IP6: From Seeds to Science—A Natural Compound’s Path to Clinical Promise
Abstract
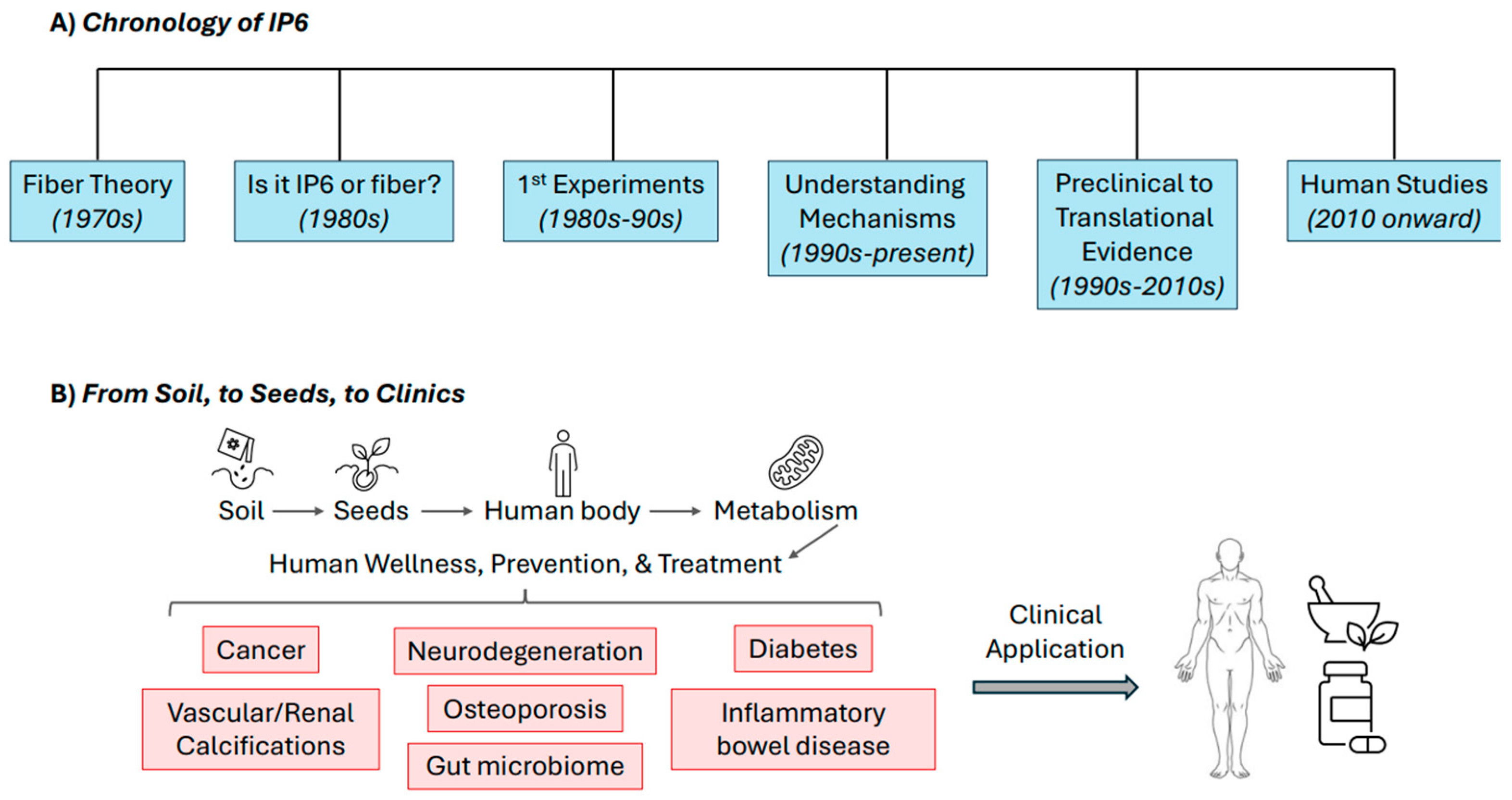
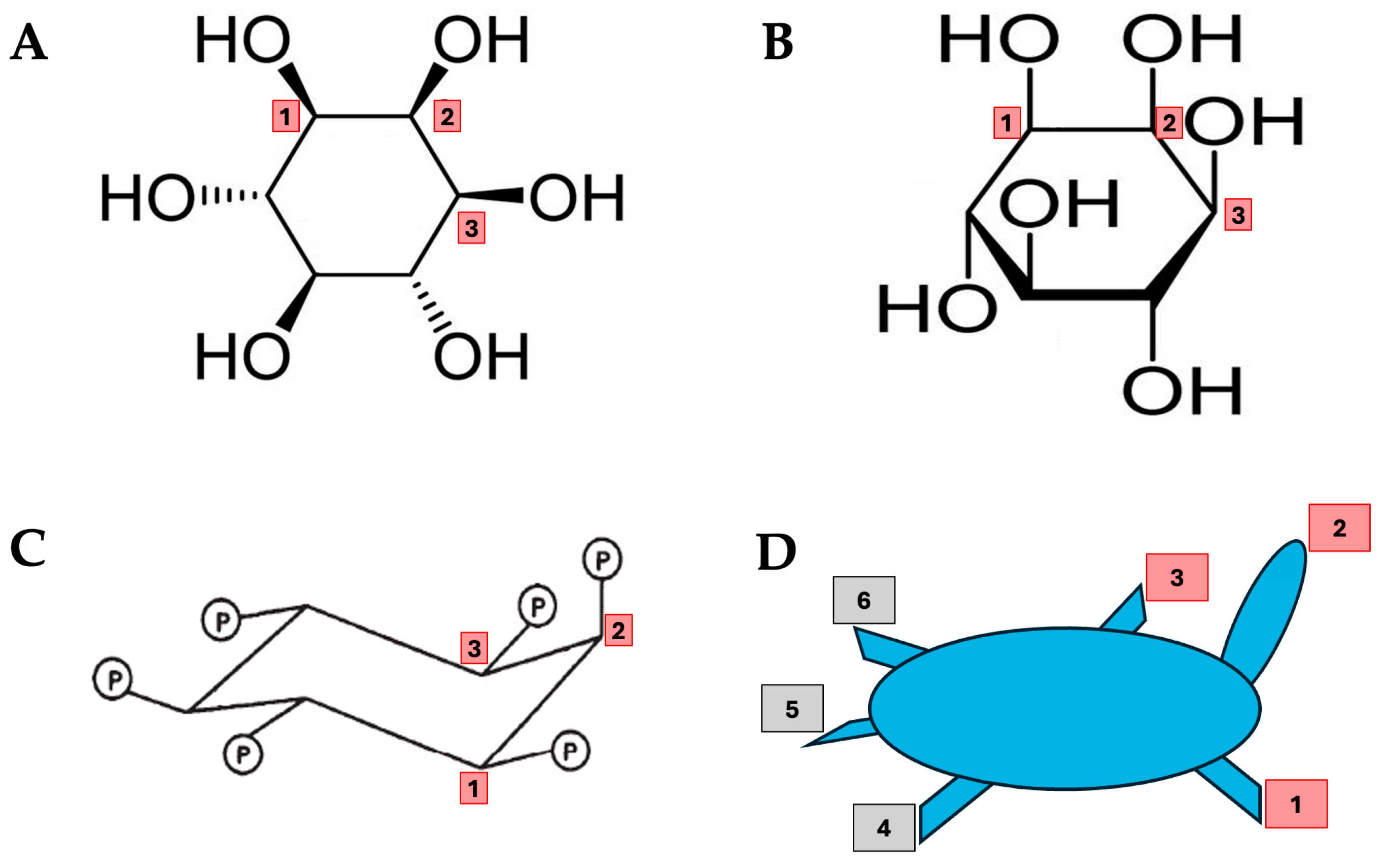
1. Introduction
2. The Antinutrient Debate
3. Modern Discoveries—Shifting Perspectives
4. IP6 as a Therapeutic Agent—Clinical Insights and Emerging Potential
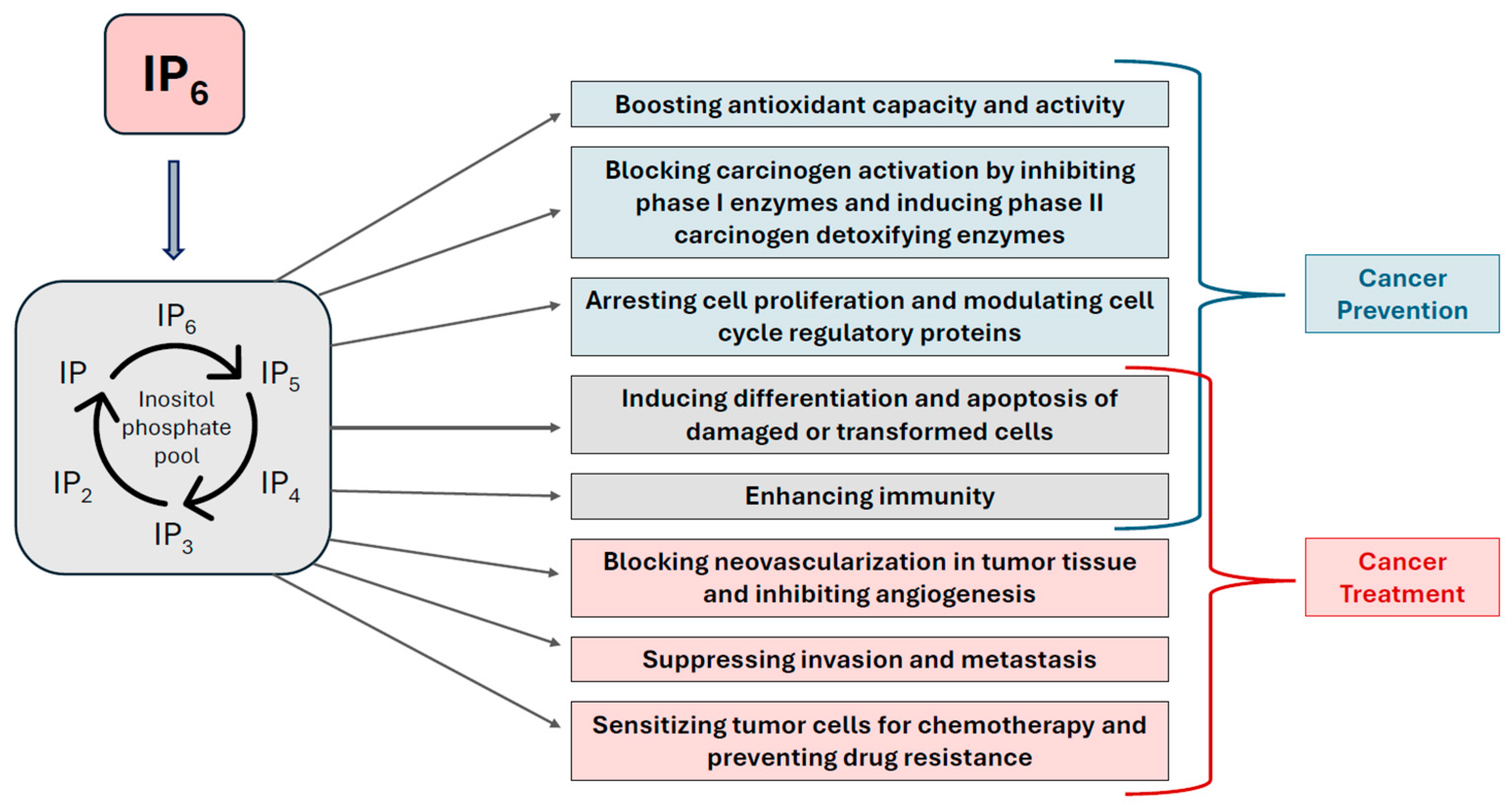
5. Summarized Molecular Mechanisms of IP6
6. Redefining the Role of IP6 in Health and Nutrition—Future Directions
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chatree, S.; Thongmaen, N.; Tantivejkul, K.; Sitticharoon, C.; Vucenik, I. Role of Inositols and Inositol Phosphates in Energy Metabolism. Molecules 2020, 25, 5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.J. A contribution to the chemistry of phytin. J. Biol. Chem. 1914, 17, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucenik, I.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Protection Against Cancer by Dietary IP6 and Inositol. Nutr. Cancer 2006, 55, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucenik, I. Anticancer Properties of Inositol Hexaphosphate and Inositol: An Overview. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, S18–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissar, J.; Ahad, T.; Naik, H.; Hussain, S. A review phytic acid: As antinutrient or nutraceutical. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 1544–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Schlemmer, U.; Frolich, W.; Prieto, R.M.; Grases, F. Phytate in foods and significance for humans: Food sources, intake, processing, bioavailability, protective role and analysis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, S330–S375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Sudhakaran, L. Regulation of immune responses by vitamin B6. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 585, 404–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grases, F.; Simonet, B.M.; Prieto, R.M.; March, J.G. Phytate levels in diverse rat tissues: Influence of dietary phytate. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 86, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, R.M.; Parker, H.; Erdman, J. Effects of dietary phytate, calcium and magnesium levels on zinc bioavailability to rats. J. Nutr. 1984, 114, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCance, R.A.; Widdowson, E.M. Mineral Metabolism on Dephytinized Bread. J. Physiol. 1942, 101, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCance, R.A.; Widdowson, E.M. Mineral Metabolism of Healthy Adults on White and Brown Bread Dietaries. J. Physiol. 