Molecular Pathogenesis of Inherited Platelet Dysfunction
Abstract
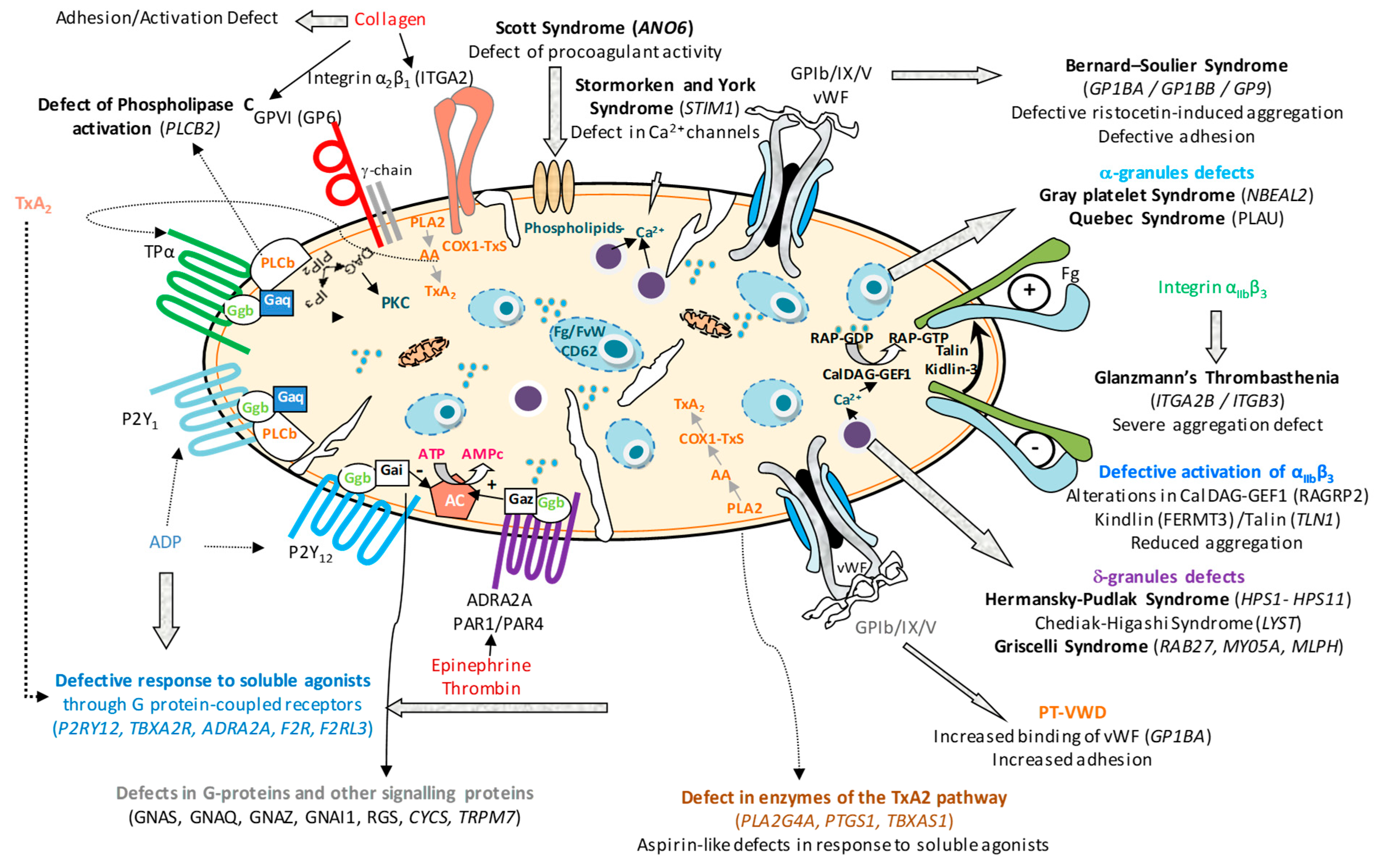
1. Preamble
2. Glanzmann’s Thrombasthenia
2.1. Introduction
2.2. Clinical Manifestations
2.3. Diagnosis
2.4. Treatment
3. Platelet Function Disorders Due to Genetic Defects in Other Platelet Receptors
3.1. Deficiency of Glycoprotein VI (GP VI)
3.2. Defects of the P2Y12 Receptor
3.3. Deficiency of the TxA2 Receptor
3.4. Alterations in the Ephrin Type B2 Receptor
4. Signal Transduction Defects
4.1. RASGRP2 (CalDAG-GEFI) Defect
4.2. Defect or Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency III (LADIII)
4.3. Defects in the TxA2 Pathway
4.4. Phospholipase C Defect
4.5. Defect of G Proteins and Their Regulators
4.6. Other Platelet Signaling Defects
5. Defects of Platelet Granules
5.1. Hermansky–Pudlak Syndrome
5.2. Chediak–Higashi Syndrome
5.3. Griscelli Syndrome
5.4. Arthrogryposis Syndrome, Renal Dysfunction and Cholestasis (ARC Syndrome)
5.5. Non Syndromic Granule Deficiencies
6. Defects in Membrane Phospholipids and/or Procoagulant Activity: Scott Syndrome
7. General Approach to IPFD Treatment
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | arachidonic acid |
| AD | autosomal dominant |
| ADP | adenosine diphosphate |
| AR | autosomal recessive |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| BDPLT18 | bleeding disorder platelet type 18 |
| BLOC | biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex |
| BSS | Bernard–Soulier syndrome |
| CDC42 | cell division control protein 42 homolog |
| CHS | Chediak–Higashi syndrome |
| COX-1 | cyclooxygenase-1 |
| DAG | diacylglycerol |
| DDAVP | desmopressin |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EPHB2 | ephrin type B2 receptor |
| FcR | Fc receptor |
| FC | flow cytometry |
| FERM | four-point-one: ezrin: radixin: moesin domain |
| FYB/ADAP | FYN-binding protein/adhesion and degranulation-promoting adapter protein |
| GDP | guanosine diphosphate |
| GEF | guanine nucleotide exchange factor |
| GGT | gamma-glutamyl transferase |
| Gi | inhibitory G protein alpha subunit |
| GP | glycoprotein |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| GPIIb/IIIa | integrin αIIbβ3 |
| GPIb/IX/V | glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex |
| Gq | G protein alpha q subunit |
| GT | Glanzmann thrombasthenia |
| GTP | guanosine triphosphate |
| HMB | heavy menstrual bleeding |
| HLH | hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis |
| HPS | Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome |
| HSCT | hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| HTS | high-throughput sequencing |
| ITGA2B | integrin subunit alpha IIb |
| ITGB3 | integrin subunit beta 3 |
| LAD-III | leukocyte adhesion deficiency type III |
| LRO | lysosome-related organelle |
| LYST | lysosomal trafficking regulator |
| mRNA | messenger ribonucleic acid |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| OMIM | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PFA-100 | platelet function analyzer-100 |
| PIP2 | phosphatidylinositol 4:5-bisphosphate |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| PLC | phospholipase C |
| PMA | phorbol myristate acetate |
| PS | phosphatidylserine |
| PTGS1 | prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 |
| QS | Quebec syndrome |
