Enhanced Innate Immunity Mediated by IL-36α in Atopic Dermatitis and Differences in Cytokine Profiles of Lymphocytes in the Skin and Draining Lymph Nodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Models and Treatment
2.2. Tissue Sampling
2.3. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.5. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (Real-Time PCR)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Administration of IL-36α Causes Exacerbation of Cutaneous Manifestations
3.2. IL-36α Induces the Recruitment of Innate Immune Cells to the Skin Tissue
3.3. Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines Are Increased by IL-36α in WT and IL-18Tg Mice
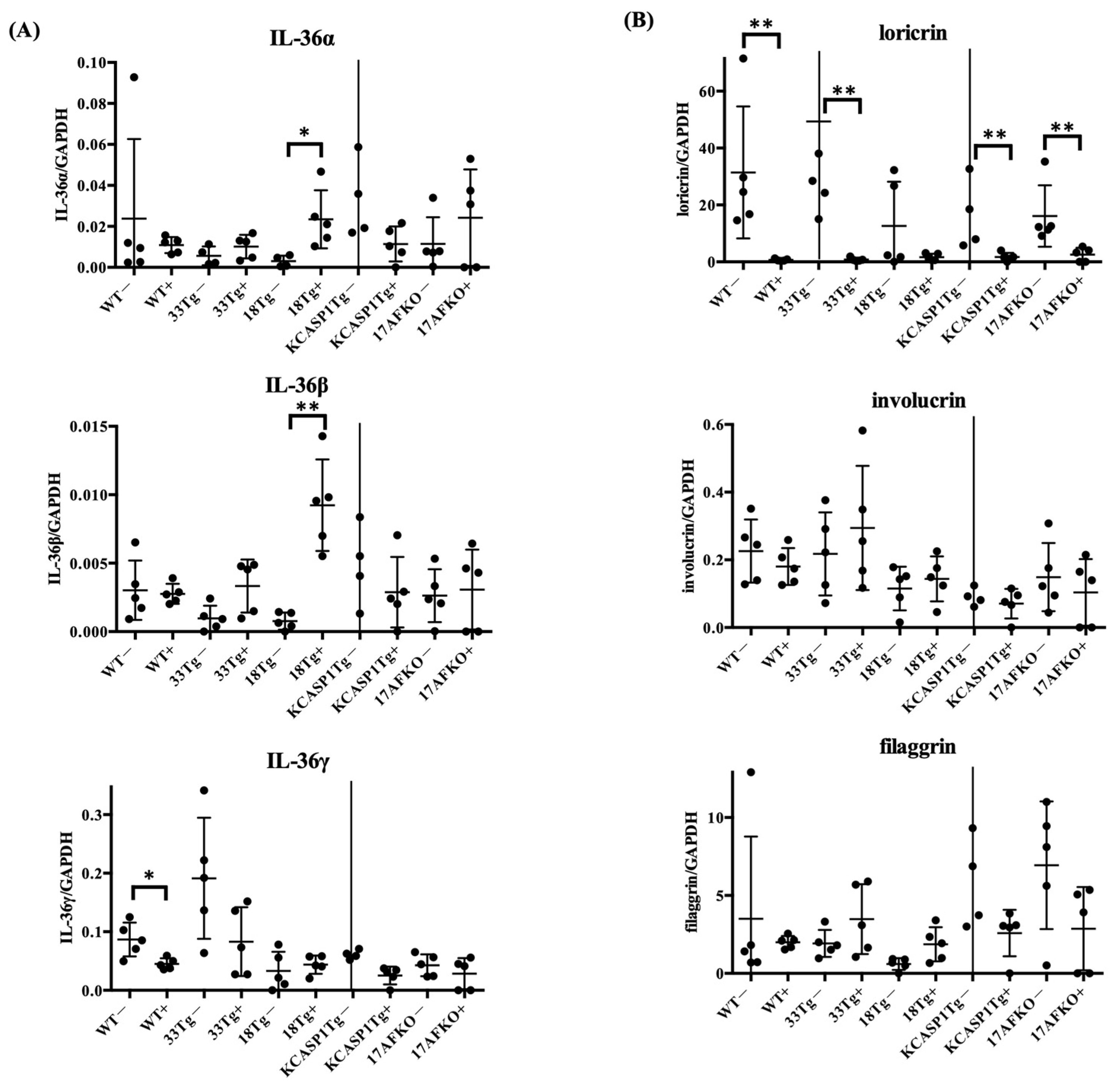
3.4. IL-36α Enhances Its Own Expression and Is Associated With Barrier Gene Downregulation
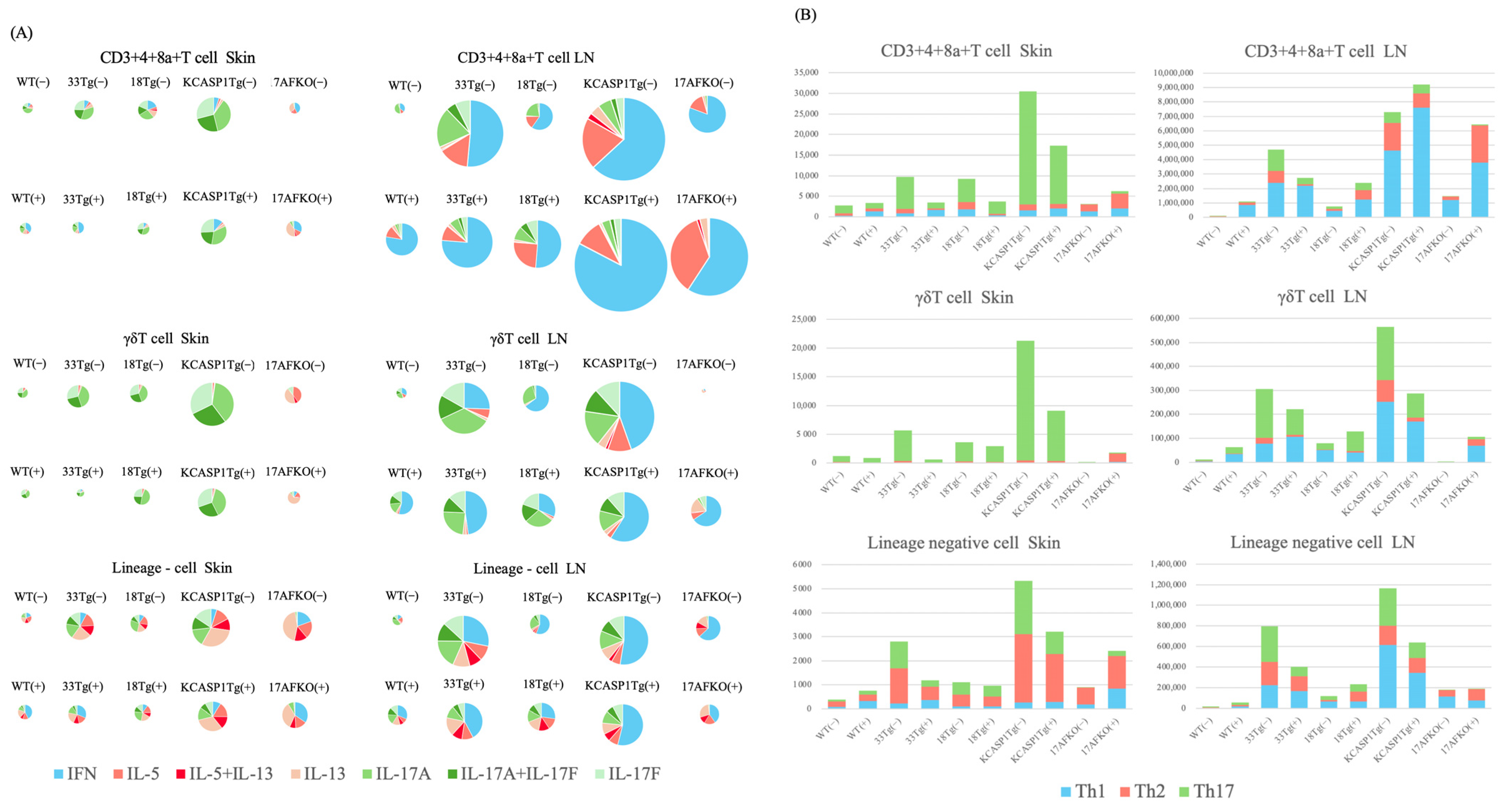
3.5. Trend of Th17 and ILC3 Predominance in the Skin and Th1 Predominance in the Lymph Node
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | atopic dermatitis |
| IL | interleukin |
| IL-33Tg | keratin 14-specific IL-33 overexpressing transgenic |
| IL-18Tg | keratin 14-specific IL-18 overexpressing transgenic |
| KCASP1Tg | keratin 14-specific caspase-1 overexpressing transgenic |
| KCASP1Tg+IL-17AFKO | KCASP1Tg+IL-17A and F knock-out |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
References
- Silverberg, J.I. Association between adult atopic dermatitis, cardiovascular disease, and increased heart attacks in three population-based studies. Allergy 2015, 70, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuabara, K.; Azfar, R.S.; Shin, D.B.; Neimann, A.L.; Troxel, A.B.; Gelfand, J.M. Cause-specific mortality in patients with severe psoriasis: A population-based cohort study in the U.K. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Matsushima, Y.; Mizutani, K.; Kawakita, F.; Fujimoto, M.; Okada, K.; Kondo, M.; Habe, K.; Suzuki, H.; Mizutani, H.; et al. The Stenosis of Cerebral Arteries and Impaired Brain Glucose Uptake by Long-Lasting Inflammatory Cytokine Release from Dermatitis Is Rescued by Anti-IL-1 Therapy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2280–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, T.; Iida, S.; Maruyama, J.; Urushima, H.; Ichishi, M.; Matsushima, Y.; Mizutani, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Sugioka, K.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Arteriosclerosis Derived from Cutaneous Inflammation Is Ameliorated by the Deletion of IL-17A and IL-17F. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Saito, H.; Maruyama, J.; Isoda, K.; Yokochi, A.; Imanaka-Yoshida, K.; Tsuda, K.; Kakeda, M.; Okamoto, R.; et al. Persistent release of IL-1s from skin is associated with systemic cardio-vascular disease, emaciation and systemic amyloidosis: The potential of anti-IL-1 therapy for systemic inflammatory diseases. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Iida, S.; Ichishi, M.; Kondo, M.; Nishimura, M.; Ichikawa, A.; Matsushima, Y.; Iwakura, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Yamanaka, K. Amelioration of Systemic Amyloidosis by Blocking IL-17A and Not by IL-17F, and Arteriosclerosis by Blocking Both IL-17A and IL-17F in an Inflammatory Skin Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, S.; Nakanishi, T.; Momose, F.; Ichishi, M.; Mizutani, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Umaoka, A.; Kondo, M.; Habe, K.; Hirokawa, Y.; et al. IL-17A Is the Critical Cytokine for Liver and Spleen Amyloidosis in Inflammatory Skin Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Mizutani, K.; Iida, S.; Matsushima, Y.; Umaoka, A.; Kondo, M.; Habe, K.; Yamanaka, K. Janus Kinase Inhibitors Ameliorated Gastrointestinal Amyloidosis and Hypoalbuminemia in Persistent Dermatitis Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Okada, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Mizutani, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Kondo, M.; Habe, K.; Mizutani, H.; Seo, N. Skin inflammation leads immunoglobulin G aggregation and deposition in multiple organs. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaoka, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Mizutani, K.; Seo, N.; Matsushima, Y.; Habe, K.; Hagimori, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Yamanaka, K. Skin Inflammation and Testicular Function: Dermatitis Causes Male Infertility via Skin-Derived Cytokines. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, K.; Isono, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Okada, K.; Umaoka, A.; Iida, S.; Habe, K.; Hagimori, K.; Yamazaki, H.; Yamanaka, K. Inflammatory Skin-Derived Cytokines Accelerate Osteoporosis in Mice with Persistent Skin Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, M.; Nakanishi, T.; Ichishi, M.; Matsushima, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Yamanaka, K. Increased Mortality Risk at Septic Condition in Inflammatory Skin Disorders and the Effect of High-Fat Diet Consumption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, K.; Shirakami, E.; Ichishi, M.; Matsushima, Y.; Umaoka, A.; Okada, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Morita, E.; Yamanaka, K. Systemic