Structural Insights into the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Its Implications for Antibody Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
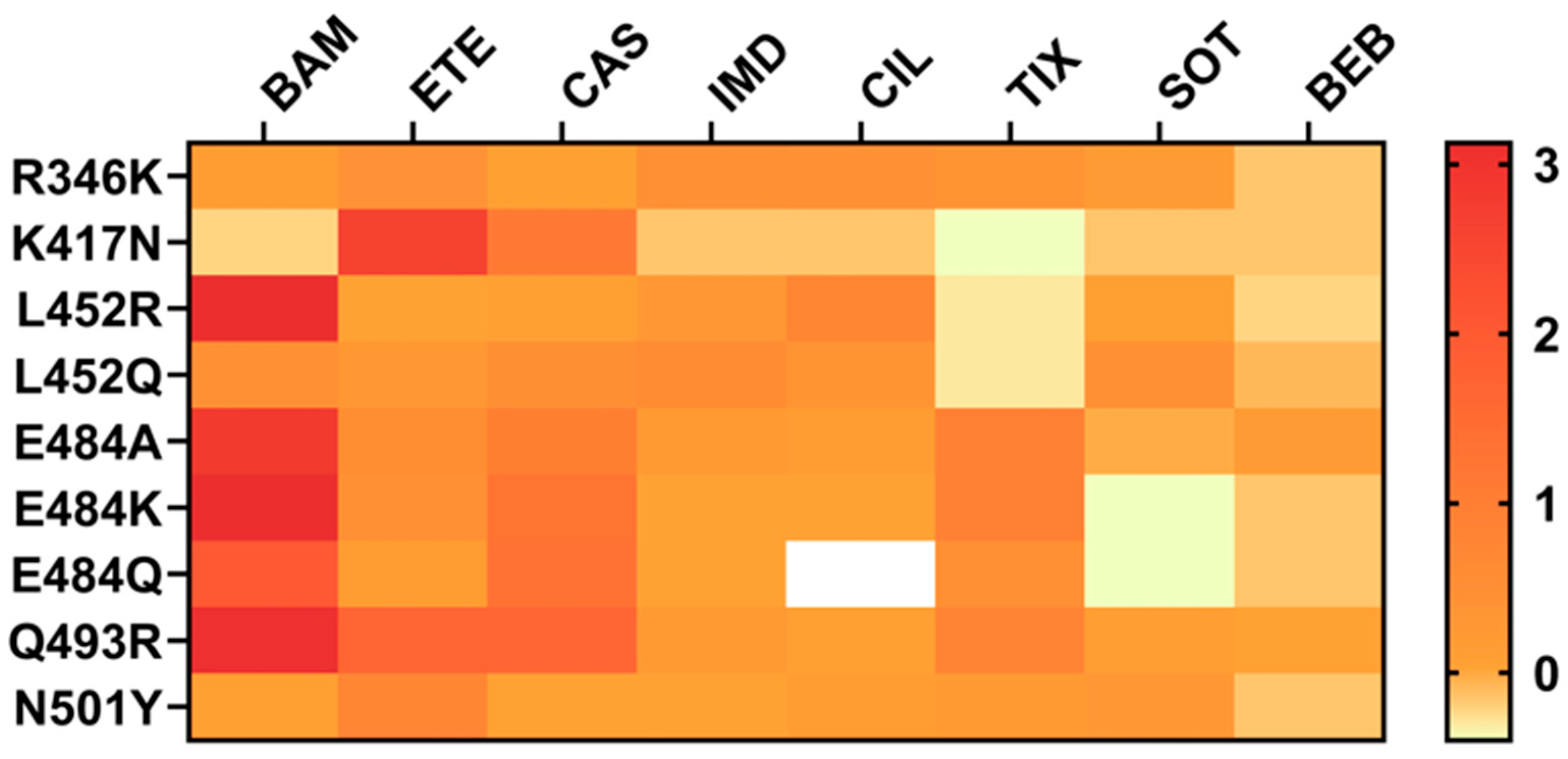
2. Structural Characteristics of RBD Mutations Associated with Antibody Resistance
- R346T and R346K
- K417N
- L452R
- E484K
- Q493R
- N501Y
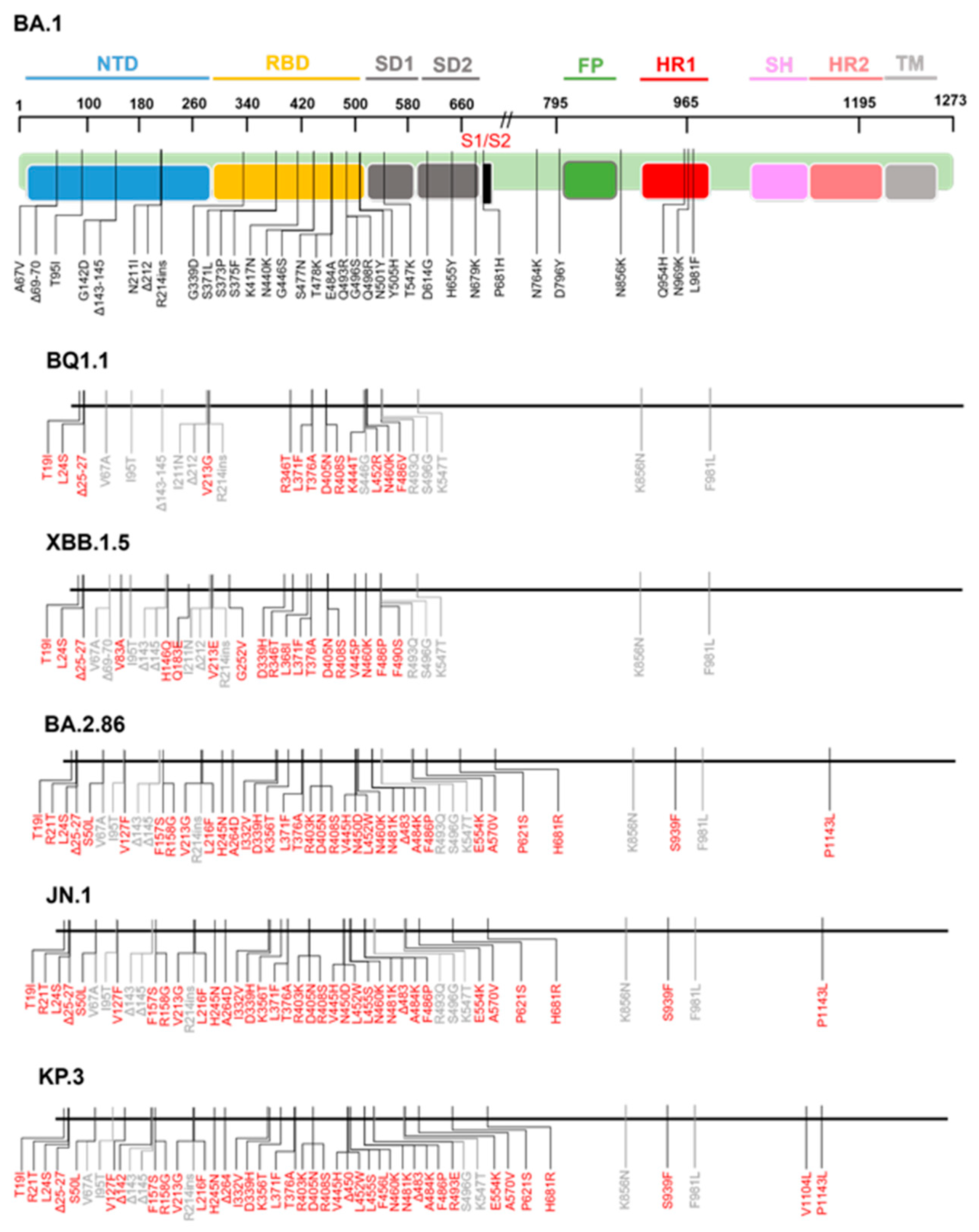
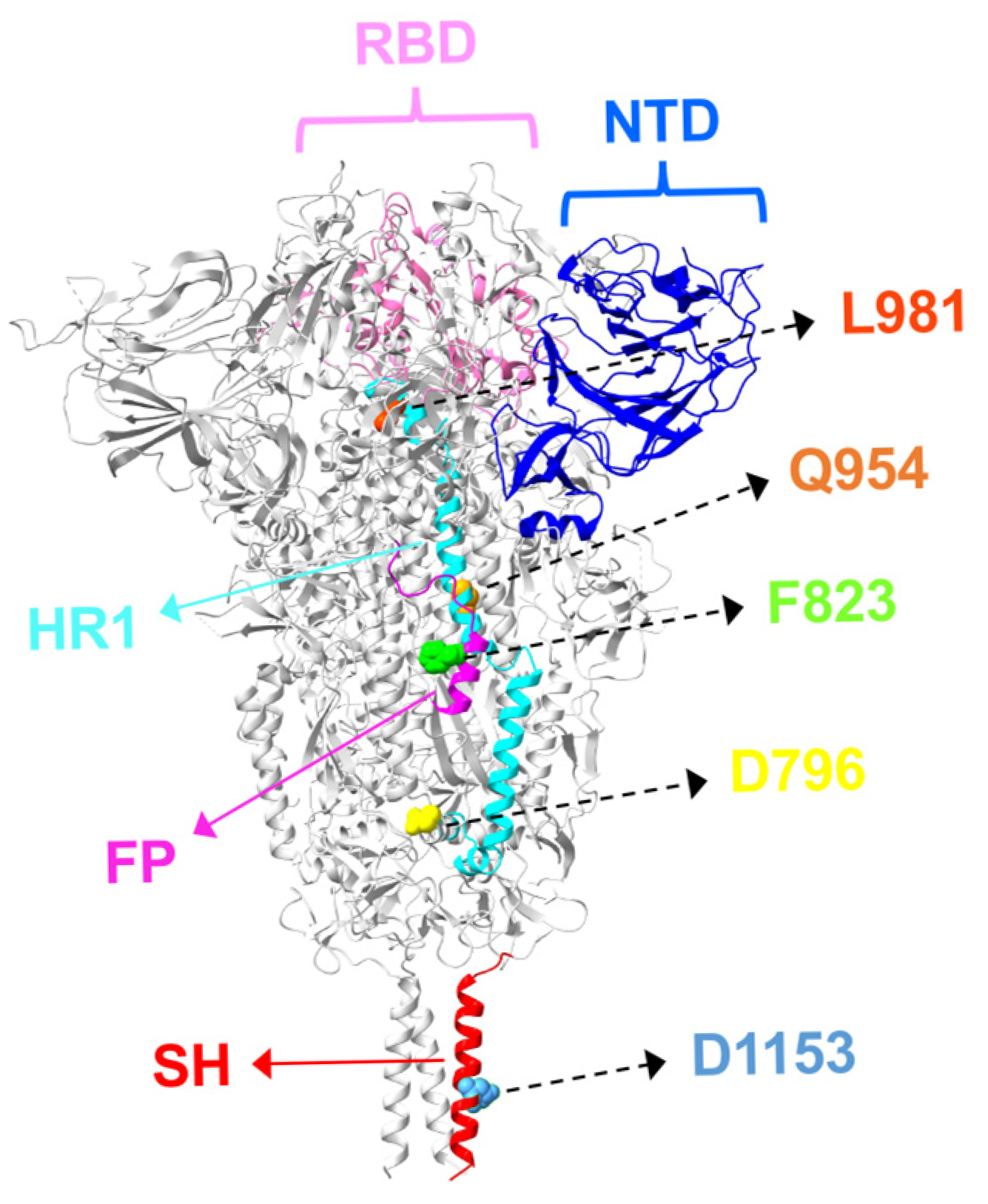
3. S2 Mutations and Antibody Resistance in Omicron Variants
3.1. Fusion Peptide Mutations and Antibody Resistance
3.2. HR1/HR2 Region Mutations and Antibody Resistance
3.3. Stem-Helix Mutations and Antibody Resistance
4. Optimizing Antibody Therapeutics with BsAbs for Breadth and Resistance
4.1. RBD–RBD-Targeting Distinct Epitopes
4.2. RBD–NTD-Targeting Dual Epitopes
4.3. Dual-Epitope-Targeting BsAbs: RBD–S2 and ACE2–S2
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harrison, A.G.; Lin, T.; Wang, P. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Pathogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 1100–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, M.M.; Haagmans, B.L. SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; Mclellan, J.S. Cryo-EM Structure of the 2019-NCoV Spike in the Prefusion Conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Spike Mutations and Immune Escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, S.M.; Shoemaker, S.R.; Hobbs, H.T.; Nguyen, A.W.; Hsieh, C.L.; Maynard, J.A.; McLellan, J.S.; Pak, J.E.; Marqusee, S. The SARS-CoV-2 Spike Reversibly Samples an Open-Trimer Conformation Exposing Novel Epitopes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2022, 29, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peisahovics, F.; Rohaim, M.A.; Munir, M. Structural Topological Analysis of Spike Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Highlight Distinctive Amino Acid Substitution Patterns. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 101, 151275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, S.; Wang, P. Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and Other Human Coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.; Zhang, L.; Krüger, N.; Rocha, C.; Sidarovich, A.; Schulz, S.; Kempf, A.; Graichen, L.; Moldenhauer, A.S.; Cossmann, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages Show Comparable Cell Entry but Differential Neutralization by Therapeutic Antibodies. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1103–1111.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, L.; Misasi, J.; Pegu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Harris, D.R.; Olia, A.S.; Talana, C.A.; Yang, E.S.; Chen, M.; et al. Structural Basis for Potent Antibody Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Including B.1.1.529. Science 2022, 376, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xu, Z.; Niu, T.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, D.; He, Q.; Sun, W.; Shi, K.; Guo, W.; et al. Key Mechanistic Features of the Trade-off between Antibody Escape and Host Cell Binding in the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Spike Proteins. EMBO J. 2024, 43, 1484–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Iketani, S.; Nair, M.S.; Li, Z.; Mohri, H.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Bowen, A.D.; Chang, J.Y.; et al. Antibody Evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5. Nature 2022, 608, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Delipan, R.; Chakraborty, D.; Kanjo, K.; Singh, R.; Singh, N.; Siddiqui, S.; Tyagi, A.; Jha, V.; Thakur, K.G.; et al. Mutations in S2 Subunit of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Spike Strongly Influence Its Conformation, Fusogenicity, and Neutralization Sensitivity. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0092223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elko, E.A.; Mead, H.L.; Nelson, G.A.; Zaia, J.A.; Ladner, J.T.; Altin, J.A. Recurrent SARS-CoV-2 Mutations at Spike D796 Evade Antibodies from Pre-Omicron Convalescent and Vaccinated Subjects. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0329123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narowski, T.M.; Raphel, K.; Adams, L.E.; Huang, J.; Vielot, N.A.; Jadi, R.; de Silva, A.M.; Baric, R.S.; Lafleur, J.E.; Premkumar, L. SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccine Induces Robust Specific and Cross-Reactive IgG and Unequal Neutralizing Antibodies in Naive and Previously Infected People. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrò, G.E.; Pappalardo, C.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Vece, M.; Lupi, C.; Lontano, A.; Di Russo, M.; Ricciardi, R.; de Waure, C. The Impact of Vaccination on COVID-19 Burden of Disease in the Adult and Elderly Population: A Systematic Review of Italian Evidence. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Lam, E.C.; St. Denis, K.; Nitido, A.D.; Garcia, Z.H.; Hauser, B.M.; Feldman, J.; Pavlovic, M.N.; Gregory, D.J.; Poznansky, M.C.; et al. Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants Escape Neutralization by Vaccine-Induced Humoral Immunity. Cell 2021, 184, 2372–2383.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyke, K.E.; Atmar, R.L.; Islas, C.D.; Posavad, C.M.; Szydlo, D.; Paul Chourdhury, R.; Deming, M.E.; Eaton, A.; Jackson, L.A.; Branche, A.R.; et al. Rapid Decline in Vaccine-Boosted Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Song, G.; Liu, H.; Yuan, M.; He, W.T.; Beutler, N.; Zhu, X.; Tse, L.V.; Martinez, D.R.; Schäfer, A.; et al. Broadly Neutralizing Anti-S2 Antibodies Protect against All Three Human Betacoronaviruses That Cause Deadly Disease. Immunity 2023, 56, 669–686.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sempowski, G.D.; Saunders, K.O.; Acharya, P.; Haynes, B.F. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies for COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment. Annu. Rev. Med. 2025, 37, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.O.; West, A.P.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Hoffmann, M.A.G.; Sharaf, N.G.; Hoffman, P.R.; Koranda, N.; Gristick, H.B.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F.; et al. Structures of Human Antibodies Bound to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Reveal Common Epitopes and Recurrent Features of Antibodies. Cell 2020, 182, 828–842.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Iketani, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bowen, A.D.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; et al. Alarming Antibody Evasion Properties of Rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB Subvariants. Cell 2023, 186, 279–286.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Huang, D.; Lee, C.-C.D.; Wu, N.C.; Jackson, A.M.; Zhu, X.; Liu, H.; Peng, L.; van Gils, M.J.; Sanders, R.W.; et al. Structural and Functional Ramifications of Antigenic Drift in Recent SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Science 2021, 373, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, S.; Kosugi, Y.; Kimura, I.; Yamasoba, D.; Sato, K.; Sato, K. Structural Insight into the Resistance of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 Variants to Cilgavimab. Viruses 2022, 14, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focosi, D.; McConnell, S.; Casadevall, A. The Omicron Variant of Concern: Diversification and Convergent Evolution in Spike Protein, and Escape from Anti-Spike Monoclonal Antibodies. Drug Resist. Updates 2022, 65, 100882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Fan, K.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, R.; Feng, R.; Jia, Z.; et al. Structural and Functional Characterizations of Infectivity and Immune Evasion of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron. Cell 2022, 185, 860–871.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; van Haperen, R.; Gutiérrez-Álvarez, J.; Li, W.; Okba, N.M.A.; Albulescu, I.; Widjaja, I.; van Dieren, B.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Sola, I.; et al. A Conserved Immunogenic and Vulnerable Site on the Coronavirus Spike Protein Delineated by Cross-Reactive Monoclonal Antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lin, S.; Chen, Z.; Cao, Y.; He, B.; Lu, G. Targetable Elements in SARS-CoV-2 S2 Subunit for the Design of Pan-Coronavirus Fusion Inhibitors and Vaccines. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Chang, S.C. SARS-CoV-2 Spike S2-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2220582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepenbrink, M.S.; Park, J.G.; Deshpande, A.; Loos, A.; Ye, C.; Basu, M.; Sarkar, S.; Khalil, A.M.; Chauvin, D.; Woo, J.; et al. Potent Universal Beta-Coronavirus Therapeutic Activity Mediated by Direct Respiratory Administration of a Spike S2 Domain-Specific Human Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurlburt, N.K.; Homad, L.J.; Sinha, I.; Jennewein, M.F.; MacCamy, A.J.; Wan, Y.H.; Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Sholukh, A.M.; Jackson, A.M.; Zhou, P.; et al. Structural Definition of a Pan-Sarbecovirus Neutralizing Epitope on the Spike S2 Subunit. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, D.; Sauer, M.M.; Czudnochowski, N.; Siong Low, J.; Alejandra Tortorici, M.; Housley, M.P.; Noack, J.; Walls, A.C.; Bowen, J.E.; Guarino, B.; et al. Broad Betacoronavirus Neutralization by a Stem Helix-Specific Human Antibody. Science 2021, 373, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchais, C.; Fernández, I.; Chalopin, B.; Bruel, T.; Rosenbaum, P.; Beretta, M.; Dimitrov, J.D.; Conquet, L.; Donati, F.; Prot, M.; et al. Broad Sarbecovirus Neutralization by Combined Memory B Cell Antibodies to Ancestral SARS-CoV-2. iScience 2024, 27, 110354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yi, C.