Combinatorial Antimicrobial Effects of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids and Antifungals on Model Fungal Organisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
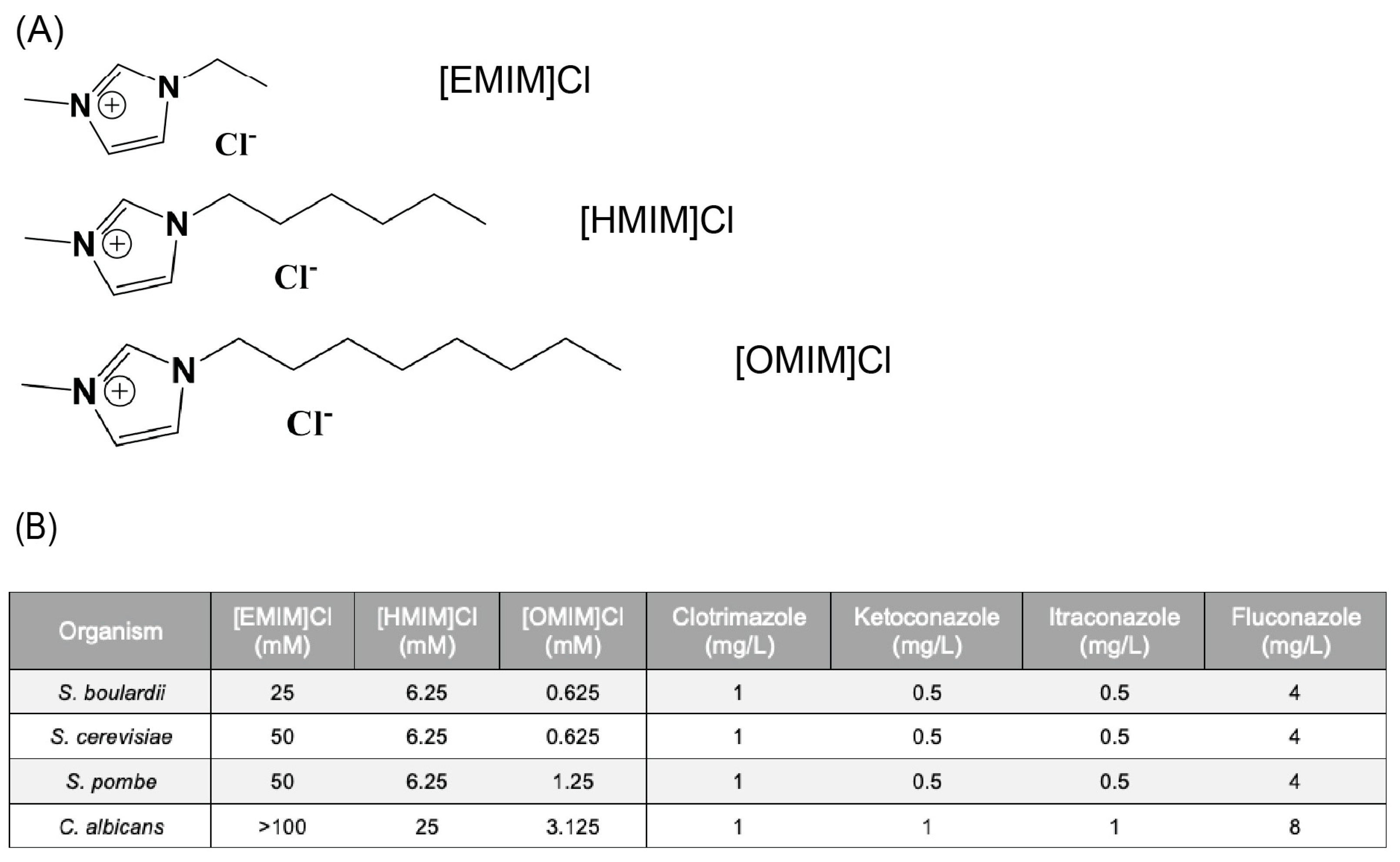
2.1. Ionic Liquids (IL)
2.2. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
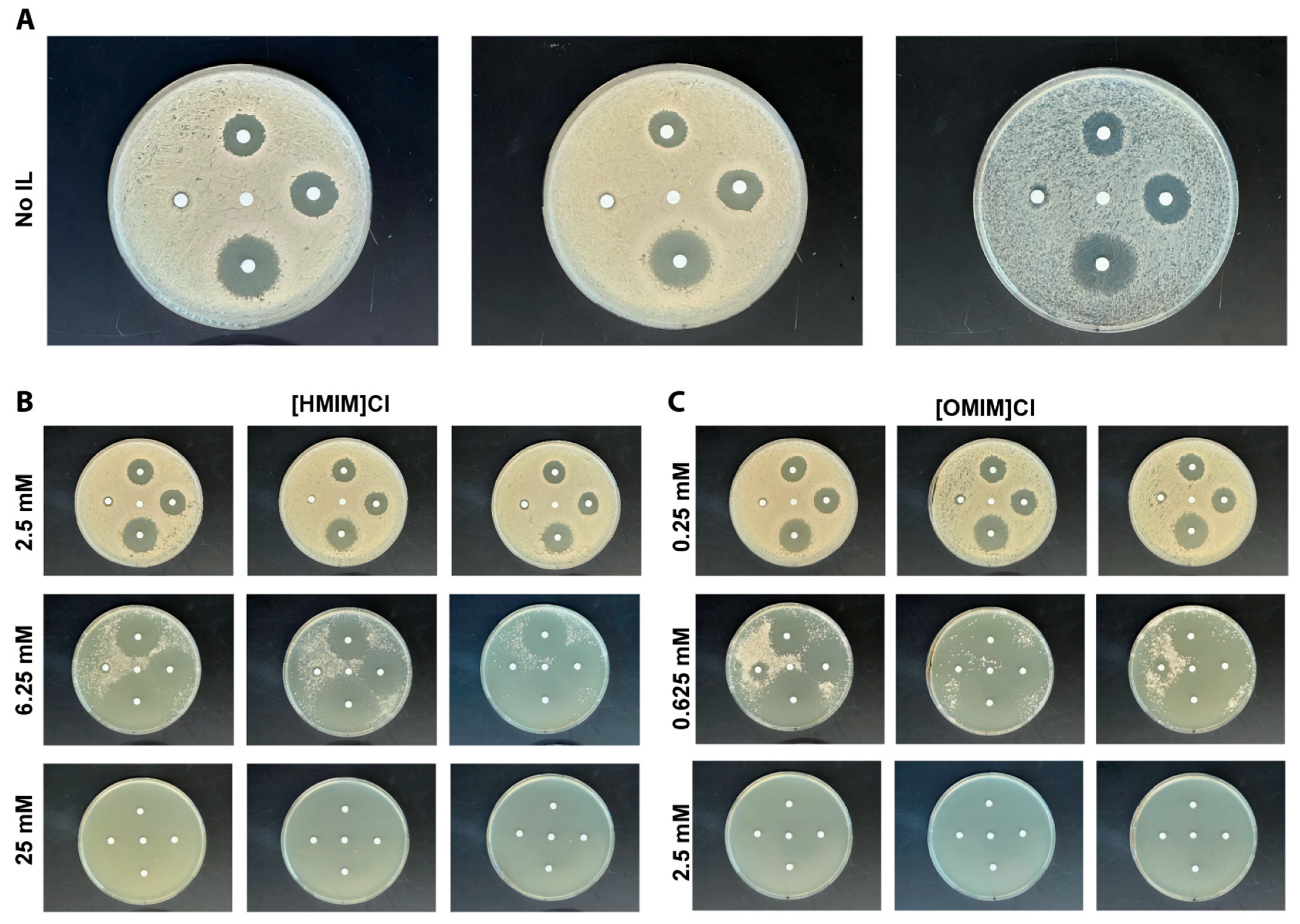
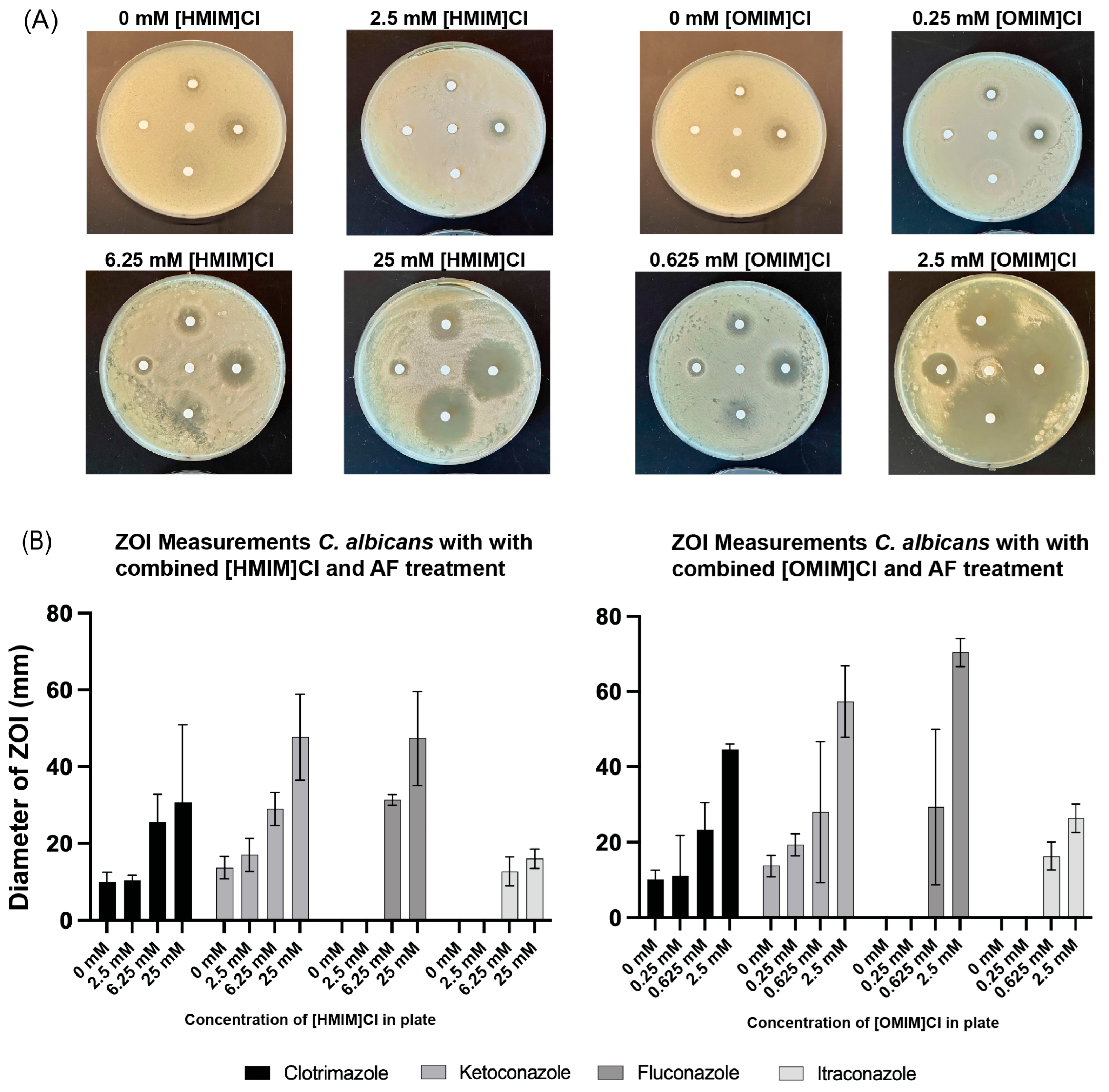
2.3. Kirby–Bauer Disk Assays
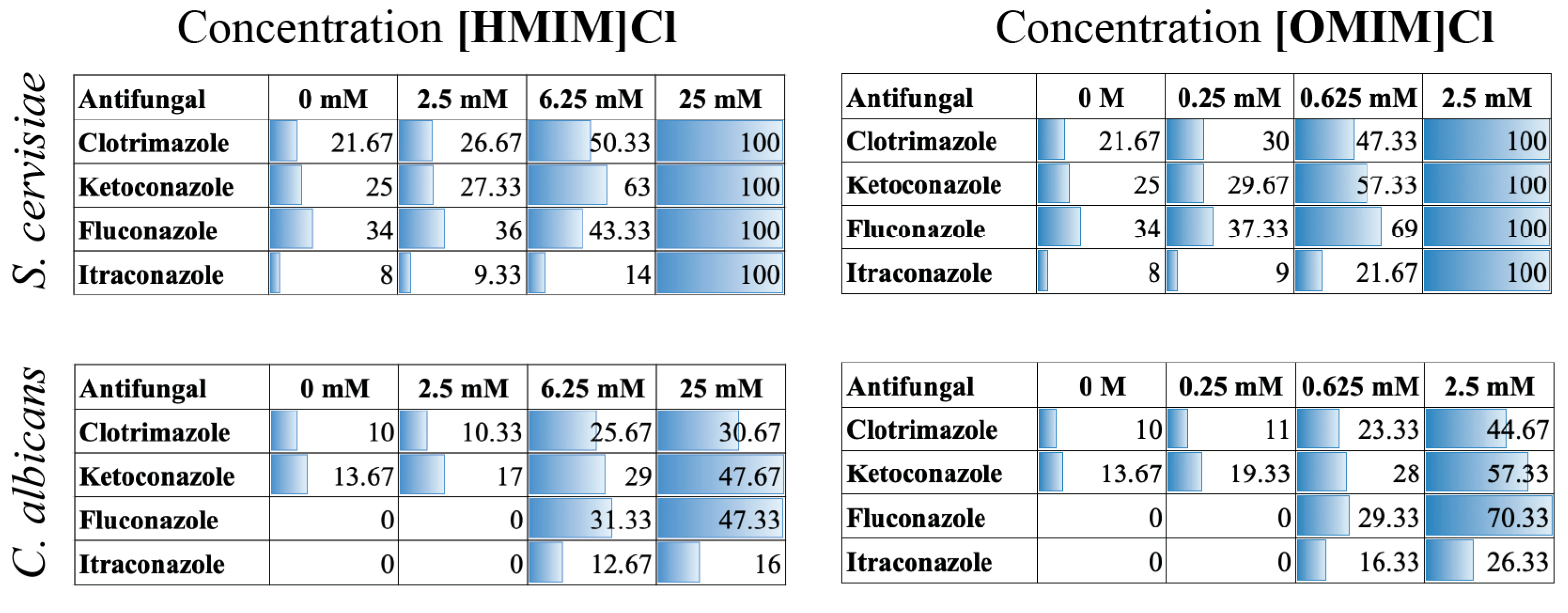
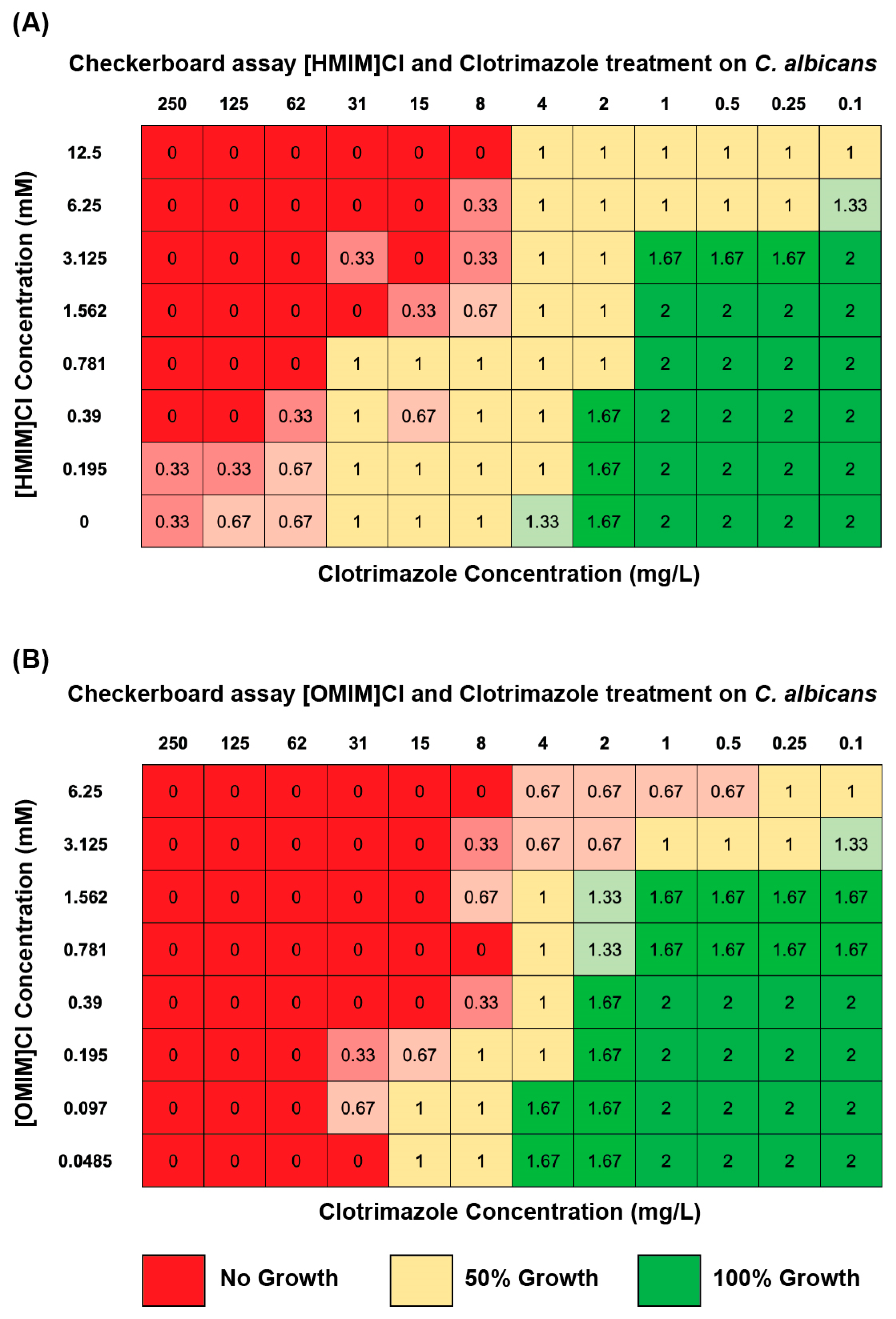
2.4. Checkerboard Assays
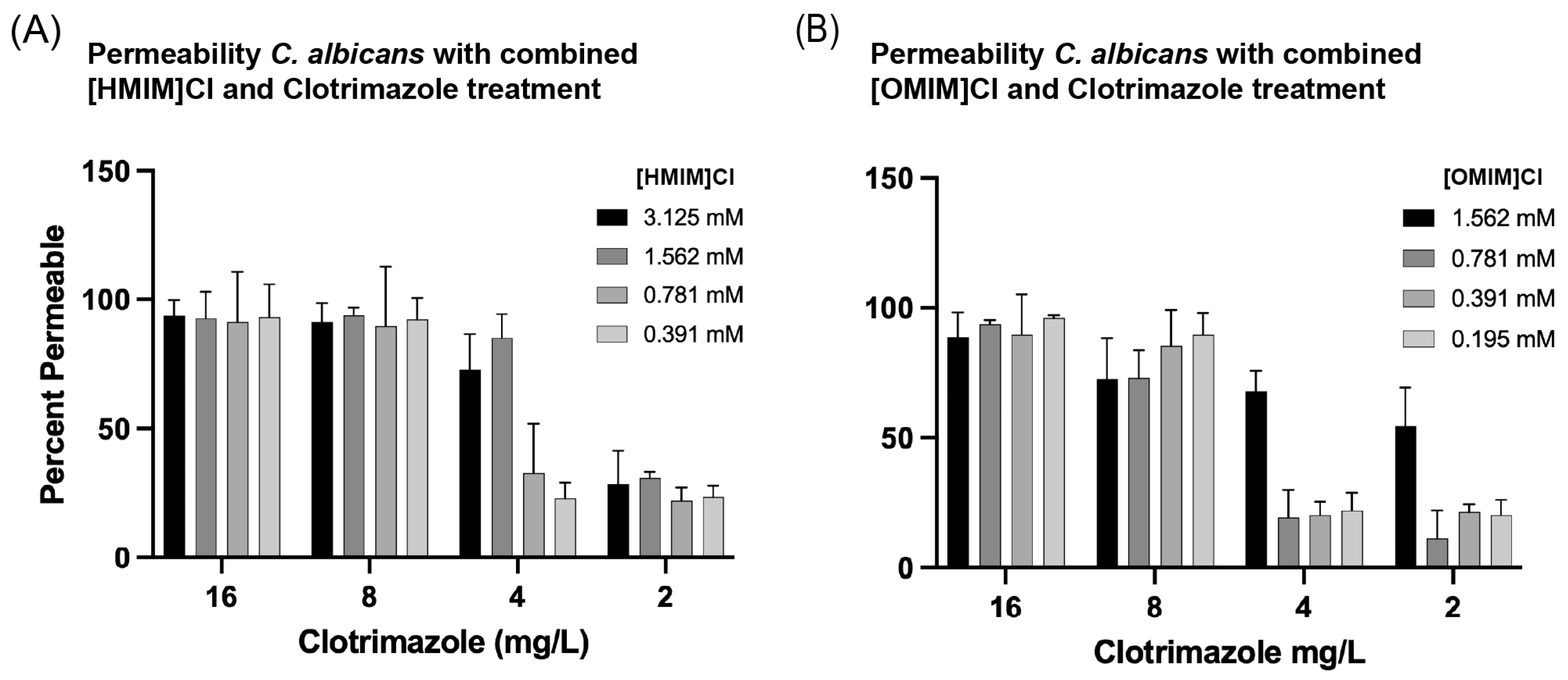
2.5. Permeability Assay Flow Cytometry
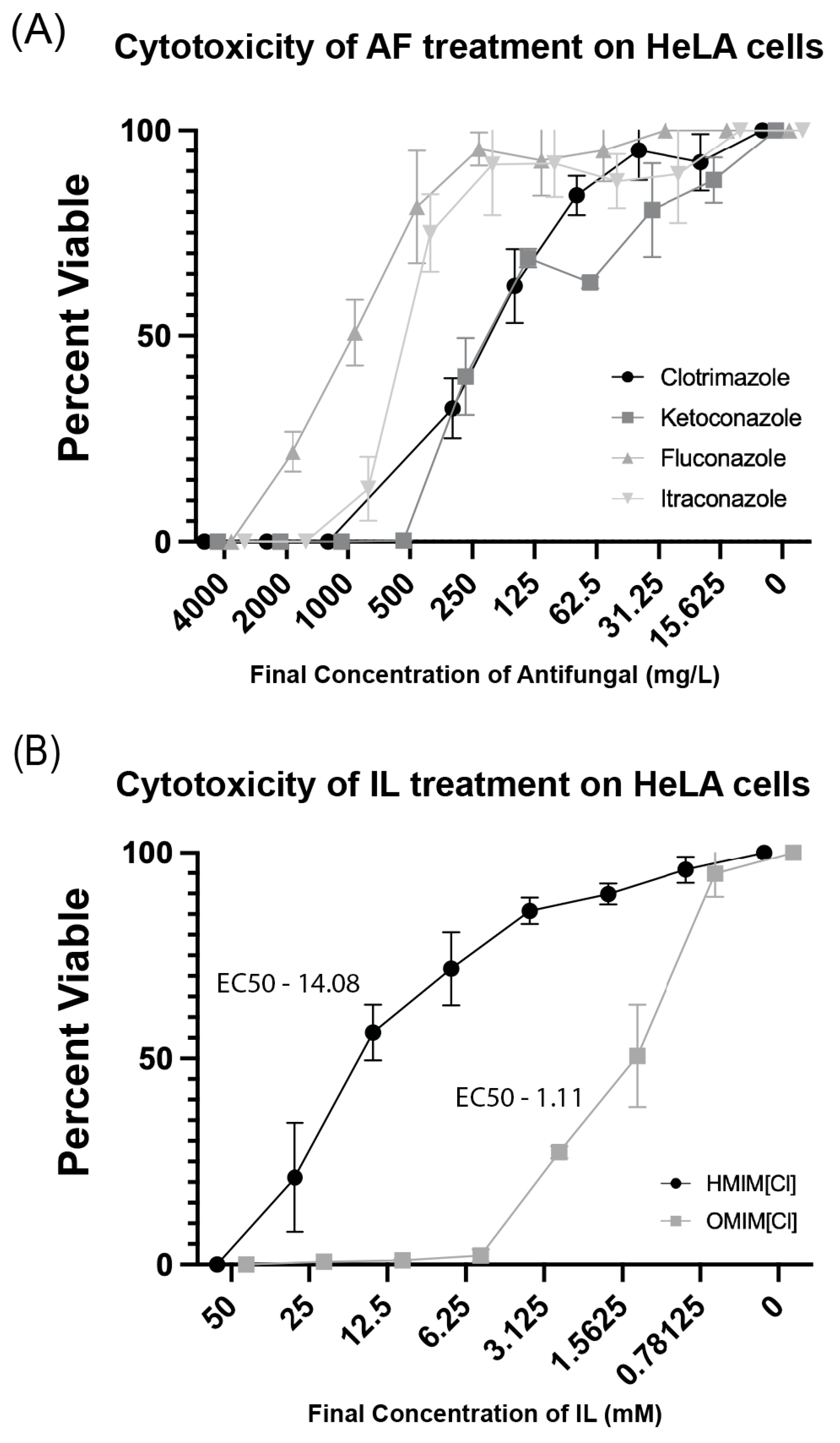
2.6. Treatment with HeLa Cells with ILs + Antifungals
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Activity of ILs and Antifungals in Yeast
3.2. Combination of ILs and Antifungals in Kirby–Bauer Disk Assays
3.3. Combination of ILs and Antifungals Using Microbroth Dilutions in Checkerboard Assay Indicate Enhanced Fungicidal Activity
3.4. Combinations of ILs + Clotrimazole Enhance Permeability of C. albicans in Liquid Culture
3.5. Ionic Liquid and AF Cytotoxic Effects on Human Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IL | Ionic Liquid |
| AF | Antifungal |
| [HMIM]Cl | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
| [OMIM]Cl | 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
Appendix A
References
