Circulating Biomarker Panorama in HIV-Associated Lymphoma: A Bridge from Early Risk Warning to Prognostic Stratification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiological Overview
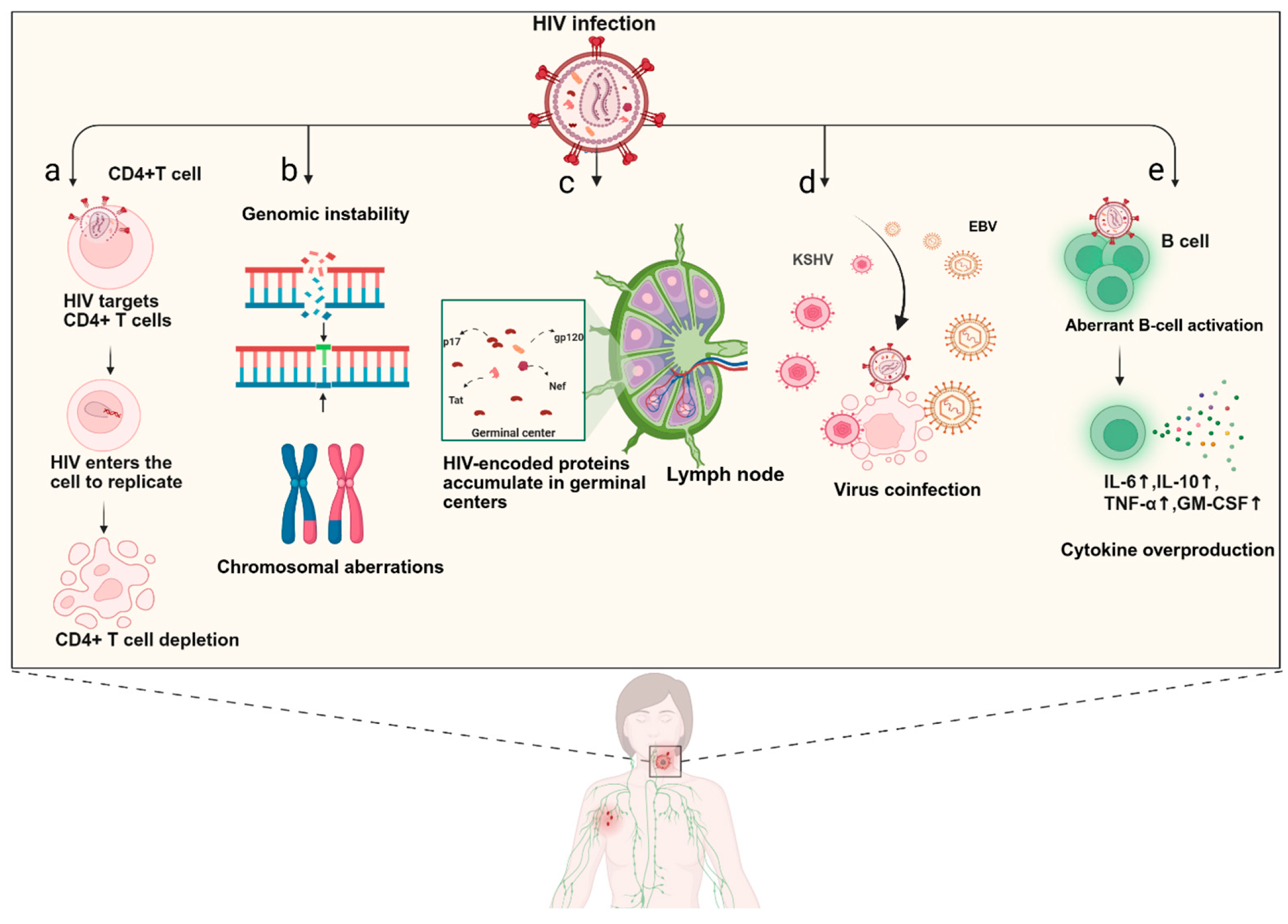
3. Pathogenesis
4. Plasma Metabolite Changes
5. Immunoinflammation-Related Biomarkers
5.1. Cytokines
5.2. Chemokines
5.3. Soluble Receptors
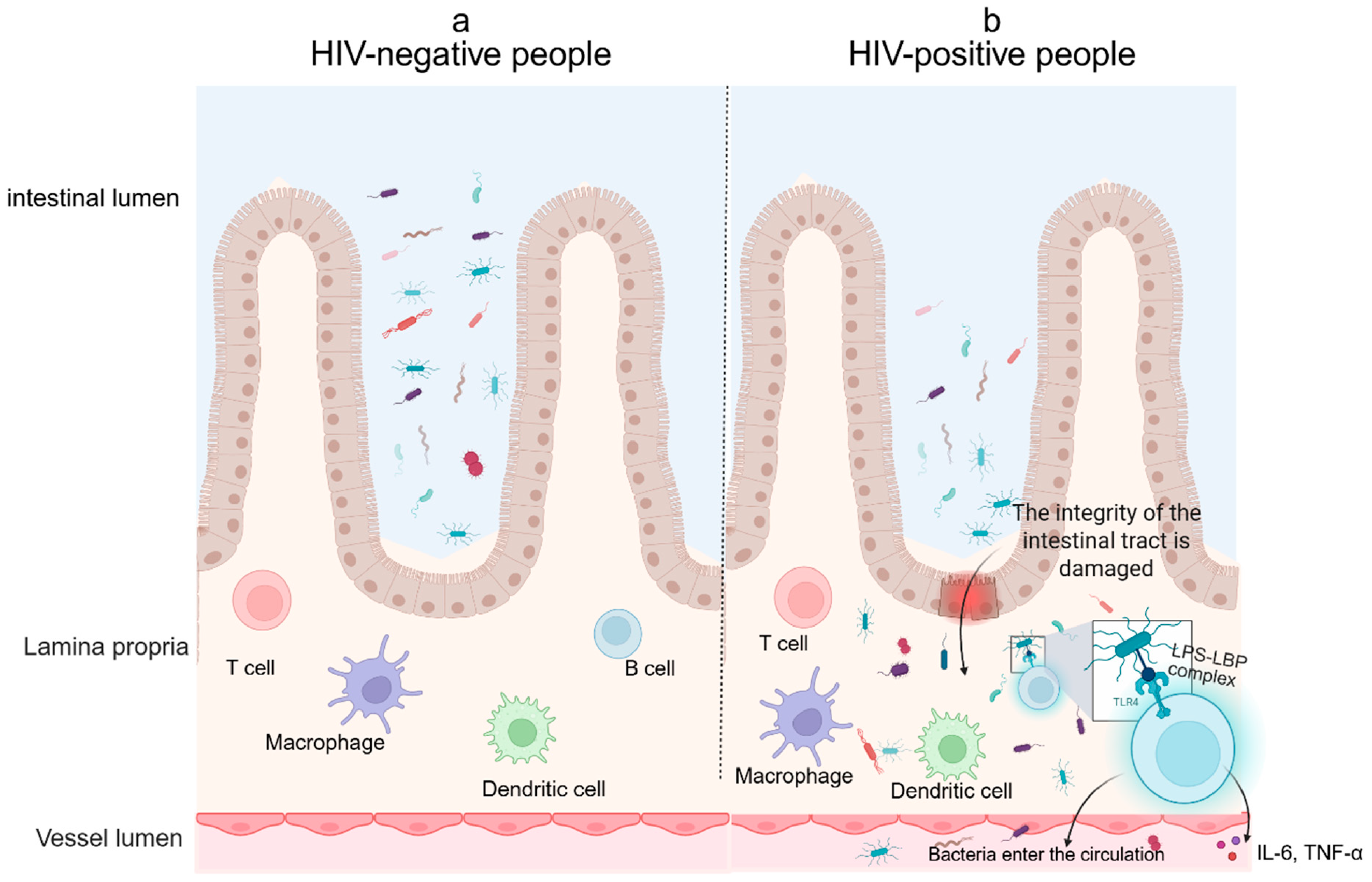
5.4. Microbial Translocation Biomarkers
6. Protein-Related Biomarkers
6.1. Immunoglobulins
6.2. PD-1 and PD-L1
6.3. Gal-1
6.4. β2-Microglobulin
6.5. Ferritin
6.6. Lactate Dehydrogenase
6.7. Other Biomarkers
7. Genetic-Related Biomarkers
7.1. MiRNAs
7.2. Circulating DNA
| Biomarker Category | Representative Biomarkers | Sample Source | Expression Trend | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNAs | miRNA SNPs miR-17 miR-21 miR-122 miR-106a miR-106b miR-223 miR-200c-3p | HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-BL cell line | Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Decreased | Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive | [193] [189] [186,187,188] [187] [189] [189] [187] [190] |
| Circulating DNA | DNA-CNAs Clonal Ig DNA cfDNA | HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients | Decreased Increased Increased | Predictive Predictive/Treatment Monitoring Predictive | [194] [204] [206] |
8. Extracellular Vesicles
9. Lymphocyte Subpopulation
9.1. CD4+ T Cells and CD4/CD8 Ratio
9.2. Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio
10. Virus-Related Biomarkers
10.1. HIV Viraemia
10.2. HIV-Encoded Proteins
10.3. EBV Viraemia
10.4. KSHV Viraemia
| Biomarker Category | Representative Biomarkers | Sample Source | Expression Trend | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV-related markers | HIV viraemia p17 p17 gene variation Tat Nef gp120 | HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients/mice HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients/mice Mice | Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased | Predictive/Prognostic Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive | [131,221,223,245,246,247,248,249,250,251] [54,264,269] [270,271,272] [54,264,269] [54,264,269] [54,264,269] |
| Other viruses | EBV viraemia KSHV viraemia | HAL patients HIV-PEL patients | Increased Increased | Predictive/Prognostic Predictive | [9,12,275,276,277,278] [279,280,281,282,283] |
11. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNAIDS. Global HIV & AIDS Statistics—Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Hernández-Ramírez, R.U.; Shiels, M.S.; Dubrow, R.; Engels, E.A. Cancer risk in HIV-infected people in the USA from 1996 to 2012: A population-based, registry-linkage study. Lancet HIV 2017, 4, e495–e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, T.M.; Morton, L.M.; Shiels, M.S.; Clarke, C.A.; Engels, E.A. Risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes in HIV-infected people during the HAART era: A population-based study. AIDS 2014, 28, 2313–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, E.P.; Engels, E.A. Cancer as a cause of death among people with AIDS in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarchoan, R.; Uldrick, T.S. HIV-Associated Cancers and Related Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; He, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Urgent Call for Attention to HIV-Associated Lymphoma: After AIDS 2024, the 25th International AIDS Conference. J. Med. Virol. 2025, 97, e70159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epeldegui, M.; Magpantay, L.; Guo, Y.; Halec, G.; Cumberland, W.G.; Yen, P.K.; Macatangay, B.; Margolick, J.B.; Rositch, A.F.; Wolinsky, S.; et al. A prospective study of serum microbial translocation biomarkers and risk of AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma. AIDS 2018, 32, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, M.A.; Rabkin, C.S.; Engels, E.A.; Busch, E.; Kopp, W.; Rager, H.; Goedert, J.J.; Chaturvedi, A.K. Markers of microbial translocation and risk of AIDS-related lymphoma. AIDS 2013, 27, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabkin, C.S.; Engels, E.A.; Landgren, O.; Schuurman, R.; Camargo, M.C.; Pfeiffer, R.; Goedert, J.J. Circulating cytokine levels, Epstein-Barr viremia, and risk of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2011, 86, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. HIV associated lymphoma: Latest updates from 2023 ASH annual meeting. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, S.K.; Samuel, M.S.; Xue, X.; Wang, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Mounier, N.; Ribera, J.M.; Spina, M.; Tirelli, U.; Weiss, R.; et al. Changes in the influence of lymphoma- and HIV-specific factors on outcomes in AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunleavy, K.; Little, R.F.; Pittaluga, S.; Grant, N.; Wayne, A.S.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Steinberg, S.M.; Yarchoan, R.; Jaffe, E.S.; Wilson, W.H. The role of tumor histogenesis, FDG-PET, and short-course EPOCH with dose-dense rituximab (SC-EPOCH-RR) in HIV-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2010, 115, 3017–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Kang, Z.; Qin, S.; Ruan, G.; Zhao, H.; Tao, X.; Xie, Z.; Peng, J. A promising prognostic model for predicting survival of patients with HIV-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the cART era. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 12470–12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Lei, H.; Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Min, H.; et al. A Visual Nomogram Survival Prediction Model in Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)-Related Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Med. Virol. 2025, 97, e70359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HIV.pdf. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/hiv.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Vaccher, E.; Chadburn, A.; Gloghini, A.; Antinori, A.; Bower, M.; Carbone, A. Lymphomas included in the AIDS case definition: An update 30 years later. Lancet HIV 2023, 10, e635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Naeeb, A.B.; Ajithkumar, T.; Behan, S.; Hodson, D.J. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. BMJ 2018, 362, k3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, J.J.; Coté, T.R.; Virgo, P.; Scoppa, S.M.; Kingma, D.W.; Gail, M.H.; Jaffe, E.S.; Biggar, R.J. Spectrum of AIDS-associated malignant disorders. Lancet 1998, 351, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coté, T.R.; Biggar, R.J.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Devesa, S.S.; Percy, C.; Yellin, F.J.; Lemp, G.; Hardy, C.; Geodert, J.J.; Blattner, W.A. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma among people with AIDS: Incidence, presentation and public health burden. AIDS/Cancer Study Group. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 73, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, P.; Cheng, M.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Ye, Y.; Shuai, P.; et al. Estimates of the global burden of non-Hodgkin lymphoma attributable to HIV: A population attributable modeling study. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 67, 102370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, S.M.; Painschab, M.S.; Horner, M.J.; Muchengeti, M.; Fedoriw, Y.; Shiels, M.S.; Gopal, S. Epidemiology of haematological malignancies in people living with HIV. Lancet HIV 2020, 7, e641–e651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, T.; Inaba, Y.; Kawasaki, Y.; Tsukada, K.; Teruya, K.; Kikuchi, Y.; Gatanaga, H.; Oka, S. Mortality and causes of death in people living with HIV in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy compared with the general population in Japan. AIDS 2020, 34, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poizot-Martin, I.; Lions, C.; Allavena, C.; Huleux, T.; Bani-Sadr, F.; Cheret, A.; Rey, D.; Duvivier, C.; Jacomet, C.; Ferry, T.; et al. Spectrum and Incidence Trends of AIDS- and Non-AIDS-Defining Cancers between 2010 and 2015 in the French Dat’AIDS Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, M.S.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Gail, M.H.; Hall, H.I.; Li, J.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Bhatia, K.; Uldrick, T.S.; Yarchoan, R.; Goedert, J.J.; et al. Cancer burden in the HIV-infected population in the United States. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, E.P.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Engels, E.A. Cumulative incidence of cancer among individuals with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in the United States. Cancer 2011, 117, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration of Observational HIV Epidemiological Research Europe (COHERE) Study Group; Bohlius, J.; Schmidlin, K.; Costagliola, D.; Fätkenheuer, G.; May, M.; Caro Murillo, A.M.; Mocroft, A.; Bonnet, F.; Clifford, G.; et al. Prognosis of HIV-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma in patients starting combination antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2009, 23, 2029–2037. [Google Scholar]
- Schommers, P.; Hentrich, M.; Hoffmann, C.; Gillor, D.; Zoufaly, A.; Jensen, B.; Bogner, J.R.; Thoden, J.; Wasmuth, J.-C.; Wolf, T.; et al. Survival of AIDS-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, and plasmablastic lymphoma in the German HIV Lymphoma Cohort. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 168, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. Progress in the Treatment of HIV-Associated Lymphoma When Combined With the Antiretroviral Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 798008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentrich, M.; Müller, M.; Wyen, C.; Pferschy, A.; Jurinovic, V.; Siehl, J.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Schürmann, D.; Hoffmann, C.; German HIV-Related Lymphoma Study Group. Stage-adapted treatment of HIV-associated Hodgkin lymphoma: Long-term results of a prospective, multicenter study. Hemasphere 2024, 8, e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Gloghini, A.; Serraino, D.; Spina, M.; Tirelli, U.; Vaccher, E. Immunodeficiency-associated Hodgkin lymphoma. Expert. Rev. Hematol. 2021, 14, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opie, J.; Mohamed, Z.; Chetty, D.; Bailey, J.; Brown, K.; Verburgh, E.; Hardie, D. Hodgkin lymphoma: The role of EBV plasma viral load testing in an HIV-endemic setting. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 25, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, M.; Navarro, J.-T.; Moltó, J.; Ribera, J.-M.; Tapia, G. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in the HIV Setting. Cancers 2023, 15, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, V.; Garzino-Demo, A. HIV-associated lymphoma in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy: Shifting the immunological landscape. Pathog. Dis. 2015, 73, ftv044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Maso, L.; Franceschi, S. Epidemiology of non-Hodgkin lymphomas and other haemolymphopoietic neoplasms in people with AIDS. Lancet Oncol. 