with full-length and/or C terminally truncated recombinant α2PI and examined the effect of supplementation on clot lysis and clot structure. The NPB form, although to a much lesser extent than the PB form, was able to extend the lysis time, and if increasing amounts of the NPB form were added to a constant amount of PB form corresponding to approximately normal plasma levels, further prolongation was observed. Both forms of α2PI affected the clot structure, increasing the thickness of fibrin fibers and reducing the pore size. Because the two forms bind to fibrin by different mechanisms, we were able to detect the greatest effect when both forms were present in proportions like those in normal plasma, rather than when only one form was present, albeit at a 100% normal plasma concentration. Mechanisms that determine fibrin structure are not yet fully understood. However, numerous studies have reported alterations in fibrin structure associated with various thrombotic conditions. In several studies, reduced pore size, formation of thinner fibrin fibers, and reduced permeability have been linked to decreased fibrinolytic capacity and increased risk of thrombosis. Conversely, other studies report the formation of thicker fibrin fibers along with increased lysis time and reduced permeability [37]. These latter findings support our results. However, in our case, the impact of clot structural changes on fibrinolysis caused by the binding of α2PI to fibrin cannot be separated from direct plasmin inhibition. It can be assumed that both mechanisms contribute to the reduction of the overall fibrinolytic capacity. Figure 6 summarizes the putative mechanisms through which α2PI C-terminal variants influence fibrin properties.
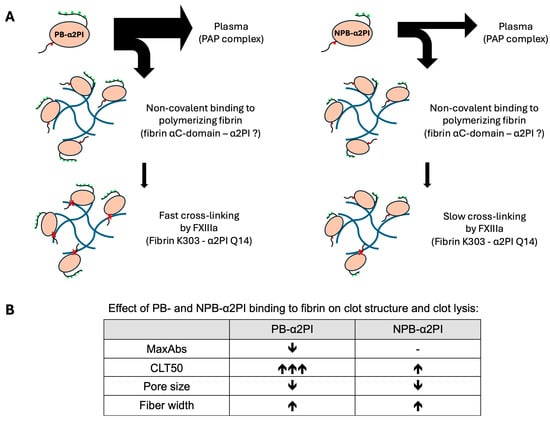
Figure 6.
Putative mechanisms through which PB- and NPB-α2PI influence fibrin properties and clot lysis. (A) Binding of PB- and NPB-α2PI to fibrin: A higher amount of PB-α2PI is bound to the clot than NPB-α2PI. However, the amount of the fibrin-bound fraction relative to the original plasma concentration is lower for the PB variant compared to the NPB variant. (The thickness of the arrows reflects the concentration ratios detected in our experiments.). The site for the non-covalent interaction with fibrin is unknown in the α2PI molecule but is most likely different from the C-terminal part, as the interaction is Lys-independent [12]. When activated FXIII (FXIIIa) is present in sufficient quantities, PB-α2PI is rapidly cross-linked to fibrin and can no longer be detected in the clot in a non-covalently bound monomeric form. Conversely, NPB-α2PI is a less efficient substrate for FXIII, allowing it to be present in greater amounts in a non-covalently attached form within the clot. The green dots represent Lys residues in the C-terminal part of α2PI, which are important for binding to plasminogen. The red dot represents the FXIII cross-linking site (Q14), while red ‘x’ indicates covalent cross-linking. In the case of the NPB-α2PI variant, the last two Lys residues are absent, which significantly affects its interaction with plasmin, resulting in this variant being 10-times less potent as an inhibitor of plasmin [38]. (B) Effect of PB- and NPB-α2PI binding to fibrin on clot structure and clot lysis: PB-α2PI reduces the maximal clot density and significantly extends the clot lysis time in a concentration-dependent manner. In contrast, NPB-α2PI has no significant impact on clot density and only a moderate effect on lysis time. Both variants decrease pore size and increase the thickness of fibrin fibers.
