MTPrompt-PTM: A Multi-Task Method for Post-Translational Modification Prediction Using Prompt Tuning on a Structure-Aware Protein Language Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
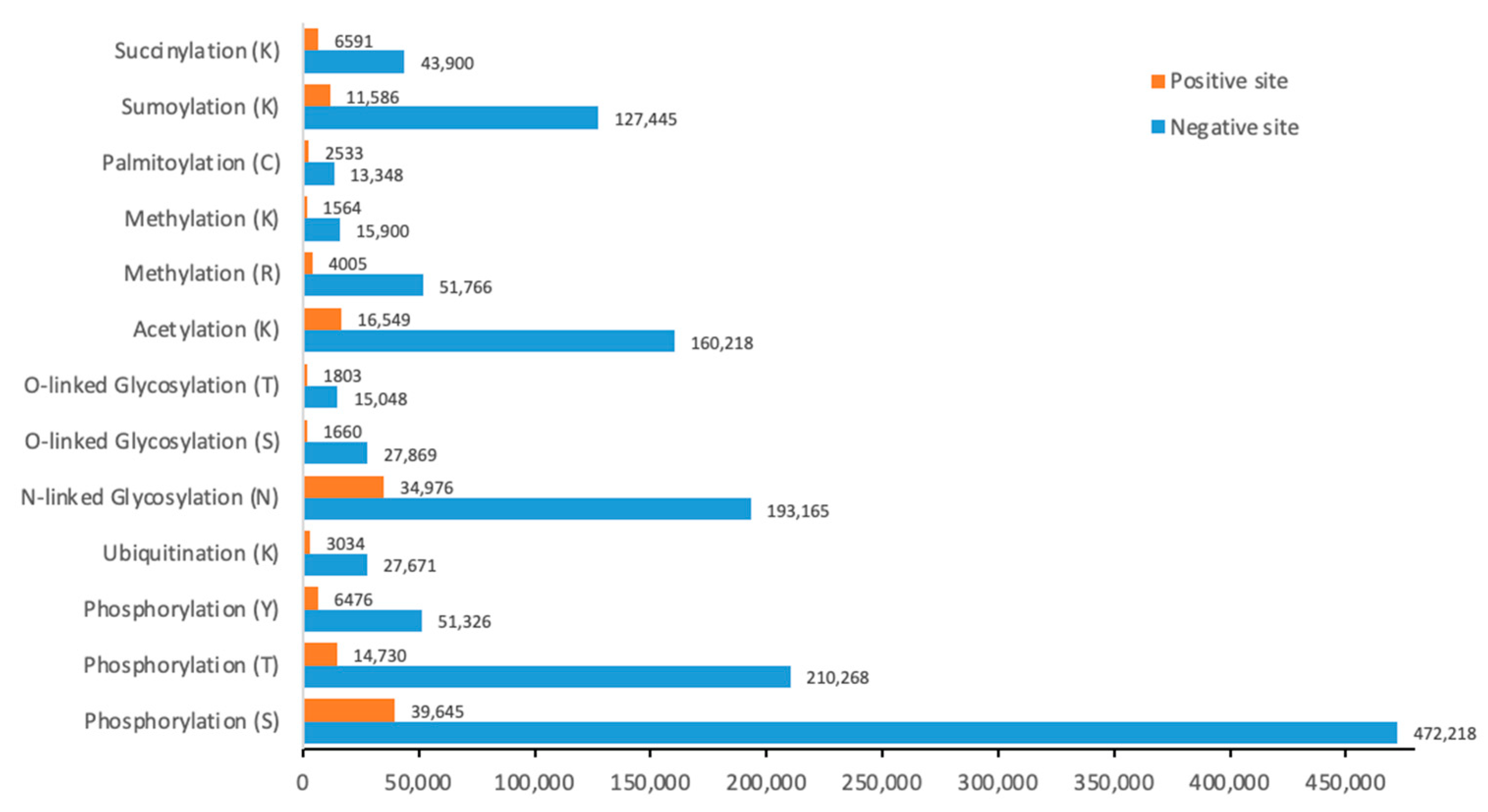
2.1. Dataset and Data Processing
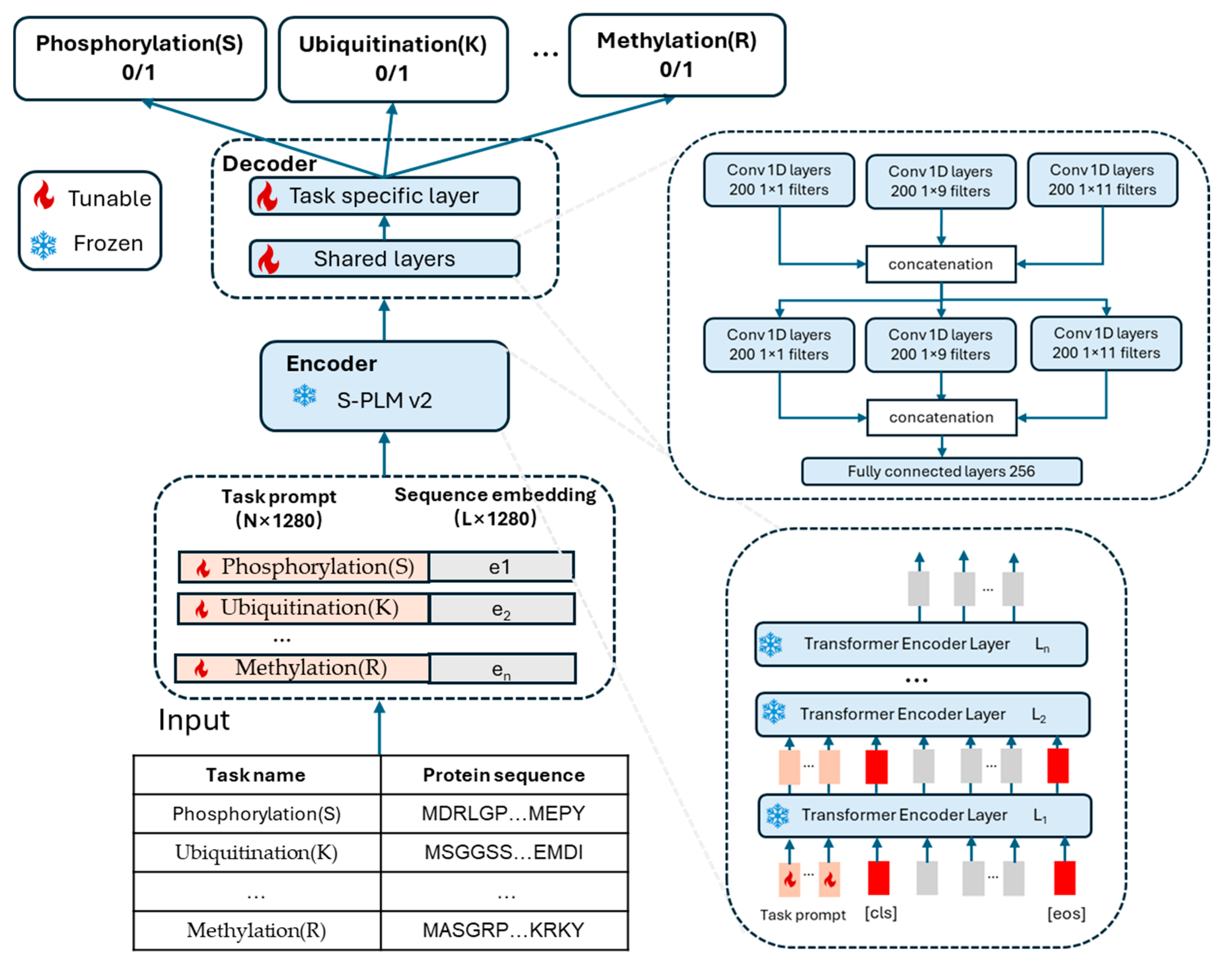
2.2. Architecture of MTPrompt-PTM
2.3. Prompt Tuning on MTPrompt-PTM
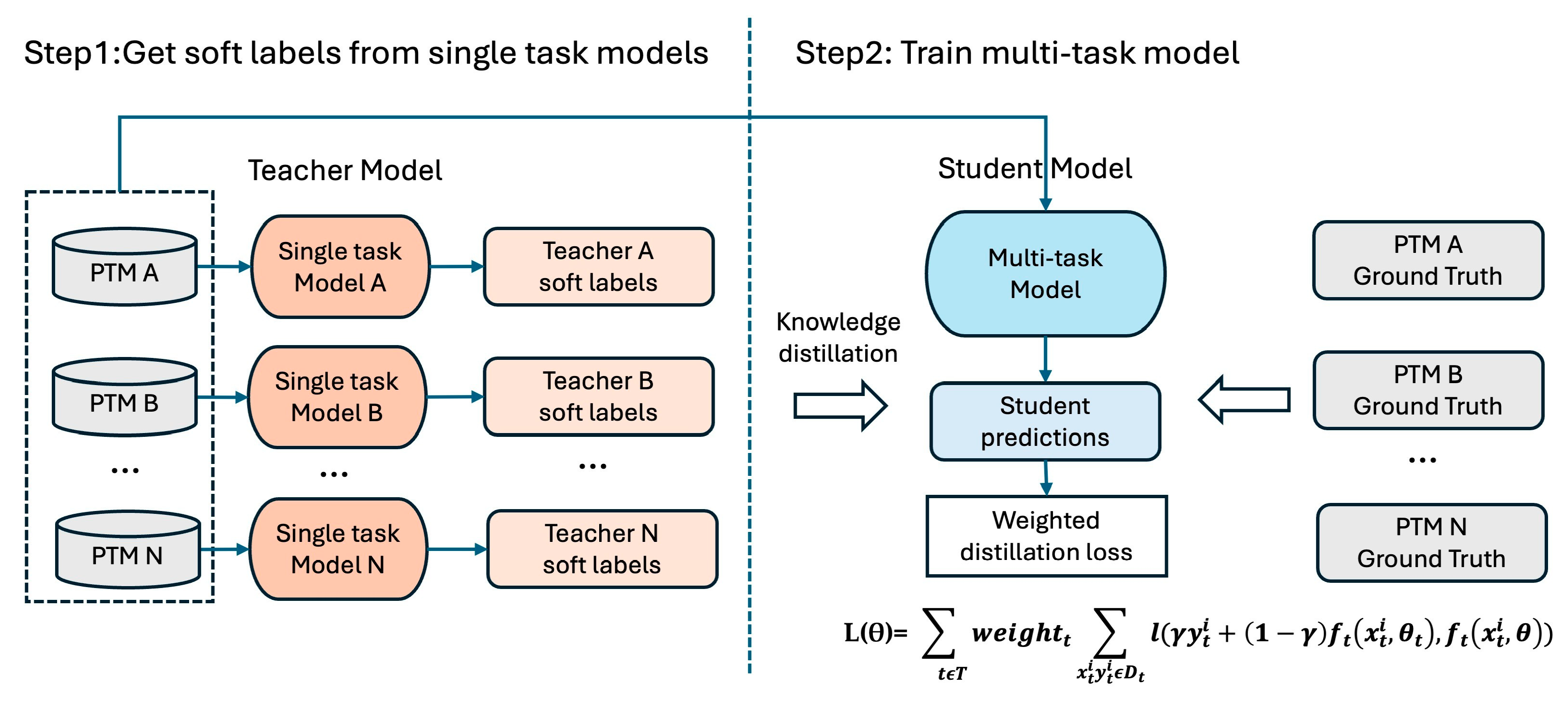
2.4. Multi-Task Training of MTPrompt-PTM
3. Results
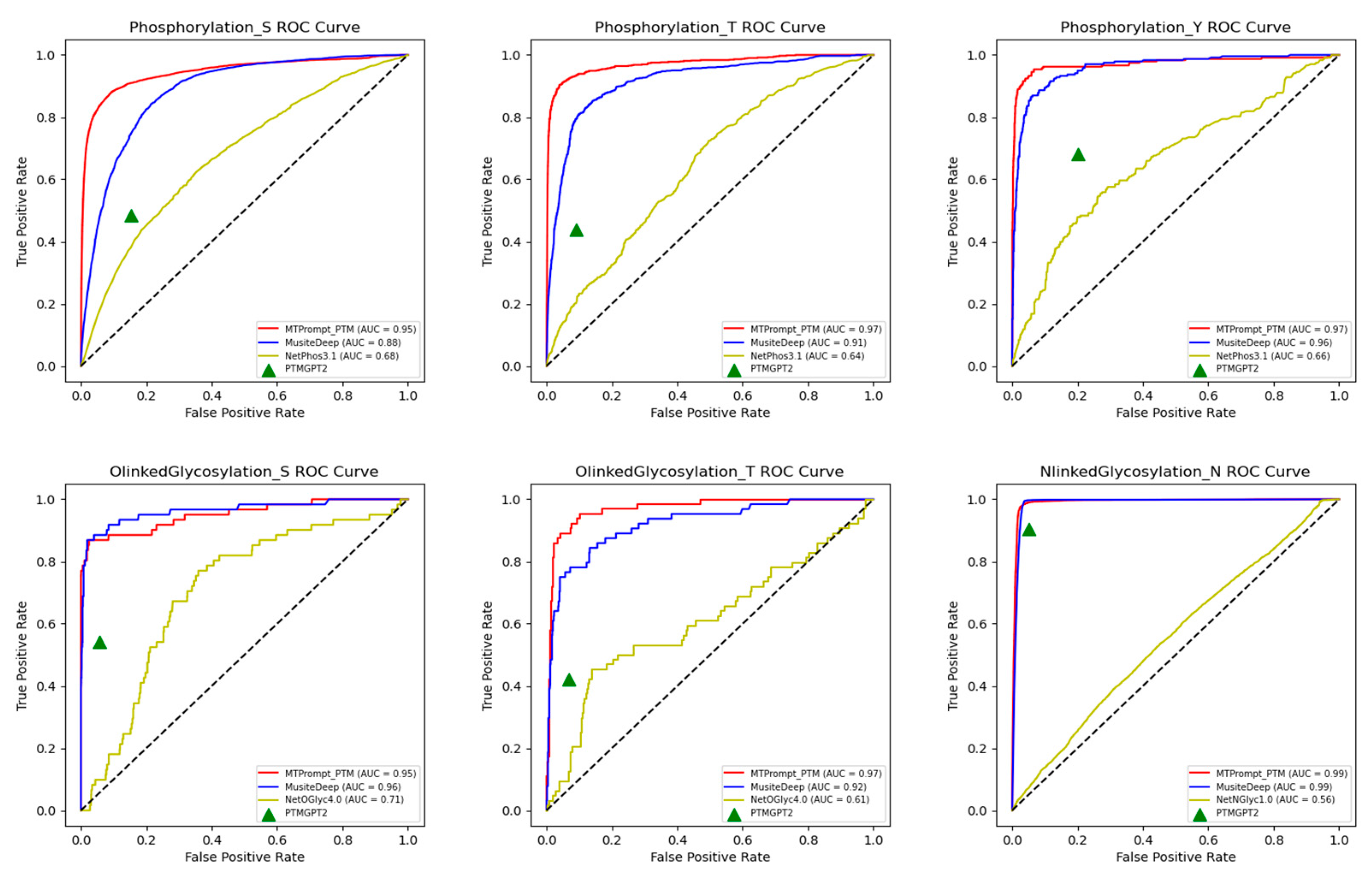
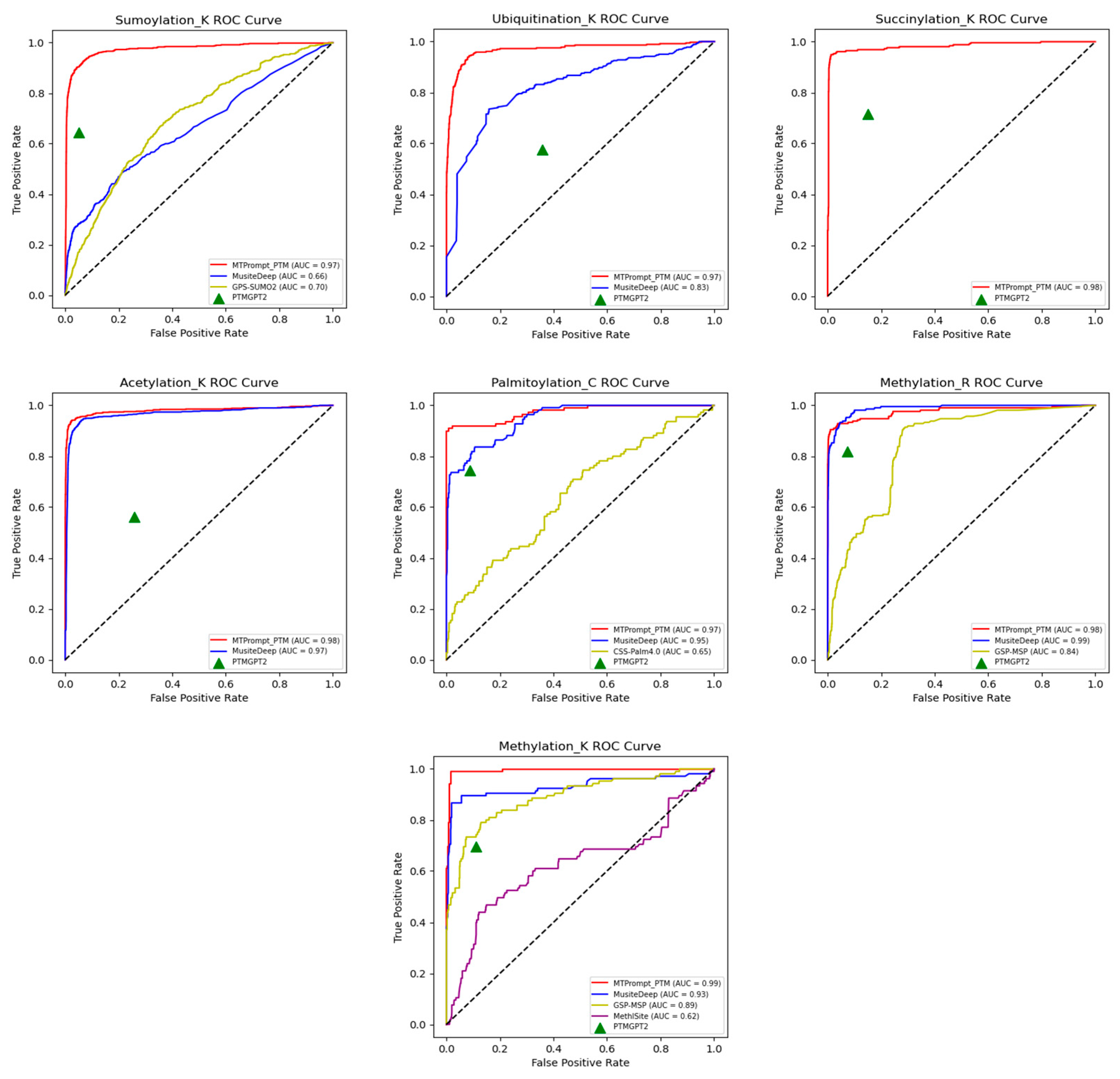
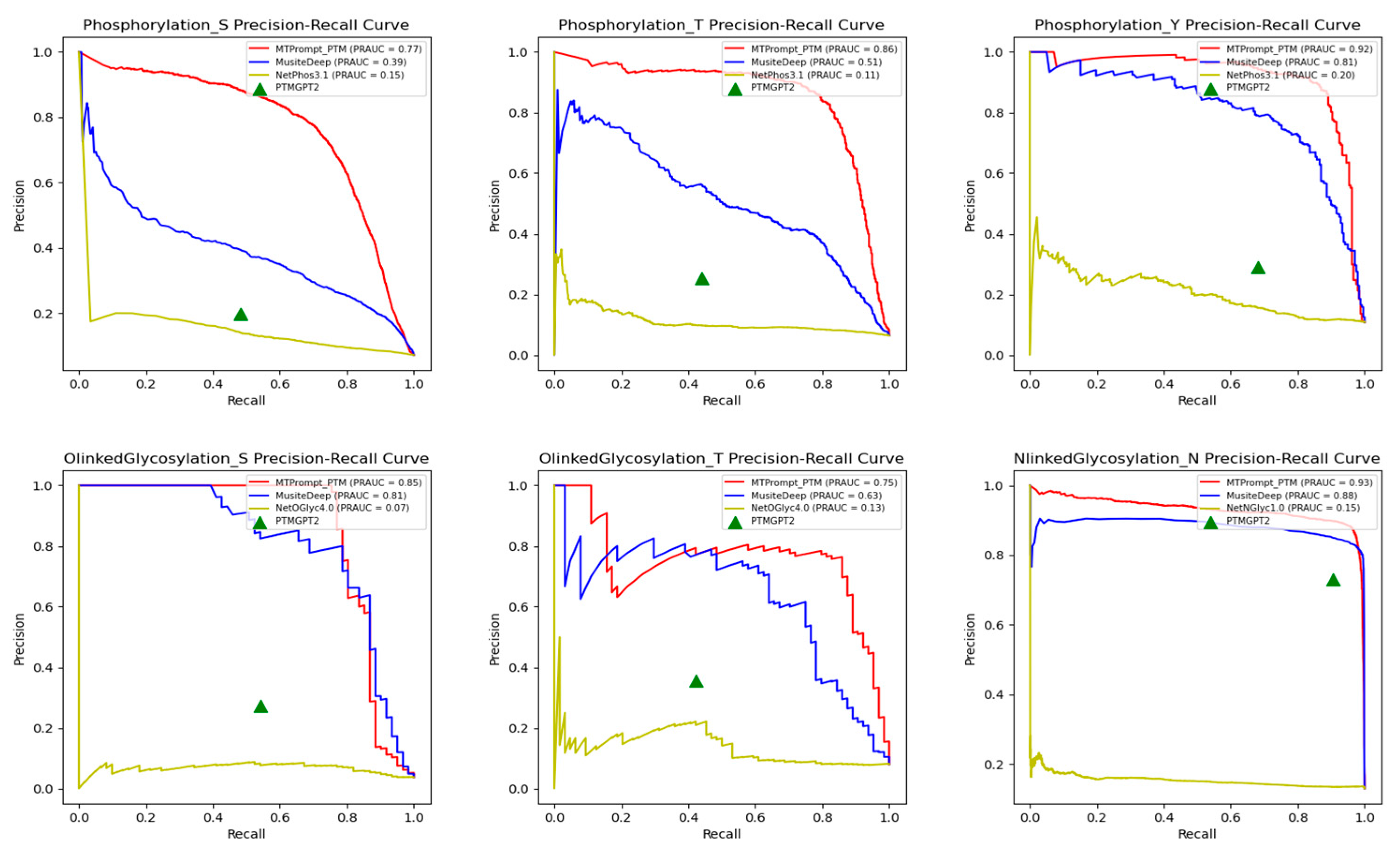
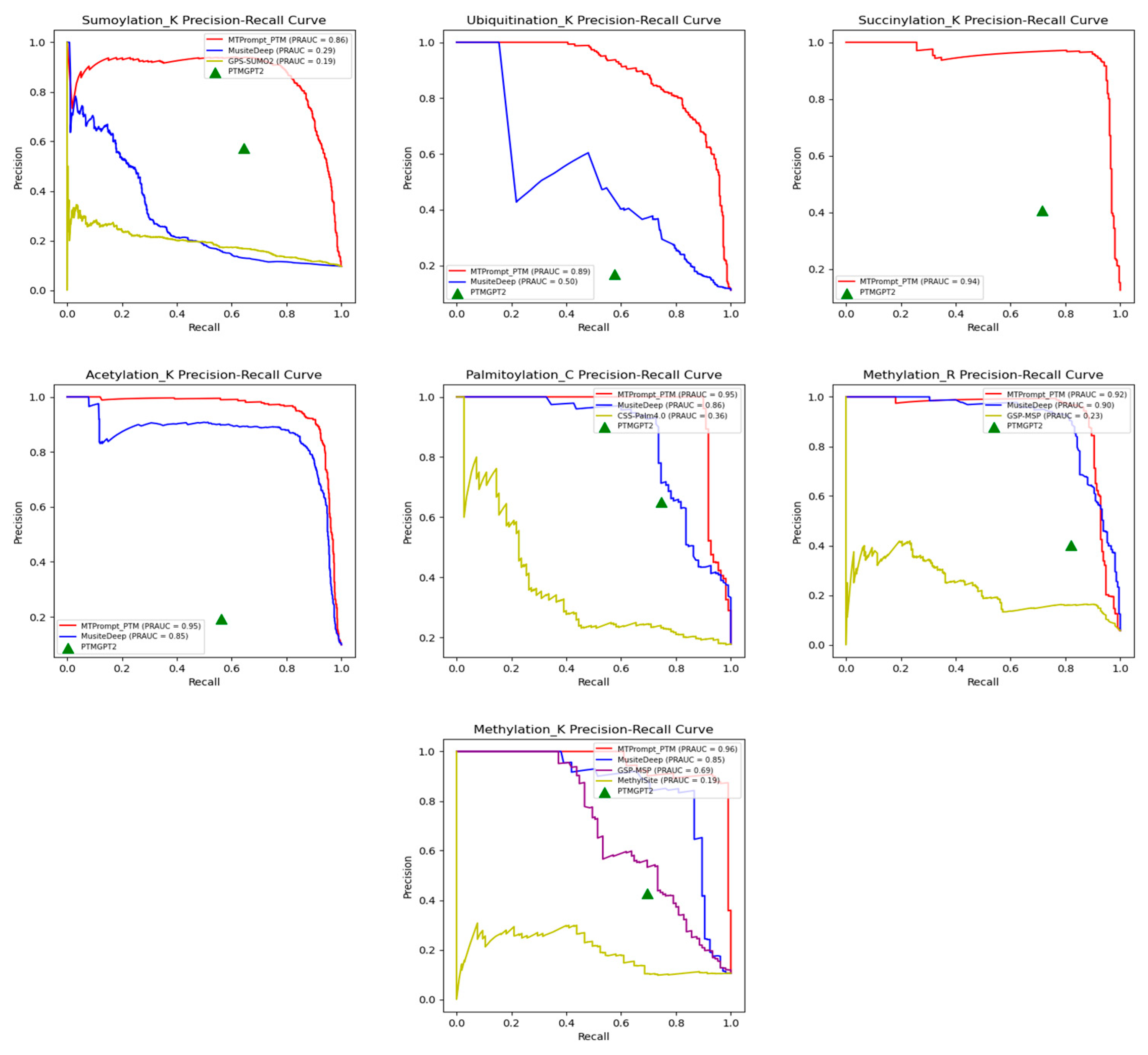
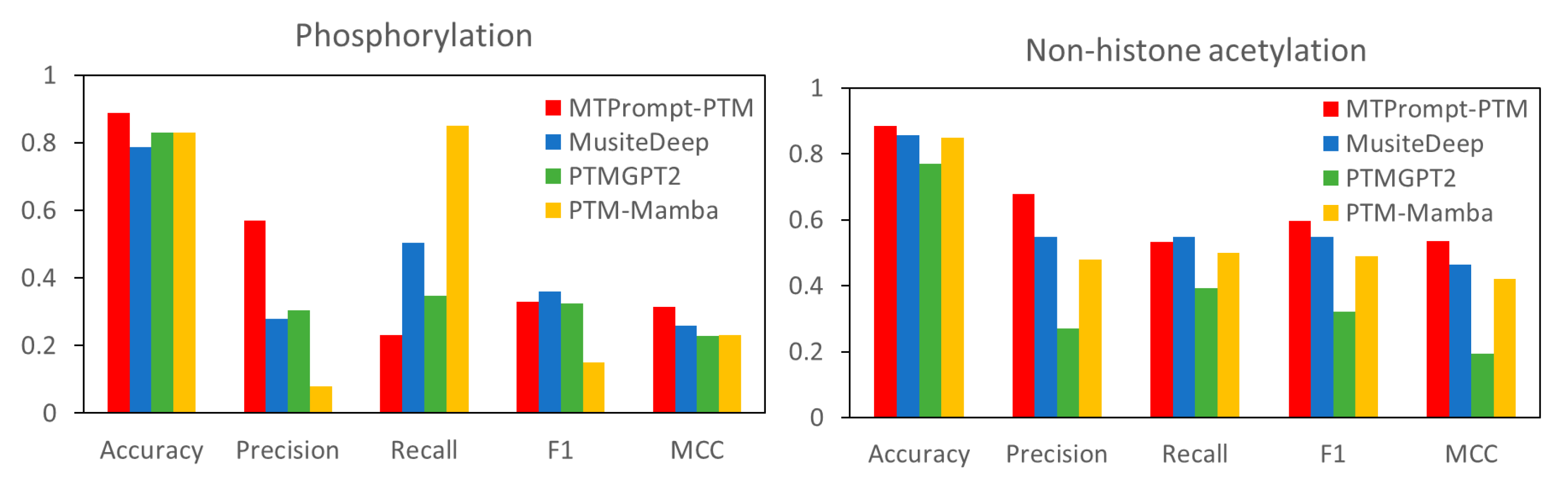
3.1. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Tools
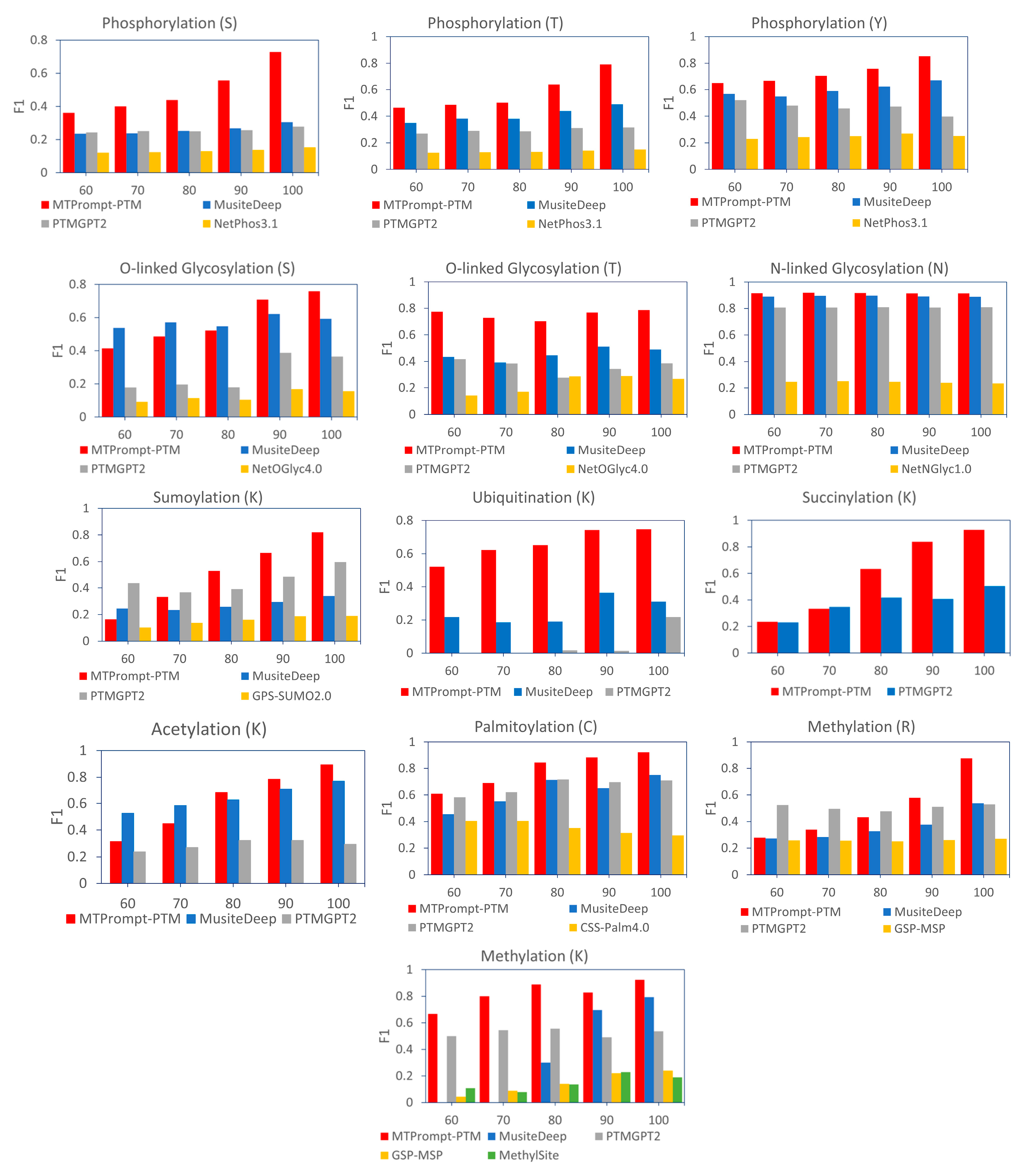
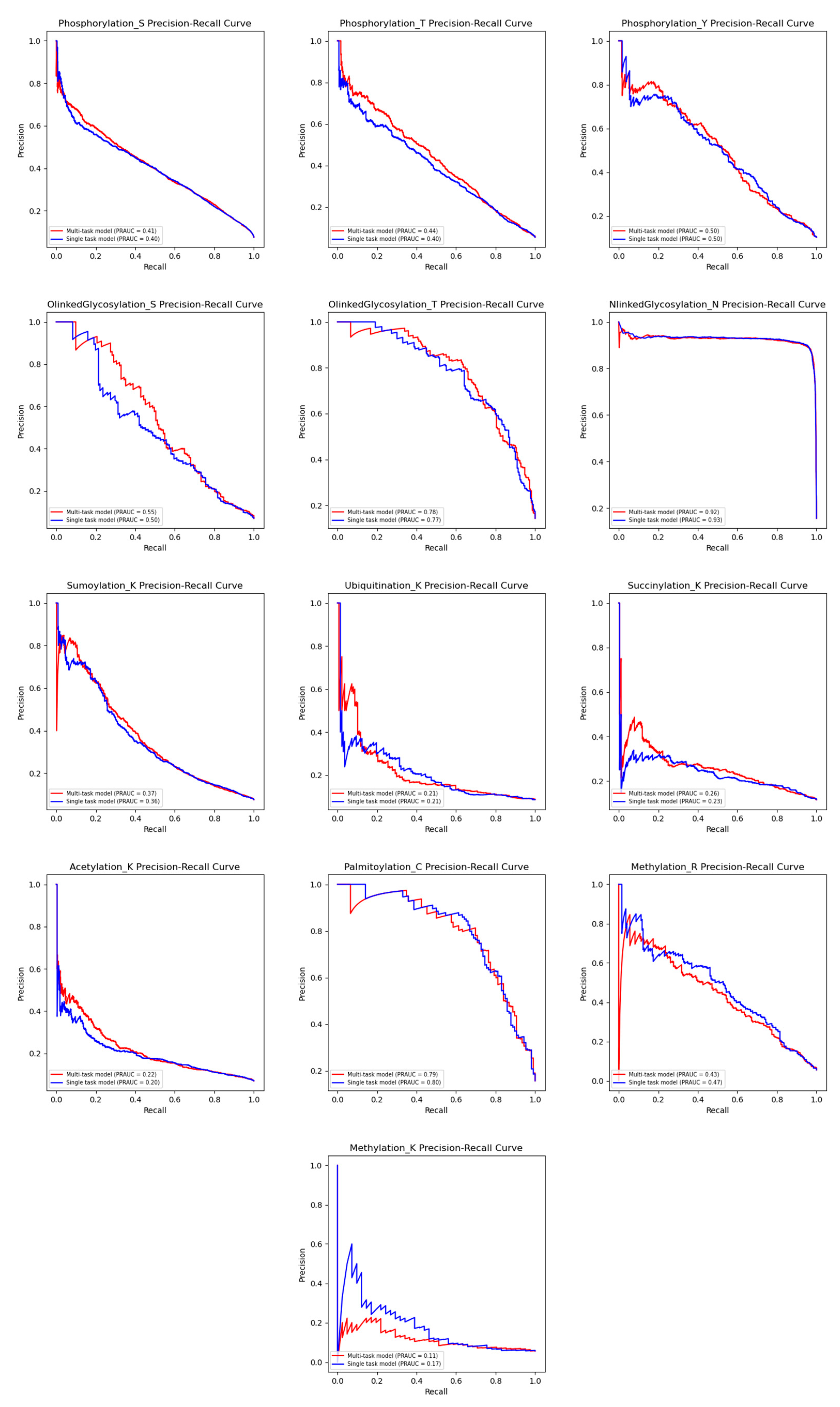
3.2. Comparison with Single-Task Models on Different PTM Types
3.3. Ablation Study
3.3.1. Comparison with Multi-Task Model Without Knowledge Distillation on Different PTM Types
3.3.2. Comparison with Fine-Tuning the Last Two Layers of S-PLM on Different PTM Types
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humphrey, S.J.; James, D.E.; Mann, M. Protein phosphorylation: A major switch mechanism for metabolic regulation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, L.D.; Gevaert, K.; De Smet, I. Protein language: Post-translational modifications talking to each other. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deribe, Y.L.; Pawson, T.; Dikic, I. Post-translational modifications in signal integration. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, G.A.; Baliban, R.C.; Floudas, C.A. Proteome-wide post-translational modification statistics: Frequency analysis and curation of the swiss-prot database. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Bilgin, M.; Snyder, M. Proteomics. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 783–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.V.; Blagoev, B.; Gnad, F.; Macek, B.; Kumar, C.; Mortensen, P.; Mann, M. Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell 2006, 127, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renart, J.; Reiser, J.; Stark, G.R. Transfer of proteins from gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and detection with antisera: A method for studying antibody specificity and antigen structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 3116–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Song, J. Large-scale comparative assessment of computational predictors for lysine post-translational modification sites. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 21, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaili, F.; Pourmirzaei, M.; Ramazi, S.; Shojaeilangari, S.; Yavari, E. A Review of Machine Learning and Algorithmic Methods for Protein Phosphorylation Sites Prediction. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.04311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, N.; Gammeltoft, S.; Brunak, S. Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 294, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Brunak, S. Prediction of glycosylation across the human proteome and the correlation to protein function. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2002, 7, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ullah, S.; Xue, Y. Computational prediction of methylation types of covalently modified lysine and arginine residues in proteins. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 18, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggar, K.K.; Ruiz-Blanco, Y.B.; Charih, F.; Fang, Q.; Connolly, J.; Frensemier, K.; Adhikary, H.; Li, S.S.C.; Green, J.R. MethylSight: Taking a wider view of lysine methylation through computer-aided discovery to provide insight into the human methyl-lysine proteome. bioRxiv 2018. bioRxiv:274688. [Google Scholar]
- Ertelt, M.; Mulligan, V.K.; Maguire, J.B.; Lyskov, S.; Moretti, R.; Schiffner, T.; Meiler, J.; Schroeder, C.T. Combining machine learning with structure-based protein design to predict and engineer post-translational modifications of proteins. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2024, 20, e1011939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zeng, S.; Xu, C.; Qiu, W.; Liang, Y.; Joshi, T.; Xu, D. MusiteDeep: A deep-learning framework for general and kinase-specific phosphorylation site prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3909–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liang, Y.; Xu, D. Capsule network for protein post-translational modification site prediction. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, D.; Yuchi, J.; He, F.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, S.; Li, J.; Xu, D. MusiteDeep: A deep-learning based webserver for protein post-translational modification site prediction and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W140–W146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, M.; Wei, Y.; Huang, X.; Han, C.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lu, T.; Peng, D.; et al. GPS-SUMO 2.0: An updated online service for the prediction of SUMOylation sites and SUMO-interacting motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W238–W247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Akin, H.; Rao, R.; Hie, B.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, W.; Smetanin, N.; Verkuil, R.; Kabeli, O.; Shmueli, Y.; et al. Evolutionary-scale prediction of atomic-level protein structure with a language model. Science 2023, 379, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar, A.; Heinzinger, M.; Dallago, C.; Rihawi, G.; Wang, Y.; Jones, L.; Gibbs, T.; Feher, T.; Angerer, C.; Steinegger, M.; et al. ProtTrans: Towards cracking the language of life’s code through self-supervised deep learning and high performance computing. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.06225. [Google Scholar]
- Pakhrin, S.C.; Pokharel, P.; Bhattarai, A.; Kc, D.B. LMNglyPred: Prediction of human N-linked glycosylation sites using embeddings from a pre-trained protein language model. Glycobiology 2023, 33, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkuhlani, A.; Gad, W.; Roushdy, M.; Voskoglou, M.G.; Salem, A.M. PTG-PLM: Predicting Post-Translational Glycosylation and Glycation Sites Using Protein Language Models and Deep Learning. Axioms 2022, 11, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, S.; Pratyush, P.; Ismail, H.D.; Ma, J.; KC, D.B. Integrating Embeddings from Multiple Protein Language Models to Improve Protein O-GlcNAc Site Prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, P.; Kandel, J.; Tayara, H.; Chong, K.T. Post-translational modification prediction via prompt-based fine-tuning of a GPT-2 model. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, T.; Schussheim, B.; Vincoff, S.; Chatterjee, P. PTM-Mamba: A PTM-aware protein language model with bidirectional gated Mamba blocks. Nat. Methods 2025, 22, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bludau, I.; Willems, S.; Zeng, W.-F.; Strauss, M.T.; Hansen, F.M.; Tanzer, M.C.; Karayel, O.; Schulman, B.A.; Mann, M. The structural context of posttranslational modifications at a proteome-wide scale. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Abbas, U.L.; Shao, Q.; Chen, J.; Xu, D. S-PLM: Structure-aware Protein Language Model via Contrastive Learning between Sequence and Structure. Adv. Sci. 2023, 12, e2404212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, B.; Al-Rfou, R.; Constant, N. The Power of Scale for Parameter-Efficient Prompt Tuning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.08691. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, N.; Ofer, D.; Peleg, Y.; Rappoport, N.; Linial, M. ProteinBERT: A universal deep-learning model of protein sequence and function. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbeck, P.V.; Kornhauser, J.M.; Tkachev, S.; Bin Zhang, B.; Skrzypek, E.; Murray, B.; Latham, V.; Sullivan, M. PhosphoSitePlus: A comprehensive resource for investigating the structure and function of experimentally determined post-translational modifications in man and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D261–D270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Chen, X.; Cheng, K.; Chen, N.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, F.; Sun, H.; Wong, K.-C. TransPTM: A transformer-based model for non-histone acetylation site prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Pourmirzaei, M.; Shao, Q.; Wang, D.; Xu, D. Enhancing Structure-aware Protein Language Models with Efficient Fine-tuning for Various Protein Prediction Tasks. bioRxiv 2025. bioRxiv:2025.04.23.650337. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, B.; Eismann, S.; Suriana, P.; Townshend, R.J.L.; Dror, R. Learning from Protein Structure with Geometric Vector Perceptrons. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Virtual Event, Austria, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, K.; Luong, M.-T.; Khandelwal, U.; Manning, C.D.; Le, Q.V. BAM! Born-Again Multi-Task Networks for Natural Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 5931–5937. [Google Scholar]
- Steentoft, C.; Vakhrushev, S.Y.; Joshi, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Vester-Christensen, M.B.; Schjoldager, K.T.; Lavrsen, K.; Dabelsteen, S.; Pedersen, N.B.; Marcos-Silva, L.; et al. Precision mapping of the human O-GalNAc glycoproteome through SimpleCell technology. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Xue, Y.; Yao, X.; Xu, Y. CSS-Palm: Palmitoylation site prediction with a clustering and scoring strategy (CSS). Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 894–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wen, L.; Gao, X.; Jin, C.; Xue, Y.; Yao, X. CSS-Palm 2.0: An updated software for palmitoylation sites prediction. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2008, 21, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Model | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning-Based | NetPhos 3.1 NetNGlyc 1.0 GPS-MSP MethylSight Ertelt et al. | Use manually designed features with classical ML models such as ANNs or SVM. | Easy to interpret and efficient for small datasets, producing well-established tools in early PTM prediction research. | Cannot capture long-range dependencies, rely heavily on expert-crafted features, and generalize poorly to unseen data. |
| Deep Learning-Based | MusiteDeep CapsNet-PTM GPS-SUMO 2.0 | Leverage CNNs, CapsuleNets, and other DL architectures to automatically learn features from sequence data. | Automatically learn features from raw data and offer better performance on large-scale datasets. | Rely on local sequence windows, ignore structural information, are usually trained separately for each PTM type, and require large, labeled datasets. |
| Protein Language Model-Based | Lmnglypred PTG-PLM O-GlcNAc PTM-GPT2 PTM-Mamba | Use embeddings from large-scale pre-trained PLMs or fine-tune PLMs for PTM prediction. | Capture long-range sequence dependencies, benefit from massive pre-training, support transfer learning and generalization. | Lack of direct structural context and rarely leverage effective joint learning across multiple PTM types. |
| PTM Type | PTM Annotation in UniProt | Number of Protein Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphorylation (S) | Phosphoserine; Diphosphoserine; O-(2-cholinephosphoryl)serine; (Microbial infection) Phosphoserine; O-(pantetheine4′phosphoryl)serine; (Microbial infection) O-(2-cholinephosphoryl) serine | 12,230 |
| Phosphorylation (T) | (Microbial infection) Phosphothreonine; Phosphothreonine | 8551 |
| Phosphorylation (Y) | Phosphotyrosine | 3782 |
| Ubiquitination (K) | (Microbial infection) Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in ubiquitin); Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in ubiquitin and interchain with MARCHF2); Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in ubiquitin) | 1225 |
| N-Linked Glycosylation (N) | N-linked (GlcNAc…) (paucimannose) asparagine; N-linked (GlcNAc…) (keratan sulfate) asparagine; N-linked (GlcNAc…) (complex) asparagine; N-linked (GlcNAc) asparagine; N-linked (Glc…) asparagine; N-linked (GlcNAc…) (hybrid) asparagine; N-linked (GalNAc…) asparagine; N-linked (GlcNAc…) (polylactosaminoglycan) asparagine; N-linked (GlcNAc…) asparagine; N-linked (Hex) asparagine; N-linked (HexNAc…) asparagine; N-linked (GlcNAc…) (high mannose) asparagine | 12,285 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (S) | O-linked (Xyl…) (dermatan sulfate) serine; O-linked (Fuc…) serine; O-linked (Xyl…) (heparan sulfate) serine; O-linked (HexNAc…) serine; O-linked (Fuc) serine; O-linked (GalNAc…) serine; O-linked (Xyl…) serine; O-linked (Hex…) serine; O-linked (GlcA) serine; O-linked (GlcNAc) serine; O-linked (GalNAc) serine; O-linked (Man…) serine; O-linked (Xyl…) (glycosaminoglycan) serine; O-linked (Hex) serine; O-linked (GlcNAc…) serine; O-linked (Glc…) serine; O-linked (Xyl…) (chondroitin sulfate) serine; O-linked (Man) serine | 942 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (T) | O-linked (GlcNAc…) threonine; O-linked (Xyl…) (keratan sulfate) threonine; O-linked (Hex) threonine; O-linked (GalNAc) threonine; O-linked (GalNAc…) threonine; O-linked (GlcNAc) threonine; (Microbial infection) O-linked (Glc) threonine; O-linked (Fuc) threonine; O-linked (HexNAc) threonine; O-linked (Man6P…) threonine; O-linked (Man…) threonine; O-linked (Fuc…) threonine; O-linked (HexNAc…) threonine; O-linked (Hex…) threonine; O-linked (Man) threonine | 694 |