1942, 101, 44–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.R.; Fox, F.W.; Irving, J.T. Studies in human mineral metabolism: 1. The effect of bread rich in phytate phosphorus on the metabolism of certain mineral salts with special reference to calcium. Biochem. J. 1948, 42, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruickshank, E.W.; Duckworth, J.; Kosterlitz, H.W.; Warnock, G.M. The digestibility of the phytic acid of oatmeal in adult man. J. Physiol. 1945, 104, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, N.T. Effects of Phytic Acid on Mineral Availability. In Dietary Fiber in Health and Disease; Vahouny, G.V., Kritchevsky, D., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1982; pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, H.W.; Leenhardt, F.; Coudray, C.; Remesy, C. Minerals and phytic acid interactions: Is it a real problem for human nutrition? Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallauf, J.; Rimbach, G. Nutritional significance of phytic acid and phytase. Arch. Tierernahr. 1997, 50, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlemmer, U.; Jany, K.D.; Berk, A.; Schulz, E.; Rechkemmer, G. Degradation of phytate in the gut of pigs--pathway of gastro-intestinal inositol phosphate hydrolysis and enzymes involved. Arch. Tierernahr. 2001, 55, 255–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsuddin, A.M.; Elsayed, A.; Ullah, A. Suppression of large intestinal cancer in F344 rats by inositol hexaphosphate. Carcinogenesis 1988, 9, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsuddin, A.M.; Ullah, A. Inositol hexaphosphate inhibits large intestinal cancer in F344 rats 5 months after induction by azoxymethane. Carcinogenesis 1989, 10, 625–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Dose-dependent inhibition of large intestinal cancer by inositol hexaphosphate in F344 rats. Carcinogenesis 1990, 11, 2219–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucenik, I.; Yang, G.Y.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Inositol hexaphosphate and inositol inhibit DMBA-induced rat mammary cancer. Carcinogenesis 1995, 16, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivapurkar, N.; Tang, Z.C.; Frost, A.; Alabaster, O. A rapid dual organ rat carcinogenesis bioassay for evaluating the chemoprevention of breast and colon cancer. Cancer Lett. 1996, 100, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretlow, T.P.; O’Riordan, M.A.; Somich, G.A.; Amini, S.B.; Pretlow, T.G. Aberrant crypts correlate with tumor incidence in F344 rats treated with azoxymethane and phytate. Carcinogenesis 1992, 13, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challa, A.; Rao, D.R.; Reddy, B.S. Interactive suppression of aberrant crypt foci induced by azoxymethane in rat colon by phytic acid and green tea. Carcinogenesis 1997, 18, 2023–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saied, I.T.