Influence of the Maillard Reaction on the Properties of Gelatin/Zein Nanofibers Loaded with Dihydromyricetin Prepared by Electro-Blowing Spinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Liquids for Electrospinning
2.3. Fiber Fabrication Process
2.4. Maillard Reaction
2.5. Characterization of the Fiber Properties
2.6. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities
3. Results and Discussion
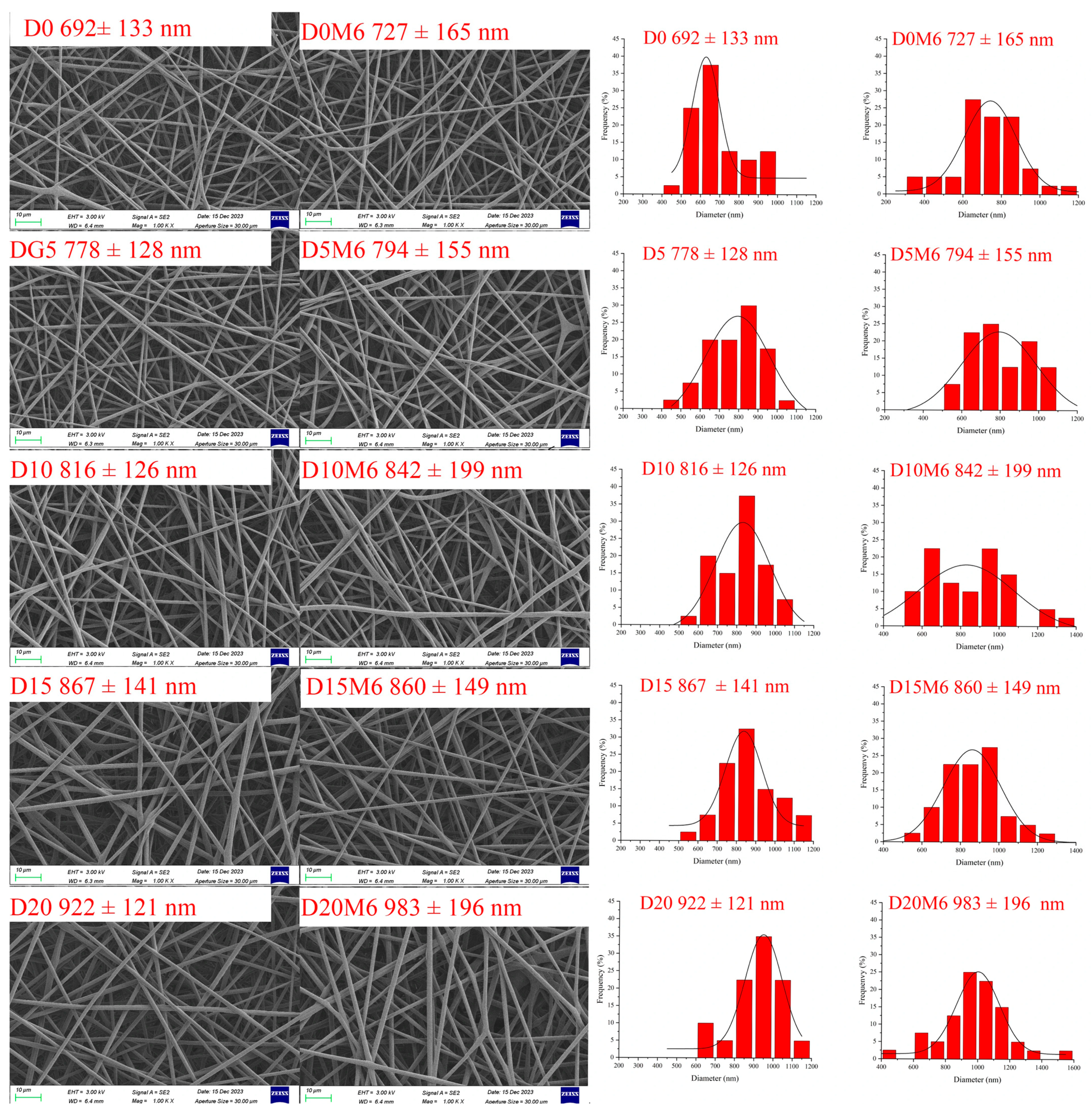
3.1. Morphology of Nanofibers
3.2. FTIR Spectra
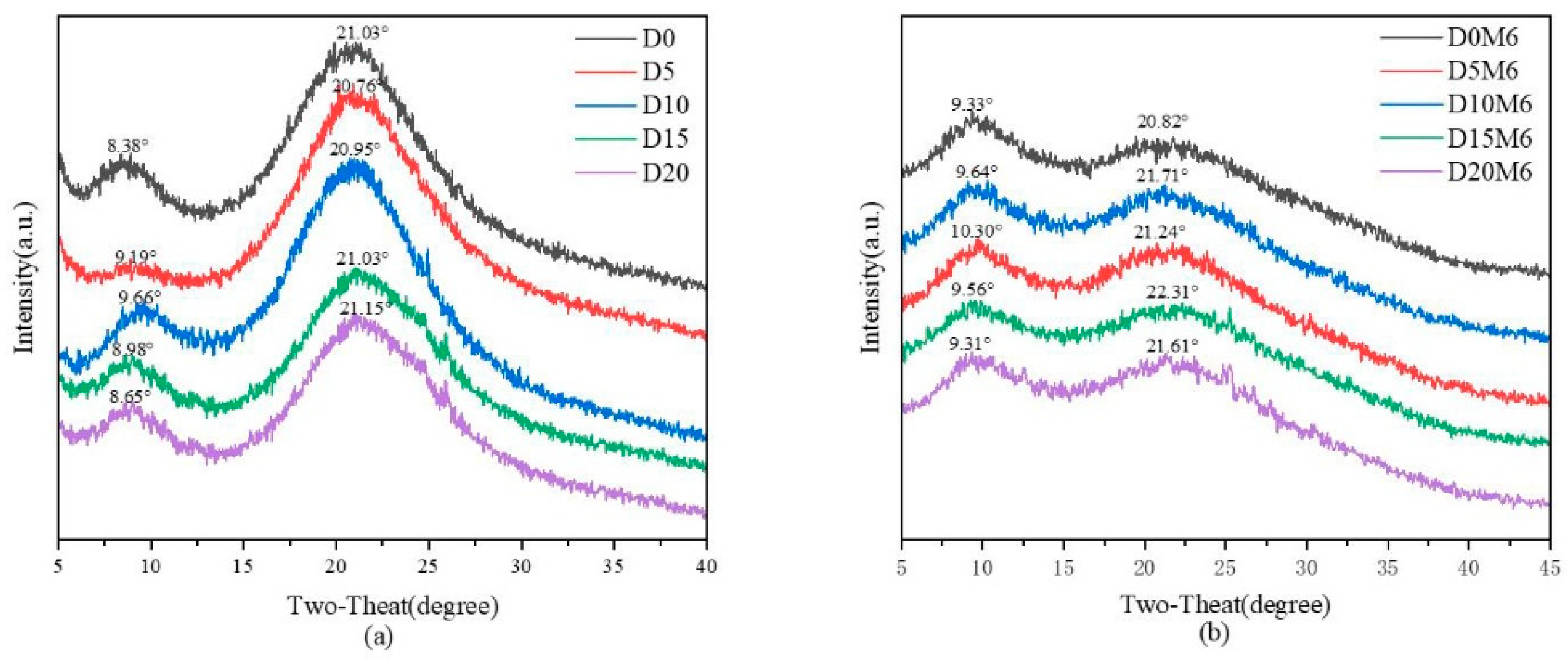
3.3. XRD Spectra
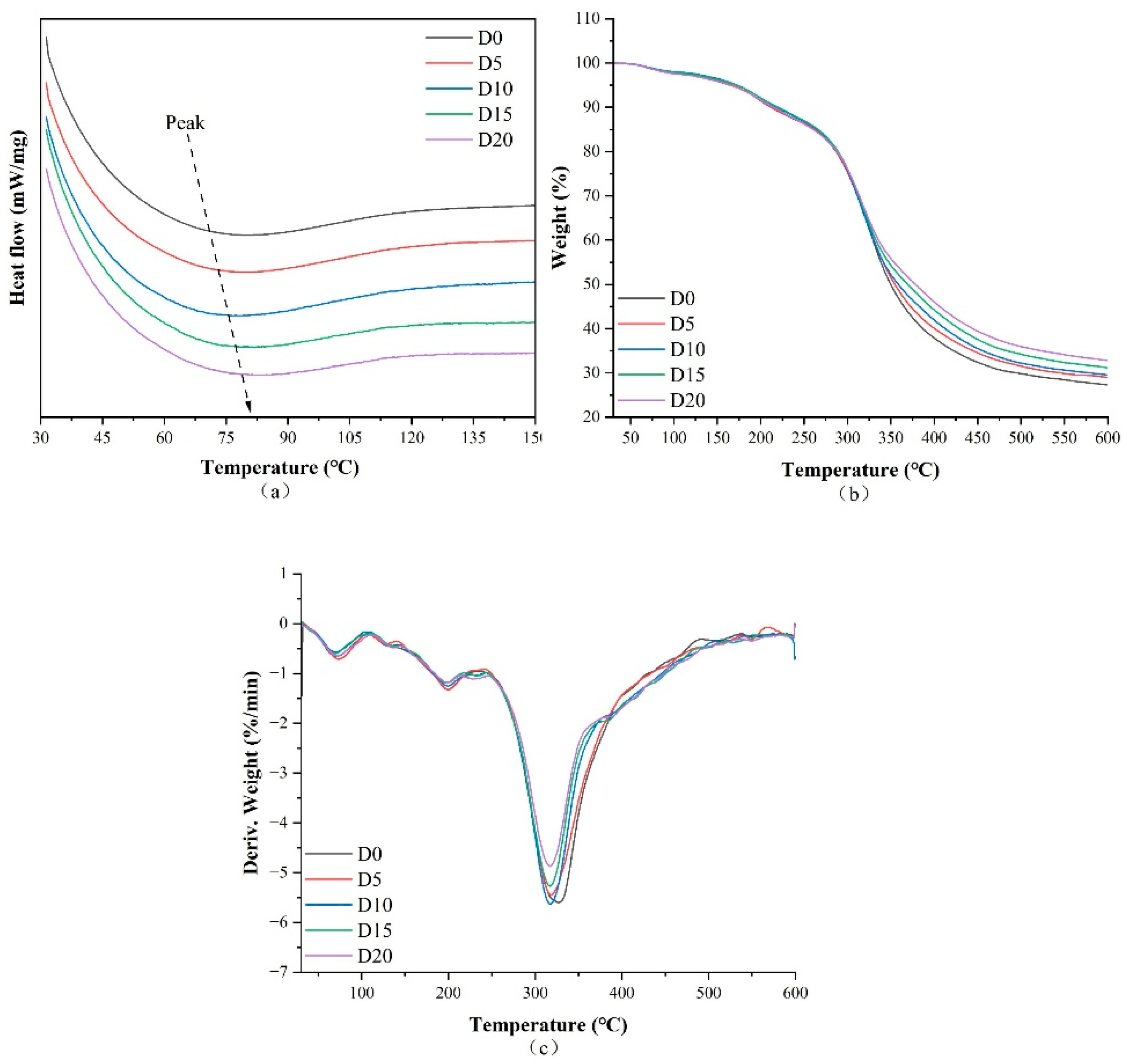
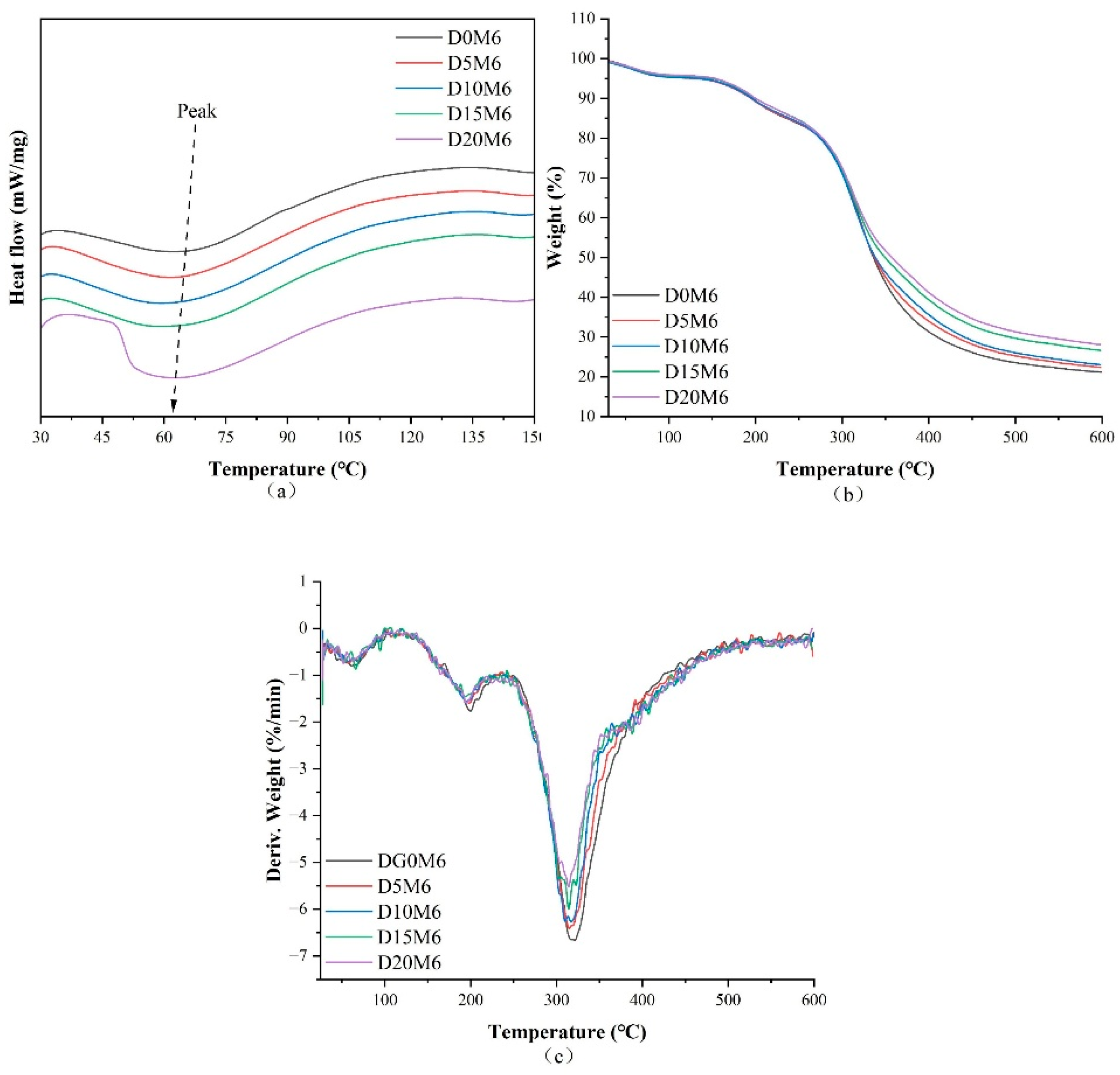
3.4. Thermal Characteristics
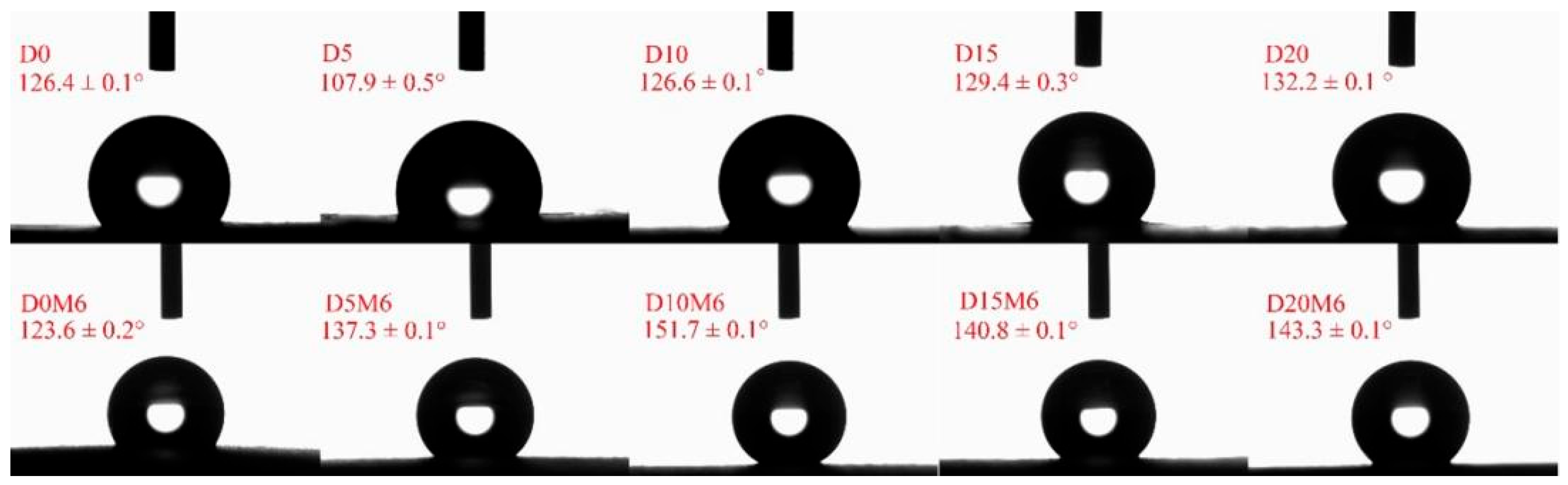
3.5. WCA
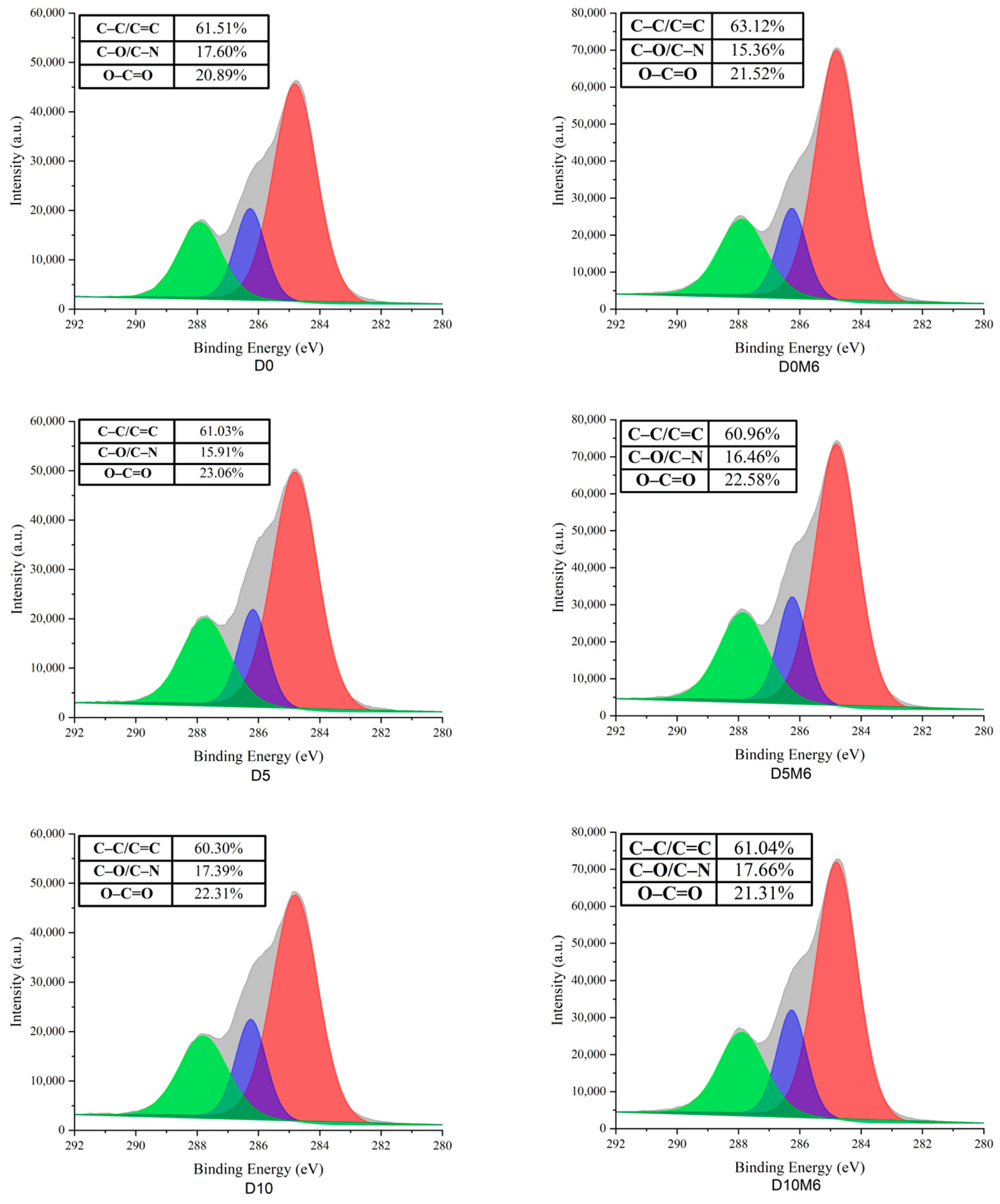
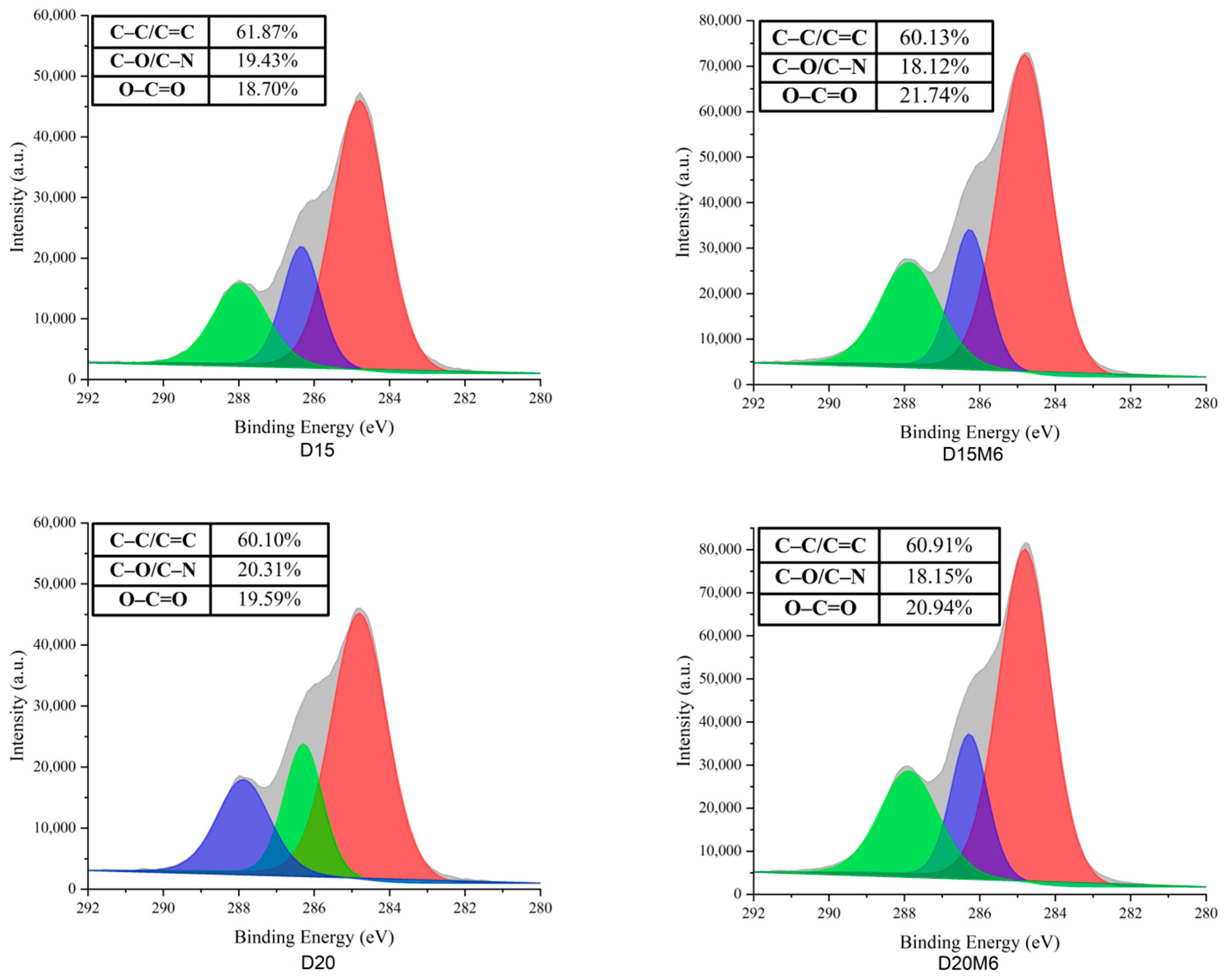
3.6. Surface Elemental Analysis
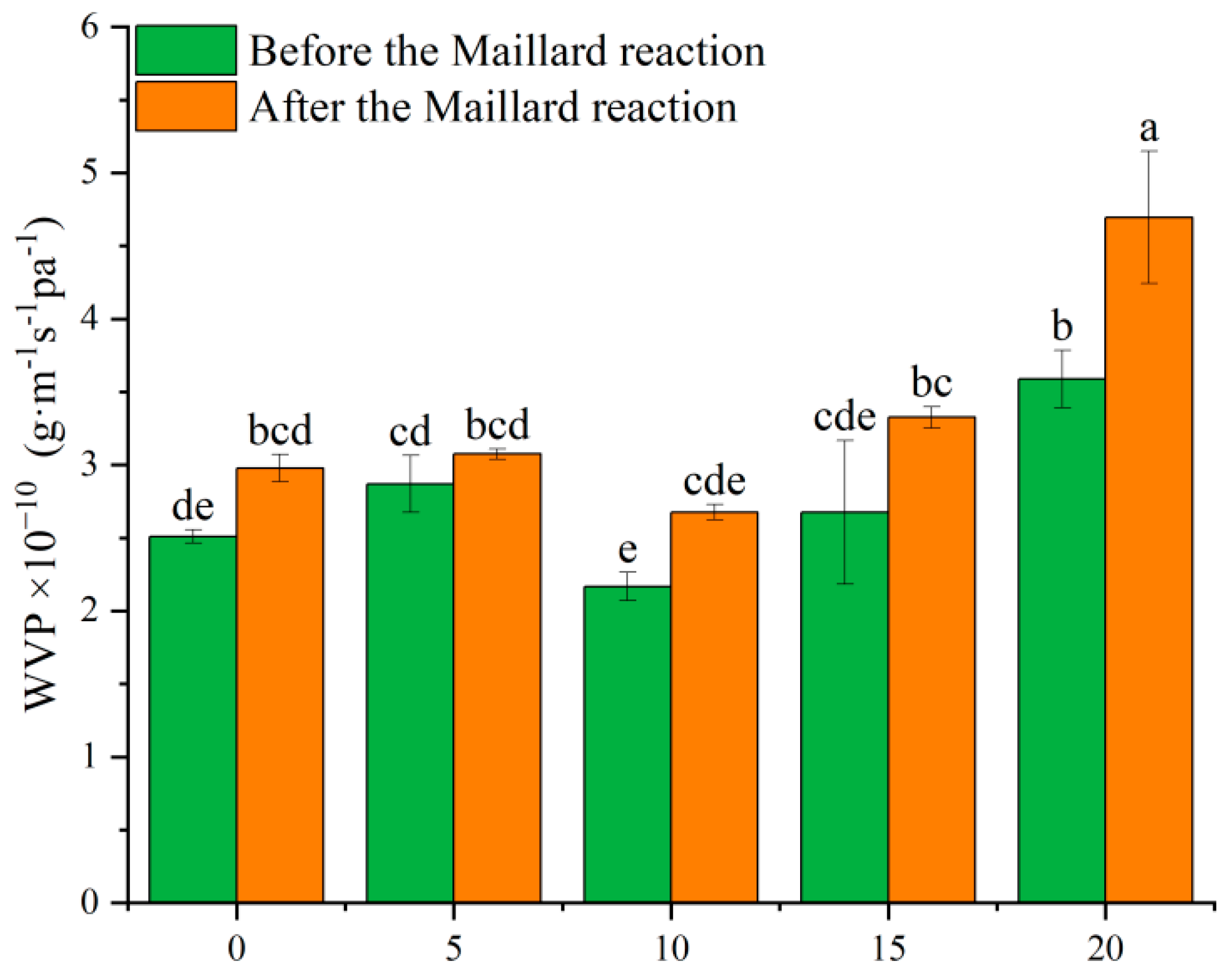
3.7. WVP
3.8. Mechanical Characteristics
3.9. Antioxidant Activities
3.10. Antibacterial Activities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; You, W.; Wang, W.; Tian, W.; Chen, F.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Dihydromyricetin-Incorporated Multilayer Nanofibers Accelerate Chronic Wound Healing by Remodeling the Harsh Wound Microenvironment. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 1556–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, B. Interaction between Iron and Dihydromyricetin Extracted from Vine Tea. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5926–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhang, S.; Chu, L. Fabrication and Characterization of Dihydromyricetin-Loaded Microcapsules Stabilized by Glyceryl Monostearate and Whey Protein–Xanthan Gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 128039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, R.; Ma, H.; Liang, G.; Liu, B. An Investigation on Pickering Nano-Emulsions Stabilized by Dihydromyricetin/High-Amylose Corn Starch Composite Particles: Preparation Conditions and Carrier Properties. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Chen, L.; Lin, S.; Cao, H.; Teng, H. A Designed Self-Microemulsion Delivery System for Dihydromyricetin and Its Dietary Intervention Effect on High-Fat-Diet Fed Mice. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 132954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ding, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, N.; Chai, G.