Inner Ear Pharmacotherapy for Residual Hearing Preservation in Cochlear Implant Surgery: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy & Study Selection
2.2. Outcome Measures
2.3. Quality Assessment
3. Results
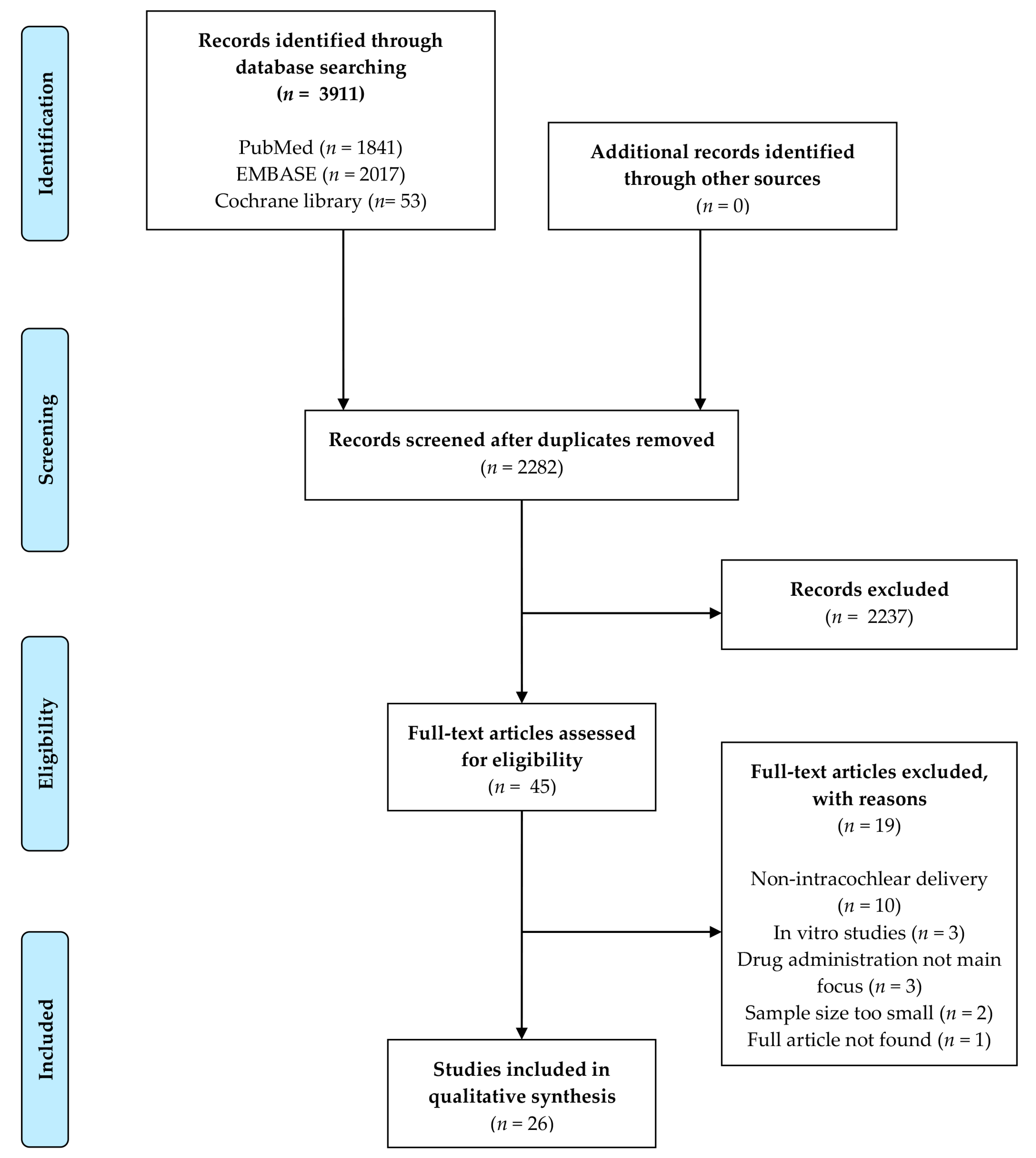
3.1. Systematic Search
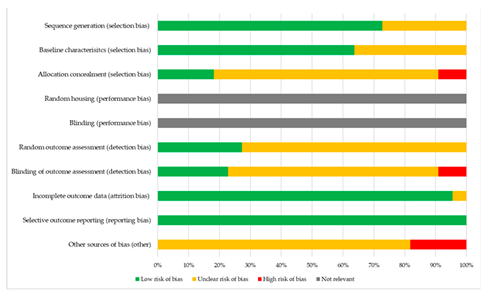
3.2. Quality Assessment
3.3. Pharmaceutical Interventions
3.3.1. Glucocorticoids
Intracochlear Injection
Intracochlear Microcatheter
Drug-Eluting Electrode
3.3.2. Non-Glucocorticoids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Von Ilberg, C.A.; Baumann, U.; Kiefer, J.; Tillein, J.; Adunka, O.F. Electric-Acoustic Stimulation of the Auditory System: A Review of the First Decade. Audiol. Neurotol. 2011, 16 (Suppl. 2), 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghi, A.A.; Polak, M.; He, J.; Telischi, F.F.; Balkany, T.J.; Van De Water, T.R. Pattern of Hearing Loss in a Rat Model of Cochlear Implantation Trauma. Otol. Neurotol. 2005, 26, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, S.; Monksfield, P.; Kel, G.; Connolly, T.; Souter, M.; Chang, A.; Marovic, P.; O’Leary, J.; Richardson, R.; Eastwood, H. Relations between cochlear histopathology and hearing loss in experimental cochlear implantation. Hear. Res. 2013, 298, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantz, B.J.; Turner, C.; Gfeller, K.E.; Lowder, M.W. Preservation of Hearing in Cochlear Implant Surgery: Advantages of Combined Electrical and Acoustical Speech Processing. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salt, A.N.; Hirose, K. Communication pathways to and from the inner ear and their contributions to drug delivery. Hear. Res. 2018, 362, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, P.A.; Begg, E.J.; Zhang, M.; Keast, A.T.; Murray, D.P.; Balkany, T.J. Intratympanic Versus Intravenous Delivery of Methylprednisolone to Cochlear Perilymph. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plontke, S.K.; Biegner, T.; Kammerer, B.; Delabar, U.; Salt, A. Dexamethasone Concentration Gradients Along Scala Tympani After Application to the Round Window Membrane. Otol. Neurotol. 2008, 29, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plontke, S.K.; Salt, A.N. Simulation of Application Strategies for Local Drug Delivery to the Inner Ear. ORL 2006, 68, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, B.; Chiang, H.; Valentini, C.; Yu, M.; Kysar, J.W.; Lalwani, A.K. Inner ear delivery: Challenges and opportunities. Laryngoscope 2019, 5, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, H.; Salt, A.; Biegner, T.; Kammerer, B.; Delabar, U.; Hartsock, J.J.; Plontke, S.K. Dexamethasone Levels and Base-to-Apex Concentration Gradients in the Scala Tympani Perilymph after Intracochlear Delivery in the Guinea Pig. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, C.; Venkatagiri, P.K.; Lo, J.; Eastwood, H.T.; Bester, C.W.; Briggs, R.J.S.; O’Leary, S.J. Glucocorticoid for Hearing Preservation After Cochlear Implantation: A Systemic Review and Meta-analysis of Animal Studies. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; de Vries, R.B.M.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, S.H.; Black, N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1998, 52, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Q.; Tykocinski, M.; Stathopoulos, D.; Cowan, R. Effects of steroids and lubricants on electrical impedance and tissue response following cochlear implantation. Cochlea Implant. Int. 2007, 8, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, S.; Ye, Q.; Radeloff, A.; Kiefer, J.; Gstoettner, W.; Tillein, J. Protection of Inner Ear Function after Cochlear Implantation: Compound Action Potential Measurements after Local Application of Glucocorticoids in the Guinea Pig Cochlea. ORL 2011, 73, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, A.