HIIT Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization and Sympathetic Nerve Density to Induce Adipose Tissue Browning in T2DM Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method and Materials
2.1. Animals
2.2. Induction of T2DM
2.3. High-Intensity Interval Training
2.4. Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT)
2.5. Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT)
2.6. Adiposity Index
2.7. Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) Staining
2.8. Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.10. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Analysis
2.11. Western Blotting
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Exercise Intervention Improves Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Sensitivity in T2DM Mice
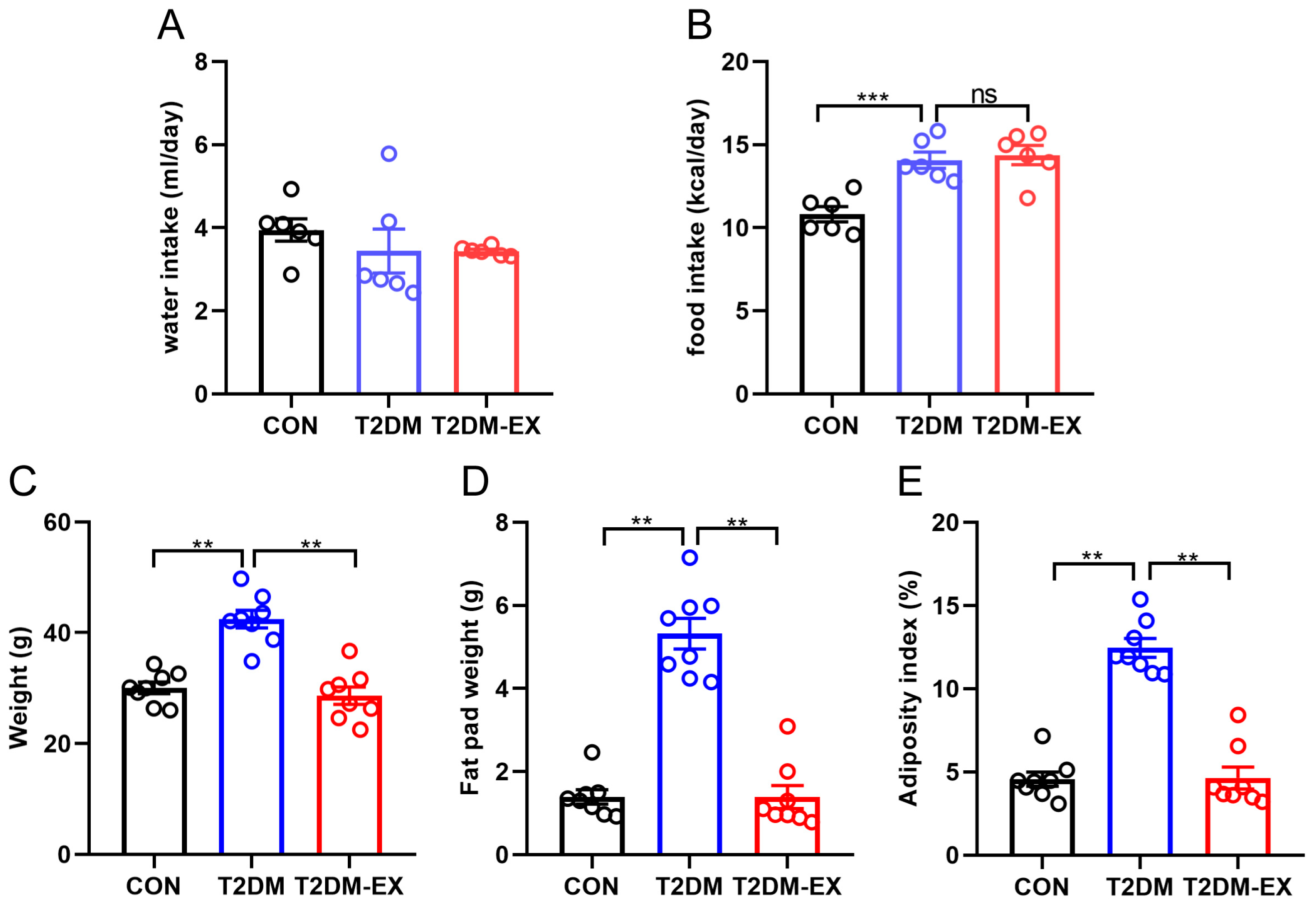
3.2. Exercise Intervention Reduces Adiposity in T2DM Mice
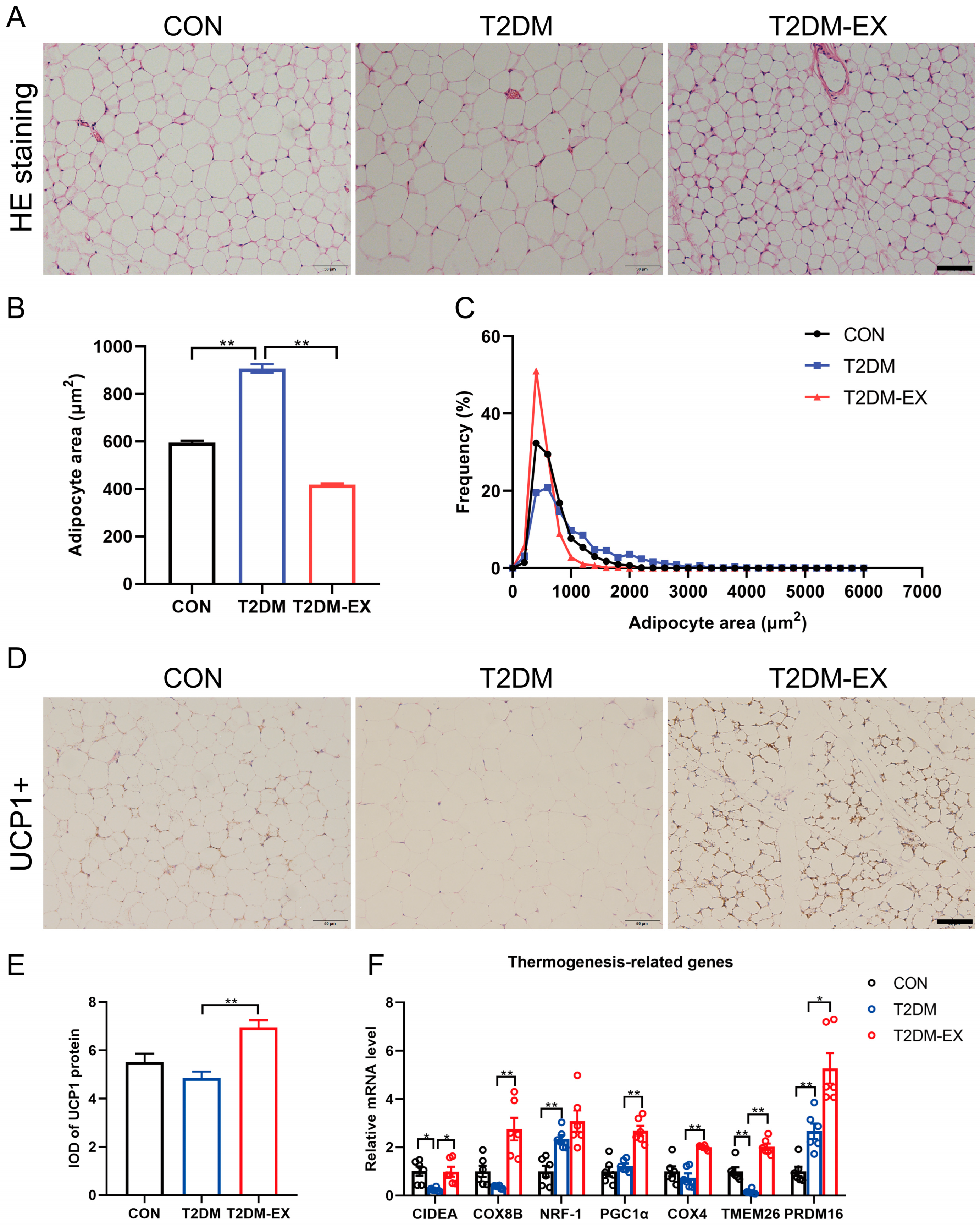
3.3. Exercise Intervention Induces iWAT Browning in T2DM Mice
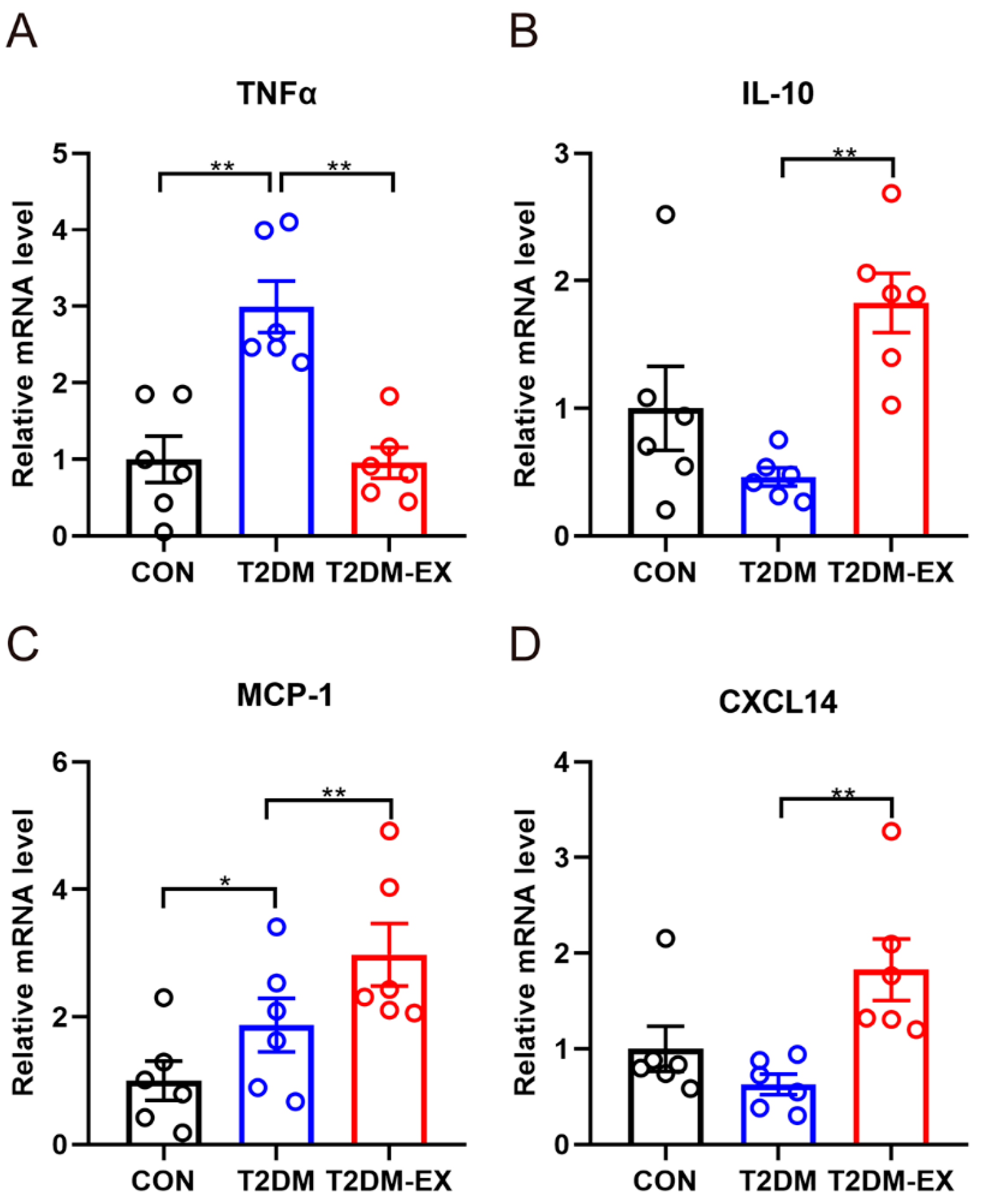
3.4. The Effects of Exercise Intervention and T2DM on Inflammatory Factors in iWAT
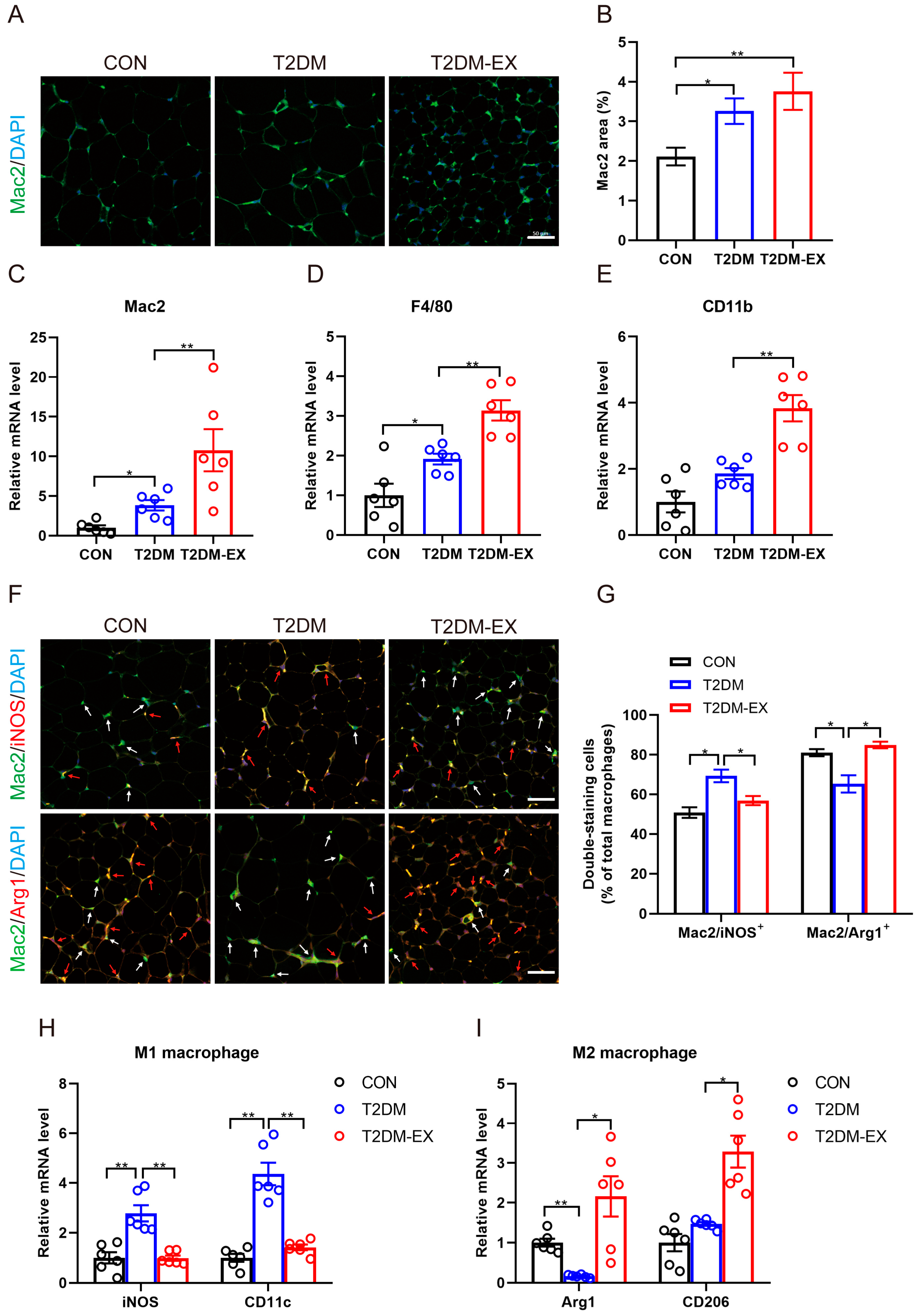
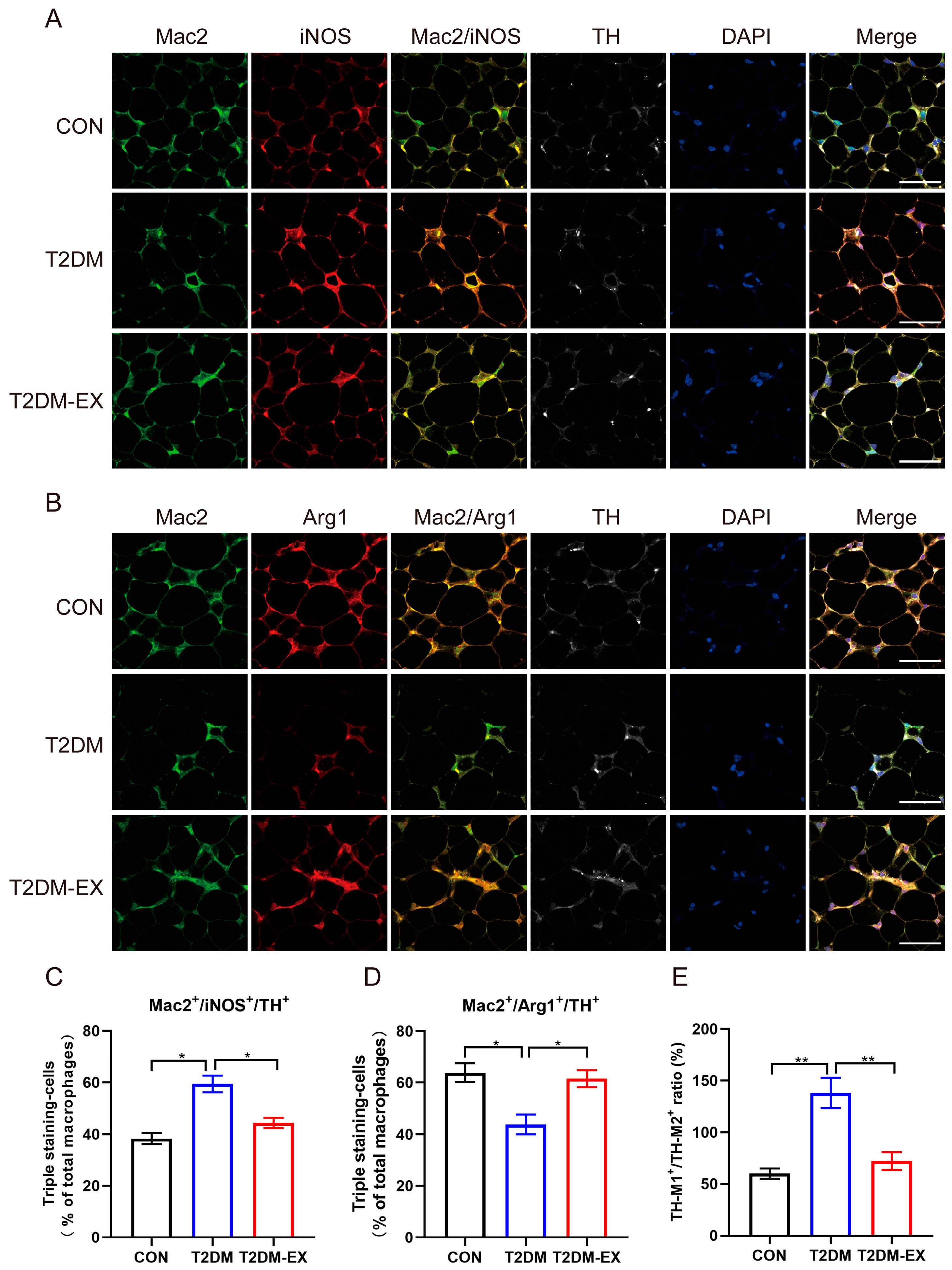
3.5. The Effects of Exercise Intervention on Macrophage Infiltration and Polarization in T2DM Mice
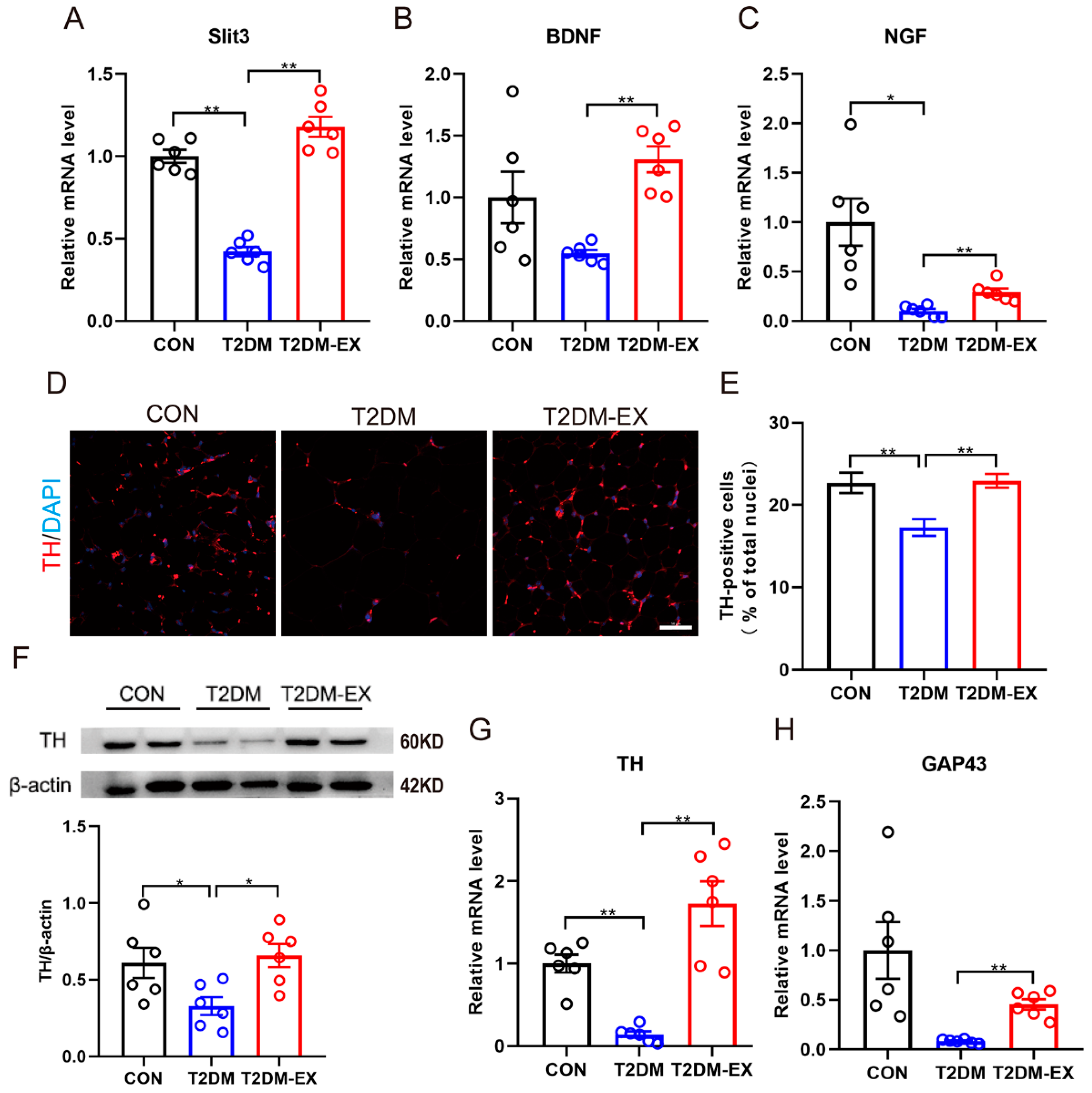
3.6. Exercise Intervention Increases Sympathetic Nerve Density and Partially Activates Its Activity in iWAT
3.7. Linking Macrophage Phenotype to Local Sympathetic Nerves
