Transcriptome-Guided Identification of Drugs for Repurposing to Treat Age-Related Hearing Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Dissection of Cochlear Substructures and Isolation of RNA
2.3. RNA Sequencing
2.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) and Functional Enrichment Analyses
2.5. Drug Identification
2.6. Curated Gene Lists
3. Results
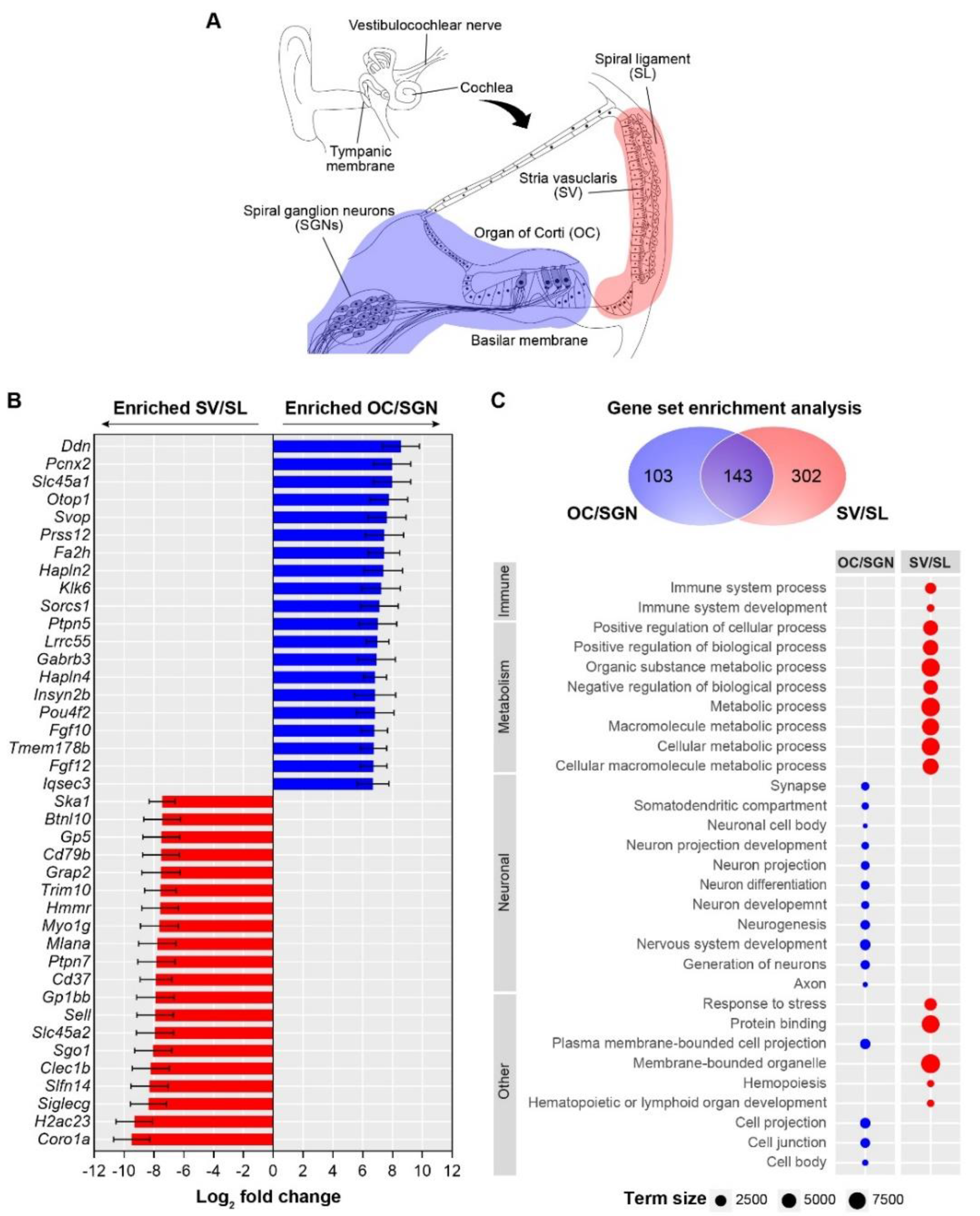
3.1. Cochlear Substructures Show Distinct Gene Enrichment
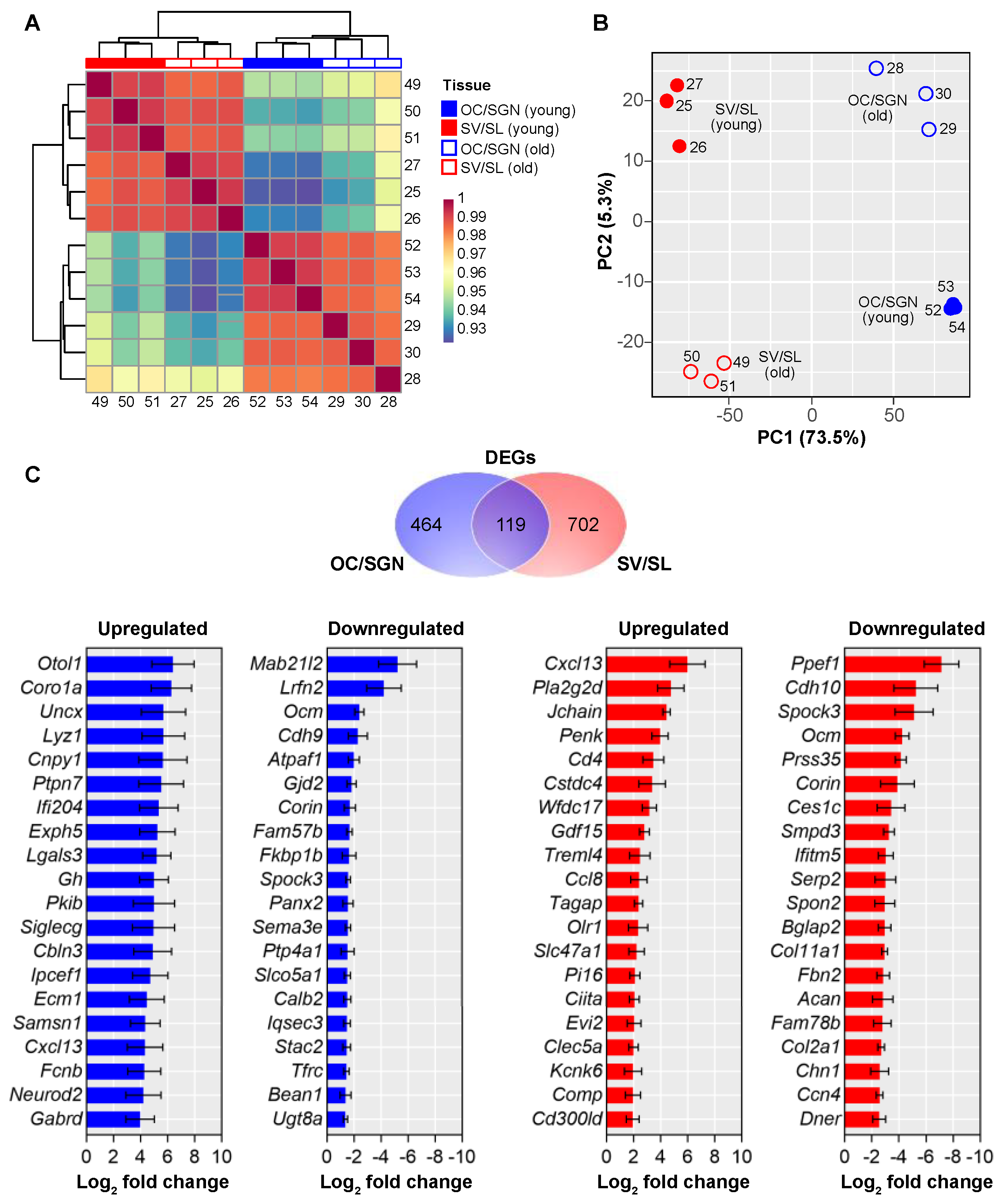
3.2. Cochlear Substructures Show Distinct Age-Related Changes in Gene Expression
3.3. Cochlear Substructures Show Distinct Changes in the Expression of Genes Associated with Ageing, Senescence, and Deafness as Well as Gene Enrichment with Ageing
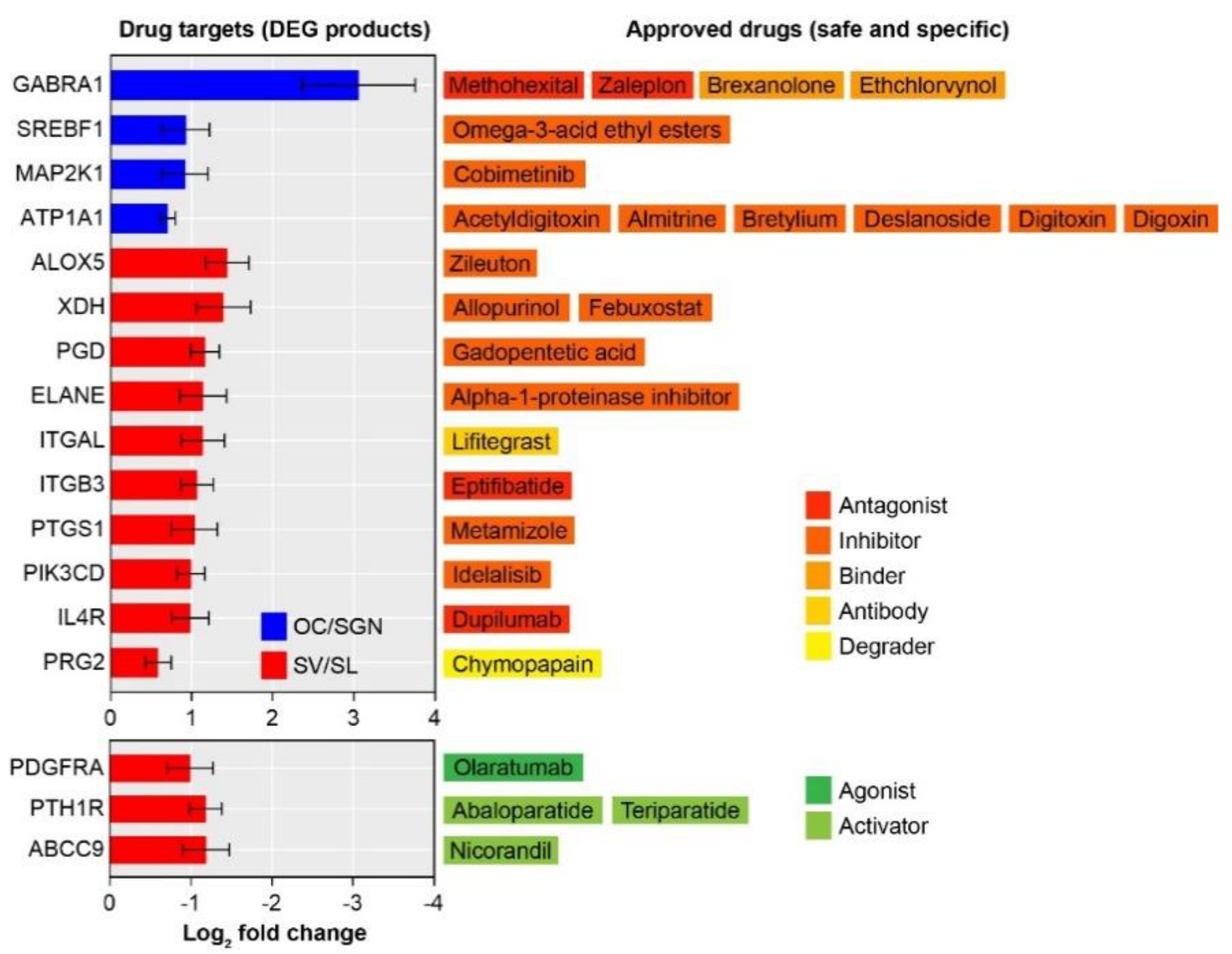
3.4. Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies Substructure-Enriched and Depleted Targets Suitable for Drug Repurposing
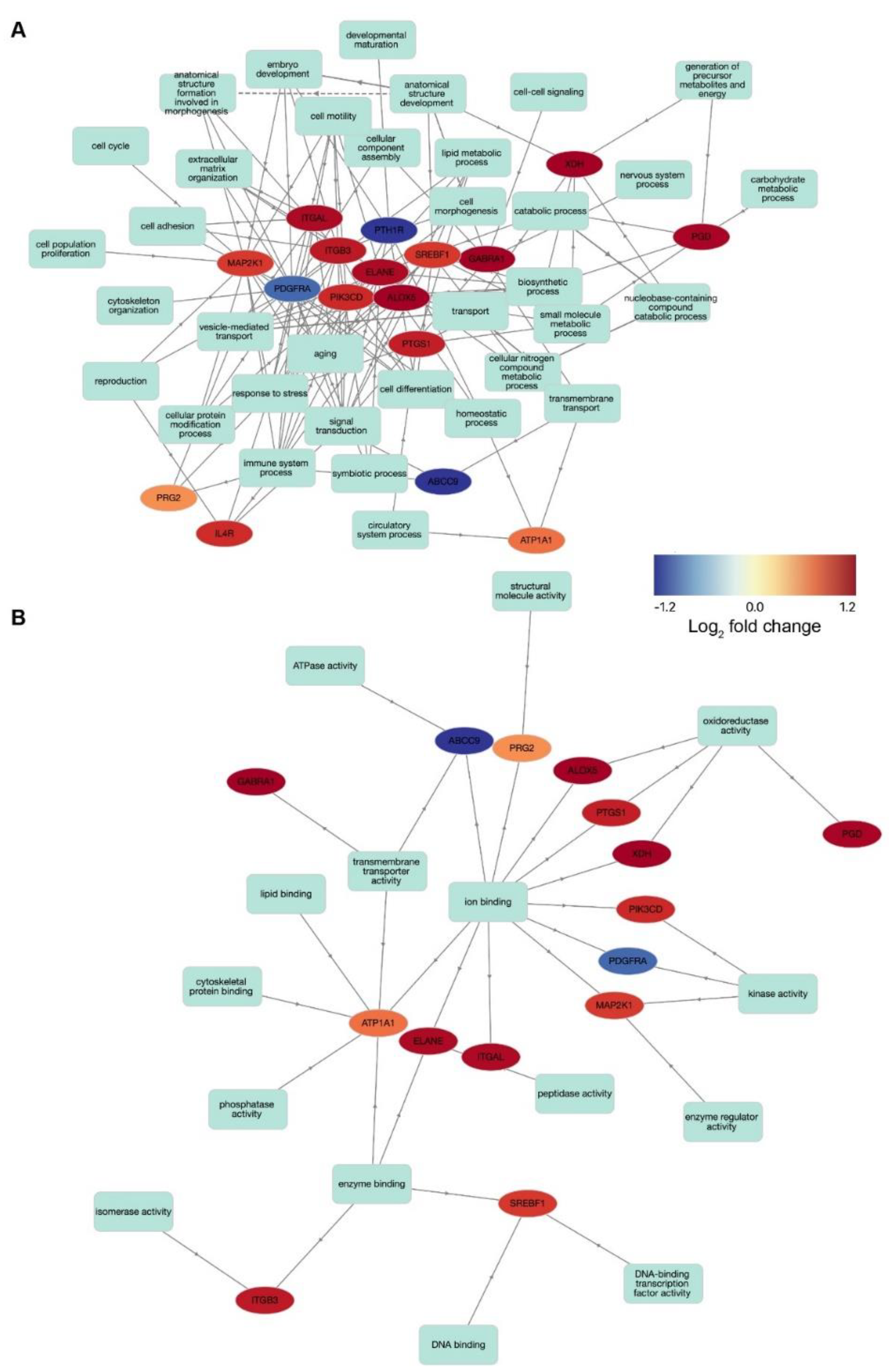
3.5. Potential Drug Targets Link Several Biological Pathways and Functional Mechanisms
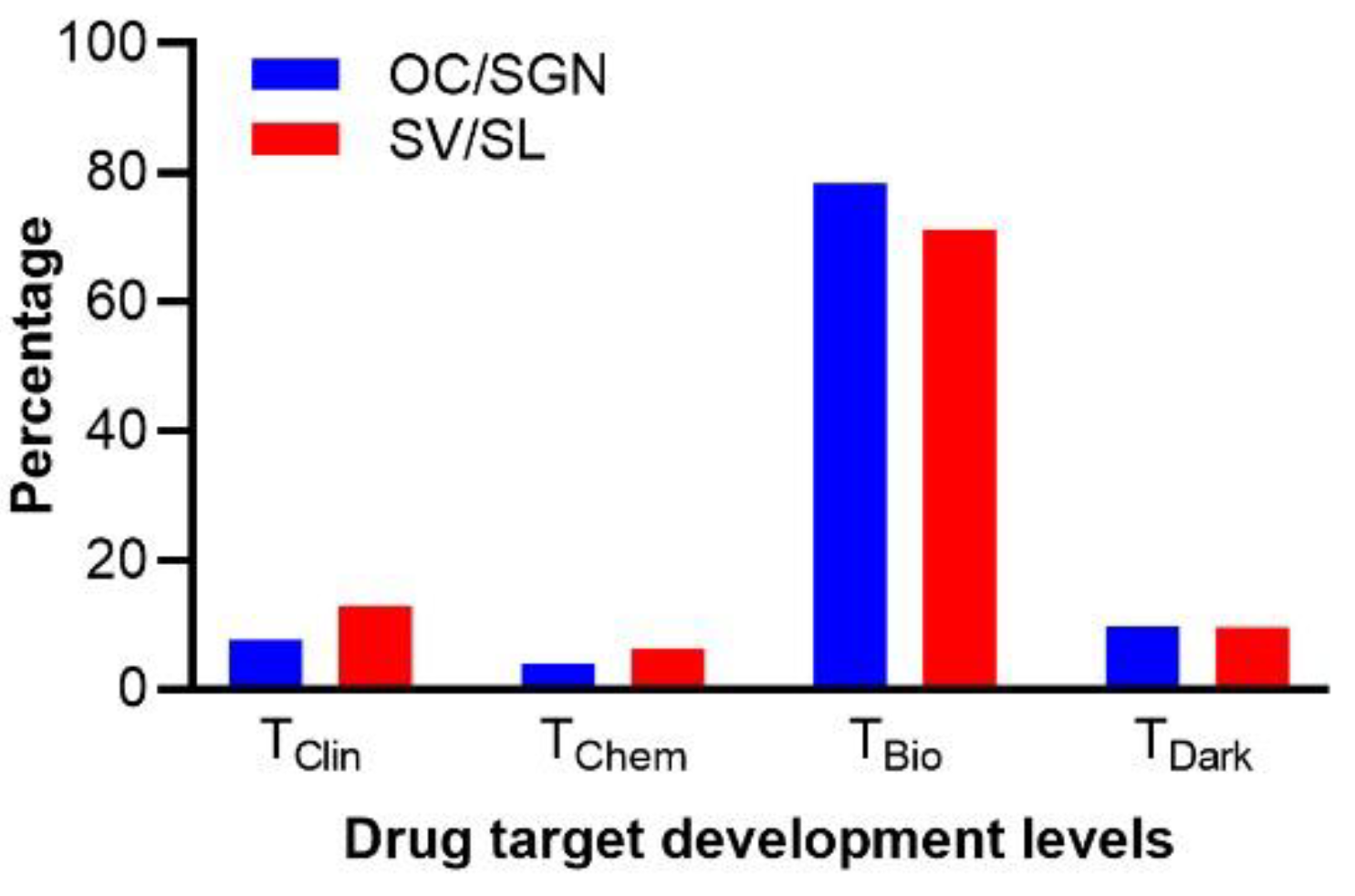
3.6. Characterization of the Druggable Genetic Landscape for Treatment of Age-Related Loss of Cochlear Function
4. Discussion
4.1. Overview
4.2. Drugs Poised for Repurposing to Treat Age-Related Loss of Cochlear Function
4.3. Limitations of This Study
4.4. Outlook and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vos, T.; Allen, C.; Arora, M.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brown, A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 310 Diseases and Injuries, 1990–2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1545–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, L.M.; Kamenov, K.; Briant, P.S.; Orji, A.U.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Abdoli, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Afshin, A.; Ahmed, H.; et al. Hearing Loss Prevalence and Years Lived with Disability, 1990–2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2021, 397, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Z.; Yan, D. Ageing and Hearing Loss. J. Pathol. 2007, 211, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, D.S.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Klein, B.E.K.; Klein, R.; Wiley, T.L.; Nondahl, D.M. The Impact of Hearing Loss on Quality of Life in Older Adults. Gerontologist 2003, 43, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P.R.; Feeny, D.; Tomlinson, G.; Cushing, S.; Chen, J.M.; Krahn, M.D. Health-Related Quality of Life Changes Associated With Hearing Loss. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughrey, D.G.; Kelly, M.E.; Kelley, G.A.; Brennan, S.; Lawlor, B.A. Association of Age-Related Hearing Loss With Cognitive Function, Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, U.; Barr-Gillespie, P.G. New Treatment Options for Hearing Loss. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 346–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.A.; Kitterick, P.T.; Chong, L.Y.; Edmondson-Jones, M.; Barker, F.; Hoare, D.J. Hearing Aids for Mild to Moderate Hearing Loss in Adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 9, CD012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourévitch, B.; Edeline, J.-M.; Occelli, F.; Eggermont, J.J. Is the Din Really Harmless? Long-Term Effects of Non-Traumatic Noise on the Adult Auditory System. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-Z.; O’Malley, J.T.; de Gruttola, V.; Liberman, M.C. Age-Related Hearing Loss Is Dominated by Damage to Inner Ear Sensory Cells, Not the Cellular Battery That Powers Them. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 6357–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-Z.; O’Malley, J.T.; de Gruttola, V.; Liberman, M.C. Primary Neural Degeneration in Noise-Exposed Human Cochleas: Correlations with Outer Hair Cell Loss and Word-Discrimination Scores. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 4439–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Nomoto, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Kuwahata, N.; Ogawa, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Ito, J.; Omori, K. Age-Dependent Degeneration of the Stria Vascularis in Human Cochleae. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paplou, V.; Schubert, N.M.A.; Pyott, S.J. Age-Related Changes in the Cochlea and Vestibule: Shared Patterns and Processes. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, H.R.R.; Freidin, M.B.; Zainul Abidin, F.N.; Payton, A.; Dawes, P.; Munro, K.J.; Morton, C.C.; Moore, D.R.; Dawson, S.J.; Williams, F.M.K. GWAS Identifies 44 Independent Associated Genomic Loci for Self-Reported Adult Hearing Difficulty in UK Biobank. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisina, R.D.; Budzevich, M.; Zhu, X.; Martinez, G.V.; Walton, J.P.; Borkholder, D.A. Animal Model Studies Yield Translational Solutions for Cochlear Drug Delivery. Hear. Res. 2018, 368, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowson, M.G.; Hertzano, R.; Tucci, D.L. Emerging Therapies for Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, J.; Johnston, E.; Walker, D.; Jones, M.; Ionescu, C.M.; Wagle, S.R.; Kovacevic, B.; Brown, D.; Mikov, M.; Mooranian, A.; et al. A Review on Recent Advancement on Age-Related Hearing Loss: The Applications of Nanotechnology, Drug Pharmacology, and Biotechnology. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug Repurposing: Progress, Challenges and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburn, T.T.; Thor, K.B. Drug Repositioning: Identifying and Developing New Uses for Existing Drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.R.; Tian, C.; Gagnon, L.H.; Jiang, H.; Ding, D.; Salvi, R. Effects of Cdh23 Single Nucleotide Substitutions on Age-Related Hearing Loss in C57BL/6 and 129S1/Sv Mice and Comparisons with Congenic Strains. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, J.R.; Allen, P.D.; O’Neill, W.E. Age-Related Hearing Loss in C57BL/6J Mice Has Both Frequency-Specific and Non-Frequency-Specific Components That Produce a Hyperacusis-Like Exaggeration of the Acoustic Startle Reflex. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2007, 8, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowl, M.R.; Dawson, S.J. Age-Related Hearing Loss. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a033217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reijntjes, D.O.J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.; Schubert, N.M.A.; van Tuinen, M.; Vijayakumar, S.; Jones, T.A.; Jones, S.M.; Gratton, M.A.; Xia, X.-M.; et al. Sodium-Activated Potassium Channels Shape Peripheral Auditory Function and Activity of the Primary Auditory Neurons in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munnamalai, V.; Sienknecht, U.J.; Duncan, R.K.; Scott, M.K.; Thawani, A.; Fantetti, K.N.; Atallah, N.M.; Biesemeier, D.J.; Song, K.H.; Luethy, K.; et al. Wnt9a Can Influence Cell Fates and Neural Connectivity across the Radial Axis of the Developing Cochlea. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 8975–8988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Use R! Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24275-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps, Version 1.0.12. 2015. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. G:Profiler: A Web Server for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Conversions of Gene Lists (2019 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheils, T.K.; Mathias, S.L.; Kelleher, K.J.; Siramshetty, V.B.; Nguyen, D.-T.; Bologa, C.G.; Jensen, L.J.; Vidović, D.; Koleti, A.; Schürer, S.C.; et al. TCRD and Pharos 2021: Mining the Human Proteome for Disease Biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1334–D1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A Major Update to the DrugBank Database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Ezzat, A.; Zhu, H.; Mendelsohn, E. Dbparser: “DrugBank” Database XML Parser, Version 1.2.0. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/dbparser/index.html (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Pomaznoy, M.; Ha, B.; Peters, B. GOnet: A Tool for Interactive Gene Ontology Analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacutu, R.; Thornton, D.; Johnson, E.; Budovsky, A.; Barardo, D.; Craig, T.; Diana, E.; Lehmann, G.; Toren, D.; Wang, J.; et al. Human Ageing Genomic Resources: New and Updated Databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1083–D1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Camp, G.; Smith, R. Hereditary Hearing Loss. Available online: https://hereditaryhearingloss.org (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- Ohlemiller, K.K.; Jones, S.M.; Johnson, K.R. Application of Mouse Models to Research in Hearing and Balance. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2016, 17, 493–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, R.; Hartmann, C.H.; Rodriguez, K.A.; Denny, A.D.; Busuttil, R.A.; Dollé, M.E.T.; Calder, R.B.; Chisholm, G.B.; Pollock, B.H.; Klein, C.A.; et al. Increased Cell-to-Cell Variation in Gene Expression in Ageing Mouse Heart. Nature 2006, 441, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Jimenez, C.P.; Eling, N.; Chen, H.-C.; Vallejos, C.A.; Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Connor, F.; Stojic, L.; Rayner, T.F.; Stubbington, M.J.T.; Teichmann, S.A.; et al. Aging Increases Cell-to-Cell Transcriptional Variability upon Immune Stimulation. Science 2017, 355, 1433–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, E.; Herbomel, P.; Kawakami, A.; Takeda, H.; Nagasawa, H. Otolith Matrix Proteins OMP-1 and Otolin-1 Are Necessary for Normal Otolith Growth and Their Correct Anchoring onto the Sensory Maculae. Mech. Dev. 2005, 122, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.R.; Chia, C.; Wu, L.; Kujawa, S.G.; Liberman, M.C.; Goodrich, L.V. Sensory Neuron Diversity in the Inner Ear Is Shaped by Activity. Cell 2018, 174, 1229–1246.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Babola, T.; Pregernig, G.; So, K.S.; Nguyen, M.; Su, S.-S.M.; Palermo, A.T.; Bergles, D.E.; Burns, J.C.; Müller, U. Hair Cell Mechanotransduction Regulates Spontaneous Activity and Spiral Ganglion Subtype Specification in the Auditory System. Cell 2018, 174, 1247–1263.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Xiong, H.; Liu, Y.; Pang, J.; Lin, H.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y. Transcriptomic Analysis Highlights Cochlear Inflammation Associated with Age-Related Hearing Loss in C57BL/6 Mice Using next Generation Sequencing. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramulu, P.; Kennedy, M.; Xiong, W.H.; Williams, J.; Cowan, M.; Blesh, D.; Yau, K.W.; Hurley, J.B.; Nathans, J. Normal Light Response, Photoreceptor Integrity, and Rhodopsin Dephosphorylation in Mice Lacking Both Protein Phosphatases with EF Hands (PPEF-1 and PPEF-2). Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 8605–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Puel, J.-L. Presbycusis: An Update on Cochlear Mechanisms and Therapies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.A.; Nolan, L.S.; Cadge, B.A.; Matthews, L.J.; Schulte, B.A.; Dubno, J.R.; Steel, K.P.; Dawson, S.J. Whole Exome Sequencing in Adult-Onset Hearing Loss Reveals a High Load of Predicted Pathogenic Variants in Known Deafness-Associated Genes and Identifies New Candidate Genes. BMC Med. Genom. 