Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications of Alamandine Receptor MrgD Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with Development of Metastatic Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients Clinical and Pathological Characteristics
3.2. MrgD Expression in Primary Tumor According to Clinical and Pathological Variables
3.2.1. MrgD Expression Does Not Change Depending on Patients’ Ages or Sex
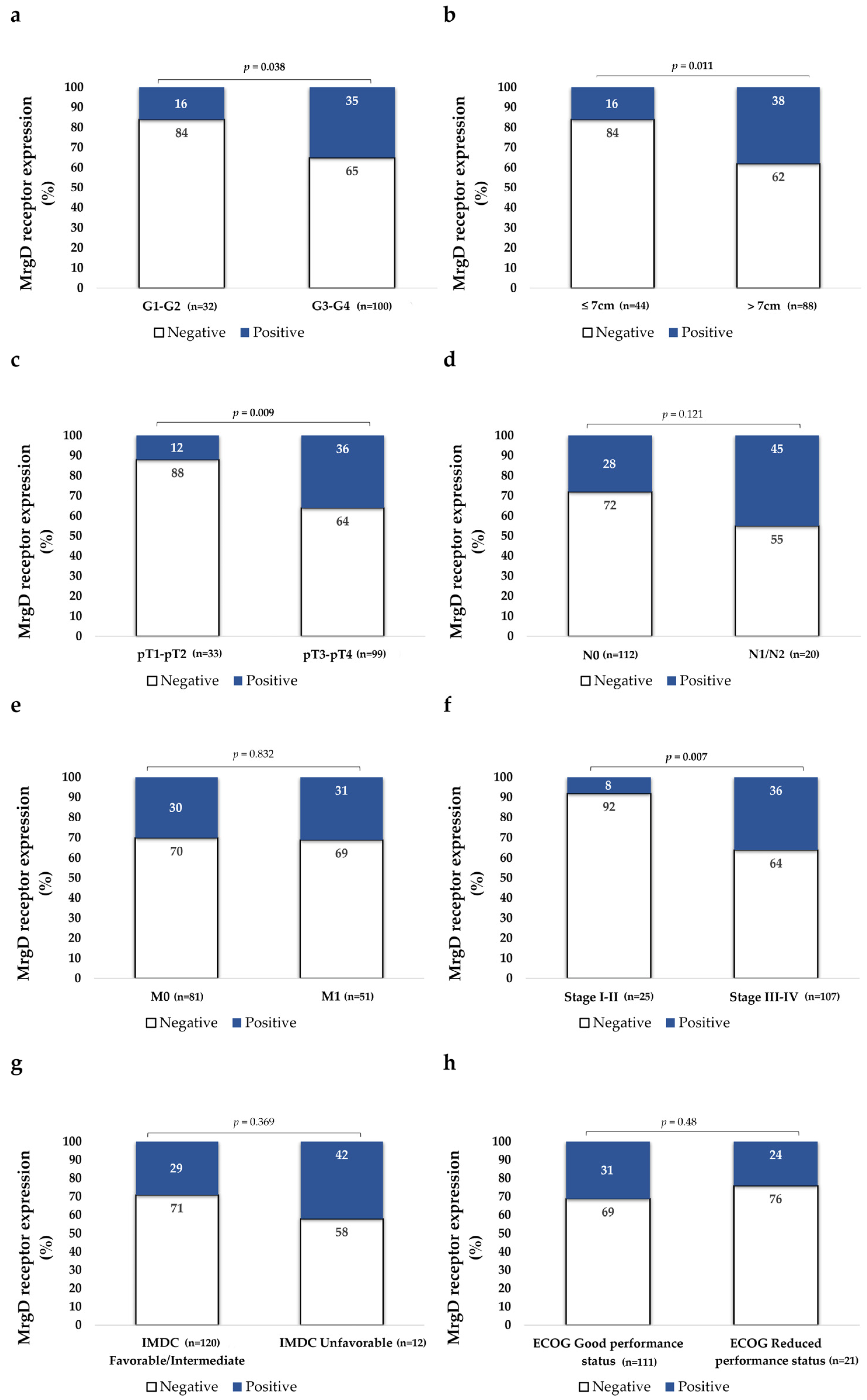
3.2.2. MrgD Expression Is Higher in High-Grade Primary mccRCCs
3.2.3. MrgD Expression Is Higher in Larger and Non-Organ-Confined Tumors
3.2.4. MrgD Staining Is More Intense in Higher-Stage Tumors
3.2.5. MrgD Expression Does Not Change Depending on ECOG Performance Status and IMDC Risk Classification
3.3. MrgD Expression in Primary Tumor According to Treatment Response
3.3.1. MrgD Expression Associated with Unfavorable Response to TKIs in First-Line Therapy
3.3.2. MrgD Expression Was Lower in Tumors with Unfavorable Responses to mTORC1 Inhibitors in Second-Line Therapy
3.4. MrgD Expression in mccRCC According to Patients’ Survival
3.4.1. MrgD Expression Is Associated with Worse Overall Survival (OS) for mccRCC Patients
3.4.2. MrgD Expression Is Associated with Worse Disease-Free Survival (DFS) for Patients with Metachronous Metastases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, M.; Jackson-Spence, F.; Beltran, L.; Day, E.; Suarez, C.; Bex, A.; Powles, T.; Szabados, B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet 2024, 404, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLO-BOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLennan, G.T.; Cheng, L. Neoplasms of the kidney. In Urologic Surgical Pathology, 3rd ed.; Bostwick, D.G., Cheng, L., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 76–156. [Google Scholar]
- Escudier, B.; Porta, C.; Schmidinger, M.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Bex, A.; Khoo, V.; Grünwald, V.; Gillessen, S.; Horwich, A.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, L.; Senatore, E.; Feliciello, S.; Chiuso, F.; Insabato, L.; Feliciello, A. Kidney cancer: From tumor biology to innovative therapeutics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2024, 1880, 189240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, E.A.; Rumble, R.B.; Van Veldhuizen, P.J. Management of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: ASCO Guideline Q&A. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2023, 19, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragan-Carrillo, R.; Saad, E.; Saliby, R.M.; Sun, M.; Albiges, L.; Bex, A.; Heng, D.; Mejean, A.; Motzer, R.J.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. First and second-line treatments in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2025, 87, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.C.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Harshman, L.C.; A Bjarnason, G.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; MacKenzie, M.; Wood, L.; Donskov, F.; Tan, M.-H.; et al. External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, S.; Calderon, L.; Khaleel, S.; Hakimi, A.A. Current and future biomarkers in the management of renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 50, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczuk, P.; Szczylik, C.; Porta, C.; Czarnecka, A.M. Renin angiotensin system deregulation as renal cancer risk factor. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5059–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, P.V.; Adib, E.; Weise, N.; Curran, C.; Stewart, T.; Freeman, D.; Nassar, A.H.; Abou Alaiwi, S.; Bakouny, Z.; McGregor, B.A.; et al. Impact of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on outcomes in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2022, 20, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskelinen, T.; Veitonmäki, T.; Kotsar, A.; Tammela, T.L.J.; Pöyhönen, A.; Murtola, T.J. Improved renal cancer prognosis among users of drugs targeting renin-angiotensin system. Cancer Causes Control 2022, 33, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, B.; Attar, Z.; Firouzabadi, N. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) signaling pathways and cancer: Foes versus allies. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourão, T.C.; Bezerra, S.M.; Santos, V.E.; Brazão, E.S., Jr.; da Costa, W.H.; Zequi, S.C. Role of the Renin-Angiotensin System components in renal cell carcinoma: A Literature Review. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2023, 24, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortune, K.; Ali, S.; Masur, J.; Viscuse, P.; Devitt, M.; Dreicer, R.; Skelton, W.P., 4th. Impact of Renin-Angiotensin System inhibitors on response to PD1/L1 inhibitors in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2024, 23, 102256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, I.; Matsukawa, A.; Kardoust Parizi, M.; Miszczyk, M.; Fazekas, T.; Schulz, R.J.; Mancon, S.; Litterio, G.; Laukhtina, E.; Kawada, T.; et al. The impact of concomitant medications on the overall survival of patients treated with systemic therapy for advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2024, 22, 102237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giani, J.F.; Veiras, L.C.; Shen, J.Z.Y.; Bernstein, E.A.; Cao, D.; Okwan-Duodu, D.; Khan, Z.; Gonzalez-Villalobos, R.A.; Bernstein, K.E. Novel roles of the renal angiotensin-converting enzyme. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2021, 529, 111257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Bhat, S.A.; Shibata, T.; Giani, J.F.; Rader, F.; Bernstein, K.E.; Khan, Z. Diverse biological functions of the renin-angiotensin system. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 44, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, M.; Steckelings, U.M.; Alenina, N.; Santos, R.A.S.; Ferrario, C.M. Alternative Renin-Angiotensin System. Hypertension 2024, 81, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolley-Hitze, T.; Jouan, F.; Martin, B.; Mottier, S.; Edeline, J.; Moranne, O.; Le Pogamp, P.; Belaud-Rotureau, M.A.; Patard, J.J.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; et al. Angiotensin-2 receptors (AT1-R and AT2-R), new prognostic factors for renal clear-cell carcinoma? Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrinaga, G.; Pérez, I.; Sanz, B.; Blanco, L.; López, J.I.; Cándenas, M.L.; Pinto, F.M.;; Gil, J.; Irazusta, J.; Varona, A. Angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE and ACE2) are downregulated in renal tumors. Regul. Pept. 2010, 165, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Errarte, P.; Beitia, M.; Perez, I.; Manterola, L.; Lawrie, C.H.; Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Calvete-Candenas, J.; Unda, M.; López, J.I.; Larrinaga, G. Expression and activity of angiotensin-regulating enzymes is associated with prognostic outcome in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Yang, Y.; Song, R.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Ma, Q.; Yang, L.; Meng, R.; Tao, T.; Wang, S.; et al. 5 Ang-(1-7) promotes the migration and invasion of human renal cell carcinoma cells via Mas-mediated AKT signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, P.; Soh, H.J.; Chen, C.H.; Saxena, R.; Amin, S.; Naughton, M.; Joslin, P.N.; Moore, A.; Bakouny, Z.; O’Callaghan, C.; et al. ACE2 abrogates tumor resistance to VEGFR inhibitors suggesting angiotensin-(1-7) as a therapy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabc0170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczuk, P.; Trzcinska-Danielewicz, J.; Koperski, L.; Girstun, A.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A. Angiotensin-(1-7) can promote cell migration and tumor growth of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 73, 715–724. [Google Scholar]