| Acetylation (K) | N6-acetyllysine; N6-acetyl-N6-methyllysine; (Microbial infection) N6-acetyllysine | 6009 |
| Palmitoylation (C) | N-palmitoyl cysteine; S-palmitoyl cysteine | 1531 |
| Methylation (R) | Asymmetric dimethylarginine; N5-[4-(S-L-cysteinyl)-5-methyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-L-ornithine (Arg-Cys) (interchain with C-151 in KEAP1); Symmetric dimethylarginine; Dimethylated arginine; Omega-N-methylated arginine; Omega-N-methylarginine | 1680 |
| Methylation (K) | N6-acetyl-N6-methyllysine; N6-methyllysine; N6,N6,N6-trimethyllysine; N6-methylated lysine; N6,N6-dimethyllysine | 578 |
| SUMOylation (K) | Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in SUMO; Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in SUMO1, SUMO2 and SUMO3); Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in /SUMO5); Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in SUMO); Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in SUMO3); Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in SUMO1); Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in SUMO2 and SUMO3); Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in SUMO1 and SUMO2); Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in SUMO1P1/SUMO5); Glycyl lysine isopeptide (Lys-Gly) (interchain with G-Cter in SUMO2) | 3724 |
| Succinylation (K) | N6-succinyllysine | 2069 |
| PTM Type | Method | Accuracy | F1 | MCC | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphorylation (S) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.964 | 0.736 | 0.718 | 0.772 | 0.704 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.706 | 0.311 | 0.328 | 0.187 | 0.917 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.821 | 0.281 | 0.225 | 0.198 | 0.483 | |
| NetPhos3.1 | 0.289 | 0.155 | 0.09 | 0.085 | 0.905 | |
| Phosphorylation (T) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.975 | 0.811 | 0.798 | 0.787 | 0.836 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.903 | 0.512 | 0.505 | 0.378 | 0.793 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.88 | 0.32 | 0.272 | 0.252 | 0.439 | |
| NetPhos3.1 | 0.429 | 0.153 | 0.103 | 0.085 | 0.802 | |
| Phosphorylation (Y) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.973 | 0.873 | 0.858 | 0.877 | 0.87 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.921 | 0.705 | 0.678 | 0.593 | 0.87 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.785 | 0.407 | 0.342 | 0.29 | 0.681 | |
| NetPhos3.1 | 0.613 | 0.262 | 0.154 | 0.165 | 0.634 | |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (S) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.983 | 0.774 | 0.765 | 0.762 | 0.787 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.956 | 0.6 | 0.616 | 0.454 | 0.885 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.929 | 0.363 | 0.351 | 0.273 | 0.541 | |