Summarizing the previous literature data in line with the results of our study, it seems that the cross-linking of the fast-acting PB-α2PI form to fibrin by FXIII is crucial for preventing early fibrin mesh degradation. However, the incorporation of the PB form is limited to approximately 38% of the amount in plasma. The NPB form is non-covalently incorporated into the clot independently of FXIII activity and, although a slow plasmin inhibitor, can further enhance the inhibition of fibrinolysis, but it is not sufficient on its own to prevent early fibrinolysis.
This study should be interpreted in the context of its limitations. The study group is rather young, with a mean age of 33.2 ± 13.4 years, which could influence the generalizability of the results. The lack of reaction with the PB-α2PI-specific antibody is only indirect evidence that the PB variant is not present in the clot due to non-covalent binding to fibrin. It cannot be excluded that non-covalent binding to fibrin renders the epitope of the antibody used inaccessible.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, in our study, we found that NPB-α2PI can bind non-covalently to fibrin, and this binding contributes to changes in clot structure and inhibition of fibrinolysis. Since most previous clinical studies only examined α2PI activity, which does not reflect the plasma levels of NPB-α2PI, little is known about the amount of NPB-α2PI in different diseases. Therefore, further studies are needed to investigate the extent and effect of C terminal truncation in different pathological conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biom15081127/s1: Supplementary Figure S1. Correlation of plasma FXIII activity with FXIII antigen levels; Supplementary Figure S2. Correlation of plasma α2PI activity with total-, PB-, NPB-α2PI antigen levels, and percentage of NPB-α2PI in the plasma; Supplementary Figure S3. Correlation of plasma PB-α2PI/NPB-α2PI ratio with MaxAbs, CLT50, and AUC; Supplementary Figure S4. Correlation of incorporated total-, PB-, and NPB-α2PI antigen levels with MaxAbs, CLT50, and AUC; Confocal laser scanning microscopy images of the in vitro plasma clots.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, É.K., B.B. and R.B.; α2PI measurements, investigation of α2PI incorporation into the clot, B.B. and É.K.; performing clot lysis assay, R.O.-K. and R.B.; clot structure analysis with confocal laser scanning microscopy, R.B., D.P. and P.S.; image analysis, D.P. and Z.H.; writing—original draft preparation, R.B. and É.K.; writing—review and editing, É.K., Z.B. (Zsuzsanna Bereczky) and Z.B. (Zsuzsa Bagoly); funding acquisition, É.K. and Z.B. (Zsuzsanna Bereczky). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Research, Development and Innovation Office (NKFIH) [K120633 to É. Katona, K139293 to Zs. Bereczky], University of Debrecen Scientific Research Bridging Fund [DETKA to É. Katona], and the Hungarian Academy of Sciences [MTA-DE Lendület “Momentum” Hemostasis and Stroke Research Group, grant number LP2024-1/2024 to Z. Bagoly]. APC was funded by the University of Debrecen.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted following the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Regional Ethics Committee et the University of Debrecen (ETT TUKEB: 54005-3/2016/EKU) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| α2PI | Alpha2-plasmin inhibitor, alpha2-antiplasmin |
| APCE | Antiplasmin cleaving enzyme |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| CLT50 | 50% clot lysis time |
| DP | Deficient plasma |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FXIII | Blood coagulation factor XIII |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| IAA | Iodoacetamide |
| NPB-α2PI | Plasminogen non-binding alpha2-plasmin inhibitor |
| PAP-complex | Plasmin-α2-antiplasmin complex |
| PB-α2PI | Plasminogen-binding alpha2-plasmin inhibitor |
| sFAP | Soluble fibroblast activation protein |
| TAFI | Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor |
| t-PA | Tissue-type plasminogen activator |
References