2018, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, S.; Tai, F.W.J.; Delmaghani, S.; Lelli, A.; Singh-Estivalet, A.; Dupont, T.; Niasme-Grare, M.; Michel, V.; Wolff, N.; Bahloul, A.; et al. Ultrarare Heterozygous Pathogenic Variants of Genes Causing Dominant Forms of Early-Onset Deafness Underlie Severe Presbycusis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 31278–31289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprea, T.I.; Bologa, C.G.; Brunak, S.; Campbell, A.; Gan, G.N.; Gaulton, A.; Gomez, S.M.; Guha, R.; Hersey, A.; Holmes, J.; et al. Unexplored Therapeutic Opportunities in the Human Genome. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilder, A.G.M.; Su, M.P.; Blackshaw, H.; Lustig, L.; Staecker, H.; Lenarz, T.; Safieddine, S.; Gomes-Santos, C.S.; Holme, R.; Warnecke, A. Hearing Protection, Restoration, and Regeneration: An Overview of Emerging Therapeutics for Inner Ear and Central Hearing Disorders. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuth, O.; McLean, W.J.; Eatock, R.A.; Pyott, S.J. Distribution of Na,K-ATPase α Subunits in Rat Vestibular Sensory Epithelia. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2014, 15, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Langhans, S.A. Transcriptional Regulators of Na,K-ATPase Subunits. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatou, S.; Yamada, M.; Mochizuki, H.; Shiraishi, A.; Joko, T.; Nishida, T. The Effects of Dexamethasone on the Na,K-ATPase Activity and Pump Function of Corneal Endothelial Cells. Curr. Eye Res. 2009, 34, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.A.; Kuijpers, W.; Curfs, J.H. Occurrence of NaK-ATPase Isoforms during Rat Inner Ear Development and Functional Implications. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2001, 258, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, B.A.; Schmiedt, R.A. Lateral Wall Na, K-ATPase and Endocochlear Potentials Decline with Age in Quiet-Reared Gerbils. Hear. Res. 1992, 61, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Liu, H.; Qi, W.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, H.; Gross, K.; Salvi, R. Ototoxic Effects and Mechanisms of Loop Diuretics. J. Otol. 2016, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijntjes, D.; Pyott, S.J. The Afferent Signaling Complex: Regulation of Type I Spiral Ganglion Neuron Responses in the Auditory Periphery. Hear. Res. 2016, 336, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, N.; Ding, B.; Zhu, X.; Frisina, R.D. Chronic Inflammation—Inflammaging—in the Ageing Cochlea: A Novel Target for Future Presbycusis Therapy. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X. Physiopathology of the Cochlear Microcirculation. Hear. Res. 2011, 282, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-S.S.; Kang, S.