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Up-regulation of the tumor suppressor gene p53 and WAF1 gene expression by IP6 in HT-29 human colon carcinoma cell line. Anticancer Res. 1998, 18, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vucenik, I.; Tantivejkul, K.; Zhang, Z.S.; Cole, K.E.; Saied, I.; Shamsuddin, A.M. IP6 treatment of liver cancer. I. IP6 inhibits growth and reverses transformed phenotype in HepG2 human liver cancer cell line. Anticancer Res. 1998, 18, 4083–4090. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuddin, A.M.; Baten, A.; Lalwani, N.D. Effect of inositol hexaphosphate on growth and differentiation in K562 erythroleukemia cell line. Cancer Lett. 1992, 64, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliliers, G.L.; Servida, F.; Fracchiolla, N.S.; Ricci, C.; Borsotti, C.; Colombo, G.; Soligo, D. Effect of inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) on human normal and leukaemic haematopoietic cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 117, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Venkatraman, G.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Growth inhibition and differentiation of HT-29 cells in vitro by inositol hexaphosphate (phytic acid). Carcinogenesis 1993, 14, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsuddin, A.M.; Yang, G.-Y. Inositol hexaphosphate inhibits growth and induces differentiation of PC-3 human prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 1995, 16, 1975–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R. Inositol hexaphosphate inhibits growth, and induces G1 arrest and apoptotic death of prostate carcinoma DU145: Modulation of CDKI-CDK-cyclin and pRb-related protein-E2F complexes. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, S.; Matsuda, M.; Yoshida, H.; Hirata, M. Inositol hexakisphosphate blocks tumor cell growth by activating apoptotic machinery as well as by inhibiting the Akt/NFκB-mediated cell survival pathway. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucenik, I.; Tomazic, V.J.; Fabian, D.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Antitumor activity of phytic acid (inositol hexaphosphate) in murine transplanted and metastatic fibrosarcoma, a pilot study. Cancer Lett. 1992, 65, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucenik, I.; Kalebic, T.; Tantivejkul, K.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Novel anticancer function of inositol hexaphosphate (IP6): Inhibition of human rhabdomyosarcoma in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Res. 1998, 18, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Vucenik, I.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Cancer inhibition by inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) and inositol: From laboratory to clinic. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3778S–3784S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vucenik, I.; Ramakrishna, G.; Tantivejkul, K.; Anderson, L.M.; Ramljak, D. Inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) blocks proliferation of human breast cancer cells through a PKCdelta-dependent increase in p27Kip1 and decrease in retinoblastoma protein (pRb) phosphorylation. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 91, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzarri, M.; Dinicola, S.; Bevilacqua, A.; Cucina, A. Broad Spectrum Anticancer Activity of Myo-Inositol and Inositol Hexakisphosphate. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 2016, 5616807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, E.; Eaton, J.W. Antioxidant functions of phytic acid. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1990, 8, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, E.; Empson, K.L.; Eaton, J.W. Phytic acid. A natural antioxidant. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 11647–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J.; Irvine, R.F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature 1989, 341, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menniti, F.S.; Oliver, K.G.; Pytney, J.W., Jr.; Shears, S.B. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling: New view of InsP5 and InsP6. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1993, 18, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shears, S.B.; Ganapathi, S.B.; Gokhale, N.A.; Schenk, T.M.H.; Wang, H.; Weaver, J.D.; Zaremba, A.; Zhou, Y. Defining signal transduction by inositol phosphates. Subcell. Biochem. 2012, 59, 389–412. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.P.; Mills, S.J.; Potter, B.V. The “other” inositols and their phosphates: Synthesis, biology, and medicine (with recent advances in myo-inositol chemistry). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 1614–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisson, R.S.; Shi, E.; Kan, M.; Yamaguchi, F.; McKeehan, W.; Rudnicka-Nawrot, M.; Palczewski, K. Inositol hexaphosphate (InsP6): An antagonist of fibroblast growth factor receptor binding and activity. In vitro. Cell. Dev. Biol. 1994, 30, 783–789. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Ma, W.Y.; Hecht, S.S.; Dong, Z. Inositol hexaphosphate inhibits cell transformation and activator protein 1 activation by targeting phosphatidylinositol-3′ kinase. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 2873–2878. [Google Scholar]