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magliano, D.J.; Boyko, E.J. Committee International Diabetes Federation. In IDF Diabetes Atlas; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaley, J.A.; Colberg, S.R.; Corcoran, M.H.; Malin, S.K.; Rodriguez, N.R.; Crespo, C.J.; Kirwan, J.P.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise/Physical Activity in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: A Consensus Statement from the American College of Sports Medicine. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, A.; Krause, F.N.; Moran, A.; MacCannell, A.D.V.; Scragg, J.L.; McNally, B.D.; Boateng, E.; Murfitt, S.A.; Virtue, S.; Wright, J.; et al. Brown and beige adipose tissue regulate systemic metabolism through a metabolite interorgan signaling axis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, M.P. Mechanisms of insulin resistance related to white, beige, and brown adipocytes. Mol. Metab. 2020, 34, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.O.; Olvera, A.C.; Marti, A.; Fang, S.; White, J.R.; Westphal, M.; Hewezi, R.; AshShareef, S.T.; García-Peña, L.M.; Koneru, J.; et al. OPA1 Regulates Lipid Metabolism and Cold-Induced Browning of White Adipose Tissue in Mice. Diabetes 2022, 71, 2572–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Nguyen, K.D.; Goh, Y.P. Macrophage-mediated inflammation in metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, T.; Ackerman, S.E.; Shen, L.; Engleman, E. Role of innate and adaptive immunity in obesity-associated metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rached, M.T.; Millership, S.J.; Pedroni, S.M.A.; Choudhury, A.I.; Costa, A.S.H.; Hardy, D.G.; Glegola, J.A.; Irvine, E.E.; Selman, C.; Woodberry, M.C.; et al. Deletion of myeloid IRS2 enhances adipose tissue sympathetic nerve function and limits obesity. Mol. Metab. 2019, 20, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Ruiz, H.H.; Jhun, K.; Finan, B.; Oberlin, D.J.; van der Heide, V.; Kalinovich, A.V.; Petrovic, N.; Wolf, Y.; Clemmensen, C.; et al. Alternatively activated macrophages do not synthesize catecholamines or contribute to adipose tissue adaptive thermogenesis. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Heier, C.; Meng, X.; Bakiri, L.; Pototschnig, I.; Tang, Z.; Schauer, S.; Baumgartner, V.J.; Grabner, G.F.; Schabbauer, G.; et al. An immune-sympathetic neuron communication axis guides adipose tissue browning in cancer-associated cachexia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2112840119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Okamoto, S.; Shiuchi, T.; Toda, C.; Takagi, K.; Sato, T.; Saito, K.; Yokota, S.; Minokoshi, Y. Sympathetic Nerve Activity Maintains an Anti-Inflammatory State in Adipose Tissue in Male Mice by Inhibiting TNF-α Gene Expression in Macrophages. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3680–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.; Santosa, S. Putting ATM to BED: How Adipose Tissue Macrophages Are Affected by Bariatric Surgery, Exercise, and Dietary Fatty Acids. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1893–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereijo, R.; Gavalda-Navarro, A.; Cairo, M.; Quesada-Lopez, T.; Villarroya, J.; Moron-Ros, S.; Sanchez-Infantes, D.; Peyrou, M.; Iglesias, R.; Mampel, T.; et al. CXCL14, a Brown Adipokine that Mediates Brown-Fat-to-Macrophage Communication in Thermogenic Adaptation. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 750–763.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, N.; Yano, H.; Yokogawa, Y.; Suzuki, K. Exercise training inhibits inflammation in adipose tissue via both suppression of macrophage infiltration and acceleration of phenotypic switching from M1 to M2 macrophages