Multi-Omics Integration Reveals Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease via Gut–Brain Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Groups
2.2. Ethical Review
2.3. Behavioral Testing
2.4. Tissue Processing and Histopathology
2.5. Nissl Staining
2.6. Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.7. ELISA
2.8. 16S rDNA Profiling of Gut Microbiota
2.9. Bioinformatics Analysis of 16S Amplicon Sequencing
2.10. UPLC-MS/MS Metabolomics Profiling
2.11. Metabolomics Data Processing and Annotation
2.12. Evidence of Metabolite-Target Interactions
2.13. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.14. Other Statistical Analysis
3. Results
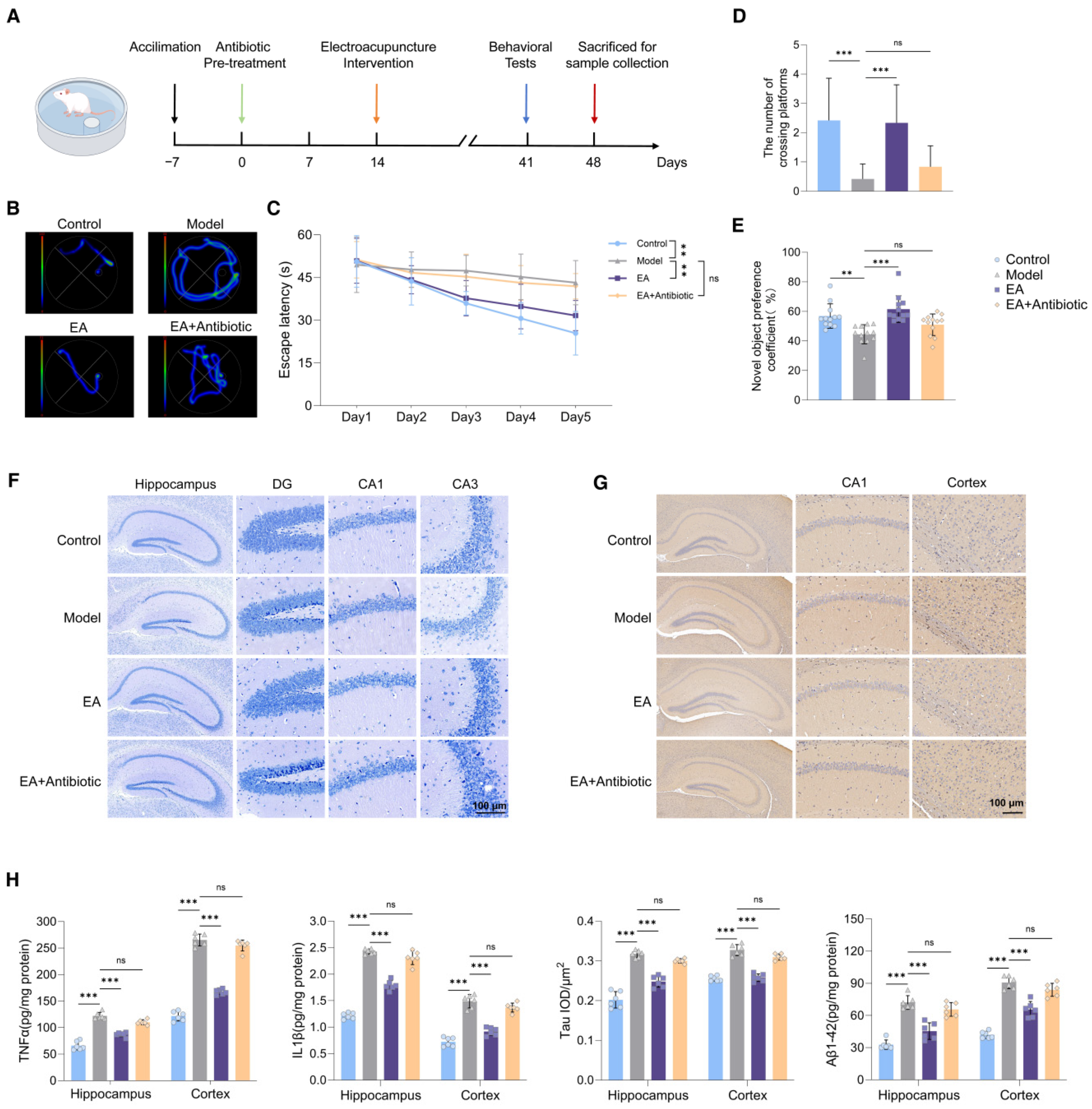
3.1. EA Alleviated Neuroinflammation and Restored Impaired Cognitive Functions of AD Model
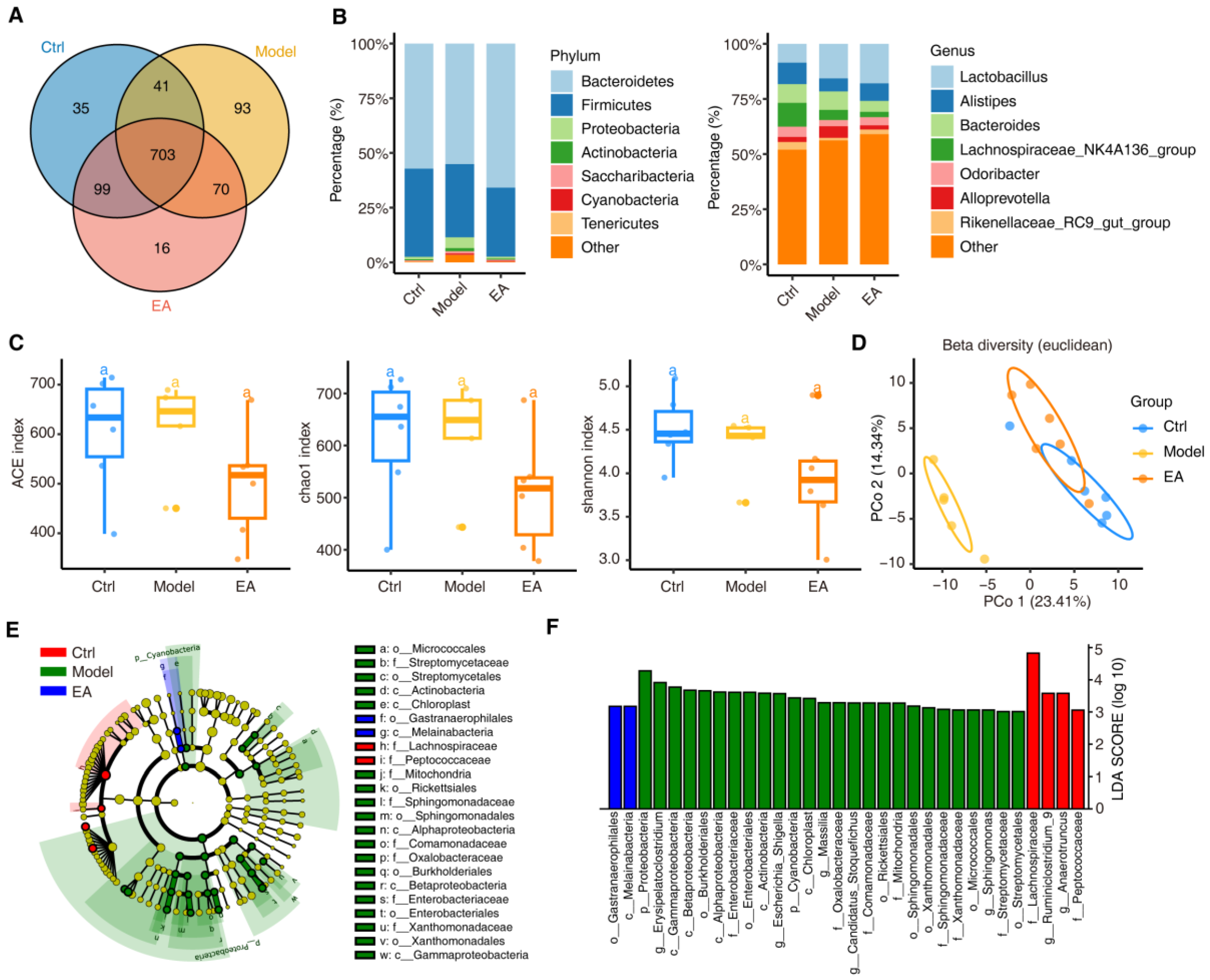
3.2. EA Alters Gut Microbial Diversity to Restore Microbiome Balance in AD Model
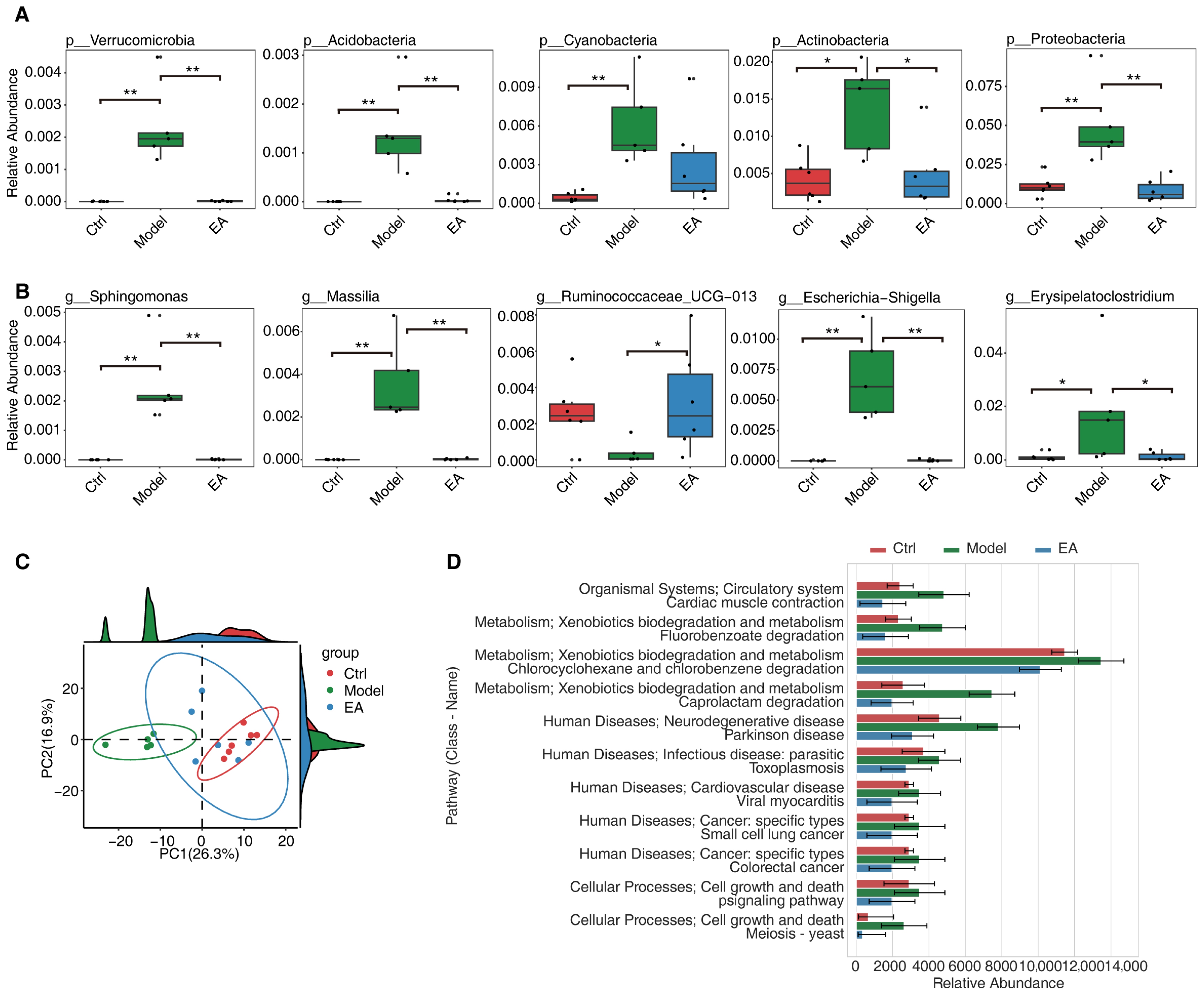
3.3. EA Restores Gut Microbial and Functional Imbalances in AD Model
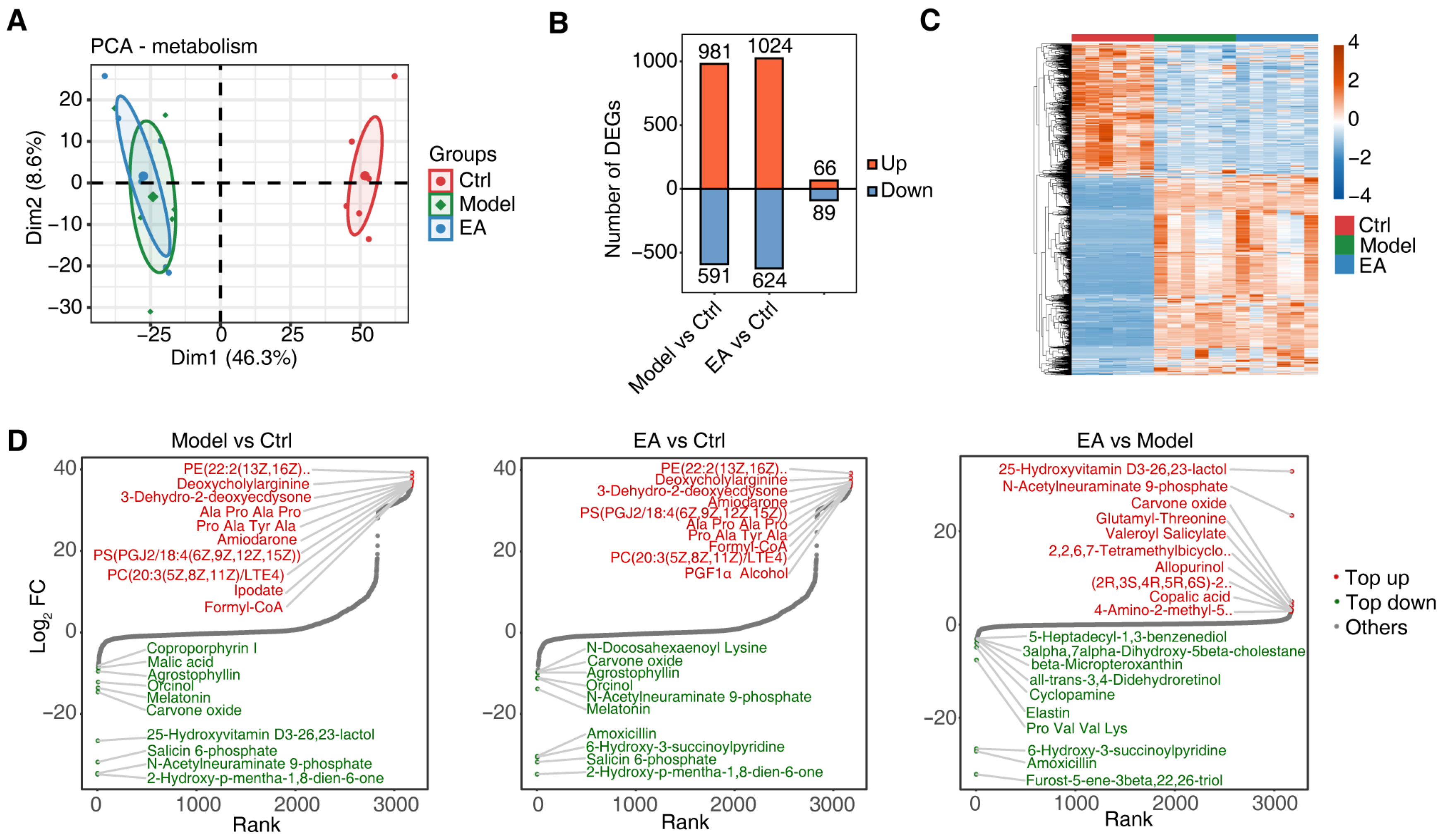
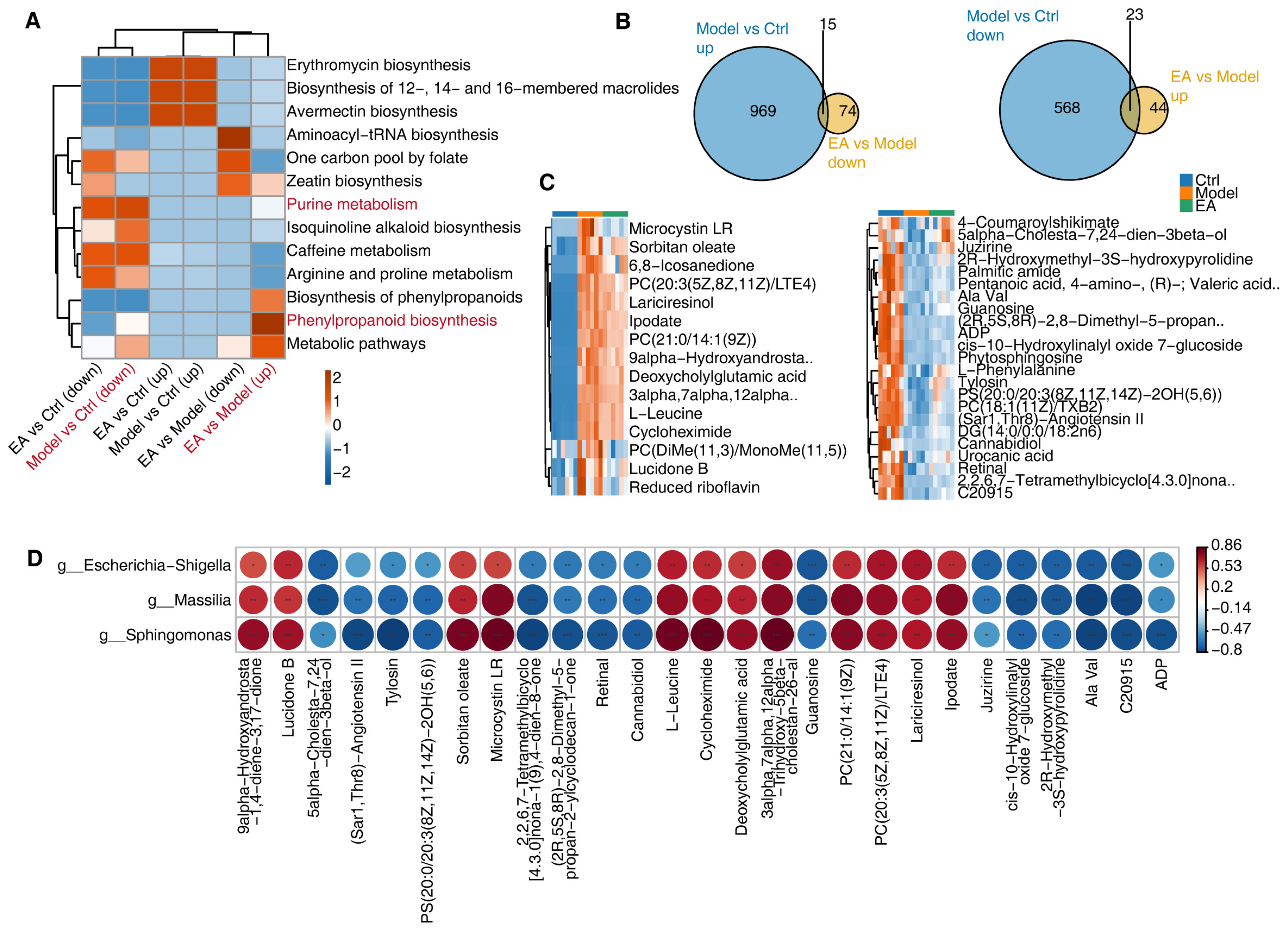
3.4. EA Influences Metabolic Function by Regulating Gut Microbiota
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Metabolites and Gut Microbiota and Regulatory Mechanisms of EA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Recent advances in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms, clinical trials and new drug development strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beata, B.K.; Wojciech, J.; Johannes, K.; Piotr, L.; Barbara, M. Alzheimer’s Disease-Biochemical and Psychological Background for Diagnosis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1059. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Xing, C.; Long, W.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, R.F. Impact of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological diseases: The gut-brain axis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megur, A.; Baltriukienė, D.; Bukelskienė, V.; Burokas, A. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Alzheimer’s Disease: Neuroinflammation Is to Blame? Nutrients 2020, 13, 37. [Google Scholar]