Dermatitis Model Mice Exhibit Atrophy of Visceral Adipose Tissue and Increase Stromal Cells via Skin-Derived Inflammatory Cytokines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towne, J.E.; Garka, K.E.; Renshaw, B.R.; Virca, G.D.; Sims, J.E. Interleukin (IL)-1F6, IL-1F8, and IL-1F9 signal through IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP to activate the pathway leading to NF-kappaB and MAPKs. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 13677–13688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; O’Siorain, J.R.; Kundig, T.M.; Mellett, M. Molecular aspects of Interleukin-36 cytokine activation and regulation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2024, 52, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelez, H.; Choon, S.E.; Marrakchi, S.; Burden, A.D.; Tsai, T.F.; Morita, A.; Navarini, A.A.; Zheng, M.; Xu, J.; Turki, H.; et al. Trial of Spesolimab for Generalized Pustular Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenin, S.H.; Khattri, S.; Lebwohl, M.G. Spesolimab use in treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum. JAAD Case Rep. 2023, 34, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, S.; Muramatsu, K.; Mizuno, A.; Hayashi, A.; Mizutani, Y.; Ujiie, H.; Sugiura, K.; Yamanaka, K. Improvement of acute phase symptoms of pemphigus foliaceus with Spesolimab. JAAD Case Rep. 2024, 55, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Chi, C.C.; Chung, W.H.; Chen, C.B. Generalized pustular psoriasis: Immunological mechanisms, genetics, and emerging therapeutics. Trends Immunol. 2025, 46, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.L.; Liu, Q.W.; Dong, X.W.; Bai, Y.P. Biologics for generalized pustular psoriasis: A systematic review and single-arm meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1462158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Santana, Y.E.; Leon, G.; St Leger, D.; Fallon, P.G.; Walsh, P.T. Keratinocyte interleukin-36 receptor expression orchestrates psoriasiform inflammation in mice. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3, e201900586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, K.; Fujita, H.; Komine, M.; Yamanaka, K.; Akiyama, M. The role of interleukin-36 in health and disease states. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 1910–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettiol, A.; Fagni, F.; Mattioli, I.; Bagni, G.; Vitiello, G.; Grassi, A.; Della Bella, C.; Benagiano, M.; Troilo, A.; Holownia, K.S.; et al. Serum Interleukin-36 alpha as a Candidate Biomarker to Distinguish Behcet’s Syndrome and Psoriatic Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, K.; Tanaka, M.; Tsutsui, H.; Kupper, T.S.; Asahi, K.; Okamura, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kayagaki, N.; Black, R.A.; et al. Skin-specific caspase-1-transgenic mice show cutaneous apoptosis and pre-endotoxin shock condition with a high serum level of IL-18. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, G.; Weninger, W. Pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: A short review. Cogent Biol. 2015, 1, 1103459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Q.; Naseer, T.; Minshall, E.M.; Song, Y.L.; Boguniewicz, M.; Leung, D.Y. In vivo expression of IL-12 and IL-13 in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershko, A.Y.; Suzuki, R.; Charles, N.; Alvarez-Errico, D.; Sargent, J.L.; Laurence, A.; Rivera, J. Mast cell interleukin-2 production contributes to suppression of chronic allergic dermatitis. Immunity 2011, 35, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Haneda, T.; Mizutani, H.; Yoshimoto, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Yamanishi, K. Skin-specific expression of IL-33 activates group 2 innate lymphoid cells and elicits atopic dermatitis-like inflammation in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13921–13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Hosotani, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Yasuda, K.; Nagai, M.; Jitsukawa, O.; Gomi, F.; Nakanishi, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Expression of IL-33 in ocular surface epithelium induces atopic keratoconjunctivitis with activation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, H.; Tsutsui, H.; Murakami, T.; Yumikura-Futatsugi, S.; Yamanaka, K.; Tanaka, M.; Iwakura, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S.; et al. IL-18 contributes to the spontaneous development of atopic dermatitis-like inflammatory skin lesion independently of IgE/stat6 under specific pathogen-free conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11340–11345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Mizutani, H.; Tsutsui, H.; Noben-Trauth, N.; Yamanaka, K.; Tanaka, M.; Izumi, S.; Okamura, H.; Paul, W.E.; Nakanishi, K. IL-18 induction of IgE: Dependence on CD4+ T cells, IL-4 and STAT6. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, A.M.; Baliwag, J.; Chen, C.S.; Guzman, A.M.; Stoll, S.