in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 16, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.N.; Tang, Y.; He, Z.; Ma, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Pan, D.; Zhu, C.; Qian, S.; et al. Slit3 secreted from M2-like macrophages increases sympathetic activity and thermogenesis in adipose tissue. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1536–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, Y.; Boura-Halfon, S.; Cortese, N.; Haimon, Z.; Sar Shalom, H.; Kuperman, Y.; Kalchenko, V.; Brandis, A.; David, E.; Segal-Hayoun, Y.; et al. Brown-adipose-tissue macrophages control tissue innervation and homeostatic energy expenditure. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzgalska, R.M.; Seixas, E.; Seidman, J.S.; Link, V.M.; Sánchez, N.M.; Mahú, I.; Mendes, R.; Gres, V.; Kubasova, N.; Morris, I.; et al. Sympathetic neuron-associated macrophages contribute to obesity by importing and metabolizing norepinephrine. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colberg, S.R.; Sigal, R.J.; Fernhall, B.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Blissmer, B.J.; Rubin, R.R.; Chasan-Taber, L.; Albright, A.L.; Braun, B. Exercise and type 2 diabetes: The American College of Sports Medicine and the American Diabetes Association: Joint position statement executive summary. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2692–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karstoft, K.; Winding, K.; Knudsen, S.H.; Nielsen, J.S.; Thomsen, C.; Pedersen, B.K.; Solomon, T.P. The effects of free-living interval-walking training on glycemic control, body composition, and physical fitness in type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwoudt, S.; Fealy, C.E.; Foucher, J.A.; Scelsi, A.R.; Malin, S.K.; Pagadala, M.; Rocco, M.; Burguera, B.; Kirwan, J.P. Functional