- Almeida, F.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Coelho, C. The Still Underestimated Problem of Fungal Diseases Worldwide. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Santos, G.C.; Vasconcelos, C.C.; Lopes, A.J.O.; de Sousa Cartágenes, M.D.S.; Filho, A.K.D.B.; do Nascimento, F.R.F.; Ramos, R.M.; Pires, E.R.R.B.; de Andrade, M.S.; Rocha, F.M.G.; et al. Candida Infections and Therapeutic Strategies: Mechanisms of Action for Traditional and Alternative Agents. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojic, E.M.; Darouiche, R.O. Candida infections of medical devices. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islayem, M.; Agha, A.; Al Bataineh, M.T.; Alazzam, A. Modification of surface topographies to inhibit candida biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, A.; Rocha, M.; Pereirinha, P.; Tomé, R.; Costa, E. Antifungals: From Pharmacokinetics to Clinical Practice. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorand, T.; Kocsis, B. Recent advances in antifungal agents. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkow, E.L.; Lockhart, S.R. Fluconazole resistance in Candida species: A current perspective. Infect. Drug Resist. 2017, 10, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentefria, A.; Pippi, B.; Lana, D.D.; Donato, K.; de Andrade, S. Antifungals discovery: An insight into new strategies to combat antifungal resistance. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 66, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobile, C.J.; Johnson, A.D. Candida albicans Biofilms and Human Disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campitelli, M.; Zeineddine, N.; Samaha, G.; Maslak, S. Combination Antifungal Therapy: A Review of Current Data. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2017, 9, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, P.D.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Maragakis, L.L. Combination Therapy for Treatment of Infections with Gram-Negative Bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttner, A.; Bielicki, J.; Clements, M.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Muller, A.; Paccaud, J.-P.; Mouton, J. Oral amoxicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid: Properties, indications and usage. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montelongo-Peralta, L.Z.; León-Buitimea, A.; Palma-Nicolás, J.P.; Gonzalez-Christen, J.; Morones-Ramírez, J.R. Antibacterial Activity of combinatorial treatments composed of transition-metal/antibiotics against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Dai, C.; Shen, Z.; Tang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhai, B.; Zhao, L.; Hao, Z. Mechanism of Synergy Between Tetracycline and Quercetin Against Antibiotic Resistant Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, S.A.; Huigens, R.W.; Cavanagh, J.; Melander, C. Synergistic effects between conventional antibiotics and 2-aminoimidazole-derived antibiofilm agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2112–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novy, P.; Urban, J.; Leuner, O.; Vadlejch, J.; Kokoska, L. In vitro synergistic effects of baicalin with oxytetracycline and tetracycline against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1298–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, D.; Mukherjee, A. Effect of water and ionic liquids on biomolecules. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addicoat, M.; Atkin, R.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Gomes, M.C.; Firestone, M.; Gardas, R.; Halstead, S.; Hardacre, C.; Hardwick, L.J.; Holbrey, J.; et al. Structure and dynamics of ionic liquids: General discussion. Faraday Discuss. 2018, 206, 291–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, O.C.; Mancini, E.; Caputo, G.; Vaden, T.D. Quantitative evaluation of myoglobin unfolding in the presence of guanidinium hydrochloride and ionic liquids in solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, C. Proteins in Ionic Liquids: Current Status of Experiments and Simulations. Top Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, T. Ionic Liquids as Tool to Improve Enzymatic Organic Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10567–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumbri, K.; Rahman, M.B.A.; Abdulmalek, E.; Ahmad, H.; Micaelo, N.M. An