| RASGRP2 | RAS guanyl-releasing protein 2 |
| RGS | regulator of G-protein signaling |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| SFK | Src family kinases |
| SS | Scott syndrome |
| TBXA2R | thromboxane A2 receptor |
| TMEM16F | transmembrane protein 16F (Anoctamin 6) |
| TPα | thromboxane receptor alpha isoform |
| TRAP | thrombin receptor-activating peptide |
| TxA2 | thromboxane A2 |
| VASP | vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein |
| VWD | von Willebrand disease |
| VWF | von Willebrand factor |
References
- Nurden, P.; Stritt, S.; Favier, R.; Nurden, A.T. Inherited platelet diseases with normal platelet count: Phenotypes, genotypes and diagnostic strategy. Haematologica 2021, 106, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Barqueros, V.; Revilla, N.; Sanchez, A.; Zamora Canovas, A.; Rodriguez-Alen, A.; Marin-Quilez, A.; Gonzalez-Porras, J.R.; Vicente, V.; Lozano, M.L.; Bastida, J.M.; et al. Inherited Platelet Disorders: An Updated Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.K. Inherited platelet function disorders: Overview and disorders of granules, secretion, and signal transduction. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2013, 27, 585–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero, J.P.; Lee, K.; Branchford, B.R.; Bray, P.F.; Freson, K.; Lambert, M.P.; Luo, M.; Mohan, S.; Ross, J.E.; Bergmeier, W.; et al. Glanzmann thrombasthenia: Genetic basis and clinical correlates. Haematologica 2020, 105, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurden, A.T.; Nurden, P. Glanzmann Thrombasthenia 10 Years Later: Progress Made and Future Directions. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2025, 51, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurden, A. Profiling the Genetic and Molecular Characteristics of Glanzmann Thrombasthenia: Can It Guide Current and Future Therapies? J. Blood Med. 2021, 12, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurden, A.T.; Pillois, X.; Fiore, M.; Alessi, M.C.; Bonduel, M.; Dreyfus, M.; Goudemand, J.; Gruel, Y.; Benabdallah-Guerida, S.; Latger-Cannard, V.; et al. Expanding the Mutation Spectrum Affecting alphaIIbbeta3 Integrin in Glanzmann Thrombasthenia: Screening of the ITGA2B and ITGB3 Genes in a Large International Cohort. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khair, K.; Fletcher, S.; Jenner, K.; Holland, M. One day at a time: Life with Glanzmann thrombasthenia—Qualitative results from the GT 360 study. Haemoph. Off. J. World Fed. Hemoph. 2024, 30, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, N.; Rivard, G.E.; Bonnefoy, A. Glanzmann Thrombasthenia: Perspectives from Clinical Practice on Accurate Diagnosis and Optimal Treatment Strategies. J. Blood Med. 2021, 12, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeng-Tuudah, D.; Tarawah, A.; Ozkan, M.; Abdul-Kadir, R. Obstetric and Gynaecological Challenges and Outcomes in Women and Girls With Glanzmann’s Thrombasthenia. Haemoph. Off. J. World Fed. Hemoph. 2025, 31, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Guiu, I.; Anton, A.I.; Padilla, J.; Velasco, F.; Lucia, J.F.; Lozano, M.; Cid, A.R.; Sevivas, T.; Lopez-Fernandez, M.F.; Vicente, V.; et al. Functional and molecular characterization of inherited platelet disorders in the Iberian Peninsula: Results from a collaborative study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Fuentes, A.; Perez-Botero, J.; Bastida, J.M.; Rivera, J. Diagnosis of Inherited Platelet Disorders: Clinical Evaluation and Functional and Molecular Assays. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.N.; Caen, J.P.; Nurden, A.T. Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia: The spectrum of clinical disease. Blood 1990, 75, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, M.C.; Di Minno, G.; d’Oiron, R.; Zotz, R. New Insights Into the Treatment of Glanzmann Thrombasthenia. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2016, 30, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurden, A.T.; Pillois, X. ITGA2B and ITGB3 gene mutations associated with Glanzmann thrombasthenia. Platelets 2018, 29, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Canovas, A.; de la Morena-Barrio, B.; Marin-Quilez, A.; Sierra-Aisa, C.; Male, C.; Fernandez-Mosteirin, N.; Trapero-Marugan, M.; Padilla, J.; Garrido-Rodriguez, P.; Sanchez-Fuentes, A.; et al. Targeted long-read sequencing identifies and characterizes structural variants in cases of inherited platelet disorders. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH. 2024, 22, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.E.; Zhang, B.M.; Lee, K.; Mohan, S.; Branchford, B.R.; Bray, P.; Dugan, S.N.; Freson, K.; Heller, P.G.; Kahr, W.H.A.; et al. Specifications of the variant curation guidelines for ITGA2B/ITGB3: ClinGen Platelet Disorder Variant Curation Panel. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecci, A.; Balduini, C.L. Inherited thrombocytopenias: An updated guide for clinicians. Blood Rev. 2021, 48, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurden, A.T.; Nurden, P. Inherited thrombocytopenias: History, advances and perspectives. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2004–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazni, I.; Stapley, R.; Morgan, N.V. Inherited Thrombocytopenia: Update on Genes and Genetic Variants Which may be Associated With Bleeding. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurden, A.T.; Pillois, X.; Fiore, M.; Heilig, R.; Nurden, P. Glanzmann thrombasthenia-like syndromes associated with Macrothrombocytopenias and mutations in the genes encoding the alphaIIbbeta3 integrin. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2011, 37, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Minno, G.; Zotz, R.B.; d’Oiron, R.; Bindslev, N.; Di Minno, M.N.; Poon, M.C. The international, prospective Glanzmann Thrombasthenia Registry: Treatment modalities and outcomes of non-surgical bleeding episodes in patients with Glanzmann thrombasthenia. Haematologica 2015, 100, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Giraudet, J.S.; Alessi, M.C.; Falaise, C.; Desprez, D.; d’Oiron, R.; Voisin, S.; Hurtaud, M.F.; Boutroux, H.; Saultier, P.; et al. Emergency management of patients with Glanzmann thrombasthenia: Consensus recommendations from the French reference center for inherited platelet disorders. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurden, A.T. Acquired Antibodies to alphaIIbbeta3 in Glanzmann Thrombasthenia: From Transfusion and Pregnancy to Bone Marrow Transplants and Beyond. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Firah, N.; Pillois, X.; Nurden, P.; Heilig, R.; Nurden, A.T. Natural history of platelet antibody formation against alphaIIbbeta3 in a French cohort of Glanzmann thrombasthenia patients. Haemoph. Off. J. World Fed. Hemoph. 2012, 18, e201–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saultier, P.; Grino, M.; Falaise, C.; Voisin, S.; Lavenu-Bombled, C.; Ibrahim-Kosta, M.; Petit, A.; Boutroux, H.; Desprez, D.; Fiore, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant activated factor VII in Glanzmann thrombasthenia: A systematic literature review. Haemoph. Off. J. World Fed. Hemoph. 2025, 31, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegering, V.; Sauer, K.; Winkler, B.; Eyrich, M.; Schlegel, P.G. Indication for allogeneic stem cell transplantation in Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia. Hamostaseologie 2013, 33, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cid, A.R.; Montesinos, P.; Sanchez-Guiu, I.; Haya, S.; Lorenzo, J.I.; Sanz, J.; Moscardo, F.; Puig, N.; Planelles, D.; Bonanad, S.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in an adult patient with Glanzmann thrombasthenia. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 1887–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, V.R.; Weber, J.; Samelson-Jones, B.J. Gene Therapy for Inherited Bleeding Disorders. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 47, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.A.; White, G.C., 2nd. Gene therapy for platelet disorders: Studies with Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2003, 1, 2300–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, P.S.; Zivkovic, M.; Ostergaard, H.; Bonde, A.C.; Elm, T.; Lovgreen, M.N.; Schluckebier, G.; Johansson, E.; Olsen, O.H.; Olsen, E.H.N.; et al. A bispecific antibody approach for the potential prophylactic treatment of inherited bleeding disorders. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 3, 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangin, P.H.; Gardiner, E.E.; Ariens, R.A.S.; Jandrot-Perrus, M. Glycoprotein VI interplay with fibrin(ogen) in thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2023, 21, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandrot-Perrus, M.; Hermans, C.; Mezzano, D. Platelet glycoprotein VI genetic quantitative and qualitative defects. Platelets 2019, 30, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurden, A.T. Clinical significance of altered collagen-receptor functioning in platelets with emphasis on glycoprotein VI. Blood Rev. 2019, 38, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, A.; Khattak, S.; Thomas, M.R. GPVI inhibition: Advancing antithrombotic therapy in cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2024, 10, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, M. P2Y12 receptors: Structure and function. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2015, 13 (Suppl. S1), S10–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecchi, A.; Femia, E.A.; Paoletta, S.; Dupuis, A.; Ohlmann, P.; Gachet, C.; Jacobson, K.A.; Machura, K.; Podda, G.M.; Zieger, B.; et al. Inherited dysfunctional platelet P2Y12 receptor mutations associated with bleeding disorders. Hamostaseologie 2016, 36, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavone, M.; Femia, E.A.; Cattaneo, M. P2Y(1)(2) receptor gene mutations associated with bleeding. Platelets 2017, 28, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, J.; Lozano, M.L.; Navarro-Nunez, L.; Vicente, V. Platelet receptors and signaling in the dynamics of thrombus formation. Haematologica 2009, 94, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundell, S.J.; Mumford, A. TBXA2R gene variants associated with bleeding. Platelets 2018, 29, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Sage, T.; Rana, R.H.; Schenk, M.P.; Ali, M.S.; Unsworth, A.J.; Jones, C.I.; Stainer, A.R.; Kriek, N.; Moraes, L.A.; et al. EphB2 regulates contact-dependent and contact-independent signaling to control platelet function. Blood 2015, 125, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrou, E.; Soukaseum, C.; Favier, R.; Adam, F.; Elaib, Z.; Kauskot, A.; Bordet, J.C.; Ballerini, P.; Loyau, S.; Feng, M.; et al. A mutation of the human EPHB2 gene leads to a major platelet functional defect. Blood 2018, 132, 2067–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, M.C.; Andrews, R.K. EPHB2 regulates platelet activation. Blood 2018, 132, 2002–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canault, M.; Alessi, M.C. RasGRP2 Structure, Function and Genetic Variants in Platelet Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma-Barqueros, V.; Ruiz-Pividal, J.; Bohdan, N.; Vicente, V.; Bastida, J.M.; Lozano, M.; Rivera, J. RASGRP2 gene variations associated with platelet dysfunction and bleeding. Platelets 2019, 30, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broojerdi, M.H.; Tabibian, S.; Shabestari, R.M.; Barati, M.; Shanaki, M.; Safa, M. Identification of novel RASGRP2 mutations in patients with platelet dysfunction. Transfus. Apher. Sci. Off. J. World Apher. Assoc. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Haemapheresis 2025, 64, 104202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, S.; Pereira, M.; Lau, C.; Goncalves, A.; Monteiro, C.; Goncalves, M.; Oliveira, J.; Moreira, L.; Cruz, E.; Santos, R.; et al. CalDAG-GEFI Deficiency in a Family with Symptomatic Heterozygous and Homozygous Carriers of a Likely Pathogenic Variant in RASGRP2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognoni, E.; Ruppert, R.; Fassler, R. The kindlin family: Functions, signaling properties and implications for human disease. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, L.; Howarth, K.; McDowall, A.; Patzak, I.; Evans, R.; Ussar, S.; Moser, M.; Metin, A.; Fried, M.; Tomlinson, I.; et al. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-III is caused by mutations in KINDLIN3 affecting integrin activation. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, M.; Mastenbroek, T.G.; Mattheij, N.J.A.; de Witt, S.; Clemetson, K.J.; Kirschner, J.; Schulz, A.S.; Vraetz, T.; Speckmann, C.; Braun, A.; et al. Variable impairment of platelet functions in patients with severe, genetically linked immune deficiencies. Haematologica 2018, 103, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, D.; van Leeuwen, K.; Madkaikar, M.; Kambli, P.M.; Gupta, M.; Mathews, V.; Rawat, A.; Kuhns, D.B.; Holland, S.M.; de Boer, M.; et al. Hematologically important mutations: Leukocyte adhesion deficiency (second update). Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2023, 99, 102726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Fuentes, A.; Marín Quílez, A.; Zamora, A.; Rivera, J. Inherited platelet function disorders: Signal transduction defects. In Platelets in Disease: Hemorrhagic Disorders, 1st ed.; Gresele, P., López, J.A., Angiolillo, D.J., Page, C.P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Palma-Barqueros, V.; Bohdan, N.; Revilla, N.; Vicente, V.; Bastida, J.M.; Rivera, J. PTGS1 gene variations associated with bleeding and platelet dysfunction. Platelets 2021, 32, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Barqueros, V.; Crescente, M.; de la Morena, M.E.; Chan, M.V.; Almarza, E.; Revilla, N.; Bohdan, N.; Minano, A.; Padilla, J.; Allan, H.E.; et al. A novel genetic variant in PTGS1 affects N-glycosylation of cyclooxygenase-1 causing a dominant-negative effect on platelet function and bleeding diathesis. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, E83–E88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freson, K.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Jaeken, J.; Eyssen, M.; Arnout, J.; Vermylen, J.; Van Geet, C. Genetic variation of the extra-large stimulatory G protein alpha-subunit leads to Gs hyperfunction in platelets and is a risk factor for bleeding. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, L.; Di Michele, M.; Giets, E.; Thys, C.; Wittevrongel, C.; De Vos, R.; Overbergh, L.; Waelkens, E.; Jaeken, J.; Van Geet, C.; et al. Platelet Gs hypofunction and abnormal morphology resulting from a heterozygous RGS2 mutation. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2010, 8, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayne, C.; Roux, M.; Gruel, Y.; Poggi, M.; Pouplard, C.; Peiretti, F.; Tregouet, D.A.; Nurden, P.; Alessi, M.C. A gain of function variant in RGS18 candidate for a familial mild bleeding syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2024, 23, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizing, M.; Malicdan, M.C.V.; Wang, J.A.; Pri-Chen, H.; Hess, R.A.; Fischer, R.; O’Brien, K.J.; Merideth, M.A.; Gahl, W.A.; Gochuico, B.R. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome: Mutation update. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 543–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.H.Y.; Kahr, W.H.A. Molecular basis of platelet granule defects. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2025, 23, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaninetti, C.; Greinacher, A. Diagnosis of Inherited Platelet Disorders on a Blood Smear. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondi, F.; Cirsmaru, R.A.; Conti, C.; Follenzi, A.; Gresele, P.; Olgasi, C.; Bury, L. Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Targeted Therapies. IUBMB Life 2025, 77, e70025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbert, M.L.; Malicdan, M.C.V.; Introne, W.J. Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2023, 30, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, S.; Soldatos, A.; Toro, C.; Zein, W.M.; Snow, J.; Lehky, T.J.; Malicdan, M.C.V.; Introne, W.J. Chediak-Higashi Syndrome: Hair-to-toe spectrum. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2024, 52, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, M.; Nicoli, E.R.; Kuptanon, C.; Roney, J.C.; Serra-Vinardell, J.; Sharma, P.; Adams, D.R.; Gallin, J.I.; Holland, S.M.; Rosenzweig, S.D.; et al. Spectrum of LYST mutations in Chediak-Higashi syndrome: A report of novel variants and a comprehensive review of the literature. J. Med. Genet. 