Designing New Chimeric Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptides to Enhance Efficacy Toward the ESKAPE+E: Beyond Sequence Extension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peptides
2.2. Solubility Test
2.3. Bacterial Cultures
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity
2.5. Analysis of Bacterial Membrane Integrity
2.6. In Vitro Translation Assays
2.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Design and Characteristics of Chimeric Peptides
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity Against ESKAPE+E Pathogens
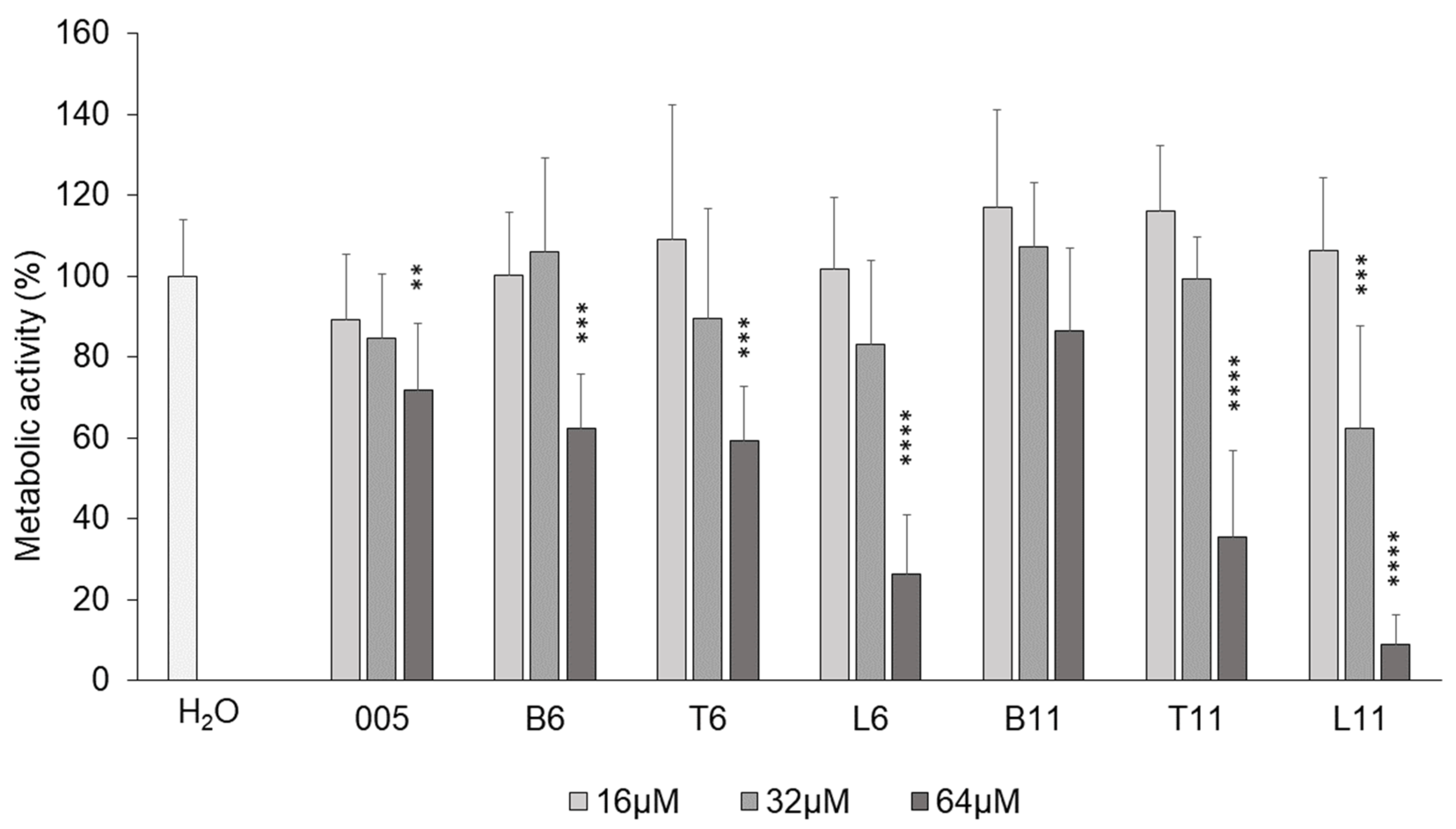
3.3. Cytotoxicity Against Human Cell Line A549
3.4. Interaction with the Bacterial Membrane
3.5. Inhibition of Protein Synthesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMPs | Antimicrobial peptides |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| CFU | Colony-forming unit |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FluC | Firefly luciferase |
| GRAVY | Grand average of hydropathicity |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| MBC | Minimal bactericidal concentration |
| MHB | Mueller–Hinton broth |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay |
| OD | Optical density |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| PrAMPs | Proline-rich antimicrobial peptides |
| RP-HPLC | Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
References
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Sahl, H.-G. Antimicrobial and Host-Defense Peptides as New Anti-Infective Therapeutic Strategies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, A.; Alhanout, K.; Duval, R.E. Bacteriocins, Antimicrobial Peptides from Bacterial Origin: Overview of Their Biology and Their Impact against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mookherjee, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Haagsman, H.P.; Davidson, D.J. Antimicrobial Host Defence Peptides: Functions and Clinical Potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlapuu, M.; Håkansson, J.; Ringstad, L.; Björn, C. Antimicrobial Peptides: An Emerging Category of Therapeutic Agents. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, E.M.; Trampari, E.; Siasat, P.; Gaya, M.S.; Alav, I.; Webber, M.A.; Blair, J.M.A. Molecular Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance Revisited. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijksteel, G.S.; Ulrich, M.M.W.; Middelkoop, E.; Boekema, B.K.H.L. Review: Lessons Learned From Clinical Trials Using Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 616979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epand, R.M.; Vogel, H.J. Diversity of Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Mechanisms of Action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 1999, 1462, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, N.G.; Li, W.; Hossain, M.A.; Separovic, F.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Wade, J.D. (Re)Defining the Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptide Family and the Identification of Putative New Members. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 607769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, M.; Mardirossian, M.; Nguyen, F.; Seefeldt, A.C.; Guichard, G.; Scocchi, M.; Innis, C.A.; Wilson, D.N. Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptides Targeting Protein Synthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florin, T.; Maracci, C.; Graf, M.; Karki, P.; Klepacki, D.; Berninghausen, O.; Beckmann, R.; Vázquez-Laslop, N.; Wilson, D.N.; Rodnina, M.V.; et al. An Antimicrobial Peptide That Inhibits Translation by Trapping Release Factors on the Ribosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, T.O.; Morici, M.; Berger, M.; Safdari, H.A.; Lele, D.S.; Beckert, B.; Kaur, K.J.; Wilson, D.N. Structural Basis for Translation Inhibition by the Glycosylated Drosocin Peptide. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennaro, R.; Skerlavaj, B.; Romeo, D. Purification, Composition, and Activity of Two Bactenecins, Antibacterial Peptides of Bovine Neutrophils. Infect. Immun. 1989, 57, 3142–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardirossian, M.; Grzela, R.; Giglione, C.; Meinnel, T.; Gennaro, R.; Mergaert, P.; Scocchi, M. The Host Antimicrobial Peptide Bac71-35 Binds to Bacterial Ribosomal Proteins and Inhibits Protein Synthesis. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benincasa, M.; Scocchi, M.; Podda, E.; Skerlavaj, B.; Dolzani, L.; Gennaro, R. Antimicrobial Activity of Bac7 Fragments against Drug-Resistant Clinical Isolates. Peptides 2004, 25, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seefeldt, A.C.; Graf, M.; Pérébaskine, N.; Nguyen, F.; Arenz, S.; Mardirossian, M.; Scocchi, M.; Wilson, D.N.; Innis, C.A. Structure of the Mammalian Antimicrobial Peptide Bac7(1–16) Bound within the Exit Tunnel of a Bacterial Ribosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 2429–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardirossian, M.; Sola, R.; Beckert, B.; Valencic, E.; Collis, D.W.P.; Borišek, J.; Armas, F.; Di Stasi, A.; Buchmann, J.; Syroegin, E.A.; et al. Peptide Inhibitors of Bacterial Protein Synthesis with Broad Spectrum and SbmA-Independent Bactericidal Activity against Clinical Pathogens. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 9590–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasi, A.; Bozzer, S.; Pacor, S.; de Pascale, L.; Morici, M.; Favero, L.; Spazzapan, M.; Pegoraro, S.; Bulla, R.; Wilson, D.N.; et al. The Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptide B7-005: Low Bacterial Resistance, Safe for Human Cells and Effective in Zebrafish Embryo Bacteraemia Model. Open Biol. 2024, 14, 240286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE Pathogens: Antimicrobial Resistance, Epidemiology, Clinical Impact and Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Tanwar, M.; Singh, T.P.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, P. An Escape from ESKAPE Pathogens: A Comprehensive Review on Current and Emerging Therapeutics against Antibiotic Resistance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasi, A.; Capolla, S.; Morici, M.; Bozzer, S.; Berger, M.; Pacor, S.; Pham, T.D.; Spurio, R.; Fabbretti, A.; Macor, P.; et al. Mechanistic Divergence and Differential Antibacterial Potency of the Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptide B7-005 Across ESKAPE+E Pathogens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2025, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Sola, R.; Mardirossian, M.; Beckert, B.; De Luna, L.S.; Prickett, D.; Tossi, A.; Wilson, D.N.; Scocchi, M. Characterization of Cetacean Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptides Displaying Activity against Eskape Pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, B.J.H.; Gruppen, H. Prediction of Molar Extinction Coefficients of Proteins and Peptides Using UV Absorption of the Constituent Amino Acids at 214 Nm To Enable Quantitative Reverse Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5445–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Ara, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Takai, Y.; Okumura, Y.; Baba, M.; Datsenko, K.A.; Tomita, M.; Wanner, B.L.; Mori, H. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 In-frame, Single-gene Knockout Mutants: The Keio Collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 2006.0008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, M.; Holm, M.; Rundlet, E.J.; Morici, M.; Koller, T.O.; Maviza, T.P.; Pogorevc, D.; Osterman, I.A.; Müller, R.; Blanchard, S.C.; et al. The Cyclic Octapeptide Antibiotic Argyrin B Inhibits Translation by Trapping EF-G on the Ribosome during Translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2114214119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardirossian, M.; Sola, R.; Degasperi, M.; Scocchi, M. Search for Shorter Portions of the Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptide Fragment Bac5(1–25) That Retain Antimicrobial Activity by Blocking Protein Synthesis. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; Chou, S.; Shan, A. Importance of Tryptophan in Transforming an Amphipathic Peptide into a Pseudomonas Aeruginosa-Targeted Antimicrobial Peptide. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupuleti, M.; Chalupka, A.; Mörgelin, M.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Tryptophan End-Tagging of Antimicrobial Peptides for Increased Potency against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2009, 1790, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.I.; Prenner, E.J.; Vogel, H.J. Tryptophan- and Arginine-Rich Antimicrobial Peptides: Structures and Mechanisms of Action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 1184–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Nazir, S.; Haque, M.N.u.; Maharjan, R.; Khan, F.-A.; Olleik, H.; Courvoisier-Dezord, E.; Maresca, M.; Shaheen, F. Synthesis of Second-Generation Analogs of Temporin-SHa Peptide Having Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial and Anticancer Effects. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Felix, L.; Basu, A.; Kollala, S.S.; Chhonker, Y.S.; Ganesan, N.; Murry, D.J.; Mylonakis, E. Design and Evaluation of Short Bovine Lactoferrin-Derived Antimicrobial Peptides against Multidrug-Resistant Enterococcus faecium. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Walt, M.; Möller, D.S.; van Wyk, R.J.; Ferguson, P.M.; Hind, C.K.; Clifford, M.; Do Carmo Silva, P.; Sutton, J.M.; Mason, A.J.; Bester, M.J.; et al. QSAR Reveals Decreased Lipophilicity of Polar Residues Determines the Selectivity of Antimicrobial Peptide Activity. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 26030–26049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Fa, K.; Liu, H.; Waigh, T.A.; McBain, A.; Lu, J.R. Hydrophobic Control of the Bioactivity and Cytotoxicity of de Novo-Designed Antimicrobial Peptides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34609–34620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roque-Borda, C.A.; Primo, L.M.D.G.; Franzyk, H.; Hansen, P.R.; Pavan, F.R. Recent Advances in the Development of Antimicrobial Peptides against ESKAPE Pathogens. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladokhin, A.S.; Selsted, M.E.; White, S.H. CD Spectra of Indolicidin Antimicrobial Peptides Suggest Turns, Not Polyproline Helix. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 12313–12319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Song, G.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Peptide | Sequence | Residues | % of Positive Charges | % Proline | GRAVY Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B7-005 | WRIRRRWPRLPRPRWR | 16 | 50 | 18.8 | −2.20 |
