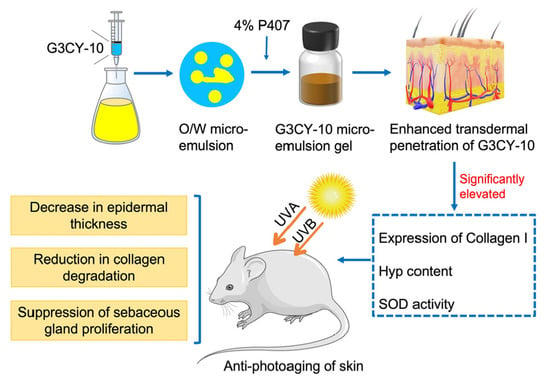
Enhancing Transdermal Delivery: The Role of Gecko-Derived Cathelicidin Peptide G3CY-10 in UV-Induced Skin Photoaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peptide Synthesis
2.2. Preparation of Blank Microemulsions
2.3. Identification and Evaluation of Microemulsion Type and Quality
2.4. Preparation of Microemulsion Gel
2.5. Ethical Considerations
2.6. Effects of Microemulsion Gel on the Transdermal Delivery of G3CY-10
2.7. Mouse Model of Skin Photoaged and Peptide Treatment
2.8. Histomorphological Analysis
2.9. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.10. Detection of Skin Inflammation-Related Indicators
2.11. Detection of Antioxidant Indicators in Skin Tissue
2.12. Determination of Collagen Content in Skin
2.13. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Quality Assessment of the G3CY-10 Microemulsion Gel Delivery System
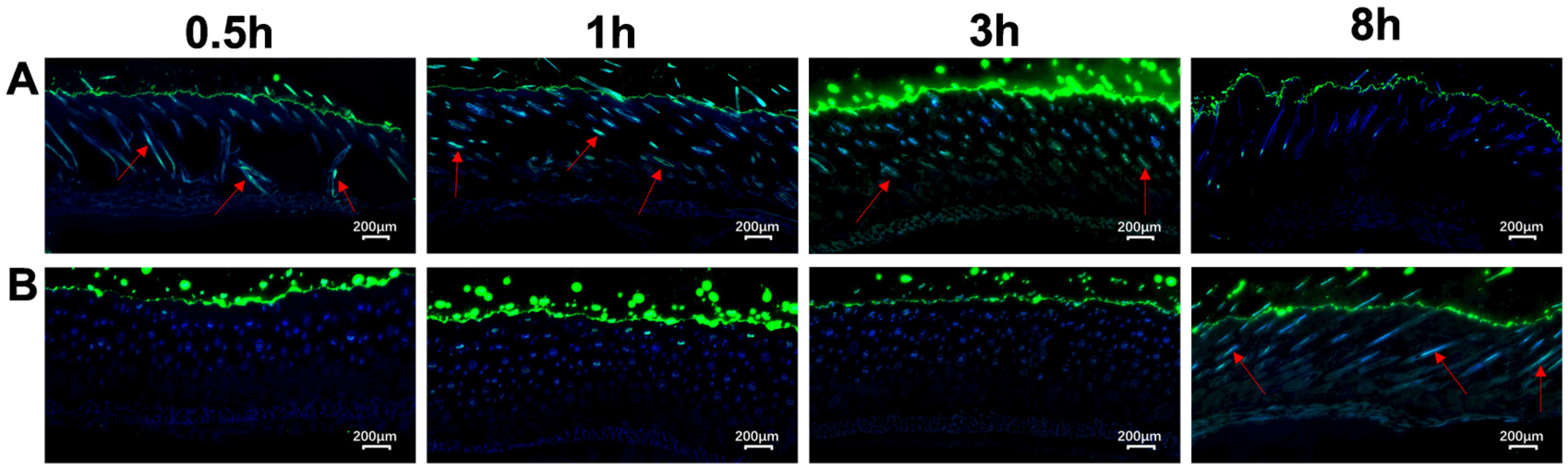
3.2. Evaluation of the Transdermal Enhancement Effects of G3CY-10 Microemulsion Gel
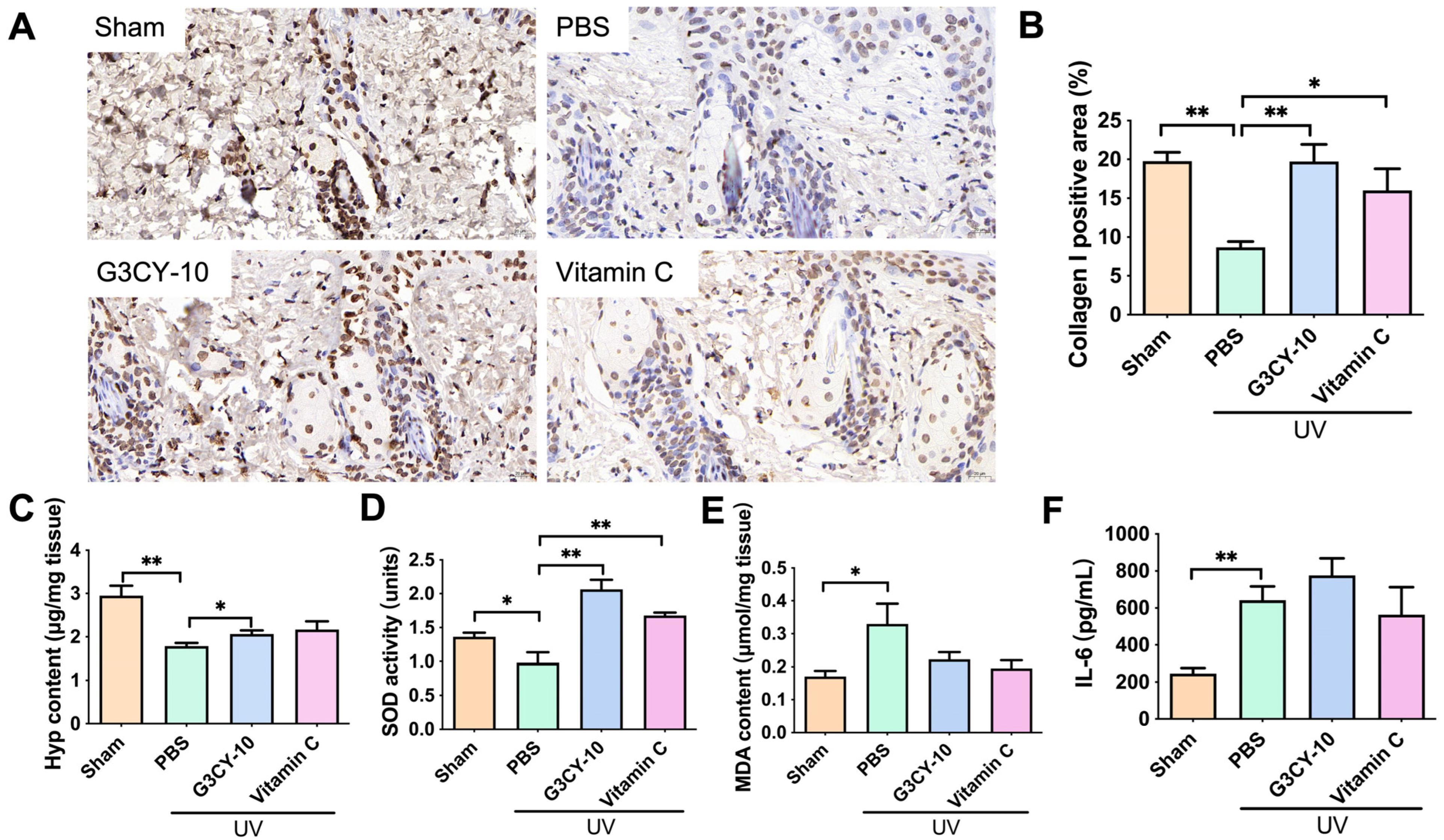
3.3. Study on the Anti-Skin Photoaging Effects of G3CY-10
3.4. The Mechanism of G3CY-10 in Anti-Skin Photoaging Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| Km | The mass ratio of surfactant to cosurfactant |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| MED | Minimal erythema dose |
| HE | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| DAB | Diaminobenzidine |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| Hyp | Hydroxyproline |
| Vc | Vitamin C |
References
- Guan, L.L.; Lim, H.W.; Mohammad, T.F. Sunscreens and Photoaging: A Review of Current Literature. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammeyer, A.; Luiten, R.M. Oxidation events and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 21, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, H. Role of antioxidants in the skin: Anti-aging effects. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 58, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Jain, A.; Gulbake, A.; Shilpi, S.; Hurkat, P.; Jain, S.K. Peptide and Protein Delivery Using New Drug Delivery Systems. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2013, 30, 293–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egito, E.S.T.; Amaral-Machado, L.; Alencar, E.N.; Oliveira, A.G. Microemulsion systems: From the design and architecture to the building of a new delivery system for multiple-route drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 2108–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumala, P.; Jungnickel, C.; Kozlowska-Tylingo, K.; Jacyna, B.; Cal, K. Transdermal transport of collagen and hyaluronic acid using water in oil microemulsion. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, V.; Yadav, P.; Verma, A.; Pandit, J.K. Ex vivo and in vivo evaluation of microemulsion based transdermal delivery of E-coli specific T4 bacteriophage: A rationale approach to treat bacterial infection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 107, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Z.; Wang, Y.J.; Han, F.; Yao, H.M.; Li, S.M. Gelatin-stabilised microemulsion-based organogels facilitates percutaneous penetration of cyclosporin a in vitro and dermal pharmacokinetics in vivo. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 3000–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Li, X.J.; Fu, Z.; Yang, M.F.; Bian, W.X.; Wang, S.Y.; Song, Y.L.; Tang, J.; et al. Cathelicidin-OA1, a novel antioxidant peptide identified from an amphibian, accelerates skin wound healing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.Z.; Wei, L.; Che, H.L.; Shen, Y.; Mi, K.; Bian, H.; Yang, H.L.; Wu, J.; Mu, L.X. Cathelicidin-NV from Nanorana ventripunctata effectively protects HaCaT cells, ameliorating ultraviolet B-induced skin photoaging. Peptides 2022, 150, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.S.; Lu, C.G.; Liu, Z.L.; Wang, W.B.; Lu, S.X.; Sun, Z.X.; Wang, G.N. Derivatives of gecko cathelicidin-related antioxidant peptide facilitate skin wound healing. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 890, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Atiya, A.; Akhtar, S.; Yadav, Y.; Qureshi, K.A.; Jaremko, M.; Mahmood, S. Optimization of a Cefuroxime Axetil-Loaded Liquid Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System: Enhanced Solubility, Dissolution and Caco-2 Cell Uptake. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguansajapong, V.; Sakdiset, P.; Puttarak, P. Development of Oral Microemulsion Spray Containing Pentacyclic Triterpenes-Rich Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. Extract for Healing Mouth Ulcers. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.Y.; Cai, T.G.; Liu, Q.; Whitney, J.C.C.; Du, M.L.; Ma, Q.Q.; Zhang, R.H.; Yang, L.; Cole, S.P.C.; Cai, Y. Preparation and evaluation of spirulina polysaccharide nanoemulsions. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, J.; Sen, S.O.; Nayak, A.K.; Sen, K.K. Development and evaluation of microemulsions for transdermal delivery of insulin. ISRN Pharm. 2011, 2011, 780150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Shi, N.N.; Cai, S.S.; Qiao, X.; Chu, P.; Wang, H.; Long, F.D.; Yang, H.X.