2024, 61, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano-Jaramillo, L.M.; Lugo-Reyes, S.O.; Cruz Munoz, M.E.; Scheffler-Mendoza, S.C.; Duran McKinster, C.; Yamazaki-Nakashimada, M.A.; Espinosa-Padilla, S.E.; Saez-de-Ocariz Gutierrez, M.D.M. Diagnostic and therapeutic caveats in Griscelli syndrome. Scand. J. Immunol. 2021, 93, e13034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafol, J.; Gnidovec Strazisar, B.; Drole Torkar, A.; Homan, M.; Bertok, S.; Mlinaric, M.; Sikonja, J.; Kovac, J.; Perkovic Benedik, M.; Kersnik Levart, T.; et al. VIPAS39 related arthrogryposis-renal dysfunction-cholestasis syndrome-case report and systematic review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2024, 19, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, C.P.; Rivard, G.E. Quebec platelet disorder. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2011, 4, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Soomro, A.; Tasneem, S.; Abatti, L.E.; Alizada, A.; Yuan, X.; Uuskula-Reimand, L.; Antounians, L.; Alvi, S.A.; Paterson, A.D.; et al. Enhancer-gene rewiring in the pathogenesis of Quebec platelet disorder. Blood 2020, 136, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toti, F.; Satta, N.; Fressinaud, E.; Meyer, D.; Freyssinet, J.M. Scott syndrome, characterized by impaired transmembrane migration of procoagulant phosphatidylserine and hemorrhagic complications, is an inherited disorder. Blood 1996, 87, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montague, S.J.; Price, J.; Pennycott, K.; Pavey, N.J.; Martin, E.M.; Thirlwell, I.; Kemble, S.; Monteiro, C.; Redmond-Motteram, L.; Lawson, N.; et al. Comprehensive functional characterization of a novel ANO6 variant in a new patient with Scott syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2024, 22, 2281–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millington-Burgess, S.L.; Harper, M.T. Gene of the issue: ANO6 and Scott Syndrome. Platelets 2020, 31, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.; Halligan, K. The Bleeding Child: Recognizing Inherited Platelet Function Disorders. Pediatr. Rev. 2025, 46, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresele, P.; Falcinelli, E.; Bury, L. Inherited platelet function disorders. Diagnostic approach and management. Hamostaseologie 2016, 36, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.; Poon, M.C. Inherited platelet functional disorders: General principles and practical aspects of management. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2018, 57, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, S.; Noris, P.; Bury, L.; Heller, P.G.; Santoro, C.; Kadir, R.A.; Butta, N.C.; Falcinelli, E.; Cid, A.R.; Fabris, F.; et al. Bleeding risk of surgery and its prevention in patients with inherited platelet disorders. The Surgery in Platelet disorders And Therapeutic Approach (SPATA) study. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
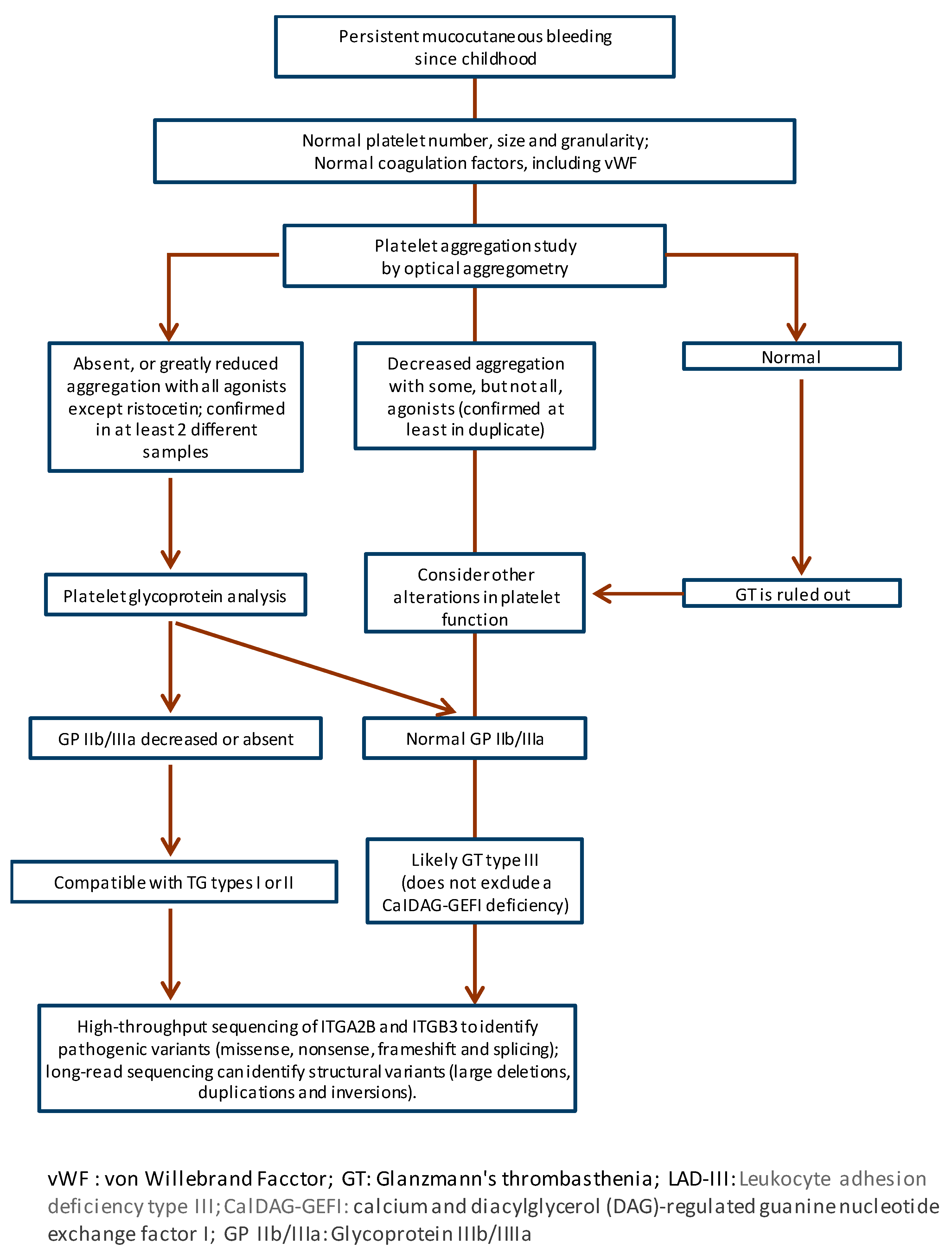
| Level of αIIbβ3 | Frequency Relative | Platelet Phenotype | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | <5% | 75–80% | Absence of platelet aggregation and clot retraction. Empty platelet fibrinogen storage pool |