2003, 4, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidano, G.; Pasqualucci, L.; Capello, D.; Berra, E.; Deambrogi, C.; Rossi, D.; Maria Larocca, L.; Gloghini, A.; Carbone, A.; Dalla-Favera, R. Aberrant somatic hypermutation in multiple subtypes of AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2003, 102, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolcetti, R.; Gloghini, A.; Caruso, A.; Carbone, A. A lymphomagenic role for HIV beyond immune suppression? Blood 2016, 127, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurain, K.; Ramaswami, R.; Yarchoan, R. The role of viruses in HIV-associated lymphomas. Semin. Hematol. 2022, 59, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Volpi, C.C.; Gualeni, A.V.; Gloghini, A. Epstein-Barr virus associated lymphomas in people with HIV. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2017, 12, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhan, A.; Bayleyegn, B.; Getaneh, Z. HIV/AIDS Associated Lymphoma: Review. Blood Lymphat. Cancer 2022, 12, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Xie, X.; Li, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xu, G.; Ma, B.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, L.; et al. The single-cell immune landscape of HIV-associated aggressive B-cell lymphoma. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2025, 5, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Zetterberg, H.; Masters, C.L.; Lista, S.; Kiddle, S.J.; Batrla, R.; Blennow, K. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer disease: Mapping the road to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Narazaki, M.; Metwally, H.; Kishimoto, T. Historical overview of the interleukin-6 family cytokine. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Han, S.; Ma, Z. Advances in IL-7 Research on Tumour Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Rutz, S.; Crellin, N.K.; Valdez, P.A.; Hymowitz, S.G. Regulation and functions of the IL-10 family of cytokines in inflammation and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 71–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’mello, K.P.; Zhao, L.; Kaser, E.C.; Zhu, Z.; Xiao, H.; Wakefield, M.R.; Bai, Q.; Fang, Y. The role of interleukins and the widely studied TNF-α in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Med. Oncol. 2021, 38, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, C.; Gu, J.; Huang, X.; You, L.; Zhou, Z.; Jin, J. Cytokine profiles in patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: IL-6 and IL-10 levels are associated with adverse clinical features and poor outcomes. Cytokine 2023, 169, 156289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacinović-Duletić, A.; Stifter, S.; Dvornik, S.; Skunca, Z.; Jonjić, N. Correlation of serum IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10 levels with clinicopathological features and prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2008, 30, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlefsen, K.L.; Martínez-Maza, O.; Madeleine, M.M.; Magpantay, L.; Mirick, D.K.; Kopecky, K.J.; LaCroix, A.Z.; De Roos, A.J. Cytokines in serum in relation to future non-Hodgkin lymphoma risk: Evidence for associations by histologic subtype. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgood, H.D.; Au, W.-Y.; Kim, H.N.; Liu, J.; Hu, W.; Tse, J.; Song, B.; Wong, K.-F.; Lee, J.-J.; Chanock, S.J.; et al. IL10 and TNF variants and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma among three Asian populations. Int. J. Hematol. 2013, 97, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, E.C.; Boscardin, W.J.; Detels, R.; Jacobson, L.P.; Smith, M.W.; O’Brien, S.J.; Chmiel, J.S.; Rinaldo, C.R.; Lai, S.; Martínez-Maza, O. Non-Hodgkin’s B cell lymphoma in persons with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is associated with increased serum levels of IL10, or the IL10 promoter-592 C/C genotype. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 109, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.-L.; Breen, E.C.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Aissani, B.; Martinson, J.J.; Margolick, J.B.; Kaslow, R.A.; Jacobson, L.P.; Ambinder, R.F.; Chanock, S.; et al. Cytokine signaling pathway polymorphisms and AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma risk in the multicenter AIDS cohort study. AIDS 2010, 24, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, E.C.; Hussain, S.K.; Magpantay, L.; Jacobson, L.P.; Detels, R.; Rabkin, C.S.; Kaslow, R.A.; Variakojis, D.; Bream, J.H.; Rinaldo, C.R.; et al. B-cell stimulatory cytokines and markers of immune activation are elevated several years prior to the diagnosis of systemic AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, Z.; Kay, D.G.; Cool, M.; Jothy, S.; Rebai, N.; Jolicoeur, P. Transgenic mice expressing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in immune cells develop a severe AIDS-like disease. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curreli, S.; Krishnan, S.; Reitz, M.; Lunardi-Iskandar, Y.; Lafferty, M.K.; Garzino-Demo, A.; Zella, D.; Gallo, R.C.; Bryant, J. B cell lymphoma in HIV transgenic mice. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendrame, E.; Hussain, S.K.; Breen, E.C.; Magpantay, L.I.; Widney, D.P.; Jacobson, L.P.; Variakojis, D.; Knowlton, E.R.; Bream, J.H.; Ambinder, R.F.; et al. Serum levels of cytokines and biomarkers for inflammation and immune activation, and HIV-associated non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.K.; Zhu, W.; Chang, S.-C.; Breen, E.C.; Vendrame, E.; Magpantay, L.; Widney, D.; Conn, D.; Sehl, M.; Jacobson, L.P.; et al. Serum levels of the chemokine CXCL13, genetic variation in CXCL13 and its receptor CXCR5, and HIV-associated non-hodgkin B-cell lymphoma risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolen, B.M.; Breen, E.C.; Bream, J.H.; Jenkins, F.J.; Kingsley, L.A.; Rinaldo, C.R.; Lokshin, A.E. Circulating mediators of inflammation and immune activation in AIDS-related non-hodgkin lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievin, R.; Hendel-Chavez, H.; Baldé, A.; Lancar, R.; Algarte-Génin, M.; Krzysiek, R.; Costagliola, D.; As-soumou, L.; Taoufik, Y.; Besson, C. Increased Production of B-Cell Activating Cytokines and Altered Peripheral B-Cell Subset Distribution during HIV-Related Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epeldegui, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Martínez, A.C.; Widney, D.P.; Magpantay, L.I.; Regidor, D.; Mitsuyasu, R.; Sparano, J.A.; Ambinder, R.F.; Martínez-Maza, O. Predictive Value of Cytokines and Immune Activation Biomarkers in AIDS-Related Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated with Rituximab plus Infusional EPOCH (AMC-034 trial). Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.E.; Lensing, S.; Chang, D.; Magpantay, L.I.; Mitsuyasu, R.; Ambinder, R.F.; Sparano, J.A.; Mar-tínez-Maza, O.; Epeldegui, M. Immune Activation and Microbial Translocation as Prognostic Biomarkers for AIDS-Related Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in the AMC-034 Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4642–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.; Patel, M.; Suchard, M.; Gededzha, M.; Ranchod, H.; Howard, W.; Snyman, T.; Wiggill, T. Derangements of immunological proteins in HIV-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: The frequency and prognostic impact. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1340096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolin, M.T.; Tedeschi, R.; Bidoli, E.; Zanussi, S.; Pratesi, C.; Vaccher, E.; Tirelli, U.; De Paoli, P. Multiplex analysis of blood cytokines as a prognostic tool in HIV related non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients: A potential role of interleukin-7. Cytokine 2012, 60, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnik, A.; Yoshie, O. Chemokines: A new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity 2000, 12, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarsheth, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Zou, W. Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luster, A.D. Chemokines—Chemotactic cytokines that mediate inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2004, 4, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Adah, D.; Tariq, M.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. CXCL13/CXCR5 signaling axis in cancer. Life Sci. 2019, 227, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, M.D.; Ngo, V.N.; Ansel, K.M.; Ekland, E.H.; Cyster, J.G.; Williams, L.T. A B-cell-homing chemokine made in lymphoid follicles activates Burkitt’s lymphoma receptor-1. Nature 1998, 391, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.-H.; Liu, S.-Z.; Wang, G.-Z.; Zhou, G.-B. CXCL13 in Cancer and Other Diseases: Biological Functions, Clinical Significance, and Therapeutic Opportunities. Life 2021, 11, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdue, M.P.; Hofmann, J.N.; Kemp, T.J.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Lan, Q.; Park, J.-H.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Hildesheim, A.; Pinto, L.A.; Rothman, N. A prospective study of 67 serum immune and inflammation markers and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2013, 122, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, L.; Cabrelle, A.; Facco, M.; Carollo, D.; Miorin, M.; Tosoni, A.; Pizzo, P.; Binotto, G.; Nicolardi, L.; Zambello, R.; et al. Homeostatic chemokines drive migration of malignant B cells in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood 2004, 104, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Wong, V.S.; Kadoch, C.; Gao, H.-X.; Barajas, R.; Chen, L.; Josephson, S.A.; Scott, B.; Douglas, V.; Maiti, M.; et al. CXCL13 plus interleukin 10 is highly specific for the diagnosis of CNS lymphoma. Blood 2013, 121, 4740–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtova, A.V.; Tamayo, A.T.; Ford, R.J.; Burger, J.A. Mantle cell lymphoma cells express high levels of CXCR4, CXCR5, and VLA-4 (CD49d): Importance for interactions with the stromal microenvironment and specific targeting. Blood 2009, 113, 4604–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Ryu, K.J.; Hong, M.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, W.S. The serum CXCL13 level is associated with the Glasgow Prognostic Score in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma patients. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonneau, B.; Wang, A.H.; Maurer, M.J.; Asmann, Y.W.; Zent, C.S.; Link, B.K.; Ansell, S.M.; Weiner, G.J.; Ozsan, N.; Feldman, A.L.; et al. CXCR5 polymorphisms in non-Hodgkin lymphoma risk and prognosis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Förster, R.; Schweigard, G.; Johann, S.; Emrich, T.; Kremmer, E.; Nerl, C.; Lipp, M. Abnormal expression of the B-cell homing chemokine receptor BLR1 during the progression of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Blood 1997, 90, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagigi, A.; Mowafi, F.; Phuong Dang, L.V.; Tenner-Racz, K.; Atlas, A.; Grutzmeier, S.; Racz, P.; Chiodi, F.; Nilsson, A. Altered expression of the receptor-ligand pair CXCR5/CXCL13 in B cells during chronic HIV-1 infection. Blood 2008, 112, 4401–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.K.; Hessol, N.A.; Levine, A.M.; Breen, E.C.; Anastos, K.; Cohen, M.; D’Souza, G.; Gustafson, D.R.; Silver, S.; Martínez-Maza, O. Serum biomarkers of immune activation and subsequent risk of non-hodgkin B-cell lymphoma among HIV-infected women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 2084–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widney, D.P.; Gui, D.; Popoviciu, L.M.; Said, J.W.; Breen, E.C.; Huang, X.; Kitchen, C.M.R.; Alcantar, J.M.; Smith, J.B.; Detels, R.; et al. Expression and Function of the Chemokine, CXCL13, and Its Receptor, CXCR5, in Aids-Associated Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. AIDS Res. Treat. 2010, 2010, 164586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Villegas, J.M.; de Medeiros, R.M.; Ellwanger, J.H.; Santos, B.R.; de Melo, M.G.; de Matos Almeida, S.E.; Chies, J.A.B. High CXCL10/IP-10 levels are a hallmark in the clinical evolution of the HIV infection. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 57, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liovat, A.-S.; Rey-Cuillé, M.-A.; Lécuroux, C.; Jacquelin, B.; Girault, I.; Petitjean, G.; Zitoun, Y.; Venet, A.; Bar-ré-Sinoussi, F.; Lebon, P.; et al. Acute plasma biomarkers of T cell activation set-point levels and of disease progression in HIV-1 infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploquin, M.J.; Madec, Y.; Casrouge, A.; Huot, N.; Passaes, C.; Lécuroux, C.; Essat, A.; Boufassa, F.; Jacquelin, B.; Jochems, S.P.; et al. Elevated Basal Pre-infection CXCL10 in Plasma and in the Small Intestine after Infection Are Associated with More Rapid HIV/SIV Disease Onset. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chung, Y.-S.; Yoon, C.-H.; Shin, Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, B.-S.; Kim, S.S. Interferon-inducible protein 10 (IP-10) is associated with viremia of early HIV-1 infection in Korean patients. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, D.E.; Makinson, A.; Kuster, N.; Nagot, N.; Rubbo, P.-A.; Bollore, K.; Foulongne, V.; Cartron, G.; Olive, D.; Reynes, J.; et al. Increased T-cell activation and Th1 cytokine concentrations prior to the diagnosis of B-cell lymphoma in HIV infected patients. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-L.; Shi, Z.-H.; Wang, X.; Gu, K.-S.; Zhai, Z.-M. Prognostic significance of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and CC chemokine receptor 2 in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delespesse, G.; Suter, U.; Mossalayi, D.; Bettler, B.; Sarfati, M.; Hofstetter, H.; Kilcherr, E.; Debre, P.; Dalloul, A. Expression, structure, and function of the CD23 antigen. Adv. Immunol. 1991, 49, 149–191. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy, J.Y.; Lecoanet-Henchoz, S.; Aubry, J.P.; Gauchat, J.F.; Graber, P. CD23 and B-cell activation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1995, 7, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roos, A.J.; Mirick, D.K.; Edlefsen, K.L.; LaCroix, A.Z.; Kopecky, K.J.; Madeleine, M.M.; Magpantay, L.; Martínez-Maza, O. Markers of B-cell activation in relation to risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4733–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Reinisch, W.; Willheim, M.; Hilgarth, M.; Gasché, C.; Mader, R.; Szepfalusi, S.; Steger, G.; Berger, R.; Lechner, K.; Boltz-Nitulescu, G. Soluble CD23 reliably reflects disease activity in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 1994, 12, 2146–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beguin, Y.; Lampertz, S.; De Groote, D.; Igot, D.; Malaise, M.; Fillet, G. Soluble CD23 and other receptors (CD4, CD8, CD25, CD71) in serum of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 1993, 7, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar]
- Camerini, D.; Walz, G.; Loenen, W.A.; Borst, J.; Seed, B. The T cell activation antigen CD27 is a member of the nerve growth factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor gene family. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 3165–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquot, S. CD27/CD70 interactions regulate T dependent B cell differentiation. Immunol. Res. 2000, 21, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, G.; De Carli, M.; Almerigogna, F.; Daniel, C.K.; D’Elios, M.M.; Zancuoghi, G.; Vinante, F.; Pizzolo, G.; Romagnani, S. Preferential expression of CD30 by human CD4+ T cells producing Th2-type cytokines. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, L.V.P.; Nilsson, A.; Ingelman-Sundberg, H.; Cagigi, A.; Gelinck, L.B.S.; Titanji, K.; De Milito, A.; Grutzmeier, S.; Hedlund, J.; Kroon, F.P.; et al. Soluble CD27 induces IgG production through activation of antigen-primed B cells. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 271, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Milito, A.; Aleman, S.; Marenzi, R.; Sonnerborg, A.; Fuchs, D.; Zazzi, M.; Chiodi, F. Plasma levels of soluble CD27: A simple marker to monitor immune activation during potent antiretroviral therapy in HIV-1-infected subjects. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 127, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Bertero, M.T.; Converso, M.; Stacchini, A.; Vinante, F.; Romagnani, S.; Pizzolo, G. Circulating levels of soluble CD30, a marker of cells producing Th2-type cytokines, are increased in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and correlate with disease activity. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1995, 13, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Bohnhorst, J.Ø.; Bjørgan, M.B.; Thoen, J.E.; Jonsson, R.; Natvig, J.B.; Thompson, K.M. Abnormal B cell differentiation in primary Sjögren’s syndrome results in a depressed percentage of circulating memory B cells and elevated levels of soluble CD27 that correlate with Serum IgG concentration. Clin. Immunol. 2002, 103, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yawetz, S.; Cumberland, W.G.; van der Meyden, M.; Martínez-Maza, O. Elevated serum levels of soluble CD23 (sCD23) precede the appearance ofacquired immunodeficiency syndrome--associated non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood 1995, 85, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widney, D.; Gundapp, G.; Said, J.W.; van der Meijden, M.; Bonavida, B.; Demidem, A.; Trevisan, C.; Taylor, J.; Detels, R.; Martínez-Maza, O. Aberrant expression of CD27 and soluble CD27 (sCD27) in HIV infection and in AIDS-associated lymphoma. Clin. Immunol. 1999, 93, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, E.C.; Fatahi, S.; Epeldegui, M.; Boscardin, W.J.; Detels, R.; Martínez-Maza, O. Elevated serum soluble CD30 precedes the development of AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin’s B cell lymphoma. Tumour Biol. 2006, 27, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossolasco, S.; Nilsson, A.; de Milito, A.; Lazzarin, A.; Linde, A.; Cinque, P.; Chiodi, F. Soluble CD23 in cerebrospinal fluid: A marker of AIDS-related non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in the brain. AIDS 2001, 15, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevriti, A.; Lamprou, M.; Mourkogianni, E.; Skoulas, N.; Giannakopoulou, M.; Sajib, M.S.; Wang, Z.; Matthe-olabakis, G.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Marazioti, A.; et al. The Role of Soluble CD163 (sCD163) in Human Physiology and Pathophysiology. Cells 2024, 13, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wen, Y. Lessons from Epstein-Barr virus DNA detection in cerebrospinal fluid as a diagnostic tool for EBV-induced central nervous system dysfunction among HIV-positive patients. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.; Vari, F.; Keane, C.; Crooks, P.; Nourse, J.P.; Seymour, L.A.; Gottlieb, D.; Ritchie, D.; Gill, D.; Gandhi, M.K. Serum CD163 and TARC as disease response biomarkers in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, N.A.; Andrusaite, A.; Andersen, P.; Lawson, M.; Alcon-Giner, C.; Leclaire, C.; Caim, S.; Le Gall, G.; Shaw, T.; Connolly, J.P.R.; et al. Antibiotics induce sustained dysregulation of intestinal T cell immunity by perturbing macrophage homeostasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaao4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudd, J.C.; Brenchley, J.M. Gut Mucosal Barrier Dysfunction, Microbial Dysbiosis, and Their Role in HIV-1 Disease Progression. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214 (Suppl. 2), S58–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, G.; Tincati, C.; Silvestri, G. Microbial translocation in the pathogenesis of HIV infection and AIDS. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, N.G.; Douek, D.C. Microbial translocation in HIV infection: Causes, consequences and treatment opportunities. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatt, N.R.; Funderburg, N.T.; Brenchley, J.M. Microbial translocation, immune activation, and HIV disease. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; Schacker, T.W.; Asher, T.E.; Silvestri, G.; Rao, S.; Kazzaz, Z.; Bornstein, E.; Lam-botte, O.; Altmann, D.; et al. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shive, C.L.; Jiang, W.; Anthony, D.D.; Lederman, M.M. Soluble CD14 is a nonspecific marker of monocyte activation. AIDS 2015, 29, 1263–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.D.; Ramos, R.A.; Tobias, P.S.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Mathison, J.C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science 1990, 249, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, I.; Granucci, F. Role of CD14 in host protection against infections and in metabolism regulation. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funaoka, H.; Kanda, T.; Fujii, H. Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein (I-FABP) as a new biomarker for intestinal diseases. Rinsho Byori. 2010, 58, 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Pelsers, M.M.A.L.; Namiot, Z.; Kisielewski, W.; Namiot, A.; Januszkiewicz, M.; Hermens, W.T.; Glatz, J.F.C. Intestinal-type and liver-type fatty acid-binding protein in the intestine. Tissue distribution and clinical utility. Clin. Biochem. 2003, 36, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.I.; Hossain, M.; Islam, S.; Akter, A.; Nishat, N.S.; Nila, T.A.; Rafique, T.A.; Leung, D.T.; Calderwood, S.B.; Ryan, E.T.; et al. An assessment of potential biomarkers of environment enteropathy and its association with age and microbial infections among children in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, N.G.; Wand, H.; Roque, A.; Law, M.; Nason, M.C.; Nixon, D.E.; Pedersen, C.; Ruxrungtham, K.; Lew-in, S.R.; Emery, S.; et al. Plasma levels of soluble CD14 independently predict mortality in HIV infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papasavvas, E.; Pistilli, M.; Reynolds, G.; Bucki, R.; Azzoni, L.; Chehimi, J.; Janmey, P.A.; DiNubile, M.J.; Ondercin, J.; Kostman, J.R.; et al. Delayed loss of control of plasma lipopolysaccharide levels after therapy interruption in chronically HIV-1-infected patients. AIDS 2009, 23, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, N.; Singh, R.; Sharma, A.; Das, B.K.; Vajpayee, M. Comparative evaluation of microbial translocation products (LPS, sCD14, IgM Endocab) in HIV-1 infected Indian individuals. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.W.; Cavacini, L. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S41–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Hoyer, K.; Ochoa-Grullón, J.; Fernández-Arquero, M.; Cárdenas, M.; Pérez de Diego, R.; Sánchez-Ramón, S. Serum Free Immunoglobulins Light Chains: A Common Feature of Common Variable Immunodeficiency? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, F.; De Filippi, R.; Laurenti, L.; Zirlik, K.; Recchia, A.G.; Gentile, M.; Morelli, E.; Vigna, E.; Gigliotti, V.; Calemma, R.; et al. The cumulative amount of serum-free light chain is a strong prognosticator in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011, 118, 6353–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Witzig, T.E.; Maurer, M.J.; Habermann, T.M.; Link, B.K.; Micallef, I.N.M.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Ansell, S.M.; Colgan, J.P.; Inwards, D.J.; Porrata, L.F.; et al. Elevated monoclonal and polyclonal serum immunoglobulin free light chain as prognostic factors in B- and T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maurer, M.J.; Micallef, I.N.M.; Cerhan, J.R.; Katzmann, J.A.; Link, B.K.; Colgan, J.P.; Habermann, T.M.; In-wards, D.J.; Markovic, S.N.; Ansell, S.M.; et al. Elevated serum free light chains are associated with event-free and overall survival in two independent cohorts of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.A.; Maurer, M.J.; Cerhan, J.R.; Katzmann, J.A.; Ansell, S.M.; Habermann, T.M.; Macon, W.R.; Weiner, G.J.; Link, B.K.; Witzig, T.E. Elevated serum free light chains are associated with inferior event free and overall survival in Hodgkin lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2011, 86, 998–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgren, O.; Goedert, J.J.; Rabkin, C.S.; Wilson, W.H.; Dunleavy, K.; Kyle, R.A.; Katzmann, J.A.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Engels, E.A. Circulating serum free light chains as predictive markers of AIDS-related lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, L.; Borges, Á.H.; Harvey, R.; Bower, M.; Grulich, A.; Silverberg, M.; Weber, J.; Ristola, M.; Viard, J.-P.; Bogner, J.R.; et al. The extent of B-cell activation and dysfunction preceding lymphoma development in HIV-positive people. HIV Med. 2018, 19, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibas, M.; Trotta, M.P.; Cozzi-Lepri, A.; Lorenzini, P.; Pinnetti, C.; Rizzardini, G.; Angarano, G.; Caramello, P.; Sighinolfi, L.; Mastroianni, C.M.; et al. Role of serum free light chains in predicting HIV-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma and Hodgkin’s lymphoma and its correlation with antiretroviral therapy. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibas, M.; Lorenzini, P.; Cozzi-Lepri, A.; Calcagno, A.; di Giambenedetto, S.; Costantini, A.; Castagna, A.; Manfrin, V.; Monforte, A.D.; Antinori, A.; et al. Polyclonal serum-free light chains elevation in HIV-infected patients. AIDS 2012, 26, 2107–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grulich, A.E.; Wan, X.; Law, M.G.; Milliken, S.T.; Lewis, C.R.; Garsia, R.J.; Gold, J.; Finlayson, R.J.; Cooper, D.A.; Kaldor, J.M. B-cell stimulation and prolonged immune deficiency are risk factors for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in people with AIDS. AIDS 2000, 14, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engels, E.A.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Landgren, O.; Moore, R.D. Immunologic and virologic predictors of AIDS-related non-hodgkin lymphoma in the highly active antiretroviral therapy era. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2010, 54, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Zheng, X.; Niu, M.; Zhu, S.; Ge, H.; Wu, K. Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Current advances and future directions. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature 2017, 541, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epeldegui, M.; Conti, D.V.; Guo, Y.; Cozen, W.; Penichet, M.L.; Martínez-Maza, O. Elevated numbers of PD-L1 expressing B cells are associated with the development of AIDS-NHL. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Cai, S.; Xiao, Y.; Xia, M.; Chen, H.; Xie, Z.; Tang, X.; He, H.; Peng, J.; Chen, J. Expression and prognostic significance of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Qian, J.; Ding, L.; Yin, S.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Galectin-1: A Traditionally Immunosuppressive Protein Displays Context-Dependent Capacities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeno-Laurent, F.; Watanabe, R.; Teague, J.E.; Kupper, T.S.; Clark, R.A.; Dimitroff, C.J. Galectin-1 inhibits the viability, proliferation, and Th1 cytokine production of nonmalignant T cells in patients with leukemic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2012, 119, 3534–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vase, M.Ø.; Ludvigsen, M.; Bendix, K.; Dutoit, S.H.; Hjortebjerg, R.; Petruskevicius, I.; Møller, M.B.; Pedersen, G.; Denton, P.W.; Honoré, B.; et al. Predictive value of galectin-1 in the development and progression of HIV-associated lymphoma. AIDS 2017, 31, 2311–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, P.A.; Cunningham, B.A.; Berggård, I.; Edelman, G.M. 2-Microglobulin—A free immunoglobulin domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 1697–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, Y.; Su, Y.; Chung, L.W.K.; Cheng, T. Beta2-microglobulin: Emerging as a promising cancer therapeutic target. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, P.; Deng, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, L.; Mei, F.; Huang, S.; Chen, X.; Yan, Y.; et al. Plasma proteomic analysis reveals altered protein abundances in HIV-infected patients with or without non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 3876–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, J.C.; de Marques, M.O.; Pereira, J.; Braga, W.M.T.; Hamerschlak, N.; Tabacof, J.; Ferreira, P.R.A.; Col-leoni, G.W.B.; Baiocchi, O.C.G. Factors associated with survival in patients with lymphoma and HIV. AIDS 2023, 37, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botafogo, V.; Usas, A.; Verdú-Bou, M.; Moreno, M.; Fernández-Rivas, G.; Cardona, P.-J.; Fondelli, F.; Mar-tínez-Cáceres, E.; Doladé, M.; Blanco, I.; et al. Profile of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Differences between HIV-Negative and HIV-Positive Patients. Blood 2024, 144, 6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymulewska-Konopko, K.; Reszeć-Giełażyn, J.; Małeczek, M. Ferritin as an Effective Prognostic Factor and Potential Cancer Biomarker. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzner, Y.; Konijn, A.M.; Hershko, C. Serum ferritin in hematologic malignancies. Am. J. Hematol. 1980, 9, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.J.; Kim, T.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Jo, J.-C.; Lee, W.S.; Shin, H.-J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.S. Poor prognostic impact of high serum ferritin levels in patients with a lower risk of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Int. J. Hematol. 2020, 111, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehn, L.H.; Salles, G. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 842–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hu, L.; Sun, Q.; He, C.; Yan, D.; Ye, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; et al. The Addition of Ferritin Enhanced the Prognostic Value of International Prognostic Index in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 823079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.; Wiggill, T.; Mia, Z.; Patel, M. Tumour-associated macrophages in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: The prognostic and therapeutic impact in a South African centre with high HIV seroprevalence. Immunol. Res. 2024, 72, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claps, G.; Faouzi, S.; Quidville, V.; Chehade, F.; Shen, S.; Vagner, S.; Robert, C. The multiple roles of LDH in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Niu, X.; Yin, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Xuan, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Ratio of Immune Response to Tumor Burden Predicts Survival Via Regulating Functions of Lymphocytes and Monocytes in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusconi, C.; Re, A.; Bandiera, L.; Crucitti, L.; Spina, M.; Gini, G.; Paulli, M.; Lucioni, M.; Facchetti, F.; Goteri, G.; et al. Cell-of-Origin Identification and Prognostic Correlation in HIV-Associated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas: Results of an Italian Multicentric Study. Blood 2018, 132, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Lei, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Guo, B.; Hu, R.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of newly diagnosed patients with HIV-associated aggressive B-cell NHL in China. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 5067–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Shen, Y.; Song, W.; Qi, T.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guan, L.; Lu, H. Clinical and prognostic analysis of 78 patients with human immuno-deficiency virus associated non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Chinese population. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2017, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painschab, M.S.; Kasonkanji, E.; Zuze, T.; Kaimila, B.; Tomoka, T.; Nyasosela, R.; Nyirenda, R.; Dhungel, B.M.; Mulenga, M.; Chikasema, M.; et al. Mature outcomes and prognostic indices in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Malawi: A prospective cohort. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Min, H.; Huang, Y.; Wei, G.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Tang, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. Impact of initial chemotherapy cycles and clinical characteristics on outcomes for HIV-associated diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients: The Central and Western China AIDS Lymphoma League 001 study (CALL-001 study). Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1153790. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, R.; Tao, Y.; Bertero, L.; Feng, L.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z.; Guan, J.; Liao, B.; Li, L.; et al. Construction and validation of prognostic scoring models to risk stratify patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome-related diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chen, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, D.; Hu, S. The clinical features and prognosis of 100 AIDS-related lymphoma cases. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderuccio, J.P.; Olszewski, A.J.; Evens, A.M.; Collins, G.P.; Danilov, A.V.; Bower, M.; Jagadeesh, D.; Zhu, C.; Sperling, A.; Kim, S.