Current and Emerging Roles of GLP1 Receptor Agonists Across the Spectrum of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
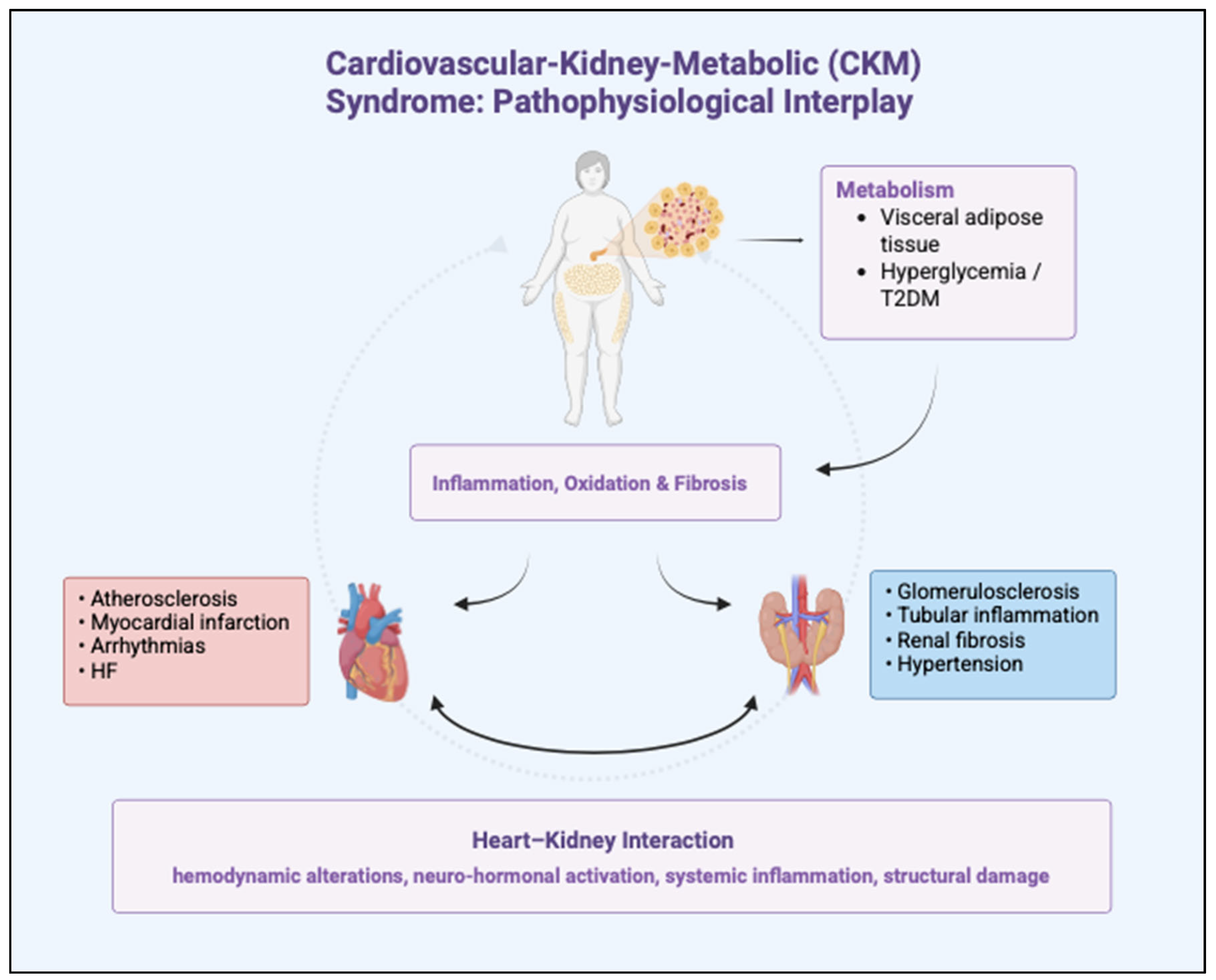
1.2. Cardio-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome
1.3. Cardiovascular Implications
1.4. Methods
2. Focus on Mechanisms of Action of GLP1-RAs in HF
2.1. Systemic Metabolic Effects
2.2. Cardiovascular-Specific Effects
2.3. Renal Protective Mechanisms
3. Clinical Evidence for GLP1-RAs in HF Management
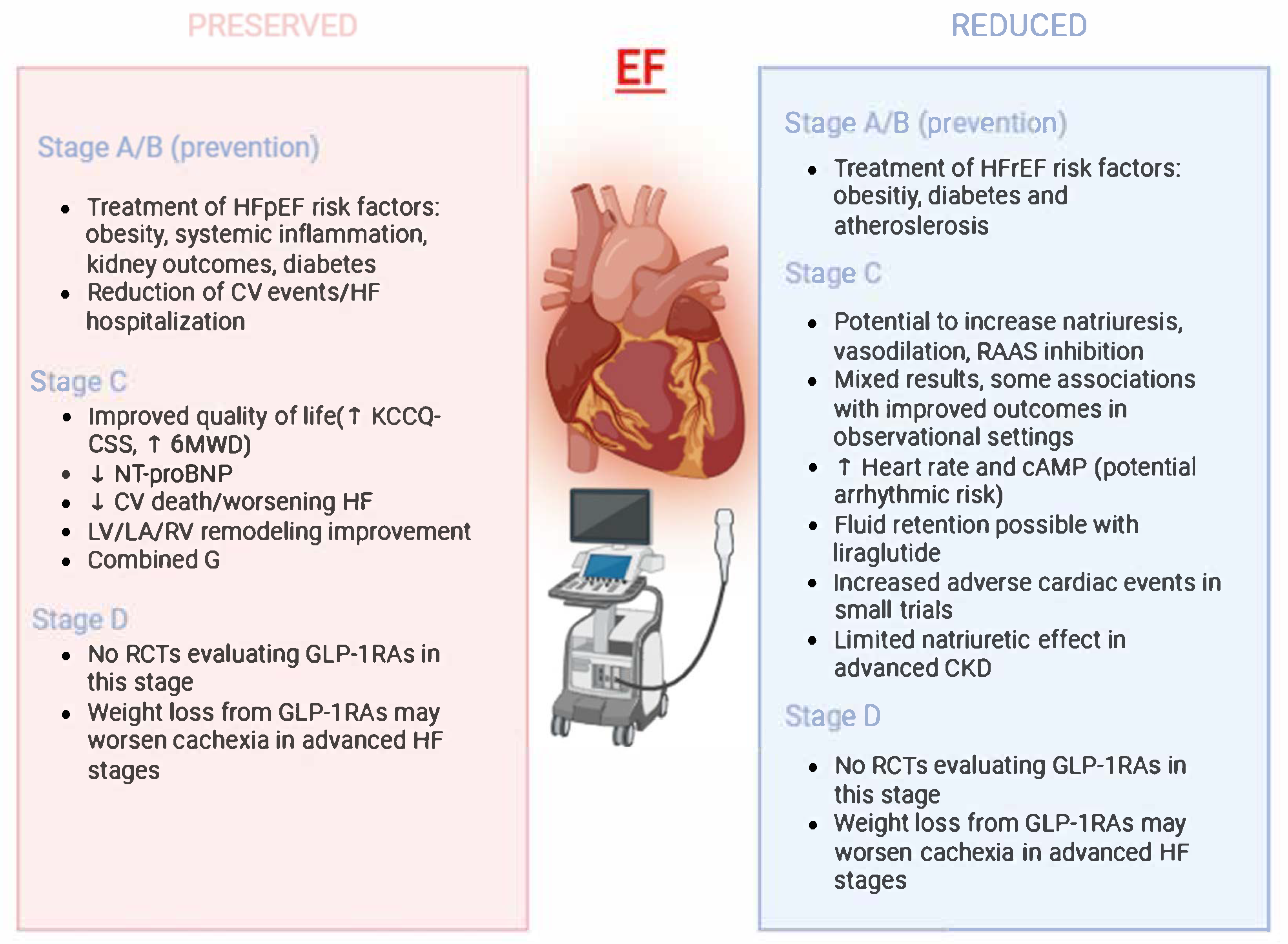
3.1. Stage A and B: Evidence in HF Prevention and Pre-HF
3.2. Stage C/D in HFpEF Management: Putative Implications
3.3. HFrEF-Specific Mechanistic Rationale vs. Clinical Outcome Evidence
| Trial | Intervention | MACE Reduction | CV Death Reduction | HF Hospitalization Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEADER (2016) [16] | Liraglutide | Yes | Trend | Not statistically significant |
| SUSTAIN-6 (2016) [17] | Semaglutide | Yes | Yes | No |
| SELECT (2023) [18] | Semaglutide | Yes (20%) | Yes | Yes |
| FLOW (2024) [58] | Semaglutide | Yes (29%) | Yes | Yes |
| HARMONY (2018) [73] | Albiglutide | N/A | N/A | Yes |
3.4. Concerns Regarding Fluid Retention and Arrhythmic Risk
3.5. Potential Benefits in Patients with Overlapping Cardiometabolic Conditions in HFrEF
4. Considerations for Clinical Practice
4.1. Current Indications and Patient Selection
4.2. Follow-Up, Side Effect Management, and Risk Stratification
5. Ongoing and Upcoming Clinical Trials
Studies Focused on HFpEF, Particularly in Obesity-Driven and Metabolic HF Phenotypes: Combination Therapies and Dual-Agonist Agents
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savarese, G.; Becher, P.M.; Lund, L.H.; Seferovic, P.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Coats, A.J.S. Global burden of heart failure: A comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 3272–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858, Erratum in Lancet 2019, 393, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Aparicio, H.J.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2021 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e254–e743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, E895–E1032, Erratum in Circulation 2022, 145, e1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.; Claggett, B.; de Boer, R.A.; DeMets, D.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.; Martinez, F.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner–La Rocca, H.-P.; Choi, D.-J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Sharma, K.; Shah, S.J.; Ho, J.E. Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. JACC 2023, 81, 1810–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndumele, C.E.; Rangaswami, J.; Chow, S.L.; Neeland, I.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Khan, S.S.; Coresh, J.; Mathew, R.O.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; et al. Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health: A Presidential Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 1606–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenen, M.; Hill, M.A.; Cohen, P.; Sowers, J.R. Obesity, Adipose Tissue and Vascular Dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 951–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siam, N.H.; Snigdha, N.N.; Tabasumma, N.; Parvin, I. Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease: Exploring Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Treatment Strategies. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes—State-of-the-art. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyke, C.; Heller, R.S.; Kirk, R.K.; Ørskov, C.; Reedtz-Runge, S.; Kaastrup, P.; Hvelplund, A.; Bardram, L.; Calatayud, D.; Knudsen, L.B. GLP-1 Receptor Localization in Monkey and Human Tissue: Novel Distribution Revealed with Extensively Validated Monoclonal Antibody. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Colhoun, H.M.; Deanfield, J.; Emerson, S.S.; Esbjerg, S.; Hardt-Lindberg, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kahn, S.E.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Zile, M.R.; Kramer, C.M.; Baum, S.J.; Litwin, S.E.; Menon, V.; Ge, J.; Weerakkody, G.J.; Ou, Y.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiborod, M.N.; Abildstrøm, S.Z.; Borlaug, B.A.; Butler, J.; Rasmussen, S.; Davies, M.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kitzman, D.W.; Lindegaard, M.L.; Møller, D.V.; et al. Semaglutide in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margulies, K.B.; Hernandez, A.F.; Redfield, M.M.; Givertz, M.M.; Oliveira, G.H.; Cole, R.; Mann, D.L.; Whellan, D.J.; Kiernan, M.S.; Felker, G.M.; et al. Effects of Liraglutide on Clinical Stability Among Patients with Advanced Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorsal, A.; Kistorp, C.; Holmager, P.; Tougaard, R.S.; Nielsen, R.; Hänselmann, A.; Nilsson, B.; Møller, J.E.; Hjort, J.; Rasmussen, J.; et al. Effect of liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue, on left ventricular function in stable chronic heart failure patients with and without diabetes (LIVE)—A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 19, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Verma, S.; Vaidya, S.; Kalia, K.; Tiwari, V. Recent updates on GLP-1 agonists: Current advancements & challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykova, A.; Serova, M.; Chashkina, M.; Kosharnaya, R.; Salpagarova, Z.; Andreev, D.; Giverts, I. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in the Context of Pathophysiology of Diverse Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Phenotypes: Potential Benefits and Mechanisms of Action. Card. Fail. Rev. 2024, 10, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secher, A.; Jelsing, J.; Baquero, A.F.; Hecksher-Sørensen, J.; Cowley, M.A.; Dalbøge, L.S.; Hansen, G.; Grove, K.L.; Pyke, C.; Raun, K.; et al. The arcuate nucleus mediates GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide-dependent weight loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4473–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrell, J.; El Bekay, R.; Peral, B.; Garcia-Fuentes, E.; Megia, A.; Macías-González, M.; Fernández Real, J.; Jiménez-Gómez, Y.; Escoté, X.; Pachón, G.; et al. Study of the Potential Association of Adipose Tissue GLP-1 Receptor with Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 4072–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobellis, G.; Mohseni, M.; Bianco, S.D.; Banga, P.K. Liraglutide causes large and rapid epicardial fat reduction. Obesity 2017, 25, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koepp, K.E.; Obokata, M.; Reddy, Y.N.; Olson, T.P.; Borlaug, B.A. Hemodynamic and Functional Impact of Epicardial Adipose Tissue in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Mori, Y. Anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory properties of glucagon-like peptide-1, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypepide, and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in experimental animals. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jojima, T.; Uchida, K.; Akimoto, K.; Tomotsune, T.; Yanagi, K.; Iijima, T.; Suzuki, K.; Kasai, K.; Aso, Y. Liraglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by enhancing AMP-activated protein kinase and cell cycle regulation, and delays atherosclerosis in ApoE deficient mice. Atherosclerosis 2017, 261, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 33, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foer, D.; Strasser, Z.H.; Cui, J.; Cahill, K.N.; Boyce, J.A.; Murphy, S.N.; Karlson, E.W. Association of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbations among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 208, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, H.F.; Waqas, S.A.; Batool, R.M.; Salim, H.; Minhas, A.M.K.; Hasni, S.F.; Alsaid, A.; Sannino, A.; Afzal, A.M.; Khan, M.S. The effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists on cardiac remodeling in heart failure patients with preserved and reduced ejection fraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2025, 30, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Mangmool, S.; Parichatikanond, W. Multifaceted Roles of GLP-1 and Its Analogs: A Review on Molecular Mechanisms with a Cardiotherapeutic Perspective. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, F.K.; Sposito, A.C. Cardiovascular effects of Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huixing, L.; Di, F.; Daoquan, P. Effect of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Prognosis of Heart Failure and Cardiac Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Ther. 2023, 45, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.M.; Borlaug, B.A.; Zile, M.R.; Ruff, D.; DiMaria, J.M.; Menon, V.; Ou, Y.; Zarante, A.M.; Hurt, K.C.; Murakami, M.; et al. Tirzepatide Reduces LV Mass and Paracardiac Adipose Tissue in Obesity-Related Heart Failure. JACC 2024, 85, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M. The Adipokine Hypothesis of Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. JACC 2025, 86, 1269–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispino, S.P.; Segreti, A.; Nafisio, V.; Valente, D.; Crisci, F.; Ferro, A.; Cavallari, I.; Nusca, A.; Ussia, G.P.; Grigioni, F. The Role of SGLT2-Inhibitors Across All Stages of Heart Failure and Mechanisms of Early Clinical Benefit: From Prevention to Advanced Heart Failure. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Sealfon, R.; Menon, R.; Eadon, M.T.; Lake, B.B.; Steck, B.; Anjani, K.; Parikh, S.; Sigdel, T.K.; Zhang, G.; et al. A reference tissue atlas for the human kidney. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skov, J.; Dejgaard, A.; Frøkiær, J.; Holst, J.J.; Jonassen, T.; Rittig, S.; Christiansen, J.S. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1): Effect on Kidney Hemodynamics and Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Healthy Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E664–E671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carraro-Lacroix, L.R.; Malnic, G.; Girardi, A.C.C. Regulation of Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3 by glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist exendin-4 in renal proximal tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2009, 297, F1647–F1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.B.; Hastrup, S.; Underwood, C.R.; Wulff, B.S.; Fleckner, J. Functional importance of GLP-1 receptor species and expression levels in cell lines. Regul. Pept. 2012, 175, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badve, S.V.; Bilal, A.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Sattar, N.; Gerstein, H.C.; Ruff, C.T.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on kidney and cardiovascular disease outcomes: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 13, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.; Karlsson, C.; Schrauwen, P.; Parker, V.E. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonism and end-organ protection. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 36, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Valadez, J.M.; Tahsin, M.; Masharani, U.; Park, M.; Hunink, M.G.M.; Yeboah, J.; Li, L.; Weber, E.; Berkalieva, A.; Avezaat, L.; et al. Potential Mediators for Treatment Effects of Novel Diabetes Medications on Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes: A Meta-Regression Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e032463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.J.; Liang, Y.; Girouard, M.P.; Bhatt, A.S.; Sandhu, A.T.; Sauer, A.J.; Greene, S.J.; Harrington, J.; Go, A.S.; Ambrosy, A.P. Changing the paradigm in heart failure: Shifting from treatment to prevention. Heart Fail. Rev. 2024, 30, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallari, I.; Crispino, S.P.; Segreti, A.; Ussia, G.P.; Grigioni, F. Practical Guidance for the Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2023, 23, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2097–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, J.E.; Gabrielli, L.; Ocaranza, M.P.; MacNab, P.; Fernández, R.; Grassi, B.; Jofré, P.; Verdejo, H.; Acevedo, M.; Cordova, S.; et al. New Mechanisms to Prevent Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Using Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonism (GLP-1 RA) in Metabolic Syndrome and in Type 2 Diabetes: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.P.; Saraiva, F.; Sharma, A.; Vasques-Nóvoa, F.; Angélico-Gonçalves, A.; Leite, A.R.; Borges-Canha, M.; Carvalho, D.; Packer, M.; Zannad, F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes with and without chronic heart failure: A meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled outcome trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Bethel, M.A.; Mentz, R.J.; Thompson, V.P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Buse, J.B.; Chan, J.C.; Choi, J.; Gustavson, S.M.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Effects of Once-Weekly Exenatide on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudim, M.; White, J.; Pagidipati, N.J.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Wainstein, J.; Murin, J.; Iqbal, N.; Öhman, P.; Lopes, R.D.; Reicher, B.; et al. Effect of Once-Weekly Exenatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With and Without Heart Failure and Heart Failure–Related Outcomes. Circulation 2019, 140, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wharton, S.; Blevins, T.; Connery, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Raha, S.; Liu, R.; Ma, X.; Mather, K.J.; Haupt, A.; Robins, D.; et al. Daily Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Orforglipron for Adults with Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Tuttle, K.R.; Rossing, P.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.; Bakris, G.; Baeres, F.M.; Idorn, T.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Lausvig, N.L.; et al. Effects of Semaglutide on Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezin, A.E.; Berezin, A.A.; Lichtenauer, M. Emerging Role of Adipocyte Dysfunction in Inducing Heart Failure Among Obese Patients with Prediabetes and Known Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 583175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussher, J.R.; Drucker, D.J. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: Cardiovascular benefits and mechanisms of action. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocaranza, M.P.; Riquelme, J.A.; García, L.; Jalil, J.E.; Chiong, M.; Santos, R.A.S.; Lavandero, S. Counter-regulatory renin–angiotensin system in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withaar, C.; Meems, L.M.G.; Markousis-Mavrogenis, G.; Boogerd, C.J.; Silljé, H.H.W.; Schouten, E.M.; Dokter, M.M.; A Voors, A.; Westenbrink, B.D.; Lam, C.S.P.; et al. The effects of liraglutide and dapagliflozin on cardiac function and structure in a multi-hit mouse model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 117, 2108–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.-H.; Bai, X.-J.; Zhang, W.-W.; Wang, J.; Bai, F.; Yan, C.-P.; James, E.; Bose, H.S.; Wang, N.-P.; Zhao, Z.-Q. Liraglutide attenuates cardiac remodeling and improves heart function after abdominal aortic constriction through blocking angiotensin II type 1 receptor in rats. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, ume 13, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, D.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Albert, M.A.; Buroker, A.B.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Hahn, E.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; McEvoy, J.W.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A report of the american college of cardiology/American heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation 2019, 140, e596–e646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; Ostrominski, J.W.; Wang, X.; Shah, S.J.; Borlaug, B.A.; Butler, J.; Davies, M.J.; Kitzman, D.W.; Verma, S.; Abildstrøm, S.Z.; et al. Effect of Semaglutide on Cardiac Structure and Function in Patients with Obesity-Related Heart Failure. JACC 2024, 84, 1587–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.; Shah, S.J.; Petrie, M.C.; A Borlaug, B.; Abildstrøm, S.Z.; Davies, M.J.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kitzman, D.W.; Møller, D.V.; Verma, S.; et al. Semaglutide versus placebo in people with obesity-related heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A pooled analysis of the STEP-HFpEF and STEP-HFpEF DM randomised trials. Lancet 2024, 403, 1635–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Zile, M.R.; Kramer, C.M.; Baum, S.J.; Hurt, K.; Litwin, S.E.; Murakami, M.; Ou, Y.; Upadhyay, N.; Packer, M. Effects of tirzepatide on circulatory overload and end-organ damage in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and obesity: A secondary analysis of the SUMMIT trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 31, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Wadid, M.; Makwana, B.; Kumar, A.; Khadke, S.; Bhatti, A.; Banker, A.; Husami, Z.; Labib, S.; Venesy, D.; et al. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Among Patients with Overweight or Obesity, Diabetes, and HFpEF on SGLT2 Inhibitors. JACC Heart Fail. 2024, 12, 1814–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Platt, M.J.; Shibasaki, T.; E Quaggin, S.; Backx, P.H.; Seino, S.; A Simpson, J.; Drucker, D.J. GLP-1 receptor activation and Epac2 link atrial natriuretic peptide secretion to control of blood pressure. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesti, L.; Trico, D. Cardioprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in heart failure: Myth or truth? World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbirk, M.; Nørrelund, H.; Møller, N.; Holst, J.J.; Schmitz, O.; Nielsen, R.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Nielsen, S.S.; Nielsen, T.T.; Eiskjær, H.; et al. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of 48-h glucagon-like peptide-1 infusion in compensated chronic patients with heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2010, 298, H1096–H1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, J.S.; Packer, M.; Ferreira, J.P. Increased Risk of Heart Failure Hospitalization with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Meta-Analysis of the EXSCEL and FIGHT Trials. J. Card. Fail. 2023, 29, 1107–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepore, J.J.; Olson, E.; Demopoulos, L.; Haws, T.; Fang, Z.; Barbour, A.M.; Fossler, M.; Davila-Roman, V.G.; Russell, S.D.; Gropler, R.J. Effects of the Novel Long-Acting GLP-1 Agonist, Albiglutide, on Cardiac Function, Cardiac Metabolism, and Exercise Capacity in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2016, 4, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, M.; Biber, M.E.; Stolfo, D.; Sinagra, G.; Benson, L.; Dahlström, U.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Cosentino, F.; Mol, P.G.M.; Rosano, G.M.C.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists use and associations with outcomes in heart failure and type 2 diabetes: Data from the Swedish Heart Failure and Swedish National Diabetes Registries. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2024, 10, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakobishvili, Z.; Raz, T.; Netzer, D.; Arbel, R. Real World Outcomes of Glucagon Like Peptide1 Receptor Agonists (GLP1-RA) in Diabetic Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merza, N.; Akram, M.; Mengal, A.; Rashid, A.M.; Mahboob, A.; Faryad, M.; Fatima, Z.; Ahmed, M.; Ansari, S.A. The Safety and Efficacy of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Heart Failure Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Metra, M.; Lund, L.H.; Milicic, D.; Costanzo, M.R.; Filippatos, G.; Gustafsson, F.; Tsui, S.; Barge-Caballero, E.; De Jonge, N.; et al. Advanced heart failure: A position statement of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1505–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Fonarow, G.C.; McGuire, D.K.; Hernandez, A.F.; Vaduganathan, M.; Rosenstock, J.; Handelsman, Y.; Verma, S.; Anker, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and Heart Failure. Circulation 2020, 142, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajdlich, M.; Nowicki, M. The impact of GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide on blood pressure profile, hydration, natriuresis in diabetic patients with severely impaired kidney function. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Mann, J.F.; Fonseca, V.; Mosenzon, O.; Raz, I.; Goldman, B.; Idorn, T.; Von Scholten, B.J.; Poulter, N.R. Effects of Liraglutide Versus Placebo on Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease. Circulation 2018, 138, 2908–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.-F.; Nikolskaya, A.; A Jaye, D.; Sigg, D.C. Glucagon-like peptide-1 enhances cardiac L-type Ca2+ currents via activation of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase A pathway. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2011, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrens, X.H.; Lehnart, S.E.; Marks, A.R. Intracellular Calcium Release and Cardiac Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2005, 67, 69–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, P.D.; Purohit, A.; Hund, T.J.; E Anderson, M. Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II: Linking Heart Failure and Arrhythmias. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1661–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartupee, J.; Mann, D.L. Neurohormonal activation in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, C. GLP-1 receptor agonists in heart failure: How far to expand use? Lancet 2024, 404, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driggin, E.; Goyal, P. Malnutrition and Sarcopenia as Reasons for Caution with GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Use in HFpEF. J. Card. Fail. 2024, 30, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S.; Das, A.K.; Sahay, R.K.; Baruah, M.P.; Tiwaskar, M.; Das, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Saboo, B.; Bantwal, G.; Bhattacharya, S.; et al. Consensus Recommendations on GLP-1 RA Use in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: South Asian Task Force. Diabetes Ther. 2019, 10, 1645–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskinas, K.C.; Van Craenenbroeck, E.M.; Antoniades, C.; Blüher, M.; Gorter, T.M.; Hanssen, H.; Marx, N.; A McDonagh, T.; Mingrone, G.; Rosengren, A.; et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: An ESC clinical consensus statement. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 4063–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, R.W.; Mailhac, A.; Løhde, J.B.; Pottegård, A. Real-world evidence on the utilization, clinical and comparative effectiveness, and adverse effects of newer GLP-1RA-based weight-loss therapies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 66–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Ferrari, C.; Tadros, M. GLP-1RA Essentials in Gastroenterology: Side Effect Management, Precautions for Endoscopy and Applications for Gastrointestinal Disease Treatment. Gastroenterol. Insights 2024, 15, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisco, G.; De Tullio, A.; Disoteo, O.; Piazzolla, G.; Guastamacchia, E.; Sabbà, C.; De Geronimo, V.; Papini, E.; Triggiani, V. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and thyroid cancer: Is it the time to be concerned? Endocr. Connect. 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, M.; Chela, H.; Amin, N.; Hunter, R.; Anwar, J.; Tahan, V.; Daglilar, E. Pancreatitis Risk Associated with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, Considered as a Single Class, in a Comorbidity-Free Subgroup of Type 2 Diabetes Patients in the United States: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, R.; Mihalache, A.; Noori, A.; Shor, R.; Kohly, R.P.; Popovic, M.M.; Muni, R.H. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Risk of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. JAMA Ophthalmol 2025, 143, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memel, Z.; Gold, S.L.; Pearlman, M.; Muratore, A.; Martindale, R. Impact of GLP- 1 Receptor Agonist Therapy in Patients High Risk for Sarcopenia. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2025, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghusn, W.; Hurtado, M.D. Glucagon-like Receptor-1 agonists for obesity: Weight loss outcomes, tolerability, side effects, and risks. Obes. Pillars 2024, 12, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.F.; Eltawansy, S.; Naveed, M.A.; Javid, S.; Binashikhbubkr, N.; Sharma, G.; Ikram, M.; Faiz, M.; Ahmad, H.; Zulfiqar, M.S.; et al. E-107 | Role of GLP-1 and Dual GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Angiogr. Interv. 2025, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronne, L.J.; Horn, D.B.; le Roux, C.W.; Ho, W.; Falcon, B.L.; Valderas, E.G.; Das, S.; Lee, C.J.; Glass, L.C.; Senyucel, C.; et al. Tirzepatide as Compared with Semaglutide for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 393, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Bajaj, H.S.; Broholm, C.; Eliasen, A.; Garvey, W.T.; le Roux, C.W.; Lingvay, I.; Lyndgaard, C.B.; Rosenstock, J.; Pedersen, S.D. Cagrilintide–Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 393, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; Blüher, M.; Contreras, C.K.O.; Davies, M.J.; Lehmann, E.W.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; Rubino, D.; Sbraccia, P.; Wadden, T.; Zeuthen, N.; et al. Coadministered Cagrilintide and Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 393, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Jiang, H.; Bi, Y.; Li, H.; Tian, J.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, W.; Huang, C.; Chen, L.; et al. Once-Weekly Mazdutide in Chinese Adults with Obesity or Overweight. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiborod, M.N.; Platz, E.; Wharton, S.; le Roux, C.W.; Brueckmann, M.; Hussain, S.A.; Unseld, A.; Startseva, E.; Kaplan, L.M. Survodutide for the Treatment of Obesity. JACC Heart Fail. 2024, 12, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study/Trial | Population | Intervention | Main Findings | Key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEADER (2016) [16] | T2DM + high CV risk | Liraglutide | Reduced CV events and mortality; no statistically significant reduction in HF hospitalizations | HR for MACE: 0.87 (95% CI 0.78–0.97, p < 0.001) HR for CV deaths: 0.78 (95% CI 0.66–0.93, p = 0.007) |
| SUSTAIN-6 (2016) [17] | T2DM + high CV risk | Semaglutide | Reduced MACE; no benefit on HF hospitalization | HR for MACE: 0.74 (95% CI 0.58–0.95, p < 0.001) |