insight into structure and stability of DNA in ionic liquids from molecular dynamics simulation and experimental studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 14036–14046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.D.; Paterna, N.J.; Senetra, A.S.; Casey, K.R.; Trieu, P.D.; Caputo, G.A.; Vaden, T.D.; Carone, B.R. Synergistic interactions of ionic liquids and antimicrobials improve drug efficacy. iScience 2021, 24, 101853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.K.K.; Nancharaiah, Y.V. Alkylimidazolium Ionic Liquids as Antifungal Alternatives: Antibiofilm Activity Against Candida albicans and Underlying Mechanism of Action. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrekker, C.M.L.; Sokolovicz, Y.C.A.; Raucci, M.G.; Selukar, B.S.; Klitzke, J.S.; Lopes, W.; Leal, C.A.M.; de Souza, I.O.P.; Galland, G.B.; dos Santos, J.H.Z.; et al. Multitask Imidazolium Salt Additives for Innovative Poly(l-lactide) Biomaterials: Morphology Control, Candida spp. Biofilm Inhibition, Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Biocompatibility, and Skin Tolerance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21163–21176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rando, O.J. Genome-wide mapping of nucleosomes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 2010, 470, 105–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, T.; Alves-Rodrigues, I.; Gómez-Escoda, B.; Dutta, C.