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Ward, N.L.; Johnston, A. IL-36 promotes myeloid cell infiltration, activation, and inflammatory activity in skin. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 6053–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, V.L.; Kuczma, M.; Maxim, E.; Denning, T.L. IL-36 cytokines and gut immunity. Immunology 2021, 163, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Todorovic, V. Interleukin-36: Structure, Signaling and Function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 21, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, A.; Nishida, A. Pro- and anti-inflammatory roles of interleukin (IL)-33, IL-36, and IL-38 in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 58, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, T.; Newstead, M.W.; Zeng, X.; Nanjo, Y.; Peters-Golden, M.; Kaku, M.; Standiford, T.J. Interleukin-36γ and IL-36 receptor signaling mediate impaired host immunity and lung injury in cytotoxic Pseudomonas aeruginosa pulmonary infection: Role of prostaglandin E2. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, U.; Scholler, J.; Gurgel, J.; Renshaw, B.; Sims, J.E.; Gabel, C.A. Externalization of the leaderless cytokine IL-1F6 occurs in response to lipopolysaccharide/ATP activation of transduced bone marrow macrophages. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4021–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Garcet, S.; Li, X.; Cueto, I.; Salud-Gnilo, C.; Kunjravia, N.; Yamamura, K.; Gonzalez, J.; Murai-Yamamura, M.; Rambhia, D.; et al. Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide LL37 Induces Toll-Like Receptor 8 and Amplifies IL-36γ and IL-17C in Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 832–841.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Chen, H.X.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.J.; Yue, Q.; Xiao, M.; Li, J.W. IL-36 cytokine expression and its relationship with p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways in psoriasis vulgaris skin lesions. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2013, 33, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachen, K.L.; Arnold Greving, C.N.; Towne, J.E. Role of IL-36 cytokines in psoriasis and other inflammatory skin conditions. Cytokine 2022, 156, 155897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigne, S.; Palmer, G.; Martin, P.; Lamacchia, C.; Strebel, D.; Rodriguez, E.; Olleros, M.L.; Vesin, D.; Garcia, I.; Ronchi, F.; et al. IL-36 signaling amplifies Th1 responses by enhancing proliferation and Th1 polarization of naive CD4+ T cells. Blood 2012, 120, 3478–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Archer, N.K.; Dillen, C.A.; Wang, Y.; Ashbaugh, A.G.; Ortines, R.V.; Kao, T.; Lee, S.K.; Cai, S.S.; Miller, R.J.