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zheng, R.; Zhao, Y.; et al. A Poloxamer 407/Chitosan-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel Dressing for Diabetic Wound Healing via Oxygen Production and Dihydromyricetin Release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Ding, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Ma, S.; Ding, Q.; Liu, W. Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Chitosan-Loaded Dihydromyricetin-Based Nanofiber Membrane Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing by Anti-Inflammatory and Regulating Autophagy-Associated Protein Expression. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Sun, R.; Xia, Q. Solid Self-emulsifying Delivery System (S-SEDS) of Dihydromyricetin: A New Way for Preparing Functional Food. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Chen, X.; Xie, Y.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W. Application of Essential Oil as a Sustained Release Preparation in Food Packaging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wu, M.; Yu, D.-G. Nanofibers-Based Food Packaging. ES Food Agrofor. 2022, 7, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; An, J.; Tian, C.; Shang, L.; Tao, Y.; Deng, L. Air-Assisted Electrospinning of Dihydromyricetin-Loaded Dextran/Zein/Xylose Nanofibers and Effects of the Maillard Reaction on Fiber Properties. Molecules 2024, 29, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Gan, C.; Shi, H.; Qu, K.; Jing, L.; Lu, M.; Su, B.; Yu, H.; Yuan, H.; Chen, J.; et al. Gastric Floating Pill Enhances the Bioavailability and Drug Efficacy of Dihydromyricetin in Vivo. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Jiang, B.; Ashraf, W.; Bin Tahir, A.; Ul Haq, F. Improving the Functional Characteristics of Thymol-Loaded Pullulan and Whey Protein Isolate-Based Electrospun Nanofiber. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hu, X.; Cang, W.; Ji, S.; Wu, R.; Wu, J. Biofilm-Based Probiotic Delivery System and Its Application in the Food Industry. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurić, M.; Donsì, F.; Maslov Bandić, L.; Jurić, S. Natural-Based Electrospun Nanofibers: Challenges and Potential Applications in Agri-Food Sector. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Bae, J.H.; Hasegawa, Y.; An, S.; Kim, I.