Physical Properties of Lens Membranes in Animals with Different Lifespans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Model Membranes
2.2.1. PL Composition
2.2.2. Chol Content
2.3. Conventional and Saturation-Recovery Electron Paramagnetic Resonance
3. Results
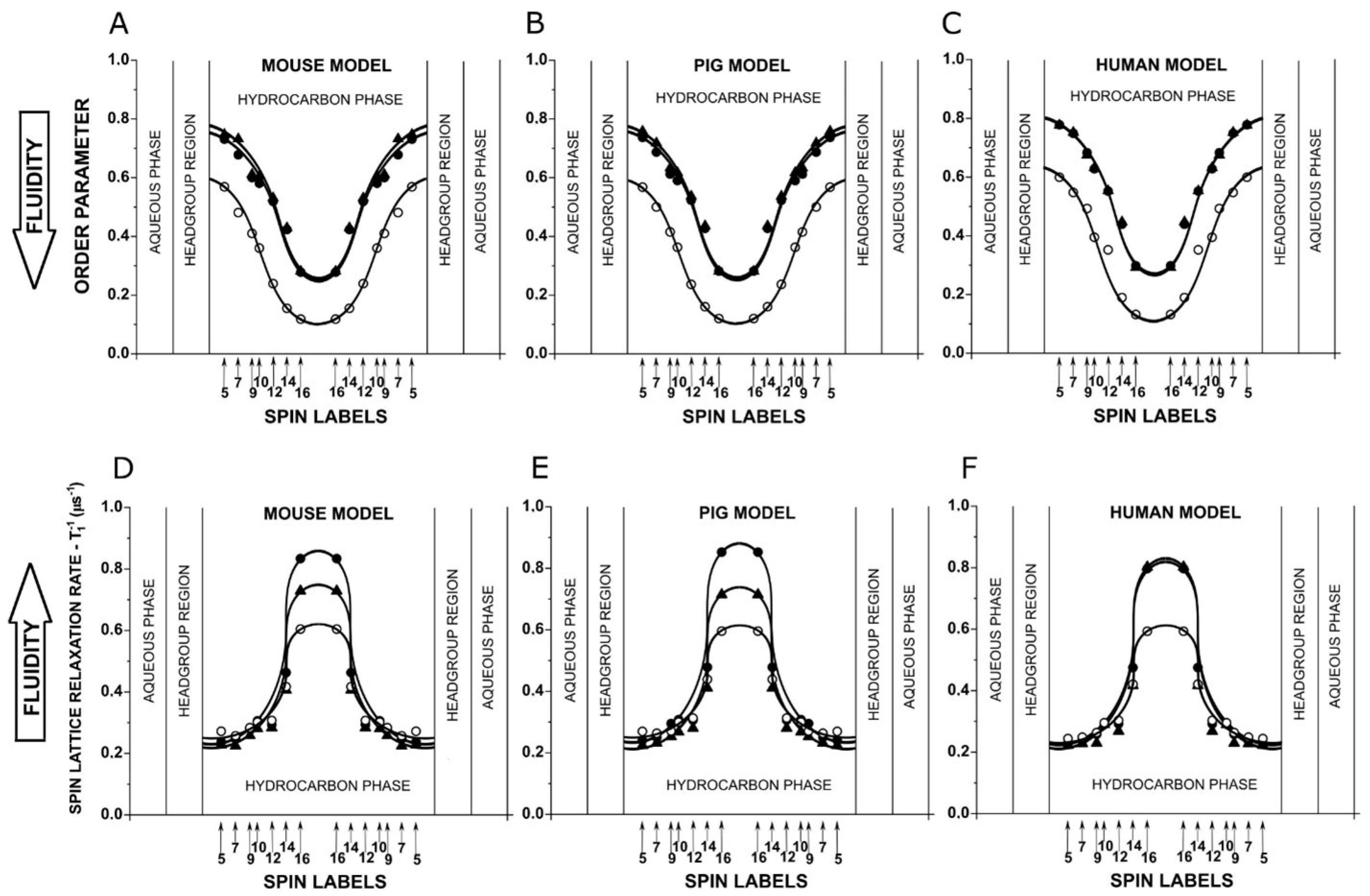
3.1. Profiles of PL Acyl Chain Order and Fluidity
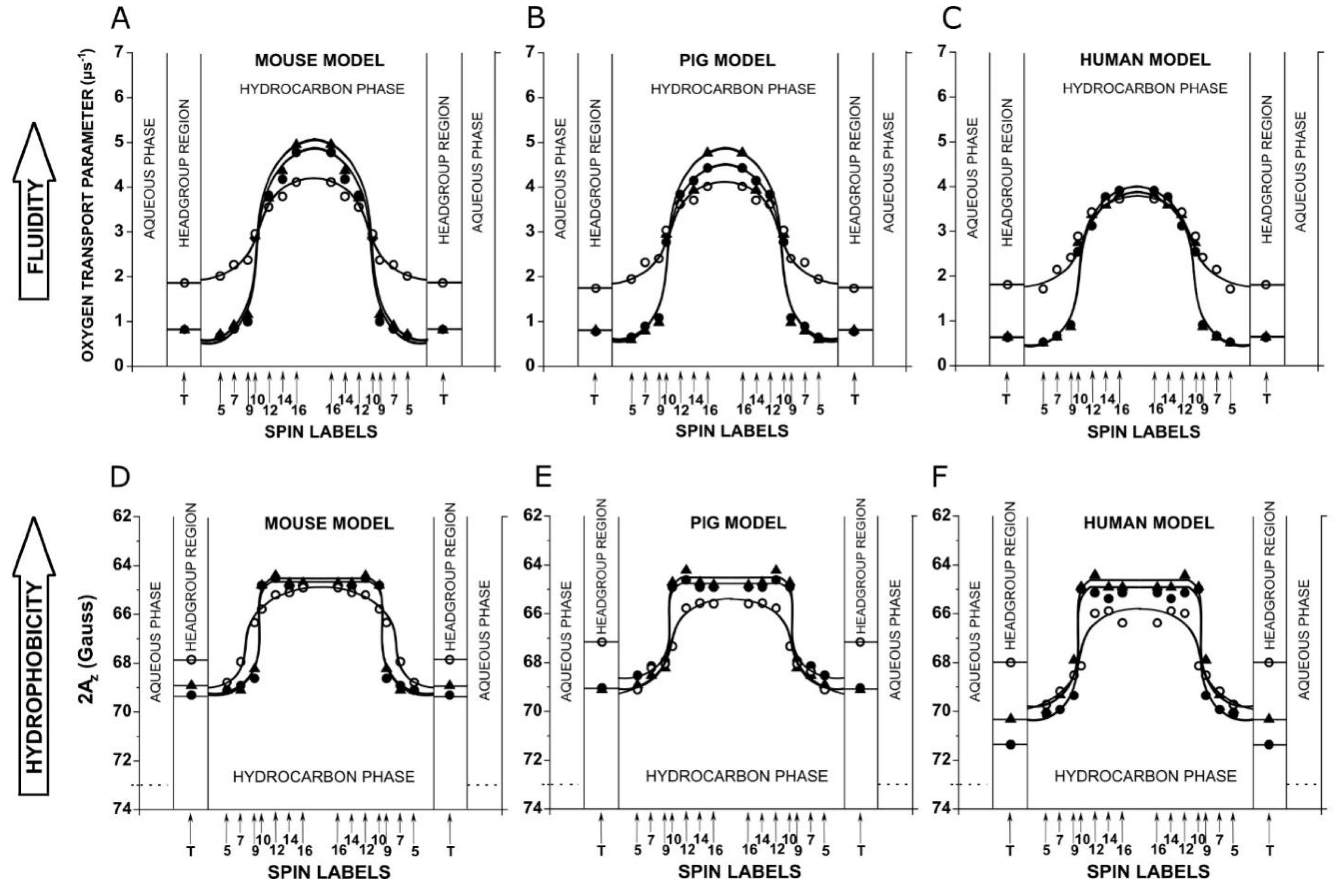
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of the Environment of Spin Labels (OTP and Hydrophobicity)
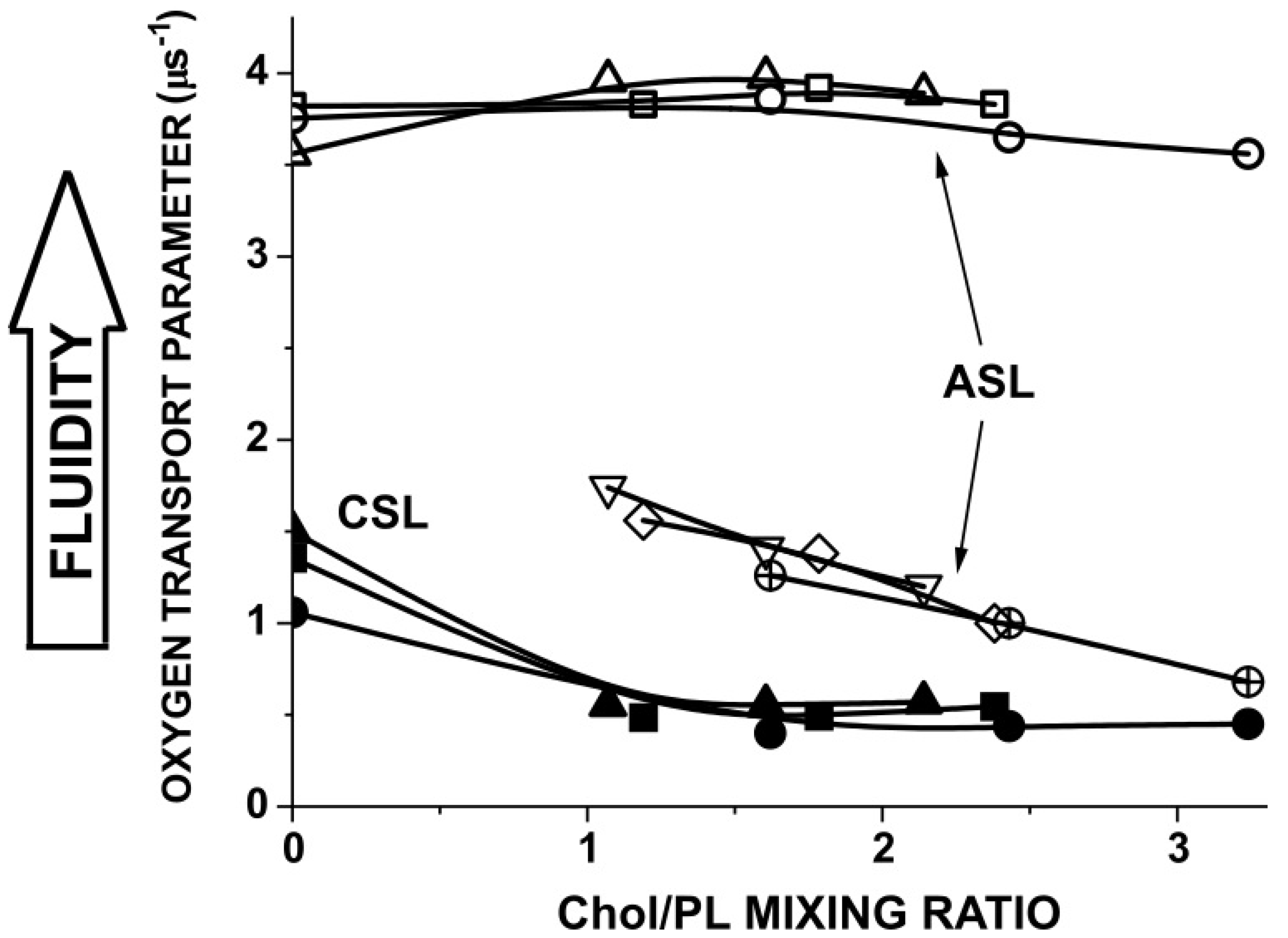
3.3. Membrane Properties Sensed by Chol-Analog Spin Labels
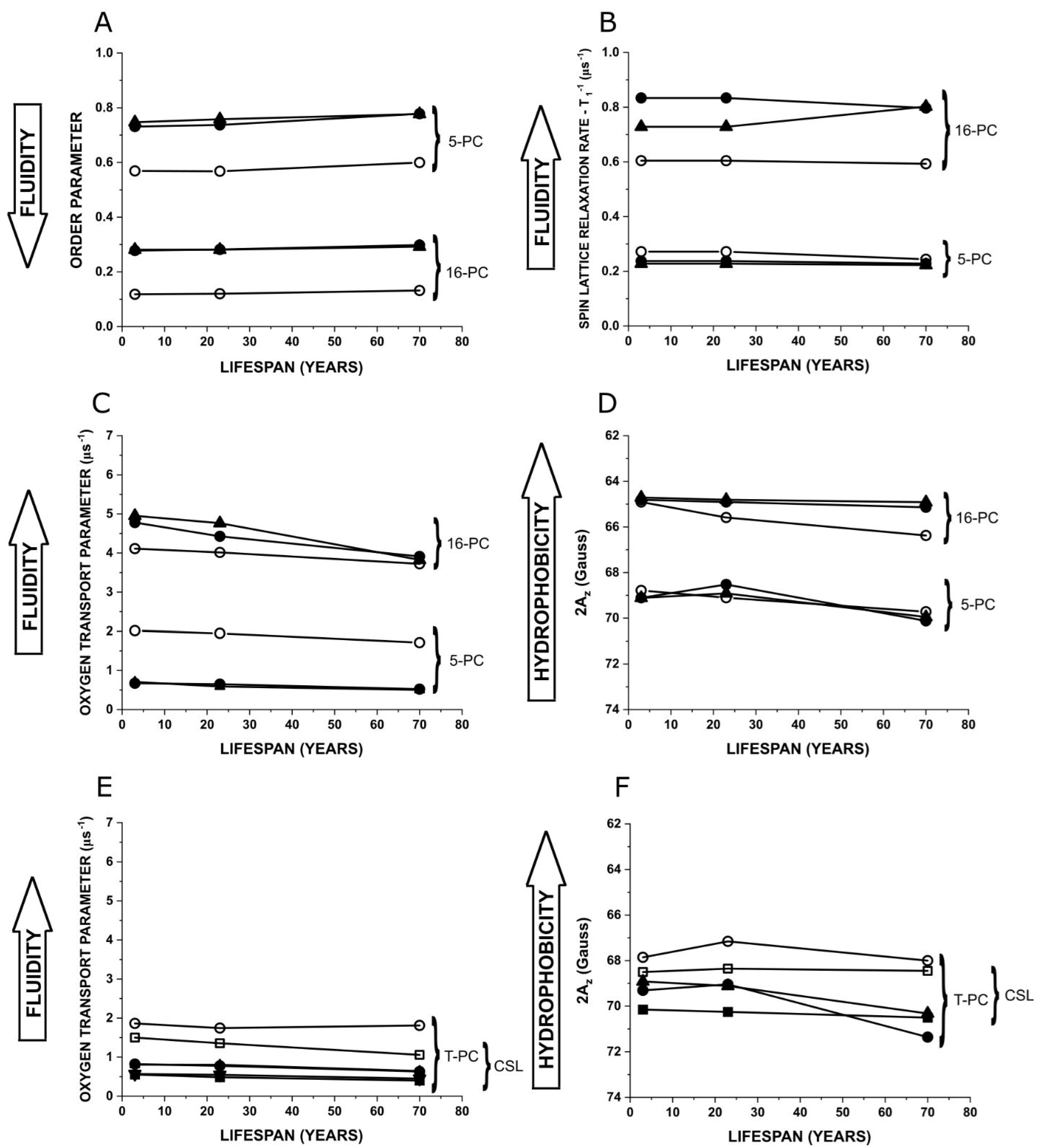
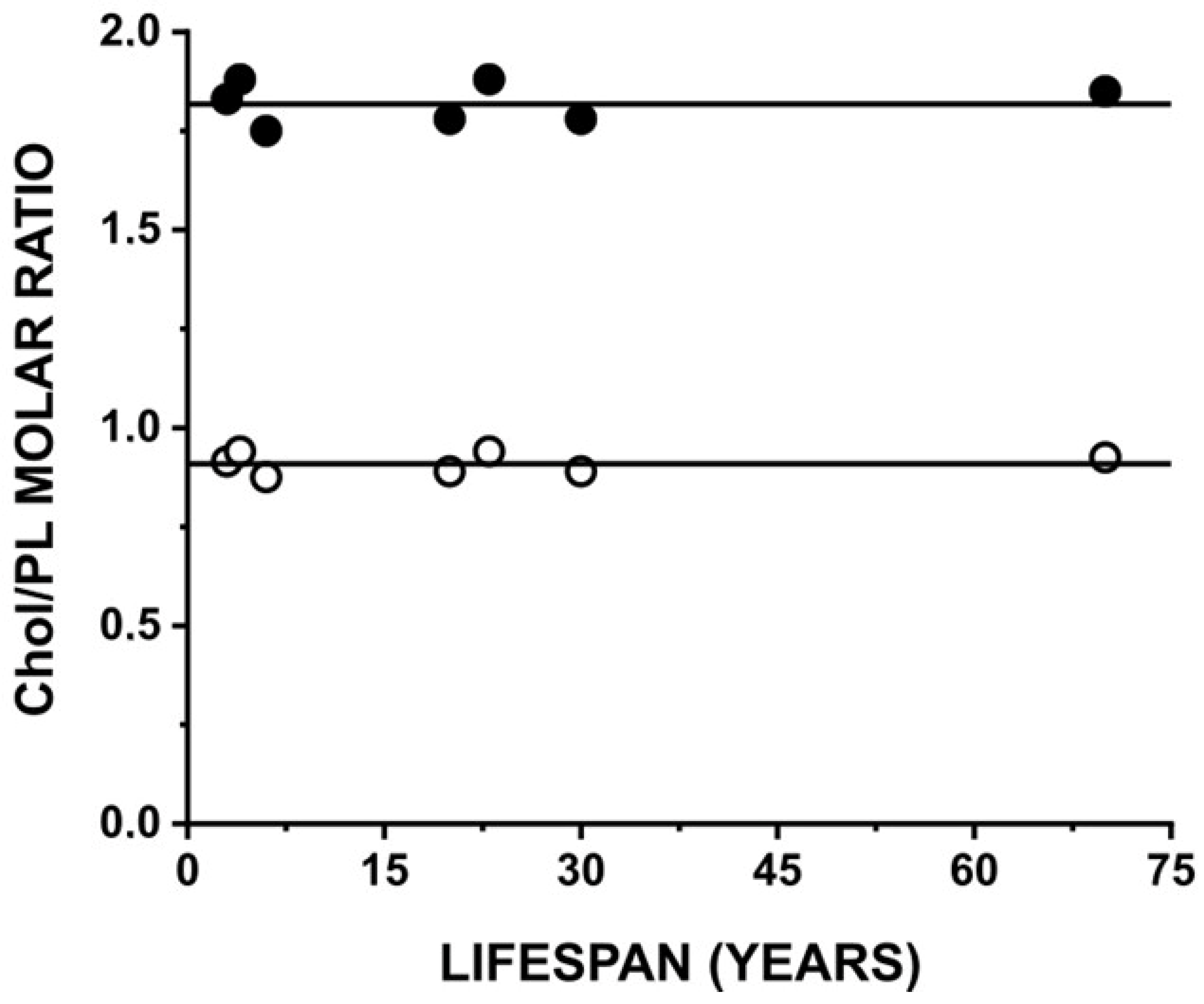
3.4. Changes in Membrane Properties as a Function of Lifespan
3.5. Changes in the Chol Saturation Limit and the CST in Fiber Cell Membranes as a Function of Lifespan
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASL | Androstane spin label |
| CBD | Cholesterol bilayer domain |
| Chol | Cholesterol |
| CSL | Cholestane spin label |
| CST | Cholesterol solubility threshold |
| DHSM | Dihydrosphingomyelin |
| EPR | Electron paramagnetic resonance |
| LLM | Lens lipid membrane |
| n-PC | 1-Palmitoyl-2-(n-doxylstearoyl)phosphatidylcholine |
| O | Oleic |
| OTP | Oxygen transport parameter |
| P | Palmitic |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PL | Phospholipid |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| SM | Sphingomyelin |
| SR | Saturation recovery |
| T-PC | Tempocholine-1-palmitoyl-2-oleoylphosphatidic acid ester |
| TPX | Methylpentene polymer |
| T1 | Relaxation time |
| 9-SASL | Ninedoxylstearic acid spin label |
References
- Borchman, D.; Yappert, M.C.; Afzal, M. Lens Lipids and Maximum Lifespan. Exp. Eye Res. 2004, 79, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchman, D.; Stimmelmayr, R.; George, J.C. Whales, Lifespan, Phospholipids, and Cataracts. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 2289–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panz, T.; Lepiarczyk, M.; Zuber, A. Comparing the Content of Lipids Derived from the Eye Lenses of Various Species. