The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Modulating the Immune Microenvironment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Advances in the Immune Microenvironment and lncRNAs in TNBC
2.1. Biological Functions of lncRNAs in TNBC
2.1.1. Mechanisms of Gene Regulation in TNBC
2.1.2. Regulation of Cell Signaling in TNBC
2.1.3. Role of lncRNAs in Cellular Metabolism in TNBC
2.1.4. LncRNAs as Novel Diagnostic Markers for TNBC
2.2. Characterization of the Immune Microenvironment in TNBC
2.2.1. Immune Cell Composition
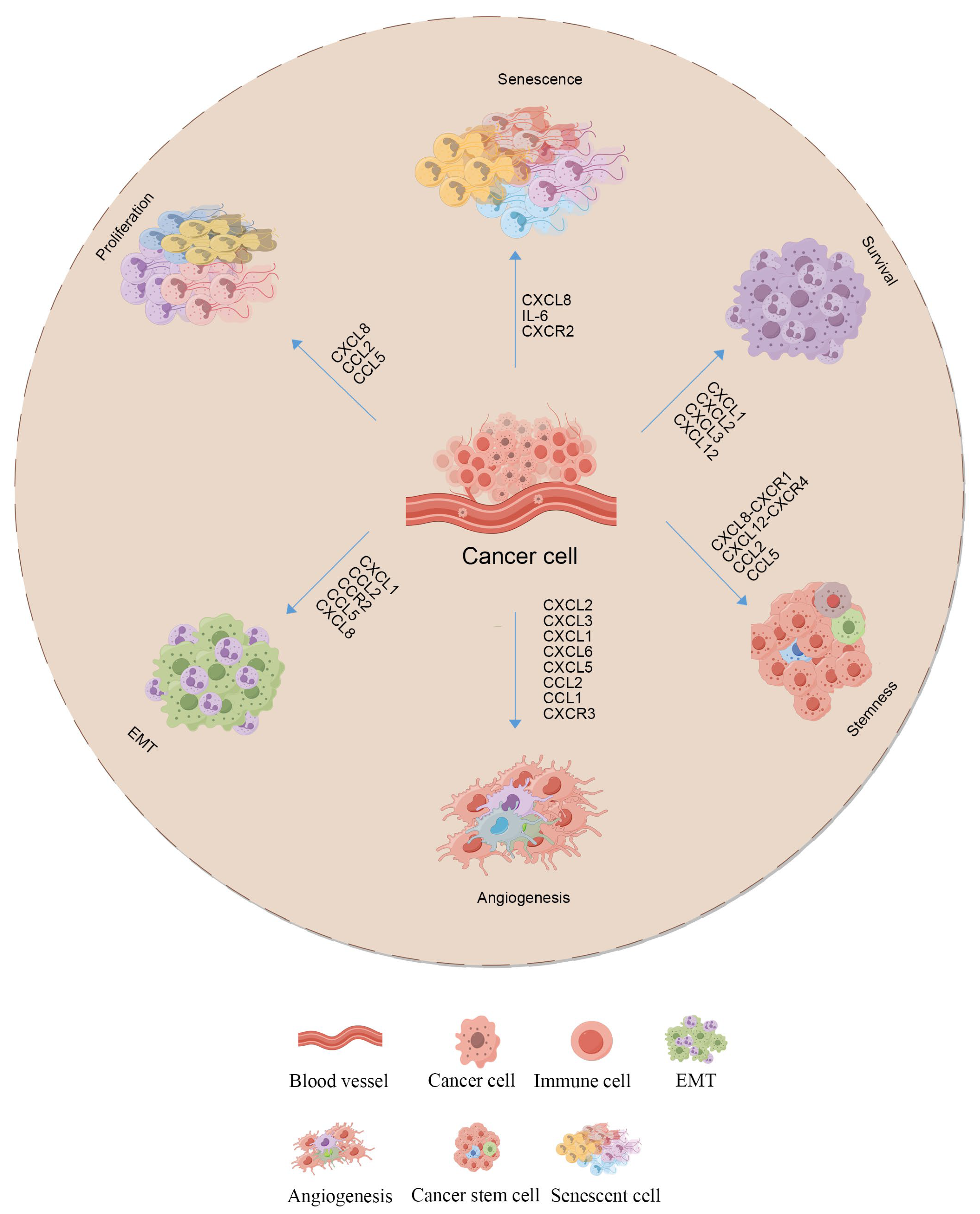
2.2.2. Cytokines and Their Roles
2.2.3. Role of lncRNAs in Microenvironment Remodeling
3. Role of lncRNAs in the TNBC Immune Microenvironment
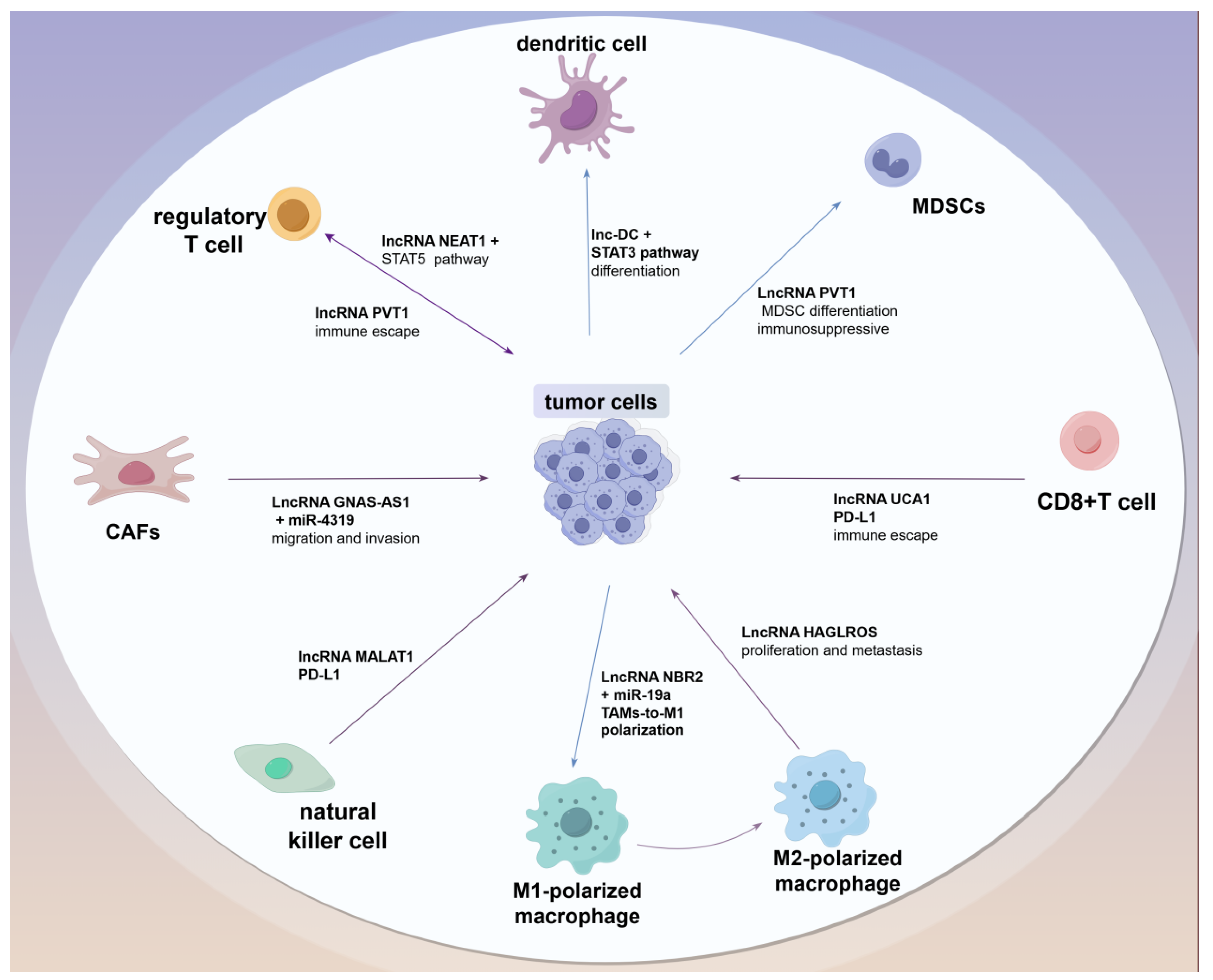
3.1. LncRNAs Regulate Different Subtypes of Immune Cells
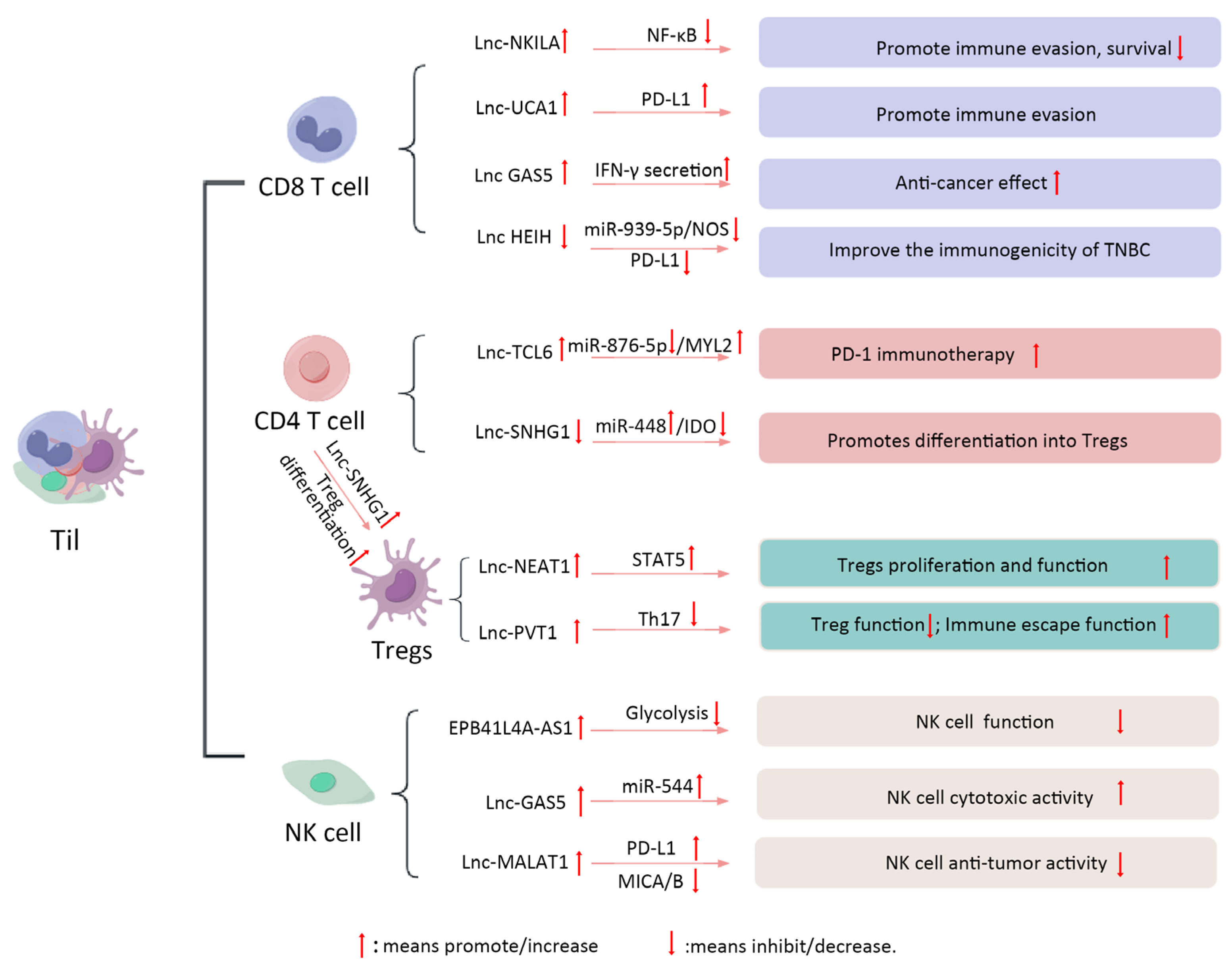
3.2. TIL
3.3. Tumor-Associated Fibroblasts
3.4. Dendritic Cells
3.5. MDSCs
3.6. Effect of lncRNA on the Polarization of TAMs
4. Mechanisms of lncRNA-Mediated Immune Escape
4.1. Regulation of Immune Checkpoints
4.2. Apoptosis and Immune Escape
4.3. Holistic View of lncRNA-TME Interactions
5. Potential of lncRNAs as Therapeutic Targets
5.1. Therapeutic Strategies for lncRNA Targeting
5.2. Challenges and Future Directions in Clinical Applications
5.3. Future Directions in Clinical Applications
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Triple-negative breast cancer | TNBC |
| long non-coding RNAs | lncRNAs |
| breast cancer | BC |
| immune microenvironment | IME |
| tumor-associated macrophages | TAMs |
| tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes | TILs |
| Polycomb repressive complex 2 | PRC2 |
| microRNAs | miRNAs |
| tricarboxylic acid | TCA |
| plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 | PAI-1 |
| dendritic cells | DCs |
| natural killer | NK |
| regulatory T cells | Tregs |
| myeloid-derived suppressor cells | MDSCs |
| immune checkpoint inhibitors | ICIs |
| glutamic acid-leucine-arginine | ELR |
| breast cancer stem cells | BCSCs |
| tumor immune microenvironment | TME |
| cancer-associated fibroblasts | CAFs |
| activation-induced cell death | AICD |
| nitric oxide synthase | NOS |
| interferon-gamma | IFN-γ |
| tumor necrosis factor receptor | GITR |
| antisense oligonucleotides | ASOs |
| RNA interference | RNAi |
References
- Fan, Y.; He, S. The Characteristics of Tumor Microenvironment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2022, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, H.; Cai, D.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z. FA2H Exhibits Tumor Suppressive Roles on Breast Cancers via Cancer Stemness Control. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loizides, S.; Constantinidou, A. Triple negative breast cancer: Immunogenicity, tumor microenvironment, and immunotherapy. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1095839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs: Definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencivenga, D.; Stampone, E.; Vastante, A.; Barahmeh, M.; Della Ragione, F.; Borriello, A. An Unanticipated Modulation of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors: The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs. Cells 2022, 11, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Ye, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, M.; Cai, C. PVT1 affects EMT and cell proliferation and migration via regulating p21 in triple-negative breast cancer cells cultured with mature adipogenic medium. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.H.; Chu, E.T.-J.; Spektor, R.; Soloway, P.D. Long non-coding RNA regulation of reproduction and development. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 82, 932–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, E.T.; Showalter, S.A. Biophysical insights into glucose-dependent transcriptional regulation by PDX1. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of Sam68 in post-transcriptional gene regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 23402–23419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervouet, E.; Vallette, F.M.; Cartron, P.-F. Dnmt1/Transcription factor interactions: An alternative mechanism of DNA methylation inheritance. Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Huang, H.; Hu, J.; Yu, Y.; Ma, X.; Xu, M.; Ming, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; et al. LINC00571 drives tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolism in triple-negative breast cancer through HNRNPK/ILF2/IDH2 axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B. Long non-coding RNA DRHC inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells in triple negative breast cancer by downregulating long non-coding RNA HOTAIR. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3817–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-Vázquez, L.A.; Méndez-García, A.; Chamu-García, V.; Rodríguez, A.L.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Paul, S. The applications of CRISPR/Cas-mediated microRNA and lncRNA editing in plant biology: Shaping the future of plant non-coding RNA research. Planta 2023, 259, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, J.; Wasson, M.