| NetOGlyc4.0 | 0.718 | 0.151 | 0.163 | 0.085 | 0.672 | |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (T) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.962 | 0.786 | 0.769 | 0.724 | 0.859 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.87 | 0.49 | 0.47 | 0.357 | 0.781 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.892 | 0.386 | 0.329 | 0.355 | 0.422 | |
| NetOGlyc4.0 | 0.801 | 0.267 | 0.196 | 0.19 | 0.453 | |
| N-Linked Glycosylation (N) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.977 | 0.915 | 0.903 | 0.889 | 0.944 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.967 | 0.887 | 0.875 | 0.802 | 0.992 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.944 | 0.808 | 0.782 | 0.73 | 0.905 | |
| NetNGlyc1.0 | 0.294 | 0.233 | 0.033 | 0.136 | 0.825 | |
| SUMOylation (K) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.97 | 0.838 | 0.823 | 0.878 | 0.802 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.901 | 0.332 | 0.299 | 0.472 | 0.256 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.92 | 0.606 | 0.563 | 0.572 | 0.644 | |
| GPS-SUMO2.0 | 0.187 | 0.187 | 0.081 | 0.103 | 0.978 | |
| Ubiquitination (K) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.956 | 0.782 | 0.764 | 0.879 | 0.704 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.681 | 0.367 | 0.318 | 0.236 | 0.831 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.634 | 0.259 | 0.14 | 0.167 | 0.575 | |
| Succinylation (K) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.983 | 0.933 | 0.923 | 0.944 | 0.922 |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.834 | 0.519 | 0.452 | 0.408 | 0.715 | |
| Acetylation (K) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.981 | 0.899 | 0.889 | 0.924 | 0.877 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.948 | 0.778 | 0.762 | 0.671 | 0.926 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.724 | 0.286 | 0.199 | 0.192 | 0.562 | |
| Palmitoylation (C) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.974 | 0.926 | 0.91 | 0.943 | 0.909 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.916 | 0.759 | 0.708 | 0.774 | 0.745 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.883 | 0.695 | 0.626 | 0.651 | 0.745 | |
| CSS-Palm4.0 | 0.183 | 0.3 | -0.03 | 0.177 | 0.982 | |
| Methylation (R) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.989 | 0.892 | 0.889 | 0.967 | 0.829 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.915 | 0.565 | 0.59 | 0.399 | 0.967 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.921 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.403 | 0.819 | |
| GSP-MSP | 0.734 | 0.274 | 0.304 | 0.162 | 0.881 | |
| Methylation (K) | MTPrompt-PTM | 0.976 | 0.883 | 0.87 | 0.901 | 0.867 |
| MusiteDeep | 0.952 | 0.791 | 0.768 | 0.728 | 0.867 | |
| PTMGPT2 | 0.869 | 0.529 | 0.477 | 0.427 | 0.695 | |
| GSP-MSP | 0.337 | 0.234 | 0.162 | 0.133 | 0.962 | |
| MethylSight | 0.384 | 0.19 | 0.022 | 0.11 | 0.686 |
| Kinase Type | Number of Kinase Sites in Training Set | Method | Number of Kinase Sites in Testing Set | Number of Predicted Kinase Sites in Testing Set | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGC | 879 | MTPrompt-PTM | 17 | 15 | 0.882 |
| MusiteDeep | 17 | 14 | 0.824 | ||
| PTMGPT2 | 17 | 7 | 0.412 | ||
| NetPhos3.1 | 17 | 12 | 0.706 | ||
| CAMK | 392 | MTPrompt-PTM | 2 | 1 | 0.5 |
| MusiteDeep | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||