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2011, 49, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Deeley, J.M.; Mitchell, T.W.; Wei, X.; Korth, J.; Nealon, J.R.; Blanksby, S.J.; Truscott, R.J.W. Human Lens Lipids Differ Markedly from Those of Commonly Used Experimental Animals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2008, 1781, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, J.L.; Bardygula-Nonn, L.G.; Glonek, T.; Greiner, J.V. Interspecies Comparisons of Lens Phospholipids. Curr. Eye Res. 1995, 14, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekhyuse, R.M. Lipids in Tissues of the Eye. IV. Influence of Age and Species Differences on the Phospholipid Composition of the Lens. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1970, 218, 546–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimmelmayr, R.; Borchman, D. Lens Lipidomes among Phocidae and Odobenidae. Aquat. Mamm. 2018, 44, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natterson-Horowitz, B.; Moore, B.A.; Reynolds, A.; Espericueta, L.; Head, J.M.; Lam, D.; Turner, R.; Williams, D.M.; Blumstein, D.T. Cataracts Across the Tree of Life: A Roadmap for Prevention and Biomedical Innovation. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 249, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, A.; Tsuda, M.; Akino, T.; Ohnishi, S.; Terayama, Y. Protein-Phospholipid-Cholesterol Interaction in the Photolysis of Invertebrate Rhodopsin. Biochemistry 1983, 22, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M.; Widomska, J.; Mainali, L.; Raguz, M. High Cholesterol/Low Cholesterol: Effects in Biological Membranes: A Review. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 75, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeagle, P.L. The Biophysics and Cell Biology of Cholesterol: A Hypothesis for the Essential Role of Cholesterol in Mammalian Cells. In Cholesterol in Membrane Models; Yeagle, P.L., Finegold, L., Eds.; CRC-Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Epand, R.M. Role of Membrane Lipids in Modulating the Activity of Membrane-Bound Enzymes. In The Structure of Biological Membranes; Yeagle, P.L., Ed.; CRC-Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 499–509. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, J.B.; Yu, Y.; Klauda, J.B. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Human Ocular Lens with Age and Cataract. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2022, 1864, 184025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Róg, T.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M. Cholesterol Effects on a Mixed-Chain Phosphatidylcholine Bilayer: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Biochimie 2006, 88, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Wisniewska, A.; Yin, J.J.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Hydrophobic Barriers of Lipid Bilayer Membranes Formed by Reduction of Water Penetration by Alkyl Chain Unsaturation and Cholesterol. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 7670–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, A.; Subczynski, W.K.; Hyde, J.S. Oxygen Transport Parameter in Membranes as Deduced by Saturation Recovery Measurements of Spin-Lattice Relaxation Times of Spin Labels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 1854–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; Subczynski, W.K. Phases and Domains in Sphingomyelin-Cholesterol Membranes: Structure and Properties Using EPR Spin-Labeling Methods. Eur. Biophys. J. 2012, 41, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Widomska, J.; Feix, J.B. Physical Properties of Lipid Bilayers from EPR Spin Labeling and Their Influence on Chemical Reactions in a Membrane Environment. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchman, D.; Yappert, M.C. Lipids and the Ocular Lens. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2473–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Raguz, M.; Widomska, J.; Mainali, L.; Konovalov, A. Functions of Cholesterol and the Cholesterol Bilayer Domain Specific to the Fiber-Cell Plasma Membrane of the Eye Lens. J. Membr. Biol. 2012, 245, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; O’Brien, W.J.; Subczynski, W.K. Properties of Fiber Cell Plasma Membranes Isolated from the Cortex and Nucleus of the Porcine Eye Lens. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 97, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; O’Brien, W.J.; Subczynski, W.K. Properties of Membranes Derived from the Total Lipids Extracted from the Human Lens Cortex and Nucleus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; O’Brien, W.J.; Subczynski, W.K. Changes in the Properties and Organization of Human Lens Lipid Membranes Occurring with Age. Curr. Eye Res. 2017, 42, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichow, S.L.; Gonen, T. Lipid-Protein Interactions Probed by Electron Crystallography. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carola Hunte, S.R. Lipids and Membrane Protein Structures. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2008, 18, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Briggs, M.M.; McIntosh, T.J. Water Permeability of Aquaporin-4 Channel Depends on Bilayer Composition, Thickness, and Elasticity. Biophys. J. 2012, 103, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Canty, J.T.; Briggs, M.M.; McIntosh, T.J. The Water Permeability of Lens Aquaporin-0 Depends on Its Lipid Bilayer Environment. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 113, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.W.; Nourmohammadi, S.; Ramesh, S.A.; Yool, A.J. Aquaporin Ion Conductance Properties Defined by Membrane Environment, Protein Structure, and Cell Physiology. Biophys. Rev. 2022, 14, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonen, T.; Cheng, Y.; Sliz, P.; Hiroaki, Y.; Fujiyoshi, Y.; Harrison, S.C.; Walz, T. Lipid-Protein Interactions in Double-Layered Two-Dimensional AQP0 Crystals. Nature 2005, 438, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hite, R.K.; Gonen, T.; Harrison, S.C.; Walz, T. Interactions of Lipids with Aquaporin-0 and Other Membrane Proteins. Pflugers Arch. 2009, 456, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raguz, M.; Widomska, J.; Dillon, J.; Gaillard, E.R.; Subczynski, W.K. Characterization of Lipid Domains in Reconstituted Porcine Lens Membranes Using EPR Spin-Labeling Approaches. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mainali, L.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M.; Subczynski, W.K. Formation of Cholesterol Bilayer Domains Precedes Formation of Cholesterol Crystals in Membranes Made of the Major Phospholipids of Human Eye Lens Fiber Cell Plasma Membranes. Curr. Eye Res. 2020, 45, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.D.; Akbuǧa, J.; Baş, A.L. In Vitro Evaluation of Enrofloxacin-Loaded MLV Liposomes. Drug Deliv. 