-H.; et al. HIV-associated Burkitt lymphoma: Outcomes from a US-UK collaborative analysis. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2852–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, G.; Tao, Y.; Tang, X.; Feng, L.; Liao, B.; Liu, B.; Guan, J.; Li, L.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of AIDS-Related Burkitt Lymphoma in China: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 23, 15330338231214236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, B.; Wang, W.; Lin, M.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.I.; Chen, L.; Wahed, A.; Nguyen, A.; Ma, H.Y.; Medeiros, L.J.; et al. HIV-associated plasmablastic lymphoma in the era of HAART: A single-center experience of 21 patients. AIDS 2020, 34, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, P.; Feng, E.; Chen, X.; Gao, H.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, X. Clinicopathological analysis of primary central nervous system lymphoma in patients with or without HIV infection. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 73, 152383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Zheng, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y. Development of a novel prognostic nomogram for AIDS-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A retrospective study from northern China. Clin. Exp. Med. 2025, 25, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, D.R.; Burgener, A.; Ball, T.B. Proteomics as a novel HIV immune monitoring tool. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2013, 8, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Sabaa, A.; Shen, Q.; Lennmyr, E.B.; Enblad, A.P.; Gammelgård, G.; Molin, D.; Hein, A.; Freyhult, E.; Ka-mali-Moghaddam, M.; Höglund, M.; et al. Plasma protein biomarker profiling reveals major differences between acute leukaemia, lymphoma patients and controls. New Biotechnol. 2022, 71, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnum, S.M.; Webb-Robertson, B.-J.M.; Hessol, N.A.; Smith, R.D.; Zangar, R.C. Plasma biomarkers for detecting Hodgkin’s lymphoma in HIV patients. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vase, M.Ø.; Ludvigsen, M.; Bendix, K.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Mller, M.B.; Pedersen, C.; Pedersen, G.; Obel, N.; Larsen, C.S.; d’Amore, F.; et al. Proteomic profiling of pretreatment serum from HIV-infected patients identifies candidate markers predictive of lymphoma development. AIDS 2016, 30, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, D.; Villén, J.; Shin, C.; Camargo, F.D.; Gygi, S.P.; Bartel, D.P. The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 2008, 455, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, J.; Kong, D.; Huang, M.; Xu, C.; Kim, T.-K.; Etheridge, A.; Luo, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, K. Current State of Circulating MicroRNAs as Cancer Biomarkers. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1138–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, P.T.B.; Clark, I.M.; Le, L.T.T. MicroRNA-Based Diagnosis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Ochiya, T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, C.M. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in human solid tumors. Cancer Lett. 2013, 329, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparello, J.; Papi, C.; Zurlo, M.; Gambari, L.; Manicardi, A.; Rozzi, A.; Ferrarini, M.; Corradini, R.; Gambari, R.; Finotti, A. MicroRNAs miR-584-5p and miR-425-3p Are Up-Regulated in Plasma of Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Patients: Targeting with Inhibitor Peptide Nucleic Acids Is Associated with Induction of Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers 2022, 15, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.-L.; Ren, L.-F.; Wang, H.-P.; Bai, Z.-T.; Zhang, L.; Meng, W.-B.; Zhu, K.-X.; Ding, F.-H.; Miao, L.; Yan, J.; et al. Plasma microRNAs as potential new biomarkers for early detection of early gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1580–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Wong, Y.S.; Goh, B.K.P.; Chan, C.Y.; Cheow, P.C.; Chow, P.K.H.; Lim, T.K.H.; Goh, G.B.B.; Krishna-moorthy, T.L.; Kumar, R.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Gal, S.; Dunlop, H.M.; Pushkaran, B.; Liggins, A.P.; Pulford, K.; Banham, A.H.; Pezzella, F.; Boultwood, J.; Wainscoat, J.S.; et al. Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.; Paulsen, I.W.; Hansen, J.W.; Tholstrup, D.; Hother, C.; Sørensen, E.; Petersen, M.S.; Nielsen, K.R.; Rostgaard, K.; Larsen, M.A.H.; et al. The value of circulating microRNAs for early diagnosis of B-cell lymphoma: A case-control study on historical samples. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulci, V.; Chiaretti, S.; Goldoni, M.; Azzalin, G.; Carucci, N.; Tavolaro, S.; Castellano, L.; Magrelli, A.; Citarella, F.; Messina, M.; et al. Quantitative technologies establish a novel microRNA profile of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2007, 109, 4944–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Fabbri, M.; Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drees, E.E.E.; Pegtel, D.M. Circulating miRNAs as Biomarkers in Aggressive B Cell Lymphomas. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, D.; Hairul Islam, V.I.; Thirugnanasambantham, K.; Saravanan, S. Relevance of miR-21 in HIV and non-HIV-related lymphomas. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 8387–8393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, D.R.; Bhatia, K.; Bream, J.H.; D’Souza, G.; Rinaldo, C.R.; Wolinsky, S.; Detels, R.; Martínez-Maza, O. B-cell activation induced microRNA-21 is elevated in circulating B cells preceding the diagnosis of AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphomas. AIDS 2012, 26, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, D.R.; Hussain, S.K.; Tran, W.-C.; D’souza, G.; Bream, J.H.; Achenback, C.J.; Ayyavoo, V.; Detels, R.; Martínez-Maza, O. Serum microRNAs in HIV-infected individuals as pre-diagnosis biomarkers for AIDS-NHL. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2014, 66, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Sekizuka, T.; Uehara, T.; Hishima, T.; Mine, S.; Fukumoto, H.; Sato, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Kuroda, M.; Katano, H. Next-generation sequencing of miRNAs in clinical samples of Epstein-Barr virus-associated B-cell lymphomas. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, D.R.; Li, X.; Jamieson, B.D.; Martínez-Maza, O. Overexpression of microRNAs from the miR-17-92 paralog clusters in AIDS-related non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramorola, B.R.; Goolam-Hoosen, T.; Alves de Souza Rios, L.; Mowla, S. Modulation of Cellular MicroRNA by HIV-1 in Burkitt Lymphoma Cells-A Pathway to Promoting Oncogenesis. Genes 2021, 12, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.; Browne, G.; Tulchinsky, E. ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop: At the crossroads of signal transduction in cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-M.; Gaur, A.B.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peckham-Gregory, E.C.; Thapa, D.R.; Martinson, J.; Duggal, P.; Penugonda, S.; Bream, J.H.; Chang, P.-Y.; Dandekar, S.; Chang, S.-C.; Detels, R.; et al. MicroRNA-related polymorphisms and non-Hodgkin lymphoma susceptibility in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiirikainen, M.I.; Mullaney, B.P.; Holly, E.A.; Pallavicini, M.G.; Jensen, R.H. DNA copy number alterations in HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients with diffuse large-cell lymphomas. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2001, 27, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hybel, T.E.; Sørensen, E.F.; Enemark, M.H.; Hemmingsen, J.K.; Simonsen, A.T.; Lauridsen, K.L.; Møller, M.B.; Pedersen, C.; Pedersen, G.; Obel, N.; et al. Characterization of the genomic landscape of HIV-associated lymphoma reveals heterogeneity across histological subtypes. AIDS 2024, 38, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, M.; Labreche, K.; Veyri, M.; Désiré, N.; Bouzidi, A.; Seck-Thiam, F.; Charlotte, F.; Rousseau, A.; Morin, V.; Nakid-Cordero, C.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus and immune status imprint the immunogenomics of non-Hodgkin lymphomas occurring in immune-suppressed environments. Haematologica 2024, 109, 3615–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pott, C.; Kotrova, M.; Darzentas, N.; Brüggemann, M.; Khouja, M.; EuroClonality-NGS Working Group. cfDNA-Based NGS IG Analysis in Lymphoma. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2453, 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, S.L.; Patel, M.; Omar, T.; Pather, S.; Martinson, N.; Ambinder, R. Molecular Diagnostics for AIDS Lymphoma Diagnosis in South Africa and the Potential for Other Low- and Middle-Income Countries. J. Glob. Oncol. 2018, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Oki, Y.; Neuberg, D.S.; Faham, M.; Cummings, C.; Klinger, M.; Weng, L.; Bhattar, S.; Lacasce, A.S.; Jacobsen, E.D.; et al. Detection of circulating tumour DNA in patients with aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 163, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.M.; Green, M.R.; Bratman, S.V.; Scherer, F.; Liu, C.L.; Kunder, C.A.; Takahashi, K.; Glover, C.; Keane, C.; Kihira, S.; et al. Noninvasive monitoring of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunoglobulin high-throughput sequencing. Blood 2015, 125, 3679–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladetto, M.; Brüggemann, M.; Monitillo, L.; Ferrero, S.; Pepin, F.; Drandi, D.; Barbero, D.; Palumbo, A.; Passera, R.; Boccadoro, M.; et al. Next-generation sequencing and real-time quantitative PCR for minimal residual disease detection in B-cell disorders. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roschewski, M.; Dunleavy, K.; Pittaluga, S.; Moorhead, M.; Pepin, F.; Kong, K.; Shovlin, M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Staudt, L.M.; Lai, C.; et al. Circulating tumour DNA and CT monitoring in patients with untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A correlative biomarker study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkozy, C.; Huet, S.; Carlton, V.E.H.; Fabiani, B.; Delmer, A.; Jardin, F.; Delfau-Larue, M.-H.; Hacini, M.; Ribrag, V.; Guidez, S.; et al. The prognostic value of clonal heterogeneity and quantitative assessment of plasma circulating clonal IG-VDJ sequences at diagnosis in patients with follicular lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8765–8774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner-Johnston, N.D.; Gellert, L.; Gocke, C.D.; Lemas, V.M.; Lee, J.; Martínez-Maza, O.; Ambinder, R.F. Clonal immunoglobulin DNA in the plasma of patients with AIDS lymphoma. Blood 2011, 117, 4860–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, D.M.; Scherer, F.; Jin, M.C.; Soo, J.; Craig, A.F.M.; Esfahani, M.S.; Chabon, J.J.; Stehr, H.; Liu, C.L.; Tib-shirani, R.