Real-Time SPR Biosensing to Detect and Characterize Fast Dissociation Rate Binding Interactions Missed by Endpoint Detection and Implications for Off-Target Toxicity Screening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies
2.2. In Vitro Transcription and Translation of SPOC Arrays
2.3. Fluorescent Assay
2.4. Surface Plasmon Resonance Assay
2.5. Data Analysis
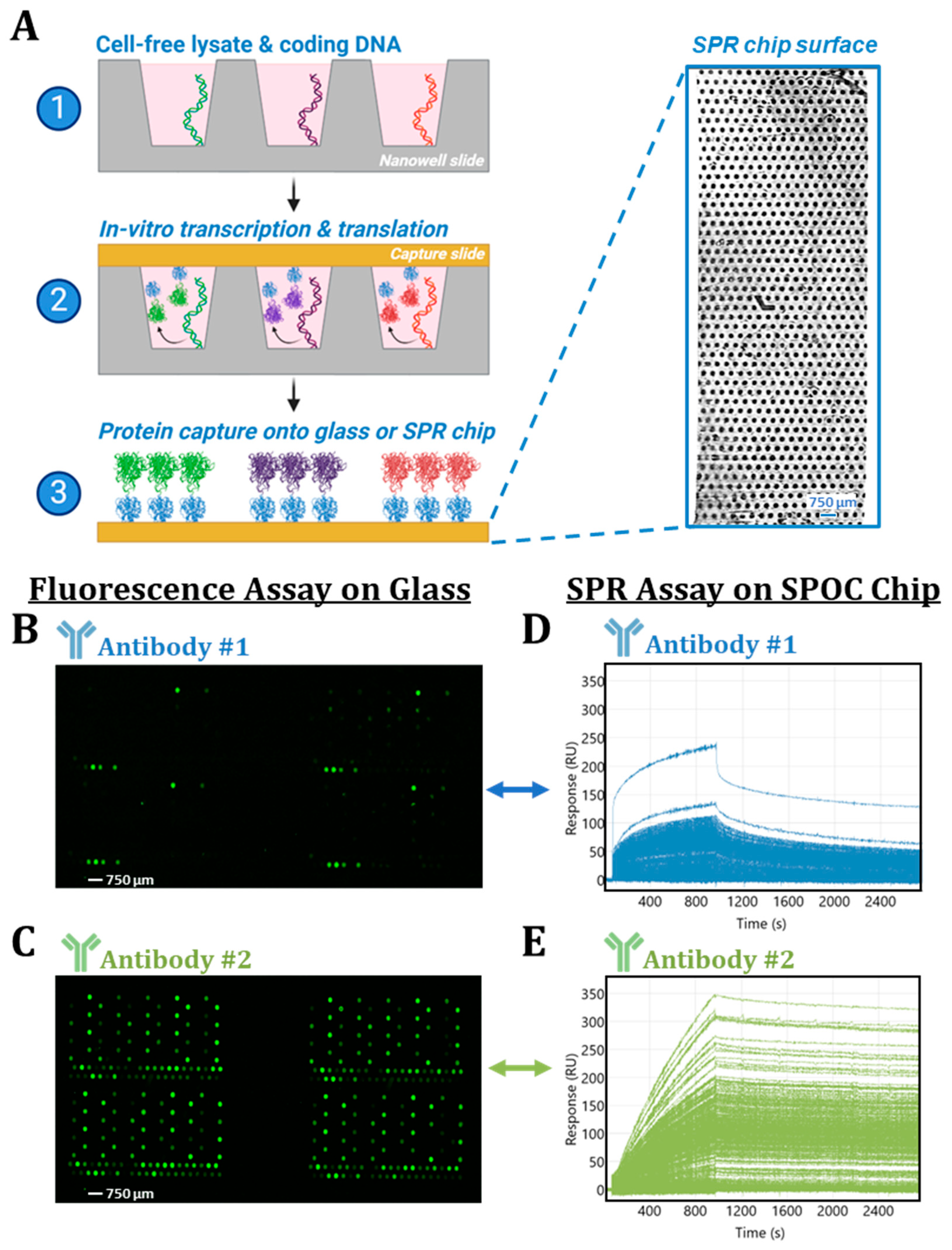
3. Results
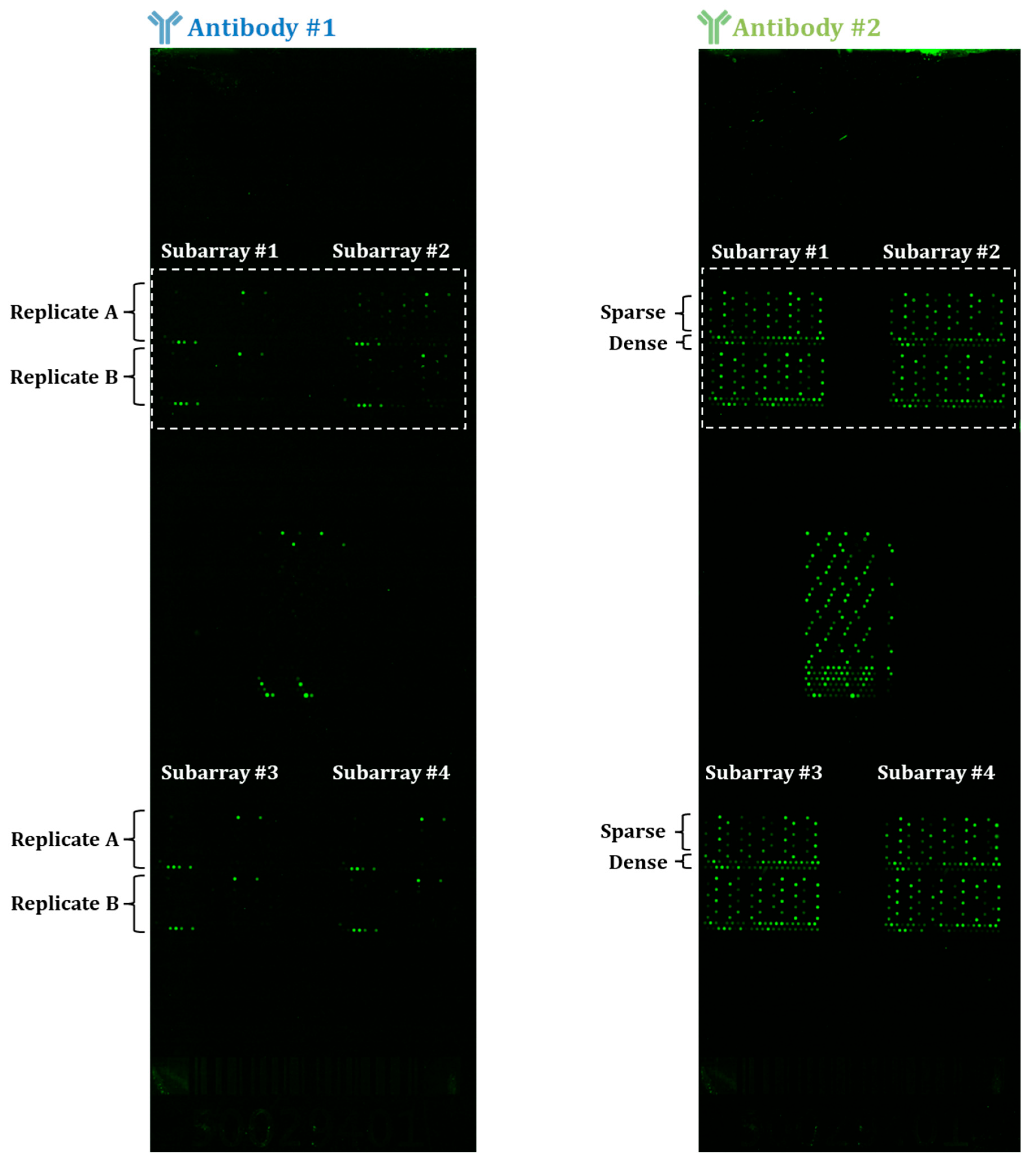
3.1. Disparities in Fluorescent-Based Endpoint Detection
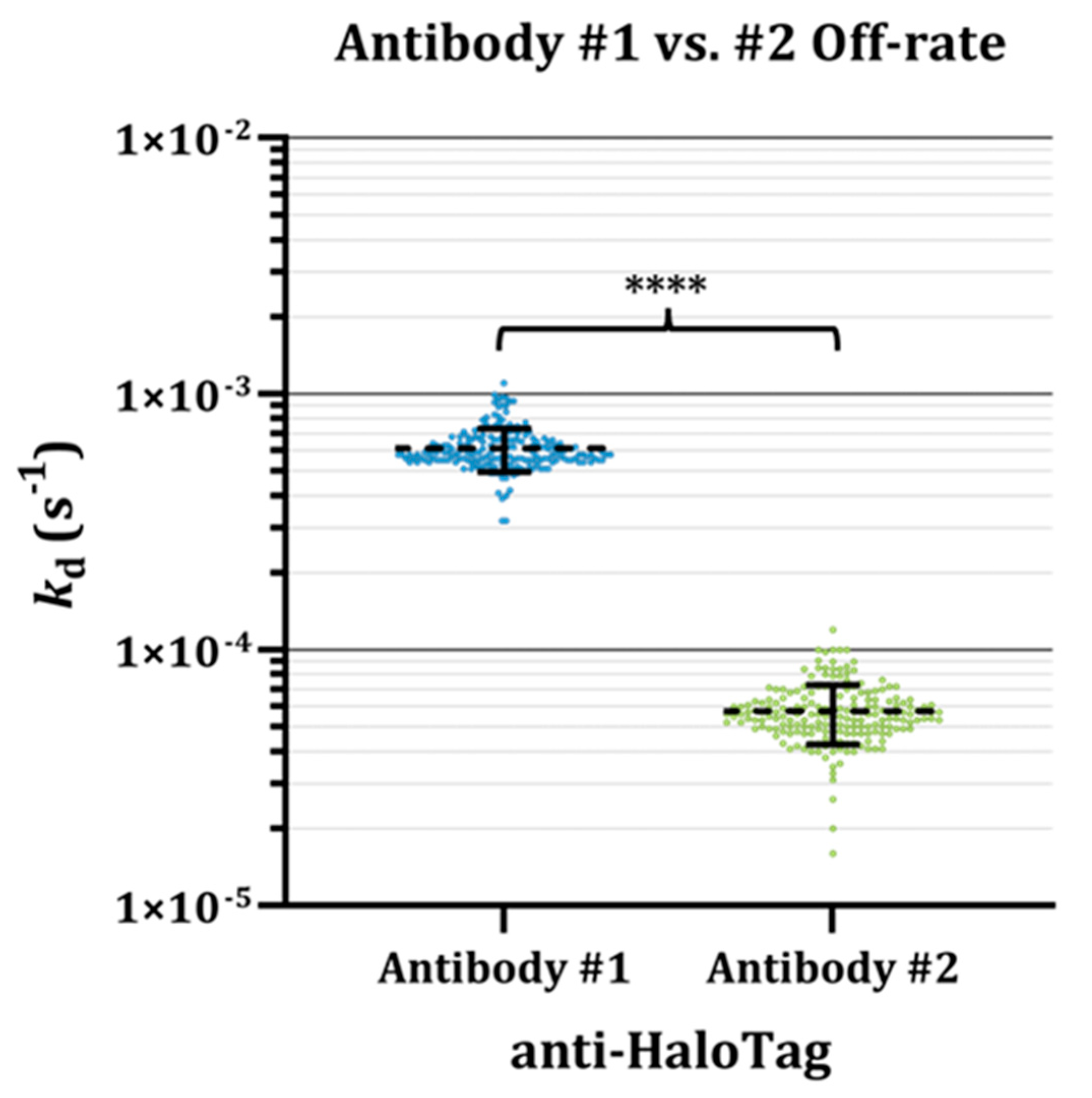
3.2. Insights from Label-Free Kinetic Screening
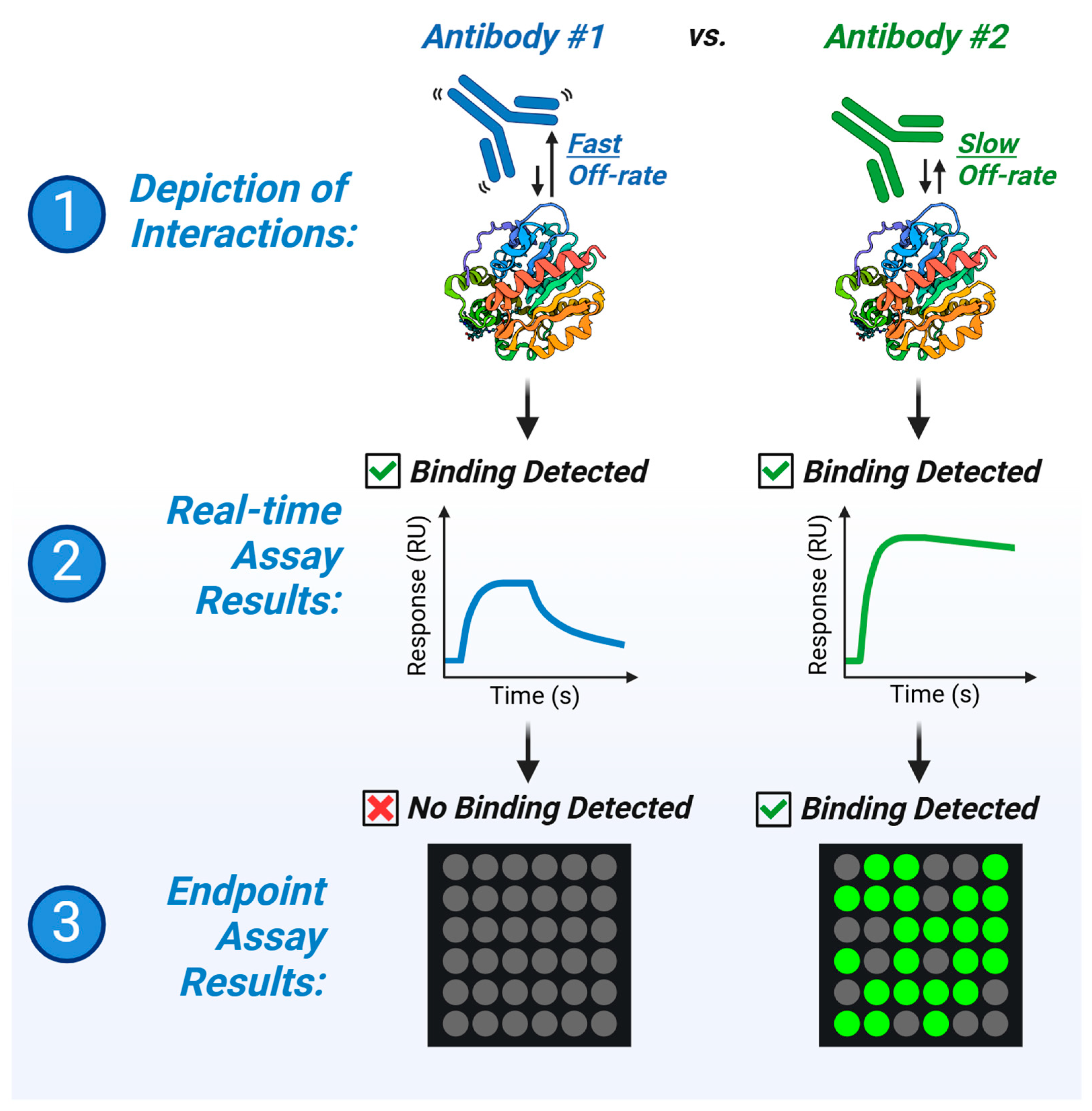
3.3. Fast Kinetics of Antibody #1 Partially Underlie Disparities in Endpoint Assay Results
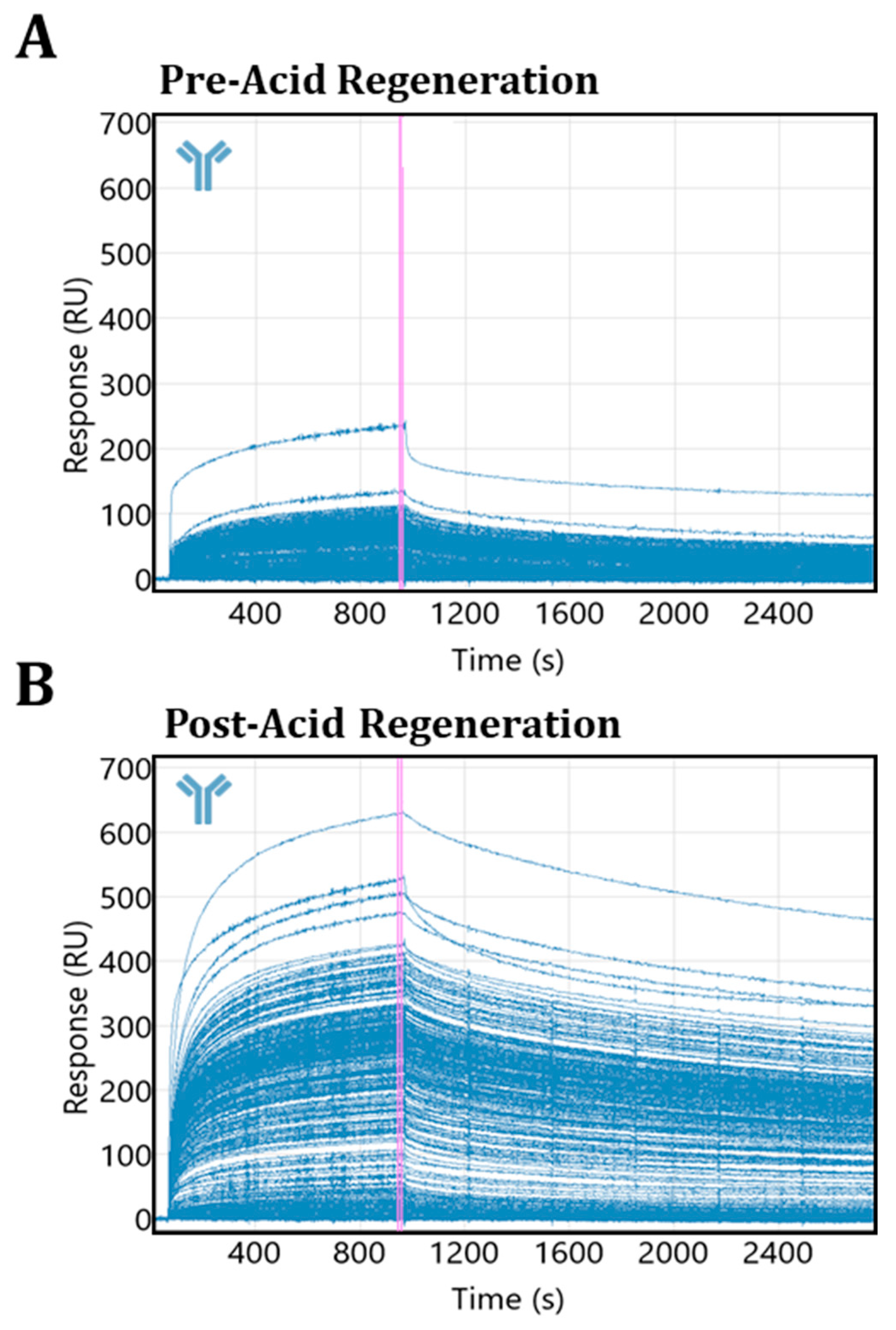
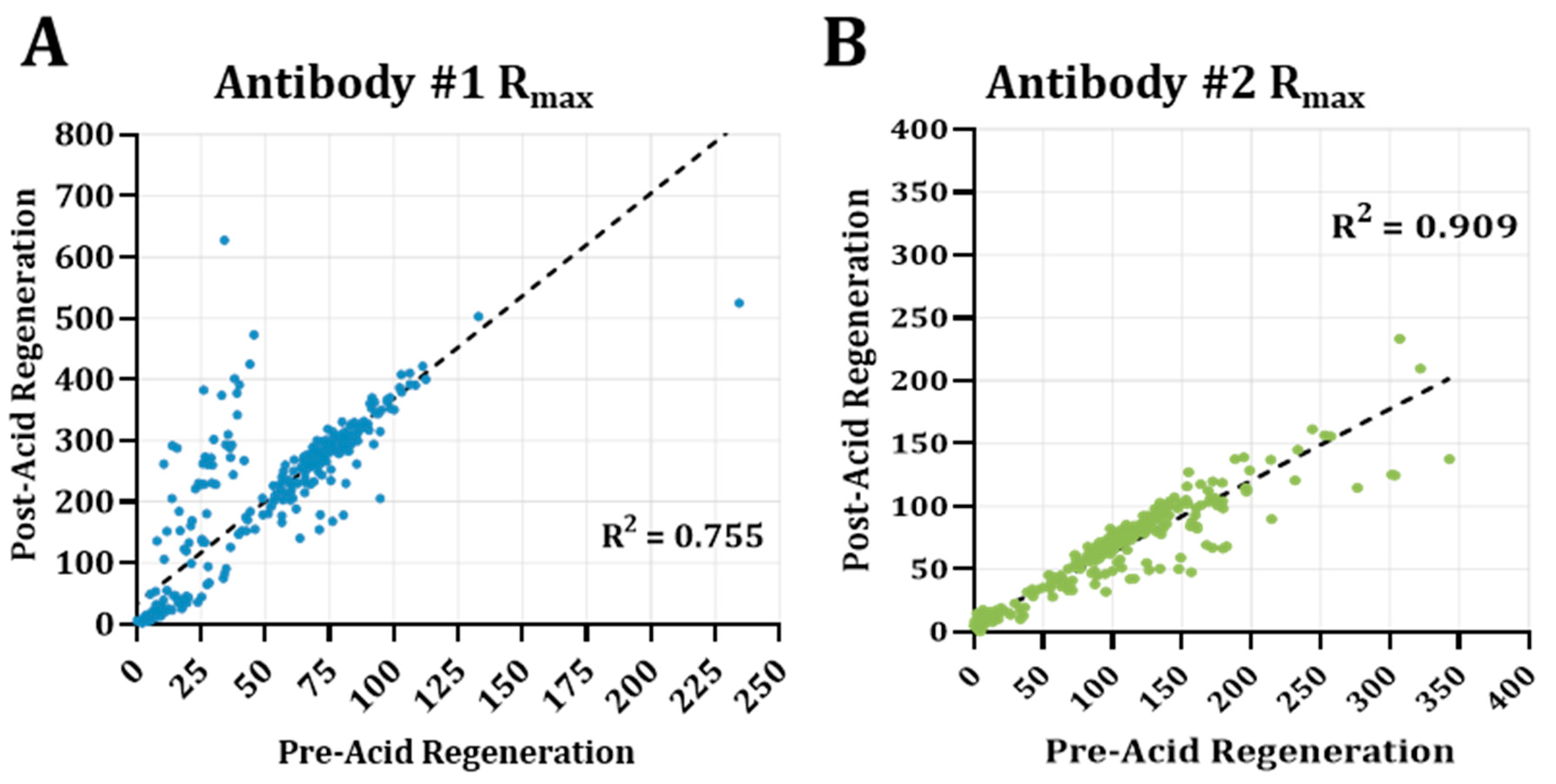
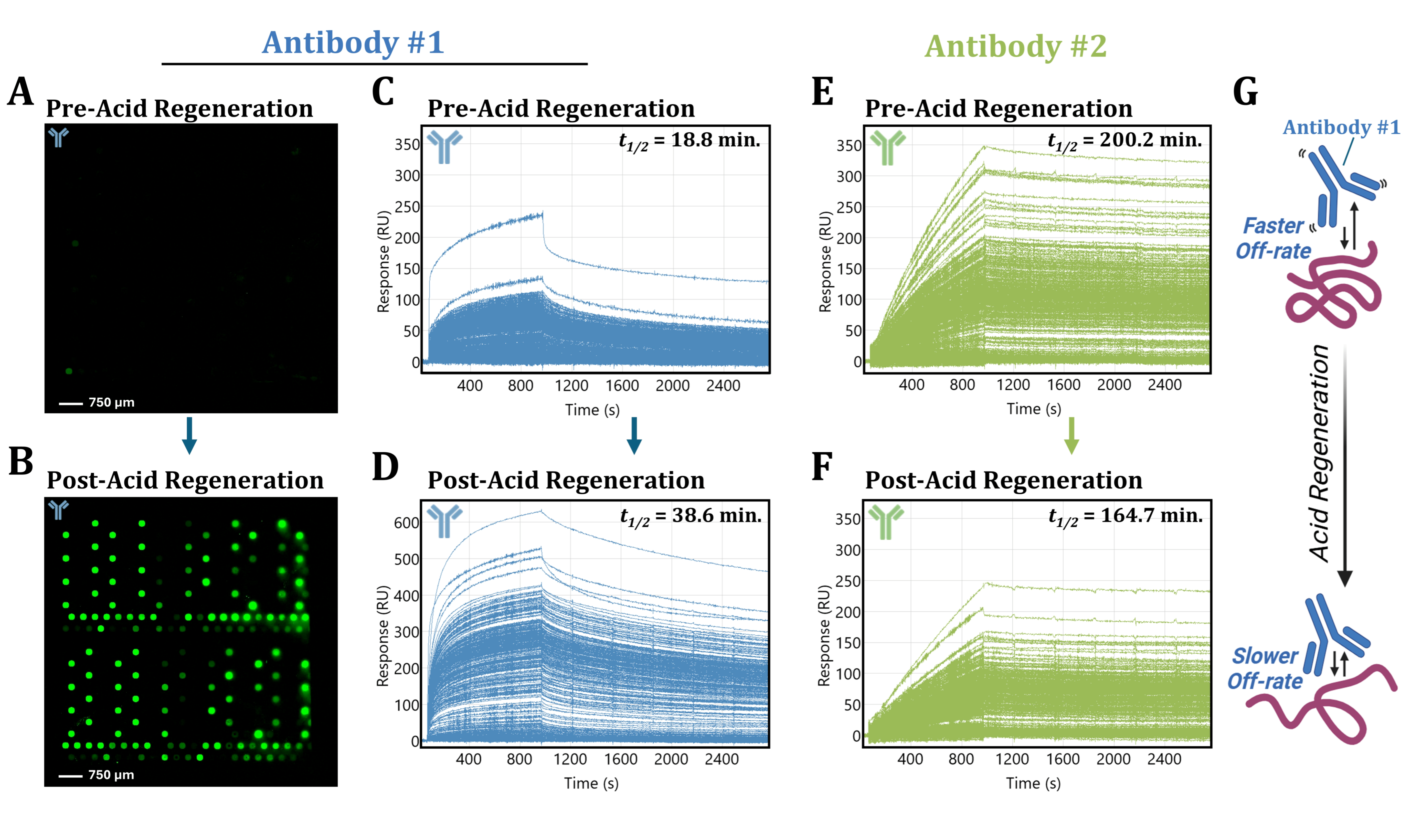
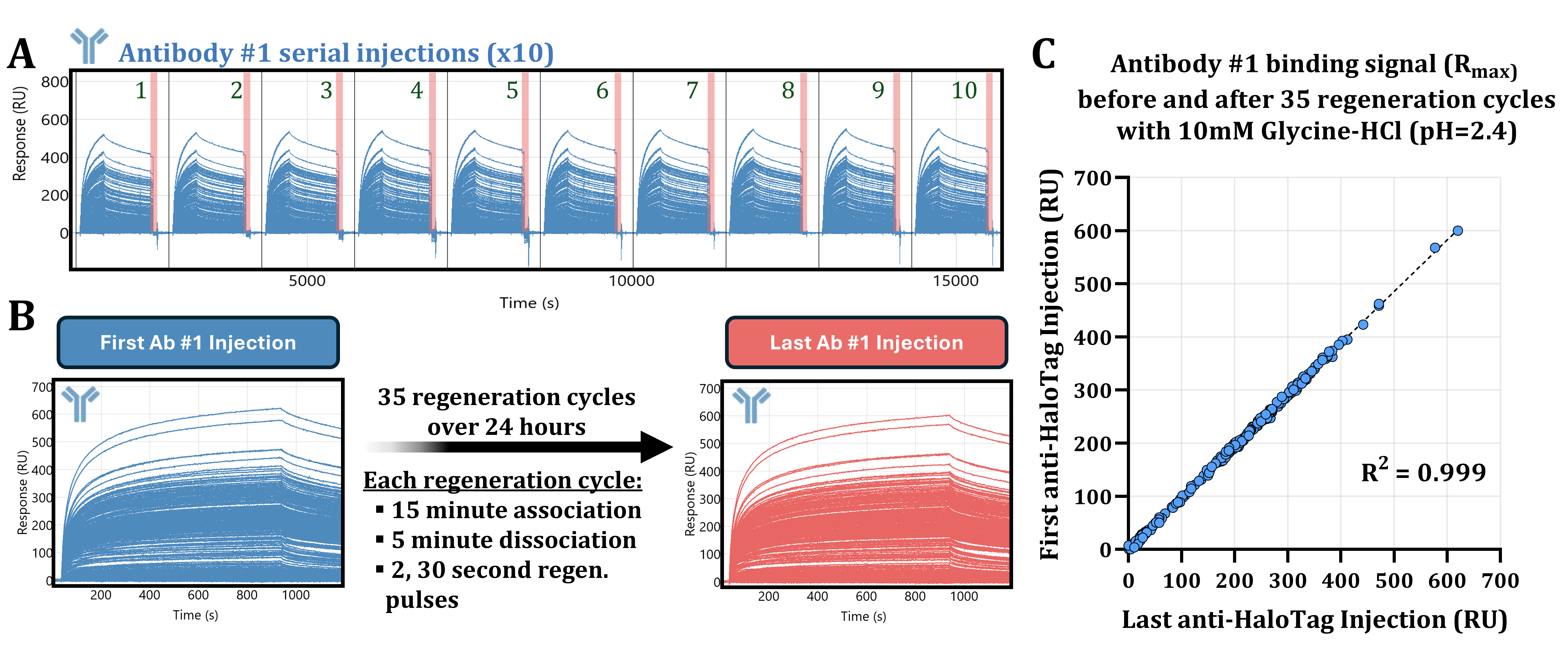
3.4. Acidic Buffer Treatment Drastically Enhances Antibody #1 Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SPOC | Sensor-integrated proteome on chip |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| IVTT | In vitro transcription and translation |
| ka | Association rate |
| kd | Dissociation rate |
| KD | Equilibrium dissociation constant or binding affinity |
| t1/2 | Half-life of bound complex |
| Rmax | Maximum binding response |
| CAR-T | Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy |
| ADCs | Antibody drug conjugates |
| ADR | Adverse drug reaction |
| TPD | Targeted protein degradation |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PBST-M | PBS containing Tween-20 and milk |
| RU | Response unit |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
Appendix A


References