- You, M.; Chen, N.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, L.; He, H.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Hong, G. The gut microbiota-brain axis in neurological disorders. MedComm 2024, 5, e656. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, W. Drug-microbiota interactions: An emerging priority for precision medicine. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wu, L.; Peng, G.; Han, Y.; Tang, R.; Ge, J.; Zhang, L.; Jia, L.; Yue, S.; Zhou, K.; et al. Altered microbiomes distinguish Alzheimer’s disease from amnestic mild cognitive impairment and health in a Chinese cohort. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 80, 633–643. [Google Scholar]
- Askarova, S.; Umbayev, B.; Masoud, A.R.; Kaiyrlykyzy, A.; Safarova, Y.; Tsoy, A.; Olzhayev, F.; Kushugulova, A. The Links Between the Gut Microbiome, Aging, Modern Lifestyle and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Erny, D.; Dokalis, N.; Mezö, C.; Castoldi, A.; Mossad, O.; Staszewski, O.; Frosch, M.; Villa, M.; Fuchs, V.; Mayer, A.; et al. Microbiota-derived acetate enables the metabolic fitness of the brain innate immune system during health and disease. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 2260–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Cao, X.; Xin, M.; Guan, R. Treatment of Depression with Acupuncture Based on Pathophysiological Mechanism. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, H.; Cao, S.; Xie, L.; Ren, P.; Wang, J.; Shi, B. Revealing the magic of acupuncture based on biological mechanisms: A literature review. Biosci. Trends. 2022, 16, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, P.; Kang, Z.; Zhou, D.S. Exploring Mechanism of Electroacupuncture in Modulating Neuroinflammation Based on Intestinal Flora and Its Metabolites. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2025, 31, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Han, J.; Yu, T.; Shi, J.; Zhao, L.; Nie, K. Acupuncture for patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, A. Protective Role of Electroacupuncture Against Cognitive Impairment in Neurological Diseases. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2025, 23, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Lin, W.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, K.; Wei, W.; Huo, Q.; Cui, S.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Xu, N.; et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates beta-amyloid pathology and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer disease via a novel mechanism involving activation of TFEB (transcription factor EB). Autophagy 2021, 17, 3833–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Xu, A.J. Electroacupuncture ameliorates neuroinflammation in animal models. Acupunct. Med. 2022, 40, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Ma, Z.; Tang, R.; Wang, X.; Wei, K.; Yang, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xie, C.; et al. Efficacy of acupuncture in patients with mild Alzheimer’s disease and its impact on gut microbiota: Study protocol for a randomized sham-controlled trial. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1014113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Deng, P.; Chen, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H. Electroacupuncture and human iPSC-derived small extracellular vesicles regulate the gut microbiota in ischemic stroke via the brain-gut axis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1107559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, A.; Pang, B.; Wu, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, N.; Ye, T. Electroacupuncture pretreatment alleviates spasticity after stroke in rats by inducing the NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway and the gut-brain axis. Brain Res. 2024, 1822, 148643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Tian, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Ren, J. Electroacupuncture could balance the gut microbiota and improve the learning and memory abilities of Alzheimer’s disease animal model. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, E.J. Electroacupuncture attenuates cognition impairment via anti-neuroinflammation in an Alzheimer’s disease animal model. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Luo, X.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Xiao, X.P.; Huang, Z.Q.; Yu, S.Y.; Sun, J.Y.; Liu, M.J.; et al. Metabolomics Analysis of Electroacupuncture Pretreatment Induced Neuroprotection on Mice with Ischemic Stroke. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2023, 51, 1127–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search clustering orders of magnitude faster than, B.L.A.S.T. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, B.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic units in marker-gene data analysis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. SINTAX: A simple non-Bayesian taxonomy classifier for 16S and ITS sequences. bioRxiv 2016, 074161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Cheng, T.; Yu, B.; Bolton, E.E. An update on PUG-REST: RESTful interface for programmatic access to PubChem. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W563–W570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.; Davies, M.; Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Velankar, S.; Petryszak, R.; Hastings, J.; Bellis, L.; McGlinchey, S.; Overington, J.P. UniChem: A unified chemical structure cross-referencing and identifier tracking system. J. Cheminform. 2013, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaulton, A.; Bellis, L.J.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Davies, M.; Hersey, A.; Light, Y.; McGlinchey, S.; Michalovich, D.; Al-Lazikani, B.; et al. ChEMBL: A large-scale bioactivity database for drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 40, D1100–D1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiser, M.J.; Roth, B.L.; Armbruster, B.N.; Ernsberger, P.; Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. Relating protein pharmacology by ligand chemistry. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gao, Q.; Ma, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Shi, N.; Niu, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Cai, J. Causality of Opportunistic Pathogen Klebsiella pneumoniae to Hypertension Development. Hypertension 2022, 79, 2743–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.Z.; Zou, C.J.; Mei, X.; Li, X.F.; Luo, H.; Shen, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, X.X.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y. Targeting neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: From mechanisms to clinical applications. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 708–715. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, M.; Yang, H. Microglia in the Neuroinflammatory Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 856376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiola, A.S.; Cardona, A.E. The IL-1β phenomena in neuroinflammatory diseases. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassol, I.; Ibañez, M.; Bustamante, J.P. Key features and guidelines for the application of microbial alpha diversity metrics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Leyrolle, Q.; Koistinen, V.; Kärkkäinen, O.; Layé, S.; Delzenne, N.; Hanhineva, K. Microbiota-derived metabolites as drivers of gut-brain communication. Gut Microbes. 2022, 14, 2102878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, M.K.; Banerjee, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Dutta, D. Metabolic disorder in Alzheimer’s disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 781–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczowska-Łącka, I.; Hurła, M.; Banaszek, N.; Kobylarek, D.; Szymanowicz, O.; Kozubski, W.; Dorszewska, J. Selected Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Energy Metabolism Disorders in Neurological Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 4132–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Hu, L.; Duan, J.; Che, H.