The Future of Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment: Combination Therapy (Polypill) or Biomarker-Guided Personalized Intervention?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
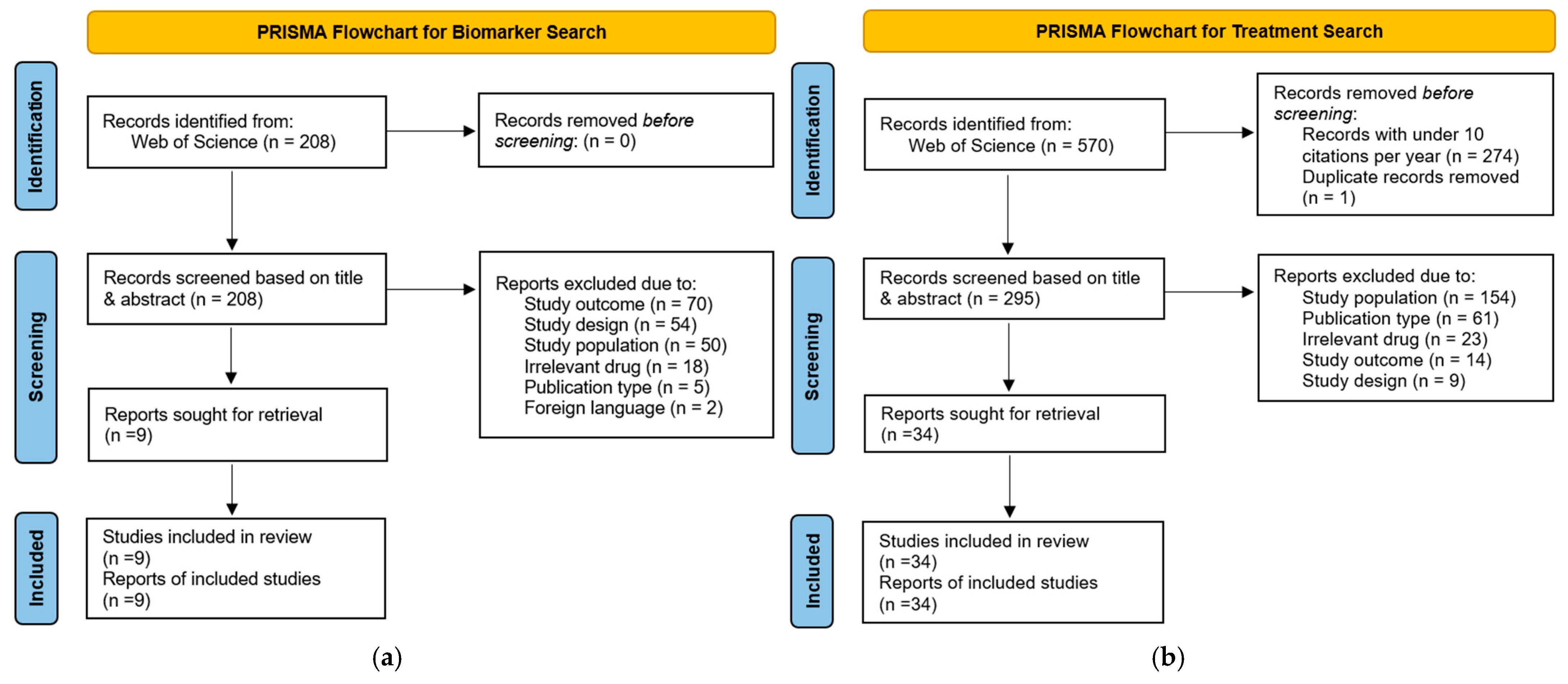
3. Results
3.1. Therapeutic Landscape of CKD Management
3.1.1. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
3.1.2. Non-Steroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists (ns-MRAs)
3.1.3. Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitors (ASIs)
3.1.4. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors
3.1.5. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RA)
3.1.6. Endothelin Receptor Antagonists (ERA)
3.2. Combination Therapy Approaches
3.2.1. Latest Evidence
3.2.2. Advantages & Disadvantages of Combination Therapy
3.3. Biomarker-Guided Interventions
3.3.1. Urinary Peptide Signatures for Predicting Treatment Response
3.3.2. Immune System Related Biomarkers
3.3.3. Additional Predictors of Kidney Outcomes
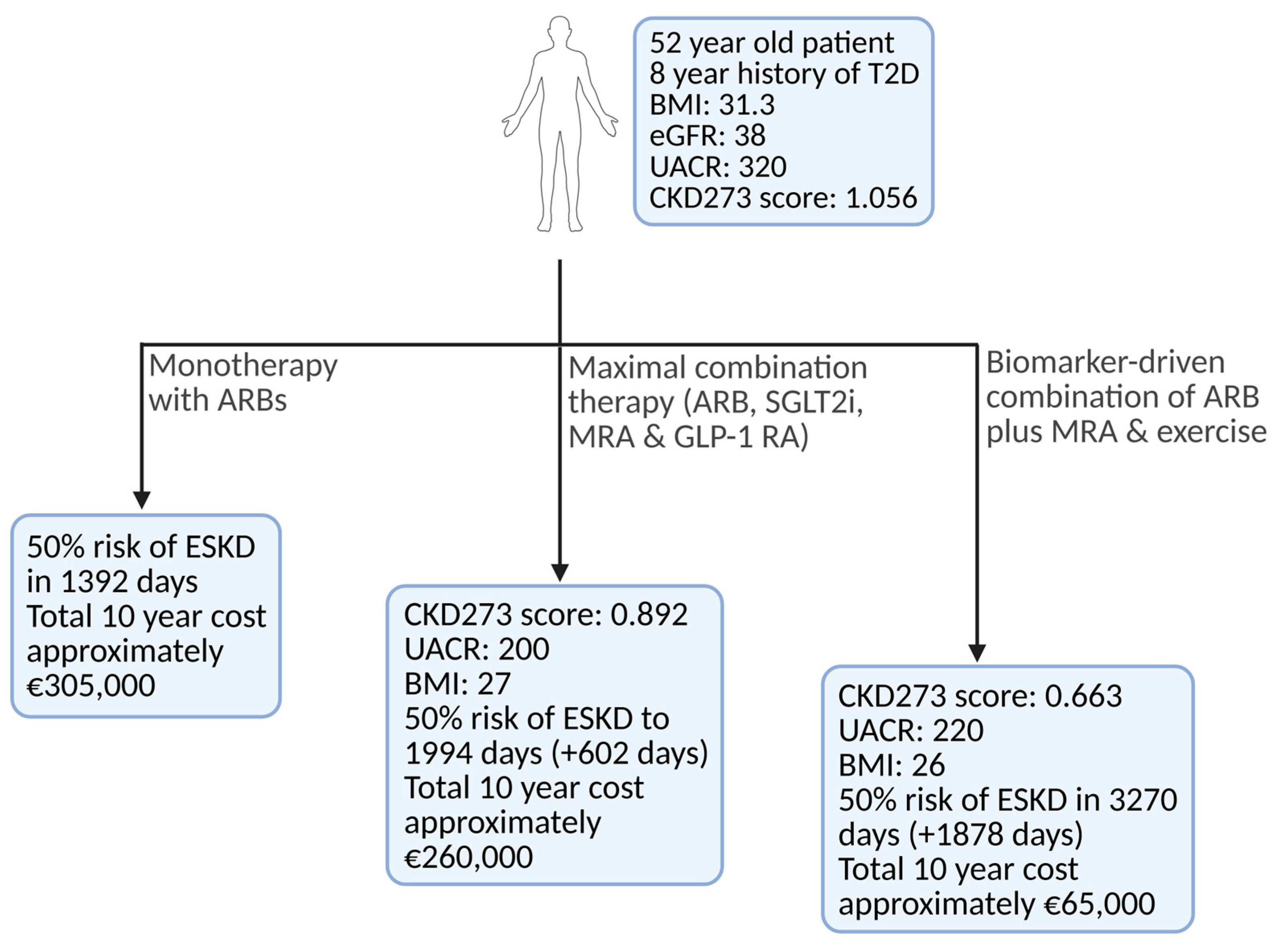
3.3.4. Future Directions and Clinical Implications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| Ang II | Angiotensin II |
| ARB | Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| CAD160 | Coronary Artery Disease classifier with 160 peptides |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| CKD273 | Chronic Kidney Disease classifier with 273 peptides |
| CR | Complete Remission |
| CYC | Cyclophosphamide |
| DKD | Diabetic Kidney Disease |
| DPP4i | Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (mL/min/1.73 m2) |
| ERA | Endothelin Receptor Antagonist |
| ESKD | End-Stage Kidney Disease |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FSGS | Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis |
| GLP-1RA | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist |
| HF | Heart Failure |
| HF2 | Heart Failure classifier version 2 |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| IFTA | Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy |
| IgA | Immunoglobulin A |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| K+ | Potassium |
| KFRE | Kidney Failure Risk Equation |
| KRT | Kidney Replacement Therapy |
| MACE | Major Adverse Cardiovascular Event |
| MAKE | Major Adverse Kidney Event |
| MCD | Minimal Change Disease |
| MesGN | Mesangial Glomerulonephritis |
| MI | Myocardial Infarction |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| MPA | Microscopic Polyangiitis |
| MPGN | Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis |
| NFKB | Nuclear Factor Kappa B |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| NS | Nephrotic Syndrome |
| ns-MRA | Non-steroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| pMN | Primary Membranous Nephropathy |
| PLN | Proliferative Lupus Nephritis |
| PLR | Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| PR | Partial Remission |
| Q1 | First Quintile |
| Q5 | Fifth Quintile |
| QALYs | Quality-Adjusted Life Years |
| RAAS | Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System |
| RASi | Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitor |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| RTX | Rituximab |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 |
| SGLT2i | Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor |
| sIL-2R | Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor |
| SLE | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| SRNS | Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome |
| T2D | Type 2 Diabetes |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| TIN | Tubulointerstitial Nephritis |
| UACR | Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (mg/g) |
| uProt | Urinary Protein |
| WNT-β | Wnt/β-catenin signaling |
Appendix A
Search Queries
References
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.; James, M.; Wiebe, N.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Manns, B.; Klarenbach, S.; Tonelli, M. Cause of Death in Patients with Reduced Kidney Function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2015, 26, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, C.J.; Wanner, C.; Luyckx, V.; Stevens, K.; Cerqueira, S.; Darwish, R.; Fernandez Fernandez, B.; Fiel, D.; Filev, R.; Grieger, M.; et al. ABCDE to Identify and Prevent Chronic Kidney Disease: A Call to Action. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2025, 1–13, gfaf057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolpe, S.; Kowall, B.; Scholz, C.; Stang, A.; Blume, C. High Unawareness of Chronic Kidney Disease in Germany. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, A.; Harhay, M.N.; Ong, A.C.M.; Tummalapalli, S.L.; Ortiz, A.; Fogo, A.B.; Fliser, D.; Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Fontana, M.; Nangaku, M.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease and the Global Public Health Agenda: An International Consensus. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.K.; Knicely, D.H.; Grams, M.E. Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and Management: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Ahmed, S.B.; Carrero, J.J.; Foster, B.; Francis, A.; Hall, R.K.; Herrington, W.G.; Hill, G.; Inker, L.A.; Kazancıoğlu, R.; et al. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Al-Ghamdi, S.M.G.; Li, G.; Wu, M.-S.; Stafylas, P.; Retat, L.; Card-Gowers, J.; Barone, S.; Cabrera, C.; Garcia Sanchez, J.J. Global Economic Burden Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Pragmatic Review of Medical Costs for the Inside CKD Research Programme. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 4405–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Neumiller, J.J.; Tuttle, K.R. Combination Therapy: An Upcoming Paradigm to Improve Kidney and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2025, 40, i3–i17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasson, A.N.; Cherney, D.Z. Renal Hyperfiltration Related to Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity in Human Disease. World J. Diabetes 2012, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patera, F.; Gatticchi, L.; Cellini, B.; Chiasserini, D.; Reboldi, G. Kidney Fibrosis and Oxidative Stress: From Molecular Pathways to New Pharmacological Opportunities. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.-Y.; Liu, X.-S.; Huang, X.-R.; Yu, X.-Q.; Lan, H.-Y. Diverse Role of TGF-β in Kidney Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plonsky-Toder, M.; Magen, D.; Pollack, S. Innate Immunity and CKD: Is There a Significant Association? Cells 2023, 12, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mina, I.K.; Iglesias-Martinez, L.F.; Ley, M.; Fillinger, L.; Perco, P.; Siwy, J.; Mischak, H.; Jankowski, V. Investigation of the Urinary Peptidome to Unravel Collagen Degradation in Health and Kidney Disease. Proteomics 2024, 1–13, e202400279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Fu, P.; Ma, L. Kidney Fibrosis: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Medicines. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Keane, W.F.; Mitch, W.E.; Parving, H.H.; Remuzzi, G.; Snapinn, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Shahinfar, S.; et al. Effects of Losartan on Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Clarke, W.R.; Berl, T.; Pohl, M.A.; Lewis, J.B.; Ritz, E.; Atkins, R.C.; Rohde, R.; Raz, I.; et al. Renoprotective Effect of the Angiotensin-Receptor Antagonist Irbesartan in Patients with Nephropathy Due to Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ONTARGET Investigators; Yusuf, S.; Teo, K.K.; Pogue, J.; Dyal, L.; Copland, I.; Schumacher, H.; Dagenais, G.; Sleight, P.; Anderson, C. Telmisartan, Ramipril, or Both in Patients at High Risk for Vascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Kolkhof, P.; Bakris, G.; Bauersachs, J.; Haller, H.; Wada, T.; Zannad, F. Steroidal and Non-Steroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Cardiorenal Medicine. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Chan, J.C.; Cooper, M.E.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Haller, H.; Remuzzi, G.; Rossing, P.; Schmieder, R.E.; Nowack, C.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Albuminuria in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2015, 314, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, B.; Filippatos, G.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Bakris, G.L.; Rossing, P.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; et al. Cardiovascular Events with Finerenone in Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2252–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Anker, S.D.; Rossing, P.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Gebel, M.; Ruilope, L.M.; et al. Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes with Finerenone in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: The FIDELITY Pooled Analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippatos, G.; Anker, S.D.; Agarwal, R.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G.L.; Tasto, C.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Lage, A.; et al. Finerenone Reduces Risk of Incident Heart Failure in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: Analyses From the FIGARO-DKD Trial. Circulation 2022, 145, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafidis, P.; Agarwal, R.; Pitt, B.; Wanner, C.; Filippatos, G.; Boletis, J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Toto, R.; et al. Outcomes with Finerenone in Participants with Stage 4 CKD and Type 2 Diabetes: A FIDELITY Subgroup Analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Ruilope, L.M.; Anker, S.D.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Rossing, P.; Fried, L.; Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Sarafidis, P.; Ahlers, C.; et al. A Prespecified Exploratory Analysis from FIDELITY Examined Finerenone Use and Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, P.; Filippatos, G.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Chan, J.C.N.; Kooy, A.; McCafferty, K.; Schernthaner, G.; et al. Finerenone in Predominantly Advanced CKD and Type 2 Diabetes with or Without Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Therapy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Tu, W.; Farjat, A.E.; Farag, Y.M.K.; Toto, R.; Kaul, S.; Lawatscheck, R.; Rohwedder, K.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Impact of Finerenone-Induced Albuminuria Reduction on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: A Mediation Analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruilope, L.M.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Rossing, P.; Sarafidis, P.; Schmieder, R.E.; Joseph, A.; Rethemeier, N.; et al. Blood Pressure and Cardiorenal Outcomes with Finerenone in Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes. Hypertension 2022, 79, 2685–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Vaduganathan, M.; Claggett, B.; Jhund, P.S.; Desai, A.S.; Henderson, A.D.; Lam, C.S.P.; Pitt, B.; Senni, M.; et al. Finerenone in Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Filippatos, G.; Claggett, B.L.; Desai, A.S.; Jhund, P.S.; Henderson, A.; Brinker, M.; Kolkhof, P.; Schloemer, P.; Lay-Flurrie, J.; et al. Finerenone in Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease with Type 2 Diabetes: FINE-HEART Pooled Analysis of Cardiovascular, Kidney and Mortality Outcomes. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 3758–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Pitt, B.; Palmer, B.F.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Burgess, E.; Filippatos, G.; Malyszko, J.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossignol, P.; Rossing, P.; et al. A Comparative Post Hoc Analysis of Finerenone and Spironolactone in Resistant Hypertension in Moderate-to-Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Rossignol, P.; Romero, A.; Garza, D.; Mayo, M.R.; Warren, S.; Ma, J.; White, W.B.; Williams, B. Patiromer vs. Placebo to Enable Spironolactone Use in Patients with Resistant Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease (AMBER): A Phase 2, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2019, 394, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-Z.; Bao, W.; Zheng, Q.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Sun, L.-Y. Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 819327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, S.B.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Desai, N.R.; Guo, L.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Pantalone, K.M.; Wanner, C.; Hamacher, S.; Fatoba, S.T.; Horvat-Broecker, A.; et al. First Interim Results from FINE-REAL: A Prospective, Non-Interventional, Phase 4 Study Providing Insights into the Use and Safety of Finerenone in a Routine Clinical Setting. J. Nephrol. 2024, 37, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail, N. Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitors for Treatment of Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease. Arch. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 6, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Hauske, S.J.; Canziani, M.E.; Caramori, M.L.; Cherney, D.; Cronin, L.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Hugo, C.; Nangaku, M.; Rotter, R.C.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Aldosterone Synthase Inhibition with and without Empagliflozin for Chronic Kidney Disease: A Randomised, Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet 2024, 403, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, P.K.; Tuttle, K.R.; Staplin, N.; Hauske, S.J.; Zhu, D.; Sardell, R.; Cronin, L.; Green, J.B.; Agrawal, N.; Arimoto, R.; et al. The Potential for Improving Cardio-Renal Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease with the Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitor Vicadrostat (BI 690517): A Rationale for the EASi-KIDNEY Trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2024, 40, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Jardine, M.J.; Oshima, M.; Hockham, C.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Schutte, A.E.; Arnott, C.; Chang, T.I.; et al. Blood Pressure Effects of Canagliflozin and Clinical Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: Insights from the CREDENCE Trial. Circulation 2021, 143, 1735–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Langkilde, A.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Sjostrom, C.D.; Stefansson, B.V.; Toto, R.D.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin on the Rate of Decline in Kidney Function in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease with and without Type 2 Diabetes: A Prespecified Analysis from the DAPA-CKD Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Toto, R.D.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Correa-Rotter, R.; et al. A Pre-Specified Analysis of the DAPA-CKD Trial Demonstrates the Effects of Dapagliflozin on Major Adverse Kidney Events in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Jongs, N.; Stefansson, B.V.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Langkilde, A.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Rossing, P.; Nowicki, M.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Dapagliflozin in Patients with Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis: A Prespecified Analysis of the Dapagliflozin and Prevention of Adverse Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease (DAPA-CKD) Trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2022, 37, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongs, N.; Greene, T.; Chertow, G.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Langkilde, A.M.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Sjostrom, C.D.; Stefansson, B.V.; Toto, R.D.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin on Urinary Albumin Excretion in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease with and without Type 2 Diabetes: A Prespecified Analysis from the DAPA-CKD Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, P.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Vart, P.; Jongs, N.; Docherty, K.F.; Jhund, P.S.; Kober, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease or Heart Failure: Pooled Analysis of the DAPA-CKD and DAPA-HF Trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The, E.-K.C.G.; Herrington, W.G.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.B.; Hauske, S.J.; Emberson, J.R.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K.J.; et al. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Charbonnel, B.; Cosentino, F.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; McGuire, D.K.; Pratley, R.; Shih, W.J.; Frederich, R.; Maldonado, M.; Pong, A.; et al. Effects of Ertugliflozin on Kidney Composite Outcomes, Renal Function and Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Analysis from the Randomised VERTIS CV Trial. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Ferrannini, E.; Umpierrez, G.E.; Peters, A.L.; Rosenstock, J.; Powell, D.R.; Davies, M.J.; Banks, P.; Agarwal, R. Efficacy and Safety of Sotagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Stage 3 Chronic Kidney Disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 1646–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasu, H.; Yano, Y.; Kanegae, H.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Nangaku, M.; Hirakawa, Y.; Sugawara, Y.; Nakagawa, N.; Tani, Y.; Wada, J.; et al. Kidney Outcomes Associated with SGLT2 Inhibitors vs. Other Glucose-Lowering Drugs in Real-World Clinical Practice: The Japan Chronic Kidney Disease Database. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, Y.H.; Teo, Y.N.; Syn, N.L.; Kow, C.S.; Yoong, C.S.Y.; Tan, B.Y.Q.; Yeo, T.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Lin, W.; Sia, C.-H. Effects of Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Outcomes in Patients Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized-Controlled Trials. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, S.; Rossini, A.; Poli, R.; Dughera, F.; Pia, A.; Terzolo, M.; Reimondo, G. Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 738848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, M.; Jardine, M.J.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Cannon, C.P.; Charytan, D.M.; de Zeeuw, D.; Edwards, R.; Greene, T.; Levin, A.; et al. Insights from CREDENCE Trial Indicate an Acute Drop in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate during Treatment with Canagliflozin with Implications for Clinical Practice. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Langkilde, A.M.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Kashihara, N.; Rossing, P.; Sjostrom, C.D.; Stefansson, B.V.; et al. Correlates and Consequences of an Acute Change in eGFR in Response to the SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin in Patients with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 2094–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Clinical Implications of an Acute Dip in eGFR after SGLT2 Inhibitor Initiation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2021, 16, 1278–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.-H.; Tang, Y.-S.; Chen, J.-Y.; Pan, H.-C.; Liao, H.-W.; Chu, W.-K.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Wu, V.-C.; Heung, M. Abrupt Decline in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate after Initiating Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Predicts Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, P.; Boyce, R.; Sanchez, J.J.G.; Sjostrom, C.D.; Stefansson, B.; Nolan, S.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Chertow, G.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; et al. Extrapolated Longer-Term Effects of the DAPA-CKD Trial: A Modelling Analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2023, 38, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Tuttle, K.R.; Rossing, P.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.E.; Bakris, G.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Idorn, T.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Lausvig, N.L.; et al. Effects of Semaglutide on Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Ørsted, D.D.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Marso, S.P.; Poulter, N.R.; Rasmussen, S.; Tornøe, K.; Zinman, B.; Buse, J.B. Liraglutide and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Buse, J.B.; Idorn, T.; Leiter, L.A.; Pratley, R.E.; Rasmussen, S.; Vilsboll, T.; Wolthers, B.; Perkovic, V. Potential Kidney Protection with Liraglutide and Semaglutide: Exploratory Mediation Analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G.; Belmar, N.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Busch, R.; Charytan, D.M.; Hadjadj, S.; Gillard, P.; Gorriz, J.L.; et al. Effects of Semaglutide with and without Concomitant SGLT2 Inhibitor Use in Participants with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease in the FLOW Trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2849–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, P.; Caramori, M.L.; Chan, J.C.N.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Hurst, C.; Khunti, K.; Liew, A.; Michos, E.D.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Olowu, W.A.; et al. Executive Summary of the KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update Based on Rapidly Emerging New Evidence. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, D.E.; Pollock, D.M. Endothelin Antagonists for Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Parving, H.-H.; Andress, D.L.; Bakris, G.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Hou, F.-F.; Kitzman, D.W.; Kohan, D.; Makino, H.; McMurray, J.J.V.; et al. Atrasentan and Renal Events in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease (SONAR): A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2019, 393, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Alpers, C.E.; Barratt, J.; Bieler, S.; Diva, U.; Inrig, J.; Komers, R.; Mercer, A.; Noronha, I.L.; et al. Sparsentan in Patients with IgA Nephropathy: A Prespecified Interim Analysis from a Randomised, Double-Blind, Active-Controlled Clinical Trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, Y.Y. Sparsentan: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.B.; Mottl, A.K.; Bakris, G.