Evaluation of Feline Exosome Mediated Renal Regeneration in Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Feeding and Care
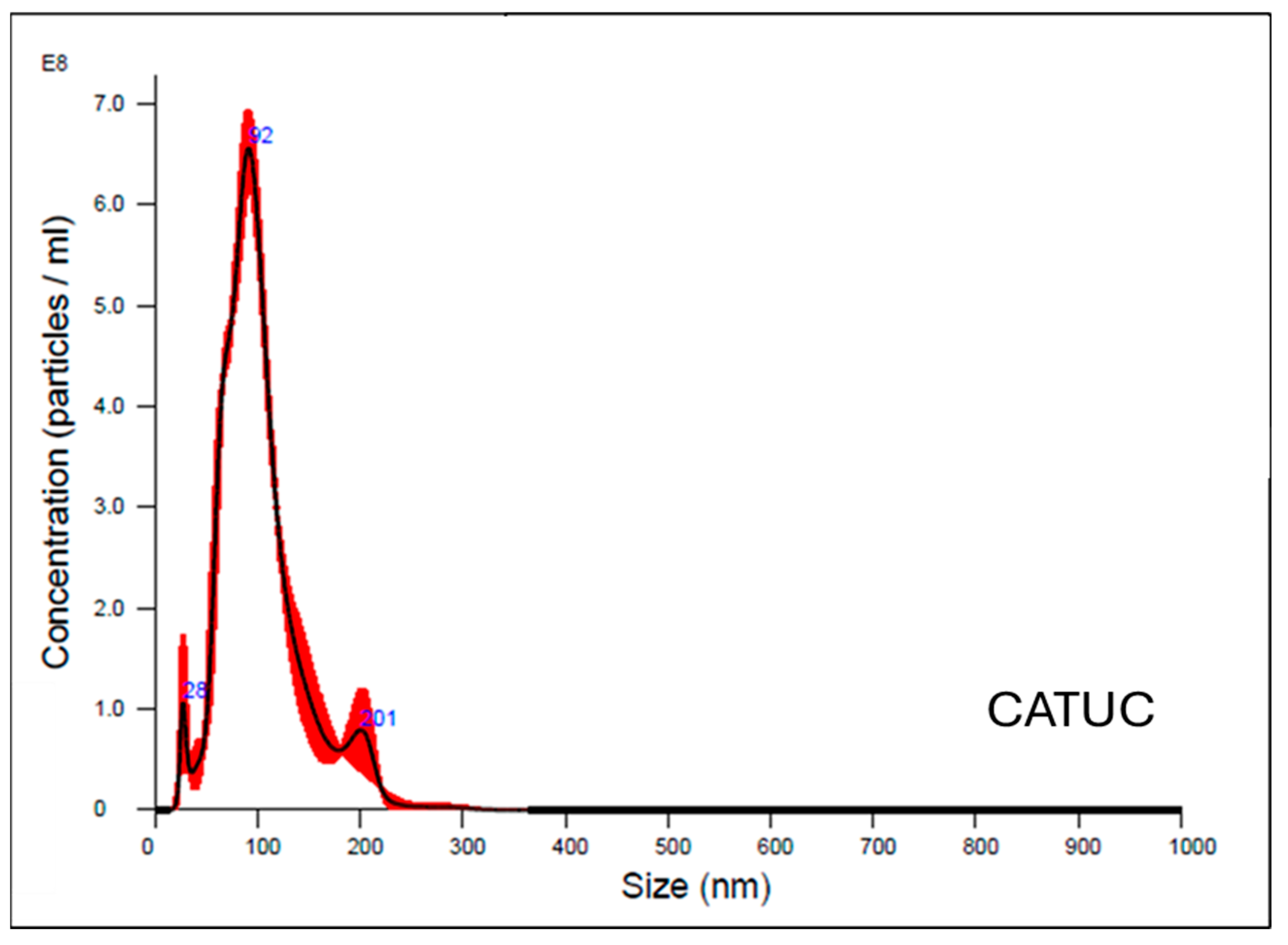
2.3. Exosome Characterization
2.4. Size Distribution Analysis
2.5. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Induction
2.6. Exosome Therapeutic Treatment
2.7. Animal Assessment and Sample Collection
2.8. Histopathological Analysis
2.9. Data Analysis and Writing
3. Results
3.1. Chronic Kidney Disease Induction
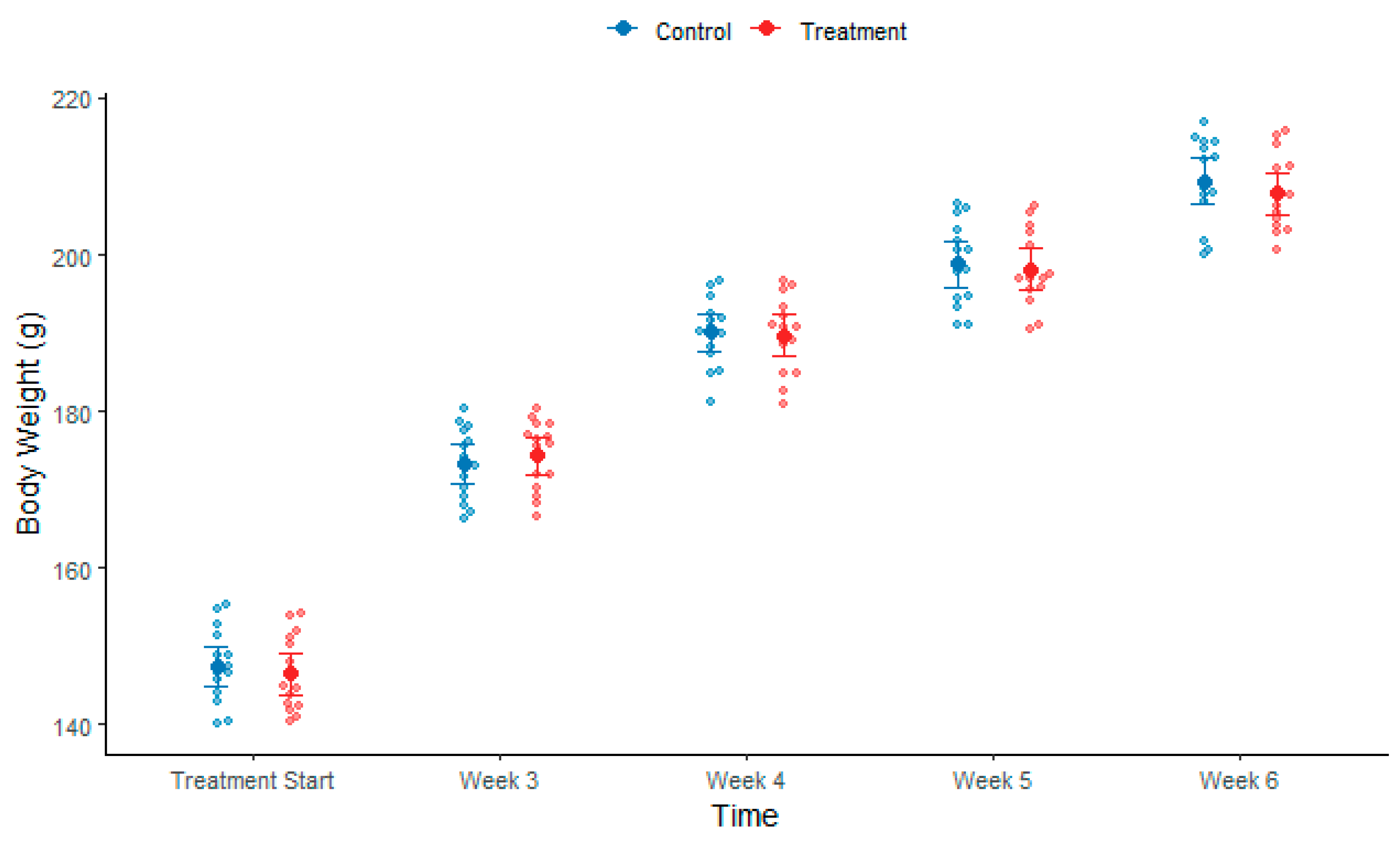
3.1.1. Body Weight During Induction
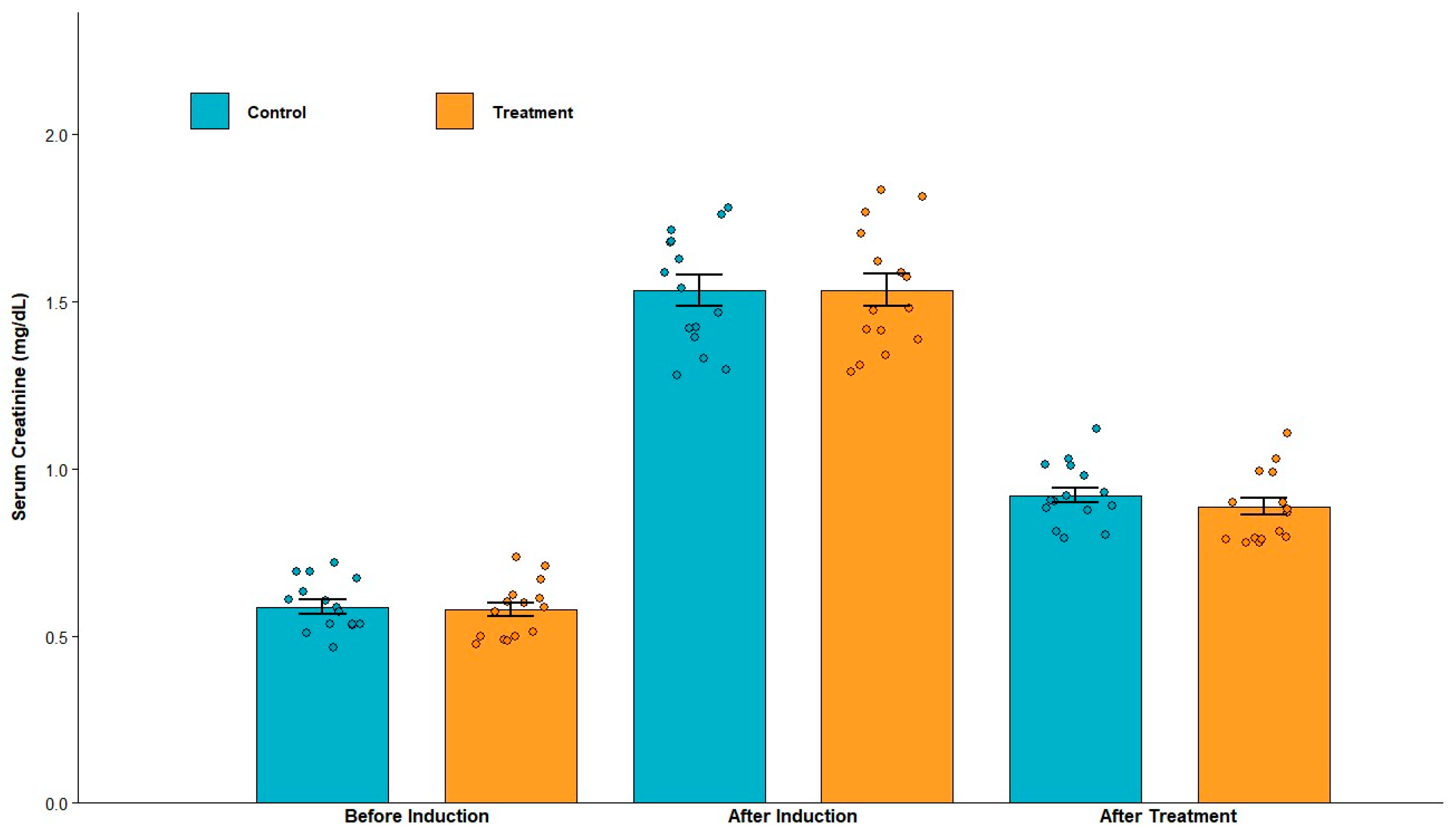
3.1.2. Serum Creatinine and Urinary Protein Levels After Induction
3.2. Exosome Therapeutic Treatment
3.2.1. Body Weight After Exosome Treatment
3.2.2. Serum Creatinine and Urinary Protein Levels After Treatment
3.3. Histological Analysis
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reiss, A.B.; Jacob, B.; Zubair, A.; Srivastava, A.; Johnson, M.; De Leon, J. Fibrosis in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Targets. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx-Schütt, K.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Jankowski, J.; Matsushita, K.; Nardone, M.; Marx, N. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. Eur. Heart J. 2025, 46, 2148–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharief, S.; Hsu, C.Y. The transition from the pre-ESRD to ESRD phase of CKD: Much remains to be learned. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoux, F.; Bartiromo, M. How to improve quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease: A personal view. J. Nephrol. 