high-intensity training improves pancreatic β-cell function in adults with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 313, E314–E320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, S.; Thoma, C.; Houghton, D.; Trenell, M.I. High-intensity interval training: A review of its impact on glucose control and cardiometabolic health. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, E.M.; Steinberg, G.R. Emerging Role of AMPK in Brown and Beige Adipose Tissue (BAT): Implications for Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, M.A.; Pincu, Y.; Martin, S.A.; Woods, J.A.; Baynard, T. Moderate exercise training provides modest protection against adipose tissue inflammatory gene expression in response to high-fat feeding. Physiol. Rep. 2014, 2, e12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, T.; Paulsen, S.K.; Bruun, J.M.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. Exercise training versus diet-induced weight-loss on metabolic risk factors and inflammatory markers in obese subjects: A 12-week randomized intervention study. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E824–E831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, R.L.; Jeon, J.Y.; Liu, F.F.; Maratos-Flier, E. Voluntary exercise improves insulin sensitivity and adipose tissue inflammation in diet-induced obese mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E586–E594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanishi, N.; Mizokami, T.; Yano, H.; Suzuki, K. Exercise attenuates M1 macrophages and CD8+ T cells in the adipose tissue of obese mice. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.G.; Araujo, T.G.; Carvalho, B.M.; Guadagnini, D.; Rocha, G.Z.; Bagarolli, R.A.; Carvalheira, J.B.; Saad, M.J. Acute exercise induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization in diet-induced obese rats. Obesity 2013, 21, 2545–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerbach, P.; Nordby, P.; Bendtsen, L.Q.; Mehlsen, J.L.; Basnet, S.K.; Vestergaard, H.; Ploug, T.; Stallknecht, B. Differential effects of endurance training and weight loss on plasma adiponectin multimers and adipose tissue macrophages in younger, moderately overweight men. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R490–R498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, T.J.; Skiba, D.S.; Touyz, R.M.; Harrison, D.G. The role of infiltrating immune cells in dysfunctional adipose tissue. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahrendorf, M.; Swirski, F.K. Abandoning M1/M2 for a Network Model of Macrophage Function. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, M.; Haluzik, M. The role of adipose tissue immune cells in obesity and low-grade inflammation. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 222, R113–R127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, S.; Gong, B.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H.; Qi, W.; Zhou, T.; et al. IL-25-induced shifts in macrophage polarization promote development of beige fat and improve metabolic homeostasis in mice. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannerås, L.; Cajander, S.; Lönn, M.; Stener-Victorin, E. Acupuncture and exercise restore adipose tissue expression of sympathetic markers and improve ovarian morphology in rats with dihydrotestosterone-induced PCOS. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 296, R1124–R1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, N.; Xia, J.; Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Huang, J.; Hu, M.; Liao, J. Aerobic Exercise Prevents Arterial Stiffness and Attenuates Hyperexcitation of Sympathetic Nerves in Perivascular Adipose Tissue of Mice after Transverse Aortic Constriction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszkiewicz, M.; Wood, E.; Koizar, S.; Willows, J.; Anderson, R.; Tseng, Y.H.; Godwin, J.; Townsend, K.L. The involvement of neuroimmune cells in adipose innervation. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zeng, W. Whole-tissue 3D imaging reveals intra-adipose sympathetic plasticity regulated by NGF-TrkA signal in cold-induced beiging. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Forward Primer Sequences | Reverse Primer Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Cidea | 5′-GCCTGCAGGAACTTATCAGC-3′ | 5′-AGAACTCCTCTGTGTCCACCA-3′ |
| COX8B | 5′-TGTGGGGATCTCAGCCATAGT-3′ | 5′-AGTGGGCTAAGACCCATCCTG-3′ |
| NRF-1 | 5′-GCCGTCGGAGCACTTACT-3′ | 5′-CTGTTCCAATGTCACCACC-3′ |
| PGC1α | 5′-GAAAGGGCCAAACAGAGAGA-3′ | 5′-GTAAATCACACGGCGCTCTT-3′ |
| COX4 | 5′-TGAATGGAAGACAGTTGTGGG-3′ | 5′-GATCGAAAGTATGAGGGATGGG-3′ |
| TMEM26 | 5′-ACCCTGTCATCCCACAGAG-3′ | 5′-TGTTTGGTGGAGTCCTAAGGTC-3′ |
| PRDM16 | 5′-CCTAAGGTGTGCCCAGCA-3′ | 5′-CACCTTCCGCTTTTCTACCC-3′ |
| TNFα | 5′-GACGTGGAACTGGCAGAAGAG-3′ | 5′-TTGGTGGTTTGTGAGTGTGAG-3′ |
| IL-10 | 5′-GCTCTTACTGACTGGCATGAG-3′ | 5′-CGCAGCTCTAGGAGCATGTG-3′ |
| MCP-1 | 5′-TTAAAAACCTGGATCGGAACCAA-3′ | 5′-GCATTAGCTTCAGATTTACGGGT-3′ |
| Mac2 | 5′-AGACAGCTTTTCGCTTAACGA-3′ | 5′-GGGTAGGCACTAGGAGGAGC-3′ |
| F4/80 | 5′-TTGTACGTGCAACTCAGGACT-3′ | 5′-GATCCCAGAGTGTTGATGCAA-3′ |
| CD11b | 5′-TAATGACTCTGCGTTTGCCCTG-3′ | 5′-ATTGGAGCTGCCCACAATGAG-3′ |
| iNOS | 5′-GTTCTCAGCCCAACAATACAAGA-3′ | 5′-GTGGACGGGTCGATGTCAC-3′ |