-R.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, D.-S.; Shin, S.-A.; Park, Y.-H. Effects of dexamethasone on intracochlear inflammation and residual hearing after cochleostomy: A comparison of administration routes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paasche, G.; Bockel, F.; Tasche, C.; Lesinski-Schiedat, A.; Lenarz, T. Changes of Postoperative Impedances in Cochlear Implant Patients: The Short-Term Effects of Modified Electrode Surfaces and Intracochlear Corticosteroids. Otol. Neurotol. 2006, 27, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paasche, G.; Tasche, C.; Stöver, T.; Lesinski-Schiedat, A.; Lenarz, T. The Long-Term Effects of Modified Electrode Surfaces and Intracochlear Corticosteroids on Postoperative Impedances in Cochlear Implant Patients. Otol. Neurotol. 2009, 30, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenzler, N.K.; Salcher, R.; Timm, M.; Gaertner, L.; Lenarz, T.; Warnecke, A. Intracochlear administration of steroids with a catheter during human cochlear implantation: A safety and feasibility study. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, A.A.; Adil, E.; He, J.; Graves, R.; Balkany, T.J.; Van De Water, T.R. Local Dexamethasone Therapy Conserves Hearing in an Animal Model of Electrode Insertion Trauma-Induced Hearing Loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivero, R.J.; Joseph, D.E.; Angeli, S.; He, J.; Chen, S.; Eshraghi, A.A.; Balkany, T.J.; Van De Water, T.R. Dexamethasone Base Conserves Hearing from Electrode Trauma-Induced Hearing Loss. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 2028–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheper, V.; Hessler, R.; Hütten, M.; Wilk, M.; Jolly, C.; Lenarz, T.; Paasche, G. Local inner ear application of dexamethasone in cochlear implant models is safe for auditory neurons and increases the neuroprotective effect of chronic electrical stimulation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, M.; Jalessi, M.; Salehian, P.; Farahmandghavi, F.; Emamjomeh, H.; Mirzadeh, H.; Imani, M.; Jolly, C. Dexamethasone eluting cochlear implant: Histological study in animal model. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2013, 14, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jolly, C.; Braun, S.; Janssen, T.; Scherer, E.; Steinhoff, J.; Ebenhoch, H.; Lohner, A.; Stark, T.; Kiefer, J. Effects of a dexamethasone-releasing implant on cochleae: A functional, morphological and pharmacokinetic study. Hear. Res. 2015, 327, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douchement, D.; Terranti, A.; Lamblin, J.; Salleron, J.; Siepmann, F.; Siepmann, J.; Vincent, C. Dexamethasone eluting electrodes for cochlear implantation: Effect on residual hearing. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2014, 16, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, E.; Bohorquez, J.; Goncalves, S.; Perez, E.; Dinh, C.T.; Garnham, C.; Hessler, R.; Eshraghi, A.A.; Van De Water, T.R. Electrode array-eluted dexamethasone protects against electrode insertion trauma induced hearing and hair cell losses, damage to neural elements, increases in impedance and fibrosis: A dose response study. Hear. Res. 2016, 337, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astolfi, L.; Simoni, E.; Giarbini, N.; Giordano, P.; Pannella, M.; Hatzopoulos, S.; Martini, A. Cochlear implant and inflammation reaction: Safety study of a new steroid-eluting electrode. Hear. Res. 2016, 336, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, N.; Gausterer, J.C.; Honeder, C.; Mötz, M.; Schöpper, H.; Zhu, C.; Saidov, N.; Gabor, F.; Arnoldner, C. Long-term effects and potential limits of intratympanic dexamethasone-loaded hydrogels combined with dexamethasone-eluting cochlear electrodes in a low-insertion trauma Guinea pig model. Hear. Res. 2019, 384, 107825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stathopoulos, D.; Chambers, S.; Enke, Y.L.; Timbol, G.; Risi, F.; Miller, C.; Cowan, R.; Newbold, C. Development of a safe dexamethasone-eluting electrode array for cochlear implantation. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2014, 15, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilk, M.; Hessler, R.; Mugridge, K.; Jolly, C.; Fehr, M.; Lenarz, T.; Scheper, V. Impedance Changes and Fibrous Tissue Growth after Cochlear Implantation Are Correlated and Can Be Reduced Using a Dexamethasone Eluting Electrode. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, S.; Newbold, C.; Stathopoulos, D.; Needham, K.; Miller, C.; Risi, F.; Enke, Y.L.; Timbol, G.; Cowan, R. Protecting against electrode insertion trauma using dexamethasone. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2018, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, K.; Stathopoulos, D.; Newbold, C.; Leavens, J.; Risi, F.; Manouchehri, S.; Durmo, I.; Cowan, R. Electrode impedance changes after implantation of a dexamethasone-eluting intracochlear array. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2019, 21, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, R.; O’Leary, S.; Birman, C.; Plant, K.; English, R.; Dawson, P.; Risi, F.; Gavrilis, J.; Needham, K.; Cowan, R. Comparison of electrode impedance measures between a dexamethasone-eluting and standard Cochlear™ Contour Advance® electrode in adult cochlear implant recipients. Hear. Res. 2020, 390, 107924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, A.A.; He, J.; Mou, C.H.; Polak, M.; Zine, A.; Bonny, C.; Balkany, T.J.; Van De Water, T.R. D-JNKI-1 Treatment Prevents the Progression of Hearing Loss in a Model of Cochlear Implantation Trauma. Otol. Neurotol. 2006, 27, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihler, F.; Pelz, S.; Coors, M.; Matthias, C.; Canis, M. Application of a TNF-alpha-inhibitor into the scala tympany after cochlear electrode insertion trauma in guinea pigs: Preliminary audiologic results. Int. J. Audiol. 2014, 53, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikkawa, Y.S.; Nakagawa, T.; Ying, L.; Tabata, Y.; Tsubouchi, H.; Ido, A.; Ito, J. Growth factor-eluting cochlear implant electrode: Impact on residual auditory function, insertional trauma, and fibrosis. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheper, V.; Hoffmann, A.; Gepp, M.M.; Schulz, A.; Hamm, A.; Pannier, C.; Hubka, P.; Lenarz, T.; Schwieger, J. Stem Cell Based Drug Delivery for Protection of Auditory Neurons in a Guinea Pig Model of Cochlear Implantation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bas, E.; Anwar, M.R.; Goncalves, S.; Dinh, C.T.; Bracho, O.R.; Chiossone, J.A.; Van De Water, T.R. Laminin-coated electrodes improve cochlear implant function and post-insertion neuronal survival. Neuroscience 2019, 410, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, J.K.-L.; Lo, J.; Chambers, S.A.; Hampson, A.J.; Eastwood, H.T.; O’Leary, S.J. Intracochlear tPA infusion may reduce fibrosis caused by cochlear implantation surgery. Acta Oto-Laryngologica 2019, 139, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, A.N.; Hartsock, J.J.; Hou, J.; Piu, F. Comparison of the Pharmacokinetic Properties of Triamcinolone and Dexamethasone for Local Therapy of the Inner Ear. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leake, P.A.; Hradek, G.T.; Snyder, R.L. Chronic electrical stimulation by a cochlear implant promotes survival of spiral ganglion neurons after neonatal deafness. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 412, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenzlin, S.; Vincent, C.; Munzke, L.; Gnansia, D.; Siepmann, J. Predictability of drug release from cochlear implants. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.P.; O’Leary, S.J.; Shepherd, R.K.; Robins-Browne, R.M.; Clark, G.M. Pneumococcal meningitis post-cochlear implantation: Potential routes of infection and pathophysiology. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2010, 143, S15–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | Subjects | Intracochlear Delivery | Drug | Control | Total Ears | Follow-Up Duration | Primary Endpoint (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huang, 2007 | Guinea pigs, Cats | Injection | DEX, TRIAM | Multiple groups | n = 47 | 5 m | Impedance, histology |
| Braun, 2011 | Guinea pigs | Injection | DEX, TRIAM | No injection; AP injection | n = 30 | 90 d | CAP, histology |
| Lyu, 2018 | Guinea pigs | Injection | DEX | No injection | n = 180 | 60 d | ABR, histology |
| Paasche, 2006 | Humans | Injection | TRIAM | No injection | n = 13 | 35 d | Impedance |
| Paasche, 2009 | Humans | Injection | TRIAM | No injection | n = 15 | ≥3 y | Impedance |
| Prenzler, 2018 | Humans | Injection | TRIAM | No injection | n = 10 | 90 d | Impedance |
| Eshraghi, 2007 | Guinea pigs | Osmotic pump | DEX | AP-pump | n = 28 | 30 d | ABR |
| Vivero, 2008 | Guinea pigs | Osmotic pump | DEX | No pump; AP pump | n = 88 | 30 d | ABR, HC counting |
| Scheper, 2017 | Guinea pigs | Multiple methods | DEX | Multiple groups | n = 24 | 27 d | ABR, SGN survival |
| Farhadi, 2013 | Guinea pigs | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = 30 | 13 d | Histology |
| Liu, 2015 | Guinea pigs | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = 35 | 6 m | ABR, OAE, histology |
| Douchement, 2015 | Gerbils | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = 48 | 1 y | ABR |
| Bas, 2016 | Guinea pigs | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = ? | 90 d | ABR, impedance, histology |
| Astolfi, 2016 | Guinea pigs | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = 32 | 14 d | CAP, histology |
| Ahmadi, 2019 | Guinea pigs | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = 20 | 4 m | ABR, impedance, histology |
| Stathopoulos, 2014 | Guinea pigs | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = 66 | 90 d | ABR, histology |
| Wilk, 2016 | Guinea pigs | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = 33 | 91 d | ABR, impedance, histology |
| Chambers, 2019 | Guinea pigs | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = 24 | 28 d | ABR, histology |
| Needham, 2020 | Guinea pigs | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = 50 | 40 d | Impedance, histology |
| Briggs, 2020 | Humans | Drug-eluting electrode | DEX | Non-eluting electrode | n = 24 | 2 y | Impedance |
| Eshraghi, 2006 | Guinea pigs | Osmotic pump | D-JNKI-1 | Multiple groups | n = 37 | 7 d | ABR, OAE, HC counting |
| Ihler, 2014 | Guinea pigs | Osmotic pump | Etanercept | No pump; AP pump | n = 15 | 28 d | ABR |
| Kikkawa, 2014 | Guinea pigs | Drug-eluting electrode | IGF1, HGF or IGF1 + HGF | Multiple groups | n = 25 | 28 d | ABR, histology |
| Scheper, 2019 | Guinea pigs | Multiple methods | MSCs | Multiple groups | n = 30 | 28 d | ABR, impedance, histology |
| Bas, 2019 | Rats | Drug-eluting electrode | Laminin | Non-eluting electrode | n = 20 | 28 d | ABR, impedance, histology |
| Choong, 2019 | Guinea pigs | Injection | tPA | Saline | n = 21 | 14 d | ABR, histology |
