Residue-Specific Structural and Dynamical Coupling of Protein and Hydration Water Revealed by Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Selection and System Setup
2.2. MD Simulations
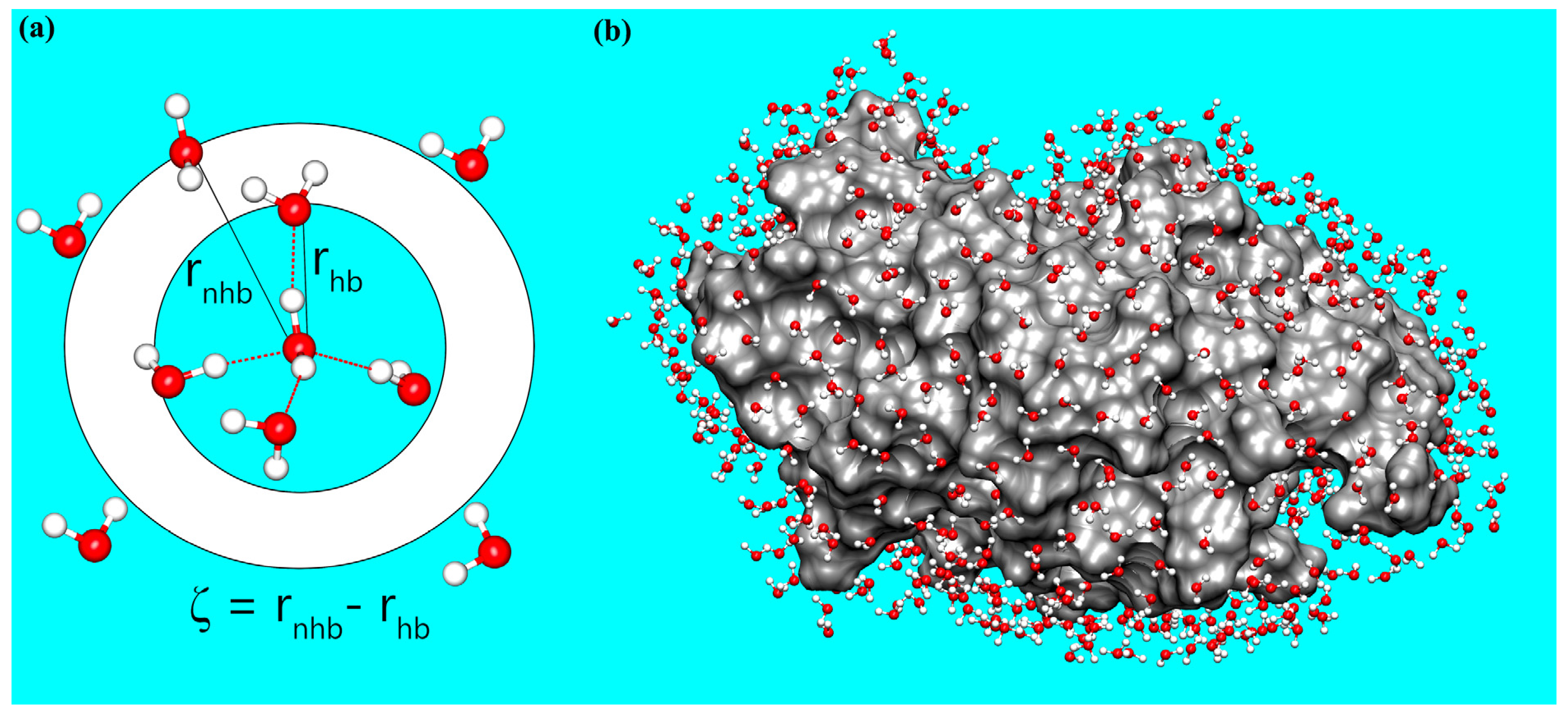
2.3. Calculating the Structural Order Parameter of Water
2.4. Calculation of Root-Mean-Square Fluctuation (RMSF)
2.5. Calculation of Solvent-Accessible Surface Area (SASA)
2.6. Estimating the Relaxation Time
2.7. Calculating the Water Structural Ordering Velocity
3. Results and Discussion
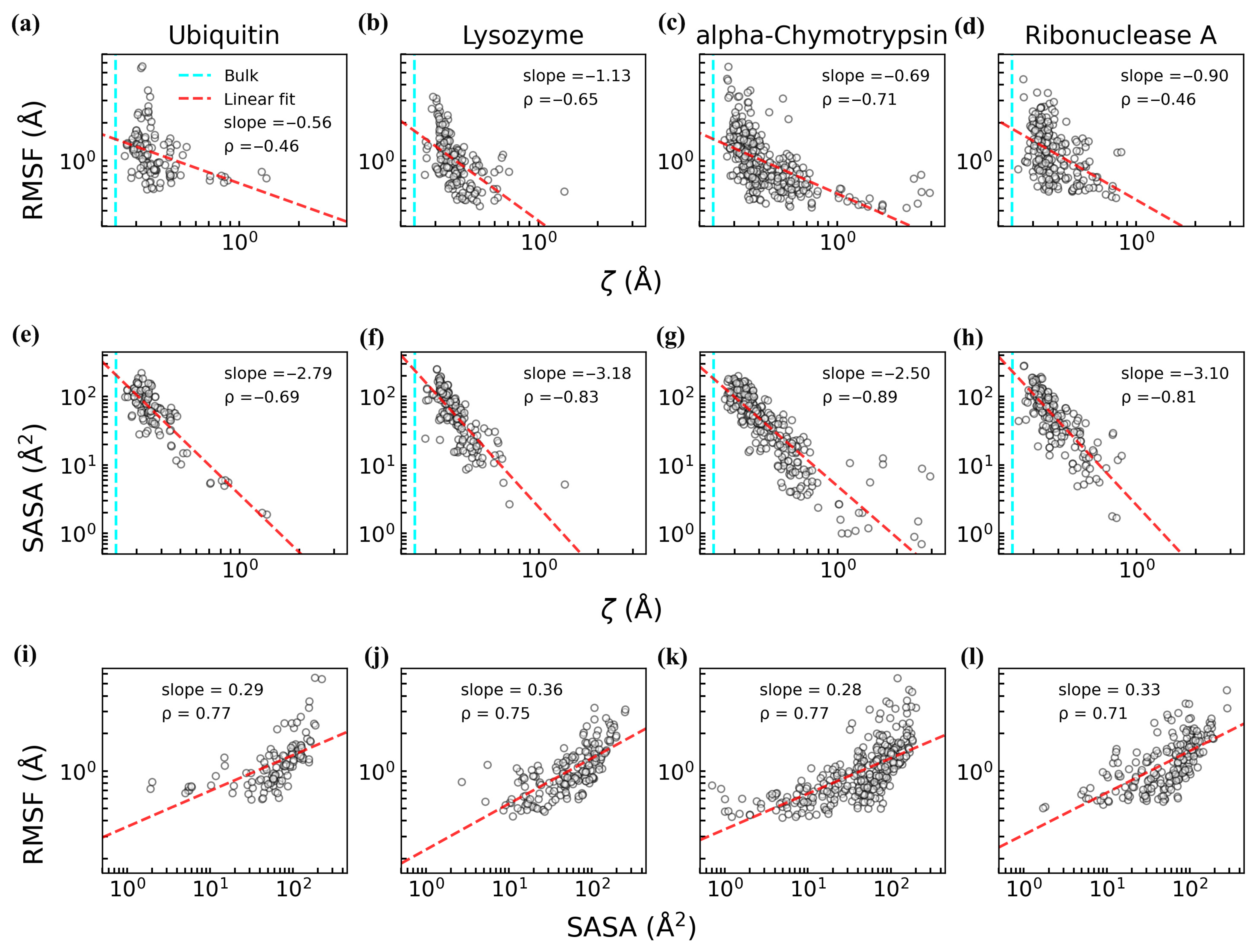
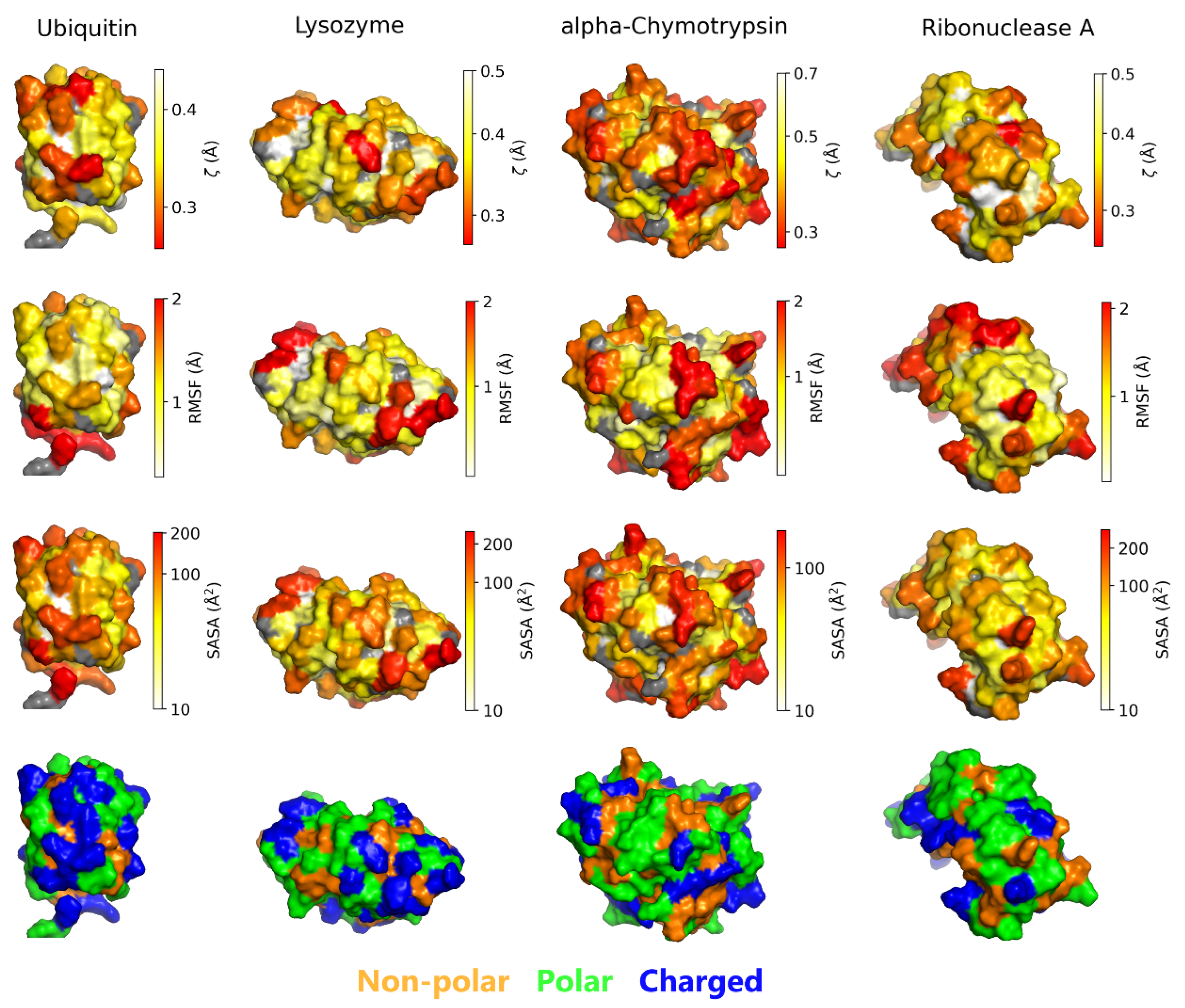
3.1. Residue-Specific Effects on Hydration Water Structure
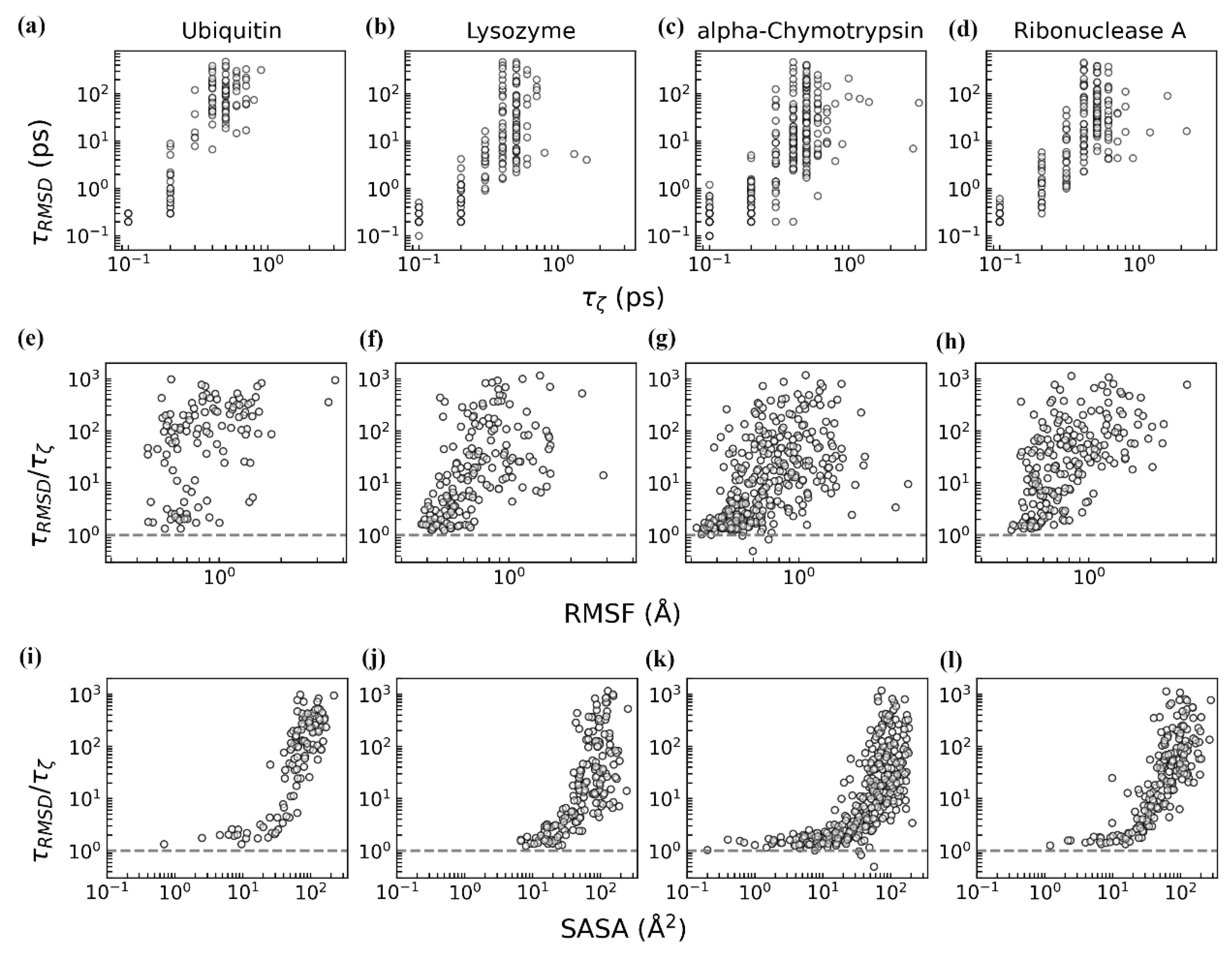
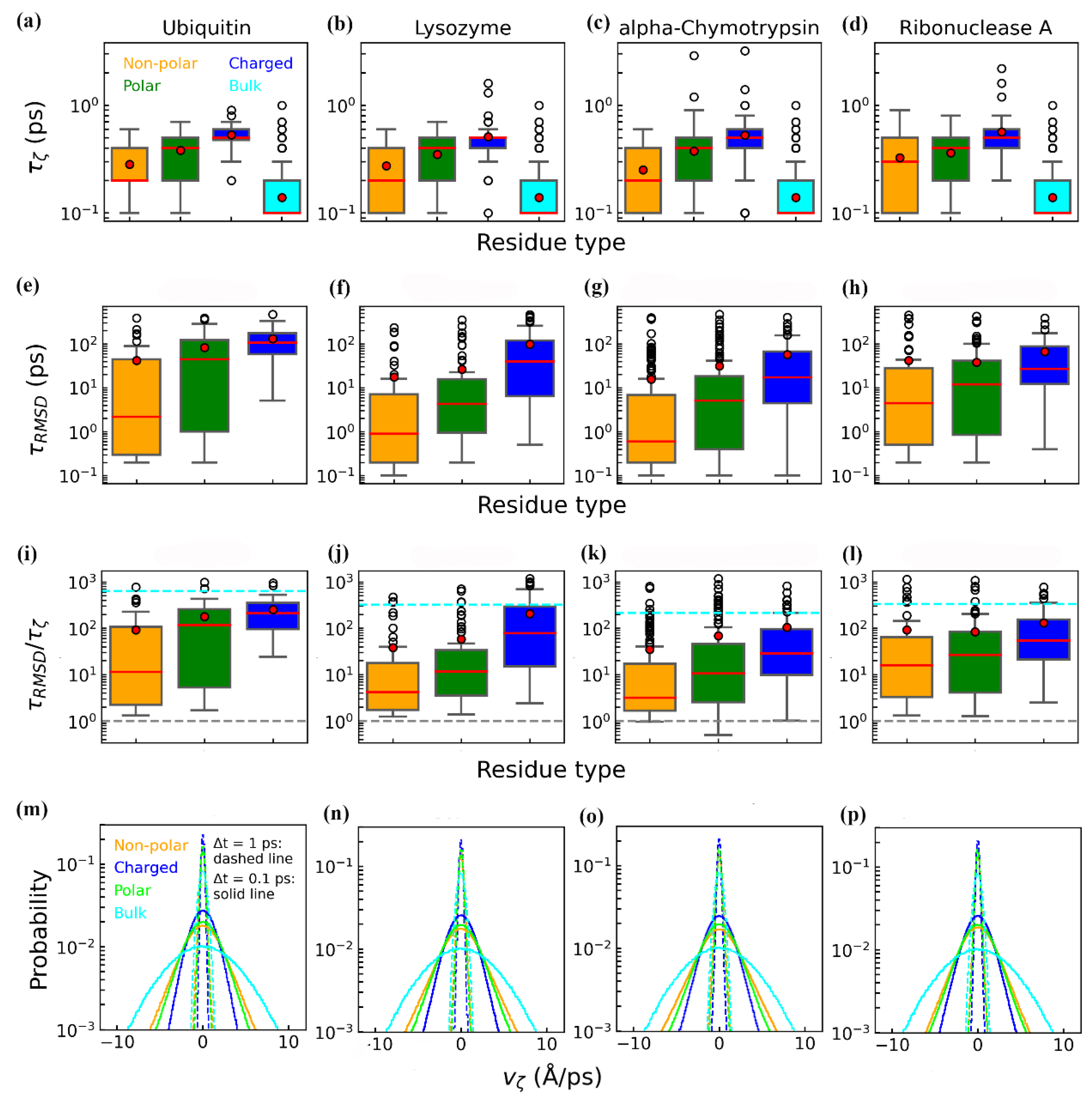
3.2. Dynamics of Protein–Water Relaxation
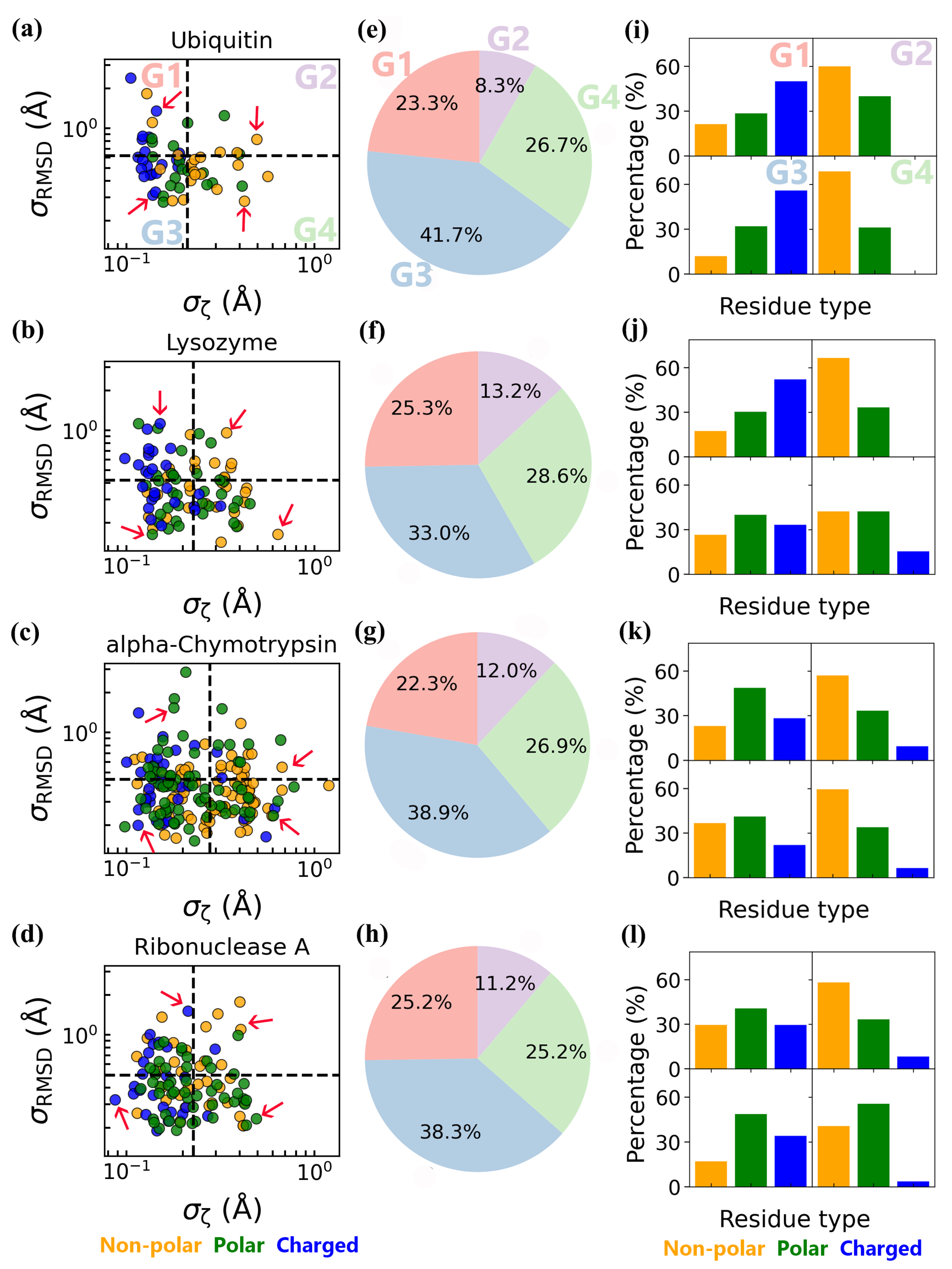
3.3. Coupled Protein–Water Fluctuations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Persson, F.; Söderhjelm, P.; Halle, B. The Geometry of Protein Hydration. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 215101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laage, D.; Elsaesser, T.; Hynes, J.T. Water Dynamics in the Hydration Shells of Biomolecules. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10694–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Y.; Onuchic, J.N. Water Mediation in Protein Folding and Molecular Recognition. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2006, 35, 389–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.S.; García, A.E.; Onuchic, J.N. Protein Folding Mediated by Solvation: Water Expulsion and Formation of the Hydrophobic Core Occur after the Structural Collapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, J.-E.; Onuchic, J.N.; Brooks, C.L. Probing the Folding Free Energy Landscape of the Src-SH3 Protein Domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16064–16068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfromm, T.; Vogel, M. On the Coupling of Protein and Water Dynamics in Confinement: Spatially Resolved Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 150, 245101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirò, G.; Fichou, Y.; Gallat, F.-X.; Wood, K.; Gabel, F.; Moulin, M.; Härtlein, M.; Heyden, M.; Colletier, J.-P.; Orecchini, A.; et al. Translational Diffusion of Hydration Water Correlates with Functional Motions in Folded and Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellissent-Funel, M.