2007, 14, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovska, O. An Overview: Methods for Preparation and Characterization of Liposomes as Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. Phytopharm. Res. 2013, 3, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Sanson, A.; Ptak, M.; Rigaud, J.L.; Gary-Bobo, C.M. An ESR Study of the Anchoring of Spin-Labeled Stearic Acid in Lecithin Multilayers. Chem Phys Lipids 1976, 17, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egret-Charlier, M.; Sanson, A.; Ptak, M. Ionization of Fatty Acids at the Lipid—Water Interface. FEBS Lett 1978, 89, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.K.; So, L.; Spector, A. Membrane Cholesterol and Phospholipid in Consecutive Concentric Sections of Human Lenses. J. Lipid Res. 1985, 26, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.K.; So, L.; Spector, A. Age-Dependent Changes in the Distribution and Concentration of Human Lens Cholesterol and Phospholipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Lipids Lipid Metab. 1987, 917, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Buboltz, J.T.; Feigenson, G.W. Maximum Solubility of Cholesterol in Phosphatidylcholine and Phosphatidylethanolamine Bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1999, 1417, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epand, R.M. Cholesterol in Bilayers of Sphingomyelin or Dihydrosphingomyelin at Concentrations Found in Ocular Lens Membranes. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 3102–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epand, R.M.; Bain, A.D.; Sayer, B.G.; Bach, D.; Wachtel, E. Properties of Mixtures of Cholesterol with Phosphatidylcholine or with Phosphatidylserine Studied by 13C Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatti, C.R.; Lamy, M.T.; Epand, R.M. Cationic Amphiphiles and the Solubilization of Cholesterol Crystallites in Membrane Bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bach, D.; Wachtel, E.; Borochov, N.; Senisterra, G.; Epand, R.M. Phase Behaviour of Heteroacid Phosphatidylserines and Cholesterol. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1992, 63, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Castro-Roman, F.; Porcar, L.; Butler, P.; Bautista, P.J.; Krzyzanowski, N.; Perez-Salas, U. Cholesterol Solubility Limit in Lipid Membranes Probed by Small Angle Neutron Scattering and MD Simulations. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9313–9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Felix, C.C.; Klug, C.S.; Hyde, J.S. Concentration by Centrifugation for Gas Exchange EPR Oximetry Measurements with Loop-Gap Resonators. J. Magn. Reson. 2005, 176, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, D. Electron Spin Resonance: Spin Labels. In Membrane spectroscopy; Grell, E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1981; pp. 51–142. [Google Scholar]
- Mainali, L.; Camenisch, T.G.; Hyde, J.S.; Subczynski, W.K. Saturation Recovery EPR Spin-Labeling Method for Quantification of Lipids in Biological Membrane Domains. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2017, 48, 1355–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, J.S. Saturation Recovery. In Foundations of Modern EPR; Eaton, S., Salikhov, K.M., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 1998; pp. 607–618. [Google Scholar]
- Seelig, J. Anisotropic Motion in Liquid Crystalls Structures. In Spin Labeling Theory and Applications; Berliner, L., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; San Francisco, CA, USA; London, UK, 1976; pp. 371–409. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, I.C.P.; Butler, K.W. Oriented Lipid Structures in Model Membranes. In Spin Labeling Theory and Applications; Berliner, L., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; San Francisco, CA, USA; London, UK, 1976; pp. 411–451. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, O.H.; Jost, P. Lipid Spin Labels in Biological Membranes. In Spin Labeling Theory and Applications; Berliner, L., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; San Francisco, CA, USA; London, UK, 1976; pp. 453–523. [Google Scholar]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Oxygen Permeability of Phosphatidylcholine-Cholesterol Membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4474–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak, M.J.; Small, D.M.; Shipley, G.G. Nature of the Thermal Pretransition of Synthetic Phospholipids: Dimyristolyl- and Dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry 1976, 15, 4575–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak, M.J.; Small, D.M.; Shipley, G.G. Temperature and Compositional Dependence of the Structure of Hydrated Dimyristoyl Lecithin. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 6068–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, J.F.; Wilkinson, D.A. Lecithin Bilayers. Density Measurement and Molecular Interactions. Biophys. J. 1978, 23, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, T.J. The Effect of Cholesterol on the Structure of Phosphatidylcholine Bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 1978, 513, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, L.J.; McAlister, M.; Fuller, N.; Rand, R.P.; Parsegian, V.A. Interactions between Neutral Phospholipid Bilayer Membranes. Biophys. J. 1982, 37, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, N.P.; Lieb, W.R. The Structure of Lipid Bilayers and the Effects of General Anaesthetics. An X-Ray and Neutron Diffraction Study. J. Mol. Biol. 1979, 133, 469–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, D. Molecular Order and T1-Relaxation, Cross-Relaxation in Nitroxide Spin Labels. J. Magn. Reson. 2018, 290, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.H.; Haas, D.A.; Mailer, C. Molecular Dynamics in Liquids: Spin-Lattice Relaxation of Nitroxide Spin Labels. Science 1994, 263, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M.; McElhaney, R.N.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Molecular Dynamics of 1-Palmitoyl-2-Oleoylphosphatidylcholine Membranes Containing Transmembrane α-Helical Peptides with Alternating Leucine and Alanine Residues. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 3939–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M.; Subczynski, W.K.; Kusumi, A. Influence of Phospholipid Unsaturation on the Cholesterol Distribution in Membranes. Biochimie 1991, 73, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, O.H.; Dehlinger, P.J.; Van, S.P. Shape of the Hydrophobic Barrier of Phospholipid Bilayers (Evidence for Water Penetration in Biological Membranes). J. Membr. Biol. 1974, 15, 159–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguz, M.; Mainali, L.; Widomska, J.; Subczynski, W.K. Using Spin-Label Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) to Discriminate and Characterize the Cholesterol Bilayer Domain. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2011, 164, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buboltz, J.T. A More Efficient Device for Preparing Model-Membrane Liposomes by the Rapid Solvent Exchange Method. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2009, 80, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buboltz, J.T.; Feigenson, G.W. A Novel Strategy for the Preparation of Liposomes: Rapid Solvent Exchange. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 1999, 1417, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsina, R.; Trossi-Torres, G.; Thieme, J.; O’Dell, M.; Khadka, N.K.; Mainali, L. Alpha-Crystallin Association with the Model of Human and Animal Eye Lens-Lipid Membranes Is Modulated by Surface Hydrophobicity of Membranes. Curr. Eye Res. 2022, 47, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Collery, R.F.; Widomska, J. Why Has Evolution Selected for the Human Eye Lens to Use an Extremely High Cholesterol Content as a Protective Mechanism against Opacification? Exp. Eye Res. 2025, 254, 110320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Widomska, J. Spin-Lattice Relaxation Rates of Lipid Spin Labels as a Measure of Their Rotational Diffusion Rates in Lipid Bilayer Membranes. Membranes 2022, 12, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raguz, M.; Subczynski, W.K. Physical Properties of Lens Membranes in Animals with Different Lifespans. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060851
Raguz M, Subczynski WK. Physical Properties of Lens Membranes in Animals with Different Lifespans. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(6):851. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060851
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaguz, Marija, and Witold Karol Subczynski. 2025. "Physical Properties of Lens Membranes in Animals with Different Lifespans" Biomolecules 15, no. 6: 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060851
APA StyleRaguz, M., & Subczynski, W. K. (2025). Physical Properties of Lens Membranes in Animals with Different Lifespans. Biomolecules, 15(6), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060851