| Study | Sequence Generation (Selection Bias) | Baseline Characterisitcs (Selection Bias) | Allocation Concealment (Selection Bias) | Random Housing (Performance Bias) | Blinding (Performance Bias) | Random Outcome Assessment (Detection Bias) | Blinding of Outcome Assessment (Detection Bias) | Incomplete Outcome Data (Attition Bias) | Selective Outcome Reporting (Reporting Bias) | Other Sources of Bias (Other) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eshraghi, 2006 | + | + | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | ? |
| Huang, 2007 | + | ? | - | NR | NR | ? | - | + | + | ? |
| Eshragi, 2007 | + | ? | ? | NR | NR | + | ? | + | + | ? |
| Vivero, 2008 | + | ? | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | - |
| Braun, 2011 | ? | ? | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | ? |
| Farhadi, 2013 | + | + | ? | NR | NR | + | ? | + | + | ? |
| Stathopoulos, 2014 | ? | ? | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | ? |
| Kikkawa, 2014 | ? | + | ? | NR | NR | ? | + | + | + | ? |
| Ihler, 2014 | + | + | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | ? |
| Douchement, 2015 | + | + | + | NR | NR | ? | ? | ? | + | ? |
| Liu, 2015 | ? | ? | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | ? |
| Wilk, 2016 | + | + | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | ? |
| Bas, 2016 | + | + | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | - |
| Astolfi, 2016 | + | + | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | ? |
| Scheper, 2017 | + | + | + | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | ? |
| Lyu, 2018 | ? | ? | ? | NR | NR | + | + | + | + | - |
| Chambers, 2019 | + | + | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | ? |
| Scheper, 2019 | + | + | + | NR | NR | + | + | + | + | ? |
| Choong, 2019 | + | + | + | NR | NR | + | + | + | + | ? |
| Bas, 2019 | ? | ? | ? | NR | NR | ? | ? | + | + | ? |
| Ahmadi, 2019 | + | + | ? | NR | NR | + | + | + | + | - |
| Needham, 2020 | + | + | - | NR | NR | ? | - | + | + | ? |
| Study | Reporting | External Validity | Internal Validity—Bias | Internal Validity—Confounding | Power | Total | Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paasche, 2006 | 9 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 18 (64%) | Fair |
| Paasche, 2009 | 9 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 18 (64%) | Fair |
| Prenzler, 2018 | 8 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 18 (64%) | Fair |
| Briggs, 2020 | 9 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 19 (68%) | Fair |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parys, Q.-A.; Van Bulck, P.; Loos, E.; Verhaert, N. Inner Ear Pharmacotherapy for Residual Hearing Preservation in Cochlear Implant Surgery: A Systematic Review. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040529
Parys Q-A, Van Bulck P, Loos E, Verhaert N. Inner Ear Pharmacotherapy for Residual Hearing Preservation in Cochlear Implant Surgery: A Systematic Review. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(4):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040529
Chicago/Turabian StyleParys, Quentin-Alexandre, Pauline Van Bulck, Elke Loos, and Nicolas Verhaert. 2022. "Inner Ear Pharmacotherapy for Residual Hearing Preservation in Cochlear Implant Surgery: A Systematic Review" Biomolecules 12, no. 4: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040529
APA StyleParys, Q.-A., Van Bulck, P., Loos, E., & Verhaert, N. (2022). Inner Ear Pharmacotherapy for Residual Hearing Preservation in Cochlear Implant Surgery: A Systematic Review. Biomolecules, 12(4), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040529