-C.; Hassanali, A.; Havenith, M.; Henchman, R.; Pohl, P.; Sterpone, F.; Van Der Spoel, D.; Xu, Y.; Garcia, A.E. Water Determines the Structure and Dynamics of Proteins. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7673–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattea, C.; Qvist, J.; Halle, B. Dynamics at the Protein-Water Interface from 17O Spin Relaxation in Deeply Supercooled Solutions. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, A.C.; Laage, D. Water Dynamics in Protein Hydration Shells: The Molecular Origins of the Dynamical Perturbation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 7715–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterpone, F.; Stirnemann, G.; Laage, D. Magnitude and Molecular Origin of Water Slowdown Next to a Protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4116–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboué-Dijon, E.; Laage, D. Comparative Study of Hydration Shell Dynamics around a Hyperactive Antifreeze Protein and around Ubiquitin. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 141, 22D529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallat, F.-X.; Laganowsky, A.; Wood, K.; Gabel, F.; van Eijck, L.; Wuttke, J.; Moulin, M.; Härtlein, M.; Eisenberg, D.; Colletier, J.-P.; et al. Dynamical Coupling of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Their Hydration Water: Comparison with Folded Soluble and Membrane Proteins. Biophys. J. 2012, 103, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi, S.; Roh, J.H.; Kisliuk, A.; Mamontov, E.; Tyagi, M.; Woodson, S.A.; Briber, R.M.; Sokolov, A.P. Dynamics of Biological Macromolecules: Not a Simple Slaving by Hydration Water. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilov, Y.; Leuchter, J.D.; Levy, Y. On the Coupling between the Dynamics of Protein and Water. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 8243–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Russo, J.; Tanaka, H. Common Microscopic Structural Origin for Water’s Thermodynamic and Dynamic Anomalies. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 224502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brini, E.; Fennell, C.J.; Fernandez-Serra, M.; Hribar-Lee, B.; Lukšič, M.; Dill, K.A. How Water’s Properties Are Encoded in Its Molecular Structure and Energies. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12385–12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, J.; Tanaka, H. Understanding Water’s Anomalies with Locally Favoured Structures. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errington, J.R.; Debenedetti, P.G. Relationship between Structural Order and the Anomalies of Liquid Water. Nature 2001, 409, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuszko, A.; Wojciechowski, M.; Bruździak, P.; Rakowska, P.W.; Stangret, J. Characteristics of Hydration Water around Hen Egg Lysozyme as the Protein Model in Aqueous Solution. FTIR Spectroscopy and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 15765–15773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, K.; Strazdaite, S.; DeVries, A.L.; Lotze, S.; Olijve, L.L.C.; Voets, I.K.; Bakker, H.J. Observation of Ice-like Water Layers at an Aqueous Protein Surface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17732–17736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accordino, S.R.; Malaspina, D.C.; Rodriguez Fris, J.A.; Alarcón, L.M.; Appignanesi, G.A. Temperature Dependence of the Structure of Protein Hydration Water and the Liquid-Liquid Transition. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 031503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camisasca, G.; Iorio, A.; De Marzio, M.; Gallo, P. Structure and Slow Dynamics of Protein Hydration Water. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R. The Structural Order of Protein Hydration Water. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2022, 74, 095602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, D.; Laloni, A.; Filabozzi, A.; Heyden, M. Pressure Effects on Collective Density Fluctuations in Water and Protein Solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11410–11415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchionna, S.; Briganti, G.; Londei, P.; Cammarano, P. Water Induced Effects on the Thermal Response of a Protein. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 158101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahanayake, J.N.; Mitchell-Koch, K.R. Entropy Connects Water Structure and Dynamics in Protein Hydration Layer. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 14765–14777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, M.; Yousif, R.; Berkowicz, S.; Das, S.; Schlesinger, D.; Perakis, F. Wide-Angle X-Ray Scattering and Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Supercooled Protein Hydration Water. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 18308–18313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzel, F.; Smith, J.C. Is the First Hydration Shell of Lysozyme of Higher Density than Bulk Water? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5378–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratani, E.; Sasai, M. Molecular Scale Precursor of the Liquid–Liquid Phase Transition of Water. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 108, 3264–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, M.J.; Poole, P.H. Mixturelike Behavior Near a Liquid-Liquid Phase Transition in Simulations of Supercooled Water. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 115706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; LaCour, R.A.; Qian, N.; Heindel, J.P.; Lang, X.; Zhao, R.; Head-Gordon, T.; Min, W. Water Structure and Electric Fields at the Interface of Oil Droplets. Nature 2025, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Tanaka, H. Impact of Local Symmetry Breaking on the Physical Properties of Tetrahedral Liquids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1980–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y. Quantitative Insights into Tightly and Loosely Bound Water in Hydration Shells of Amino Acids. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 10080–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yu, P.; Dong, T.; Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, J. Chasing Weakly-Bound Biological Water in Aqueous Environment near the Peptide Backbone by Ultrafast 2D Infrared Spectroscopy. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, M.; Born, B.; Heyden, M.; Tworowski, D.; Fields, G.B.; Sagi, I.; Havenith, M. Correlated Structural Kinetics and Retarded Solvent Dynamics at the Metalloprotease Active Site. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Wang, M.; Ni, Z.; Pei, R.; Shi, F.; Ye, S. Intermolecular Protein–Water Coupling Impedes the Coupling Between the Amide A and Amide I Mode in Interfacial Proteins. Langmuir 2024, 40, 6587–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, P.; Macro, N.; Kang, M.