- Lautner, R.Q.; Villela, D.C.; Fraga-Silva, R.A.; Silva, N.; Verano-Braga, T.; Costa-Fraga, F.; Jankowski, J.; Jankowski, V.; Sousa, F.; Alzamora, A.; et al. Discovery and characterization of alamandine: A novel component of the renin-angiotensin system. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleifenbaum, J. Alamandine and its receptor MrgD pair up to join the protective arm of the renin-angiotensin system. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Hong, Q.; Xie, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, Y. Alamandine/MrgD axis prevents TGF-β1-mediated fibroblast activation via regulation of aerobic glycolysis and mitophagy. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Uno, M.; Kaneta, Y.; Fukuchi, K.; Nishigohri, H.; Hasegawa, J.; Komori, H.; Takeda, S.; Enomoto, K.; Nara, F.; et al. MRGD, a MAS-related G-protein coupled receptor, promotes tumorigenesis and is highly expressed in lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, T.; Zhang, X.; Dang, Y.; Gan, T.; Chen, G. Expression and clinical contribution of MRGD mRNA in non-small cell lung cancers. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2015, 20, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, F.A.; Rodrigues-Ribeiro, L.; Melo-Braga, M.N.; Passos-Silva, D.G.; Sampaio, W.O.; Gorshkov, V.; Kjeldsen, F.; Verano-Braga, T.; Santos, R.A.S. Phosphoproteomic studies of alamandine signaling in CHO-MrgD and human pancreatic carcinoma cells: An antiproliferative effect is unveiled. Proteomics 2022, 22, e2100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrinaga, G.; Valdivia, A.; Arrieta-Aguirre, I.; Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Ugalde-Olano, A.; Loizaga-Iriarte, A.; Santos-Martín, A.; Pérez-Fernández, A.; Angulo, J.C.; López, J.I. The Expression of alamandine receptor MrgD in clear cell renal cell carcinoma is associated with a worse prognosis and unfavorable response to antiangiogenic therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, J.C.; Larrinaga, G.; Lecumberri, D.; Iturregui, A.M.; Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Lawrie, C.H.; Armesto, M.; Dorado, J.F.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; Pulido, R.; et al. Predicting survival of metastatic clear cell renal cell cancer treated with VEGFR-TKI-based sequential therapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, S.B.; Byrd, D.R.; Compton, C.C.; Fritz, A.G.; Greene, F.L.; Trotti, A. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Assayag, J.; Kim, C.; Chu, H.; Webster, J. The prognostic value of Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status on overall survival among patients with metastatic prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1194718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajewski, K.M.; Nishino, M.; Ramaiya, N.H.; Choueiri, T.K. RECIST 1.1 compared with RECIST 1.0 in patients with ad-vanced renal cell carcinoma receiving vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W282–W288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.D.; Shah, S.N.; Rini, B.I.; Lieber, M.L.; Remer, E.M. Morphology, Attenuation, Size, and Structure (MASS) criteria: Assessing response and predicting clinical outcome in metastatic renal cell carcinoma on antiangiogenic targeted therapy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Human Protein Atlas. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000172938-MRGPRD/cancer/renal+cancer#IHC (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Fedchenko, N.; Reifenrath, J. Different approaches for interpretation and reporting of immunohistochemistry analysis results in the bone tissue—A review. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armesto, M.; Nemours, S.; Arestín, M.; Bernal, I.; Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Manrique, M.; Basterretxea, L.; Larrinaga, G.; Angulo, J.C.; Lecumberri, D.; et al. Identification of miRNAs and Their Target Genes Associated with Sunitinib Resistance in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 5, 6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Yang, X. Systemic immune-inflammation index is a promising noninvasive marker to predict survival of lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.G.; Booth, C.M.; Eisenhauer, E.A. Disease-free survival as an end-point in the treatment of solid tumours -perspectives from clinical trials and clinical practice. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2298–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, C.; Laruelle, A.; Rocha, A.; López, J.I. Convergent insights into intratumor heterogeneity. Trends Cancer 2024, 10, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Echevarría, E.; Unda, M.; Loizaga-Iriarte, A.; Pérez-Fernández, A.; Angulo, J.C.; López, J.I.; Larrinaga, G. Clinical implications of (Pro)renin Receptor (PRR) expression in renal tumours. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahma, O.E.; Hodi, F.S. The Intersection between Tumor Angiogenesis and Immune Suppression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5449–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinter, M.; Jain, R.K. Targeting the renin-angiotensin system to improve cancer treatment: Implications for immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Okuyama, R.; Kawakami, Y. Renin-angiotensin system in the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1277, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Gao, W.; Miao, J.; Xu, Z.; Sun, L. Alamandine, a derivative of angiotensin-(1-7), alleviates sepsis-associated renal inflammation and apoptosis by inhibiting the PI3K/Ak and MAPK pathways. Peptides 2021, 146, 170627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysocki, J.; Ye, M.; Soler, M.J.; Gurley, S.B.; Xiao, H.D.; Bernstein, K.E.; Coffman, T.M.; Chen, S.; Batlle, D. ACE and ACE2 activity in diabetic mice. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2132–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavina Mikusic, N.L.; Silva, M.G.; Erra Díaz, F.A.; Pineda, A.M.; Ferragut, F.; Gómez, K.A.; Mazzitelli, L.; Gonzalez Maglio, D.H.; Nuñez, M.; Santos, R.A.S.; et al. Alamandine, a protective component of the renin-angiotensin system, reduces cellular proliferation and interleukin-6 secretion in human macrophages through MasR-MrgDR heteromerization. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 229, 116480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Nishimura, S.; Fukuchi, K.; Kaneta, Y.; Oda, Y.; Komori, H.; Takeda, S.; Haga, T.; Agatsuma, T.; Nara, F. Identification of physiologically active substances as novel ligands for MRGPRD. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 816159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Van Theemsche, K.M.; Van Remoortel, S.; Snyders, D.J.; Labro, A.J.; Timmermans, J.P. Constitutive, basal, and β-alanine-mediated activation of the human Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor D induces release of the inflammatory cytokine IL-6 and is dependent on NF-κB signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variables | n = 132 |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| ≤60 years | 69 |
| >60 years | 63 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 93 |
| Female | 39 |
| Fuhrman grade | |
| Low (G1–G2) | 32 |
| High (G3–G4) | 100 |
| Diameter | |
| ≤7 cm | 44 |
| >7 cm | 88 |
| Local invasion (pT) | |
| Organ-confined (pT1–pT2) | 33 |
| Not confined (pT3–pT4) | 99 |
| Lymph node invasion (N) | |
| No | 112 |
| Yes | 20 |
| Metastasis (M) | |