| B7-B6 | WRIRRRWPRLPRPRWRPLPFPR | 22 | 41 | 27.3 | −1.72 |
| B7-T6 | WRIRRRWPRLPRPRWRPRFPPP | 22 | 41 | 31.8 | −1.97 |
| B7-L6 | WRIRRRWPRLPRPRWRPWFPPR | 22 | 41 | 27.3 | −1.94 |
| B7-B11 | WRIRRRWPRLPRPRWRPLPFPRPGPRP | 27 | 37 | 33.3 | −1.76 |
| B7-T11 | WRIRRRWPRLPRPRWRPRFPPPFPIPR | 27 | 37 | 33.3 | −1.62 |
| B7-L11 | WRIRRRWPRLPRPRWRPWFPPRFPIPR | 27 | 37 | 29.6 | −1.59 |
| Bacterial Strain | MIC (μM) § | |||||||
| 005 # | B6 | T6 | L6 | B11 | T11 | L11 | ||
| E. coli | ATCC 25922 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| E. coli | BW 25113 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 |
| E. coli | BW 25113 ΔsbmA | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| E. faecium | ATCC 19434 | 32 | 8 | 16 | 4 | 16 | 4 | 4 |
| S. aureus | ATCC 25923 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 16 | 4 |
| K. pneumoniae | ATCC 700603 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| A. baumannii | ATCC 19606 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| P. aeruginosa | ATCC 27853 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 16 | 16 | 8 |
| E. cloacae | ATCC 13047 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Bacterial Strain | MBC (μM) | |||||||
| 005 | B6 | T6 | L6 | B11 | T11 | L11 | ||
| E. coli | ATCC 25922 | 2 | 2 | 0.5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| E. coli | BW 25113 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| E. coli | BW 25113 ΔsbmA | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| E. faecium | ATCC 19434 | >64 | >64 | >64 | 32 | >64 | 32 | 16 |
| S. aureus | ATCC 25923 | 16 | 16 | 32 | 8 | 32 | 16 | 8 |
| K. pneumoniae | ATCC 700603 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 4 |
| A. baumannii | ATCC 19606 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| P. aeruginosa | ATCC 27853 | 16 | 16 | 32 | 8 | 16 | 16 | 8 |
| E. cloacae | ATCC 13047 | 16 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Stasi, A.; de Pascale, L.; Morici, M.; Wilson, D.N.; Scocchi, M.; Mardirossian, M. Designing New Chimeric Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptides to Enhance Efficacy Toward the ESKAPE+E: Beyond Sequence Extension. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060776
Di Stasi A, de Pascale L, Morici M, Wilson DN, Scocchi M, Mardirossian M. Designing New Chimeric Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptides to Enhance Efficacy Toward the ESKAPE+E: Beyond Sequence Extension. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(6):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060776
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Stasi, Adriana, Luigi de Pascale, Martino Morici, Daniel N. Wilson, Marco Scocchi, and Mario Mardirossian. 2025. "Designing New Chimeric Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptides to Enhance Efficacy Toward the ESKAPE+E: Beyond Sequence Extension" Biomolecules 15, no. 6: 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060776
APA StyleDi Stasi, A., de Pascale, L., Morici, M., Wilson, D. N., Scocchi, M., & Mardirossian, M. (2025). Designing New Chimeric Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptides to Enhance Efficacy Toward the ESKAPE+E: Beyond Sequence Extension. Biomolecules, 15(6), 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060776