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Measurements As Early Outcome Predictors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2845–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, S.L.; Patel, M.; Lakha, A.; Philip, V.; Omar, T.; Ashmore, P.; Pather, S.; Haley, L.M.; Zheng, G.; Stone, J.; et al. Feasibility of Cell-Free DNA Collection and Clonal Immunoglobulin Sequencing in South African Patients With HIV-Associated Lymphoma. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2021, 7, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urabe, F.; Kosaka, N.; Ito, K.; Kimura, T.; Egawa, S.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C29–C39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular vesicle-mediated immunoregulation in cancer. Int. J. Hematol. 2023, 117, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ochiya, T. How cancer cells dictate their microenvironment: Present roles of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, A.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2018, 560, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asleh, K.; Dery, V.; Taylor, C.; Davey, M.; Djeungoue-Petga, M.-A.; Ouellette, R.J. Extracellular vesicle-based liquid biopsy biomarkers and their application in precision immuno-oncology. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofori, K.; Bhagat, G.; Rai, A.J. Exosomes and extracellular vesicles as liquid biopsy biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Current state of the art and unmet clinical needs. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.A.; Godwin, A.K.; Abdelhakim, H. The multifaceted roles of extracellular vesicles for therapeutic intervention with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucl. Acids 2024, 5, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.E.; Lensing, S.; Chang, D.; Magpantay, L.I.; Mitsuyasu, R.; Ambinder, R.F.; Sparano, J.A.; Mar-tínez-Maza, O.; Epeldegui, M. Plasma extracellular vesicles bearing PD-L1, CD40, CD40L or TNF-RII are significantly reduced after treatment of AIDS-NHL. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, L.E.; Magpantay, L.I.; Guo, Y.; Hegde, P.; Detels, R.; Hussain, S.K.; Epeldegui, M. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers for AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma risk. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1259007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussini, C.; Lorenzini, P.; Cozzi-Lepri, A.; Lapadula, G.; Marchetti, G.; Nicastri, E.; Cingolani, A.; Lichtner, M.; Antinori, A.; Gori, A.; et al. CD4/CD8 ratio normalisation and non-AIDS-related events in individuals with HIV who achieve viral load suppression with antiretroviral therapy: An observational cohort study. Lancet HIV 2015, 2, e98–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, G.V.; Bower, M.; Mandalia, S.; Powles, T.; Nelson, M.R.; Gazzard, B.G. Changes in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related lymphoma since the introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Blood 2000, 96, 2730–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbing, J.; Gazzard, B.; Mandalia, S.; Teague, A.; Waterston, A.; Marvin, V.; Nelson, M.; Bower, M. Antiretroviral treatment regimens and immune parameters in the prevention of systemic AIDS-related non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2177–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, O.; Pedersen, C.; Cozzi-Lepri, A.; Antunes, F.; Miller, V.; Gatell, J.M.; Katlama, C.; Lazzarin, A.; Skinhøj, P.; Barton, S.E.; et al. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma in HIV-infected patients in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Blood 2001, 98, 3406–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiguet, M.; Boué, F.; Cadranel, J.; Lang, J.-M.; Rosenthal, E.; Costagliola, D.; Clinical Epidemiology Group of the FHDH-ANRS CO4 Cohort. Effect of immunodeficiency, HIV viral load, and antiretroviral therapy on the risk of individual malignancies (FHDH-ANRS CO4): A prospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reekie, J.; Kosa, C.; Engsig, F.; Monforte, A.d.; Wiercinska-Drapalo, A.; Domingo, P.; Antunes, F.; Clumeck, N.; Kirk, O.; Lundgren, J.D.; et al. Relationship between current level of immunodeficiency and non-acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-defining malignancies. Cancer 2010, 116, 5306–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, M.J.; Chao, C.; Leyden, W.A.; Xu, L.; Horberg, M.A.; Klein, D.; Towner, W.J.; Dubrow, R.; Quesen-berry, C.P.; Neugebauer, R.S.; et al. HIV infection, immunodeficiency, viral replication, and the risk of cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 2551–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswami, R.; Chia, G.; Dalla Pria, A.; Pinato, D.J.; Parker, K.; Nelson, M.; Bower, M. Evolution of HIV-Associated Lymphoma Over 3 Decades. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2016, 72, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polesel, J.; Clifford, G.M.; Rickenbach, M.; Dal Maso, L.; Battegay, M.; Bouchardy, C.; Furrer, H.; Hasse, B.; Levi, F.; Probst-Hensch, N.M.; et al. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma incidence in the Swiss HIV Cohort Study before and after highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2008, 22, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, I.A.; Moineddin, R.; Brooks, J.D.; Antoniou, T.; Gillis, J.L.; Kendall, C.E.; Cooper, C.; Cotterchio, M.; Salters, K.; Smieja, M.; et al. Associations of CD4 Cell Count Measures With Infection-Related and Infection-Unrelated Cancer Risk Among People With HIV. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2024, 96, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathoma, A.; Sartorius, B.; Mahomed, S. The Trends and Risk Factors of AIDS-Defining Cancers and Non-AIDS-Defining Cancers in Adults Living with and without HIV: A Narrative Review. J. Cancer Epidemiol. 2024, 2024, 7588928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, J.L.; Bian, A.; Jenkins, C.A.; Shepherd, B.E.; Sigel, K.; Gill, M.J.; Kitahata, M.M.; Silverberg, M.J.; Mayor, A.M.; Coburn, S.B.; et al. CD4/CD8 Ratio and Cancer Risk Among Adults With HIV. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 114, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sanz, J.; Díaz-Álvarez, J.; Rosas, M.; Ron, R.; Iribarren, J.A.; Bernal, E.; Gutiérrez, F.; Ruiz Sancho, A.; Cabello, N.; Olalla, J.; et al. Expanding HIV clinical monitoring: The role of CD4, CD8, and CD4/CD8 ratio in predicting non-AIDS events. EBioMedicine 2023, 95, 104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chammartin, F.; Mocroft, A.; Egle, A.; Zangerle, R.; Smith, C.; Mussini, C.; Wit, F.; Vehreschild, J.J.; d’Arminio Monforte, A.; Castagna, A.; et al. Measures of Longitudinal Immune Dysfunction and Risk of AIDS and Non-AIDS Defining Malignancies in Antiretroviral-Treated People With Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 78, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caby, F.; Guiguet, M.; Weiss, L.; Winston, A.; Miro, J.M.; Konopnicki, D.; Le Moing, V.; Bonnet, F.; Reiss, P.; Mussini, C.; et al. CD4/CD8 Ratio and the Risk of Kaposi Sarcoma or Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in the Context of Efficiently Treated Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection: A Collaborative Analysis of 20 European Cohort Studies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, R.; Bortolin, M.T.; Bidoli, E.; Zanussi, S.; Pratesi, C.; Vaccher, E.; Tirelli, U.; De Paoli, P. Assessment of immunovirological features in HIV related non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients and their impact on outcome. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 53, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Mo, P.; Xiong, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y. Survival of HIV associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma in China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, R.; Martínez-Sanz, J.; Herrera, S.; Ramos-Ruperto, L.; Díez, A.; Sainz, T.; Álvarez-Díaz, N.; Correa-Pérez, A.; Muriel, A.; López-Alcalde, J.; et al. CD4/CD8 ratio and CD8+ T-cell count as prognostic markers for non-AIDS mortality in people living with HIV. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1343124. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Quan, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Jun, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y. The Disparity of Circulating Immune Cell Subsets and Inflammatory Status between HIV-Positive and HIV-Negative Patients with Lymphoma. Blood 2024, 144, 6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, S.K.; Xue, X.; Wang, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Kaplan, L.D.; Ribera, J.-M.; Oriol, A.; Spina, M.; Tirelli, U.; Boue, F.; et al. A new prognostic score for AIDS-related lymphomas in the rituximab-era. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Qin, S.; Ruan, G.; Lu, A.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Peng, J. A Novel Prognostic Score Including the CD4/CD8 for AIDS-Related Lymphoma. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 919446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuki, E.; Bohn, O.L.; El Jamal, S.; Pichardo, J.D.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Younes, A.; Teruya-Feldstein, J. Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio May Serve as a Better Prognostic Indicator Than Tumor-associated Macrophages in DLBCL Treated With Rituximab. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2019, 27, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; He, B.; Liu, X.; Yue, J.; Ying, H.; Pan, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Gao, T.; et al. Prognostic value of pre-operative inflammatory response biomarkers in gastric cancer patients and the construction of a predictive model. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, L.; Wu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y. Pretreatment lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratios predict AIDS-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma overall survival. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 3907–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.; Wiggill, T.; Lawrie, D.; Machaba, M.; Patel, M. The prognostic impact of monocyte fluorescence, immunosuppressive monocytes and peripheral blood immune cell numbers in HIV-associated Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, Á.H.; Silverberg, M.J.; Wentworth, D.; Grulich, A.E.; Fätkenheuer, G.; Mitsuyasu, R.; Tambussi, G.; Sabin, C.A.; Neaton, J.D.; Lundgren, J.D.; et al. Predicting risk of cancer during HIV infection: The role of inflammatory and coagulation biomarkers. AIDS 2013, 27, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.H.; Dubrow, R.; Silverberg, M.J. Factors contributing to risk for cancer among HIV-infected individuals, and evidence that earlier combination antiretroviral therapy will alter this risk. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2014, 9, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, S.G. HIV infection, inflammation, immunosenescence, and aging. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration of Observational HIV Epidemiological Research Europe (COHERE) Study Group; Bohlius, J.; Schmidlin, K.; Costagliola, D.; Fätkenheuer, G.; May, M.; Caro-Murillo, A.M.; Mocroft, A.; Bonnet, F.; Clifford, G.; et al. Incidence and risk factors of HIV-related non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy: A European multicohort study. Antivir. Ther. 2009, 14, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Zoufaly, A.; Stellbrink, H.-J.; der Heiden, M.A.; Kollan, C.; Hoffmann, C.; van Lunzen, J.; Hamouda, O.; Clin-Surv Study Group. Cumulative HIV viremia during highly active antiretroviral therapy is a strong predictor of AIDS-related lymphoma. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, C.J.; Buchanan, A.L.; Cole, S.R.; Hou, L.; Mugavero, M.J.; Crane, H.M.; Moore, R.D.; Haubrich, R.H.; Gopal, S.; Eron, J.J.; et al. HIV viremia and incidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in patients successfully treated with antiretroviral therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffieux, Y.; Mwansa-Kambafwile, J.; Metekoua, C.; Tombe-Nyahuma, T.; Bohlius, J.; Muchengeti, M.; Egger, M.; Rohner, E. HIV-1 Viremia and Cancer Risk in 2.8 Million People: The South African HIV Cancer Match Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, ciae652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Cole, S.R.; Achenbach, C.J.; Dittmer, D.P.; Richardson, D.B.; Miller, W.C.; Mathews, C.; Althoff, K.N.; Moore, R.D.; Eron, J.J.; et al. Cancer risk in HIV patients with incomplete viral suppression after initiation of antiretroviral therapy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvstam, O.; Marrone, G.; Medstrand, P.; Treutiger, C.J.; Svedhem, V.; Gisslén, M.; Björkman, P. Associations Between Plasma Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Ribonucleic Acid Levels and Incidence of Invasive Cancer in People With HIV After Initiation of Combination Antiretroviral Therapy. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021, 8, ofab131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, S.; Patel, M.R.; Yanik, E.L.; Cole, S.R.; Achenbach, C.J.; Napravnik, S.; Burkholder, G.A.; Reid, E.G.; Ro-driguez, B.; Deeks, S.G.; et al. Association of early HIV viremia with mortality after HIV-associated lymphoma. AIDS 2013, 27, 2365–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifone, C.; Richard, C.; Pagliuzza, A.; Dufour, C.; Lemieux, A.; Clark, N.M.; Janaka, S.K.; Fennessey, C.M.; Keele, B.E.; Fromentin, R.; et al. Contribution of intact viral genomes persisting in blood and tissues during ART to plasma viral rebound in SHIV-infected rhesus macaques. iScience 2025, 28, 111998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amand, M.; Adams, P.; Schober, R.; Iserentant, G.; Servais, J.-Y.; Moutschen, M.; Seguin-Devaux, C. The anti-caspase 1 inhibitor VX-765 reduces immune activation, CD4+ T cell depletion, viral load, and total HIV-1 DNA in HIV-1 infected humanized mice. Elife 2023, 12, e83207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, N.; Zhu, Z.; Qiao, H.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Gou, J.; Lu, M.; He, Y.; Lu, H.; et al. Comparing acute versus AIDS ART initiation on HIV-1 integration sites and clonal expansion. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, J.; Xiao, Q.; He, S.; Fu, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Immune Characteristics and Immunotherapy of HIV-Associated Lymphoma. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 9984–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmakova, A.; Hugot, C.; Kozhevnikova, Y.; Schwager Karpukhina, A.; Tsimailo, I.; Gérard, L.; Boutboul, D.; Oksenhendler, E.; Szewczyk-Roszczenko, O.; Roszczenko, P.; et al. Chronic HIV-1 Tat action induces HLA-DR downregulation in B cells: A mechanism for lymphoma immune escape in people living with HIV. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Amine, R.; Germini, D.; Zakharova, V.V.; Tsfasman, T.; Sheval, E.V.; Louzada, R.A.N.; Dupuy, C.; Bil-hou-Nabera, C.; Hamade, A.; Najjar, F.; et al. HIV-1 Tat protein induces DNA damage in human peripheral blood B-lymphocytes via mitochondrial ROS production. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germini, D.; Tsfasman, T.; Klibi, M.; El-Amine, R.; Pichugin, A.; Iarovaia, O.V.; Bilhou-Nabera, C.; Subra, F.; Bou Saada, Y.; Sukhanova, A.; et al. HIV Tat induces a prolonged MYC relocalization next to IGH in circulating B-cells. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sall, F.B.; El Amine, R.; Markozashvili, D.; Tsfasman, T.; Oksenhendler, E.; Lipinski, M.; Vassetzky, Y.; Germi-ni, D. HIV-1 Tat protein induces aberrant activation of AICDA in human B-lymphocytes from peripheral. Blood J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 15678–15685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbay, B.; Germini, D.; Bissenbaev, A.K.; Musinova, Y.R.; Sheval, E.V.; Vassetzky, Y.; Dokudovskaya, S. HIV-1 Tat Activates Akt/mTORC1 Pathway and AICDA Expression by Downregulating Its Transcriptional Inhibitors in B Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Duan, Z.; Yu, G.; Fan, M.; Scharff, M.D. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Tat Protein Aids V Region Somatic Hypermutation in Human B Cells. mBio 2018, 9, e02315–e02317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, L.; Marechal, V.; Schneider, V.; Barthet, C.; Rozenbaum, W.; Moisan-Coppey, M.; Coppey, J.; Nicolas, J.C. Production of HIV-1 by human B cells infected in vitro: Characterization of an EBV genome-negative B cell line chronically synthetizing a low level of HIV-1 after infection. Virology 1998, 244, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valyaeva, A.A.; Tikhomirova, M.A.; Feng, J.; Zharikova, A.A.; Potashnikova, D.M.; Musinova, Y.R.; Mironov, A.A.; Vassetzky, Y.S.; Sheval, E.V. Compensatory reactions of B cells in response to chronic HIV-1 Tat exposure. J. Cell Physiol. 2025, 240, e31459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, V.A.; Lafferty, M.K.; Marchionni, L.; Bryant, J.L.; Gallo, R.C.; Garzino-Demo, A. Expression of HIV-1 matrix protein p17 and association with B-cell lymphoma in HIV-1 transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13168–13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccuri, F.; Giagulli, C.; Bugatti, A.; Benetti, A.; Alessandri, G.; Ribatti, D.; Marsico, S.; Apostoli, P.; Slevin, M.A.; Rusnati, M.; et al. HIV-1 matrix protein p17 promotes angiogenesis via chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14580–14585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccuri, F.; Rueckert, C.; Giagulli, C.; Schulze, K.; Basta, D.; Zicari, S.; Marsico, S.; Cervi, E.; Fiorentini, S.; Slevin, M.; et al. HIV-1 matrix protein p17 promotes lymphangiogenesis and activates the endothelin-1/endothelin B receptor axis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, S.; Marini, E.; Caracciolo, S.; Caruso, A. Functions of the HIV-1 matrix protein p17. New Microbiol. 2006, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Popovic, M.; Tenner-Racz, K.; Pelser, C.; Stellbrink, H.-J.; van Lunzen, J.; Lewis, G.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Gallo, R.C.; Racz, P. Persistence of HIV-1 structural proteins and glycoproteins in lymph nodes of patients under highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14807–14812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, D.; Song, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, A.; Xu, J.; Guo, W.; Wu, M.; Shi, Y.; et al. High expression of HIV-1 matrix protein p17 in both lymphoma and lymph node tissues of AIDS patients. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 237, 154061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giagulli, C.; Marsico, S.; Magiera, A.K.; Bruno, R.; Caccuri, F.; Barone, I.; Fiorentini, S.; Andò, S.; Caruso, A. Opposite effects of HIV-1 p17 variants on PTEN activation and cell growth in B cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolcetti, R.; Giagulli, C.; He, W.; Selleri, M.; Caccuri, F.; Eyzaguirre, L.M.; Mazzuca, P.; Corbellini, S.; Campi-longo, F.; Marsico, S.; et al. Role of HIV-1 matrix protein p17 variants in lymphoma pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14331–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccuri, F.; Messali, S.; Zani, A.; Campisi, G.; Giovanetti, M.; Zanussi, S.; Vaccher, E.; Fabris, S.; Bugatti, A.; Focà, E.; et al. HIV-1 mutants expressing B cell clonogenic matrix protein p17 variants are increasing their prevalence worldwide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2122050119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liang, T.; Liang, B.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Zheng, X.; Li, P.; Chen, S.; et al. Diagnostic value of EBV-DNA in CSF for PCNSL in AIDS patients with focal brain lesions: A meta-analysis of diagnostic test. Medicine 2022, 101, e31793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMahon, E.M.; Glass, J.D.; Hayward, S.D.; Mann, R.B.; Becker, P.S.; Charache, P.; McArthur, J.C.; Ambinder, R.F. Epstein-Barr virus in AIDS-related primary central nervous system lymphoma. Lancet 1991, 338, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul-Haq, I.; Dalla Pria, A.; Suardi, E.; Pinato, D.J.; Froeling, F.; Forni, J.; Randell, P.; Bower, M. Blood Epstein-Barr virus DNA does not predict outcome in advanced HIV-associated Hodgkin lymphoma. Med. Oncol. 2018, 35, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, C.; Rebe, K.; van der Plas, H.; Myer, L.; Hardie, D.R. The predictive value of cerebrospinal fluid Epstein-Barr viral load as a marker of primary central nervous system lymphoma in HIV-infected persons. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 42, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinque, P.; Brytting, M.; Vago, L.; Castagna, A.; Parravicini, C.; Zanchetta, N.; D’Arminio Monforte, A.; Wah-ren, B.; Lazzarin, A.; Linde, A. Epstein-Barr virus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with AIDS-related primary lymphoma of the central nervous system. Lancet 1993, 342, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, N.D.; Randall, C.; Painschab, M.; Seguin, R.; Kaimila, B.; Kasonkanji, E.; Zuze, T.; Krysiak, R.; Sanders, M.K.; Elliott, A.; et al. High pretreatment plasma Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA level is a poor prognostic marker in HIV-associated, EBV-negative diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Malawi. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, A.; Cesarman, E.; Spina, M.; Gloghini, A.; Schulz, T.F. HIV-associated lymphomas and gamma-herpesviruses. Blood 2009, 113, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, S.R.; de Oliveira, D.E. HIV, EBV and KSHV: Viral cooperation in the pathogenesis of human malignancies. Cancer Lett. 2011, 305, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurain, K.; Yarchoan, R.; Uldrick, T.S. Treatment of Kaposi Sarcoma Herpesvirus-Associated Multicentric Castleman Disease. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 32, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uldrick, T.S.; Polizzotto, M.N.; Yarchoan, R. Recent advances in Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus-associated multicentric Castleman disease. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2012, 24, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Vaccher, E.; Gloghini, A. Hematologic cancers in individuals infected by HIV. Blood 2022, 139, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biomarker Category | Representative Biomarkers | Sample Source | Expression Trend | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokines | IL-1α IL-1β IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 IL-7 IL-8 IL-10 IL10 SNPs IL-11 IL-12p40 IL-13 IL-15 IL-18 IL-29 GM-CSF Neopterin TNF-α TGF-β IFN-γ BAFF/BLyS | HIV-NHL patients Mice HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients/mice HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients/mice HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients Mice HIV-NHL patients/mice HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients/mice HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients/mice HIV-DLBCL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients | Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased | Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive/Prognostic Prognostic Prognostic Predictive/Prognostic Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive Prognostic Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive Prognostic Prognostic Prognostic | [9] [54] [9] [9] [52,54,55,56,59,60,61] [62] [62] [50,52,54,55,56,59,60,61] [50,51] [7] [54] [9,54] [62] [7] [7] [9,54] [55,56] [54,55,56] [61] [62] [59,60] |