-C.D.; Brown, J.M.; Fernando, W.; Marcato, P. LncRNA-miRNA axes in breast cancer: Novel points of interaction for strategic attack. Cancer Lett. 2021, 509, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gao, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Wei, X. Long non-coding RNA PTCSC3 suppresses triple-negative breast cancer by downregulating long non-coding RNA MIR100HG. Oncol. Lett. 2023, 26, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, L.; Su, Z. Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in the metabolic reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 232, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, M.; Guo, J.; Ma, J.; Qiu, M.; Yang, Z. The function of non-coding RNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Open Med. 2021, 16, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Xia, L. The role of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer microenvironment. Pathol. Res. Pr. Pract. 2023, 248, 154707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashmawy, N.E.; Hussien, F.Z.; El-Feky, O.A.; Hamouda, S.M.; Al-Ashmawy, G.M. Serum LncRNA-ATB and FAM83H-AS1 as diagnostic/prognostic non-invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Fu, Y.; Zeng, N.; Yin, J.; Li, Q. LncRNA FAM83H-AS1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression by regulating the miR-136-5p/metadherin axis. Aging 2020, 12, 3594–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhathami, A.G.; Hadi, A.; Alfaifi, M.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Verma, A.K.; Beg, M.M.A. Serum-Based lncRNA ANRIL, TUG1, UCA1, and HIT Expressions in Breast Cancer Patients. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 9997212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Feng, J.; Cui, M.; Yang, J.; Wan, X.; Xie, D.; Liu, J. LncRNA MIAT Services as a Noninvasive Biomarker for Diagnosis and Correlated with Immune Infiltrates in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Women’s Health 2021, 13, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Fattah, A.A.A.; Sadik, N.A.H.; Shaker, O.G.; Mohamed Kamal, A.; Shahin, N.N. Serum Long Non-Coding RNAs PVT1, HOTAIR, and NEAT1 as Potential Biomarkers in Egyptian Women with Breast Cancer. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yue, X.; Sun, Q. Serum exosomal lncRNA XIST is a potential non-invasive biomarker to diagnose recurrence of triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 7602–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. The expression of lncRNA-MALAT1 in breast cancer patients and its influences on prognosis. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2020, 66, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Jin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, L. High serum exosomal long non-coding RNA DANCR expression confers poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; You, X.; Liang, Z.; Cao, H. Circulating DNA of HOTAIR in serum is a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 152, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swellam, M.; El Magdoub, H.M.; Shawki, M.A.; Adel, M.; Hefny, M.M.; El-Shazly, S.S. Clinical impact of LncRNA XIST and LncRNA NEAT1 for diagnosis of high-risk group breast cancer patients. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2021, 45, 100709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zheng, K.; Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zou, T.; Liu, D. Overexpression of serum exosomal HOTAIR is correlated with poor survival and poor response to chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Kuo, W.-L.; Stilwell, J.L.; Takano, H.; Lapuk, A.V.; Fridlyand, J.; Mao, J.-H.; Yu, M.; Miller, M.A.; Santos, J.L.; et al. Amplification of PVT1 contributes to the pathophysiology of ovarian and breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. For. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5745–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neve, R.M.; Chin, K.; Fridlyand, J.; Yeh, J.; Baehner, F.L.; Fevr, T.; Clark, L.; Bayani, N.; Coppe, J.-P.; Tong, F.; et al. A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamo, A.; Atashpaz, S.; Germain, P.-L.; Zanella, M.; D’Agostino, G.; Albertin, V.; Chenoweth, J.; Micale, L.; Fusco, C.; Unger, C.; et al. 7q11.23 dosage-dependent dysregulation in human pluripotent stem cells affects transcriptional programs in disease-relevant lineages. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Placencio, V.R.; DeClerck, Y.A. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in Cancer: Rationale and Insight for Future Therapeutic Testing. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Xu, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, X.; Cheng, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Inhibition of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 impairs myeloid differentiation in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Deng, Y.; Long, Z. NEAT1/miR-181c Regulates Osteopontin (OPN)-Mediated Synoviocyte Proliferation in Osteoarthritis. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 3775–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Xiao, S.; Wei, W.; Liu, J. Determination of Serum Exosomal H19 as a Noninvasive Biomarker for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 2563–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.-J.; Tan, X.-L.; Guo, L. The long non-coding RNA DANCR regulates the inflammatory phenotype of breast cancer cells and promotes breast cancer progression via EZH2-dependent suppression of SOCS3 transcription. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, S.; Zeng, Y.; Cai, Y.; Luo, H. BANCR-Containing Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Breast Cancer Resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Lv, C.; Luo, Z. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived lncRNA signature as a putative biomarker in breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1028664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavelu, L.; Moglad, E.; Gupta, G.; Menon, S.V.; Gaur, A.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, M.; Chahar, M.; Sivaprasad, G.V.; Deorari, M. GAS5 lncRNA: A biomarker and therapeutic target in breast cancer. Pathol. Res. Pr. Pract. 2024, 260, 155424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Chen, K.; Fan, H.; Jin, F. The synergistic effect of CDKN2B-AS1 and SPC25 on triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Shin, C.H.; Ji, H.; Jeong, S.D.; Park, M.-S.; Won, H.-H.; Pandey, P.R.; Tsitsipatis, D.; Gorospe, M.; Kim, H.H. hnRNPK-regulated LINC00263 promotes malignant phenotypes through miR-147a/CAPN2. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ke, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Ao, L.; Zou, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Nie, J.; Wu, C.; et al. LncRNA MIR100HG promotes cell proliferation in triple-negative breast cancer through triplex formation with p27 loci. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.-N.; Qu, H.-J.; Gong, W.-J.; Xiang, J.-Y.; Yang, M.-M.; Zhang, W. LncRNA AWPPH and miRNA-21 regulates cancer cell proliferation and chemosensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer by interacting with each other. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 14860–14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collina, F.; Aquino, G.; Brogna, M.; Cipolletta, S.; Buonfanti, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Di Bonito, M.; Cantile, M.; Botti, G. LncRNA HOTAIR up-regulation is strongly related with lymph nodes metastasis and LAR subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eades, G.; Wolfson, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, Q. lincRNA-RoR and miR-145 regulate invasion in triple-negative breast cancer via targeting ARF6. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S.K.; Tu, J.H.; Hu, Y.Y.; Xiong, Q.Y. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes relapse of breast cancer patients with postoperative fever. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 3186–3197. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, J.; Hu, L.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Pu, L.; Xiong, S. The Significance of Long Non-coding RNA HULC in Predicting Prognosis and Metastasis of Cancers: A Meta-Analysis. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 25, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Li, C.; Xing, Z.; Hu, Q.; Liang, K.; Han, L.; Wang, C.; Hawke, D.H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The LINK-A lncRNA activates normoxic HIF1α signalling in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Hou, M.; Zhan, Y.; Sheng, X. LncRNA PTCSC3 inhibits triple-negative breast cancer cell proliferation by downregulating lncRNA H19. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 15083–15088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, O.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Lv, L.; Ma, R.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Tan, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, E.; et al. C-MYC-induced upregulation of lncRNA SNHG12 regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration in triple-negative breast cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yu, D.; Shi, H.; Li, J.; Meng, L. Reduced lncRNA Aim enhances the malignant invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells mainly by activating Wnt/β-catenin/mTOR/PI3K signaling. Pharmazie 2017, 72, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; Hu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Fan, L.; Tang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Shan, W.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LINP1 regulates repair of DNA double-strand breaks in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfinejad, P.; Kazemi, T.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Shanehbandi, D.; Jadidi Niaragh, F.; Safaei, S.; Asadi, M.; Baradaran, B. PD-1/PD-L1 axis importance and tumor microenvironment immune cells. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhao, S.; Suo, C.; Shi, J.; Xue, M.Z.; Ruan, M.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; et al. Multi-Omics Profiling Reveals Distinct Microenvironment Characterization and Suggests Immune Escape Mechanisms of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5002–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landskron, G.; De la Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 149185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.-N.; Ding, H.-Y.; Li, H.; Yang, R.; Huang, J.-Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.-H.; Wang, Y.-J.; Hu, C.-M.; An, Y.-L.; et al. Photosensitive small extracellular vesicles regulate the immune microenvironment of triple negative breast cancer. Acta Biomater. 