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, L.; Xia, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Gu, C.; Lu, X.; Fu, Y.; et al. Neutralization Mechanism of a Human Antibody with Pan-Coronavirus Reactivity Including SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, M.M.; Tortorici, M.A.; Park, Y.J.; Walls, A.C.; Homad, L.; Acton, O.J.; Bowen, J.E.; Wang, C.; Xiong, X.; de van der Schueren, W.; et al. Structural Basis for Broad Coronavirus Neutralization. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chang, F.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Teng, S.; Zhang, J.; He, R.; et al. Monoclonal Antibodies Constructed from COVID-19 Convalescent Memory B Cells Exhibit Potent Binding Activity to MERS-CoV Spike S2 Subunit and Other Human Coronaviruses. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1056272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siong Low, J.; Jerak, J.; Alejandra Tortorici, M.; McCallum, M.; Pinto, D.; Cassotta, A.; Foglierini, M.; Mele, F.; Abdelnabi, R.; Weynand, B.; et al. ACE2-Binding Exposes the SARS-CoV-2 Fusion Peptide to Broadly Neutralizing Coronavirus Antibodies. Science 2022, 377, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreano, E.; Nicastri, E.; Paciello, I.; Pileri, P.; Manganaro, N.; Piccini, G.; Manenti, A.; Pantano, E.; Kabanova, A.; Troisi, M.; et al. Extremely Potent Human Monoclonal Antibodies from COVID-19 Convalescent Patients. Cell 2021, 184, 1821–1835.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M Brouwer, P.J.; Caniels, T.G.; van der Straten, K.; Snitselaar, J.L.; Aldon, Y.; Bangaru, S.; Torres, J.L.; A Okba, N.M.; Claireaux, M.; Kerster, G.; et al. Potent Neutralizing Antibodies from COVID-19 Patients Define Multiple Targets of Vulnerability. Science 2020, 369, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, T.F.; Zhao, F.; Huang, D.; Beutler, N.; Burns, A.; He, W.; Limbo, O.; Smith, C.; Song, G.; Woehl, J.; et al. Isolation of Potent SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies and Protection from Disease in a Small Animal Model. Science 2020, 369, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakharkar, M.; Garrett Rappazzo, C.; Wieland-Alter, W.F.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Wrapp, D.; Esterman, E.S.; Kaku, C.I.; Wec, A.Z.; Geoghegan, J.C.; McLellan, J.S.; et al. Prolonged Evolution of the Human B Cell Response to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabg6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.; Baum, A.; Pascal, K.E.; Russo, V.; Giordano, S.; Wloga, E.; Fulton, B.O.; Yan, Y.; Koon, K.; Patel, K.; et al. Studies in Humanized Mice and Convalescent Humans Yield a SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Cocktail. Science 2020, 369, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, A.; Fulton, B.O.; Wloga, E.; Copin, R.; Pascal, K.E.; Russo, V.; Giordano, S.; Lanza, K.; Negron, N.; Ni, M.; et al. Antibody Cocktail to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Prevents Rapid Mutational Escape Seen with Individual Antibodies. Science 2020, 369, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong Joon Kim, J.; Sang, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Shi, Y. Nanobodies: Robust Miniprotein Binders in Biomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 195, 114726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Xu, C.; Tian, M.; Shi, G.; Bai, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, S. A Panel of Multivalent Nanobodies Broadly Neutralizing Omicron Subvariants and Recombinant. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gasparo, R.; Pedotti, M.; Simonelli, L.; Nickl, P.; Muecksch, F.; Cassaniti, I.; Percivalle, E.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Mazzola, F.; Magrì, D.; et al. Bispecific IgG Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 Variants and Prevents Escape in Mice. Nature 2021, 593, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.A.; Gramespacher, J.A.; Pance, K.; Rettko, N.J.; Solomon, P.; Jin, J.; Lui, I.; Elledge, S.K.; Liu, J.; Bracken, C.J.; et al. Bispecific VH/Fab Antibodies Targeting Neutralizing and Non-Neutralizing Spike Epitopes Demonstrate Enhanced Potency against SARS-CoV-2. MAbs 2021, 13, 1893426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kay Gonzales-Wartz, K.; Huang, D.; Yuan, M.; Peterson, M.; Liang, J.; Beutler, N.; Torres, J.L.; Cong, Y.; Postnikova, E.; et al. Bispecific Antibodies Targeting Distinct Regions of the Spike Protein Potently Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabj5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzou, P.L.; Tao, K.