2008, 21, S7–S8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.; Lewis, R.D.; Morgan, A.R.; Whyte, M.B.; Hanif, W.; Bain, S.C.; Davies, S.; Dashora, U.; Yousef, Z.; Patel, D.C.; et al. A narrative review of chronic kidney disease in clinical practice: Current challenges and future perspectives. Adv. Ther. 2021, 39, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A.; Guerra, J.M.A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Jha, V.; Kramer, H.; Nicholas, S.B.; Pavkov, M.E.; Wanner, C.; Wong, L.P.; Cheung, M.; et al. Preventing chronic kidney disease and maintaining kidney health: Conclusions from a kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) controversies conference. Kidney. Int. 2025, 108, P555–P571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.; Gadegbeku, C. Targeting the standardized blood pressure: New guidelines for blood pressure management in chronic kidney disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 1321–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.P.; Shi, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.Q.; Liu, Y. Recommended intakes of protein and energy in patients with chronic kidney disease: From guidelines of KDOQI and KDIGO in 2020. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 101, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Muthu, S.; Bapat, A.; Jain, R.; Jeyaraman, N.; Jeyaraman, M. Exosomal therapy—A new frontier in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Investig. 2021, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, J.; Caja, S.; Strano Moraes, M.C.; Couto, N.; Costa-Silva, B. Exosome-based cell-cell communication in the tumor microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.J.; Jensen, S.S.; Lim, J.W.E. Proteomic profiling of exosomes: Current perspectives. Proteomics 2008, 8, 4083–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Tian, W. Physiological and pathological impact of exosomes of adipose tissue. Cell Prolif. 