- Efanov, A.M.; Zaitsev, S.V.; Berggren, P.O. Inositol hexakisphosphate stimulates non-Ca2+-mediated and primes Ca2+-mediated exocytosis of insulin by activation of protein kinase C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4435–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, X.; Singh, R.P.; Agarwal, R. Impairment of erbB1 receptor and fluid phase endocytosis and associated mitogenic signaling by inositol hexaphosphate in human prostate carcinoma DU145 cells. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 2225–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brehm, M.A.; Windhorst, S. New options of cancer treatment employing InsP6. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 163, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vucenik, I.; Passaniti, A.; Vitolo, M.I.; Tantivejkul, K.; Eggleton, P.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Anti-angiogenic activity of inositol hexaphosphate (IP6). Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.C.; Kleiger, G. Regulation of cullin-RING E3 ligase dynamics by inositol hexakisphosphate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6292–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.O.; Bracarense, A.P. Phytic Acid: From Antinutritional to Multiple Protection Factor of Organic Systems. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, R1357–R1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilworth, L.; Stennett, D.; Omoruyi, F. Cellular and Molecular Activities of IP6 in Disease Prevention and Therapy. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, Y.; Yang, C.H.; Chen, S.K.; Yen, Y.C.; Wang, C.S. Inositol hexaphosphate modulates the behavior of macrophages through alteration of gene expression involved in pathways of pro- and anti-inflammatory responses, and resolution of inflammation pathways. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3240–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawszczyk, J.; Orchel, A.; Kapral, M.; Hollek, A.; Weglarz, L. Phytic acid down-regulates IL-8 secretion from colonic epithelial cells by influencing mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2012, 69, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Baten, A.; Ullah, A.; Tomazic, V.J.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Inositol-phosphate-induced enhancement of natural killer cell activity correlates with tumor suppression. Carcinogenesis 1989, 10, 1595–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.L. Inositol hexaphosphate-induced enhancement of natural killer cell activity correlates with suppression of colon carcinogenesis in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 5044–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.T.; Song, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, C.P.; Zhao, H.C.; Han, Y.S.; Wang, C.H.; Yang, N.; Xu, Z.; Tao, M.; et al. IP6 reduces colorectal cancer metastasis by mediating the interaction of gut microbiota with host genes. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 979135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucenik, I.; Zhang, Z.S.; Shamsuddin, A.M. IP6 in treatment of liver cancer. II. Intra-tumoral injection of IP6 regresses pre-existing human liver cancer xenotransplanted in nude mice. Anticancer Res. 1998, 18, 4091–4096. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.R.; Sharma, G.; Mallikarjuna, G.U.; Dhanalakshmi, S.; Aragwal, C.; Agrwal, R. In vivo suppression of hormone-refractory prostate cancer growth by inositol hexaphosphate: Induction of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Kanthasamy, A.G.; Reddy, M.B. Neuroprotective effect of the natural iron chelator, phytic acid in a cell culture model of Parkinson’s disease. Toxicology 2008, 245, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onu, C.J.; Adu, M.; Chakkour, M.; Kumar, V.; Greenberg, M.L. Inositol Phosphates and Synthesizing Enzymes: Implications in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantivejkul, K.; Vucenik, I.; Eiseman, J.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) enhances the anti-proliferative effects of adriamycin and tamoxifen in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 79, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Jia, Q.; Liao, X.; Fan, T.; Mou, L.; Song, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; et al. Inositol hexaphosphate enhances chemotherapy by reversing senescence induced by persistently activated PERK and diphthamide modification of eEF2. Cancer Lett. 2024, 582, 216591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Papalou, O.; Soulage, C. Effectiveness of Myo- and d-chiro-inositol in the treatment of metabolic disorders. In A Guide to Clinical Inositols; Unfer, V., Dewailly, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua, A.; Dinicola, S.; Bizzarri, M. Treating PCOS with inositols: Choosing the most appropriate myo- to d-chiro-inositol ratio. In A Guide to Clinical Inositols; Unfer, V., Dewailly, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Druzijanić, N.; Druzijanić, A.; Vucenik, I. IP6 + Ins in the Treatment of Colon Cancer Patients During Chemotherapy: Observational Clinical Study. In Advances in Diagnosis and Therapy of Colorectal Carcinoma; Chen, J., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2024; Chapter 7. [Google Scholar]