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. Thiol-Functionalized Cellulose Nanofiber Membranes for the Effective Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions in Water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alav, A.; Kutlu, N.; Kına, E.; Meral, R. A Novel Green Tea Extract-Loaded Nanofiber Coating for Kiwi Fruit: Improved Microbial Stability and Nutritional Quality. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Aayush, K.; Sharma, K.; Bose, I.; Khan, A.A.; Atanassova, M.; Yang, T.; Murariu, O.C.; Sharma, S.; Caruso, G. Fiber and Nanofiber Based Edible Packaging for Enhancing the Shelf Life of Food: A Review. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnabawy, E.; Sun, D.; Shearer, N.; Shyha, I. Electro-Blown Spinning: New Insight into the Effect of Electric Field and Airflow Hybridized Forces on the Production Yield and Characteristics of Nanofiber Membranes. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2023, 8, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, J. Electrospun Konjac Glucomannan-Gelatin/Polycaprolactone Bilayer Nanofibrous Films with Improved Hydrophobicity and Mechanical Properties for Food Packaging. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayazi, D.; Zandi, M.; Ganjloo, A.; Dardmeh, N. Bioactive Electrospun Zein Fibers Integrated with ZnO Nanoparticles: In Vitro Investigations. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.; Zhang, M.; Xiang, L.; Xiang, A.; Zhou, H. Edible Antibacterial Gelatin/Zein Fiber Films Loaded with Cinnamaldehyde for Extending the Shelf Life of Strawberries by Electrospinning Approach. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Venugopal, J.; Huang, Z.-M.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Crosslinking of the Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers. Polymer 2006, 47, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, J.; Sun, Y.; Shi, N.; Li, C.; Kong, W. Zein-Based Nanofibers for Drug Delivery: Classes and Current Applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 3199–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huner, A. Fast-Dissolving Electroactive Drug Delivery Systems: Gelatin/Poly (Sulphonic Acid Diphenyl Aniline) Electrospun Nanofibers. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yoon, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Jin, H.