2023, 167, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timperi, E.; Gueguen, P.; Molgora, M.; Magagna, I.; Kieffer, Y.; Lopez-Lastra, S.; Sirven, P.; Baudrin, L.G.; Baulande, S.; Nicolas, A.; et al. Lipid-Associated Macrophages Are Induced by Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Mediate Immune Suppression in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3291–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovgaard, E.S.; Nielsen, D.; Hogdall, E.; Balslev, E. Triple negative breast cancer—Prognostic role of immune-related factors: A systematic review. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed Khaja, A.S.; Toor, S.M.; El Salhat, H.; Faour, I.; Ul Haq, N.; Ali, B.R.; Elkord, E. Preferential accumulation of regulatory T cells with highly immunosuppressive characteristics in breast tumor microenvironment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33159–33171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiri, S.; Alizadeh, A.M.; Baradaran, B.; Farhanghi, B.; Shanehbandi, D.; Khodayari, S.; Khodayari, H.; Tavassoli, A. Dendrosomal curcumin suppresses metastatic breast cancer in mice by changing m1/m2 macrophage balance in the tumor microenvironment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 3917–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palakurthi, B.; Fross, S.R.; Guldner, I.H.; Aleksandrovic, E.; Liu, X.; Martino, A.K.; Wang, Q.; Neff, R.A.; Golomb, S.M.; Lewis, C.; et al. Targeting CXCL16 and STAT1 augments immune checkpoint blockade therapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, L.T.; Williams, L.A.; Midkiff, B.R.; Kirk, E.L.; Troester, M.A.; Calhoun, B.C. Quantitative analysis of breast cancer tissue composition and associations with tumor subtype. Hum. Pathol. 2022, 123, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, K.A.; Popel, A.S.; Pandey, N.B. Heterogeneity of chemokine cell-surface receptor expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Mehraj, U.; Mushtaq, U.; Mir, M.A.; Saleem, A.; Macha, M.A.; Lone, M.N.; Hamid, A.; Zargar, M.A.; Ahmad, S.M.; Wani, N.A. Chemokines in triple-negative breast cancer heterogeneity: New challenges for clinical implications. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortezaee, K. CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in the microenvironment of solid tumors: A critical mediator of metastasis. Life Sci. 2020, 249, 117534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, R.R.; Bhamidipati, P. γδ T Cell-Mediated Immune Responses for Cancer Therapy: Special Focus on Breast Cancer. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 42, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, Y.; Gu, J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Situ, H.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Z. Network-pharmacology-based validation of TAMS/CXCL-1 as key mediator of XIAOPI formula preventing breast cancer development and metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraj, U.; Qayoom, H.; Mir, M.A. Prognostic significance and targeting tumor-associated macrophages in cancer: New insights and future perspectives. Breast Cancer 2021, 28, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Singh, R.K. Chemokines orchestrate tumor cells and the microenvironment to achieve metastatic heterogeneity. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 447–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.; Chen, Q.; Lin, C.; Dong, H. Linc00514 promotes breast cancer metastasis and M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via Jagged1-mediated notch signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Han, G.; Jin, L.; Fan, Y.; Xu, G.; Yuan, D.; Zheng, J.; et al. Overexpression of LncRNA BM466146 Predicts Better Prognosis of Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 628757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Y.-N.; Qi, W.-C.; Xia, B.-R.; Lou, G.; Jin, W.-L. Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment: Biological Properties and Therapeutic Potential. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 697083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Philips, A.V.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Qiao, N.; Wu, Y.; Harrington, S.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Akcakanat, A.; et al. PD-L1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Jonas, S.F.; Bataillon, G.; Criscitiello, C.; Salgado, R.; Loi, S.; Viale, G.; Lee, H.J.; Dieci, M.V.; Kim, S.B.; et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) who did not receive adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Ferre, R.A.; Jonas, S.F.; Salgado, R.; Loi, S.; de Jong, V.; Carter, J.M.; Nielsen, T.O.; Leung, S.; Riaz, N.; Chia, S.; et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. JAMA 2024, 331, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, S.; Michiels, S.; Salgado, R.; Sirtaine, N.; Jose, V.; Fumagalli, D.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.L.; Bono, P.; Kataja, V.; Desmedt, C.; et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic in triple negative breast cancer and predictive for trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer: Results from the FinHER trial. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Kan, C.; Sun, M.; Yang, F.; Wong, M.; Wang, S.; Zheng, H. Mapping Breast Cancer Microenvironment Through Single-Cell Omics. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 868813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Wang, X.; Li, H. LncRNA SNHG1 regulates the differentiation of Treg cells and affects the immune escape of breast cancer via regulating miR-448/IDO. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moallemi-Rad, L.; Ghorbani, A.; Dadyar, M.; Hussen, B.M.; Rasul, M.F.; Eslami, S.; Taheri, M.; Jamali, E.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Expression of Treg-associated lncRNAs in breast cancer. Pathol. Res. Pr. Pract. 2023, 241, 154270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabbaghipour, R.; Ahmadi, E.; Entezam, M.; Rahbar Farzam, O.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Saber Sichani, A.; Jalilzadeh, N.; Jafarlou, M.; Baradaran, B. Regulatory Effects of Long Non-coding RNAs on Th17/Treg Differentiation and Imbalance. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 22, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-N.; Shen, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X. The relationship of peripheral blood lncRNA-PVT1 and miR-146a levels with Th17/Treg cytokines in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and their clinical significance. Biomol. Biomed. 2024, 24, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lachapelle, J.; Leung, S.; Gao, D.; Foulkes, W.D.; Nielsen, T.O. CD8+ lymphocyte infiltration is an independent favorable prognostic indicator in basal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshi, M.; Asaoka, M.; Tokumaru, Y.; Yan, L.; Matsuyama, R.; Ishikawa, T.; Endo, I.; Takabe, K. CD8 T Cell Score as a Prognostic Biomarker for Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, J.; Lao, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Xing, Y.; et al. NKILA lncRNA promotes tumor immune evasion by sensitizing T cells to activation-induced cell death. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1112–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Feng, R.; Kahlert, U.D.; Chen, Z.; Torres-Dela Roche, L.A.; Soliman, A.; Miao, C.; De Wilde, R.L.; Shi, W. Construction of ceRNA Networks Associated with CD8 T Cells in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 883197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafea, H.; Youness, R.A.; Abou-Aisha, K.; Gad, M.Z. LncRNA HEIH/miR-939-5p interplay modulates triple-negative breast cancer progression through NOS2-induced nitric oxide production. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 5362–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, M.; Yan, T.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, D.; Zhu, D.; et al. The Establishment and Experimental Verification of an lncRNA-Derived CD8+ T Cell Infiltration ceRNA Network in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2022, 16, 11795549221092218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewunmi, O.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.H.F.; Rosen, J.M. Targeted Inhibition of lncRNA Malat1 Alters the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Preclinical Syngeneic Mouse Models of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023, 11, 1462–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, V.C.; Wang, C.C.N.; Liao, S.H.; Chen, D.L. Cross-Platform in-silico Analyses Exploring Tumor Immune Microenvironment with Prognostic Value in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2022, 14, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. LncRNA ST7-AS1 is a Potential Novel Biomarker and Correlated With Immune Infiltrates for Breast Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 604261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekky, R.Y.; Ragab, M.F.; Manie, T.; Attia, A.A.; Youness, R.A. MALAT-1: Immunomodulatory lncRNA hampering the innate and the adaptive immune arms in triple negative breast cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 31, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-X.; Wang, S.-M.; Li, C.-Q. Four-lncRNA immune prognostic signature for triple-negative breast cancer Running title: Immune lncRNAs predict prognosis of TNBC. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 3939–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ti, W.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y. The Interaction Between Long Non-Coding RNAs and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Lung Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 714125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, C.; Yang, W.; Cheng, H.; Wang, H.; et al. Elevated exosome-transferrable lncRNA EPB41L4A-AS1 in CD56bright NK cells is responsible for the impaired NK function in neuroblastoma patients by suppressing cell glycolysis. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 250, 109322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Schmoellerl, J.; Mariani, O.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Karnoub, A.E. The LINC01119-SOCS5 axis as a critical theranostic in triple-negative breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Hu, J. Melanoma-derived exosomes induce reprogramming fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts via Gm26809 delivery. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 3085–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Deng, Y.E.; Ma, C.; Yu, Q.; Gao, D. Long non-coding RNA: Multiple effects on the differentiation, maturity and cell function of dendritic cells. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 245, 109167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, R.; Dai, J.; Lai, G.; Khan, A.U.; Yu, X.; Wu, S.; Ouyang, J.; Sang, H. Analysis of differential expression of long non-coding RNAs in exosomes derived from mature and immature dendritic cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, T.; Xia, X.; Cao, F.; Tian, J.; Xu, P.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, S. Long noncoding RNA Pvt1 regulates the immunosuppression activity of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, K.; Ma, J.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, S. LncRNA AK036396 Inhibits Maturation and Accelerates Immunosuppression of Polymorphonuclear Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells by Enhancing the Stability of Ficolin B. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Jin, Z.; Chen, G.; Gan, C. Long non-coding RNA NBR2 suppresses the progression of colorectal cancer by downregulating miR-19a to regulate M2 macrophage polarization. Chin. J. Physiol. 2023, 66, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, H.T.; Eissa, R.A.; El Tayebi, H.M. A cutting-edge immunomodulatory interlinkage between HOTAIR and MALAT1 in tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer: A personalized immunotherapeutic approach. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1032517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wu, X.; Piao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Jin, T. LncRNA HAGLROS promotes breast cancer evolution through miR-135b-3p/COL10A1 axis and exosome-mediated macrophage M2 polarization. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lin, J.; Huang, S.; Wu, X.; Deng, W.; Huang, J.; Yao, Y. YTHDF2 favors protumoral macrophage polarization and implies poor survival outcomes in triple negative breast cancer. iScience 2024, 27, 109902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, T.; Talluri, S.; Venkatabalasubramanian, S.; Dunna, N.R. Multifaceted roles of long non-coding RNAs in triple-negative breast cancer: Biology and clinical applications. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 2791–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Z.; Al-Eryani, G.; Roden, D.L.; Junankar, S.; Harvey, K.; Andersson, A.; Thennavan, A.; Wang, C.; Torpy, J.R.; Bartonicek, N.; et al. A single-cell and spatially resolved atlas of human breast cancers. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1334–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadreddini, S.; Baradaran, B.; Aghebati-Maleki, A.; Sadreddini, S.; Shanehbandi, D.; Fotouhi, A.; Aghebati-Maleki, L. Immune checkpoint blockade opens a new way to cancer immunotherapy. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 8541–8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, C.G.; Lipson, E.J.; Brahmer, J.R. Breathing new life into immunotherapy: Review of melanoma, lung and kidney cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raufi, A.G.; Klempner, S.J. Immunotherapy for advanced gastric and esophageal cancer: Preclinical rationale and ongoing clinical investigations. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 6, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Strome, S.E.; Salomao, D.R.; Tamura, H.; Hirano, F.; Flies, D.B.; Roche, P.C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; et al. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Pu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Expression of PD-L1 and prognosis in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31347–31354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Dong, P.Z.; Ren, M.J.; Song, Y.W.; Qian, X.L.; Yang, Y.L.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.M.; Liu, F.F. PD-L1 Expression Is Associated with Tumor FOXP3+ Regulatory T-Cell Infiltration of Breast Cancer and Poor Prognosis of Patient. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Milne, K.; Derocher, H.; Webb, J.R.; Nelson, B.H.; Watson, P.H. PD-L1 and intratumoral immune response in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 51641–51651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatalica, Z.; Snyder, C.; Maney, T.; Ghazalpour, A.; Holterman, D.A.; Xiao, N.; Overberg, P.; Rose, I.; Basu, G.D.; Vranic, S.; et al. Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) in common cancers and their correlation with molecular cancer type. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2965–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.; Crown, J.; Di Leo, A.; Buyse, M.; Balil, A.; Andersson, M.; Nordenskjold, B.; Lang, I.; Jakesz, R.; Vorobiof, D.; et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy with sequential or concurrent anthracycline and docetaxel: Breast International Group 02-98 randomized trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.D.; Taube, J.M.; Asch-Kendrick, R.J.; Ogurtsova, A.; Xu, H.; Sharma, R.; Meeker, A.; Argani, P.; Emens, L.A.; Cimino-Mathews, A. PD-L1 expression and the immune microenvironment in primary invasive lobular carcinomas of the breast. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Nepovimova, E.; Wu, Q.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Deoxynivalenol upregulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1α to promote an “immune evasion” process by activating STAT3 signaling. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 179, 113975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Garg, M.; Pandey, A.K. Deciphering the Mounting Complexity of the p53 Regulatory Network in Correlation to Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in Ovarian Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansara, S.; Pandey, V.; Lobie, P.E.; Sethi, G.; Garg, M.; Pandey, A.K. Mechanistic Involvement of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Oncotherapeutics Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Luo, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Y. Mechanism of immune evasion in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Huang, C.; Zou, J.; Liang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhong, Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-packaged lncRNA from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes immune evasion by downregulating HLA-A in pancreatic cancer. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davodabadi, F.; Farasati Far, B.; Sargazi, S.; Fatemeh Sajjadi, S.; Fathi-Karkan, S.; Mirinejad, S.; Ghotekar, S.; Sargazi, S.; Rahman, M.M. Nanomaterials-Based Targeting of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer: A Cutting-Edge Review of Current Trends. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202300528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coan, M.; Haefliger, S.; Ounzain, S.; Johnson, R. Targeting and engineering long non-coding RNAs for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 578–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorkova, O.; Stahl, J.; Joji, A.; Volmar, C.-H.; Zeier, Z.; Wahlestedt, C. Long non-coding RNA-targeting therapeutics: Discovery and development update. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2023, 18, 1011–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Tu, G.; Peng, M.; Zeng, H.; Wan, X.; Qiao, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, M.; Luo, H. GPER-regulated lncRNA-Glu promotes glutamate secretion to enhance cellular invasion and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4557–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghazali, M.W.; Al-Hetty, H.; Ali, Z.M.M.; Saleh, M.M.; Suleiman, A.A.; Jalil, A.T. Non-coding RNAs, another side of immune regulation during triple-negative breast cancer. Pathol. Res. Pr. Pract. 2022, 239, 154132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Yan, B.; Lu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Ma, L. Reciprocal regulation of Hsa-miR-1 and long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer development. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 7383–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, N.; Song, P.; Fu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. LncRNA GATA3-AS1 facilitates tumour progression and immune escape in triple-negative breast cancer through destabilization of GATA3 but stabilization of PD-L1. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, H.; Sun, R.; Li, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yin, C. Long non-coding RNA ZEB2-AS1 promotes the proliferation, metastasis and epithelial mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer by epigenetically activating ZEB2. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3271–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Siddika, A.; Rashel, K.M.; Auwal, A.; Soha, K.; Rahman, M.A.; Pillai, S.; Islam, F. Roles of long noncoding RNA in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 20365–20379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.; Montazeri, M.; Mashayekhi, S.; Sadeghi-Soureh, S.; Dadashpour, M.; Mousazadeh, H.; Nobakht, A.; Zarghami, N.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y. Synergistic anticancer effects of electrospun nanofiber-mediated codelivery of Curcumin and Chrysin: Possible application in prevention of breast cancer local recurrence. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2020, 55, 101402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, R.K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Khullar, N.; Sidhu, I.S.; Reddy, P.H.; Bhatti, G.K.; Bhatti, J.S. Targeting long non-coding RNAs in cancer therapy using CRISPR-Cas9 technology: A novel paradigm for precision oncology. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 379, 98–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.S.; Al-Tweigeri, T.; Al-Harbi, L.; Ujjahan, S.; Al-Mozaini, M.; Tulbah, A.; Aboussekhra, A. Long noncoding RNA DLEU2 and ROR1 pathway induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells in breast cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cai, Q.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Lu, L.; Yi, B.; Chang, R.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Bioinformatics construction and experimental validation of a cuproptosis-related lncRNA prognostic model in lung adenocarcinoma for immunotherapy response prediction. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.-W.; Chong, K.-H.; Li, C.-H.; Tu, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-R.; Lee, M.-C.; Chan, S.-H.; Wang, L.-H.; Chang, Y.-J. LOC550643, a Long Non-coding RNA, Acts as Novel Oncogene in Regulating Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 695632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, W.; Mo, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qin, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, A.; Yao, S.; et al. Targeting cholesterol biosynthesis promotes anti-tumor immunity by inhibiting long noncoding RNA SNHG29-mediated YAP activation. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 2995–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Q.; Feng, H.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, K.; Ding, J.; Gao, G. LncRNA-mediated cartilage homeostasis in osteoarthritis: A narrative review. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1326843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marima, R.; Basera, A.; Miya, T.; Damane, B.P.; Kandhavelu, J.; Mirza, S.; Penny, C.; Dlamini, Z. Exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancer: Interplay, modulation, and therapeutic avenues. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bu, N.; Luan, X.-F.; Song, Q.-Q.; Ma, B.-F.; Hao, W.; Yan, J.-J.; Wang, L.; Zheng, X.-L.; Maimaitiyiming, Y. Harnessing the potential of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: From etiology to treatment resistance and clinical applications. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1337579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| lncRNA (NCBI ID) | Role | Key Factors | Outcome | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVT1 (5820) | Oncogenic | PAI-1 | Proliferation ↑, Metastasis ↑, and angiogenesis | [30] |
| NEAT1 (283131) | Oncogenic | AKT/mTOR | Stemness ↑, Radioresistance | [23] |
| XIST (7503) | Dual | EZH2 | Metastasis modulation | [24] |
| MIR3142HG (100500816) | Oncogenic | Wnt/β-catenin | Invasion ↑, Prognosis ↓ | [37] |
| MIAT (723944) | Oncogenic | miR-150-5p, VEGFA | Lymph node metastasis ↑ | [22] |
| GAS5 (60674) | Suppressor | E2F1 | Apoptosis ↑, Chemosensitivity ↑ | [40] |
| CDKN2B-AS1 (100048912) | Oncogenic | PRC2 | Cell cycle ↑, Radioresistance | [41] |
| LINC00263 (283120) | Oncogenic | MAPK, EMT | Metastasis ↑ | [42] |
| MIR100HG (100316840) | Oncogenic | CDKN1B (p27) | Proliferation ↑ | [43] |
| PWRN1 (389803) | Oncogenic | miR-21 | Tumor growth ↑, Chemoresistance | [44] |
| HOXAT1 (100124700) | Oncogenic | PRC2/EZH2 | Metastasis ↑, Prognosis ↓ | [45] |
| LINC-ROR (84952) | Oncogenic | ZEB1 | Metastasis ↑ | [46] |
| MALAT1 (378938) | Oncogenic | PI3k/AKT/mTOR | Progression ↑, Metastasis ↑ | [47] |
| LINC00115 (340419) | Oncogenic | MMP-2/9 | Stage ↑, Survival ↓ | [48] |
| LINC01139 (387119) | Oncogenic | HIF1-α | Tumorigenesis ↑ | [49] |
| H19 (283120) | Oncogenic | E2F1 | Cell cycle ↑, Chemoresistance | [50] |
| SNHG12 (103532094) | Oncogenic | MMP13 | Lymph node metastasis ↑ | [51] |
| IGF2R-AS1 (348093) | Tumor suppressor | Wnt/β-catenin | Migration ↓, Invasion ↓ | [52] |
| PTCSC3 (100505381) | Tumor suppressor | STAT3/WNT | Proliferation ↓ | [50] |
| LINC00665 (285134) | Tumor suppressor | NHEJ repair | Radiosensitivity ↑ | [53] |
| Targets/Types | Immunotherapeutic Agent | Phase | Patient | Clinical Trials. gov ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD-1 | Pembrolizumab | II | TNBC | NCT03145961 |
| III | NCT03036488 | |||
| Ib | NCT02622074 | |||
| II | NCT03289819 | |||
| PDR001 | II | TNBC | NCT02938442 | |
| PD-L1 | Atezolizumab | III | TNBC | NCT03197935 |
| III | NCT03281954 | |||
| III | NCT02620280 | |||
| II | NCT02530489 | |||
| Durvalumab | II | TNBC | NCT02685059 | |
| I/II | NCT02489448 | |||
| PD-L1, PARP | Atezolizumab, Veliparib | II | TNBC, BRCA1/2 mutated, other BCs | NCT02849496 |
| PD-1 | Pembrolizumab | II | TNBC, IBC | NCT03121352 |
| II | TNBC | NCT03184558 | ||
| Nivolumab | II | TNBC | NCT03316586 | |
| II | NCT02499367 | |||
| JS001 | I | TNBC | NCT03251313 | |
| I | NCT03151447 | |||
| PDR001 | Ib/II | TNBC, NSCLC, TC, Melanoma | NCT02404441 | |
| I | TNBC, CRC, NSCLC | NCT02890069 | ||
| PD-L1 | Atezolizumab | II | TNBC | NCT03164993 |
| III | NCT02425891 | |||
| III | NCT03125902 | |||
| Ib/II | NCT02708680 | |||
| IIb | NCT01898117 | |||
| Durvalumab | I/II | TNBC | NCT02628132 | |
| Avelumab | Ib/II | TNBC, SCCHN, SCLC, NSCLC, Melanoma | NCT02554812 | |
| CTLA-4 | Tremelimumab | II | TNBC, UBC, PDAC | NCT02527434 |
| PD-L1, CTLA-4 | Durvalumab, | Ib | TNBC, SCCHN, SCLC, GEJ, PDAC, ESCC | NCT02658214 |
| Tremelimumab | ||||
| PD-1, PARP | Pembrolizumab, Niraparib | I/II | TNBC, OC | NCT02657889 |
| PD-L1, PARP | Durvalumab, Olaparib | II | TNBC | NCT03167619 |
| Durvalumab, | I/II | TNBC, OC, CRC, NSCLC, SCLC, CRPC | NCT02484404 | |
| Olaparib/Cediranib | ||||
| Atezolizumab, Veliparib | II | TNBC, BRCA1/2 mutated, other BCs | NCT02849496 | |
| PD-1 | Tislelizumab | III | Nasopharyngeal Cancer, Hodgkin’s lymphoma | NCT03924986 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.; Bai, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xu, B.; Hu, T. The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Modulating the Immune Microenvironment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030454
Su Y, Bai Q, Zhang W, Xu B, Hu T. The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Modulating the Immune Microenvironment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030454
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yongcheng, Qingquan Bai, Wenqing Zhang, Beibei Xu, and Tianhui Hu. 2025. "The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Modulating the Immune Microenvironment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030454
APA StyleSu, Y., Bai, Q., Zhang, W., Xu, B., & Hu, T. (2025). The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Modulating the Immune Microenvironment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential. Biomolecules, 15(3), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030454







