Minimally Invasive Free-Breathing Gating-Free Extracellular Cellular Volume Quantification for Repetitive Myocardial Fibrosis Evaluation in Rodents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Anesthesia for Animal Imaging
2.3. Subcutaneous Catheter for Gd Administration
2.4. Hematocrit
2.5. CMR Acquisition
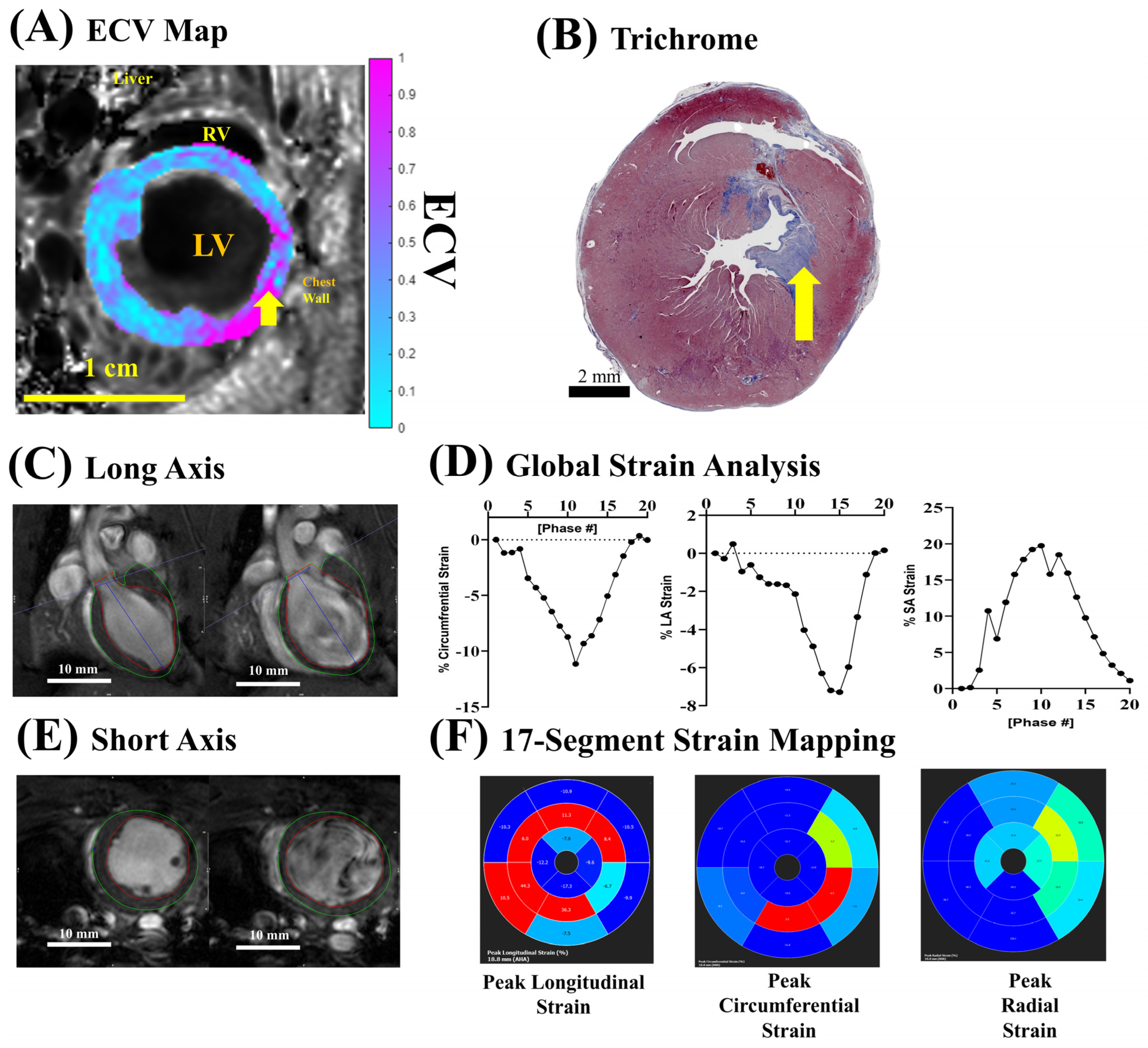
2.6. Systolic Cardiac Functions and Strain Analysis
2.7. Cardiac Phase Registration for T1 and ECV Quantification
2.8. T1 Mapping, ΔR1 Calculation, and ECV Mapping
2.9. Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
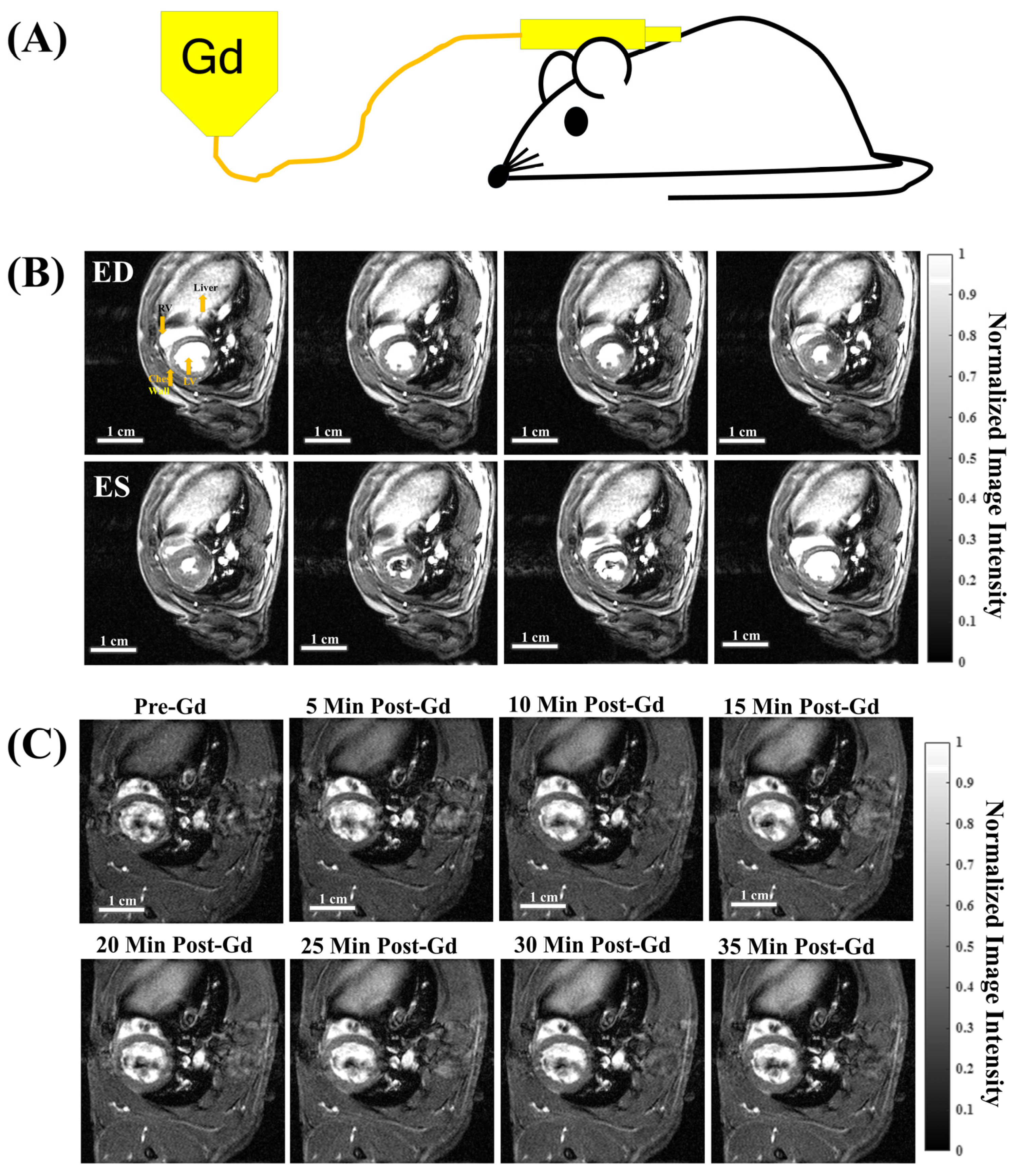
3.1. Free-Breathing, Gating-Free Cine, and Dynamic Contrast Enhancement (DCE) Time Series with a Single Bolus Subcutaneous (subQ) Gd Administration
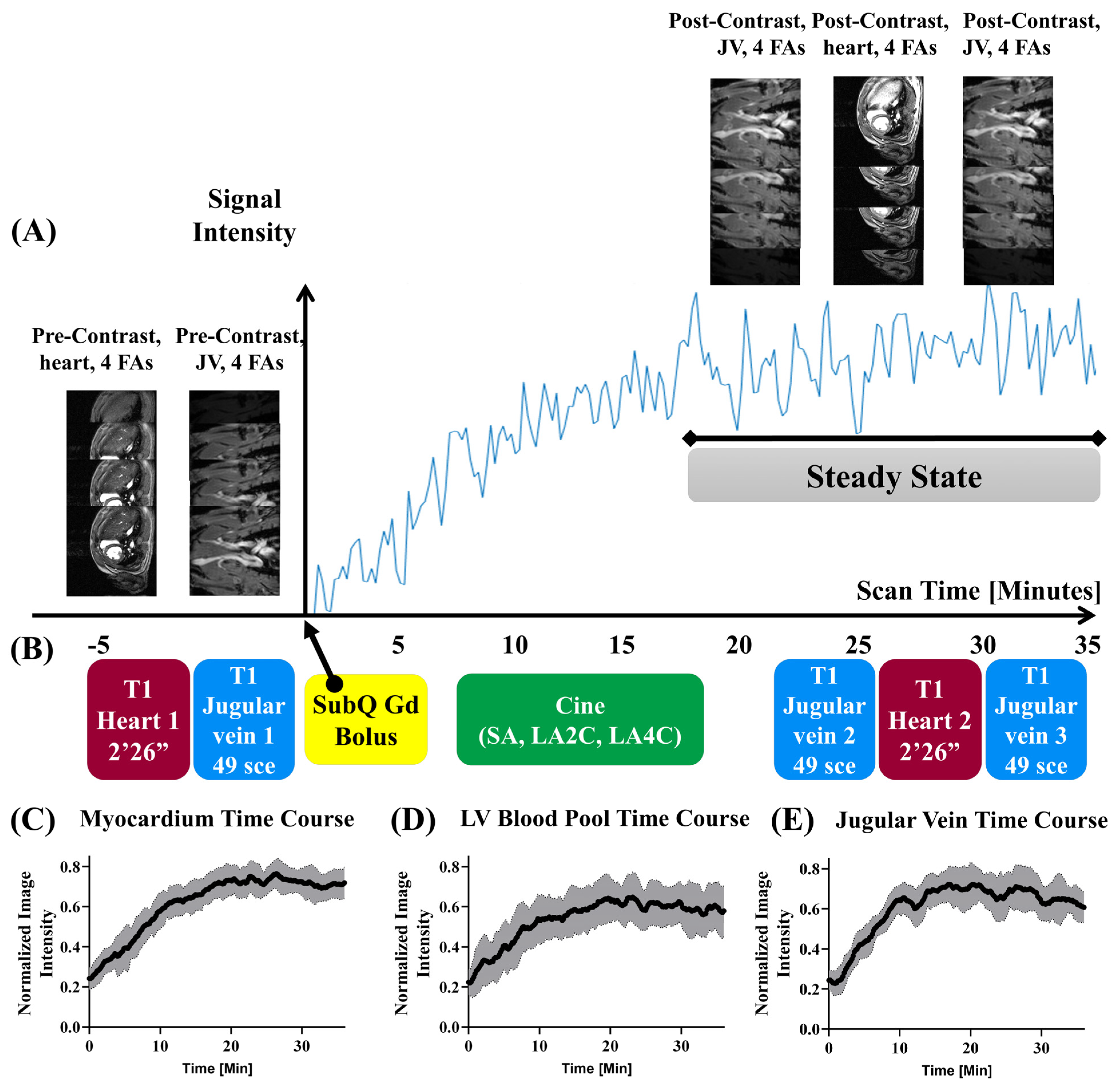
3.2. Acquisition Schema and DCE Time Courses
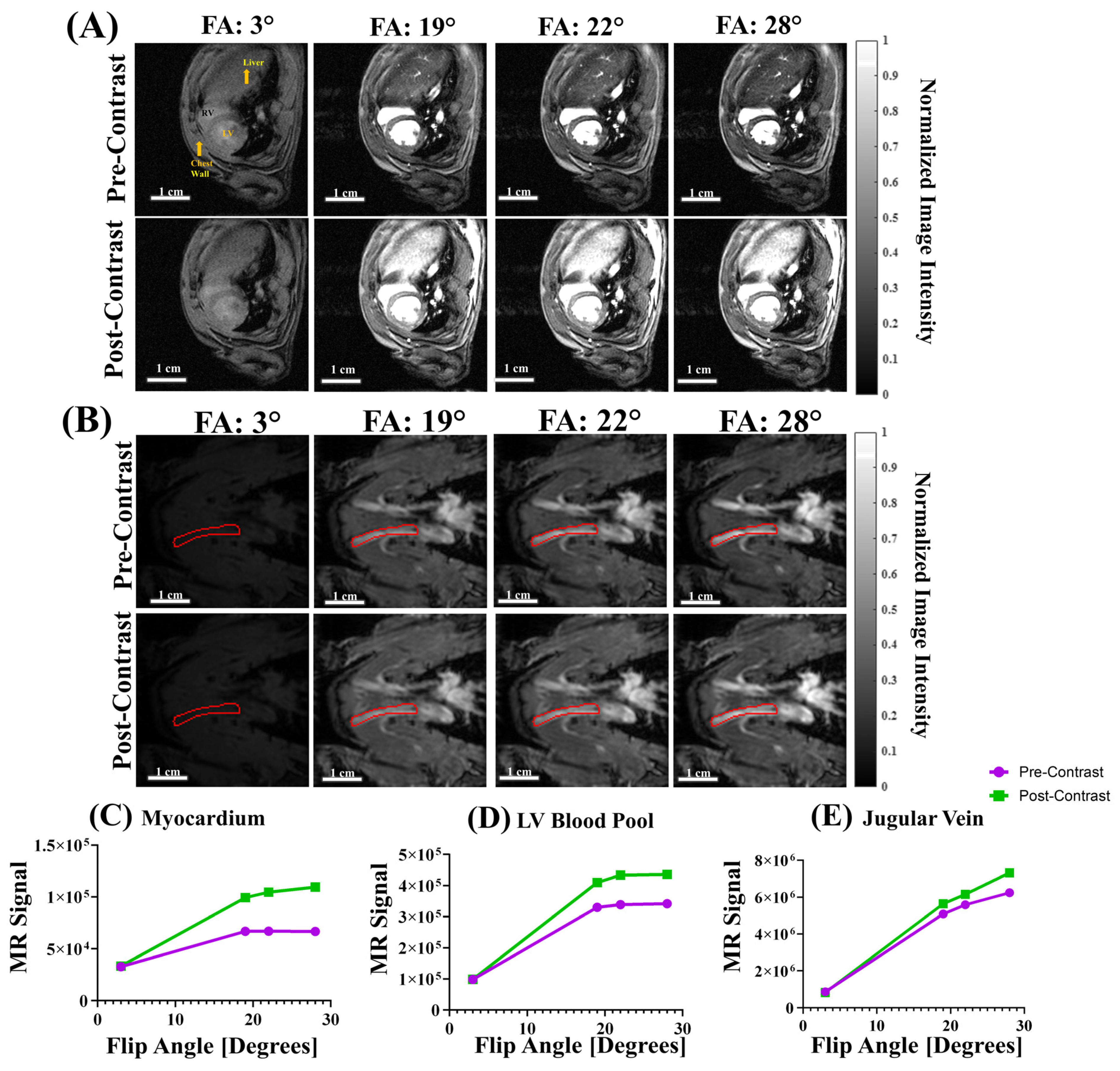
3.3. T1 Mapping with Varied Flip Angles (VFA)
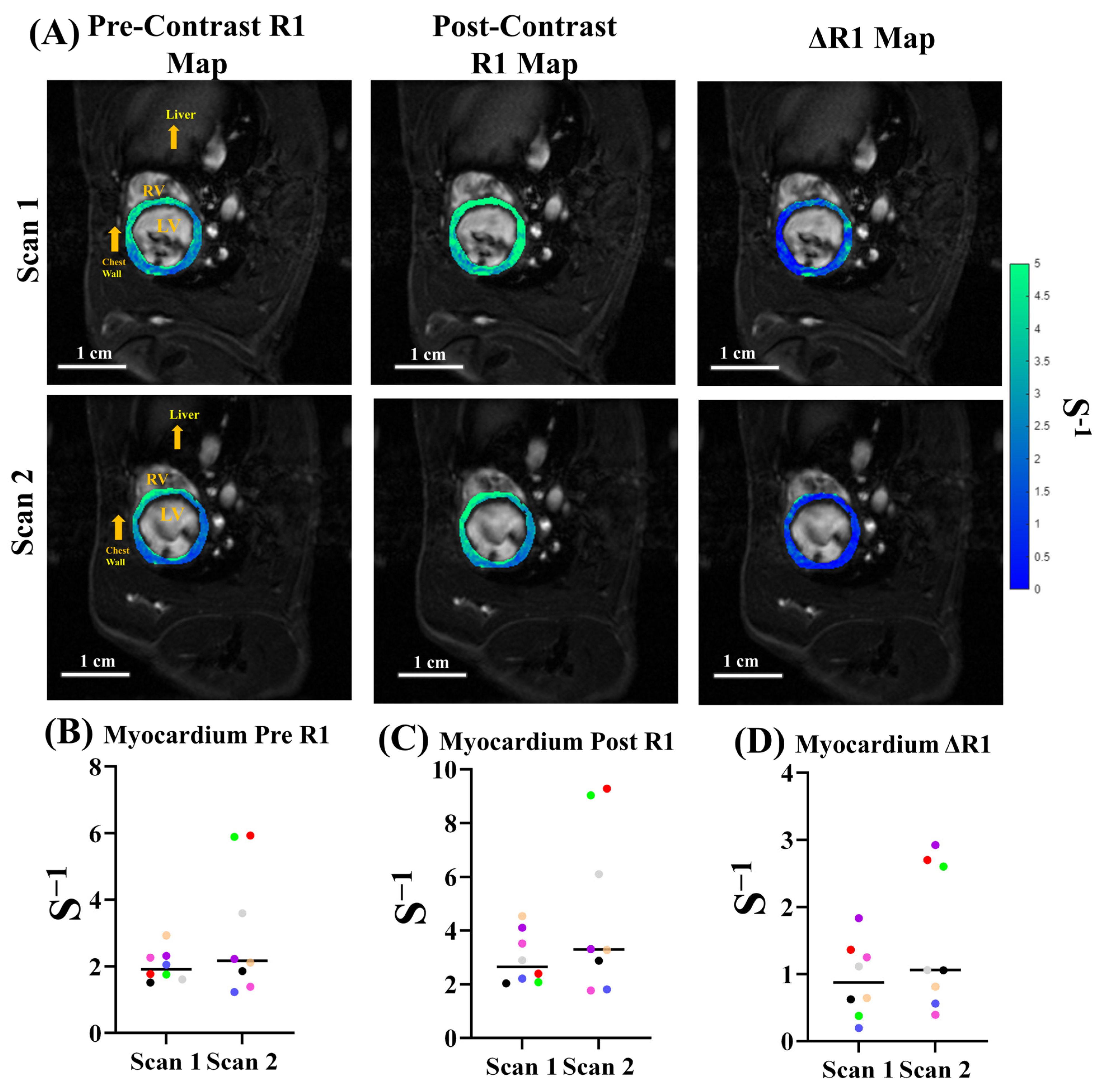
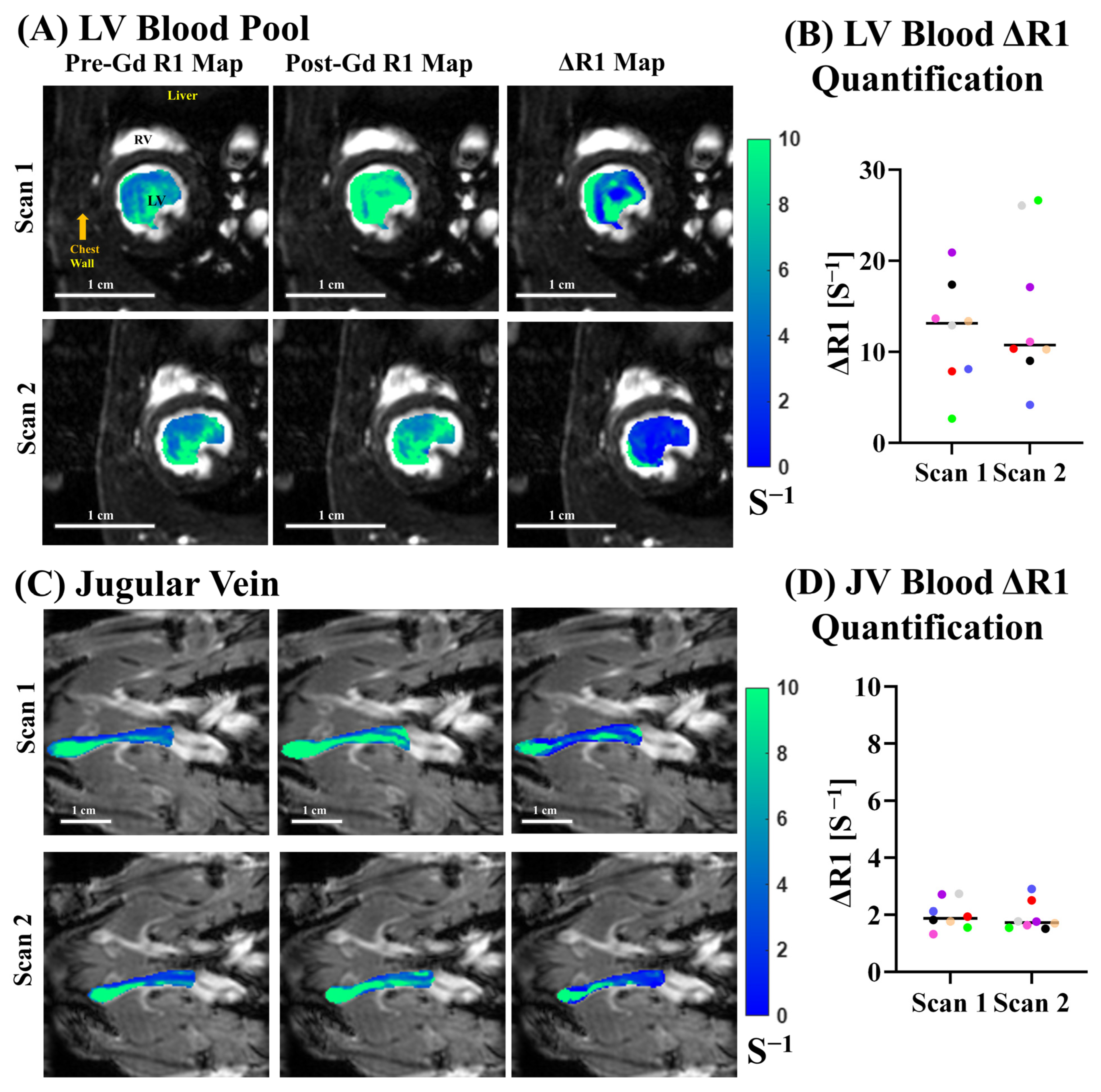
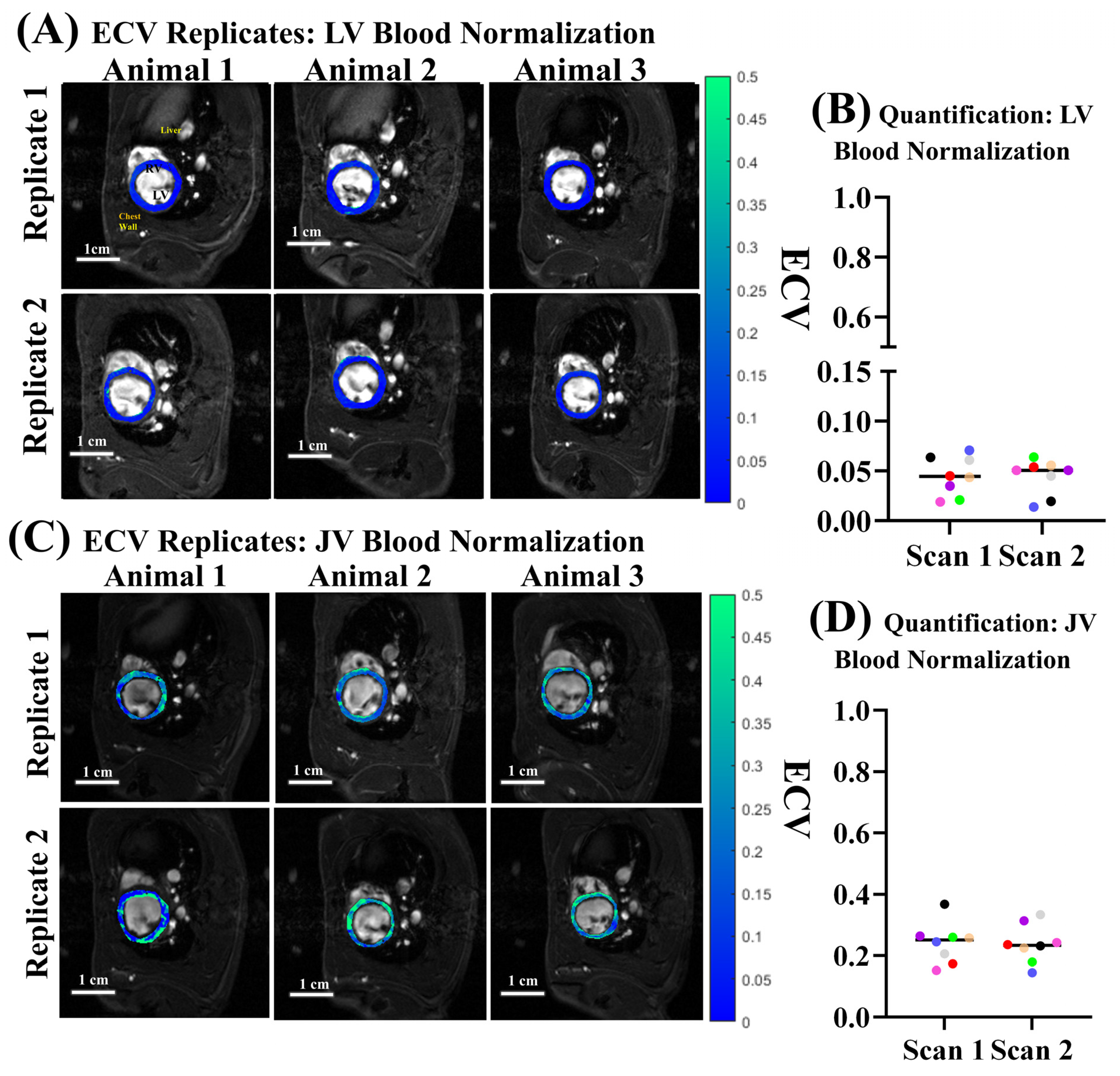
3.4. ECV Quantification and Reproducibility
3.5. ECV Quantification for Fibrosis After Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury
4. Discussion
4.1. Minimally Invasive Subcutaneous Protocol for ECV Quantification
4.2. Jugular Vein vs. LV Blood Pool Normalization
4.3. Future Work and Additional Considerations
4.4. Mouse Specific Considerations
4.5. Translation Considerations
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECV | Extracellular Volume |
| CMR | Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| Gd | Gadolinium |
| VFA | Varied Flip Angle |
| DCE | Dynamic Contrast Enhancement |
| HCM | Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy |
| CHD | Congenital Heart Disease |
| HFpEF | Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction |
| IR | Inversion Recovery |
| MOLLI | Modified Look-Locker Inversion Recovery |
| ShMOLLI | Shortened Modified Look-Locker Inversion Recovery |
