Drug Delivery Systems for Personal Healthcare by Smart Wearable Patch System
Abstract
1. Introduction
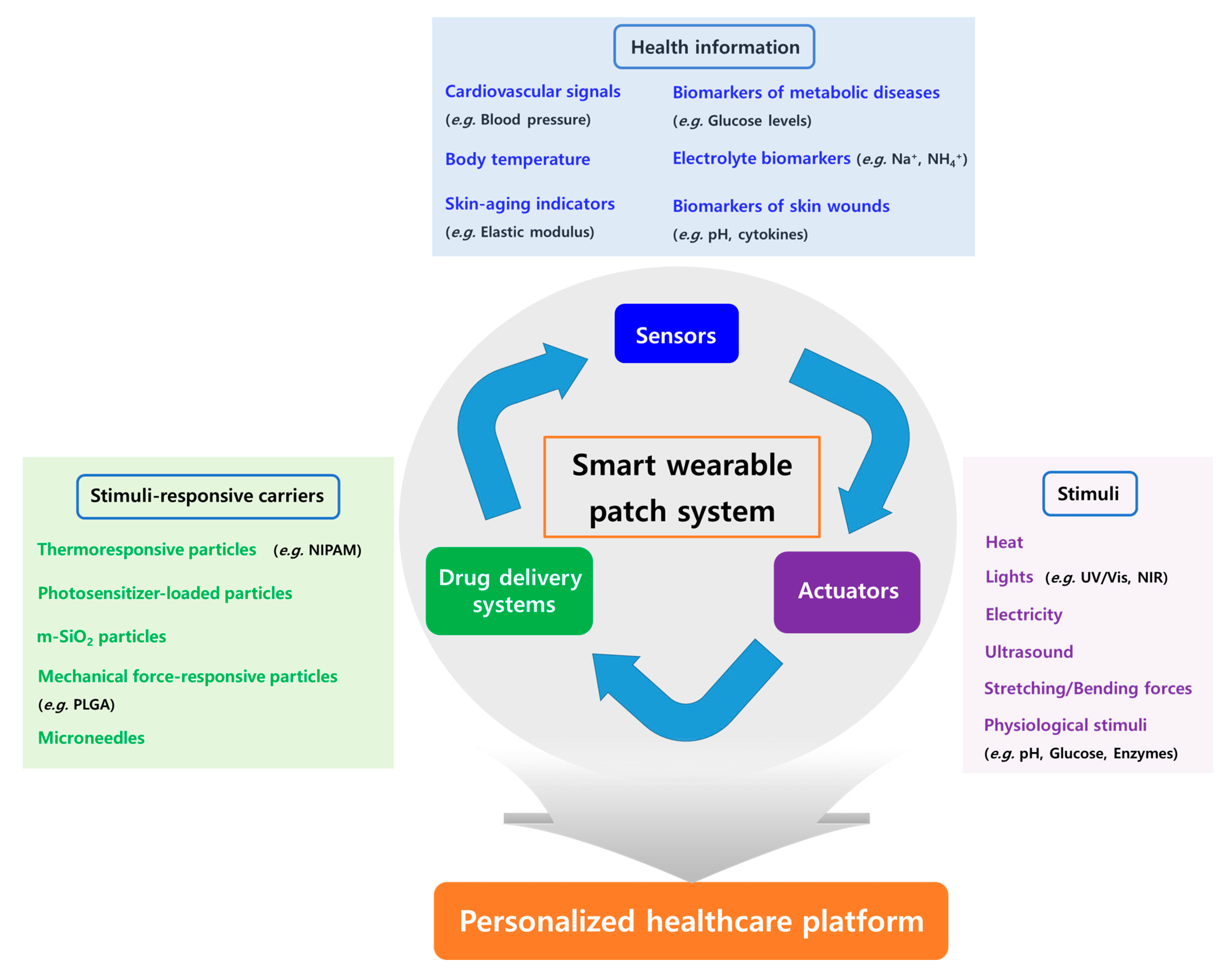
2. Basic Concept of Smart Wearable Patch Systems
3. Physical and Biochemical Information Monitored by Sensor Components
3.1. Physical Information
3.1.1. Cardiovascular Signals
3.1.2. Body Temperature
3.1.3. Skin Aging Indicators
3.2. Biochemical Information (Biomarkers) from Sweat, Interstitial Fluid (ISF), or Wounds
3.2.1. Biomarkers of Metabolic Diseases
3.2.2. Electrolyte Biomarkers
3.2.3. Biomarkers of Skin Wounds
| Type of Sensor | Monitoring | Acquired Parameters | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piezocapacitive sensor | ECG | ECG | [26] |
| Triboelectric sensor | Arterial pulse, ECG | Blood pressure | [28] |
| Mechano-acoustic sensor | Vibration, ECG | Heart murmurs | [29] |
| Resistance-based sensor | Electric resistance | Body temperature | [30] |
| 2D materials-based sensor | Electric resistance | Humidity | [32] |
| Photosensor | Conductivity | UV exposure | [34] |
| Piezoelectric sensor | Deformation of elastomer | Elastic modulus | [35] |
| Electrochemical biosensors | Conductivity | Glucose level | [38,39,40] |
| Electrochemical biosensors | Conductivity | Lactate level | [42,43] |
| Electrochemical biosensors | Conductivity | Cholesterol level | [44] |
| Electrochemical biosensors | Conductivity | Triglycerides level | [44,45] |
| Potentiometric ion sensors | Conductivity | Na+, Cl−, K+ levels | [50,52] |
| Potentiometric ion sensors | Conductivity | NH4+, Ca2+ levels | [51] |
| Electrochemical square wave anodic stripping voltammetry | Conductivity | Heavy metals | [53] |
| Potentiometric ion sensors/ Impedancemetric sensors | Conductivity/ Capacitance | pH value (H+ level) | [56,57] |
| Electrochemical biosensors | Conductivity | Uric acid, lactate Levels | [58,59] |
| Fluorescence sensor | Luminescence | Oxygen level | [60] |
| Electrochemical biosensors | Conductivity | Cytokines/interleukins | [61] |
4. DDSs in Therapeutic Components
4.1. Stimuli-Responsive Carriers in the DDSs
4.1.1. Thermoresponsive Carriers
4.1.2. Light-Responsive Carriers
4.1.3. Electrically Activated Systems
4.1.4. Mechanical Force-Responsive Carriers
4.1.5. Physiological Signal-Responsive Carriers
| Type of DDSs | Triggering Stimuli | Therapeutics | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid microparticles in hydrogel | Heat | Cefazolin and vancomycin | [64] |
| PCM-coated microneedles | Heat | Metformin | [65] |
| PCL microneedles containing LaB6 | NIR light | Doxorubicin | [66] |
| MNP-containing NIPAM-VP beads in hydrogel | Vis light | Dexamethasone | [67] |
| Porous ZnO nanoparticles | UV light | Benzophenono-3 | [68] |
| m-SiO2 nanoparticles | Iontophoresis | Doxorubicin | [69] |
| Porous microneedle | Iontophoresis | Insulin | [70] |
| PLGA nanoparticles in alginate microgel depots | Stretching force | Doxorubicin, ciprofloxacin, and insulin | [13] |
| PLGA microplate | Ultrasound | Curcumin | [72] |
| Chitosan-coated PLGA nanocapsules | Ultrasound | Insulin | [73] |
| Silica nanoparticles coated with silane derivatives | pH | Chlorhexidine | [74] |
| HA Microneedle containing alginiate-coated dextran nanoparticles loaded with glucose oxidase | Glucose & pH | Anti-PD-1 | [77] |
| Microneedle containing HA-NI nanovesicles loaded with glucose oxidase | Glucose & hypoxia | Insulin | [78] |
| HA microneedle containing thrombin-cleavable peptide–heparin conjugates | Thrombin | Heparin | [81] |
4.2. Fully Integrated Smart Wearable Patch Systems
5. Conclusions and Remarks for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Mitragotri, S.; Langer, R. Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roig-Rosello, E.; Rousselle, P. The human epidermal basement membrane: A shaped and cell instructive platform that aging slowly alters. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Langer, R. Transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, M. Corneocyte lipid envelope (CLE), the key structure for skin barrier function and ichthyosis pathogenesis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.T.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Song, J.H.; Jung, M.; Jang, M.H.; Cho, H.J.; Yoon, I.S.; et al. Novel reverse electrodialysis-driven iontophoretic system for topical and transdermal delivery of poorly permeable therapeutic agents. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.U.; Joshi, A.; Dalvi, S.V. Evaluating the efficacy of different curcumin polymorphs in transdermal drug delivery. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Jin, S.G. Microneedle for transdermal drug delivery: Current trends and fabrication. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, S.; Jain, N.; Nagaich, U. Ultra deformable vesicles for boosting transdermal delivery of 2-arylpropionic acid class drug for management of musculoskeletal pain. J. Pharm. Investig. 2022, 52, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Song, C.; Baik, S.; Kim, D.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Device-assisted transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guk, K.; Han, G.; Lim, J.; Jeong, K.; Kang, T.; Lim, E.K.; Jung, J. Evolution of wearable devices with real-time disease monitoring for personalized healthcare. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, Y.; Gao, W. Skin-interfaced sensors in digital medicine: From materials to applications. Matter 2020, 2, 1414–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikkath, J.; Subramony, J.A. Toward closed-loop drug delivery: Integrating wearable technologies with transdermal drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 113997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, J.; Yao, S.; Ye, Y.; Cui, Z.; Yu, J.; Ghosh, T.K.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, Z. Stretch-triggered drug delivery from wearable elastomer films containing therapeutic depots. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9407–9415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Song, C.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, H.R.; Kang, T.; Shin, K.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Wearable/disposable sweat-based glucose monitoring device with multistage transdermal drug delivery module. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 1601314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Qian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Ligler, F.S.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Hypoxia and H2O2 dual-sensitive vesicles for enhanced glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, K.; Honda, W.; Harada, S.; Arie, T.; Akita, S. Toward flexible and wearable human-interactive health-monitoring devices. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Q.; Feng, X.; Kuang, S.; Panwar, N.; Song, P.; Yang, C.; Yang, G.; Hemu, X.; Zhang, G.; Yoon, H.S.; et al. Self-powered, on-demand transdermal drug delivery system driven by triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.; Ahamad, N.; Dewani, M.; Awasthi, L.; Patil, R.; Banerjee, R. Wearable and implantable devices for drug delivery: Applications and challenges. Biomaterials 2022, 283, 121435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodička, S.; Susič, A.P.; Zelko, E. Implementation of a Savvy Mobile ECG Sensor for heart rhythm disorder screening at the primary healthcare level: An observational prospective study. Micromachines 2021, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyen, N.E.; Bapat, R.C.; Tan, B.; Hunt, L.A.; Jay, O.; Mündel, T. Accuracy of algorithm to non-invasively predict core body temperature using the Kenzen wearable device. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Manco, M.; Moyal, D.; Huppert, G.; Araki, H.; Banks, A.; Joshi, H.; McKenzie, R.; Seewald, A.; Griffin, G.; et al. Soft, stretchable, epidermal sensor with integrated electronics and photochemistry for measuring personal UV exposures. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 0190233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappon, G.; Vettoretti, M.; Sparacino, G.; Facchinetti, A. Continuous glucose monitoring sensors for diabetes management: A review of technologies and applications. Diabetes Metab. J. 2019, 43, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Cheng, W.; Li, Y.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y. Advanced electronic skin devices for healthcare applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 173–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bariya, M.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Javey, A. Wearable sweat sensors. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, T.Q.; Lee, N.E. Flexible and stretchable physical sensor integrated platforms for wearable human-activity monitoring and personal healthcare. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4338–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Mathewson, K.E.; Jang, K.I.; Kim, J.; Fu, H.; Huang, X.; Chava, P.; Wang, R.; et al. Soft microfluidic assemblies of sensors, circuits, and radios for the skin. Science 2014, 344, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, H.; Qi, D.; Liu, Z.; Cai, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Mechano-based transductive sensing for wearable healthcare. Small 2018, 14, 1702933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Wu, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, A.C.; Zou, H.; Chen, C.; Hu, D.; Gu, B.; Sun, B.; Wang, Z.L. A stretchable yarn embedded triboelectric nanogenerator as electronic skin for biomechanical energy harvesting and multifunctional pressure sensing. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1804944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Norton, J.J.; Qazi, R.; Zou, Z.; Ammann, K.R.; Liu, H.; Yan, L.; Tran, P.L.; Jang, K.I.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Epidermal mechano-acoustic sensing electronics for cardiovascular diagnostics and human-machine interfaces. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, 1601185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R.C.; Bonifas, A.P.; Behnaz, A.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, K.J.; Cheng, H.; Shi, M.; Bian, Z.; Liu, Z.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Ultrathin conformal devices for precise and continuous thermal characterization of human skin. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, T.Q.; Le, H.S.; Dang, T.M.L.; Ju, S.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, N.E. Freestanding, fiber-based, wearable temperature sensor with tunable thermal index for healthcare monitoring. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevate, R.; Haque, M.A.; Akhtar, F.H.; Villalobos, L.F.; Wu, T.; Peinemann, K.V. Embedding 1D conducting channels into 3D isoporous polymer films for high-performance humidity sensing. Angew. Chem. 2018, 57, 11218–11222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jeon, S.; Seo, H.; Lee, J.T.; Park, S. Fiber-based sensors and energy systems for wearable electronics. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Hong, W.G.; Yang, H.Y.; Ha, D.H.; Jun, Y.; Yun, Y.J. A wearable patch based on flexible porous reduced graphene oxide paper sensor for real-time and continuous ultraviolet radiation monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2100709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdeviren, C.; Shi, Y.; Joe, P.; Ghaffari, R.; Balooch, G.; Usgaonkar, K.; Gur, O.; Tran, P.L.; Crosby, J.R.; Meyer, M.; et al. Conformal piezoelectric systems for clinical and experimental characterization of soft tissue biomechanics. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pharr, M.; Salvatore, G.A. Lab-on-skin: A review of flexible and stretchable electronics for wearable health monitoring. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9614–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Pan, L.; Ma, Z.; Yan, K.; Cheng, W.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. All inkjet-printed amperometric multiplexed biosensors based on nanostructured conductive hydrogel electrodes. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3322–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipani, L.; Dupont, B.G.R.; Doungmene, F.; Marken, F.; Tyrrell, R.M.; Guy, R.H.; Ilie, A. Non-invasive, transdermal, path-selective and specific glucose monitoring via a graphene-based platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Hong, S.Y.; Jeong, Y.R.; Yun, J.; Park, H.; Jin, S.W.; Lee, G.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.S.; et al. Skin-attachable, stretchable electrochemical sweat sensor for glucose and pH detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13729–13740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervisevic, M.; Alba, M.; Yan, L.; Senel, M.; Gengenbach, T.R.; Prieto-Simon, B.; Voelcker, N.H. Transdermal electrochemical monitoring of glucose via high-density silicon microneedle array patch. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2270022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Sharma, S.; Cass, A.E.G.; Antiochia, R. Microneedle-based biosensor for minimally-invasive lactate detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Emaminejad, S.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Challa, S.; Chen, K.; Peck, A.; Fahad, H.M.; Ota, H.; Shiraki, H.; Kiriya, D.; et al. Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis. Nature 2016, 529, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tur-García, E.L.; Davis, F.; Collyer, S.D.; Holmes, J.L.; Barr, H.; Higson, S.P.J. Novel flexible enzyme laminate-based sensor for analysis of lactate in sweat. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantaphol, S.; Chailapakul, O.; Siangproh, W. A novel paper-based device coupled with a silver nanoparticle-modified boron-doped diamond electrode for cholesterol detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 891, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, W.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. A nanostructured conductive hydrogels-based biosensor platform for human metabolite detection. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Cánovas, R.; Jeerapan, I.; Andrade, F.J.; Wang, J. A textile-based stretchable multi-ion potentiometric sensor. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyein, H.Y.; Gao, W.; Shahpar, Z.; Emaminejad, S.; Challa, S.; Chen, K.; Fahad, H.M.; Tai, L.C.; Ota, H.; Davis, R.W.; et al. A wearable electrochemical platform for noninvasive simultaneous monitoring of Ca2+ and pH. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7216–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinovart, T.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Windmiller, J.R.; Andrade, F.J.; Wang, J. A potentiometric tattoo sensor for monitoring ammonium in sweat. Analyst. 2013, 138, 7031–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgal, V.; Mandaan, N.; Mudgal, A.; Singh, R.B.; Mishra, S. Effect of toxic metals on human health. Open Nutraceuticals J. 2010, 3, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Ortiz-Gómez, I.; Cánovas, R.; Salinas-Castillo, A.; Cuartero, M.; Crespo, G.A. Wearable potentiometric ion patch for on-body electrolyte monitoring in sweat: Toward a validation strategy to ensure physiological relevance. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 8644–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, S.T.; Fogarty, D.; Cooke, R.; Casadevall, C.D.; Salleo, A.; Parlak, O. Wearable organic electrochemical transistor patch for multiplexed sensing of calcium and ammonium ions from human perspiration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1901321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emaminejad, S.; Gao, W.; Wu, E.; Davies, Z.A.; Yin Yin Nyein, H.; Challa, S.; Ryan, S.P.; Fahad, H.M.; Chen, K.; Shahpar, Z.; et al. Autonomous Sweat Extraction and Analysis Applied to Cystic Fibrosis and Glucose Monitoring Using a Fully Integrated Wearable Platform. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4625–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Shahpar, Z.; Fahad, H.M.; Chen, K.; Emaminejad, S.; Gao, Y.; Tai, L.C.; Ota, H.; Wu, E.; et al. Wearable microsensor array for multiplexed heavy metal monitoring of body fluids. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusta, A.; Tertiș, M.; Cristea, C.; Mirel, S. Wearable sensors for the detection of biomarkers for wound infection. Biosensors 2021, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannello, F.; Ligi, D.; Canale, M.; Raffetto, J.D. Omics profiles in chronic venous ulcer wound fluid: Innovative applications for translational medicine. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 737–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafalu, P.; Tamayol, A.; Rahimi, R.; Ochoa, M.; Khalilpour, A.; Kiaee, G.; Yazdi, I.K.; Bagherifard, S.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Ziaie, B.; et al. Smart bandage for monitoring and treatment of chronic wounds. Small 2018, 14, 1703509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Sakthivel, B.; Gopalakrishnan, N.; Dahiya, R. Printed flexible electrochemical pH sensors based on CuO nanorods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 263, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifuzzaman, M.; Chhetry, A.; Zahed, M.A.; Yoon, S.H.; Park, C.I.; Zhang, S.; Barman, S.C.; Sharma, S.; Yoon, H.; Park, J.Y. Smart bandage with integrated multifunctional sensors based on MXene-functionalized porous graphene scaffold for chronic wound care management. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, B.K.; Brown, M.S.; Park, Y.; Kuan, S.; Koh, A. Skin-inspired, open mesh electrochemical sensors for lactate and oxygen monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, M.; Rahimi, R.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, H.; Yoon, C.K.; Maddipatla, D.; Narakathu, B.B.; Jain, V.; Oscai, M.M.; Morken, T.J.; et al. Integrated sensing and delivery of oxygen for next-generation smart wound dressings. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Nguyen, D.T.; Yeo, T.; Lim, S.B.; Tan, W.X.; Madden, L.E.; Jin, L.; Long, J.Y.K.; Aloweni, F.A.B.; Liew, Y.J.A.; et al. A flexible multiplexed immunosensor for point-of-care in situ wound monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Sheykhansari, S.; Nelson, B.J.; Sitti, M. Recent advances in wearable transdermal delivery systems. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafalu, P.; Kiaee, G.; Giatsidis, G.; Khalilpour, A.; Nabavinia, M.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Sonkusale, S.; Orgill, D.P.; Tamayol, A.; Khademhosseini, A. A textile dressing for temporal and dosage controlled drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Choi, T.K.; Lee, Y.B.; Cho, H.R.; Ghaffari, R.; Wang, L.; Choi, H.J.; Chung, T.D.; Lu, N.; Hyeon, T.; et al. A graphene-based electrochemical device with thermoresponsive microneedles for diabetes monitoring and therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.C.; Lin, Z.W.; Ling, M.H. Near-infrared light-activatable microneedle system for treating superficial tumors by combination of chemotherapy and photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Seong, K.Y.; Lee, E.; Yang, S.Y.; Yoon, J. Visible light-triggered on-demand drug release from hybrid hydrogels and its application in transdermal patches. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Zhong, L.; Pan, J. UV and dark-triggered repetitive release and encapsulation of benzophenone-3 from biocompatible ZnO nanoparticles potential for skin protection. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5596–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.K.; Parl, O.K.; Choi, C.; Qiao, S.; Ghaffari, R.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, M.; Hyun, W.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Cephalopod-inspired miniaturized suction cups for smart medical skin. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ye, R.; Liu, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, L. Iontophoresis-driven porous microneedle array patch for active transdermal drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2021, 121, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Bomba, H.N.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, Z. Mechanical force-triggered drug delivery. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12536–12563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciurti, E.; Primavera, R.; Di Mascolo, D.; Rizzo, A.; Balena, A.; Padmanabhan, S.K.; Rizzi, F.; Decuzzi, P.; De Vittorio, M. Ultrasound-induced deformation of PLGA-micro Plates for on-command drug release. Microelectron. Eng. 2020, 229, 111360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Yao, S.; Suo, D.; Ye, Y.; Pless, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jing, Y.; Gu, Z. Ultrasound-triggered noninvasive regulation of blood glucose levels using microgels integrated with insulin nanocapsules. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Giovannini, G.; Zhang, S.; Altenried, S.; Zuber, F.; Chen, Q.; Boesel, L.F.; Ren, Q. pH-responsive silica nanoparticles for the treatment of skin wound infections. Acta Biomater. 2022, 145, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Kim, J.O. Recent progress in cancer immunotherapy approaches based on nanoparticle delivery devices. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.T.; Karim, M.E.; Othman, I.; Chowdhury, E.H. Mitigating off-target distribution and enhancing cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells with alpha-ketoglutaric acid-modified Fe/Mg-CA nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Investig. 2022, 52, 367–386. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ye, Y.; Hochu, G.M.; Sadeghifar, H.; Gu, Z. Enhanced cancer immunotherapy by microneedle patch-assisted delivery of anti-PD1 antibody. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Di Santo, R.; Sun, W.; Ranson, D.; Ligler, F.S.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Microneedle-array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8260–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, B.; Massberg, S. Thrombosis as an intravascular effector of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonico, M.E.; Santoro, C.; Avvedimento, M.; Giugliano, G.; Mandoli, G.E.; Prastaro, M.; Franzone, A.; Piccolo, R.; Ilardi, F.; Cameli, M.; et al. Venous thromboembolism and cancer: A comprehensive review from pathophysiology to novel treatment. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Hanne, N.J.; Cui, Z.; Qian, C.; Wang, C.; Xin, H.; Cole, J.H.; Gallippi, C.M.; et al. Thrombin-responsive transcutaneous patch for auto-anticoagulant regulation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Lou, D.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Qiao, B.; Dong, S.; Ma, L.; Gao, C.; Wu, Z. Smart flexible electronics-integrated wound dressing for real-time monitoring and on-demand treatment of infected wounds. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.; Lee, J.; Qiao, S.; Ghaffari, R.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.E.; Song, C.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, D.J.; Jun, S.W.; et al. Multifunctional wearable devices for diagnosis and therapy of movement disorders. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhong, J.; Shi, Z.; Mao, Y.; Tao, T.H. Body-integrated, enzyme-triggered degradable, silk-based mechanical sensors for customized health/fitness monitoring and in situ treatment. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Jiang, P.; Li, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered iontophoretic transdermal drug delivery system driven and regulated by biomechanical motions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, Y.; Atabay, M.; Chowdhury, H.K.; Göktürk, I.; Saylan, Y.; Inci, F. Aptamer-based point-of-care devices: Emerging technologies and integration of computational methods. Biosensors 2023, 13, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Commercial Product Name | Monitoring | Disease | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Savvy patch ECG sensor | Electorcardiogram (ECG) | Heart rhythm disorder | [19] |
| Kenzen wearable device | Heart rate, Body temperature | Heat illness | [20] |
| MY UV Patch | UV exposure | UV-derived diseases (i.e., photoaging) | [21] |
| Freestyle Libre | Glucose | Diabetes | [22] |
| Dexcom G6 |
| Type of Healthcare/Diseases | Monitoring by Sensors | Type of DDSs | Triggering Stimuli | Therapeutics | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | Glucose level | PCM-coated microneedle | Heat | Metformin | [14] |
| Infected wounds | Temperature | PEG acrylate-based hydrogels containing UV-cleavable linker | UV light | Gentamicin | [82] |
| Parkinson’s disease | Muscle strain (tremor) | m-SiO2 nanoparticles | Heat | Anti-Parkinson’s disease agent/Rhodamine B dye | [83] |
| Epilepsy | Mechanical sensor | Silk fibroin hydrogel loaded with papain and gold nanoparticles | Visible light/ heat | Phenobarbital | [84] |
| Ankle injury | Mechanical sensor | Poloxamer hydrogel | Iontophoresis | Pain-relief drugs/ Rhodamine 6G dye | [85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khadka, B.; Lee, B.; Kim, K.-T. Drug Delivery Systems for Personal Healthcare by Smart Wearable Patch System. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060929
Khadka B, Lee B, Kim K-T. Drug Delivery Systems for Personal Healthcare by Smart Wearable Patch System. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(6):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060929
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhadka, Bikram, Byeongmoon Lee, and Ki-Taek Kim. 2023. "Drug Delivery Systems for Personal Healthcare by Smart Wearable Patch System" Biomolecules 13, no. 6: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060929
APA StyleKhadka, B., Lee, B., & Kim, K.-T. (2023). Drug Delivery Systems for Personal Healthcare by Smart Wearable Patch System. Biomolecules, 13(6), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060929