2016, 49, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.J.; Yang, J.J.; Lu, Y.-B.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, X.X. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. World J. Stem. Cells 2020, 12, 814–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himanshu; Gunjan; Pandey, R.P.; Mukherjee, R.; Chang, C.M. Meta-analysis study of the therapeutic impact of Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes for chronic kidney diseases. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2025, 43, 102072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Ma, J.X.; Lu, B.; Criswell, T.; Zhang, Y. Exosome-mediated renal protection: Halting the progression of fibrosis. Genes. Dis. 2024, 11, 101117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, V.; Brown, L.; Gobe, G.C. Adenine-induced chronic kidney disease in rats. Nephrology 2018, 23, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Frutos, S.; Luengo, A.; García-Jérez, A.; Hatem-Vaquero, M.; Griera, M.; O’Valle, F.; Rodríguez-Puyol, M.; Rodríguez-Puyol, D.; Calleros, L. Chronic kidney disease induced by an adenine rich diet upregulates integrin linked kinase (ILK) and its depletion prevents the disease progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinkhammer, B.M.; Djudjaj, S.; Kunter, U.; Palsson, R.; Edvardsson, V.O.; Wiech, T.; Thorsteinsdottir, M.; Hardarson, S.; Foresto-Neto, O.; Mulay, S.R.; et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of kidney injury in 2,8-Dihydroxyadenine nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Xu, F.; Liu, L.; Mao, H.; Ren, J. Unilateral ureteral obstruction model for investigating kidney interstitial fibrosis. J. Vis. Exp. 2025, 25, e67897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C.; Ferreira, Y.J.; Dragovic, R.A.; Redman, C.W.G.; Sargent, I.L. Extracellular