| SASHA | Saturation Recovery Single-Shot Acquisition |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| LV | Left Ventricle |
| JV | Jugular Vein |
| subQ | Subcutaneous |
| FLASH | Fast Low-Angle Shot |
| SA | Short Axis |
| LA2C | Long-Axis Two-Chamber |
| LA4C | Long-Axis Four-Chamber |
| EF | Ejection Fraction |
| SV | Stroke Volume |
| ED | End Diastolic |
| SVD | Singular Value Decomposition |
| LAD | Left Anterior Descending Coronary Artery |
| IRI | Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury |
References
- López, B.; Ravassa, S.; Moreno, M.U.; José, G.S.; Beaumont, J.; González, A.; Díez, J. Diffuse myocardial fibrosis: Mechanisms, diagnosis and therapeutic approaches. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauffal, V.; Di Achille, P.; Klarqvist, M.D.R.; Cunningham, J.W.; Hill, M.C.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Weng, L.C.; Morrill, V.N.; Choi, S.H.; Khurshid, S.; et al. Genetics of myocardial interstitial fibrosis in the human heart and association with disease. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. Cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1450–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.Y.; López, B.; Coelho-Filho, O.R.; Lakdawala, N.K.; Cirino, A.L.; Jarolim, P.; Kwong, R.; González, A.; Colan, S.D.; Seidman, J.G.; et al. Myocardial fibrosis as an early manifestation of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaas, V.M.; Haugaa, K.H.; Strøm, E.H.; Scott, H.; Smith, H.J.; Dahl, C.P.; Geiran, O.R.; Endresen, K.; Aakhus, S.; Amlie, J.P.; et al. Noninvasive assessment of myocardial fibrosis in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart 2014, 100, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, B.; Ariga, R.; Spartera, M.; Sivalokanathan, S.; Chan, K.; Dass, S.; Petersen, S.E.; Daniels, M.J.; Francis, J.; Smillie, R.; et al. Progression of myocardial fibrosis in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 20, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, B.; González-Fernández, V.; Dos-Subirà, L. Myocardial fibrosis in congenital heart disease. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 965204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, R.H.; Powell, A.J.; Geva, T. Myocardial Fibrosis in Congenital Heart Disease. Circ. J. Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2016, 80, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, C.S.; Khan, A.M. Myocardial fibrosis in adult congenital heart disease. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 73, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Schelbert, E.B.; Díez, J.; Butler, J. Myocardial Interstitial Fibrosis in Heart Failure: Biological and Translational Perspectives. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1696–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, W.J.; Zile, M.R. From Systemic Inflammation to Myocardial Fibrosis: The Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Paradigm Revisited. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, W.J.; Tschöpe, C. A novel paradigm for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Comorbidities drive myocardial dysfunction and remodeling through coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.K.; Kinno, M.; Liebo, M.; Yu, M.D.; Syed, M. Evolving role of myocardial fibrosis in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 12, 1573346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelbert, E.B.; Fridman, Y.; Wong, T.C.; Abu Daya, H.; Piehler, K.M.; Kadakkal, A.; Miller, C.A.; Ugander, M.; Maanja, M.; Kellman, P.; et al. Temporal Relation Between Myocardial Fibrosis and Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: Association with Baseline Disease Severity and Subsequent Outcome. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellman, P.; Wilson, J.R.; Xue, H.; Ugander, M.; Arai, A.E. Extracellular volume fraction mapping in the myocardium, part 1: Evaluation of an automated method. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2012, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellman, P.; Wilson, J.R.; Xue, H.; Bandettini, W.P.; Shanbhag, S.M.; Druey, K.M.; Ugander, M.; Arai, A.E. Extracellular volume fraction mapping in the myocardium, part 2: Initial clinical experience. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2012, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelbert, E.B.; Piehler, K.M.; Zareba, K.M.; Moon, J.C.; Ugander, M.; Messroghli, D.R.; Valeti, U.S.; Chang, C.C.; Shroff, S.G.; Diez, J.; et al. Myocardial Fibrosis Quantified by Extracellular Volume Is Associated with Subsequent Hospitalization for Heart Failure, Death, or Both Across the Spectrum of Ejection Fraction and Heart Failure Stage. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.Y.; Abbasi, S.A.; Neilan, T.G.; Shah, R.V.; Chen, Y.; Heydari, B.; Cirino, A.L.; Lakdawala, N.K.; Orav, E.J.; González, A.; et al. T1 measurements identify extracellular volume expansion in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy sarcomere mutation carriers with and without left ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.K.; Sado, D.M.; Fontana, M.; Banypersad, S.M.; Maestrini, V.; Flett, A.S.; Piechnik, S.K.; Robson, M.D.; Hausenloy, D.J.; Sheikh, A.M.; et al. T1 mapping for myocardial extracellular volume measurement by CMR: Bolus only versus primed infusion technique. JACC. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flett, A.S.; Hayward, M.P.; Ashworth, M.T.; Hansen, M.S.; Taylor, A.M.; Elliott, P.M.; McGregor, C.; Moon, J.C. Equilibrium contrast cardiovascular magnetic resonance for the measurement of diffuse myocardial fibrosis: Preliminary validation in humans. Circulation 2010, 122, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.C.; Piehler, K.M.; Kang, I.A.; Kadakkal, A.; Kellman, P.; Schwartzman, D.S.; Mulukutla, S.R.; Simon, M.A.; Shroff, S.G.; Kuller, L.H.; et al. Myocardial extracellular volume fraction quantified by cardiovascular magnetic resonance is increased in diabetes and associated with mortality and incident heart failure admission. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaf, P.; Garg, P.; Messroghli, D.R.; Broadbent, D.A.; Greenwood, J.P.; Plein, S. Cardiac T1 Mapping and Extracellular Volume (ECV) in clinical practice: A comprehensive review. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2016, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilan, T.G.; Coelho-Filho, O.R.; Shah, R.V.; Abbasi, S.A.; Heydari, B.; Watanabe, E.; Chen, Y.; Mandry, D.; Pierre-Mongeon, F.; Blankstein, R.; et al. Myocardial extracellular volume fraction from T1 measurements in healthy volunteers and mice: Relationship to aging and cardiac dimensions. JACC. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelbert, E.B.; Sabbah, H.N.; Butler, J.; Gheorghiade, M. Employing Extracellular Volume Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Measures of Myocardial Fibrosis to Foster Novel Therapeutics. Circulation. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, e005619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Lo, C.W. Diverse application of MRI for mouse phenotyping. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.; Roy, S.; Ghosh, D.; Nandi, S.K. Role of animal models in biomedical research: A review. Lab. Anim. Res. 2022, 38, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.L.H.; Roth, T.L. Animal Models and Their Contribution to Our Understanding of the Relationship Between Environments, Epigenetic Modifications, and Behavior. Genes 2019, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillmann, W.H. The rat as a model for cardiovascular disease. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2008, 5, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.; Falcão-Pires, I.; Pires, A.L.; Brás-Silva, C.; Leite-Moreira, A.F. Rodent models of heart failure: An updated review. Heart Fail. Rev. 2013, 18, 219–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgi, B.; Voight, B.F.; Bucan, M. From mouse to human: Evolutionary genomics analysis of human orthologs of essential genes. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeau, J.H. Modifier genes in mice and humans. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Rappolee, D.A.; Ruden, D.M. Epigenetic Reprogramming in Mice and Humans: From Fertilization to Primordial Germ Cell Development. Cells 2023, 12, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, T.; Hafyane, T.; Stikov, N.; Akdeniz, C.; Greiser, A.; Friedrich, M.G. Comparison of different cardiovascular magnetic resonance sequences for native myocardial T1 mapping at 3T. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2016, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujol, S.; Weingärtner, S.; Foppa, M.; Chow, K.; Kawaji, K.; Ngo, L.H.; Kellman, P.; Manning, W.J.; Thompson, R.B.; Nezafat, R. Accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of four T1 mapping sequences: A head-to-head comparison of MOLLI, ShMOLLI, SASHA, and SAPPHIRE. Radiology 2014, 272, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, J.F.; Weng, A.M.; Donhauser, J.; Greiser, A.; Chow, K.; Nordbeck, P.; Bley, T.A.; Köstler, H. T1- and ECV-mapping in clinical routine at 3 T: Differences between MOLLI, ShMOLLI and SASHA. BMC Med. Imaging 2019, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coolen, B.F.; Geelen, T.; Paulis, L.E.; Nauerth, A.; Nicolay, K.; Strijkers, G.J. Three-dimensional T1 mapping of the mouse heart using variable flip angle steady-state MR imaging. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, A.; Piccoli, M.; Monti, C.B.; Canu, T.; Cirillo, F.; Napolitano, A.; Perani, L.; Signorelli, P.; Vignale, D.; Anastasia, L.; et al. Single-shot morpho-functional and structural characterization of the left-ventricle in a mouse model of acute ischemia-reperfusion injury with an optimized 3D IntraGate cine FLASH sequence at 7T MR. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 68, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lena, B.; Bos, C.; Ferrer, C.J.; Moonen, C.T.W.; Viergever, M.A.; Bartels, L.W. Rapid 2D variable flip angle method for accurate and precise T1 measurements over a wide range of T1 values. NMR Biomed. 