- Whitebread, S.; Dumotier, B.; Armstrong, D.; Fekete, A.; Chen, S.; Hartmann, A.; Muller, P.Y.; Urban, L. Secondary Pharmacology: Screening and Interpretation of off-Target Activities–Focus on Translation. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestres, J.; Gregori-Puigjané, E.; Valverde, S.; Solé, R.V. The Topology of Drug-Target Interaction Networks: Implicit Dependence on Drug Properties and Target Families. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peón, A.; Naulaerts, S.; Ballester, P.J. Predicting the Reliability of Drug-Target Interaction Predictions with Maximum Coverage of Target Space. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norden, D.M.; Navia, C.T.; Sullivan, J.T.; Doranz, B.J. The Emergence of Cell-Based Protein Arrays to Test for Polyspecific off-Target Binding of Antibody Therapeutics. MAbs 2024, 16, 2393785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowes, J.; Brown, A.J.; Hamon, J.; Jarolimek, W.; Sridhar, A.; Waldron, G.; Whitebread, S. Reducing Safety-Related Drug Attrition: The Use of in Vitro Pharmacological Profiling. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kola, I.; Landis, J. Can the Pharmaceutical Industry Reduce Attrition Rates? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S. Why 90% of Clinical Drug Development Fails and How to Improve It? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3049–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaoui, K.; Hamon, J.; Faller, B.; Whitebread, S.; Jacoby, E.; Bender, A.; Jenkins, J.L.; Urban, L. Modeling Promiscuity Based on in Vitro Safety Pharmacology Profiling Data. Chem. Med. Chem. 2007, 2, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.U.; Hert, J.; Bissantz, C.; Hillebrecht, A.; Gerebtzoff, G.; Bendels, S.; Tillier, F.; Migeon, J.; Fischer, H.; Guba, W.; et al. Can We Discover Pharmacological Promiscuity Early in the Drug Discovery Process? Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoian, T.; Chiu, H.J.; Elayan, I.; Jagadeesh, G.; Khan, I.; Laniyonu, A.A.; Li, C.X.; Saulnier, M.; Simpson, N.; Yang, B. Secondary Pharmacology Data to Assess Potential Off-Target Activity of New Drugs: A Regulatory Perspective. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, R.J.; Jenkinson, S.; Brown, A.; Delaunois, A.; Dumotier, B.; Pannirselvam, M.; Rao, M.; Ribeiro, L.R.; Schmidt, F.; Sibony, A.; et al. The State of the Art in Secondary Pharmacology and Its Impact on the Safety of New Medicines. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.G.; Smith, G.F.; Wobst, H.J. Promiscuity of in Vitro Secondary Pharmacology Assays and Implications for Lead Optimization Strategies. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 6251–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLachlan, T.K.; Price, S.; Cavagnaro, J.; Andrews, L.; Blanset, D.; Cosenza, M.E.; Dempster, M.; Galbreath, E.; Giusti, A.M.; Heinz-Taheny, K.M.; et al. Classic and Evolving Approaches to Evaluating Cross Reactivity of MAb and MAb-like Molecules–A Survey of Industry 2008–2019. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 121, 2393785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, N.; Bae, J. Biosensors—Publication Trends and Knowledge Domain Visualization. Sensors 2019, 19, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, D.; Scognamiglio, V.; Montanari, R. Surface Plasmon Resonance Technology: Recent Advances, Applications and Experimental Cases. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 163, 117079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mol, N.J.; Fischer, M.J.E. Surface Plasmon Resonance Methods and Protocols; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 627. [Google Scholar]