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, D. Ultrafast Dynamics of Water–Protein Coupled Motions around the Surface of Eye Crystallin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3997–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Zheng, L.; Tang, Q.; Long, L.; Yamada, T.; Tyagi, M.; Sakai, V.G.; O’Neill, H.; et al. Dynamic Entity Formed by Protein and Its Hydration Water. Phys. Rev. Res. 2024, 6, 033316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K.M.; Singh, A.K.; Bikash, C.R.; Wei, J.; Tal-Gan, Y.; Vinh, N.Q.; Leitner, D.M. The Origin and Impact of Bound Water around Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Biophys. J. 2022, 121, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.C.; Khatua, P.; Bansal, N.; Sengupta, N.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Microscopic Hydration Properties of the Aβ1–42 Peptide Monomer and the Globular Protein Ubiquitin: A Comparative Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 11591–11604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vural, D.; Shrestha, U.R.; Petridis, L.; Smith, J.C. Water Molecule Ordering on the Surface of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein. Biophys. J. 2023, 122, 4326–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay-Kumar, S.; Bugg, C.E.; Cook, W.J. Structure of Ubiquitin Refined at 1.8Åresolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1987, 194, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dauter, M.; Alkire, R.; Joachimiak, A.; Dauter, Z. Triclinic Lysozyme at 0.65Å Resolution. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2007, 63, 1254–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeto, A.; Galunsky, B.; Kasche, V.; Wilson, K.S.; Lamzin, V.S. High Resolution Structure of Bovine Alpha-Chymotrypsin. PDB 2005, Entry 1YPH. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1YPH (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Wlodawer, A.; Svensson, L.A.; Sjoelin, L.; Gilliland, G.L. Structure of Phosphate-Free Ribonuclease A Refined at 1.26 .ANG. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 2705–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döpke, M.F.; Moultos, O.A.; Hartkamp, R. On the Transferability of Ion Parameters to the TIP4P/2005 Water Model Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 024501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical Sampling through Velocity Rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic Transitions in Single Crystals: A New Molecular Dynamics Method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A Linear Constraint Solver for Molecular Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle Mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) Method for Ewald Sums in Large Systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, P.