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Epicutaneous Exposure Drives Skin Inflammation via IL-36-Mediated T Cell Responses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 653–666.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Katayama, Y.; Oguma, R.; Wakabayashi, S.; Nygaard, T.; Saijo, S.; Inohara, N.; Otto, M.; Matsue, H.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Virulent PSMα Peptides Induce Keratinocyte Alarmin Release to Orchestrate IL-17-Dependent Skin Inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 667–677.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.H.; Reynolds, J.M.; Pappu, B.P.; Chen, G.; Martinez, G.J.; Dong, C. Interleukin-17C promotes Th17 cell responses and autoimmune disease via interleukin-17 receptor E. Immunity 2011, 35, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iznardo, H.; Puig, L. Exploring the Role of IL-36 Cytokines as a New Target in Psoriatic Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iznardo, H.; Puig, L. The interleukin-1 family cytokines in psoriasis: Pathogenetic role and therapeutic perspectives. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, J.; Baker, K.; Houston, A.; Brint, E. IL-36 cytokines in inflammatory and malignant diseases: Not the new kid on the block anymore. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6215–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooderham, M.J.; Van Voorhees, A.S.; Lebwohl, M.G. An update on generalized pustular psoriasis. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlanda, C.; Dinarello, C.A.; Mantovani, A. The interleukin-1 family: Back to the future. Immunity 2013, 39, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; Vieira, P.; O’Garra, A. Biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin-10. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmann, M.; Doble, R.; Bachmann, M.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Werfel, T.; Mühl, H. IL-27 Regulates IL-18 binding protein in skin resident cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; O’Garra, A. IL-10 Family Cytokines IL-10 and IL-22: From Basic Science to Clinical Translation. Immunity 2019, 50, 871–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantaert, T.; Baeten, D.; Tak, P.P.; van Baarsen, L.G. Type I IFN and TNFalpha cross-regulation in immune-mediated inflammatory disease: Basic concepts and clinical relevance. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Rodriguez, E.; Degenhardt, F.; Baurecht, H.; Wehkamp, U.; Volks, N.; Szymczak, S.; Swindell, W.R.; Sarkar, M.K.; Raja, K.; et al. Atopic Dermatitis Is an IL-13-Dominant Disease with Greater Molecular Heterogeneity Compared to Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnowicki, T.; He, H.; Krueger, J.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zysk, W.; Sitko, K.; Tukaj, S.; Zaryczanska, A.; Trzeciak, M. Altered Gene Expression of IL-35 and IL-36alpha in the Skin of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balato, A.; Zink, A.; Babino, G.; Buononato, D.; Kiani, C.; Eyerich, K.; Ziehfreund, S.; Scala, E. The Impact of Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis on Quality of Life: A Literature Research on Biomarkers. Life 2022, 12, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlando, M.; Megna, M.; Caldarola, G.; Bernardini, N.; Giofre, C.; Gisondi, P.; De Simone, C.; Cozzani, E. Eczematous reactions in patients with plaque psoriasis receiving biological therapy: An observational study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 4298–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Fan, R.; Ma, Q.; Luo, X.; Jian, H.; Chen, X.; Cao, C.; Zheng, W. Development of IL-17A inhibitor-induced atopic dermatitis-like rash in psoriasis patients: Insights into immune shift. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e14958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Kono, Y.; Iida, S.; Nakanishi, T.; Nishimura, M.; Matsushima, Y.; Kondo, M.; Habe, K.; Imai, Y. The Interplay of Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3 Lymphocytes and Cytokines in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheim, J.J.; Yang, D. Alarmins: Chemotactic activators of immune responses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2005, 17, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussion, C.; Ortega, N.; Girard, J.P. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: A novel ‘alarmin’? PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrchen, J.M.; Sunderkotter, C.; Foell, D.; Vogl, T.; Roth, J. The endogenous Toll-like receptor 4 agonist S100A8/S100A9 (calprotectin) as innate amplifier of infection, autoimmunity, and cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Alam, M.A.; Ansari, A.W.; Jochebeth, A.; Leo, R.; Al-Abdulla, M.N.; Al-Khawaga, S.; AlHammadi, A.; Al-Malki, A.; Al Naama, K.; et al. Emerging Role of the IL-36/IL-36R Axis in Multiple Inflammatory Skin Diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 144, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