| Metachronous | 81 |
| Synchronous | 51 |
| NCCN 2010 Stage | |
| Stage I-II | 25 |
| Stage III-IV | 107 |
| ECOG (*) | |
| Preserved function (ECOG 0) | 111 |
| Reduced function (ECOG 1-2) | 21 |
| IMDC (*) | |
| Favorable/Intermediate | 120 |
| Unfavorable | 12 |
| OS | 1 year | 2 years | 3 years | 4 years | 5 years | 8 years | 10 years | 15 years |
| Log-rank p= | 0.83 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.009 | 0.01 | 0.003 |
| DFS | 1 year | 2 years | 3 years | 4 years | 5 years | 8 years | 10 years | 15 years |
| Log-rank p= | 0.01 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.0009 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 |
| Cox Regression Model | 10-Year Overall Survival | 10-Year Disease-Free Survival | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | p | HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | |
| Univariate analysis | Sex | 0.22 | 0.78 | 0.52–1.16 | 0.7 | 1.11 | 0.66–1.86 |
| Age | 0.007 | 1.66 | 1.15–2.4 | 0.049 | 1.58 | 1–2.5 | |
| Grade | 0.002 | 1.99 | 1.28–3.1 | 0.001 | 2.34 | 1.42–3.86 | |
| pT | <0.001 | 2.26 | 1.43–3.55 | 0.001 | 2.32 | 1.38–3.89 | |
| N | <0.001 | 2.86 | 1.79–4.57 | 0.003 | 3.12 | 1.46–6.69 | |
| M | <0.001 | 3.12 | 2.14–4.55 | - | - | - | |
| ECOG | 0.005 | 1.91 | 1.21–3 | - | - | - | |
| IMDC | <0.001 | 4.15 | 2.35–7.33 | - | - | - | |
| MASS | <0.001 | 2.98 | 2.06–4.32 | - | - | - | |
| RECIST | <0.001 | 3.23 | 2.23–4.69 | - | - | - | |
| MrgD | 0.011 | 1.68 | 1.12–2.51 | 0.001 | 2.49 | 1.48–4.2 | |
| Multivariate analysisFinal step of Wald method | Age | 0.013 | 1.66 | 1.11–2.48 | 0.001 | 2.56 | 1.53–4.28 |
| Grade | 0.038 | 1.68 | 1.03–2.75 | 0.001 | 2.54 | 1.45–4.44 | |
| pT | 0.05 | 1.7 | 1–2.89 | 0.011 | 2.14 | 1.19–3.86 | |
| M | 0.001 | 2.28 | 1.51–3.45 | - | - | - | |
| IMDC | 0.003 | 2.7 | 1.42–5.14 | - | - | - | |
| MASS | 0.001 | 3.24 | 2.15–4.88 | - | - | - | |
| MrgD | - | - | - | 0.049 | 1.76 | 1–3.03 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larrinaga, G.; Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Arrieta-Aguirre, I.; Valdivia, A.; Lecumberri, D.; Iturregui, A.M.; Lawrie, C.H.; Armesto, M.; Dorado, J.F.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; et al. Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications of Alamandine Receptor MrgD Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with Development of Metastatic Disease. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030387
Larrinaga G, Solano-Iturri JD, Arrieta-Aguirre I, Valdivia A, Lecumberri D, Iturregui AM, Lawrie CH, Armesto M, Dorado JF, Nunes-Xavier CE, et al. Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications of Alamandine Receptor MrgD Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with Development of Metastatic Disease. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030387
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarrinaga, Gorka, Jon Danel Solano-Iturri, Inés Arrieta-Aguirre, Asier Valdivia, David Lecumberri, Ane Miren Iturregui, Charles H. Lawrie, María Armesto, Juan F. Dorado, Caroline E. Nunes-Xavier, and et al. 2025. "Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications of Alamandine Receptor MrgD Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with Development of Metastatic Disease" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030387
APA StyleLarrinaga, G., Solano-Iturri, J. D., Arrieta-Aguirre, I., Valdivia, A., Lecumberri, D., Iturregui, A. M., Lawrie, C. H., Armesto, M., Dorado, J. F., Nunes-Xavier, C. E., Pulido, R., López, J. I., & Angulo, J. C. (2025). Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications of Alamandine Receptor MrgD Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with Development of Metastatic Disease. Biomolecules, 15(3), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030387









