The Role of Klotho in Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases: Mechanisms and Research Progress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview and Basic Functions of Klotho
3. The Core Functional Network of Klotho
3.1. Aging Regulatory Mechanisms
3.1.1. Regulation of Telomerase Activity
3.1.2. DNA Damage Repair Pathways
3.2. Regulation of Oxidative Stress
3.2.1. Nrf2/ARE Signaling Axis
3.2.2. Mitochondrial Function Protection
3.3. Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
3.4. Inflammatory Regulation Network
3.5. Regulation of the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
3.6. Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling Pathway
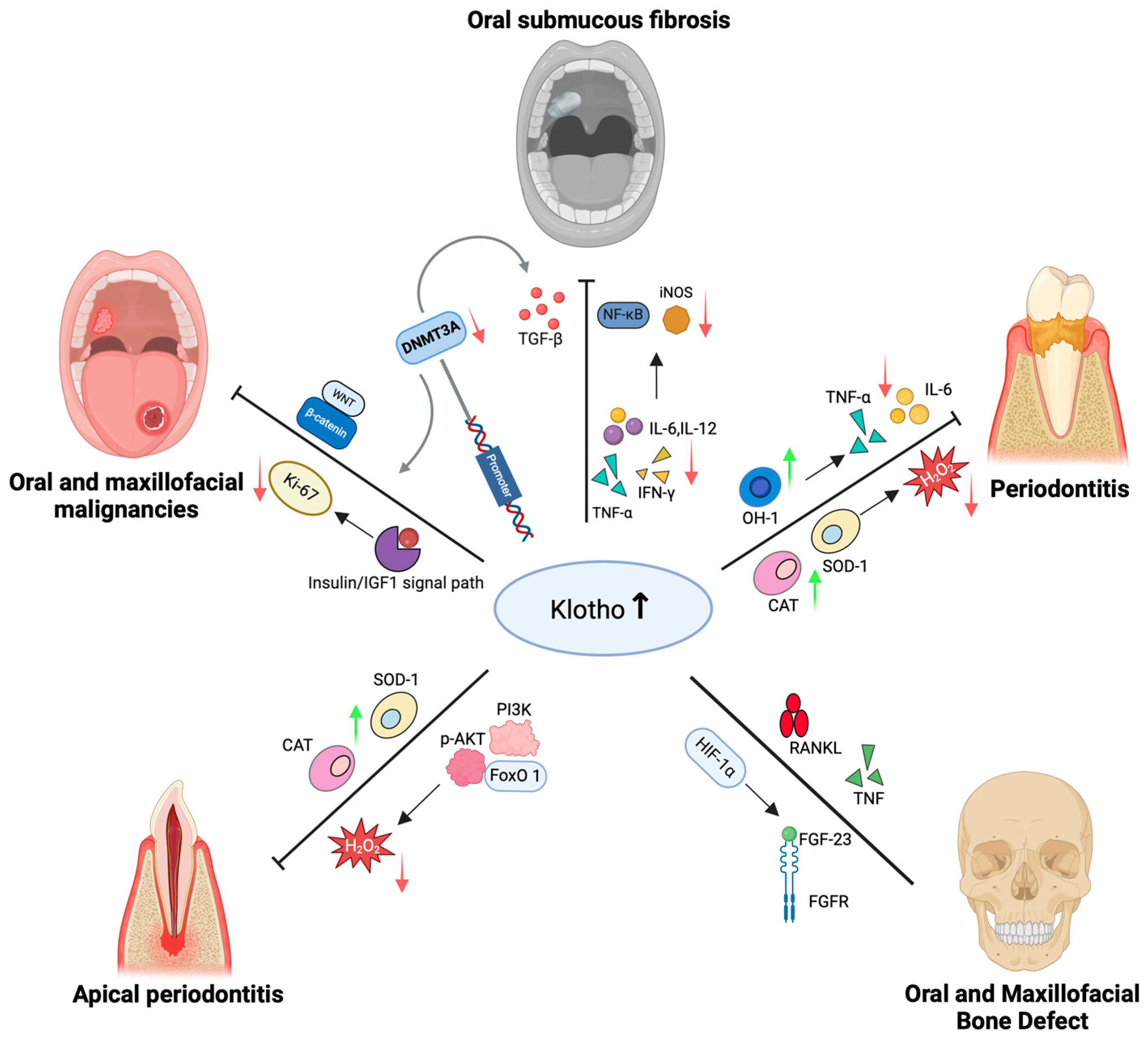
4. Mechanisms of Klotho in Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases
4.1. Role of Klotho in Periodontitis
4.2. Role of Klotho in Periapical Disease
4.3. Role of Klotho in Oral Submucous Fibrosis
4.4. Role of Klotho in Oral and Maxillofacial Malignancies
4.4.1. Role of Klotho in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
4.4.2. Role of Klotho in Salivary Gland Malignant Tumors
4.5. Role of Klotho in Oral and Maxillofacial Bone Defect
5. Discussion
- (1)
- In-depth exploration of Klotho’s interaction with signaling pathways in various oral and maxillofacial diseases.
- (2)
- Evaluation of the clinical feasibility of Klotho as a diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for oral diseases.
- (3)
- Development of Klotho-based therapeutic strategies.
- (4)
- Validation of Klotho’s role in animal models and its clinical translational potential.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Idrees, M.; Kumar, V.; Khan, A.M.; Joo, M.-D.; Lee, K.-W.; Sohn, S.-H.; Kong, I.-K. Cycloastragenol Activation of Telomerase Improves β-Klotho Protein Level and Attenuates Age-Related Malfunctioning in Ovarian Tissues. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 209, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Q.; Chen, H.; Ou, Q.; Yang, S.; Peng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yu, L.; Cheng, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y. Klotho Enhances Bone Regenerative Function of hPDLSCs via Modulating Immunoregulatory Function and Cell Autophagy. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, A.; Xue, M.; Al-Motawa, M.; Thornalley, P.J.; Rabbani, N. Glycolytic Overload-Driven Dysfunction of Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts in High Glucose Concentration, Corrected by Glyoxalase 1 Inducer. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Ghosh, S.; Gupta, S.; Sakhuja, P. Effect of Curcumin on the Expression of P53, Transforming Growth Factor-β, and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Oral Submucous Fibrosis: A Pilot Study. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2017, 8, e12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chang, H.-H.; Chan, C.-P.; Yeh, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-L.; Cheng, R.-H.; Hahn, L.-J.; Jeng, J.-H. Areca Nut Components Affect COX-2, Cyclin B1/cdc25C and Keratin Expression, PGE2 Production in Keratinocyte Is Related to Reactive Oxygen Species, CYP1A1, Src, EGFR and Ras Signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuro-o, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Aizawa, H.; Kawaguchi, H.; Suga, T.; Utsugi, T.; Ohyama, Y.; Kurabayashi, M.; Kaname, T.; Kume, E.; et al. Mutation of the Mouse Klotho Gene Leads to a Syndrome Resembling Ageing. Nature 1997, 390, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Sato, T.; Densmore, M.; Saito, H.; Schüler, C.; Erben, R.G.; Lanske, B. Deletion of PTH Rescues Skeletal Abnormalities and High Osteopontin Levels in Klotho−/− Mice. PLOS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, C.; Aboodi, G.M.; Lakschevitz, F.S.; Sun, C.; Goldberg, M.B.; Glogauer, M. Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 Down-Regulation in Oral Neutrophils Is Associated with Periodontal Oxidative Damage and Severe Chronic Periodontitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, S.; Gong, H.; Zhang, B.-K.; Yan, M. Dissecting the Crosstalk Between Nrf2 and NF-κB Response Pathways in Drug-Induced Toxicity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol 2022, 9, 809952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Z. The Protective Mechanism of Klotho Gene-Modified Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Acute Kidney Injury Induced by Rhabdomyolysis. Regen. Ther. 2021, 18, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costenbader, K.H.; Prescott, J.; Zee, R.Y.; De Vivo, I. Immunosenescence and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Does Telomere Shortening Predict Impending Disease? Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, M.; Sun, Z. Klotho Deficiency Accelerates Stem Cells Aging by Impairing Telomerase Activity. J. Gerontol. A 2019, 74, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distefano, A.; Orlando, L.; Partsinevelos, K.; Longhitano, L.; Emma, R.; Caruso, M.; Vicario, N.; Denaro, S.; Sun, A.; Giordano, A.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of Cigarette Smoke and a Heated Tobacco Product on Microglial Toxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, S.; Sun, J.; Horikoshi, Y.; Kamimura, Y.; Ike, T.; Fujino, S.; Kinugasa, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Nakashima, A.; Masaki, T.; et al. Klotho Protects Chromosomal DNA from Radiation-Induced Damage. J. Biochem. 2023, 173, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, L.; Wei, A.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Cao, W. Inhibition of DNA Methyltransferase Aberrations Reinstates Antioxidant Aging Suppressors and Ameliorates Renal Aging. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, X.; Fu, C.; Wu, X.; Peng, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y. Recombinant Klotho Protects Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells by Regulating Mitochondrial Function and the Antioxidant System during H2O2 -Induced Oxidative Stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9261565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Guo, H.; Meng, S.; Zhu, B.; Fang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yao, X.; et al. Klotho Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy by Activating Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Podocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 534, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarles, L.D. FGF-23 and α-Klotho Co-Dependent and Independent Functions. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2019, 28, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltese, G.; Koufakis, T.; Kotsa, K.; Karalliedde, J. Can Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors ‘Spin the Thread of Life’? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Typiak, M.; Piwkowska, A. Antiinflammatory Actions of Klotho: Implications for Therapy of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Huang, J.; Luo, C.; Ye, H.; Ling, X.; Wu, Q.; Shen, W.; Zhou, L. Klotho Retards Renal Fibrosis through Targeting Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Cellular Senescence in Renal Tubular Cells. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Z.; Landry, T.; Li, P.; Bunner, W.; Laing, B.T.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, H. Administration of Alpha Klotho Reduces Liver and Adipose Lipid Accumulation in Obese Mice. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosu, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Clark, J.D.; Pastor, J.V.; Nandi, A.; Gurnani, P.; McGuinness, O.P.; Chikuda, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kawaguchi, H.; et al. Suppression of Aging in Mice by the Hormone Klotho. Science 2005, 309, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Jing, W.; Si, Y.; Feng, X.; Tai, B.; Hu, D.; Lin, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Zheng, S.; et al. The Prevalence and Severity of Periodontal Disease in Mainland China: Data from the Fourth National Oral Health Survey (2015–2016). J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, V.; Garrido, M.; Rryes, A.; Fernandez, C.; Diaz, C.; Torres, V.A.; Gonzalez, P.A.; Caceres, M. Aging Envisage Imbalance of the Periodontium: A Keystone in Oral Disease and Systemic Health. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1044334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sczepanik, F.S.C.; Grossi, M.L.; Casati, M.; Goldberg, M.; Glogauer, M.; Fine, N.; Tenenbaum, H.C. Periodontitis Is an Inflammatory Disease of Oxidative Stress: We Should Treat It That Way. Periodontology 2000 2020, 84, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.J.; Nam, B.Y.; Wu, M.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Kang, S.; Park, J.T.; Yoo, T.H.; Kang, S.W.; Han, S.H. Klotho Plays a Protective Role against Glomerular Hypertrophy in a Cell Cycle-Dependent Manner in Diabetic Nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 315, F791–F805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Jiao, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, W.; Wu, S.; Li, C. Photothermal Therapy with Regulated Nrf2/NF-κB Signaling Pathway for Treating Bacteria-Induced Periodontitis. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 9, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xie, H.; Liu, Q.; Ma, F.; Wu, H. Klotho Inhibits H2O2-induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells by Regulating UCP2 Expression. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 48, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tossetta, G.; Fantone, S.; Togni, L.; Santarelli, A.; Olivieri, F.; Marzioni, D.; Rippo, M.R. Modulation of NRF2/KEAP1 Signaling by Phytotherapeutics in Periodontitis. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavoni, V.; Emanuelli, M.; Milanese, G.; Galosi, A.B.; Pompei, V.; Salvolini, E.; Campagna, R. Nrf2 Signaling in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Potential Candidate for the Development of Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibúrcio-Machado, C.S.; Michelon, C.; Zanatta, F.B.; Gomes, M.S.; Marin, J.A.; Bier, C.A. The Global Prevalence of Apical Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. Endod. J. 2021, 54, 712–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Tang, T.; Wu, Y. The Roles of Stress-induced Premature Senescence and Akt/FOXO1 Signaling in Periapical Lesions. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 2463–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Dong, H.H. FoxO Integration of Insulin Signaling with Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 233, R67–R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morii, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Doi, S.; Irifuku, T.; Sasaki, K.; Doi, T.; Nakashima, A.; Arihiro, K.; Masaki, T. microRNA-200c Regulates KLOTHO Expression in Human Kidney Cells under Oxidative Stress. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Horst, A.; Burgering, B.M.T. Stressing the Role of FoxO Proteins in Lifespan and Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 8, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Periodontitis Aggravated Pancreatic Β-cell Dysfunction in Diabetic Mice through Interleukin-12 Regulation on Klotho. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahan, K.; Sheikh, F.G.; Liu, X.; Hilger, S.; McKinney, M.; Petro, T.M. Induction of Nitric-Oxide Synthase and Activation of NF-kappaB by Interleukin-12 P40 in Microglial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7899–7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Mou, L.; Yang, F.; Tu, H.; Lin, W. Curcumin Attenuates Cyclosporine A-induced Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting Hypermethylation of the Klotho Promoter. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: Sources, Methods and Major Patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braakhuis, B.J.M.; Leemans, C.R.; Visser, O. Incidence and Survival Trends of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Netherlands between 1989 and 2011. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, J.-L. Current Clinical Outcomes Demand New Treatment Options for SCCHN. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, vi7–vi12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, Y. Klotho gene expression and its methylation level are correlated with LC3 and NSUN2 gene expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Med. Univ. Sci. Technol. Huazhong 2020, 49, 255–259. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y. Klotho Induces Cells Apoptosis via Inhibition of the Wnt/β-Cantenin Pathway in Human Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells; Nanchang University: Nanchang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Zhan, J. Klotho Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Cancers. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2013, 19, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wu, J. Klotho Inhibits Growth and Promotes Apoptosis in Human Lung Cancer Cell Line A549. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, B.R.; Uehara, O.; Matsuoka, H.; Takai, R.; Harada, F.; Utsunomiya, M.; Chujo, T.; Morikawa, T.; Shakya, M.; Yoshida, K.; et al. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Klotho and DNA Methyltransferase 3a in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2017, 50, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seta, R.; Mascitti, M.; Campagna, R.; Sartini, D.; Fumarola, S.; Santarelli, A.; Giuliani, M.; Cecati, M.; Muzio, L.L.; Emanuelli, M. Overexpression of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase in HSC-2 OSCC Cell Line: Effect on Apoptosis and Cell Proliferation. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wen, H.; Yang, D.; Ye, M.; Peng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L. Expression and significance of DDR1 in salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Shanghai J. Stomatol. 2016, 25, 322–326. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Liu, B.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; An, F. Expression and Clinical Significance of Tumor-Associated Proteins in Salivary Gland Malignancies; The First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University: Zhangjiakou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aviel-Ronen, S.; Rubinek, T.; Zadok, O.; Vituri, A.; Avivi, C.; Wolf, I.; Barshack, I. Klotho Expression in Cervical Cancer: Differential Expression in Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, I.; Levanon-Cohen, S.; Bose, S.; Ligumsky, H.; Sredni, B.; Kanety, H.; Kuro-o, M.; Karlan, B.; Kaufman, B.; Koeffler, H.P.; et al. Klotho: A Tumor Suppressor and a Modulator of the IGF-1 and FGF Pathways in Human Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 7094–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Mi, Y.; Gong, Q.; Zhang, P.; Meng, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, Y. Novel 3D Printed TPMS Scaffolds: Microstructure, Characteristics and Applications in Bone Regeneration. J. Tissue Eng. 2024, 15, 20417314241263689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Cui, C.; Rosen, C.J.; Sato, T.; Xu, R.; Li, P.; Wei, X.; Bi, R.; Yuan, Q.; Zhou, C. Klotho in Osx+-Mesenchymal Progenitors Exerts Pro-Osteogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects during Mandibular Alveolar Bone Formation and Repair. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2022, 7, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yook, J.-I.; Toan, N.K.; Seo, Y.-S.; Yu, S.-J.; Ahn, S.-G. Dysosteogenesis in the Mandibular Bone of SAMP1/Klotho-Deficient Mice. Korean J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2020, 44, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Bao, D.; Yan, F.; Chen, B. Correlation between Serum α-Klotho Levels and Different Stages of Periodontitis. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toan, N.K.; Tai, N.C.; Kim, S.; Ahn, S. Soluble Klotho Regulates Bone Differentiation by Upregulating Expression of the Transcription Factor EGR-1. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaba, H.; Kaludjerovic, J.; Hu, D.Z.; Nagano, K.; Amano, K.; Ide, N.; Sato, T.; Densmore, M.J.; Hanai, J.; Olauson, H.; et al. Klotho Expression in Osteocytes Regulates Bone Metabolism and Controls Bone Formation. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.K.; Roschger, P.; Zeitz, U.; Klaushofer, K.; Andrukhova, O.; Erben, R.G. FGF23 Regulates Bone Mineralization in a 1,25(OH)2 D3 and Klotho-Independent Manner. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portales-Castillo, I.; Simic, P. PTH, FGF-23, Klotho and Vitamin D as Regulators of Calcium and Phosphorus: Genetics, Epigenetics and Beyond. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 992666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Fan, Y. Distinct Role of Klotho in Long Bone and Craniofacial Bone: Skeletal Development, Repair and Regeneration. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Dou, C.; Lu, Y.; Duan, L.; Tan, J.; Li, J.; Kang, F.; Dong, S.; Bai, Y.; Xu, J. Klotho Upregulates the Interaction between RANK and TRAF6 to Facilitate RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis via the NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.L.; Beyerstedt, S.; Rangel, É.B. Klotho and Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Review on Cell and Gene Therapy for Chronic Kidney Disease and Acute Kidney Disease. Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disease | Targets | Results | Models | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peridontitis | Nrf2/HO-1 | enhance anti- inflammation effects | mouse peritoneal macrophages cells, Sprague−Dawley rats | [27,28] |
| SOD-1 | enhance anti- inflammation effects | mouse peritoneal macrophages cells, Sprague−Dawley rats | [27] | |
| CAT | enhance anti- inflammation effects | mouse peritoneal macrophages cells, Sprague−Dawley rats | [27] | |
| NQO1 | enhance anti- inflammation effects | mouse peritoneal macrophages cells, Sprague−Dawley rats | [27] | |
| TNF-α, IL-6 | alleviate inflammatory response | macrophage cells | [27] | |
| NF-κB pathway | attenuate pro-inflammatory mediator release | macrophage cells | [27] | |
| PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 | alleviate H2O2-induced oxidative stress | human periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs) | [15,28] | |
| Bcl-2 | enhance anti- apoptotic effect | human periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs) | [15,28] | |
| Bax, Caspase-3 | enhance anti-apoptotic effect, attenuate H2O2-Induced apoptosis | human periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs) | [15,28] | |