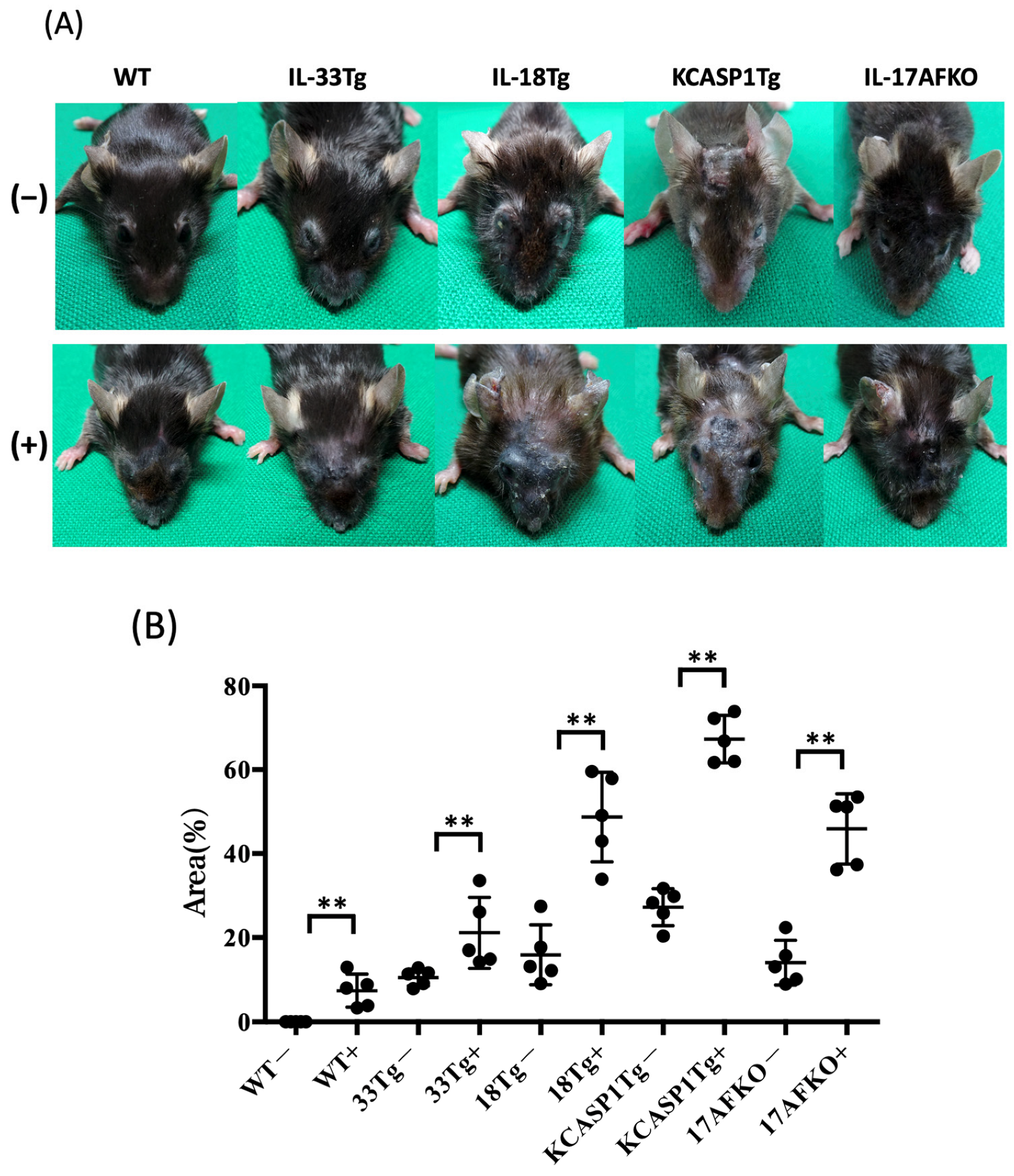
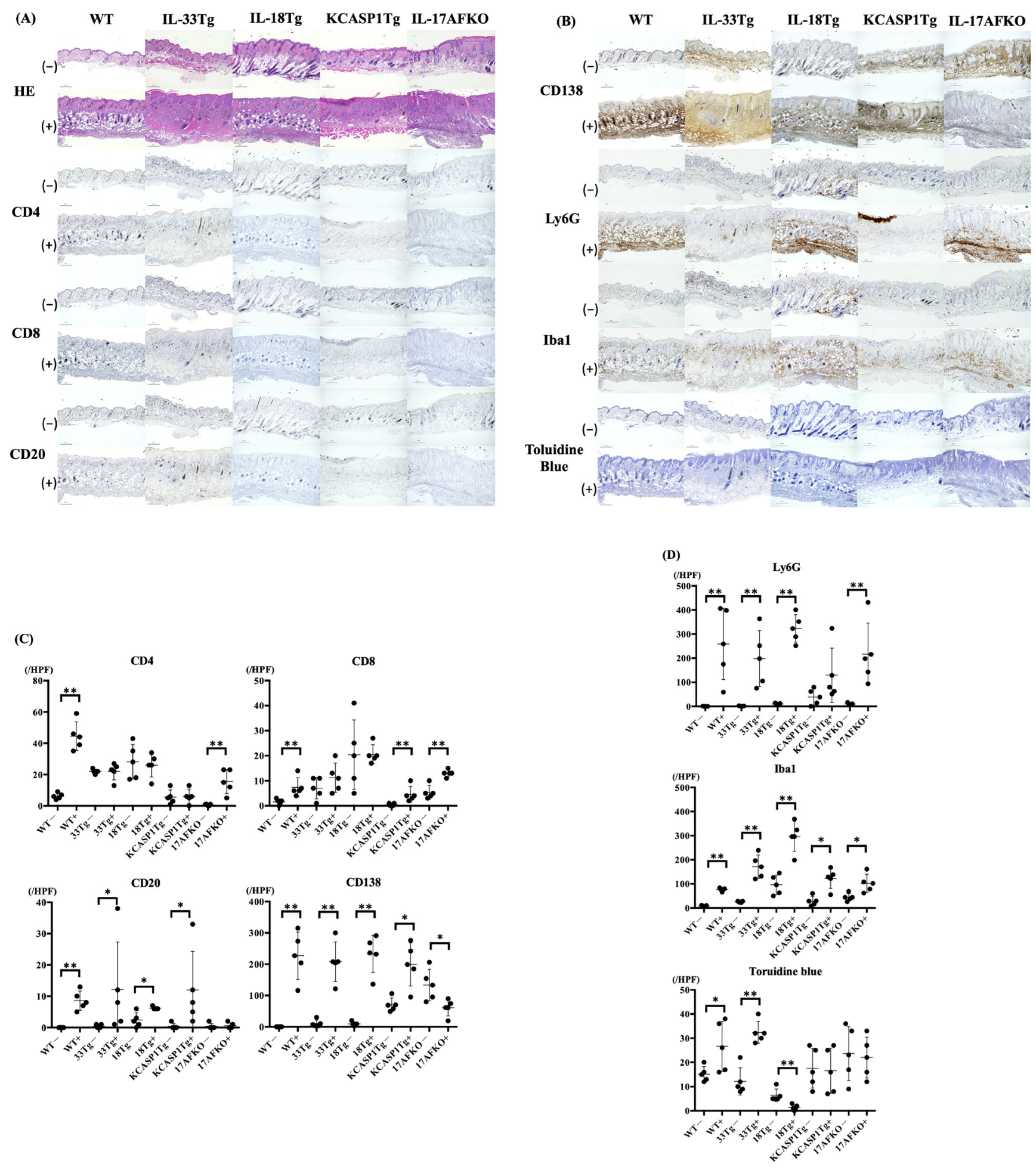
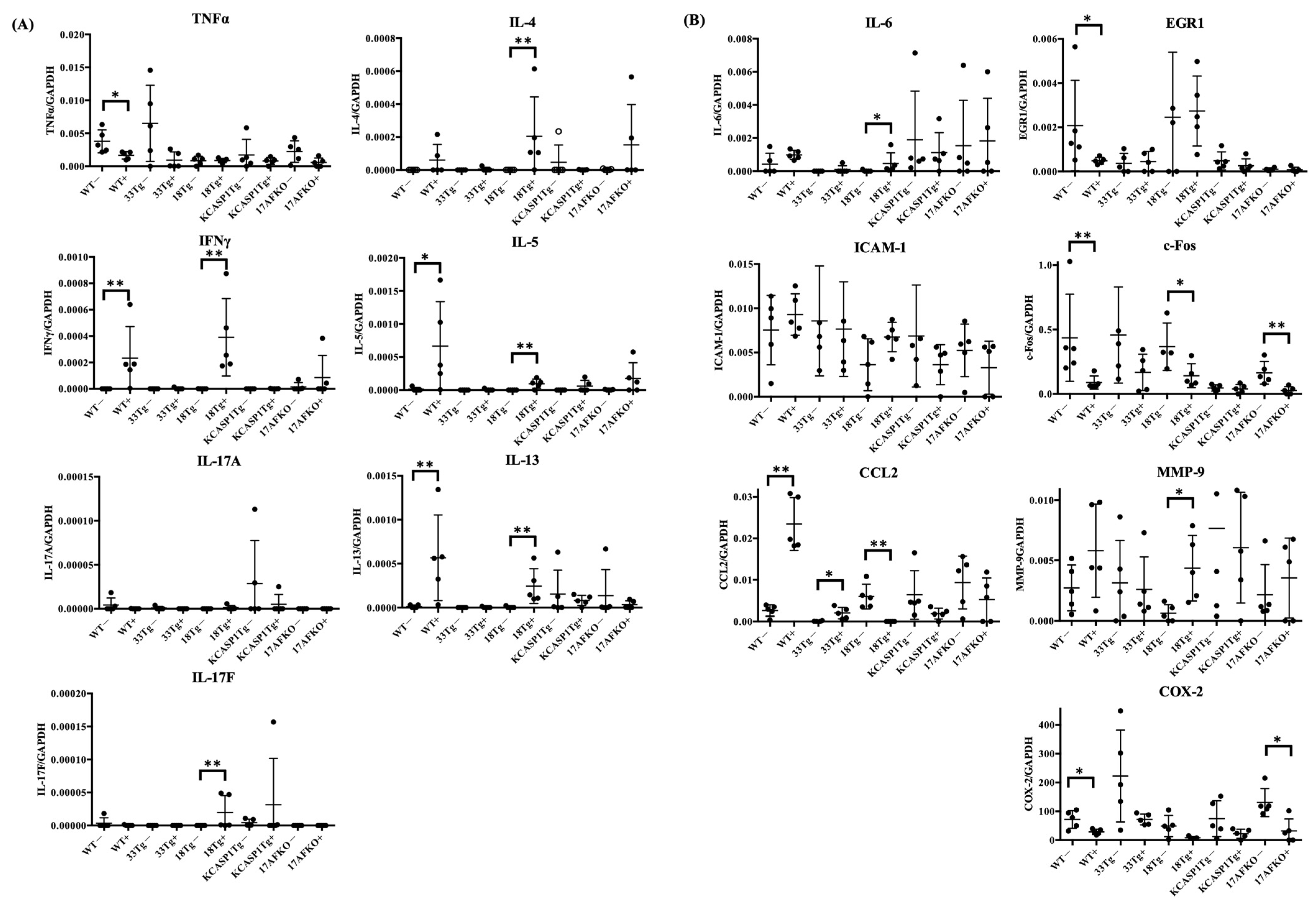
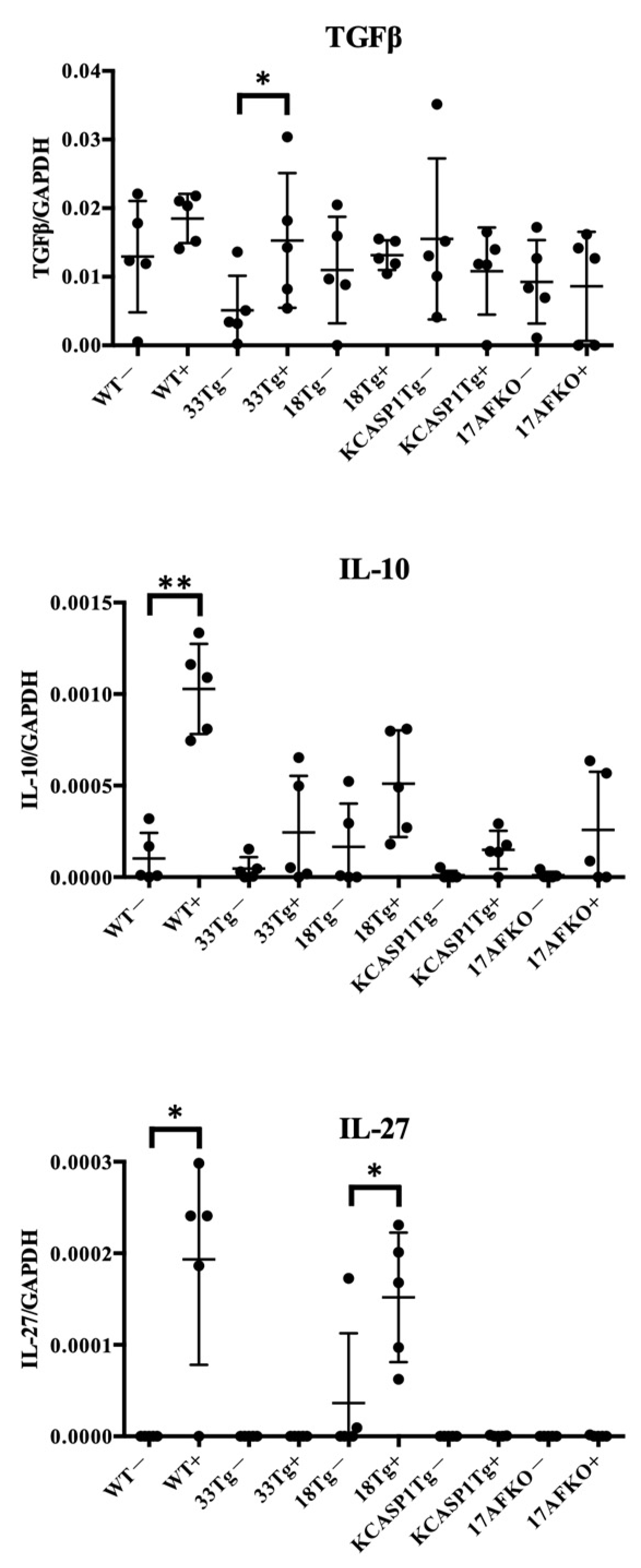
| Mouse Model | Inflammation Type | Disease Model | Post-IL-36 Immune Cells | Post-IL-36 Cytokines |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | None | Control | ↑ CD4⁺, ↑ CD8⁺, ↑ CD20⁺, ↑ CD138⁺, ↑ Ly6G⁺, ↑ Iba1⁺ | ↑ IFN-γ, ↑ IL-13, ↑ CCL2, ↓ c-Fos, ↑ IL-10 |
| IL-33Tg | Type 2 | Acute-phase AD | ↑ CD138⁺, ↑ Ly6G⁺, ↑ Iba1⁺, ↑ TB⁺ | – |
| IL-18Tg | Type 2 | Chronic-phase AD | ↑ CD138⁺, ↑ Ly6G⁺, ↑ Iba1⁺, ↓ TB⁺ | ↑ IFN-γ, ↑ IL-4, ↑ IL-5, ↑ IL-13, ↑ IL-17F, ↓ CCL2 |
| KCASP1Tg | Type 2/Type 3 | Mixed AD / Psoriasis-like | ↑ CD8⁺ | n.s. |
| KCASP1Tg + IL-17AFKO | Type 2 | AD (Type 3 -independent) | ↑ CD4⁺, ↑ CD8⁺, ↑ Ly6G⁺ | ↓ c-Fos, ↓ COX-2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ichikawa, A.; Nishimura, M.; Ichishi, M.; Imai, Y.; Matsushima, Y.; Iwakura, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Yamanishi, K.; Yamanaka, K. Enhanced Innate Immunity Mediated by IL-36α in Atopic Dermatitis and Differences in Cytokine Profiles of Lymphocytes in the Skin and Draining Lymph Nodes. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060817
Ichikawa A, Nishimura M, Ichishi M, Imai Y, Matsushima Y, Iwakura Y, Watanabe M, Yamanishi K, Yamanaka K. Enhanced Innate Immunity Mediated by IL-36α in Atopic Dermatitis and Differences in Cytokine Profiles of Lymphocytes in the Skin and Draining Lymph Nodes. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(6):817. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060817
Chicago/Turabian StyleIchikawa, Ayaka, Mai Nishimura, Masako Ichishi, Yasutomo Imai, Yoshiaki Matsushima, Yoichiro Iwakura, Masatoshi Watanabe, Kiyofumi Yamanishi, and Keiichi Yamanaka. 2025. "Enhanced Innate Immunity Mediated by IL-36α in Atopic Dermatitis and Differences in Cytokine Profiles of Lymphocytes in the Skin and Draining Lymph Nodes" Biomolecules 15, no. 6: 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060817
APA StyleIchikawa, A., Nishimura, M., Ichishi, M., Imai, Y., Matsushima, Y., Iwakura, Y., Watanabe, M., Yamanishi, K., & Yamanaka, K. (2025). Enhanced Innate Immunity Mediated by IL-36α in Atopic Dermatitis and Differences in Cytokine Profiles of Lymphocytes in the Skin and Draining Lymph Nodes. Biomolecules, 15(6), 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060817