| PTMGPT2 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | ||
| NetPhos3.1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||
| CK1 | 48 | MTPrompt-PTM | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MusiteDeep | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| PTMGPT2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| NetPhos3.1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| CMGC | 1739 | MTPrompt-PTM | 47 | 43 | 0.915 |
| MusiteDeep | 47 | 42 | 0.894 | ||
| PTMGPT2 | 47 | 21 | 0.447 | ||
| NetPhos3.1 | 47 | 40 | 0.851 | ||
| Other | 415 | MTPrompt-PTM | 9 | 1 | 0.111 |
| MusiteDeep | 9 | 3 | 0.333 | ||
| PTMGPT2 | 9 | 1 | 0.111 | ||
| NetPhos3.1 | 9 | 2 | 0.222 | ||
| STE | 174 | MTPrompt-PTM | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| MusiteDeep | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||
| PTMGPT2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||
| NetPhos3.1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||
| TK | 753 | MTPrompt-PTM | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| MusiteDeep | 4 | 4 | 1 | ||
| PTMGPT2 | 4 | 2 | 0.5 | ||
| NetPhos3.1 | 4 | 2 | 0.5 |
| F1/MCC | ||
|---|---|---|
| PTM Type (Residue) | Multi-Task Model | Single-Task Model |
| Phosphorylation (S) | 0.428/0.384 | 0.429/0.383 |
| Phosphorylation (T) | 0.461/0.432 | 0.439/0.406 |
| Phosphorylation (Y) | 0.503/0.459 | 0.498/0.448 |
| N-Linked Glycosylation (N) | 0.918/0.902 | 0.922/0.907 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (S) | 0.524/0.5 | 0.487/0.447 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (T) | 0.716/0.685 | 0.670/0.634 |
| Palmitoylation (C) | 0.74/0.697 | 0.730/0.685 |
| Acetylation (K) | 0.214/0.206 | 0.189/0.180 |
| Ubiquitination (K) | 0.081/0.129 | 0.051/0.074 |
| Succinylation (K) | 0.208/0.176 | 0.144/0.109 |
| SUMOylation (K) | 0.352/0.342 | 0.361/0.332 |
| Methylation (K) | 0/0.142 | 0.089/0.143 |
| Methylation (R) | 0.431/0.414 | 0.470/0.454 |
| F1/MCC | ||
|---|---|---|
| PTM Type (Residue) | Multi-Task Model with Knowledge Distillation | Multi-Task Model Without Knowledge Distillation |
| Phosphorylation (S) | 0.428/0.384 | 0.341/0.338 |
| Phosphorylation (T) | 0.461/0.432 | 0.389/0.381 |
| Phosphorylation (Y) | 0.503/0.459 | 0.448/0.424 |
| N-Linked Glycosylation (N) | 0.918/0.902 | 0.916/0.901 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (S) | 0.524/0.5 | 0.45/0.446 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (T) | 0.716/0.685 | 0.667/0.634 |
| Palmitoylation (C) | 0.74/0.697 | 0.719/0.678 |
| Acetylation (K) | 0.214/0.206 | 0.160/0.164 |
| Ubiquitination (K) | 0.081/0.129 | 0.081/0.129 |
| Succinylation (K) | 0.208/0.176 | 0.044/0.062 |
| SUMOylation (K) | 0.352/0.342 | 0.253/0.301 |
| Methylation (K) | 0/0.142 | 0/0.142 |
| Methylation (R) | 0.431/0.414 | 0.411/0.415 |
| AUROC/AUPRC | ||
|---|---|---|
| PTM Type | Multi-Task Model with Knowledge Distillation | Multi-Task Model Without Knowledge Distillation |
| Phosphorylation (S) | 0.866/0.409 | 0.866/0.411 |
| Phosphorylation (T) | 0.878/0.436 | 0.879/0.429 |
| Phosphorylation (Y) | 0.844/0.504 | 0.845/0.496 |
| N-Linked Glycosylation (N) | 0.990/0.924 | 0.991/0.927 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (S) | 0.870/0.552 | 0.864/0.518 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (T) | 0.933/0.784 | 0.933/0.761 |