- Brudno, J.N.; Kochenderfer, J.N. Current Understanding and Management of CAR T Cell-Associated Toxicities. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Kong, W.; He, Y. The Affinity of Antigen-Binding Domain on the Antitumor Efficacy of CAR T Cells: Moderate Is Better. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1032403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Tang, Y.; Yang, M.; Deng, G.; Liu, H. A Review of the Clinical Efficacy of FDA-Approved Antibody–drug Conjugates in Human Cancers. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, G.P.; Alpaugh, R.K. High Affinity Restricts the Localization and Tumor Penetration of Single-Chain Fv Antibody Molecules. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4750–4755. [Google Scholar]
- Datta-Mannan, A.; Choi, H.; Jin, Z.; Liu, L.; Lu, J.; Stokell, D.J.; Murphy, A.T.; Dunn, K.W.; Martinez, M.M.; Feng, Y. Reducing Target Binding Affinity Improves the Therapeutic Index of Anti-MET Antibody-Drug Conjugate in Tumor Bearing Animals. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0293703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Kong, B.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, F.; Zhang, L.; Lu, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Recent Advances in Targeted Protein Degraders as Potential Therapeutic Agents. Mol. Divers. 2024, 28, 309–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondeson, D.P.; Smith, B.E.; Burslem, G.M.; Buhimschi, A.D.; Hines, J.; Jaime-Figueroa, S.; Wang, J.; Hamman, B.D.; Ishchenko, A.; Crews, C.M. Lessons in PROTAC Design from Selective Degradation with a Promiscuous Warhead. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 78–87.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Rivera, F.P.; Levi, S.M. Unifying Catalysis Framework to Dissect Proteasomal Degradation Paradigms. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, C.V.; Cook, R.L.; Martelly, W.; Gushgari, L.R.; Mohan, M.; Takulapalli, B. Multiplexed Proteomic Biosensor Platform for Label-Free Real-Time Simultaneous Kinetic Screening of Thousands of Protein Interactions. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, V.C.; Cook, R.L.; Martelly, W.; Gushgari, L.R.; Mohan, M.; Takulapalli, B. Novel Sensor-Integrated Proteome on Chip (SPOC) Platform with Thousands of Folded Proteins on a 1.5 Sq-Cm Biosensor Chip to Enable High-Throughput Real-Time Label-Free Screening for Kinetic Analysis. bioRxiv 2024, 23, 575909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, C.G.; Luo, H.; Cai, W. HaloTag Technology: A Versatile Platform for Biomedical Applications. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszka, D.G. Improving Biosensor Analysis. J. Mol. Rec. 1999, 12, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanious, F.A.; Nguyen, B.; Wilson, W.D. Biosensor-Surface Plasmon Resonance Methods for Quantitative Analysis of Biomolecular Interactions. Methods Cell Biol. 2008, 84, 53–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylera, F.; Harth, S.; Waldherr, D.; Frisch, C.; Knappik, A. Off-Rate Screening for Selection of High-Affinity Anti-Drug Antibodies. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 441, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canziani, G.A.; Klakamp, S.; Myszka, D.G. Kinetic Screening of Antibodies from Crude Hybridoma Samples Using Biacore. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 325, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.B.; Roughley, S.D.; Matassova, N.; Brough, P.A. Off-Rate Screening (ORS) by Surface Plasmon Resonance. An Efficient Method to Kinetically Sample Hit to Lead Chemical Space from Unpurified Reaction Products. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2845–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathe, G.; Sapkota, G.P. Proteomic Approaches Advancing Targeted Protein Degradation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 786–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, K.; Coen, M.; Zhang, A.X.; Pachl, F.; Castaldi, M.P.; Dahl, G.; Boyd, H.; Scott, C.; Newham, P. Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras in Drug Development: A Safety Perspective. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.H.; Mitchell, C.A.; Loberg, L.; Pavkovic, M.; Rao, M.; Roberts, R.; Stamp, K.; Volak, L.; Wittwer, M.B.; Pettit, S. Targeted Protein Degraders: A Call for Collective Action to Advance Safety Assessment. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2022, 21, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.J.; Winkler, S.; Hughes, S.J.; Whitworth, C.; Galant, M.; Farnaby, W.; Rumpel, K.; Ciulli, A. SPR-Measured Dissociation Kinetics of PROTAC Ternary Complexes Influence Target Degradation Rate. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Bordeau, B.M.; Balthasar, J.P. Mechanisms of ADC Toxicity and Strategies to Increase ADC Tolerability. Cancers 2023, 15, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.C.; Boghaert, E.R.; Vaidya, K.S.; Mitten, M.J.; Norvell, S.; Falls, H.D.; Devries, P.J.; Cheng, D.; Meulbroek, J.A.; Buchanan, F.G.; et al. ABT-414, an Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting a Tumor-Selective EGFR Epitope. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, S.C.; Patel, N.; Logie, J.; Pan, G.; Persson, H.; Moffat, J.; Sidhu, S.S.; Shoichet, M.S. Targeting HER2+Breast Cancer Cells: Lysosomal Accumulation of Anti-HER2 Antibodies Is Influenced by Antibody Binding Site and Conjugation to Polymeric Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammood, M.; Craig, A.W.; Leyton, J.V. Impact of Endocytosis Mechanisms for the Receptors Targeted by the Currently Approved Adcs—A Necessity for Future Adc Research and Development. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, J.F. Surface Plasmon Resonance Clinical Biosensors for Medical Diagnostics. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeni, L.; Perri, C.; Cennamo, N.; Arcadio, F.; D’Agostino, G.; Salmona, M.; Beeg, M.; Gobbi, M. A Portable Optical-Fibre-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for the Detection of Therapeutic Antibodies in Human Serum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaileb, A.; Hojjat Jodaylami, M.; Coutu, J.; Ricard, P.; Lamarre, M.; Rochet, L.; Cellier-Goetghebeur, S.; MacAulay, D.; Charron, B.; Lavallée, É.; et al. Cross-Validation of ELISA and a Portable Surface Plasmon Resonance Instrument for IgG Antibody Serology with SARS-CoV-2 Positive Individuals. Analyst 2021, 146, 4905–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, D.D.; Van Zant, W.; Valiulis, S.; Malinick, A.S.; Hanson, V.; Cheng, Q. Trends in Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensing: Materials, Methods, and Machine Learning. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 5221–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeg, M.; Burti, C.; Allocati, E.; Ciafardini, C.; Banzi, R.; Nobili, A.; Caprioli, F.; Garattini, S.; Gobbi, M. Surface Plasmon Resonance Unveils Important Pitfalls of Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay for the Detection of Anti-Infliximab Antibodies in Patients’ Sera. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.L.; Martelly, W.; Agu, C.V.; Gushgari, L.R.; Moreno, S.; Kesiraju, S.; Mohan, M.; Takulapalli, B. An Approach to Produce Thousands of Single-Chain Antibody Variants on a SPR Biosensor Chip for Measuring Target Binding Kinetics and for Deep Characterization of Antibody Paratopes. bioRxiv 2025, 1, 632576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martelly, W.; Cook, R.L.; Agu, C.V.; Gushgari, L.R.; Moreno, S.; Kesiraju, S.; Mohan, M.; Takulapalli, B. Real-Time SPR Biosensing to Detect and Characterize Fast Dissociation Rate Binding Interactions Missed by Endpoint Detection and Implications for Off-Target Toxicity Screening. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060882
Martelly W, Cook RL, Agu CV, Gushgari LR, Moreno S, Kesiraju S, Mohan M, Takulapalli B. Real-Time SPR Biosensing to Detect and Characterize Fast Dissociation Rate Binding Interactions Missed by Endpoint Detection and Implications for Off-Target Toxicity Screening. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(6):882. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060882
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartelly, William, Rebecca L. Cook, Chidozie Victor Agu, Lydia R. Gushgari, Salvador Moreno, Sailaja Kesiraju, Mukilan Mohan, and Bharath Takulapalli. 2025. "Real-Time SPR Biosensing to Detect and Characterize Fast Dissociation Rate Binding Interactions Missed by Endpoint Detection and Implications for Off-Target Toxicity Screening" Biomolecules 15, no. 6: 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060882
APA StyleMartelly, W., Cook, R. L., Agu, C. V., Gushgari, L. R., Moreno, S., Kesiraju, S., Mohan, M., & Takulapalli, B. (2025). Real-Time SPR Biosensing to Detect and Characterize Fast Dissociation Rate Binding Interactions Missed by Endpoint Detection and Implications for Off-Target Toxicity Screening. Biomolecules, 15(6), 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060882