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Mann, J.F.E.; McGill, J.B.; Nangaku, M.; Rossing, P.; Scott, C.; Gay, A.; et al. Design of the COmbinatioN Effect of FInerenone anD EmpaglifloziN in Participants with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Using a UACR Endpoint Study (CONFIDENCE). Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2023, 38, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, P.; Anker, S.D.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; McGill, J.B.; Rosas, S.E.; Joseph, A.; Gebel, M.; et al. Finerenone in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes by Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Treatment: The FIDELITY Analysis. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2991–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuen, B.L.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Vart, P.; Claggett, B.L.; Fletcher, R.A.; Arnott, C.; de Oliveira Costa, J.; Falster, M.O.; Pearson, S.A.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Estimated Lifetime Cardiovascular, Kidney, and Mortality Benefits of Combination Treatment with SGLT2 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, and Nonsteroidal MRA Compared with Conventional Care in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Albuminuria. Circulation 2024, 149, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, M.; Puchades, M.J.; Garofalo, C.; Jongs, N.; D’Marco, L.; Andreucci, M.; De Nicola, L.; Gorriz, J.L.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; ROTATE-3 Study Group; et al. Albuminuria-Lowering Effect of Dapagliflozin, Eplerenone, and Their Combination in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Randomized Crossover Clinical Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, M.; Jongs, N.; Vart, P.; Stefansson, B.V.; Chertow, G.M.; Langkilde, A.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Sjostrom, C.D.; et al. The Kidney Protective Effects of the Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor, Dapagliflozin, Are Present in Patients with CKD Treated with Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossing, P.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Amod, A.; Marre, M.; Joseph, A.; Lage, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes by GLP-1RA Treatment: A Subgroup Analysis from the FIDELIO-DKD Trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Kohan, D.E.; de Zeeuw, D. New Insights from SONAR Indicate Adding Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors to an Endothelin Receptor Antagonist Mitigates Fluid Retention and Enhances Albuminuria Reduction. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Kiyosue, A.; Wheeler, D.C.; Lin, M.; Wijkmark, E.; Carlson, G.; Mercier, A.K.; Astrand, M.; Ueckert, S.; Greasley, P.J.; et al. Zibotentan in Combination with Dapagliflozin Compared with Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (ZENITH-CKD): A Multicentre, Randomised, Active-Controlled, Phase 2b, Clinical Trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 2004–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, P.; Pais, P.; Dans, A.L.; Bosch, J.; Xavier, D.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Yusoff, K.; Santoso, A.; Talukder, S.; Gamra, H.; et al. The International Polycap Study-3 (TIPS-3): Design, Baseline Characteristics and Challenges in Conduct. Am. Heart J. 2018, 206, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshandel, G.; Khoshnia, M.; Poustchi, H.; Hemming, K.; Kamangar, F.; Gharavi, A.; Ostovaneh, M.R.; Nateghi, A.; Majed, M.; Navabakhsh, B.; et al. Effectiveness of Polypill for Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases (PolyIran): A Pragmatic, Cluster-Randomised Trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, J.M.; Pocock, S.J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Quesada, A.J.; Owen, R.; Fernandez-Ortiz, A.; Sanchez, P.L.; Ortuño, F.M.; Rodriguez, J.M.V.; Domingo-Fernández, A.; et al. Polypill Strategy in Secondary Cardiovascular Prevention. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveen, A.; Kopetz, S.; Lothe, R.A. Biomarker-Guided Therapy for Colorectal Cancer: Strength in Complexity. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhardt, M.; Persson, F.; Oxlund, C.; Jacobsen, I.A.; Zürbig, P.; Mischak, H.; Rossing, P.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Predicting Albuminuria Response to Spironolactone Treatment with Urinary Proteomics in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2018, 33, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimes Campos, M.A.; Mavrogeorgis, E.; Latosinska, A.; Eder, S.; Buchwinkler, L.; Mischak, H.; Siwy, J.; Rossing, P.; Mayer, G.; Jankowski, J. Urinary Peptide Analysis to Predict the Response to Blood Pressure Medication. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.; Beige, J.; Siwy, J.; Rudnicki, M.; Wendt, R.; Ortiz, A.; Sanz, A.B.; Mischak, H.; Reich, H.N.; Nasic, S.; et al. Dynamics of Urine Proteomics Biomarker and Disease Progression in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2023, 38, 2826–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes Campos, M.A.; Andújar, I.; Keller, F.; Mayer, G.; Rossing, P.; Staessen, J.A.; Delles, C.; Beige, J.; Glorieux, G.; Clark, A.L.; et al. Prognosis and Personalized In Silico Prediction of Treatment Efficacy in Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.; Li, J.; Neuen, B.L.; Neal, B.; Arnott, C.; Parikh, C.R.; Coca, S.G.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Yavin, Y.; et al. Effects of the SGLT2 Inhibitor Canagliflozin on Plasma Biomarkers TNFR-1, TNFR-2 and KIM-1 in the CANVAS Trial. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori-Aso, S.; Nakazawa, D.; Nishio, S.; Ueda, Y.; Eguchi, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Yoshikawa, J.; Kudo, T.; Watanabe-Kusunoki, K.; Takeda-Otera, S.; et al. Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Predicts Treatment Outcome in Patients with Autoimmune Tubulointerstitial Nephritis. A Preliminary Study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 827388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiasta, A.; Wahyudi, K.; Sribudiani, Y.; Rachmadi, D. The Level of Transforming Growth Factor Beta as a Possible Predictor of Cyclophosphamide Response in Children with Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome. BioMedicine 2021, 11, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teisseyre, M.; Cremoni, M.; Boyer-Suavet, S.; Crepin, T.; Benzaken, S.; Zorzi, K.; Esnault, V.; Brglez, V.; Seitz-Polski, B. Rituximab Immunomonitoring Predicts Remission in Membranous Nephropathy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 738788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamee, M.; Ghazi, F.; Seifi, A.; Esfandiar, N.; Mohkam, M.; Dalirani, R.; Hosseini Tabatabaei, S.M.T. Assessment of Laboratory Predictors of Steroid Response in Nephrotic Syndrome. Int. J. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 16302–16308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbuna, O.; Zimmerman, B.; Manos, G.; Fortier, A.; Chirieac, M.C.; Dakin, L.A.; Friedman, D.J.; Bramham, K.; Campbell, K.; Knebelmann, B.; et al. Inaxaplin for Proteinuric Kidney Disease in Persons with Two APOL1 Variants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsia, E.; Marinaki, S.; Michelakis, I.; Liapis, G.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Boletis, J.; Tektonidou, M.G. Predictors of Early Response, Flares, and Long-Term Adverse Renal Outcomes in Proliferative Lupus Nephritis: A 100-Month Median Follow-Up of an Inception Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, I.; Ribichini, D.; Provenzano, M.; Vetrano, D.; Aiello, V.; Cianciolo, G.; Vicennati, V.; Tomassetti, A.; Moschione, G.; Berti, S.; et al. Impact of Baseline Clinical Variables on SGLT2i’s Antiproteinuric Effect in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Life 2023, 13, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Xie, D.; Bakris, G.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Hou, F.-F.; Kitzman, D.W.; Kohan, D.; Makino, H.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Perkovic, V.; et al. Early Response in Albuminuria and Long-Term Kidney Protection during Treatment with an Endothelin Receptor Antagonist: A Prespecified Analysis from the SONAR Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2021, 32, 2900–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, G.E.; von Scholten, B.J.; Mary, S.; Flores Guerrero, J.-L.; Lindhardt, M.; Reinhard, H.; Jacobsen, P.K.; Mullen, W.; Parving, H.-H.; Mischak, H.; et al. Urinary Proteomics for Prediction of Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Microalbuminuria. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontillo, C.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Schanstra, J.P.; Jacobs, L.; Zürbig, P.; Thijs, L.; Ramírez-Torres, A.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Lindhardt, M.; Klein, R.; et al. Prediction of Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 3 by CKD273, a Urinary Proteomic Biomarker. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhardt, M.; Persson, F.; Currie, G.; Pontillo, C.; Beige, J.; Delles, C.; von der Leyen, H.; Mischak, H.; Navis, G.; Noutsou, M.; et al. Proteomic Prediction and Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibition Prevention Of Early Diabetic nephRopathy in TYpe 2 Diabetic Patients with Normoalbuminuria (PRIORITY): Essential Study Design and Rationale of a Randomised Clinical Multicentre Trial. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argilés, À.; Siwy, J.; Duranton, F.; Gayrard, N.; Dakna, M.; Lundin, U.; Osaba, L.; Delles, C.; Mourad, G.; Weinberger, K.M.; et al. CKD273, a New Proteomics Classifier Assessing CKD and Its Prognosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofte, N.; Lindhardt, M.; Adamova, K.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Beige, J.; Beulens, J.W.J.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Currie, G.; Delles, C.; Dimos, I.; et al. Early Detection of Diabetic Kidney Disease by Urinary Proteomics and Subsequent Intervention with Spironolactone to Delay Progression (PRIORITY): A Prospective Observational Study and Embedded Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Pontillo, C.; Rodríguez, M.; Zürbig, P.; Mischak, H.; Ortiz, A. Novel Urinary Biomarkers for Improved Prediction of Progressive eGFR Loss in Early Chronic Kidney Disease Stages and in High Risk Individuals Without Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critselis, E.; Vlahou, A.; Stel, V.S.; Morton, R.L. Cost-Effectiveness of Screening Type 2 Diabetes Patients for Chronic Kidney Disease Progression with the CKD273 Urinary Peptide Classifier as Compared to Urinary Albumin Excretion. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2018, 33, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latosinska, A.; Mina, I.K.; Nguyen, T.M.N.; Golovko, I.; Keller, F.; Mayer, G.; Rossing, P.; Staessen, J.A.; Delles, C.; Beige, J.; et al. In Silico Prediction of Optimal Multifactorial Intervention in CKD. medRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.C.; Wang, H.; Ang, Y.G.; Lim, C.K.; Ooi, X.Y. Cost-Effectiveness of Screening for Chronic Kidney Disease in the General Adult Population: A Systematic Review. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfad137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, M.; Leibowitz, G.; Mosenzon, O. Paving the Way to Precision Medicine for Diabetic Kidney Disease: The PRIORITY Trial. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukri, A.; Mettang, T.; Scheckel, B.; Schellartz, I.; Simic, D.; Scholten, N.; Müller, M.; Stock, S. Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis in Germany from a Health Economic View-A Propensity Score Matched Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