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.P.; et al. De Novo Molecular Design of a Novel Octapeptide That Inhibits In Vivo Melanogenesis and Has Great Transdermal Ability. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6846–6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.Z.; Wei, L.; Che, H.L.; Shen, Y.; Yang, J.; Mi, K.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.L.; Mu, L.X. A Frog Peptide Ameliorates Skin Photoaging Through Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, R.E.; Logan, M.A. The determination of collagen and elastin in tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1950, 186, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sinha, V.R. Preparation and optimization of voriconazole microemulsion for ocular delivery. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, S.; Ozawa, Y.; Toda, T.; Watanabe, K.; Tometsuka, C.; Ogura, T.; Koyama, Y.; Shimizu, T. Collagen peptide and vitamin C additively attenuate age-related skin atrophy in Sod1-deficient mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.J.; Rees, G.D. Microemulsion-based media as novel drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2000, 45, 89–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, F.; Baboota, S.; Ahuja, A.; Ali, J.; Shafiq, S. Celecoxib nanoemulsion: Skin permeation mechanism and bioavailability assessment. J. Drug Target. 2008, 16, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevc, G.; Vierl, U. Nanotechnology and the transdermal route: A state of the art review and critical appraisal. J. Control. Release 2010, 141, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.P.; Wells, A.R.; Kiamco, M.M.; Leung, K.P. Dual Asymmetric Centrifugation Efficiently Produces a Poloxamer-Based Nanoemulsion Gel for Topical Delivery of Pirfenidone. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, N.U.; Akhlaq, M.H.; Zhu, K.; Ji, W.; Yi, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z. A nanoemulgel formulation of acetylated Crataegus pinnatifida polysaccharide for the treatment of skin photoaging in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 303, 140649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; Pu, Y.; Mao, S.; Nie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X. Dendrobium officinale Kimura & Migo polysaccharide and its multilayer emulsion protect skin photoaging. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318 Pt B, 116974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Xiang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, W.X.; Lv, X.L. Recent Developments in Using Microneedle Patch Technology as a More Efficient Drug Delivery System for Treating Skin Photoaging. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Low, Y.S.; Chong, H.P.; Zin, M.T.; Lee, C.Y.; Li, B.; Leolukman, M.; Kang, L. Microneedle-Mediated Delivery of Copper Peptide Through Skin. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 2678–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, H.; Zheng, J.; Mou, D.; Wan, J.; Zhang, J.; Shi, T.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, X. Iontophoresis-driven penetration of nanovesicles through microneedle-induced skin microchannels for enhancing transdermal delivery of insulin. J. Control. Release 2009, 139, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, S.; Xu, Y.; Ren, L. Functional hyaluronic acid microneedles for skin photoaging based on collagen induction and oxidative stress regulation strategies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277 Pt 2, 134080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Geng, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J. Advanced nanocarrier- and microneedle-based transdermal drug delivery strategies for skin diseases treatment. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3372–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ou, M.; Tang, S.; Deng, Z.; Liu, L.; Jiang, C.; et al. Bioactive Glycyrrhizic Acid Ionic Liquid Self-Assembled Nanomicelles for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Anti-Photoaging Signal Peptides. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2412581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Kuwajima, M.; Sukeno, A.; Ishimaru, N.; Hayashi, Y.; Wabitsch, M.; Mizusawa, N.; Itakura, M.; Yoshimoto, K. YKL-40 secreted from adipose tissue inhibits degradation of type I collagen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Fan, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Huang, S.; Yue, W.; Wu, X. The Protective Effects of Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Pupae Peptides on UV-Induced Skin Photoaging in Mice. Foods 2024, 13, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Gan, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Y. Collagen-EGCG Combination Synergistically Prevents UVB-Induced Skin Photoaging in Nude Mice. Macromol. Biosci. 2023, 23, e2300251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Youn, J.; Kim, K.; Joo da, H.; Shin, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.K.; An, I.S.; Kwon, S.; Youn, H.J.; et al. Apigenin inhibits UVA-induced cytotoxicity in vitro and prevents signs of skin aging in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.R.; Shin, J.W.; Na, J.I.; Nam, K.M.; Lee, H.S.; Park, K.C. Novel Antioxidant Tripeptide “ACQ” Can Prevent UV-Induced Cell Death and Preserve the Number of Epidermal Stem Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 359740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Song, H.; He, J.; Li, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, B. Collagen peptides promote photoaging skin cell repair by activating the TGF-β/Smad pathway and depressing collagen degradation. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6121–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Kim, P.; Lee, J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Wang, L. Anti-Photoaging Effects of Antioxidant Peptide from Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis) in In Vivo and In Vitro Models. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.L.; Ning, Y.N.; Niu, N.N.; Li, D.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Sheibani, N.; Hong, J. Steered molecular dynamic simulations of conformational lock of Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.; Kulkarni, P.; Ferris, C.; Amiji, M.M. Analgesic efficacy and safety of DALDA peptide analog delivery to the brain using oil-in-water nanoemulsion formulation. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 2724–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.; Kather, F.S.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Shah, J.; Nair, A.B. Innovations in Nanoemulsion Technology: Enhancing Drug Delivery for Oral, Parenteral, and Ophthalmic Applications. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Meher, J.G.; Raval, K.; Khan, F.A.; Chaurasia, M.; Jain, N.K.; Chourasia, M.K. Nanoemulsion: Concepts, development and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 252, 28–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeb, H.H.; Sainsbury, F. Nanoemulsions in drug delivery: Formulation to medical application. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 2507–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.K.; Mishra, N.; Yadav, K.S.; Yadav, N.P. Nanoemulsion as pharmaceutical carrier for dermal and transdermal drug delivery: Formulation development, stability issues, basic considerations and applications. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, F.; Shafiq, S.; Haq, N.; Alanazi, F.K.; Alsarra, I.A. Nanoemulsions as potential vehicles for transdermal and dermal delivery of hydrophobic compounds: An overview. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 953–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hort, M.A.; Alves, B.D.S.; Ramires Júnior, O.V.; Falkembach, M.C.; Araújo, G.M.S.; Fernandes, C.L.F.; Tavella, R.A.; Bidone, J.; Dora, C.L.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. In vivo toxicity evaluation of nanoemulsions for drug delivery. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, S.I.L.; Guimarães, B.; Gasco, P.; Blosi, M.; Costa, A.L.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.J.; Amorim, M.J.B. Nanoemulsion carriers for drug delivery: Assessment of environmental hazards. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 328, 121669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.S.; Nawaz, A.; Asmari, M.; Uddin, J.; Ullah, H.; Ahmad, S. Formulation Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel Formulations for Enhanced Topical Delivery. Gels 2022, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.H.; Abu Lila, A.S.; El-Nahas, H.M.; Ibrahim, T.M. Optimization of Potential Nanoemulgels for Boosting Transdermal Glimepiride Delivery and Upgrading Its Anti-Diabetic Activity. Gels 2023, 9, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donthi, M.R.; Munnangi, S.R.; Krishna, K.V.; Saha, R.N.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K. Nanoemulgel: A Novel Nano Carrier as a Tool for Topical Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri, M.I.; Vora, L.K.; Abu Ershaid, J.; Peng, K.; Tekko, I.A.; Donnelly, R.F. Nanoemulsion-based dissolving microneedle arrays for enhanced intradermal and transdermal delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


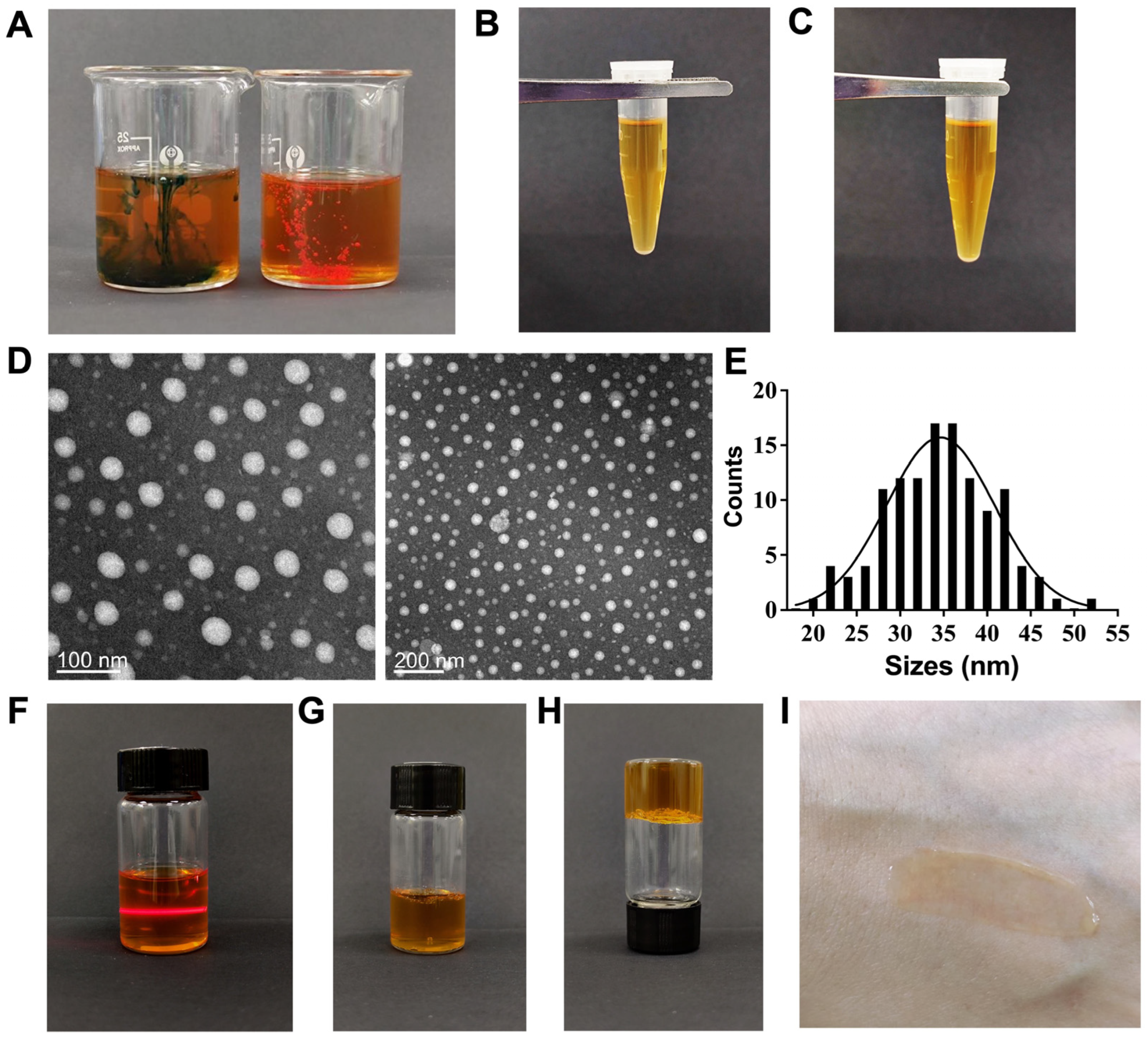

| Surfactant/Co-Surfactant | Lecithin/Anhydrous Ethanol | Span80/Anhydrous Ethanol | Tween80/Anhydrous Ethanol | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil Phase | ||||
| castor oil | − | + | + | |
| ethyl butyrate | + | − | + | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Gao, N.; Wang, J.; Cai, S. Enhancing Transdermal Delivery: The Role of Gecko-Derived Cathelicidin Peptide G3CY-10 in UV-Induced Skin Photoaging. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111515
Wang Y, Ma Z, Li F, Li X, Gao N, Wang J, Cai S. Enhancing Transdermal Delivery: The Role of Gecko-Derived Cathelicidin Peptide G3CY-10 in UV-Induced Skin Photoaging. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111515
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yunjiao, Zicheng Ma, Fengshuo Li, Xuanzeng Li, Ningyang Gao, Junhan Wang, and Shasha Cai. 2025. "Enhancing Transdermal Delivery: The Role of Gecko-Derived Cathelicidin Peptide G3CY-10 in UV-Induced Skin Photoaging" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111515
APA StyleWang, Y., Ma, Z., Li, F., Li, X., Gao, N., Wang, J., & Cai, S. (2025). Enhancing Transdermal Delivery: The Role of Gecko-Derived Cathelicidin Peptide G3CY-10 in UV-Induced Skin Photoaging. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111515


_Kwok.png)