-J.J.; Seo, M.-K.K.; Jou, I.; Woo, H.G.; Park, S.M. Role of Cysteinyl Leukotriene Signaling in a Mouse Model of Noise-Induced Cochlear Injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9911–9916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Patel, M.; Coling, D.; Hu, B.H. Transcriptional Changes in Adhesion-Related Genes Are Site-Specific during Noise-Induced Cochlear Pathogenesis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ballesteros, F.; Tassies, D.; Reverter, J.C.; Alobid, I.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M. Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Classic Cardiovascular and New Genetic Risk Factors. Audiol. Neurootol. 2012, 17, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tralau, T.; Meyer-Hoffert, U.; Schröder, J.-M.; Wiedow, O. Human Leukocyte Elastase and Cathepsin G Are Specific Inhibitors of C5a-Dependent Neutrophil Enzyme Release and Chemotaxis. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.; Wood, M.B.; Feng, H.; Schabla, N.M.; Tu, S.; Zuo, J. The Immune Response after Noise Damage in the Cochlea Is Characterized by a Heterogeneous Mix of Adaptive and Innate Immune Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Duan, X.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S.; Dai, P.; Zheng, H. A Novel PIK3CD C896T Mutation Detected in Bilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Using next Generation Sequencing: An Indication of Primary Immunodeficiency. J. Otol. 2016, 11, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Sugiura, S.; Sone, M.; Ueda, H.; Nakashima, T. Progress and Prospects in Human Genetic Research into Age-Related Hearing Impairment. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 390601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmersson, J.; Arnlöv, J.; Axelsson, T.; Basu, S. A Polymorphism in the Cyclooxygenase 1 Gene Is Associated with Decreased Inflammatory Prostaglandin F2alpha Formation and Lower Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2009, 80, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranzhofer, R.; Ruef, J. Aspirin Resistance in Coronary Artery Disease Is Correlated to Elevated Markers for Oxidative Stress but Not to the Expression of Cyclooxygenase (COX) 1/2, a Novel COX-1 Polymorphism or the PlA(1/2) Polymorphism. Platelets 2006, 17, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Talaska, A.E.; Schacht, J.; Sha, S.-H. Oxidative Imbalance in the Aging Inner Ear. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.A.; Cleveland, J.D. Gout and Hearing Impairment in the Elderly: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using the US Medicare Claims Data. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e022854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, E.D.; Gu, R.; Pierce, C.; Kil, J. Reduction of Acute Cisplatin Ototoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rats by Oral Administration of Allopurinol and Ebselen. Hear. Res. 2005, 201, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzé, A.; Sequino, L.; Saulino, C.; Attanasio, G.; Marciano, E. Effect over Time of Allopurinol on Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Guinea Pigs. Int. J. Audiol. 2003, 42, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullarky, E.; Cantley, L.C. Diverting glycolysis to combat oxidative stress. In Innovative Medicine: Basic Research and Development; Nakao, K., Minato, N., Uemoto, S., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; ISBN 978-4-431-55650-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bermúdez-Muñoz, J.M.; Celaya, A.M.; Hijazo-Pechero, S.; Wang, J.; Serrano, M.; Varela-Nieto, I. G6PD Overexpression Protects from Oxidative Stress and Age-Related Hearing Loss. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkemik, E.; Budak, H.; Ciftci, M. Effects of Some Drugs on Human Erythrocyte 6-Phosphogluconate Dehydrogenase: An in Vitro Study. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010, 25, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, J.D.; Landau, E.M.; Iyengar, R. Signaling Networks: The Origins of Cellular Multitasking. Cell 2000, 103, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-I.; Park, K.S.; Seo, S.-H.; Park, H.W. Osteoporosis and Hearing Loss: Findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2011. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 86, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milon, B.; Shulman, E.D.; So, K.S.; Cederroth, C.R.; Lipford, E.L.; Sperber, M.; Sellon, J.B.; Sarlus, H.; Pregernig, G.; Shuster, B.; et al. A Cell-Type-Specific Atlas of the Inner Ear Transcriptional Response to Acoustic Trauma. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghibiglou, C.; Martin, H.G.S.; Lai, T.W.; Cho, T.; Prasad, S.; Kojic, L.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.; Lo, E.; Zhang, S.; et al. Role of NMDA Receptor-Dependent Activation of SREBP1 in Excitotoxic and Ischemic Neuronal Injuries. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, D.I.; Shen, J.; Corey, D.P.; Chen, Z.-Y. Gene Expression by Mouse Inner Ear Hair Cells during Development. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 6366–6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, D.; Huang, C.; Nichols, C.G. Genetic Discovery of ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels in Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e007322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeland, M.F.; McClenaghan, C.; Roessler, H.I.; Savelberg, S.; Hansen, G.