| EXSCEL (2019) [55] | T2DM, ≥90% with LVEF ≥ 40% | Exenatide | No benefit in HF subgroup; benefit in those without HF | HR for first occurrence of any component of the composite outcome of death from MACE: 0.91 (95% CI 0.83–1.00, p < 0.001 for non-inferiority and p = 0.06 for superiority) |
| Ferreira et al. Meta-analysis (2023) [54] | 54,092 T2DM patients, 16% with HF | Mixed GLP-1RA | Benefit in patients without HF; no benefit in established HF | GLP1-RA did not reduce the composite of HF hospitalization or cardiovascular death in patients with HF history: HR 0.96 (95% CI: 0.84–1.08), but reduced this outcome in patients without HF history: HR 0.84 (95% CI: 0.76–0.92). GLP1-RA did not reduce all-cause death in patients with HF history: HR 0.98 (95% CI: 0.86–1.11), but reduced mortality in patients without HF history: HR 0.85 (95% CI: 0.79–0.92). |
| SELECT (2023) [18] | Obese patients, no diabetes | Semaglutide | ↓ MACE by 20%; ↓ HF-related events by 18% | HR for MACE: 0.80 (CI 0.72–0.90, p < 0.001) |
| FLOW (2024) [58] | T2DM + CKD | Semaglutide | Reduced renal and CV outcomes; ↓ CVD death (29%) | HR for major kidney disease events: 0.76 (95% CI: 0.66–0.88) HR for MACE: 0.82 (95% CI 0.68–0.98, p = 0.029) |
| STEP-HFpEF (2023) [20] | Obese HFpEF (no T2DM), LVEF ≥ 45% | Semaglutide | Improved symptoms (KCCQ-CSS), 6MWD, ↓ CRP, ↓ HF events | Estimated difference in KCCQ-CSS 7.8 points (95% CI 4.8–10.9, p < 0.001) Estimated difference in the 6 min walk distance 20.3 m (95% CI 8.6–32.1, p < 0.001) |
| STEP-HFpEF DM (2024) [65] | Obese HFpEF + T2DM | Semaglutide | Similar benefit to STEP-HFpEF; smaller weight loss ↓ NT-proBNP | Estimated difference in KCCQ-CSS 7.3 points (95% CI 4.1–10.4, p < 0.001) Estimated difference in the 6 min walk distance 14.3 m (95% CI 3.7–24.9, p = 0.008) HR for hospitalization or urgent visit for HF 0.40 (95% CI 0.15–0.92) |
| STEP-HFpEF Pooled Analysis (2024) [66] | Combined STEP trials | Semaglutide | Greater benefit in severe HFpEF ↓ CRP | Mean between-group difference in KCCQ-CSS 7·5 points (95% CI 5.3–9.8) Mean between-group difference in 6 min walk distance 17.1 m (95% CI 9.2–25.0) |
| Patel et al., (2024) [68] | HFpEF + T2DM + Obesity | GLP-1RA + SGLT2i | Combination therapy better than SGLT2i alone | HR for HF exacerbations 0.62 (95% CI 0.58–0.66, p < 0.001) HR for AKI events 0.70 (95% CI 0.65–0.75, p < 0.001) HR for new onset of AF/AFL 0.81 (95% CI 0.70–0.95, p = 0.007) |
| SUMMIT (2025) [19] | Obese HFpEF ± T2DM | Tirzepatide | ↓ CV death or worsening HF; ↑ 6MWD, ↓ CRP | HR for CV deaths or a worsening heart-failure event 0.62 (95% CI 0.41–0.95, p = 0.026) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crispino, S.P.; Nusca, A.; Ferro, A.; Cricco, R.; Ciancio, M.; Segreti, A.; Cavallari, I.; Sabatino, M.; Potena, L.; Ussia, G.P.; et al. Current and Emerging Roles of GLP1 Receptor Agonists Across the Spectrum of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111574
Crispino SP, Nusca A, Ferro A, Cricco R, Ciancio M, Segreti A, Cavallari I, Sabatino M, Potena L, Ussia GP, et al. Current and Emerging Roles of GLP1 Receptor Agonists Across the Spectrum of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111574
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrispino, Simone Pasquale, Annunziata Nusca, Aurora Ferro, Riccardo Cricco, Martina Ciancio, Andrea Segreti, Ilaria Cavallari, Mario Sabatino, Luciano Potena, Gian Paolo Ussia, and et al. 2025. "Current and Emerging Roles of GLP1 Receptor Agonists Across the Spectrum of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111574
APA StyleCrispino, S. P., Nusca, A., Ferro, A., Cricco, R., Ciancio, M., Segreti, A., Cavallari, I., Sabatino, M., Potena, L., Ussia, G. P., & Grigioni, F. (2025). Current and Emerging Roles of GLP1 Receptor Agonists Across the Spectrum of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111574