| CD11c | 5′-CTGGATAGCCTTTCTTCTGCTG-3′ | 5′-GCACACTGTGTCCGAACTC-3′ |
| Arg1 | 5′-CTCCAAGCCAAAGTCCTTAGAG-3′ | 5′-AGGAGCTGTCATTAGGGACATC-3′ |
| CD206 | 5′-CTCTGTTCAGCTATTGGACGC-3′ | 5′-CGGAATTTCTGGGATTCAGCTTC-3′ |
| Slit3 | 5′-GCGCGATTTGGAGATCCTCA-3′ | 5′-TGGAGTGTAGACGCAGAGTCC-3′ |
| BDNF | 5′-TCATACTTCGGTTGCATGAAGG-3′ | 5′-AGACCTCTCGAACCTGCCC-3′ |
| GAP43 | 5′-TGGTGTCAAGCCGGAAGATAA-3′ | 5′-GCTGGTGCATCACCCTTCT-3′ |
| TH | 5′-GTCTCAGAGCAGGATACCAAGC-3′ | 5′-CTCTCCTCGAATACCACAGCC-3′ |
| GAPDH | 5′-AACTTTGGCATTGTGGAAGG-3′ | 5′-ACACATTGGGGGTAGGAACA-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, D.; Chen, P.; Xiao, W. HIIT Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization and Sympathetic Nerve Density to Induce Adipose Tissue Browning in T2DM Mice. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030246
Guo Y, Zhang Q, Yang D, Chen P, Xiao W. HIIT Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization and Sympathetic Nerve Density to Induce Adipose Tissue Browning in T2DM Mice. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(3):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030246
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yifan, Qilong Zhang, Dan Yang, Peijie Chen, and Weihua Xiao. 2024. "HIIT Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization and Sympathetic Nerve Density to Induce Adipose Tissue Browning in T2DM Mice" Biomolecules 14, no. 3: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030246
APA StyleGuo, Y., Zhang, Q., Yang, D., Chen, P., & Xiao, W. (2024). HIIT Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization and Sympathetic Nerve Density to Induce Adipose Tissue Browning in T2DM Mice. Biomolecules, 14(3), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030246