2021, 34, e4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Trzasko, J.D.; Mostardi, P.M.; Riederer, S.J.; Manduca, A. Estimating T1 from multichannel variable flip angle SPGR sequences. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitouš, J.; Jiřík, R.; Stračina, T.; Hendrych, M.; Nádeníček, J.; Macíček, O.; Tian, Y.; Krátká, L.; Dražanová, E.; Nováková, M.; et al. T1 mapping of myocardium in rats using self-gated golden-angle acquisition. Magn. Reson. Med. 2024, 91, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messroghli, D.R.; Nordmeyer, S.; Dietrich, T.; Dirsch, O.; Kaschina, E.; Savvatis, K.; O H-Ici, D.; Klein, C.; Berger, F.; Kuehne, T. Assessment of Diffuse Myocardial Fibrosis in Rats Using Small-Animal Look-Locker Inversion Recovery T1 Mapping. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2011, 4, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho-Filho, O.R.; Shah, R.V.; Neilan, T.G.; Mitchell, R.; Moreno, H., Jr.; Kwong, R.; Jerosch-Herold, M. Cardiac magnetic resonance assessment of interstitial myocardial fibrosis and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in hypertensive mice treated with spironolactone. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, N.; Liu, D.; Fan, Z.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, L. The Dynamic Characteristics of Myocardial Contractility and Extracellular Volume in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice Investigated by 7.0T Cardiac Magnetic Resonance. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.; Hayes, G.; Flewitt, J.A.; Feuchter, P.; Lydell, C.; Howarth, A.; Pagano, J.J.; Thompson, R.B.; Kellman, P.; White, J.A. Improved accuracy and precision with three-parameter simultaneous myocardial T1 and T2 mapping using multiparametric SASHA. Magn. Reson. Med. 2022, 87, 2775–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerne, J.W.; Pathrose, A.; Sarnari, R.; Veer, M.; Chow, K.; Subedi, K.; Allen, B.D.; Avery, R.J.; Markl, M.; Carr, J.C. Left ventricular fibrosis assessment by native T1, ECV, and LGE