Å.M.; Hjellnes, H.; Arntzen, K.A.; Müller, K.I.; Dybesland, A.R.; Harter, T.; et al. ABCC9-Related Intellectual Disability Myopathy Syndrome Is a KATP Channelopathy with Loss-of-Function Mutations in ABCC9. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachajoa, H.; López-Quintero, W.; Vanegas, S.; Montoya, C.L.; Ramírez-Montaño, D. Novel Mutation in ABBC9 Gene Associated with Congenital Hypertrichosis and Acromegaloid Facial Features, without Cardiac or Skeletal Anomalies: A New Phenotype. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2018, 11, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noben-Trauth, K.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Johnson, K.R. Association of Cadherin 23 with Polygenic Inheritance and Genetic Modification of Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwanhäusser, B.; Busse, D.; Li, N.; Dittmar, G.; Schuchhardt, J.; Wolf, J.; Chen, W.; Selbach, M. Global Quantification of Mammalian Gene Expression Control. Nature 2011, 473, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanseau, P.; Agarwal, P.; Barnes, M.R.; Pastinen, T.; Richards, J.B.; Cardon, L.R.; Mooser, V. Use of Genome-Wide Association Studies for Drug Repositioning. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.C.; Ryan, A.F. Mechanisms of Sensorineural Cell Damage, Death and Survival in the Cochlea. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.H.; Schrepfer, T.; Schacht, J. Age-Related Hearing Impairment and the Triad of Acquired Hearing Loss. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orvis, J.; Gottfried, B.; Kancherla, J.; Adkins, R.S.; Song, Y.; Dror, A.A.; Olley, D.; Rose, K.; Chrysostomou, E.; Kelly, M.C.; et al. GEAR: Gene Expression Analysis Resource Portal for Community-Driven, Multi-Omic Data Exploration. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 843–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schubert, N.M.A.; van Tuinen, M.; Pyott, S.J. Transcriptome-Guided Identification of Drugs for Repurposing to Treat Age-Related Hearing Loss. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040498
Schubert NMA, van Tuinen M, Pyott SJ. Transcriptome-Guided Identification of Drugs for Repurposing to Treat Age-Related Hearing Loss. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(4):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040498
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchubert, Nick M. A., Marcel van Tuinen, and Sonja J. Pyott. 2022. "Transcriptome-Guided Identification of Drugs for Repurposing to Treat Age-Related Hearing Loss" Biomolecules 12, no. 4: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040498
APA StyleSchubert, N. M. A., van Tuinen, M., & Pyott, S. J. (2022). Transcriptome-Guided Identification of Drugs for Repurposing to Treat Age-Related Hearing Loss. Biomolecules, 12(4), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040498