| UCP2 | preserve mitochondrial function and reduce generation of ROS | human periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs) | [28] |
| Disease | Targets | Results | Models | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periapical Disease | PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 | inhibit H2O2-induced cellular senescence and nuclear translocation | human periodontal ligament cells (hPDLCs) | [30,31,33] |
| CAT, SOD | inhibit oxidative stress | human renal proximal tubular epithelium (HK-2) cells | [32] |
| Disease | Targets | Results | Models | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSF) | IL-6, IL-12 | alleviate inflammatory response | C57BL/6-db/db, inbred C57BL/ 6 mice | [34,35] |
| iNOS, NF-κB | alleviate inflammatory response | mouse microglia and astrocytes, mouse macrophages | [35] | |
| Nrf2 | attenuated HG- induced oxidative stress and apoptosis | mouse podocytes, C57BLKS/J-LepR (db/db) mice and db/m mice | [16] | |
| SOD2, NQO1, HO-1 | attenuated HG- induced oxidative stress and apoptosis | mouse podocytes, C57BLKS/J-LepR (db/db) mice and db/m mice | [16] | |
| CpG methylation | suppress TGF-β signaling | HK-2 human proximal tubule epithelial cell, C57BL/6 mice | [36] |
| Disease | Targets | Results | Models | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Wnt/β-catenin pathway | promote the expression of apoptosis- associated proteins | mouse peritoneal macrophages cells, Sprague- Dawley rats | [41] |
| DNA methyltransferases (DNMT)3a | downregulate gene expression of hypermethylation of the promoter region | mouse peritoneal macrophages cells, Sprague- Dawley rats | [40,44] | |
| Salivary Gland Malignant Tumors | insulin/IGF-1 pathway | inhibit tumor cell proliferation | MCF-7 breast cancer cells, cervical cancer cells | [47,48] |
| Ki-67 | inhibit tumor cell proliferation and invasive potential | MCF-7 breast cancer cells, cervical cancer cells | [46,48] |
| Disease | Targets | Results | Models | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral and Maxillofacial Bone Defect | TNF | alleviate inflammatory response | Klothofl/fl mice and Klotho−/− mice | [50] |
| RANKL | promote osteogenesis, alleviate inflammatory response | Klothofl/fl mice and Klotho−/− mice | [50] | |
| EGR-1 | promote osteogenic differentiation | HEK293 and MC3T3 cells | [52] | |
| FGFR1/ERK | alleviate inflammatory response | MC3T3-E1 cells, Dmp1-Cre:Klothofl/fl; tdTomatofl/+ mice Dmp1-Cre:Klotho−/−; tdTomatofl/ + mice | [53] | |
| Wnt/β-catenin pathway | alleviate inflammatory response | MC3T3-E1 cells, Dmp1-Cre:Klothofl/fl; tdTomatofl/+ mice Dmp1-Cre:Klotho−/−; tdTomatofl/ + mice | [53] | |
| FGF | promote osteogenesis | Klothofl/fl mice and Klotho−/− mice | [50,55,56] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Wang, B.; Li, J. The Role of Klotho in Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases: Mechanisms and Research Progress. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050624
Lin S, Wang B, Li J. The Role of Klotho in Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases: Mechanisms and Research Progress. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(5):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050624
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shiqi, Bozhao Wang, and Jian Li. 2025. "The Role of Klotho in Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases: Mechanisms and Research Progress" Biomolecules 15, no. 5: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050624
APA StyleLin, S., Wang, B., & Li, J. (2025). The Role of Klotho in Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases: Mechanisms and Research Progress. Biomolecules, 15(5), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050624