-L.; Hardwick, A.J. A New Order Parameter for Tetrahedral Configurations. Mol. Phys. 1998, 93, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Tong, H.; Shi, R.; Russo, J. Revealing Key Structural Features Hidden in Liquids and Glasses. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2019, 1, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Tanaka, H. Microscopic Structural Descriptor of Liquid Water. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 124503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzar, A.; Chandler, D. Hydrogen-Bond Kinetics in Liquid Water. Nature 1996, 379, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Harder, E.; Berne, B.J. Hydrogen-Bond Dynamics in the Air−Water Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 2949–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaravadivelu Devarajan, D.; Wang, J.; Szała-Mendyk, B.; Rekhi, S.; Nikoubashman, A.; Kim, Y.C.; Mittal, J. Sequence-Dependent Material Properties of Biomolecular Condensates and Their Relation to Dilute Phase Conformations. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comez, L.; Lupi, L.; Morresi, A.; Paolantoni, M.; Sassi, P.; Fioretto, D. More Is Different: Experimental Results on the Effect of Biomolecules on the Dynamics of Hydration Water. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzitutti, F.; Marchi, M.; Sterpone, F.; Rossky, P.J. How Protein Surfaces Induce Anomalous Dynamics of Hydration Water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 7584–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.; Sun, S.; Fichou, Y.; Dahlquist, F.W.; Heyden, M.; Han, S. Spatially Heterogeneous Surface Water Diffusivity around Structured Protein Surfaces at Equilibrium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17890–17901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Hassanali, A.A.; Kao, Y.-T.; Zhong, D.; Singer, S.J. Hydration Dynamics and Time Scales of Coupled Water−Protein Fluctuations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3376–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlessinger, A.; Rost, B. Protein Flexibility and Rigidity Predicted from Sequence. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005, 61, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruvinsky, A.M.; Vakser, I.A. Sequence Composition and Environment Effects on Residue Fluctuations in Protein Structures. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 133, 155101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Collanton, R.P.; Monroe, J.I.; Casey, T.M.; Shell, M.S.; Han, S.; Scott, S.L. Evidence for Entropically Controlled Interfacial Hydration in Mesoporous Organosilicas. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, J.; Pei, R.; Ye, S.; Luo, Y. Ordered Water Layer on the Macroscopically Hydrophobic Fluorinated Polymer Surface and Its Ultrafast Vibrational Dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 13074–13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Lande, A.; Babcock, N.S.; Řezáč, J.; Sanders, B.C.; Salahub, D.R. Surface Residues Dynamically Organize Water Bridges to Enhance Electron Transfer between Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11799–11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Tobias, D.J. Role of Protein-Water Hydrogen Bond Dynamics in the Protein Dynamical Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 138101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovanov, A.P.; Hautbergue, G.M.; Wilson, S.A.; Lian, L.-Y. A Simple Method for Improving Protein Solubility and Long-Term Stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8933–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, R.M.; Shende, V.R.; Motl, N.; Pace, C.N.; Scholtz, J.M. Toward a Molecular Understanding of Protein Solubility: Increased Negative Surface Charge Correlates with Increased Solubility. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Jiménez-Ángeles, F.; Nguyen, T.D.; Olvera de la Cruz, M. Water Follows Polar and Nonpolar Protein Surface Domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 19274–19281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaieda, S.; Halle, B. Internal Water and Microsecond Dynamics in Myoglobin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 14676–14687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhong, D. Dynamics and Mechanism of Ultrafast Water–Protein Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8424–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauenfelder, H.; Chen, G.; Berendzen, J.; Fenimore, P.W.; Jansson, H.; McMahon, B.H.; Stroe, I.R.; Swenson, J.; Young, R.D. A Unified Model of Protein Dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5129–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, F.; Söderhjelm, P.; Halle, B. How