-J.; Kwak, H.W. Multifunctional Fructose-Crosslinked Fibroin Film with a Developed β-Sheet Structure for Advanced Food Packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 286, 138370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.N.; Ray, C.A. Control of Maillard Reactions in Foods: Strategies and Chemical Mechanisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4537–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.W.; Park, J.; Yun, H.; Jeon, K.; Kang, D.-W. Effect of Crosslinkable Sugar Molecules on the Physico-Chemical and Antioxidant Properties of Fish Gelatin Nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Z.; Shang, L.; Deng, L. Influence of the Maillard Reaction on Properties of Air-Assisted Electrospun Gelatin/Zein/Glucose Nanofibers. Foods 2023, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Ho, T.C.; Park, J.-S.; Han, J.-M.; Surendhiran, D.; Lee, H.-J.; Zhang, W.; Chun, B.-S. Fabrication of Smart Film Based on Fish Gelatin Incorporating Phycoerythrin and Cellulose Nanofibrils to Monitor Fish Freshness. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Maierhaba, T.; An, J.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, L. Comparison of Eugenol and Dihydromyricetin Loaded Nanofibers by Electro-Blowing Spinning for Active Packaging. Food Biosci. 2023, 51, 102294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, F.; Li, S.; Sun, D.; Ma, Q.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W. Development of Electrospun Nanofiber Films Based on Pullulan/Polyvinyl Alcohol Incorporating Bayberry Pomace Anthocyanin Extract for Aquatic Products Freshness Monitoring. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxabide, A.; Uranga, J.; Guerrero, P.; De La Caba, K. Improvement of Barrier Properties of Fish Gelatin Films Promoted by Gelatin Glycation with Lactose at High Temperatures. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Sani, M.; Tavassoli, M.; McClements, D.J.; Hamishehkar, H. Multifunctional Halochromic Packaging Materials: Saffron Petal Anthocyanin Loaded-Chitosan Nanofiber/Methyl Cellulose Matrices. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Saadi, A.; Fu, K.; Taxipalati, M.; Deng, L. Fabrication and Characterization of Dextran/Zein Hybrid Electrospun Fibers with Tailored Properties for Controlled Release of Curcumin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 6355–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yu, L.; Gu, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, K.; Liang, J.; Liu, Q. Preparation of Dual-Functional Packaging Films Containing Green Tea Essential Oil Microcapsules for Strawberry Preservation: Excellent Barrier Properties and Antioxidant Activity. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Jiang, B.; Chen, J.; Ashraf, W.; Tahir, A.B. Preparation and Structural Characterization of Pullulan and Whey Protein Isolate-Based Electrospun Nanofiber. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, J.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, F.; Du, L.; Wang, D. Preparation and Characterization of Gelatin/Zein Nanofiber Films Loaded with Perillaldehyde, Thymol, or ε-Polylysine and Evaluation of Their Effects on the Preservation of Chilled Chicken Breast. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.-Q.; Lu, C.-Q.; Cui, S.-H.; Pan, L.-H.; Zhang, H.-L.; Wang, J.-H.; Luo, J.-P. Structural Identification and Immunostimulating Activity of a Laminaria Japonica Polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shi, C.; Zhou, X.; Lin, T.; Gong, Y.; Yin, M.; Fan, L.; Wang, W.; Fang, J. Preparation of a Nanoscale Dihydromyricetin-Phospholipid Complex to Improve the Bioavailability: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 138, 104994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhong, H.; Zou, Y.; Qin, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Impact of Glycation on Physical Properties of Composite Gluten/Zein Nanofibrous Films Fabricated by Blending Electrospinning. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.B.; Doğan, N.; Doğan, C.; Akgul, Y. A Novel Approach to Crosslink Gelatin Nanofibers Through Neutralization-Induced Maillard Reaction. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, C.S.; Baek, D.H.; Gang, K.D.; Lee, K.H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Characterization of Gelatin Nanofiber Prepared from Gelatin–Formic Acid Solution. Polymer 2005, 46, 5094–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Liu, X.; Ma, H.; Liu, B.; Liang, G. Multi-Scale Stabilization Mechanism of Pickering Emulsion Gels Based on Dihydromyricetin/High-Amylose Corn Starch Composite Particles. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, C. Electrospun Chitosan/Sericin Composite Nanofibers with Antibacterial Property as Potential Wound Dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 68, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhao, X.; Ao, Q. Determination of the Domain Structure of the 7S and 11S Globulins from Soy Proteins by XRD and FTIR. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liang, B.; Sheng, H.; Wang, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M. Influence of Initial Protein Structures and Xanthan Gum on the Oxidative Stability of O/W Emulsions Stabilized by Whey Protein. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Q.-T.; Li, X.-M.; Meng, R.; Zhang, B.; Jin, Z.-Y. Insight into the Stabilization Mechanism of Emulsions Stabilized by Maillard Conjugates: Protein Hydrolysates-Dextrin with Different Degree of Polymerization. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Yang, M.; Du, Z.; Wei, C.; Zhang, T.; Liu, B.; Liu, J. Ultrasound-Assisted Maillard Reaction of Ovalbumin/Xylose: The Enhancement of Functional Properties and Its Mechanism. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, F.; Du, L.; Wang, D. Fabrication and Characterization of Gelatin/Zein Nanofiber Films Loading Perillaldehyde for the Preservation of Chilled Chicken. Foods 2021, 10, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Feng, F.; Wu, D.; Zhang, H. Encapsulation of Allopurinol by Glucose Cross-Linked Gelatin/Zein Nanofibers: Characterization and Release Behavior. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, L.; Mu, R.-J.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Pang, J.; Wu, C. Effects of Konjac Glucomannan on the Structure, Properties, and Drug Release Characteristics of Agarose Hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Que, F.; Kang, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Characterization of Gelatin/Zein Nanofibers by Hybrid Electrospinning. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Study on Wettability, Mechanical Property and Biocompatibility of Electrospun Gelatin/Zein Nanofibers Cross-Linked by Glucose. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mu, R.-J.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Lin, Z.; Pang, J. Characterization and Antibacterial Activity Evaluation of Curcumin Loaded Konjac Glucomannan and Zein Nanofibril Films. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 113, 108293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, M.; Bianchi, E.; Rossi, S.; Boselli, C.; Icaro Cornaglia, A.; Malavasi, L.; Carzino, R.; Suarato, G.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Athanassiou, A.; et al. Maltodextrin-Amino Acids Electrospun Scaffolds Cross-Linked with Maillard-Type Reaction for Skin Tissue Engineering. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 133, 112593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. Enhancement and Control of Water Vapor Permeability and Thermal Conductivity of Polymers: A Review. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2023, 34, 1451–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; An, J.; Tian, C.; Shang, L.; Tao, Y.; Deng, L. Tunable Physical Properties of Electro-Blown Spinning Dextran/Zein Nanofibers Cross-Linked by Maillard Reaction. Foods 2024, 13, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, D. Water Vapor Transport Properties of Polyurethane Films for Packaging of Respiring Foods. Food Eng. Rev. 2021, 13, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.-W. Gelatin/Agar-Based Functional Film Integrated with Pickering Emulsion of Clove Essential Oil Stabilized with Nanocellulose for Active Packaging Applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 627, 127220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Du, Y.; Yuan, S.; Pang, J. Dihydromyricetin Incorporated Active Films Based on Konjac Glucomannan and Gellan Gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Park, J.; Nam, J.; Hyun, Y.; Jin, H.-J.; Kwak, H.W. Antioxidant and UV-Blocking Glucose-Crosslinked Sericin Films with Enhanced Structural Integrity. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 165, 104942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salević, A.; Stojanović, D.; Lević, S.; Pantić, M.; Đorđević, V.; Pešić, R.; Bugarski, B.; Pavlović, V.; Uskoković, P.; Nedović, V. The Structuring of Sage (Salvia Officinalis L.) Extract-Incorporating Edible Zein-Based Materials with Antioxidant and Antibacterial Functionality by Solvent Casting versus Electrospinning. Foods 2022, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pateiro, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Domínguez, R.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Lorenzo, J.M. Application of Essential Oils as Antimicrobial Agents against Spoilage and Pathogenic Microorganisms in Meat Products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 337, 108966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.-N.; Wang, F.; Yuan, Y.-T.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Yi, X. Antibacterial Activity and Mode of Action of Dihydromyricetin from Ampelopsis Grossedentata Leaves against Food-Borne Bacteria. Molecules 2019, 24, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| DSC | TGA | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | ∆H (J/g) | Peak 1 (°C) | Weight Loss (%) | Peak 2 (°C) | Weight Loss (%) | Peak 3 (°C) | Weight Loss (%) | Residue at 600 °C (%) | |