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, D.; Zhao, S. Polystyrene microplastics enhance microcystin-LR-induced cardiovascular toxicity and oxidative stress in zebrafish embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 352, 124022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yue, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, X.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, H.; et al. Gut Microbiota Interact With the Brain Through Systemic Chronic Inflammation: Implications on Neuroinflammation, Neurodegeneration, and Aging. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 796288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lista, S.; Munafò, A.; Caraci, F.; Imbimbo, C.; Emanuele, E.; Minoretti, P.; Pinto-Fraga, J.; Merino-País, M.; Crespo-Escobar, P.; López-Ortiz, S.; et al. Gut microbiota in Alzheimer’s disease: Understanding molecular pathways and potential therapeutic perspectives. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 104, 102659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cui, X.; Lin, Y.; Huang, F.; Tian, A.; Zhang, R. Gut microbiota changes in patients with Alzheimer’s disease spectrum based on 16S rRNA sequencing: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1422350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.L. Gut Microbiota and Dysbiosis in Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Pathogenesis and Treatment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 5026–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaar, B.J.H.; Hendriksen, H.M.A.; de Leeuw, F.A.; Doorduijn, A.S.; van Leeuwenstijn, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Kraaij, R.; van Duijn, C.M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Is Related to AD Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 794519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.T.; Chen, Y.H.; Yang, H.B.; Lin, J.G.; Hung, S.Y. Electroacupuncture Improves Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease and Promotes Neuronal Autophagy Activity in Mouse Brain. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 1651–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, T.; Du, Z.; Song, W.; Chen, W.; Wang, C. Electroacupuncture remodels gut microbiota and metabolites in mice with perioperative neurocognitive impairment. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 194, 112507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, G. Acupuncture Interventions for Alzheimer’s Disease and Vascular Cognitive Disorders: A Review of Mechanisms. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 6080282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, H.; Wang, Q.; Ye, R.; Bai, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, G.; Wang, Q. Anti-oxidative-initiated cognitive impairment amelioration in Alzheimer’s disease model rats through preventive transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation. Integr. Med. Res. 2023, 12, 100946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Huang, Z.S.; Yu, C.C.; Wang, X.S.; Jiang, T.; Wu, M.; Kong, L.H. Preventive electroacupuncture ameliorates D-galactose-induced Alzheimer’s disease-like inflammation and memory deficits, probably via modulating the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2021, 24, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Xiong, W.N.; Ma, Y.Y. Exploring the mechanism of action of acupuncture for Alzheimer’s disease based on the immune-metabolic network perspective. Integr. Med. Discov. 2025, 9, e25014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, J.Y.; Meng, X.L.; Yang, D.; Fan, L.H.; Xiang, L.; Wang, P. Traditional Chinese Medicine: Role in Reducing β-Amyloid, Apoptosis, Autophagy, Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Dysfunction of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yong, Y.; Wei, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ruan, W.; Li, X.; Song, J. Electroacupuncture ameliorates postoperative cognitive dysfunction and associated neuroinflammation via NLRP3 signal inhibition in aged mice. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021, 28, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, W.; Yan, Y.N.; Cheng, W.; Liu, S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.P.; Gao, Y.; Lu, W.; et al. Acupuncture Can Play an Antidepressant Role by Regulating the Intestinal Microbes and Neurotransmitters in a Rat Model of Depression. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e929027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Su, Y.; He, W.; Li, J.; Wan, H.; Jing, X. Electroacupuncture regulates inflammatory cytokines by activating the vagus nerve to enhance antitumor immunity in mice with breast tumors. Life Sci. 2021, 272, 119259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, D.; Gong, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Hong, X. Integrating 16S rDNA and metabolomics to uncover the therapeutic mechanism of electroacupuncture in type 2 diabetic rats. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1436911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; Song, J.; Tian, Q.; Du, Y. Multi-Omics Integration Reveals Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease via Gut–Brain Axis. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111486
Zhang S, Liu X, Xu S, Li W, Song J, Tian Q, Du Y. Multi-Omics Integration Reveals Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease via Gut–Brain Axis. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111486
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuai, Xinyuan Liu, Shuyu Xu, Weixian Li, Jie Song, Qing Tian, and Yanjun Du. 2025. "Multi-Omics Integration Reveals Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease via Gut–Brain Axis" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111486
APA StyleZhang, S., Liu, X., Xu, S., Li, W., Song, J., Tian, Q., & Du, Y. (2025). Multi-Omics Integration Reveals Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease via Gut–Brain Axis. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111486