in pulmonary hypertension patients. Diagnostics 2022, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, H.; Lu, M.; Sirajuddin, A.; Li, J.; An, J.; Chen, X.; Yin, G.; Lan, T.; Dai, L.; et al. Myocardial extracellular volume fraction quantified by cardiovascular magnetic resonance is increased in hypertension and associated with left ventricular remodeling. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4620–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cortes, D.R.E.; Becker-Szurszewski, T.; Hartwick, S.; Amjad, M.W.; Mohammed, S.A.; Chen, X.; Pacella, J.J.; Christodoulou, A.G.; Wu, Y.L. Minimally Invasive Free-Breathing Gating-Free Extracellular Cellular Volume Quantification for Repetitive Myocardial Fibrosis Evaluation in Rodents. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121732
Cortes DRE, Becker-Szurszewski T, Hartwick S, Amjad MW, Mohammed SA, Chen X, Pacella JJ, Christodoulou AG, Wu YL. Minimally Invasive Free-Breathing Gating-Free Extracellular Cellular Volume Quantification for Repetitive Myocardial Fibrosis Evaluation in Rodents. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(12):1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121732
Chicago/Turabian StyleCortes, Devin Raine Everaldo, Thomas Becker-Szurszewski, Sean Hartwick, Muhammad Wahab Amjad, Soheb Anwar Mohammed, Xucai Chen, John J. Pacella, Anthony G. Christodoulou, and Yijen L. Wu. 2025. "Minimally Invasive Free-Breathing Gating-Free Extracellular Cellular Volume Quantification for Repetitive Myocardial Fibrosis Evaluation in Rodents" Biomolecules 15, no. 12: 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121732
APA StyleCortes, D. R. E., Becker-Szurszewski, T., Hartwick, S., Amjad, M. W., Mohammed, S. A., Chen, X., Pacella, J. J., Christodoulou, A. G., & Wu, Y. L. (2025). Minimally Invasive Free-Breathing Gating-Free Extracellular Cellular Volume Quantification for Repetitive Myocardial Fibrosis Evaluation in Rodents. Biomolecules, 15(12), 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121732