vesicle sizing and enumeration by nanoparticle tracking analysis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 19671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvern Panalytical. NanoSight NS300 User Manual (MAN0541); Malvern Panalytical: Malvern, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford, C.; Long, G.; Wolf, J.; Okerberg, C.; Herbert, R. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of nonneoplastic lesions in toxicology studies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2002, 30, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. CSH Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb.prot4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Vlekkert, D.; Machado, E.; d’Azzo, A. Analysis of generalized fibrosis in mouse tissue sections with Masson’s trichrome staining. Bio-protoc. 2020, 10, e3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J. Welcome to the tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Su, S.; Luo, N.; Cao, G. Adenine-induced animal model of chronic kidney disease: Current applications and future perspectives. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2336128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; Tapparo, M.; Collino, F.; Chiabotto, G.; Deregibus, M.C.; Lindoso, R.S.; Neri, F.; Kholia, S.; Giunti, S.; Wen, S.; et al. Renal regenerative potential of different extracellular vesicle populations derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 2017, 23, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcayaga-Miranda, F.; Varas-Godoy, M.; Khoury, M. Harnessing the angiogenic potential of stem cell-derived exosomes for vascular regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 3409169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasoni, S.; Longaretti, L.; Rota, C.; Morigi, M.; Conti, S.; Capelli, C.; Introna, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Benigni, A. Transfer of growth factor receptor mRNA via exosomes unravels the regenerative effect of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, V.; Mistry, A.; Gobe, G.; Brown, L. Adenine-induced chronic kidney and cardiovascular damage in rats. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2013, 68, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



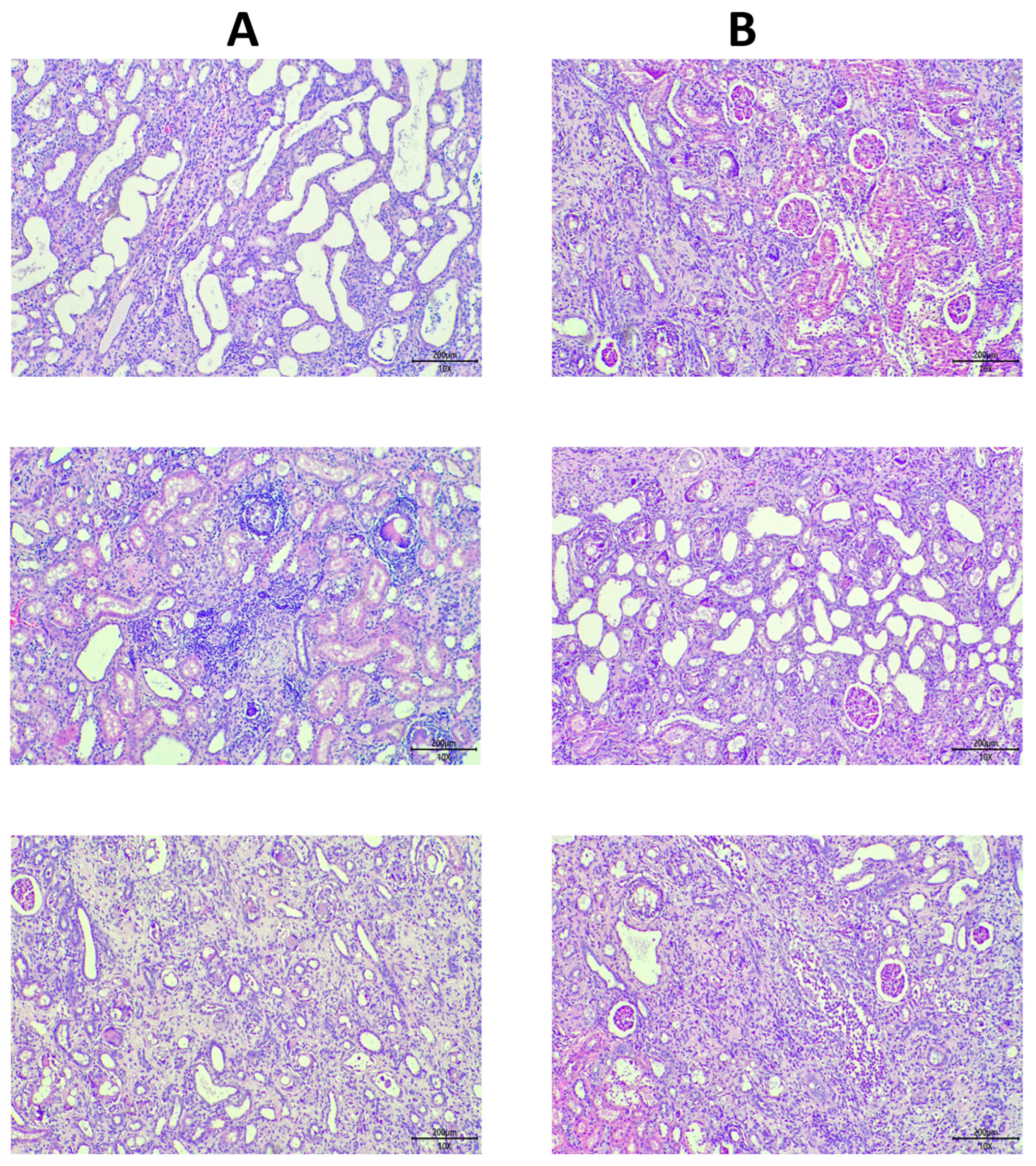
| Grade | Severity |
|---|---|
| 1 | Minimal (<10%) |
| 2 | Mild (11–39%) |
| 3 | Moderate (40–79%) |
| 4 | Marked (80–100%) |
| Feline Exosome Treated Group | |||||||||||||||
| Animal ID | 1001 | 1002 | 1003 | 1004 | 1005 | 1006 | 1007 | 1008 | 1009 | 1010 | 1011 | 1012 | 1013 | 1014 | 1015 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.5 |
| Urinary Protein (mg/dL) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Control Group | |||||||||||||||
| Animal ID | 1016 | 1017 | 1018 | 1019 | 1020 | 1021 | 1022 | 1023 | 1024 | 1025 | 1026 | 1027 | 1028 | 1029 | 1030 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| Urinary Protein (mg/dL) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Feline Exosome Treated Group | |||||||||||||||
| Animal ID | 1001 | 1002 | 1003 | 1004 | 1005 | 1006 | 1007 | 1008 | 1009 | 1010 | 1011 | 1012 | 1013 | 1014 | 1015 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.8 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.7 |
| Urinary Protein (mg/dL) | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| Control Group | |||||||||||||||
| Animal ID | 1016 | 1017 | 1018 | 1019 | 1020 | 1021 | 1022 | 1023 | 1024 | 1025 | 1026 | 1027 | 1028 | 1029 | 1030 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.4 |