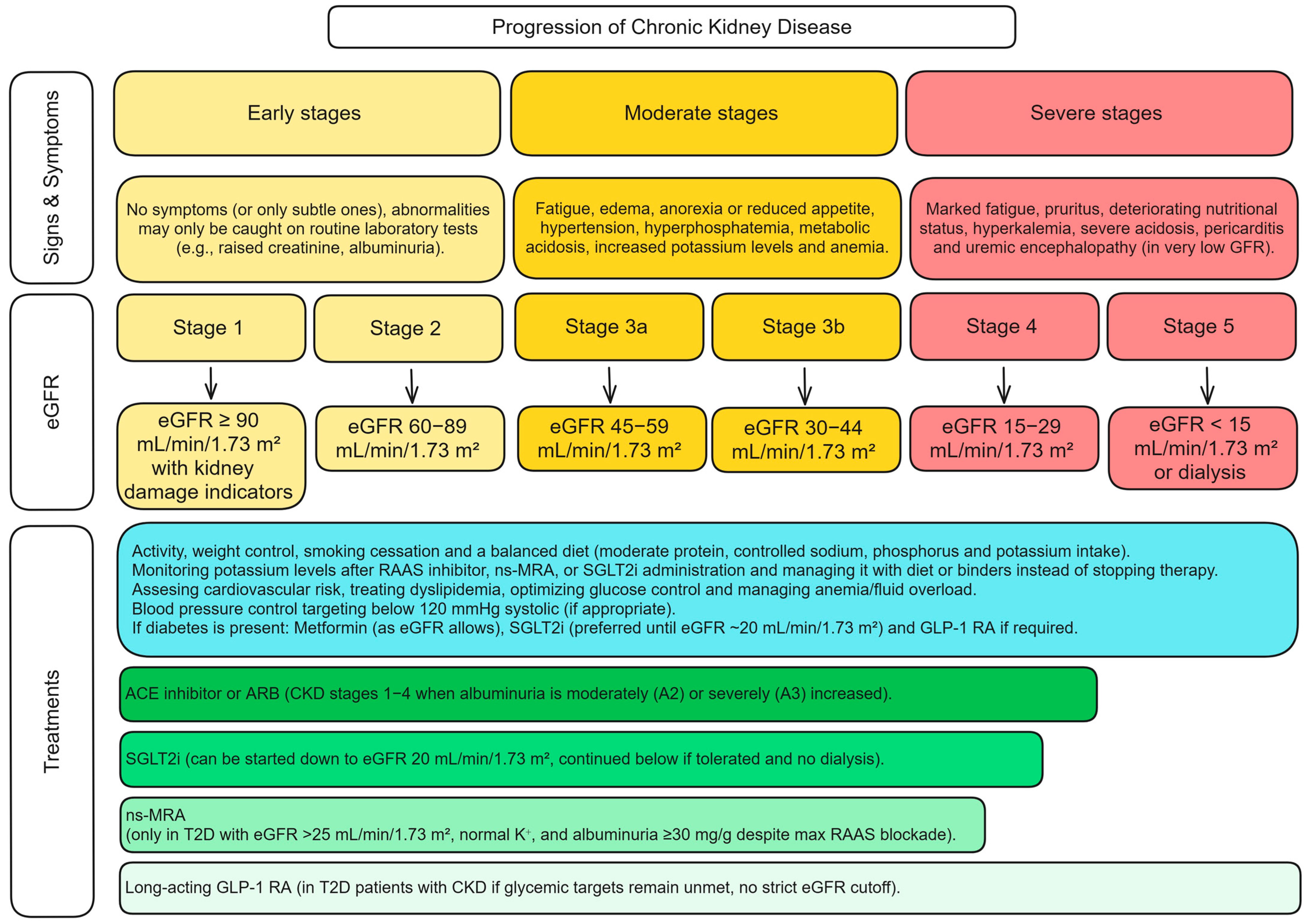
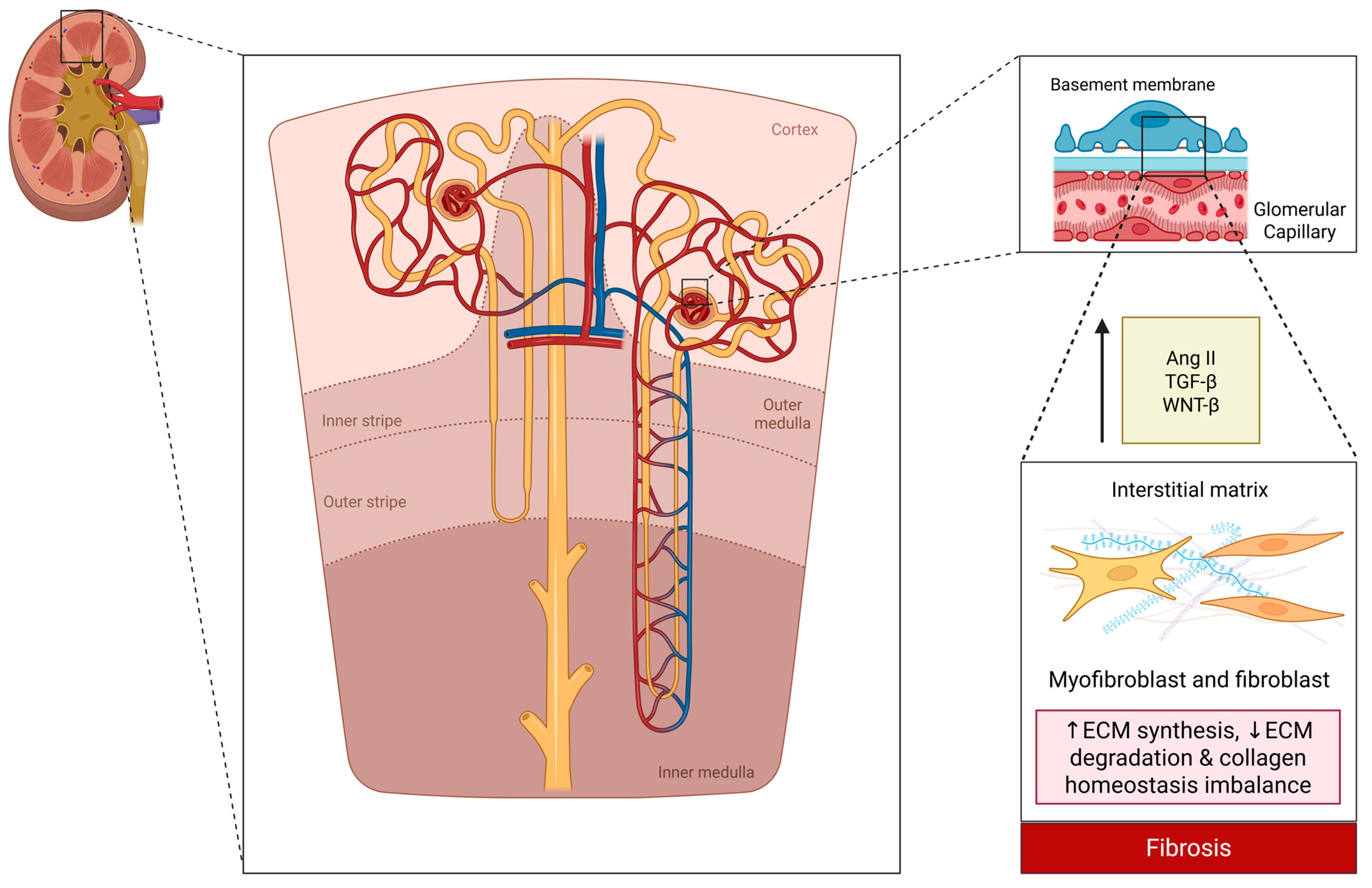
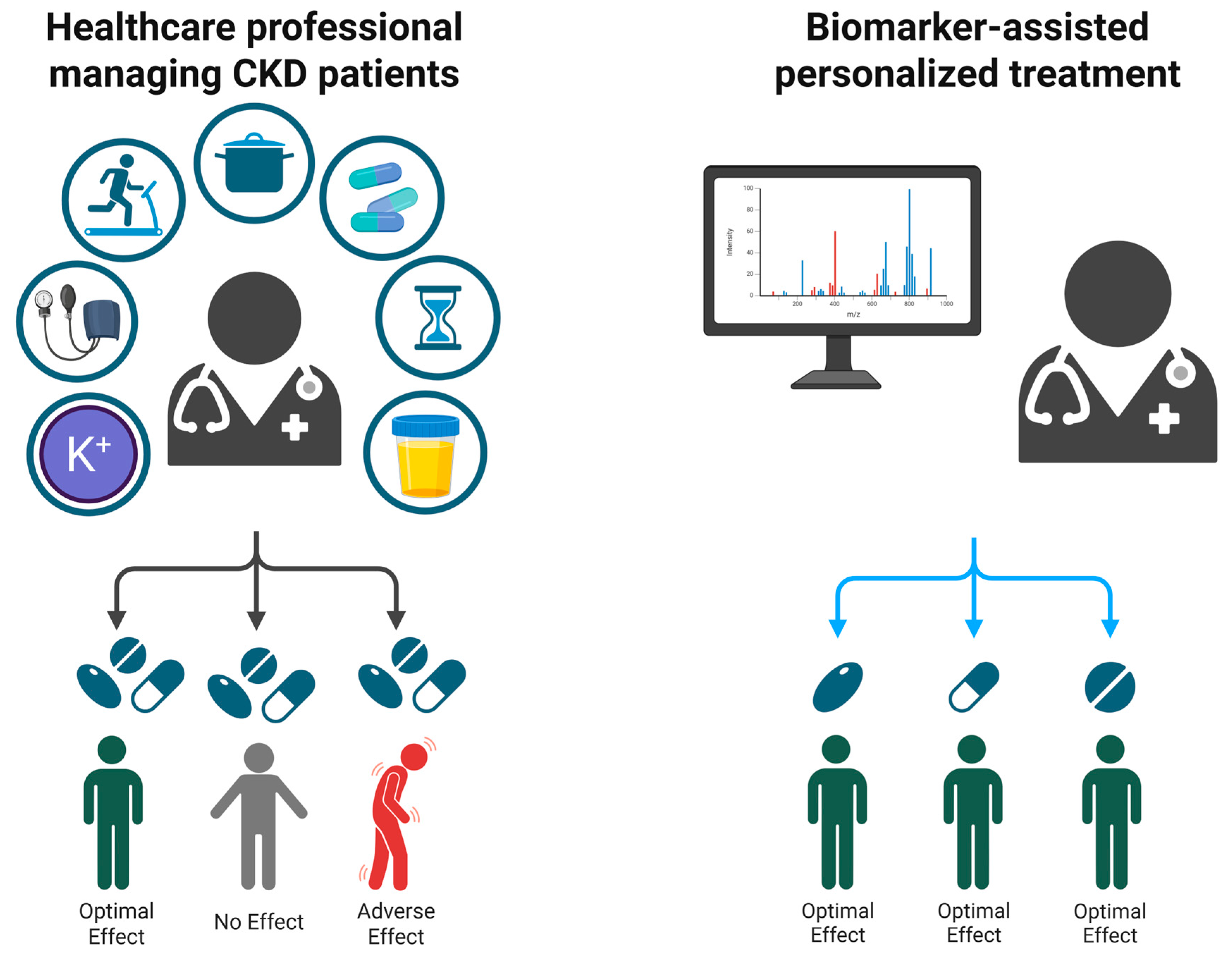
| Trial | Patients | Intervention | Key Outcome | Notable Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIDELIO-DKD (NCT02540993) [23] | 5734 individuals with T2D & CKD (eGFR 25–60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and UACR 30–300 mg/g, or eGFR 25–75 mL/min/1.73 m2 and UACR 300–5000 mg/g) | Finerenone vs. placebo (on top of RAAS blockade) | 18% risk reduction in kidney failure, ≥40% decline in eGFR, or renal death | Significant renal benefits, especially in patients with CKD and diabetes |
| FIGARO-DKD (NCT02545049) [24] | 7437 individuals with T2D & CKD (eGFR 25–90 mL/min/1.73 m2 and UACR 30–300 mg/g, or eGFR > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and UACR 300–5000 mg/g) | Finerenone vs. placebo (on top of RAAS blockade) | 13% risk reduction in CV death, non-fatal MI, non-fatal stroke, or HF hospitalization | Significant kidney & CV benefits, especially in patients with CKD and diabetes |
| Trial | Patients | Intervention | Key Outcome | Notable Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CREDENCE (NCT02065791) [42] | 4401 individuals with T2D and CKD (eGFR 30–90 mL/min/1.73 m2, UACR > 300 mg/g) | Canagliflozin vs. placebo (in addition to standard therapy) | 30% reduction in risk of kidney failure or CV death (p < 0.001). HR for kidney failure progression: 0.70 (CI, 0.59–0.82) | The trial ended early due to apparent efficacy. Acute eGFR dips are common but not predictive of worse long-term renal outcomes |
| DAPA-CKD (NCT03036150) [44] | 4304 adults with or without diabetes, CKD (eGFR 25–75 mL/min/1.73 m2, UACR 200–5000 mg/g) | Dapagliflozin vs. placebo (in addition to standard therapy) | 36% reduction in the primary composite of ≥50% eGFR decline, ESKD, or kidney/CV death (p < 0.001). Benefitting diabetic & non-diabetic CKD | Lower rates of acute kidney injury, reinforcing a favorable safety profile |
| EMPA-KIDNEY (NCT03594110) [51] | 6609 individuals with CKD (eGFR 20–45 or 45–90 mL/min/1.73 m2 with albuminuria ≥ 200 mg/g UACR) | Empagliflozin vs. placebo (in addition to standard therapy) | 28% relative risk reduction in kidney disease progression or CV death (HR 0.72, 95% CI 0.64–0.82, p < 0.001) | Reinforced renal protection of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic and non-diabetic CKD, including those with mild albuminuria |
| VERTIS CV (NCT01986881) [52] | 8246 adults with T2D and ASCVD (eGFR generally > 30 mL/min/1.73 m2, varying CKD stages) | Ertugliflozin vs. placebo (in addition to standard therapy) | Exploratory composite of sustained 40% eGFR decline, dialysis/transplant, or renal death significantly lower (HR, 0.66; CI, 0.50–0.88). UACR reduced by ~16–20% | Confirmed renal benefits of ertugliflozin in T2D with CV comorbidities, though primarily a CV safety trial |
| Trial | Patients | Intervention | Key Outcome | Notable Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEADER (NCT01179048) [62] | 9340 individuals with T2D at high risk for cardiovascular events | Liraglutide (up to 1.8 mg daily) vs. placebo | 13% reduction in MACE (HR 0.87), Significant reductions in cardiovascular death (HR 0.78), and all-cause mortality (HR 0.85) | Liraglutide not only reduced cardiovascular events but also decreased all-cause mortality in high-risk T2D patients. |
| FLOW (NCT03819153) [63] | 3533 individuals with T2D and CKD (eGFR 25–75 mL/min/1.73 m2 and UACR 100–5000 mg/g) | Semaglutide 1.0 mg weekly vs. placebo | 24% reduction in MAKE, Slowed annual eGFR decline by 1.16 mL/min/1.73 m2, Significant reductions in MACE (HR 0.82) & all-cause mortality (HR 0.80) | Semaglutide demonstrated significant benefits in reducing both kidney and cardiovascular events in patients with T2D and CKD. |
| SUSTAIN 6 (NCT01720446) [64] | 3297 individuals with T2D at high risk for cardiovascular events | Semaglutide (0.5 mg or 1.0 mg once weekly) vs. placebo | 26% reduction in MACE (HR 0.74); Significant reduction in non-fatal stroke (HR 0.61) | Semaglutide significantly reduced the risk of cardiovascular events in high-risk T2D patients. |
| Classifier | Comparison | Unadjusted HR (p-Value) | Adjusted HR (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HF2 | Per 1-SD increment | 2.59 (p < 2 × 10−16) | 1.64 (p = 1.72 × 10−18) |
| HF2 | Q5 vs. Q1 | 16.20 (p = 3.15 × 10−39) | 3.84 (p = 5.64 × 10−9) |
| CAD160 | Per 1-SD increment | 1.72 (p < 2 × 10−16) | 1.33 (p = 5.55 × 10−7) |
| CAD160 | Q5 vs. Q1 | 4.73 (p = 4.93 × 10−18) | 2.82 (p = 3.32 × 10−8) |
| CKD273 | Per 1-SD increment | 4.19 (p < 2 × 10−16) | 3.18 (p = 1.03 × 10−21) |
| CKD273 | Q5 vs. Q1 | 35.47 (p = 1.61 × 10−16) | 19.59 (p = 7.32 × 10−11) |
| Study | Patients | Intervention | Notable Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Widiasta 2021 [91] | 88 children with SRNS, 31 FSGS, 8 MPGN, 1 MesGN, 13 MCD, 62.5% male, age range 1–18 years. | CYC therapy, exclusion of calcineurin inhibitors. | TGF-β is crucial in SRNS treatment, high baseline TGF-β levels predict poor CYC response. |
