Association Between Heavy Metals Exposure and Elevated High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein: Mediating Role of Body Mass Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample
2.2. Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Preliminary Analysis
2.3.2. Mediation Analysis
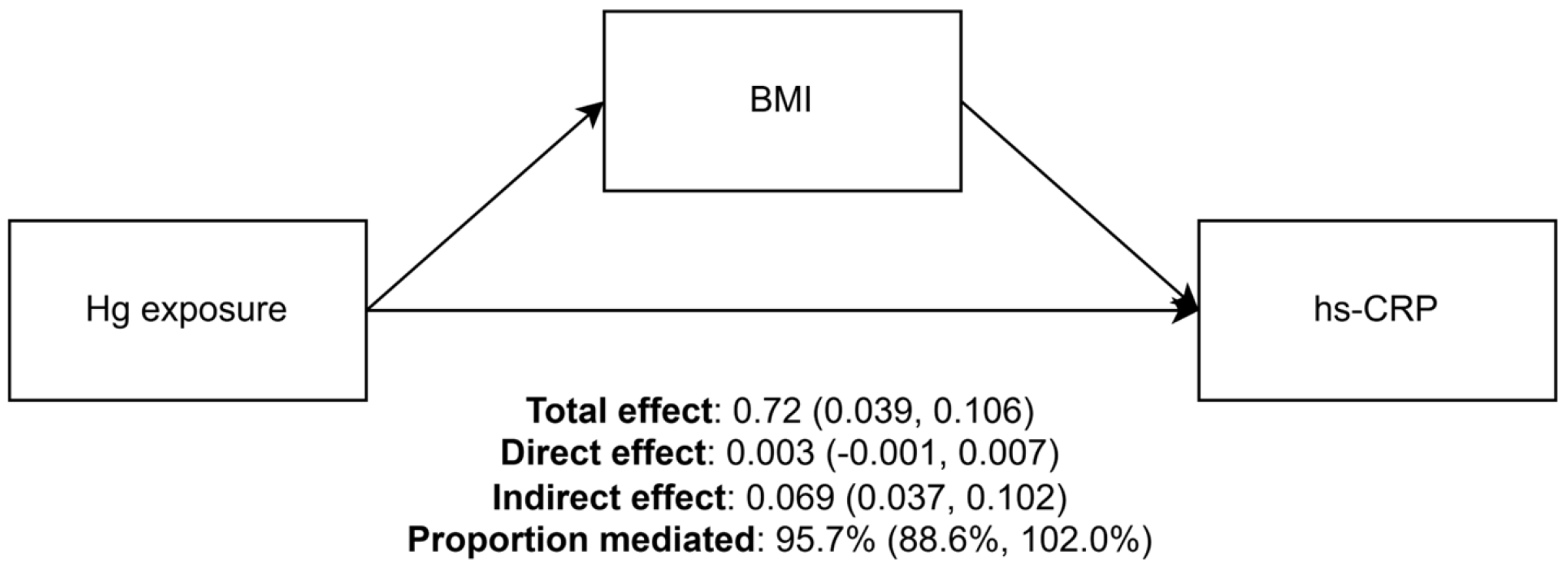
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Witkowska, D.; Slowik, J.; Chilicka, K. Heavy Metals and Human Health: Possible Exposure Pathways and the Competition for Protein Binding Sites. Molecules 2021, 26, 6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Zhou, B.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, S.; Li, N. Bibliometric overview of research trends on heavy metal health risks and impacts in 1989–2018. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, C.; Sakong, J.; Ye, S.; Son, S.Y.; Baek, K. Association of heavy metal complex exposure and neurobehavioral function of children. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2023, 35, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.; Park, J.T.; Na, S.; Kwak, K. Environment-wide association study of elevated liver enzymes: Results from the Korean National Environmental Health Survey 2018–2022. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2023, 35, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.W.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, B.G. Assessment of Lead and Mercury Exposure Levels in the General Population of Korea Using Integrated National Biomonitoring Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.G.; Seo, M.N.; Choi, B.S.; Kim, Y.D.; Lim, J.A.; Hwang, M.S.; Kwon, H.J.; Kim, Y.M.; et al. Lead, Mercury, and Cadmium Exposure in the Korean General Population. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2018, 33, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Gong, T.; Liang, P. Heavy Metal Exposure and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2024, 134, 1160–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xi, S. The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2020, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, L.; Patel, T.N. Systemic impact of heavy metals and their role in cancer development: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Cadmium and cadmium compounds. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1993, 58, 119–237. [Google Scholar]
- IARC. Inorganic and organic lead compounds. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2006, 87, 1–471. [Google Scholar]
- IARC. Beryllium, cadmium, mercury, and exposures in the glass manufacturing industry. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1993, 58, 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Ni, B.; Chen, R.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, R.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Peng, Y.; et al. Low-grade systemic inflammation links heavy metal exposures to mortality: A multi-metal inflammatory index approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paithankar, J.G.; Saini, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Sharma, A.; Chowdhuri, D.K. Heavy metal associated health hazards: An interplay of oxidative stress and signal transduction. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banait, T.; Wanjari, A.; Danade, V.; Banait, S.; Jain, J. Role of High-Sensitivity C-reactive Protein (Hs-CRP) in Non-communicable Diseases: A Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng-Gyasi, E.; Obeng-Gyasi, B. Association of combined lead, cadmium, and mercury with systemic inflammation. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1385500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savulescu-Fiedler, I.; Mihalcea, R.; Dragosloveanu, S.; Scheau, C.; Baz, R.O.; Caruntu, A.; Scheau, A.