Proteins Modify Water Dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 215103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.M.; Pezzotti, S.; Ahlers, J.; Rüttermann, M.; Levin, M.; Goldenzweig, A.; Peleg, Y.; Fleishman, S.J.; Sagi, I.; Havenith, M. Local Mutations Can Serve as a Game Changer for Global Protein Solvent Interaction. JACS Au 2021, 1, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duboué-Dijon, E.; Laage, D. Characterization of the Local Structure in Liquid Water by Various Order Parameters. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 8406–8418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.; Shi, L.; Zhao, Z.; Min, W. Probing the Structure of Water in Individual Living Cells. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impact and Structure of Water in Aqueous Octanol Mixtures: Hz-GHz Dielectric Relaxation Measurements and Computer Simulations. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 439, 114600. [CrossRef]
- Baksi, A.; Biswas, R. Does Confinement Modify Preferential Solvation and H-Bond Fluctuation Dynamics? A Molecular Level Investigation through Simulations of a Bulk and Confined Three-Component Mixture. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, P. Water Is an Active Matrix of Life for Cell and Molecular Biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13327–13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Gao, J.; Chu, X. Residue-Specific Structural and Dynamical Coupling of Protein and Hydration Water Revealed by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050660
Wang S, Gao J, Chu X. Residue-Specific Structural and Dynamical Coupling of Protein and Hydration Water Revealed by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(5):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050660
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuai, Jun Gao, and Xiakun Chu. 2025. "Residue-Specific Structural and Dynamical Coupling of Protein and Hydration Water Revealed by Molecular Dynamics Simulations" Biomolecules 15, no. 5: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050660
APA StyleWang, S., Gao, J., & Chu, X. (2025). Residue-Specific Structural and Dynamical Coupling of Protein and Hydration Water Revealed by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Biomolecules, 15(5), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050660