| Teisseyre 2021 [92] | 68 patients with primary membranous nephropathy | RTX therapy, administered as two 1 g infusions two weeks apart, was evaluated for its efficacy in achieving clinical remission in pMN patients. | Serum RTX levels predict clinical remission at months 6 and 12; undetectable RTX levels at month 3 indicate higher treatment failure risk. |
| Shiratori-Aso 2022 [90] | 62 patients diagnosed with TIN | Corticosteroids and/or immunosuppressants for autoimmune TI | Elevated serum sIL2R levels may predict therapeutic response in autoimmune TIN |
| Kapsia 2022 [95] | 100 patients with biopsy-proven PLN, mean age 31 ± 13 years, 80% female, all meeting 2019 classification criteria for SLE. | Drug therapy comparison between CYC and MPA as induction treatments, assessment of effects on kidney response, flares, and long-term outcomes in PLN patients. | Baseline proteinuria <1.5 g/day predicts time to complete response, 12-month proteinuria > 0.8 g/day correlates with flare occurrence, and interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy > 25% predicts long-term outcomes. |
| Jamee 2022 [93] | 50 pediatric patients with NS, a mean disease follow-up duration of 3.6 years | Corticosteroid therapy as the primary treatment for pediatric NS, evaluating its impact on NLR/PLR. | No significant correlation between NLR/PLR ratios and steroid response. |
| Jaimes Campos 2023 [88] | 5585 datasets were extracted, participants with urine samples at the baseline visit. Demographic covariables assessed included body mass index, age, sex, blood pressure, and eGFR. Median follow-up period: 3.74 ± 3.36 years. | Prediction of most beneficial interventions in CKD, HF, and CAD, the following interventions were investigated: MRA, SGLT2i, DPP4i, ARB, GLP1RA, olive oil, and exercise. | Significant effects of treatments on in silico urinary peptides observed. Findings support personalized strategies for cardiovascular and kidney disease management. Prospective clinical trial validation is needed for clinical utility assessment. |
| Jaimes Campos 2024 [86] | Discovery cohort (DCREN): 199 adults treated with RAS inhibitors. PRIORITY cohort: 1078 participants with T2D selected for analysis (not receiving spironolactone). DIRECTProtect 2 cohort: 1905 individuals with T2D, 365 treated with candesartan. | RAAS blocking agents studied in diabetic patients to prevent DKD progression. | DKDp189 model predicts nonresponse to RASi treatment in diabetic patients. Urinary peptides may serve as biomarkers for DKD progression. Study highlights the variability in eGFR classification methods. |
| Capelli 2023 [96] | Patients aged > 18 years with T2D and CKD stages G2 and G3. | SGLT2i in patients with T2D and proteinuric CKD, evaluating effects on proteinuria reduction and baseline predictors of response. | SGLT2i therapy reduced proteinuria by >30% in most patients. Baseline proteinuria, eGFR & BMI are key predictors of treatment response. |
| Heerspink 2021 [97] | 3668 adults with T2D and CKD (eGFR 25–75 mL/min/1.73 m², UACR 300–5000 mg/g), 98.5% on ACE/ARB therapy. | Atrasentan 0.75 mg/day added to background RAS blockade, employing a six-week “response enrichment” phase based on UACR reduction. | Early UACR response was not a causal predictor of atrasentan’s long-term kidney protection. |
| Therapy | Monthly Cost (€) | Annual Cost (€) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACE Inhibitor (Ramipril 5 mg daily) | 4.20 | 50.40 | Very inexpensive generic; ~€0.14 per unit |
| ARB (Losartan 50–100 mg daily) | 6.90 | 82.80 | Slightly more expensive, generic; ~€0.23 per unit |
| Ns-MRA (Finerenone 10–20 mg daily) | 61.20 | 734.30 | Brand drug; ~€2.04 per unit |
| SGLT2 inhibitor (Empagliflozin 10–25 mg daily) | 57.30 | 687.60 | Brand drug; ~€1.91 per unit |
| Long-acting GLP-1 RA (Semaglutide 1 mg once weekly) | 312.75 | 3755.96 | Brand drug; ~€72.23 per injection solution |
| Sparsentan 400 mg (for IgA nephropathy, once daily) | 4935.94 | 59,231.28 | Brand drug; ~€164.53 per unit |
| Dialysis [108] | ~3916 | ~47,000 | Peritoneal & Hemodialysis cost approximately the same |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biglari, S.; Mischak, H.; Beige, J.; Latosinska, A.; Siwy, J.; Banasik, M. The Future of Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment: Combination Therapy (Polypill) or Biomarker-Guided Personalized Intervention? Biomolecules 2025, 15, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060809
Biglari S, Mischak H, Beige J, Latosinska A, Siwy J, Banasik M. The Future of Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment: Combination Therapy (Polypill) or Biomarker-Guided Personalized Intervention? Biomolecules. 2025; 15(6):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060809
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiglari, Sajjad, Harald Mischak, Joachim Beige, Agnieszka Latosinska, Justyna Siwy, and Mirosław Banasik. 2025. "The Future of Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment: Combination Therapy (Polypill) or Biomarker-Guided Personalized Intervention?" Biomolecules 15, no. 6: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060809
APA StyleBiglari, S., Mischak, H., Beige, J., Latosinska, A., Siwy, J., & Banasik, M. (2025). The Future of Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment: Combination Therapy (Polypill) or Biomarker-Guided Personalized Intervention? Biomolecules, 15(6), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060809