-E.; Caruntu, C.; Benea, S.N. The Interplay between Obesity and Inflammation. Life 2024, 14, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Joseph, L.; Pilote, L. Obesity and C-reactive protein in various populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, E.; Paynter, N.P.; Erlinger, T.P. The effect of weight loss on C-reactive protein: A systematic review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpson, N.J.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Harbord, R.M.; Zacho, J.; Frayling, T.M.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Smith, G.D. C-reactive protein levels and body mass index: Elucidating direction of causation through reciprocal Mendelian randomization. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Shi, Q.; Liu, C.; Sun, Q.; Zeng, X. Effects of Endocrine-Disrupting Heavy Metals on Human Health. Toxics 2023, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinkov, A.A.; Aschner, M.; Ke, T.; Ferrer, B.; Zhou, J.C.; Chang, J.S.; Santamaria, A.; Chao, J.C.; Aaseth, J.; Skalny, A.V. Adipotropic effects of heavy metals and their potential role in obesity. Fac. Rev. 2021, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, S.M.; Varadharajan, K.; Shanmugakonar, M.; Das, S.C.; Al-Naemi, H.A. Cadmium: An Emerging Role in Adipose Tissue Dysfunction. Expo. Health 2022, 14, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Addai, F.P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, F.; Tuffour, A.; Gu, J.; Liu, G.; Shi, H. Heavy metal-induced lipogenic gene aberration, lipid dysregulation and obesogenic effect: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1611–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.C.; Ferrer, B.; Tinkov, A.A.; Caito, S.; Deza-Ponzio, R.; Skalny, A.V.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Association between Heavy Metals, Metalloids and Metabolic Syndrome: New Insights and Approaches. Toxics 2023, 11, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzetti, D.A.; Corrales, P.; Piagette, J.T.; Uranga-Ocio, J.A.; Medina-Gomez, G.; Pecanha, F.M.; Vassallo, D.V.; Miguel, M.; Wiggers, G.A. Chronic mercury at low doses impairs white adipose tissue plasticity. Toxicology 2019, 418, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Ha, K.H.; He, K.; Kim, D.J. Association between Blood Mercury Level and Visceral Adiposity in Adults. Diabetes Metab. J. 2017, 41, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.K.; Lee, I.; Lee, A.; Park, H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.H.; Hong, S.; Yoo, J.; Cheon, G.J.; et al. Lead, mercury, and cadmium exposures are associated with obesity but not with diabetes mellitus: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, H.N.; Oh, H.; Kim, M.S. The Effect of Mixture of Heavy Metals on Obesity in Individuals ≥50 Years of Age. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 3554–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehoff, N.M.; Keil, A.P.; O’Brien, K.M.; Jackson, B.P.; Karagas, M.R.; Weinberg, C.R.; White, A.J. Metals and trace elements in relation to body mass index in a prospective study of US women. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q. Trend analysis of the association of urinary metals and obesity in children and adolescents. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Zhong, L.; Ji, G.; Chen, B.; Liao, M.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. Associations between metal(loid) exposure with overweight and obesity and abdominal obesity in the general population: A cross-sectional study in China. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 140963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Park, K. Mercury exposure is associated with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Korean J. Community Nutr. 2023, 28, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangiabadian, M.; Jolfayi, A.G.