| Biomarker Category | Representative Biomarkers | Sample Source | Expression Trend | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemokines | CXCL10/IP-10 CXCL11 CXCL13/BCA-1 CXCL13 SNPs CCL2 CCL8 CCL17 CCL19 MIP-1δ MIP-1β | HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients/mice HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients Mice | Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased | Predictive/Prognostic Predictive Predictive/Prognostic Predictive Predictive/Prognostic Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive Predictive | [55,57,60,84] [57] [7,56,59,78,79] [56] [7,54,60] [57] [7] [57] [57] [54] |
| Biomarker Category | Representative Biomarkers | Sample Source | Expression Trend | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soluble receptors | sCD23 sCD25 sCD27 sCD30 sCD163 | HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients | Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased | Predictive Predictive/Treatment monitoring Predictive Predictive Predictive | [7,52,78,98,99,100,101] [60] [7,52,78,98,99,100] [7,52,78,98,99,100] [7,60] |
| Biomarker Category | Representative Biomarkers | Sample Source | Expression Trend | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbial translocation biomarkers | sCD14 LBP LPS FABP2 EndoCAb | HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients | Increased Increased Increased Increased Decreased | Predictive/Prognostic Predictive/Prognostic Predictive Predictive Predictive | [7,8,60] [7,8,60] [7,8] [7,8,60] [7,8] |
| Biomarker Category | Representative Biomarkers | Sample Source | Expression Trend | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Protein biomarkers | κ and λ FLC Total globulin IgA IgE IgG IgM PD-1 and PD-L1 Gal-1 β2-M Ferritin LDH SAA APO C-II C4-A C1Q | HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HAL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL/HL patients HIV-NHL/HL patients HIV-NHL/HL patients HIV-NHL patients | Increased Increased Unchanged Unchanged Unchanged Unchanged Increased Decreased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Increased Decreased | Predictive Still in dispute Unrelated Unrelated Unrelated Unrelated Predictive/Prognostic Predictive/Prognostic Predictive/Prognostic Prognostic Prognostic Predictive/Prognostic Predictive Predictive Predictive/Prognostic | [55,61,126,127,128] [130,131] [52,126,127] [52,126,127] [52,126,127] [52,126,127] [135,136] [139] [142,143] [61,150] [153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164] [167,168] [167,168] [167,168] [142] |
| Biomarker Category | Representative Biomarkers | Sample Source | Expression Trend | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extracellular Vesicles | PD-L1 CD40 CD40L TNF-RII IL-6Ra | HIV-NHL patients | Increased | Predictive | [215,216] |
| Biomarker Category | Representative Biomarkers | Sample Source | Expression Trend | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphocyte subpopulation | CD4+T cell CD4/CD8 ratio LMR | HIV-NHL patients HIV-NHL patients HIV-DLBCL patients | Decreased Decreased Decreased | Predictive/Prognostic Predictive/Prognostic Prognostic | [131,218,219,220,221,222,223,224,225,226,227,232,233,235,236] [226,227,228,229,230,231,234,235,237] [14,240,241] |
| Clinical Utility | Type | Biomarkers | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early Risk Prediction | Cytokines | IL-1α IL-1β IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 IL-10 IL10 SNPs IL-11 IL-12p40 IL-13 IL-18 IL-29 GM-CSF Neopterin TNF-α | Associated with immune activation and inflammation; combined monitoring of cytokine levels prior to onset of disease allows early screening of at-risk individuals. |
| Chemokines | CXCL10/IP-10 CXCL11 CXCL13/BCA-1 CXCL SNPs CCL2 CCL8 CCL17 CCL19 MIP-1δ MIP-1β | Involved in B-cell migration and immunomodulation for HAL. | |
| Soluble receptors | sCD23 sCD27 sCD30 sCD163 | Involved in the regulation of malignant B-cell pathology and associated with B-cell activation. sCD163 may also be involved in virus-driven carcinogenesis, especially in EBV-driven. | |
| Microbial translocation biomarkers | sCD14 LBP LPS FABP2 EndoCAb | Associated with immune activation and inflammation, also reflects the degree of pathological damage to the intestinal mucosa, the combined assay can be used as a biomarker for PLWH disease monitoring. | |
| Serum protein biomarkers | Κ and λ FLC PD-1 and PD-L1 Gal-1 β2-M SAA APO C-II C4-A C1Q | Responds to abnormal B-cell activation; involved in immune regulation; predicted time points may be influenced by a variety of factors; β2-M is directly associated with active tumor cell replication and increased tumor load. | |
| Genetic-related biomarkers | miRNA SNPs miR-17 miR-21 miR-122 miR-106a miR-106b miR-223 miR-200c-3p DNA-CNAs Clonal Ig DNA cfDNA | HIV-1 infection may exacerbate lymphoma progression and metastasis by remodeling the miRNA regulatory network and more significant correlation with risk of developing some specific lymphoma subtypes. Alterations in genes promote lymphoma development. | |
| Extracellular vesicles | PD-L1 CD40 CD40L TNF-RII IL-6Ra | Immunomodulatory molecules can be specifically expressed on the surface of EVs, which are involved in intercellular communication and TME regulation through ligand-receptor interactions to promote tumor progression. | |
| Lymphocyte subpopulation | CD4+T cell CD4/CD8 ratio | Sensitive to immune reconstitution and an important independent risk factor for predicting the development of HAL. | |
| Virus-related biomarkers | HIV viraemia p17 p17 gene variation Tat Nef gp120 EBV viraemia KSHV viraemia | HIV causes CD4+ T-cell depletion and chronic immune activation, indirectly increasing the risk of HAL. It can also directly increase cancer incidence through HIV-1’s own pro-cancer mechanisms. HIV proteins can drive carcinogenesis through multiple mechanisms. Synergistic carcinogenic effects of EBV and KSHV. | |
| Prognostic Stratification | Cytokines | IL-6 IL-7 IL-8 IL-15 TGF-β IFN-γ BAFF/BLyS | Elevated levels linked to poor prognosis and disease progression; multi-cytokine models offer superior predictive performance. |
| Chemokines | CXCL10/IP-10 CXCL13/BCA-1 CCL2 | Elevated levels linked to poor prognosis and disease progression. | |
| Microbial translocation biomarkers | sCD14 LBP | Significantly negatively correlated with overall survival. | |
| Serum protein biomarkers | PD-1 and PD-L1 Gal-1 β2-M Ferritin LDH SAA C1Q | Indicators of poor prognosis. Gal-1 levels in serum are low, whereas in tumors Gal-1 shows relatively high expression and is associated with a better prognosis. Ferritin as an independent prognostic indicator. Elevated LDH is strongly associated with poorer PFS and OS. HAL patients with high SAA level expression also had longer survival periods. The levels of C1Q negatively correlate with HAL survival time. | |
| Lymphocyte subpopulation | CD4+T cell CD4/CD8 ratio LMR | Associated with shorter OS and PFS in HAL. CD4/CD8 ratio <0.5 was an independent predictor of non-AIDS-related and all-cause mortality in PLWH. Combined with IPI can further improve risk prediction and prognostic assessment accuracy. | |
| Virus-related biomarkers | HIV viraemia EBV viraemia | Persistent hyperviremia can increase a patient’s risk of death. | |
| Treatment Monitoring | Cytokines | BAFF/BLyS TNF-α | Correlates with clinical response to treatment and survival. |
| Chemokines | CXCL10/IP-10 CXCL13/BCA-1 CCL2 CCL17 | Associated with inflammation, which partially declines or returns to normal after therapeutic intervention, with a potential role as a dynamic prognostic marker. Monitor disease progression and response to therapy. | |
| Soluble receptors | sCD25 | Dynamic changes may reflect treatment response. | |
| Microbial translocation biomarkers | sCD14 LBP | Dynamic post-treatment decline may reflect reversal of partial immune activation status by treatment. | |
| Serum protein biomarkers | Ferritin C1Q | Ferritin levels may reflect tumor microenvironmental Status, informing treatment. C1Q decline after treatment predicts poor prognosis. | |
| Extracellular vesicles | PD-L1 CD40 CD40L TNF-RII | Significant reduction in plasma EVs harboring PD-L1, CD40, CD40L, or TNF-RII following treatment. | |
| Virus-related biomarkers | HIV viraemia | Post-treatment decline reduces risk of HAL development. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, X.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, X.; He, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Circulating Biomarker Panorama in HIV-Associated Lymphoma: A Bridge from Early Risk Warning to Prognostic Stratification. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070993
Shu X, Xiao Q, Liu Y, Li Y, Xie X, He S, Li J, Zhang X, Liu Y. Circulating Biomarker Panorama in HIV-Associated Lymphoma: A Bridge from Early Risk Warning to Prognostic Stratification. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070993
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Xuejiao, Qing Xiao, Yi Liu, Ya Li, Xiaoqing Xie, Sanxiu He, Jun Li, Xiaomei Zhang, and Yao Liu. 2025. "Circulating Biomarker Panorama in HIV-Associated Lymphoma: A Bridge from Early Risk Warning to Prognostic Stratification" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070993
APA StyleShu, X., Xiao, Q., Liu, Y., Li, Y., Xie, X., He, S., Li, J., Zhang, X., & Liu, Y. (2025). Circulating Biomarker Panorama in HIV-Associated Lymphoma: A Bridge from Early Risk Warning to Prognostic Stratification. Biomolecules, 15(7), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070993