- Wiman, B.; Hamsten, A. The fibrinolytic enzyme system and its role in the etiology of thromboembolic disease. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1990, 16, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, N.; Saito, H.; Kamiya, T.; Koie, K.; Sakata, Y.; Kobakura, M. Congenital deficiency of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor associated with severe hemorrhagic tendency. J. Clin. Investig. 1979, 63, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meltzer, M.E.; Doggen, C.J.; de Groot, P.G.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Lisman, T. Plasma levels of fibrinolytic proteins and the risk of myocardial infarction in men. Blood 2010, 116, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, M.E.; Doggen, C.J.; de Groot, P.G.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Lisman, T. The impact of the fibrinolytic system on the risk of venous and arterial thrombosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2009, 35, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barath, B.; Bogati, R.; Miklos, T.; Kallai, J.; Mezei, Z.A.; Bereczky, Z.; Muszbek, L.; Katona, E. Effect of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor heterogeneity on the risk of venous thromboembolism. Thromb. Res. 2021, 203, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszek, E.; Malinowski, K.P.; Zabczyk, M.; Butenas, S.; Undas, A. Elevated factor XIa as a modulator of plasma fibrin clot properties in coronary artery disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 53, e14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bembenek, J.P.; Niewada, M.; Siudut, J.; Plens, K.; Czlonkowska, A.; Undas, A. Fibrin clot characteristics in acute ischaemic stroke patients treated with thrombolysis: The impact on clinical outcome. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collen, D.; Wiman, B. Fast-acting plasmin inhibitor in human plasma. Blood 1978, 51, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroi, M.; Aoki, N. Isolation and characterization of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor from human plasma. A novel proteinase inhibitor which inhibits activator-induced clot lysis. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 5956–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaki, T.; Aoki, N. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin catalyzed by activated fibrin-stabilizing factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 14767–14772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrnes, J.R.; Duval, C.; Wang, Y.; Hansen, C.E.; Ahn, B.; Mooberry, M.J.; Clark, M.A.; Johnsen, J.M.; Lorf, S.T.; Lam, W.A.; et al. Factor XIIIa-dependent retention of red blood cells in clots is mediated by fibrin alpha-chain crosslinking. Blood 2015, 126, 1940–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsurupa, G.; Yakovlev, S.; McKee, P.; Medved, L. Noncovalent interaction of alpha(2)-antiplasmin with fibrin(ogen): Localization of alpha(2)-antiplasmin-binding sites. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 7643–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, K.N.; Jackson, K.W.; Christiansen, V.J.; Chung, K.H.; McKee, P.A. A novel plasma proteinase potentiates alpha2-antiplasmin inhibition of fibrin digestion. Blood 2004, 103, 3783–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.N.; Jackson, K.W.; Christiansen, V.J.; Lee, C.S.; Chun, J.G.; McKee, P.A. Antiplasmin-cleaving enzyme is a soluble form of fibroblast activation protein. Blood 2006, 107, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangert, K.; Johnsen, A.H.; Christensen, U.; Thorsen, S. Different N-terminal forms of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor in human plasma. Biochem. J. 1993, 291 Pt 2, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sasaki, T.; Morita, T.; Iwanaga, S. Identification of the plasminogen-binding site of human alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor. J. Biochem. 1986, 99, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, P.S.; Douglas, J.T.; Locher, M.; Llinas, M.; Schaller, J. Structural/functional characterization of the alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor C-terminal peptide. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluft, C.; Los, P.; Jie, A.F.; van Hinsbergh, V.W.; Vellenga, E.; Jespersen, J.; Henny, C.P. The mutual relationship between the two molecular forms of the major fibrinolysis inhibitor alpha-2-antiplasmin in blood. Blood 1986, 67, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluft, C.; Los, P.; Jie, A.F. The molecular form of alpha 2-antiplasmin with affinity for plasminogen is selectively bound to fibrin by factor XIII. Thromb. Res. 1984, 33, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiman, B.; Nilsson, T.; Cedergren, B. Studies on a form of alpha 2-antiplasmin in plasma which does not interact with the lysine-binding sites in plasminogen. Thromb. Res. 1982, 28, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul, S.; Dekkers, D.H.W.; Ariens, R.A.S.; Leebeek, F.W.G.; Rijken, D.C.; Uitte de Willige, S. On the localization of the cleavage site in human alpha-2-antiplasmin, involved in the generation of the non-plasminogen binding form. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Uitte de Willige, S.; Miedzak, M.; Carter, A.M.; Lisman, T.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Grant, P.J.; Philippou, H.; Ariëns, R.A.S. Proteolytic and genetic variation of the alpha-2-antiplasmin C-terminus in myocardial infarction. Blood 2011, 117, 6694–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisel, J.W.; Litvinov, R.I. Fibrin Formation, Structure and Properties. Subcell. Biochem. 2017, 82, 405–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Galanakis, D.K.; Lane, B.P.; Simon, S.R. Albumin modulates lateral assembly of fibrin polymers: Evidence of enhanced fine fibril formation and of unique synergism with fibrinogen. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 2389–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teraz-Orosz, A.; Csapo, A.; Bagoly, Z.; Szekely, E.G.; Toth, E.; Kovacs, B.; Bereczky, Z.; Muszbek, L.; Katona, E. A new ELISA method for the measurement of total alpha(2)-plasmin inhibitor level in human body fluids. J. Immunol. Methods 2019, 471, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orban-Kalmandi, R.; Szegedi, I.; Sarkady, F.; Fekete, I.; Fekete, K.; Vasas, N.; Berényi, E.; Csiba, L.; Zsuzsa, B. A modified in vitro clot lysis assay predicts outcomes and safety in acute ischemic stroke patients undergoing intravenous thrombolysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Munster, S.; Fabry, B. A simplified implementation of the bubble analysis of biopolymer network pores. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 2774–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bredfeldt, J.S.; Liu, Y.; Pehlke, C.A.; Conklin, M.W.; Szulczewski, J.M.; Inman, D.R.; Keely, P.J.; Nowak, R.D.; Mackie, T.R.; Eliceiri, K.W. Computational segmentation of collagen fibers from second-harmonic generation images of breast cancer. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 16007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Vries, J.J.; Laan, D.M.; Frey, F.; Koenderink, G.H.; de Maat, M.P.M. A systematic review and comparison of automated tools for quantification of fibrous networks. Acta Biomater. 2023, 157, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risman, R.A.; Belcher, H.A.; Ramanujam, R.K.; Weisel, J.W.; Hudson, N.E.; Tutwiler, V. Comprehensive Analysis of the Role of Fibrinogen and Thrombin in Clot Formation and Structure for Plasma and Purified Fibrinogen. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Karpati, L.; Penke, B.; Katona, E.; Balogh, I.; Vamosi, G.; Muszbek, L. A modified, optimized kinetic photometric assay for the determination of blood coagulation factor XIII activity in plasma. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katona, E.; Haramura, G.; Karpati, L.; Fachet, J.; Muszbek, L. A simple, quick one-step ELISA assay for the determination of complex plasma factor XIII (A2B2). Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 83, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm-Williams, S.A. Concentration of plasminogen and antiplasmin in plasma and serum. J. Clin. Pathol. 1981, 34, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Agren, A.; Jorneskog, G.; Elgue, G.; Henriksson, P.; Wallen, H.; Wiman, B. Increased incorporation of antiplasmin into the fibrin network in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2007–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uitte de Willige, S.; Malfliet, J.; Abdul, S.; Leebeek, F.W.G.; Rijken, D.C. The level of circulating fibroblast activation protein correlates with incorporation of alpha-2-antiplasmin into the fibrin clot. Thromb. Res. 2018, 166, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leebeek, F.W.G.; Los, P.; Kluft, C. A monoclonal antibody against the COOH-terminal site of alpha2-antiplasmin reveals heterogeneity in the nonplasminogen binding form of alpha2-antiplasmin. Fibrinolysis 1996, 10, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undas, A.; Ariens, R.A. Fibrin clot structure and function: A role in the pathophysiology of arterial and venous thromboembolic diseases. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, e88–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiman, B.; Almqvist, A.; Ranby, M. The Non-Covalent Interaction between Plasmin and Alpha-2-Antiplasmin. Fibrinolysis 1989, 3, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).