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Amirkhosravi, L.; Sanjari, M. The association between heavy metal exposure and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2024, 23, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanezawa, Y.; Kashiwano, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Ohshiro, Y.; Uraguchi, S.; Kiyono, M. Methylmercury drives lipid droplet formation and adipokine expression during the late stages of adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Toxicology 2023, 486, 153446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, S.; Kim, Y.; Jang, M.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, K.; Choi, S.; Chun, C.; Khang, Y.H.; Oh, K. Data resource profile: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, Y. Associations of Blood Heavy Metals with Uric Acid in the Korean General Population: Analysis of Data from the 2016–2017 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Quality Control of the Clinical Laboratory for the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) (2017, 7th First Year); Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency: Osong, Republic of Korea, 2017.
- Keizer, R.J.; Jansen, R.S.; Rosing, H.; Thijssen, B.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.; Huitema, A.D. Incorporation of concentration data below the limit of quantification in population pharmacokinetic analyses. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Min, J.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Yang, H.I.; Park, J.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, M.Y.; Park, I.; et al. Development of the Korean Global Physical Activity Questionnaire: Reliability and validity study. Glob. Health Promot. 2020, 27, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’brien, R.M. A Caution Regarding Rules of Thumb for Variance Inflation Factors. Qual. Quant. 2007, 41, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Keele, L.; Tingley, D. A general approach to causal mediation analysis. Psychol. Methods 2010, 15, 309–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingley, D.; Yamamoto, T.; Hirose, K.; Keele, L.; Imai, K. mediation: R Package for Causal Mediation Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 59, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Multiple imputation with multivariate imputation by chained equation (MICE) package. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.H.; Kim, B.G.; Kim, J.M.; Yu, S.D.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, R.B.; Hong, Y.S. Relationship between blood mercury concentration and waist-to-hip ratio in elderly Korean individuals living in coastal areas. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2011, 44, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Park, H. Association of mercury exposure with the serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level in Korean adults. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1062741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyland, J.F.; Fillion, M.; Barbosa, F., Jr.; Shirley, D.L.; Chine, C.; Lemire, M.; Mergler, D.; Silbergeld, E.K. Biomarkers of methylmercury exposure immunotoxicity among fish consumers in Amazonian Brazil. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.I.C.; Lazaro, C.M.; Dos Santos, L.M.B.; Rentz, T.; Virgilio-da-Silva, J.V.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.M.; Cunha, F.A.S.; Santos, J.C.C.; Vercesi, A.E.; Leite, A.C.R.; et al. In vivo chronic exposure to inorganic mercury worsens hypercholesterolemia, oxidative stress and atherosclerosis in the LDL receptor knockout mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 275, 116254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.P.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.X. Trends in Blood Lead Levels in the U.S. From 1999 to 2016. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2021, 60, e179–e187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, X.; Guo, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y. Associations between patterns of blood heavy metal exposure and health outcomes: Insights from NHANES 2011–2016. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Shin, K.S.; Park, C.; Baek, K.; Son, S.Y.; Sakong, J. Risk assessment of heavy metals in tuna from Japanese restaurants in the Republic of Korea. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2023, 35, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, G.; Shin, J.; Kim, D.; Woo, J.; Sung, K.; Cho, M.; Yang, W. Assessment of Heavy Metal Exposure Levels (Pb, Hg, Cd) among South Koreans and Contribution Rates by Exposure Route—Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) Cycle 4 (2018~2020). J. Environ. Health Sci. 2023, 49, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweatt, K.; Garvey, W.T.; Martins, C. Strengths and Limitations of BMI in the Diagnosis of Obesity: What Is the Path Forward? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N (%) | |
|---|---|
| N | 4521 (100%) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 1989 (44.0%) |
| Female | 2532 (56.0%) |
| Region | |
| Urban | 3692 (81.7%) |
| Rural | 829 (18.3%) |
| Age | |
| Mean (SD) | 49.9 (16.4) |
| Education level | |
| Elementary school or below | 846 (18.7%) |
| Middle school | 454 (10.0%) |
| High school | 1489 (32.9%) |
| College or above | 1732 (38.3%) |
| Income | |
| Lowest | 788 (17.4%) |
| Low | 861 (19.0%) |
| Medium | 919 (20.3%) |
| High | 934 (20.7%) |
| Highest | 1019 (22.5%) |
| Economic activity | |
| Active | 2822 (62.4%) |
| Inactive | 1699 (37.6%) |
| Marital status | |
| Married | 3130 (69.2%) |
| Unmarried or others | 1391 (30.8%) |
| Smoking status | |
| Yes | 866 (19.2%) |
| No | 3655 (80.8%) |
| Physical activity | |
| Yes | 1995 (44.1%) |
| No | 2526 (55.9%) |
| Alcohol use | |
| Yes | 3017 (66.7%) |
| No | 1504 (33.3%) |
| Median (Q1, Q3) | Min, Max | Hg | Cd | Pb | BMI | hs-CRP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg (μg/L) | 3.15 (2.10, 4.84) | 0.29, 42.80 | 1 | ||||
| Cd (μg/L) | 0.95 (0.63, 1.38) | 0.10, 6.62 | 0.09 | 1 | |||
| Pb (μg/dL) | 1.67 (1.28, 2.21) | 0.20, 20.16 | 0.28 | 0.30 | 1 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.71 (21.51, 26.10) | 15.20, 43.56 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 1 | |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 0.60 (0.38, 1.14) | 0.07, 19.99 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.38 | 1 |
| Dependent Variables | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | hs-CRP a | ||||||||
| Univariate Model | Multivariate Model | Univariate Model | Multivariate Model | ||||||
| Exposure | Mean (SD) | β (95% CI) | p | β (95% CI) | p | β (95% CI) | p | β (95% CI) | p |
| Log-Hg a | 1.17 (0.64) | 0.93 (0.75, 1.12) | <0.001 | 0.73 (0.51, 0.96) | <0.001 | 0.11 (0.06, 0.16) | <0.001 | 0.07 (0.02, 0.13) | 0.012 |
| Log-Cd a | −0.09 (0.60) | 0.26 (0.04, 0.48) | 0.021 | 0.20 (−0.10, 0.50) | 0.196 | 0.09 (0.04, 0.14) | 0.001 | −0.00 (−0.07, 0.06) | 0.880 |
| Log-Pb a | 0.52 (0.42) | 0.94 (0.63, 1.26) | <0.001 | −0.06 (−0.41, 0.28) | 0.727 | 0.20 (0.13, 0.28) | <0.001 | −0.01 (−0.09, 0.07) | 0.809 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, S.-U.; Yoon, J.-H. Association Between Heavy Metals Exposure and Elevated High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein: Mediating Role of Body Mass Index. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111491
Baek S-U, Yoon J-H. Association Between Heavy Metals Exposure and Elevated High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein: Mediating Role of Body Mass Index. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111491
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Seong-Uk, and Jin-Ha Yoon. 2025. "Association Between Heavy Metals Exposure and Elevated High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein: Mediating Role of Body Mass Index" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111491
APA StyleBaek, S.-U., & Yoon, J.-H. (2025). Association Between Heavy Metals Exposure and Elevated High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein: Mediating Role of Body Mass Index. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111491