| Palmitoylation (C) | 0.929/0.791 | 0.925/0.792 |
| Acetylation (K) | 0.739/0.220 | 0.742/0.212 |
| Ubiquitination (K) | 0.669/0.215 | 0.669/0.215 |
| Succinylation (K) | 0.720/0.260 | 0.722/0.268 |
| SUMOylation (K) | 0.798/0.369 | 0.797/0.359 |
| Methylation (K) | 0.663/0.122 | 0.669/0.130 |
| Methylation (R) | 0.893/0.438 | 0.910/0.450 |
| F1/MCC | ||
|---|---|---|
| PTM Type | Multi-Task Model with Prompt Tuning | Multi-Task Model with Fine-Tuning in Last Two Layers of S-PLM v2 |
| Phosphorylation (S) | 0.428/0.384 | 0.355/0.340 |
| Phosphorylation (T) | 0.461/0.432 | 0.403/0.392 |
| Phosphorylation (Y) | 0.503/0.459 | 0.450/0.427 |
| N-Linked Glycosylation (N) | 0.918/0.902 | 0.916/0.900 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (S) | 0.524/0.5 | 0.49/0.481 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (T) | 0.716/0.685 | 0.548/0.554 |
| Palmitoylation (C) | 0.74/0.697 | 0.695/0.651 |
| Acetylation (K) | 0.214/0.206 | 0.214/0.206 |
| Ubiquitination (K) | 0.081/0.129 | 0.082/0.156 |
| Succinylation (K) | 0.208/0.176 | 0.11/0.124 |
| SUMOylation (K) | 0.352/0.342 | 0.268/0.304 |
| Methylation (K) | 0/0.142 | 0.048/0.152 |
| Methylation (R) | 0.431/0.414 | 0.435/0.435 |
| AUROC/AUPRC | ||
|---|---|---|
| PTM Type | Multi-Task Model with Prompt Tuning | Multi-Task Model with Fine-Tuning in Last Two Layers of S-PLM v2 |
| Phosphorylation (S) | 0.866/0.409 | 0.865/0.409 |
| Phosphorylation (T) | 0.878/0.436 | 0.882/0.434 |
| Phosphorylation (Y) | 0.844/0.504 | 0.837/0.499 |
| N-Linked Glycosylation (N) | 0.990/0.924 | 0.991/0.930 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (S) | 0.870/0.552 | 0.845/0.525 |
| O-Linked Glycosylation (T) | 0.933/0.784 | 0.922/0.757 |
| Palmitoylation (C) | 0.929/0.791 | 0.927/0.795 |
| Acetylation (K) | 0.739/0.220 | 0.739/0.220 |
| Ubiquitination (K) | 0.669/0.215 | 0.672/0.207 |
| Succinylation (K) | 0.720/0.260 | 0.717/0.259 |
| SUMOylation (K) | 0.798/0.369 | 0.792/0.354 |
| Methylation (K) | 0.663/0.122 | 0.704/0.289 |
| Methylation (R) | 0.893/0.438 | 0.903/0.461 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; He, F.; Shao, Q.; Wang, D.; Xu, D. MTPrompt-PTM: A Multi-Task Method for Post-Translational Modification Prediction Using Prompt Tuning on a Structure-Aware Protein Language Model. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060843
Han Y, He F, Shao Q, Wang D, Xu D. MTPrompt-PTM: A Multi-Task Method for Post-Translational Modification Prediction Using Prompt Tuning on a Structure-Aware Protein Language Model. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(6):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060843
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Ye, Fei He, Qing Shao, Duolin Wang, and Dong Xu. 2025. "MTPrompt-PTM: A Multi-Task Method for Post-Translational Modification Prediction Using Prompt Tuning on a Structure-Aware Protein Language Model" Biomolecules 15, no. 6: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060843
APA StyleHan, Y., He, F., Shao, Q., Wang, D., & Xu, D. (2025). MTPrompt-PTM: A Multi-Task Method for Post-Translational Modification Prediction Using Prompt Tuning on a Structure-Aware Protein Language Model. Biomolecules, 15(6), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060843