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Rhind, N.; Hidalgo, E.; Ayté, J. The DNA damage and the DNA replication checkpoints converge at the MBF transcription factor. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabeler, C.; Paterna, N.; Potluri, R.; D’aLessandro, L.R.; Bhatia, A.; Chen, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Abeje, B.; Lipchin, B.; Carone, B.R.; et al. Locus-specific differential expression of human satellite sequences in the nuclei of cancer cells and heat-shocked cells. Nucleus 2024, 15, 2431239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doern, C.D. When does 2 plus 2 equal 5? A review of antimicrobial synergy testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4124–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, K.; Tarnawsky, K.; Swinton, A.J.; Yang, D.D.; Senetra, A.S.; Caputo, G.A.; Carone, B.R.; Vaden, T.D. Correlating Lipid Membrane Permeabilities of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids with Their Cytotoxicities on Yeast, Bacterial, and Mammalian Cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI M27M44S; Performance Standards for Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts. CLSI: Malvern, PA, USA, 2022.
- Raucci, M.G.; Fasolino, I.; Pastore, S.G.; Soriente, A.; Capeletti, L.B.; Dessuy, M.B.; Giannini, C.; Schrekker, H.S.; Ambrosio, L. Antimicrobial Imidazolium Ionic Liquids for the Development of Minimal Invasive Calcium Phosphate-Based Bionanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 42766–42776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambaugh, M.A.; Denham, S.T.; Ayala, M.; Brammer, B.; Stonhill, M.A.; Brown, J.C. Synergistic and antagonistic drug interactions in the treatment of systemic fungal infections. Elife 2020, 9, e54160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.; Middleton, R.; Westmacott, D. The fractional inhibitory concentration (FIC) index as a measure of synergy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1983, 11, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-Y.; Jing, C.-Q.; Lei, W.-L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.-J. Apoptosis caused by imidazolium-based ionic liquids in PC12 cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 83, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, P.; Gallagher, H. Clotrimazole as a pharmaceutical: Past, present and future. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Andes, D.R.; Diekema, D.J.; Horn, D.L.; Reboli, A.C.; Rotstein, C.; Franks, B.; Azie, N.E. Epidemiology and outcomes of invasive candidiasis due to non-albicans species of Candida in 2496 patients: Data from the Prospective Antifungal Therapy (PATH) registry 2004–2008. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calixto, J.G.; Fetz, P.R.; Ammerman, D.; Flores, Y.R.; Caputo, G.A.; Vaden, T.D.; Carone, B.R. Combinatorial Antimicrobial Effects of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids and Antifungals on Model Fungal Organisms. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121657
Calixto JG, Fetz PR, Ammerman D, Flores YR, Caputo GA, Vaden TD, Carone BR. Combinatorial Antimicrobial Effects of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids and Antifungals on Model Fungal Organisms. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(12):1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121657
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalixto, Jesus G., Peter R. Fetz, Daniel Ammerman, Yesenia R. Flores, Gregory A. Caputo, Timothy D. Vaden, and Benjamin R. Carone. 2025. "Combinatorial Antimicrobial Effects of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids and Antifungals on Model Fungal Organisms" Biomolecules 15, no. 12: 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121657
APA StyleCalixto, J. G., Fetz, P. R., Ammerman, D., Flores, Y. R., Caputo, G. A., Vaden, T. D., & Carone, B. R. (2025). Combinatorial Antimicrobial Effects of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids and Antifungals on Model Fungal Organisms. Biomolecules, 15(12), 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121657