| D0 | 70.7 | −41.270 | 69.7 | 1.03 | 199.7 | 7.14 | 326.9 | 64.50 | 27.31 |
| D5 | 72.4 | −36.468 | 73.3 | 2.47 | 199.8 | 5.95 | 318.3 | 62.60 | 28.98 |
| D10 | 78.8 | −18.147 | 70.1 | 2.09 | 199.6 | 5.78 | 317.7 | 62.63 | 29.51 |
| D15 | 81.8 | −19.692 | 69.3 | 2.37 | 196.0 | 5.05 | 317.4 | 61.39 | 31.20 |
| D20 | 82.4 | −23.924 | 73.0 | 2.67 | 199.7 | 5.65 | 317.6 | 58.87 | 32.81 |
| D0M6 | 66.7 | −4.594 | 61.3 | 5.16 | 199.8 | 11.26 | 321.1 | 62.41 | 21.17 |
| D5M6 | 64.2 | −5.638 | 58.4 | 4.86 | 198.4 | 10.29 | 314.8 | 62.50 | 22.35 |
| D10M6 | 64.1 | −6.086 | 57.8 | 4.82 | 195.2 | 10.53 | 310.1 | 61.61 | 23.04 |
| D15M6 | 65.6 | −5.963 | 66.1 | 4.67 | 193.5 | 10.30 | 314.4 | 58.38 | 26.65 |
| D20M6 | 63.9 | −8.387 | 51.6 | 4.47 | 195.4 | 11.33 | 314.0 | 56.06 | 28.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, H.; Wu, R.; Xiao, M.; An, J.; Shang, L.; Tao, Y.; Deng, L. Influence of the Maillard Reaction on the Properties of Gelatin/Zein Nanofibers Loaded with Dihydromyricetin Prepared by Electro-Blowing Spinning. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060891
Xiang H, Wu R, Xiao M, An J, Shang L, Tao Y, Deng L. Influence of the Maillard Reaction on the Properties of Gelatin/Zein Nanofibers Loaded with Dihydromyricetin Prepared by Electro-Blowing Spinning. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(6):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060891
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Hui, Runtian Wu, Man Xiao, Jianhui An, Longchen Shang, Yexing Tao, and Lingli Deng. 2025. "Influence of the Maillard Reaction on the Properties of Gelatin/Zein Nanofibers Loaded with Dihydromyricetin Prepared by Electro-Blowing Spinning" Biomolecules 15, no. 6: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060891
APA StyleXiang, H., Wu, R., Xiao, M., An, J., Shang, L., Tao, Y., & Deng, L. (2025). Influence of the Maillard Reaction on the Properties of Gelatin/Zein Nanofibers Loaded with Dihydromyricetin Prepared by Electro-Blowing Spinning. Biomolecules, 15(6), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060891