| Type II | 5–25% | 15% | Absence of platelet aggregation. Partial or normal clot retraction Slightly reduced platelet fibrinogen storage pool |
| Type III | 25–100% (qualitative defects) | 5–10% | Absence of platelet aggregation. Clot retraction and platelet fibrinogen storage pool are highly variable |
| Pathology (OMIM) | Genes | Inheritance | Hemorrhagic Phenotype | Platelet Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2Y12 receptor (OMIM # 609821) | P2RY12 | AD/AR | Mild-moderate | Inhibited aggregation to ADP. Reduced VASP phosphorylation. |
| TxA2 receptor (OMIM # 614009) | TBXA2R | AD/AR | Mild-moderate | Reduced aggregation to AA and TxA2 analogues |
| Ephrin receptor type B2 (OMIM # 618462) | EPHB2 | AR | Moderate-severe | Aggregation and granule release inhibited with various agonists |
| GP VI receptor (OMIM # 614201) | GP6 | AR | Mild-moderate | Absence of aggregation to collagen and GP VI agonists |
| CalDAG-GEFI (OMIM # 615888) | RASGRP2 | AR | Moderate-severe | Reduced aggregation with low concentrations of collagen, arachidonic acid or ADP. Decreased activation of αIIββ3 |
| Leukocyte adhesion defect type III (kindlin-3) (OMIM # 612840) | FERMT3 | AR | Severe | Similar to Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia |
| Scott syndrome (OMIM # 262890) | AN06 | AR | Moderate-severe | Impaired annexin V binding and microparticle release |
| Pathology (OMIM) | Genes Involved | Inheritance | Hemorrhagic Phenotype | Platelet Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome HPS1: (OMIM # 203300) HPS2: (OMIM # 608233) HPS3: (OMIM # 614072) HPS4: (OMIM # 614073) HPS5: (OMIM # 614074) HPS6: (OMIM # 614075) HPS7: (OMIM # 614076) HPS8: (OMIM # 614077) HPS9: (OMIM # 614171) HPS10: (OMIM # 617050) HPS11: (OMIM # 619172) | HPS1 HPS2: AP3B1 HPS3 HPS4 HPS5, HPS6 HPS7: Dysbindin HPS8: BLOS3 HPS9: Pallidine HPS10: AP3D1 HPS11:BLOC1S5 | AR | Mild-moderate | Reduction or absence of δ granules confirmed by different techniques |
| Chediak–Higashi syndrome CHS: (OMIM # 214500) | LYST | AR | Mild-moderate | Reduction or absence of δ granules confirmed by different techniques |
| Griscelli syndromes (SG1: OMIM # 214450) (SG2: OMIM # 607624) (SG3: OMIM # 609227) |
RAB27 MY05A MLPH | AR | Mild | Reduction or absence of δ granules confirmed by different techniques |
| Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (OMIM # 267700) | UNC13D STX11 STYXBP2 | AR | Mild | Deficiency of δ and α granules, and lysosomes |
| Combined δ and α granule defects | AR/AD | Mild-moderate | Deficit of content or release of granules |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Alén, A.; Moscardó, A.; Bastida, J.M.; Rivera, J. Molecular Pathogenesis of Inherited Platelet Dysfunction. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111528
Rodríguez-Alén A, Moscardó A, Bastida JM, Rivera J. Molecular Pathogenesis of Inherited Platelet Dysfunction. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111528
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Alén, Agustín, Antonio Moscardó, José M. Bastida, and José Rivera. 2025. "Molecular Pathogenesis of Inherited Platelet Dysfunction" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111528
APA StyleRodríguez-Alén, A., Moscardó, A., Bastida, J. M., & Rivera, J. (2025). Molecular Pathogenesis of Inherited Platelet Dysfunction. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111528