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Shafer, R.W. Coronavirus Resistance Database (CoV-RDB): SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility to Monoclonal Antibodies, Convalescent Plasma, and Plasma from Vaccinated Persons. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Bhattacharya, M.; Dhama, K.; Lee, S.S.; Chakraborty, C. Can the RBD Mutation R346X Provide an Additional Fitness to the “Variant Soup,” Including Offspring of BQ and XBB of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron for the Antibody Resistance? Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 32, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Bhattacharya, M.; Chopra, H.; Bhattacharya, P.; Islam, M.A.; Dhama, K. Recently Emerged Omicron Subvariant BF.7 and Its R346T Mutation in the RBD Region Reveal Increased Transmissibility and Higher Resistance to Neutralization Antibodies: Need to Understand More under the Current Scenario of Rising Cases in China and Fears of Driving a New Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, P.; Evans, J.P.; Faraone, J.N.; Zheng, Y.M.; Carlin, C.; Anghelina, M.; Stevens, P.; Fernandez, S.; Jones, D.; Lozanski, G.; et al. Enhanced Neutralization Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants BQ.1, BQ.1.1, BA.4.6, BF.7, and BA.2.75.2. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 9–17.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Zhang, L.; Nehlmeier, I.; Kempf, A.; Cossmann, A.; Dopfer-Jablonka, A.; Schulz, S.R.; Jäck, H.M.; Behrens, G.M.N.; Pöhlmann, S.; et al. The Effect of Cilgavimab and Neutralisation by Vaccine-Induced Antibodies in Emerging SARS-CoV-2 BA.4 and BA.5 Sublineages. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1665–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheward, D.J.; Kim, C.; Fischbach, J.; Sato, K.; Muschiol, S.; A Ehling, R.; Björkström, N.K.; Hedestam, G.B.K.; Reddy, S.T.; Albert, J.; et al. Omicron sublineage BA.2.75.2 exhibits extensive escape from neutralising antibodies. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1538–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenheit, R.; Galanis, I.; Sondén, K.; Sperk, M.; Movert, E.; Bacchus, P.; Efimova, T.; Petersson, L.; Rapp, M.; Sahlén, V.; et al. Rapid Emergence of Omicron Sublineages Expressing Spike Protein R346T. Lancet Reg. Health-Eur. 2023, 24, 100564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameroni, E.; Bowen, J.E.; Rosen, L.E.; Saliba, C.; Zepeda, S.K.; Culap, K.; Pinto, D.; VanBlargan, L.A.; De Marco, A.; di Iulio, J.; et al. Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Antigenic Shift. Nature 2022, 602, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winger, A.; Caspari, T. The Spike of Concern—The Novel Variants of Sars-Cov-2. Viruses 2021, 13, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Dcosta, B.M.; Samanovic, M.I.; Herati, R.S.; Cornelius, A.; Zhou, H.; Vaill, A.; Kazmierski, W.; Mulligan, M.J.; Landau, N.R. Convalescent-Phase Sera and Vaccine-Elicited Antibodies Largely Maintain Neutralizing Titer against Global SARS-CoV-2 Variant Spikes. mBio 2021, 12, e0069621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibmer, C.K.; Ayres, F.; Hermanus, T.; Madzivhandila, M.; Kgagudi, P.; Oosthuysen, B.; Lambson, B.E.; de Oliveira, T.; Vermeulen, M.; van der Berg, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 Escapes Neutralization by South African COVID-19 Donor Plasma. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Antibody Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nature 2021, 593, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejnirattisai, W.; Zhou, D.; Supasa, P.; Liu, C.; Mentzer, A.J.; Ginn, H.M.; Zhao, Y.; Duyvesteyn, H.M.E.; Tuekprakhon, A.; Nutalai, R.; et al. Antibody Evasion by the P.1 Strain of SARS-CoV-2. Cell 2021, 184, 2939–2954.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, T.N.; Greaney, A.J.; Addetia, A.; Hannon, W.W.; Choudhary, M.C.; Dingens, A.S.; Li, J.Z.; Bloom, J.D. Prospective Mapping of Viral Mutations That Escape Antibodies Used to Treat COVID-19. Science 2021, 371, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, B.; Huynh, T. Insights into SARS-CoV-2’s Mutations for Evading Human Antibodies: Sacrifice and Survival. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 2820–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focosi, D.; Maggi, F. Neutralising Antibody Escape of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: Risk Assessment for Antibody-Based Covid-19 Therapeutics and Vaccines. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, e2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron Escapes the Majority of Existing SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, J.; Suzuki, R.; Uriu, K.; Itakura, Y.; Zahradnik, J.; Kimura, K.T.; Deguchi, S.; Wang, L.; Lytras, S.; Tamura, T.; et al. Convergent Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants Leading to the Emergence of BQ.1.1 Variant. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Zhu, X.; He, W.-T.; Zhou, P.; Kaku, C.I.; Capozzola, T.; Zhu, C.Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Yu, W.; et al. A Broad and Potent Neutralization Epitope in SARS-Related Coronaviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2205784119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zha, J.; Xu, S.; Shao, J.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, X. Structure-Based Optimization of One Neutralizing Antibody against SARS-CoV-2 Variants Bearing the L452R Mutation. Viruses 2024, 16, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.C.; Hansen, G.; Ssebyatika, G.; Ströh, L.J.; Ochulor, O.; Herold, E.; Schwarzloh, B.; Mutschall, D.; Zischke, J.; Cordes, A.K.; et al. A Human Monoclonal Antibody Neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variants Containing the L452R Mutation. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0122324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombel-Bryzek, A.; Petkov, P.; Lilkova, E.; Ilieva, N.; Litov, L.; Kubus, M.; Witkowska, D. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 RBM Mutations N501Y and E484K on ACE2 Binding: A Combined Computational and Experimental Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Zia, T.; Suleman, M.; Khan, T.; Ali, S.S.; Abbasi, A.A.; Mohammad, A.; Wei, D.Q. Higher Infectivity of the SARS-CoV-2 New Variants Is Associated with K417N/T, E484K, and N501Y Mutants: An Insight from Structural Data. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 7045–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S. E484K and N501Y SARS-CoV 2 Spike Mutants Increase ACE2 Recognition but Reduce Affinity for Neutralizing Antibody. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 102, 108424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Zhou, B.; Reddem, E.R.; Tang, B.; Chen, B.; Zhou, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Katsamba, P.S.; Au, K.K.; et al. Structural Insights into Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Elicited by Hybrid Immunity against SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2146538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisblum, Y.; Schmidt, F.; Zhang, F.; DaSilva, J.; Poston, D.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Rutkowska, M.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Michailidis, E.; et al. Escape from Neutralizing Antibodies 1 by SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Variants. eLife 2020, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anraku, Y.; Kita, S.; Onodera, T.; Sato, A.; Tadokoro, T.; Ito, S.; Adachi, Y.; Kotaki, R.; Suzuki, T.; Sasaki, J.; et al. Structural and Virological Identification of Neutralizing Antibody Footprint Provides Insights into Therapeutic Antibody Design against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzai, I.; Fujita, J.; Ono, C.; Kosaka, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Shichinohe, S.; Takada, K.; Torii, S.; Taguwa, S.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Characterization of a Neutralizing Antibody That Recognizes a Loop Region Adjacent to the Receptor-Binding Interface of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0365523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, D.A.; De Marco, A.; Ferreira, I.A.T.M.; Meng, B.; Datir, R.P.; Walls, A.C.; Kemp, S.A.; Bassi, J.; Pinto, D.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; et al. Sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 to MRNA Vaccine-Elicited Antibodies. Nature 2021, 593, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, D.; Lan, T.; He, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Baptista-Hon, D.T.; Zhang, K.; Wei, X. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant: Immune Escape and Vaccine Development. MedComm 2022, 3, e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, M.; Czudnochowski, N.; Rosen, L.E.; Zepeda, S.K.; Bowen, J.E.; Walls, A.C.; Hauser, K.; Joshi, A.; Stewart, C.; Dillen, J.R.; et al. Structural Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Immune Evasion and Receptor Engagement. Science 2022, 375, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.B.; Ma, Y.B.; Lei, Z.H.; Zhang, X.F.; Li, J.; Li, S.S.; Dong, Z.Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Q.M.; Su, J.G. Identification of Key Mutations Responsible for the Enhancement of Receptor-Binding Affinity and Immune Escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2023, 124, 108540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Zhou, H.; Dcosta, B.M.; Samanovic, M.I.; Chivukula, V.; Herati, R.S.; Hubbard, S.R.; Mulligan, M.J.; Landau, N.R. Increased Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant to Neutralization by Vaccine-Elicited and Therapeutic Antibodies. EBioMedicine 2022, 78, 103944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Evans, J.P.; Zheng, Y.M.; Carlin, C.; Saif, L.J.; Oltz, E.M.; Xu, K.; Gumina, R.J.; Liu, S.L. Evasion of Neutralizing Antibody Responses by the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.75 Variant. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1518–1526.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, K.; Geng, Q.; Herbst, M.; Wang, M.; Huang, L.; Bu, F.; Liu, B.; Aihara, H.; Li, F. Structural Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron in Human Receptor Recognition. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0082223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Iranzadeh, A.; Fonseca, V.; Giandhari, J.; Doolabh, D.; Pillay, S.; San, E.J.; Msomi, N.; et al. Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern in South Africa. Nature 2021, 592, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Tong, B.; Sun, L.; Shi, S.; Zheng, B.; Wang, Z.; Dong, X.; Zheng, P. N501Y Mutation of Spike Protein in SARS-CoV-2 Strengthens Its Binding to Receptor ACE2. eLife 2021, 10, 69091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffeber, C.; de Koning, K.; Kanaar, R.; Lebbink, J.H.G. Experimental Evidence for Enhanced Receptor Binding by Rapidly Spreading SARS-CoV-2 Variants. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 167058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, P.; Chen, Z.; Aviszus, K.; Yang, J.; Downing, W.; Jiang, C.; Liang, B.; Reynoso, L.; et al. The Basis of a More Contagious 501Y.V1 Variant of SARS-CoV-2. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein N501Y Mutation Causes Differential Species Transmissibility and Antibody Sensitivity: A Molecular Dynamics and Alchemical Free Energy Study. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2021, 6, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusvarghi, S.; Wang, W.; Herrup, R.; Neerukonda, S.N.; Vassell, R.; Bentley, L.; Eakin, A.E.; Erlandson, K.J.; Weiss, C.D. Key Substitutions in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Can Predict Resistance to Monoclonal Antibodies, but Other Substitutions Can Modify the Effects. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0111021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, R.; Qing, E.; Odle, A.; Yuan, M.; Gunawardene, C.D.; Tan, T.J.C.; So, N.; Ouyang, W.O.; Wilson, I.A.; Gallagher, T.; et al. Functional and Antigenic Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Fusion Peptide by Deep Mutational Scanning. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.J.C.; Verma, A.K.; Odle, A.; Lei, R.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Matreyek, K.A.; Perlman, S.; Wong, L.Y.R.; Wu, N.C. Evidence of Antigenic Drift in the Fusion Machinery Core of SARS-CoV-2 Spike. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2317222121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadonaite, B.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Radford, C.E.; Farrell, A.G.; Yu, T.C.; Hannon, W.W.; Zhou, P.; Andrabi, R.; Burton, D.R.; Liu, L.; et al. A Pseudovirus System Enables Deep Mutational Scanning of the Full SARS-CoV-2 Spike. Cell 2023, 186, 1263–1278.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touret, F.; Giraud, E.; Bourret, J.; Donati, F.; Tran-Rajau, J.; Chiaravalli, J.; Lemoine, F.; Agou, F.; Simon-Lorière, E.; van der Werf, S.; et al. Enhanced Neutralization Escape to Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sub-Lineages. iScience 2023, 26, 106413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Staropoli, I.; Planchais, C.; Yab, E.; Jeyarajah, B.; Rahou, Y.; Prot, M.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Lemoine, F.; Enouf, V.; et al. Escape of SARS-CoV-2 Variants KP1.1, LB.1, and KP3.3 From Approved Monoclonal Antibodies. Pathog. Immun. 2024, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entzminger, K.C.; Fleming, J.K.; Entzminger, P.D.; Espinosa, L.Y.; Samadi, A.; Hiramoto, Y.; Okumura, S.C.J.; Maruyama, T. Rapid Engineering of SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Antibodies to Increase Breadth of Neutralization Including BQ.1.1, CA.3.1, CH.1.1, XBB.1.16, and XBB.1.5. Antib. Ther. 2023, 6, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xing, X.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Ma, W.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; et al. Potent and Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies against Sarbecoviruses Elicited by Single Ancestral SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Ho, J.; Ho, D.D. Activity of Research-Grade Pemivibart against Recent SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 Sublineages. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1863–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Mellis, I.A.; Wu, M.; Mohri, H.; Gherasim, C.; Valdez, R.; Purpura, L.J.; Yin, M.T.; Gordon, A.; et al. Antibody Evasiveness of SARS-CoV-2 Subvariants KP.3.1.1 and XEC. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 115543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Shen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, X.L.; Chen, J.; Yan, R.; et al. Novel Sarbecovirus Bispecific Neutralizing Antibodies with Exceptional Breadth and Potency against Currently Circulating SARS-CoV-2 Variants and Sarbecoviruses. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Z.; Xie, X.; Lin, J.; Gao, P.; Wu, B.; El Sahili, A.; Su, H.; Liu, Y.; Ye, X.; Tan, E.Y.; et al. Engineering SARS-CoV-2 Specific Cocktail Antibodies into a Bispecific Format Improves Neutralizing Potency and Breadth. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, D.; Feng, X.; Xu, Y.; Wei, J.; Zou, Q.; Yang, Q.; Chen, J.; Jiang, X.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of ISH0339, a Tetravalent Broadly Neutralizing Bispecific Antibody against SARS-CoV-2 with Long-Term Protection. Antib. Ther. 2023, 6, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Peng, W.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Z.; Chai, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhao, X.; et al. An Engineered Bispecific Human Monoclonal Antibody against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.D.; Scherer, M.; Hutter, C.A.J.; Garaeva, A.A.; Zimmermann, I.; Wyss, M.; Rheinberger, J.; Ruedin, Y.; Earp, J.C.; Egloff, P.; et al. Biparatopic Sybodies Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern and Mitigate Drug Resistance. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, D.; Radić, L.; Brinkkemper, M.; Poniman, M.; van der Maas, L.; Torres, J.L.; Ward, A.B.; Sliepen, K.; Schinkel, J.; Sanders, R.W.; et al. Broadening Sarbecovirus Neutralization with Bispecific Antibodies Combining Distinct Conserved Targets on the Receptor Binding Domain. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2024, 20, 2388344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Heo, K.; Kim, H.J.; Yoo, Y.; Cho, H.S.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Ko, I.Y.; Woo, J.R.; Cho, Y.B.; et al. Novel Bispecific Human Antibody Platform Specifically Targeting a Fully Open Spike Conformation Potently Neutralizes Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Antiviral Res. 2023, 212, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Xia, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Huang, P.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Fang, T.; Fan, P.; et al. A Novel Bispecific Antibody Targeting Two Overlapping Epitopes in RBD Improves Neutralizing Potency and Breadth against SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2373307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, W.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, M.; Ji, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q.; et al. Combating the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (BA.1) and BA.2 with Potent Bispecific Antibodies Engineered from Non-Omicron Neutralizing Antibodies. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, A.; Ji, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Mao, Q.; Xiong, X.; Rehati, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Bispecific Antibody Exhibits Broad Neutralization against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variants XBB.1.16, BQ.1.1 and Sarbecoviruses. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhan, W.; Yang, Z.; Tu, C.; Hu, G.; Zhang, X.; Song, W.; Du, S.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, K.; et al. Broad Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Variants by an Inhalable Bispecific Single-Domain Antibody. Cell 2022, 185, 1389–1401.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Z.; Tong, J.; Lei, W.; Xie, Y.; Cui, Y.; Jia, G.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Xing, X.; et al. Deciphering a Reliable Synergistic Bispecific Strategy of Rescuing Antibodies for SARS-CoV-2 Escape Variants, Including BA.2.86, EG.5.1, and JN.1. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, A.A.; Baharani, V.A.; Dadonaite, B.; Parada, M.; Abernathy, M.E.; Wang, Z.; Lee, Y.E.; Eso, M.R.; Phung, J.; Ramos, I.; et al. Bispecific antibodies targeting the N-terminal and receptor binding domains potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Sci. Transl. Med. 2025, 17, eadq5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, M.; Chen, X.; Hu, L.; Sun, Y.; Du, R.; Qin, R.; et al. Discovery of Synergistic Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting Non-Dominant Epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 RBD and NTD. Vaccines 2025, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Qian, Z.; Ye, L.; Liu, P. A Bispecific Antibody Targeting RBD and S2 Potently Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Other Variants of Concern. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0077522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Heo, K.; Lee, Y.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, J.W.; Cho, Y.B.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, H.G.; et al. A Novel Bispecific Antibody Dual-Targeting Approach for Enhanced Neutralization against Fast-Evolving SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1271508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sato, K.; Okemoto-Nakamura, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Onodera, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Wakita, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; et al. Overcoming Antibody-Resistant SARS-CoV-2 Variants with Bispecific Antibodies Constructed Using Non-Neutralizing Antibodies. iScience 2024, 27, 109363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qian, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Y.; Shen, C. Design and Characterization of Bispecific and Trispecific Antibodies Targeting SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines 2025, 13, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, C.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cai, G.; Chu, H.; Wang, P. Bispecific Antibodies Provide Broad Neutralization of Emerging Beta-Coronaviruses by Targeting ACE2 and Viral Spikes. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2404166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, C.; Tickle, J.R.; Coles, C.H. Facilitating High Throughput Bispecific Antibody Production and Potential Applications within Biopharmaceutical Discovery Workflows. MAbs 2024, 16, 2311992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Format | Parent Antibodies | IC50 Pseudotyped Virus (nM) | IC50 Authentic Virus (nM) | Protective Efficacy | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi-Nab35B5-47D10, Bi-Nab47D10-35B5 | IgG-(scFv)2 | anti-RBD: 35B5 anti-S2: 47D10 | Bi-Nab35B5-47D10 WT: 0.046, Alpha: 0.038, Beta: 0.36, Delta: 0.079, Kappa: 0.065, BA.1: 0.15, BA.2: 0.67 Bi-Nab47D10-35B5 WT: 0.12, Alpha: 0.083, Beta: 0.78, Delta: 0.81, Kappa: 0.052, BA.1: 1.52, BA.2: 2.88 | n.a. | n.a. | [112] |
| K203.A | IgG4-(scFv)2 | anti-RBD: K102.1 anti-S2 (FP): K107.1 | D614G: 0.42 ± 0.02, Alpha: 0.33 ± 0.02, Beta: 1.29 ± 0.11, Gamma: 1.11 ± 0.10, Kappa: 5.46 ± 0.31 | WT: n.d., Delta: n.d. (More potent than K102.1) | K203.A reduced viral loads and alleviated lung pathology in hACE2-TG mice (Delta variant). | [113] |
| Bis3, Bis-Beb | IgG-scFv | anti-RBD: CvMab-6, Bebtelovimab anti-S2: CvMab-62 | Bis3 WT: 6.1, Alpha: 36.6, Delta: 141, BA.1:89 Bis-Beb BA.5.2: 1.6 × 10−3, K444T-BA.5.2: 2.8 | Bis3 WT: 24.9, Alpha: 5.6, Delta: 163, BA.1: 13.1 Bis-Beb BA.5.2.1: 2.0 × 10−2, BQ.1.1: 2.6 | n.a. | [114] |
| F-S2P6 + S309, F-S309 + S2P6 | IgG-scFv | anti-RBD: S309 anti-S2 (SH): S2P6 | F-S2P6 + S309 * WT: 0.056, Beta: 0.15, Delta: 0.28, BA.2: 0.58, BA.5: 0.62, XBB: 0.18 F-S309 + S2P6 * WT: 0.044, Beta: 0.078, Delta: 0.24, BA.2: 0.18, BA.5: 0.47, XBB: 0.16 | n.a. | F-S2P6 + S309 and F-S309 + S2P6 reduced pulmonary viral loads in SARS-CoV-2-infected mice (XBB.1.16 subvariant). | [115] |
| H11B11_S2P6 S2P6_H11B11 | Knob-into-Hole | anti-ACE2: H11B11 anti-S2 (SH): S2P6 | H11B11_S2P6 ** WT: 0.99, BA.2: 1.15, BA.5: 1.53, XBB.1.5: 1.0 SARS-CoV: 1.61 S2P6_ H11B11 ** WT: 14.65, BA.2: 14.13, BA.5: 14.87, XBB.1.5: 24.17 SARS-CoV: 12.47 | n.a. | n.a. | [116] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamamoto, Y.; Noguchi, K. Structural Insights into the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Its Implications for Antibody Resistance. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111489
Yamamoto Y, Noguchi K. Structural Insights into the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Its Implications for Antibody Resistance. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111489
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamamoto, Yuichiro, and Kohji Noguchi. 2025. "Structural Insights into the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Its Implications for Antibody Resistance" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111489
APA StyleYamamoto, Y., & Noguchi, K. (2025). Structural Insights into the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Its Implications for Antibody Resistance. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111489