| Urinary Protein (mg/dL) | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 | >30 |
| Feline Exosome Treated Group | |||||||||||||||
| Animal ID | 1001 | 1002 | 1003 | 1004 | 1005 | 1006 | 1007 | 1008 | 1009 | 1010 | 1011 | 1012 | 1013 | 1014 | 1015 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Urinary Protein (mg/dL) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Control Group | |||||||||||||||
| Animal ID | 1016 | 1017 | 1018 | 1019 | 1020 | 1021 | 1022 | 1023 | 1024 | 1025 | 1026 | 1027 | 1028 | 1029 | 1030 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | 1.1 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Urinary Protein (mg/dL) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.M.; Villanueva, B.H.A.; Minh, H.; Hussain, Q.; Chuang, K.P. Evaluation of Feline Exosome Mediated Renal Regeneration in Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121647
Lee CM, Villanueva BHA, Minh H, Hussain Q, Chuang KP. Evaluation of Feline Exosome Mediated Renal Regeneration in Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(12):1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121647
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Chien Ming, Brian Harvey Avanceña Villanueva, Hoang Minh, Qasim Hussain, and Kuo Pin Chuang. 2025. "Evaluation of Feline Exosome Mediated Renal Regeneration in Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease" Biomolecules 15, no. 12: 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121647
APA StyleLee, C. M., Villanueva, B. H. A., Minh, H., Hussain, Q., & Chuang, K. P. (2025). Evaluation of Feline Exosome Mediated Renal Regeneration in Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomolecules, 15(12), 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121647