- Bacić, I.; Druzijanić, N.; Karlo, R.; Skifić, I.; Jagić, S. Efficacy of IP6 + inositol in the treatment of breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: Prospective, randomized, pilot clinical study. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Li, W.; Ke, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zhuang, C.; Xie, S.; Wu, R.; et al. Investigating the mechanism of inositol against paclitaxel chemoresistance on triple-negative breast cancer by using 7T multiparametric MRI and mitochondrial changes. Breast Cancer Res. 2025, 27, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, S.; Baldeo, C.; Joseph, R.W. Inositol hexaphosphate plus inositol induced complete remission in stage IV melanoma: A case report. Melanoma Res. 2019, 29, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapral, M.; Wawszczyk, J.; Weglarz, L. Regulation of MicroRNA-155 and Its Related Genes Expression by Inositol Hexaphosphate in Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, A.; Sanchis, P.; Grases, F.; Masmiquel, L. Phytate Intake, Health and Disease: Let Thy Food Be Thy Medicine and Medicine Be Thy Food. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekramzadeh, M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.D. The Relevance of Phytate for the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2024, 19, 1341–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pragya; Kumar, P.; Singh, D.; Tiwari, S.K.; Chouayekh, H.; Singh, B. Phytic acid: Biosynthesis, functional attributes and conventional vis-à-vis modern approaches for reduction. Food Biosci. 2025, 71, 107204. [Google Scholar]
- Zyla, K.; Duda, A. Towards Improved Bioavailability of Cereal Inositol Phosphates, Myo-Inositol, and Phenolic Acids. Molecules 2025, 30, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, I.; Arosio, P.; Tarantino, D.; Soave, C. Biofortification for combating ‘hidden hunger’ for iron. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloot, A.P.M.; Kalschne, D.L.; Amaral, J.A.S.; Baraldi, I.J.; Canan, C. A Review of Phytic Acid Sources, Obtention, and Applications. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 39, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saverino, A.; Shamsuddin, A.M.; Vucenik, I. IP6: From Seeds to Science—A Natural Compound’s Path to Clinical Promise. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121652
Saverino A, Shamsuddin AM, Vucenik I. IP6: From Seeds to Science—A Natural Compound’s Path to Clinical Promise. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(12):1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121652
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaverino, Alissa, AbulKalam M. Shamsuddin, and Ivana Vucenik. 2025. "IP6: From Seeds to Science—A Natural Compound’s Path to Clinical Promise" Biomolecules 15, no. 12: 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121652
APA StyleSaverino, A., Shamsuddin, A. M., & Vucenik, I. (2025). IP6: From Seeds to Science—A Natural Compound’s Path to Clinical Promise. Biomolecules, 15(12), 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121652






