Deep Intronic LINE-1 Insertions in NF1: Expanding the Spectrum of Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Rearrangements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
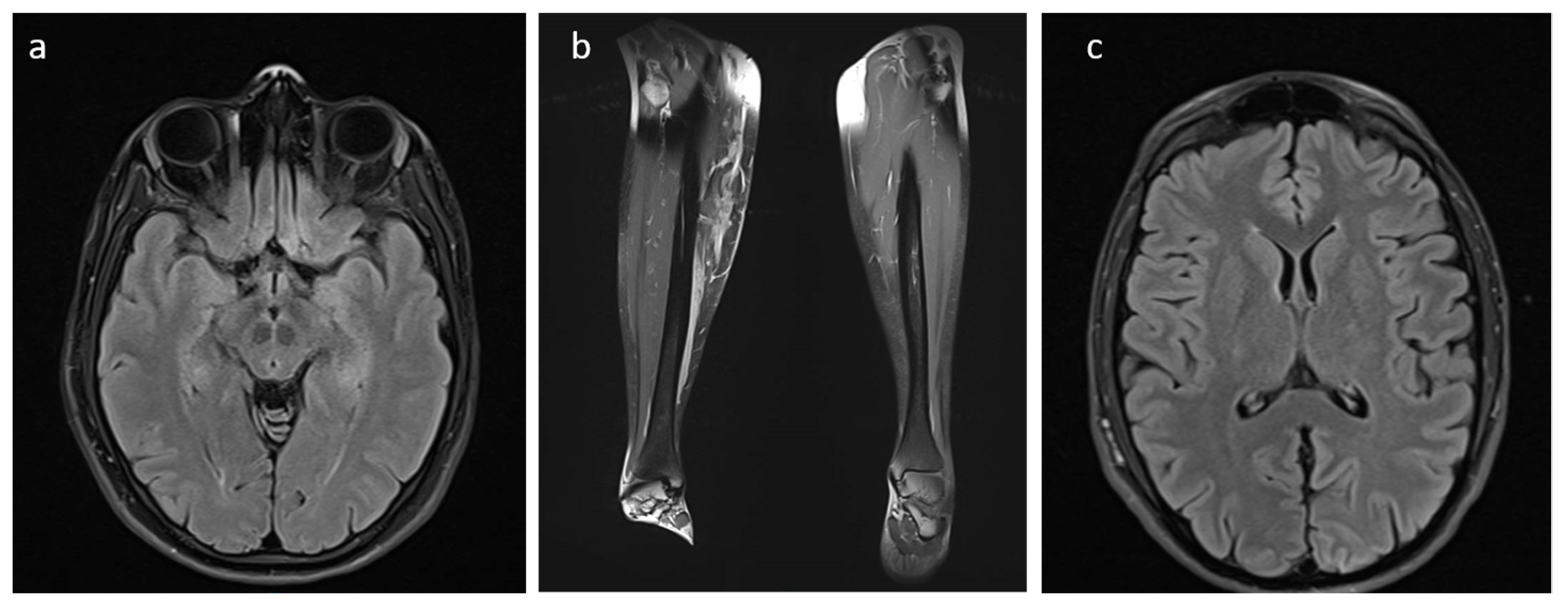
2.1. Clinical Description
2.2. gDNA and cDNA Extraction
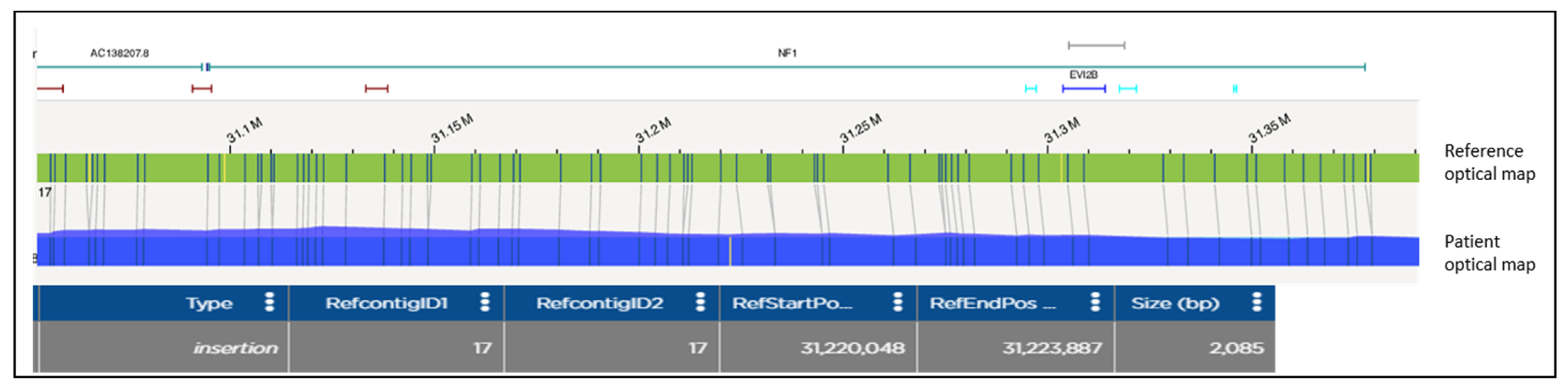
2.3. Optical Genome Mapping (OGM) and Structural Variant Calling
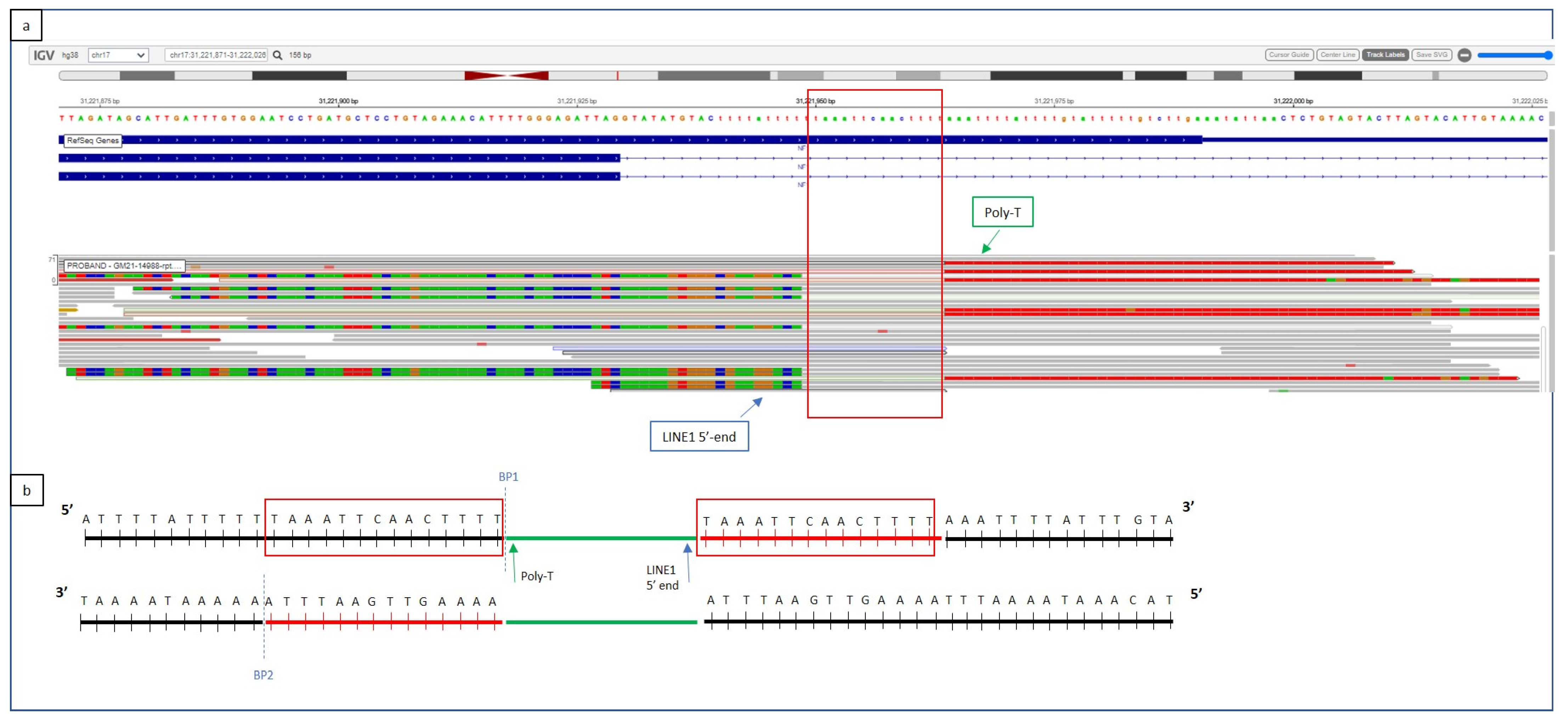
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS)
2.5. Long-Range PCR and Sanger Sequencing
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutmann, D.H.; Ferner, R.E.; Listernick, R.H.; Korf, B.R.; Wolters, P.L.; Johnson, K.J. Neurofibromatosis type 1. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.G.; Bowers, N.; Burkitt-Wright, E.; Miles, E.; Garg, S.; Scott-Kitching, V.; Penman-Splitt, M.; Dobbie, A.; Howard, E.; Ealing, J.; et al. Comprehensive RNA Analysis of the NF1 Gene in Classically Affected NF1 Affected Individuals Meeting NIH Criteria has High Sensitivity and Mutation Negative Testing is Reassuring in Isolated Cases With Pigmentary Features Only. eBioMedicine 2016, 7, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, M.C.; Martín, Y.; Hernández-Imaz, E.; Marina Hernández, A.; Meleán, G.; Valero, A.M.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, F.J.; Tellería, D.; Hernández-Chico, C. A highly sensitive genetic protocol to detect NF1 mutations. J. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 13, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legius, E.; Messiaen, L.; Wolkenstein, P.; Pancza, P.; Avery, R.A.; Berman, Y.; Blakeley, J.; Babovic-Vuksanovic, D.; Cunha, K.S.; Ferner, R.; et al. Revised diagnostic criteria for neurofibromatosis type 1 and Legius syndrome: An international consensus recommendation. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesi, V.; Lepri, F.R.; Dentici, M.L.; Genovese, S.; Sallicandro, E.; Bejo, K.; Dallapiccola, B.; Capolino, R.; Novelli, A.; Digilio, M.C. Intragenic inversions in NF1 gene as pathogenic mechanism in neurofibromatosis type 1. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 30, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douben, H.C.W.; Nellist, M.; van Unen, L.; Elfferich, P.; Kasteleijn, E.; Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; Louwen, J.; van Veghel-Plandsoen, M.; de Valk, W.; Saris, J.J.; et al. High-yield identification of pathogenic NF1 variants by skin fibroblast transcriptome screening after apparently normal diagnostic DNA testing. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 2130–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmer, K.; Callens, T.; Wernstedt, A.; Messiaen, L. The NF1 gene contains hotspots for L1 endonuclease-dependent de novo insertion. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koster, R.; Brandão, R.D.; Tserpelis, D.; van Roozendaal, C.E.P.; van Oosterhoud, C.N.; Claes, K.B.M.; Paulussen, A.D.C.; Sinnema, M.; Vreeburg, M.; van der Schoot, V.; et al. Pathogenic neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) RNA splicing resolved by targeted RNAseq. NPJ Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurahashi, H.; Shaikh, T.; Takata, M.; Toda, T.; Emanuel, B.S. The constitutional t (17;22): Another translocation mediated by palindromic AT-rich repeats. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 72, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, K.H. Our Conflict with Transposable Elements and Its Implications for Human Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancks, D.C.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr. Roles for retrotransposon insertions in human disease. Mob. DNA 2016, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chénais, B. Transposable Elements and Human Diseases: Mechanisms and Implication in the Response to Environmental Pollutants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Moran, J.V.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr.; Boeke, J.D. Human L1 retrotransposon encodes a conserved endonuclease required for retrotransposition. Cell 1996, 87, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazazian, H.H., Jr. Mobile elements: Drivers of genome evolution. Science 2004, 303, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.S.; Szak, S.T.; Boeke, J.D. Transcriptional disruption by the L1 retrotransposon and implications for mammalian transcriptomes. Nature 2004, 429, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perepelitsa-Belancio, V.; Deininger, P. RNA truncation by premature polyadenylation attenuates human mobile element activity. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leier, A.; Moore, M.; Liu, H.; Daniel, M.; Hyde, A.M.; Messiaen, L.; Korf, B.R.; Selvakumaran, J.; Ciszewski, L.; Lambert, L.; et al. Targeted exon skipping of NF1 exon 17 as a therapeutic for neurofibromatosis type I. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 28, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ars, E.; Kruyer, H.; Morell, M.; Pros, E.; Serra, E.; Ravella, A.; Estivill, X.; Lázaro, C. Recurrent mutations in the NF1 gene are common among neurofibromatosis type 1 patients. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Yang, X.; Hu, X.; Li, S. Fifty-four novel mutations in the NF1 gene and integrated analyses of the mutations that modulate splicing. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alesi, V.; Genovese, S.; Lepri, F.R.; Catino, G.; Loddo, S.; Orlando, V.; Di Tommaso, S.; Morgia, A.; Martucci, L.; Di Donato, M.; et al. Deep Intronic LINE-1 Insertions in NF1: Expanding the Spectrum of Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Rearrangements. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13050725
Alesi V, Genovese S, Lepri FR, Catino G, Loddo S, Orlando V, Di Tommaso S, Morgia A, Martucci L, Di Donato M, et al. Deep Intronic LINE-1 Insertions in NF1: Expanding the Spectrum of Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Rearrangements. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(5):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13050725
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlesi, Viola, Silvia Genovese, Francesca Romana Lepri, Giorgia Catino, Sara Loddo, Valeria Orlando, Silvia Di Tommaso, Alessandra Morgia, Licia Martucci, Maddalena Di Donato, and et al. 2023. "Deep Intronic LINE-1 Insertions in NF1: Expanding the Spectrum of Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Rearrangements" Biomolecules 13, no. 5: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13050725
APA StyleAlesi, V., Genovese, S., Lepri, F. R., Catino, G., Loddo, S., Orlando, V., Di Tommaso, S., Morgia, A., Martucci, L., Di Donato, M., Digilio, M. C., Dallapiccola, B., Novelli, A., & Capolino, R. (2023). Deep Intronic LINE-1 Insertions in NF1: Expanding the Spectrum of Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Rearrangements. Biomolecules, 13(5), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13050725





