The Effect of Novel Selenopolysaccharide Isolated from Lentinula edodes Mycelium on Human T Lymphocytes Activation, Proliferation, and Cytokines Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biosynthesis and Isolation of Se-Le-30
2.2. PBMCs Isolation
2.3. Preparation for Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.4. Proliferation Assay
2.5. Activation Assay
2.6. Multiplex Cytokine Profiling
2.7. Cell Viability Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
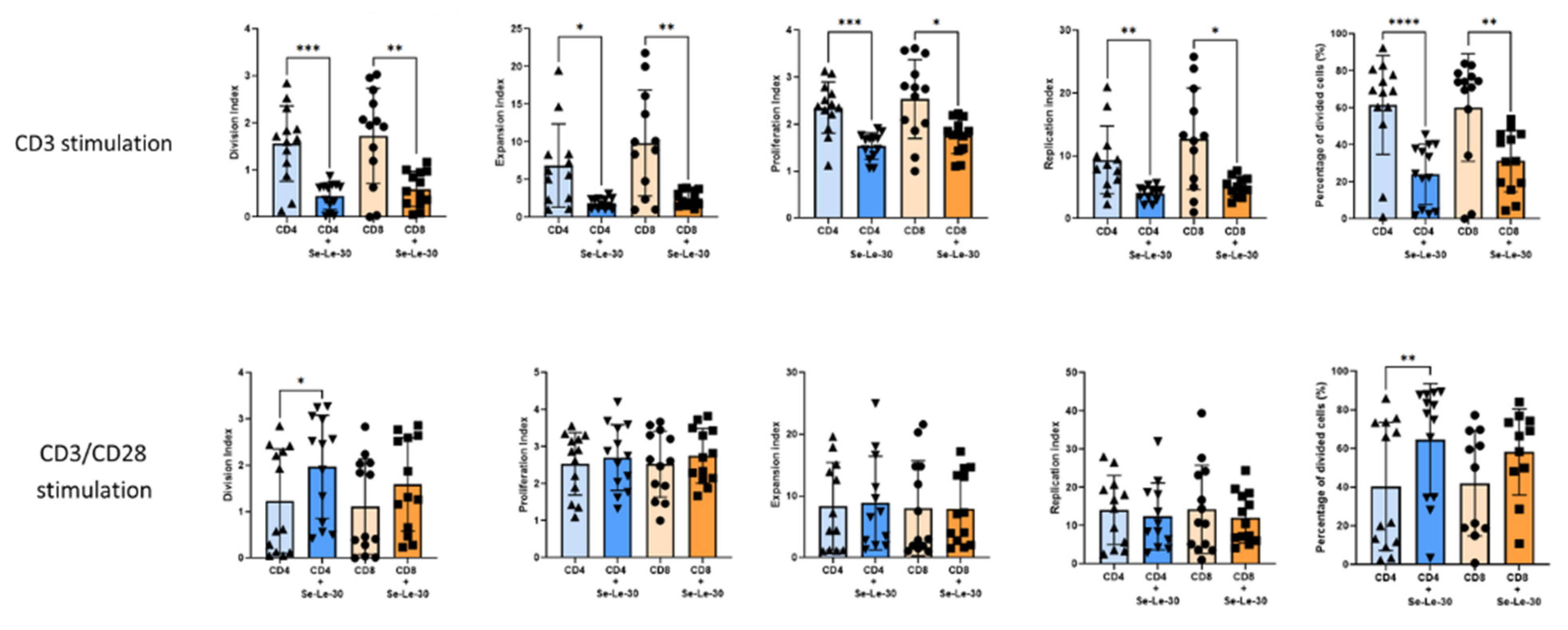
3.1. Effects of Se-Le-30 on Human CD4+ and CD8 + T Cells Proliferation
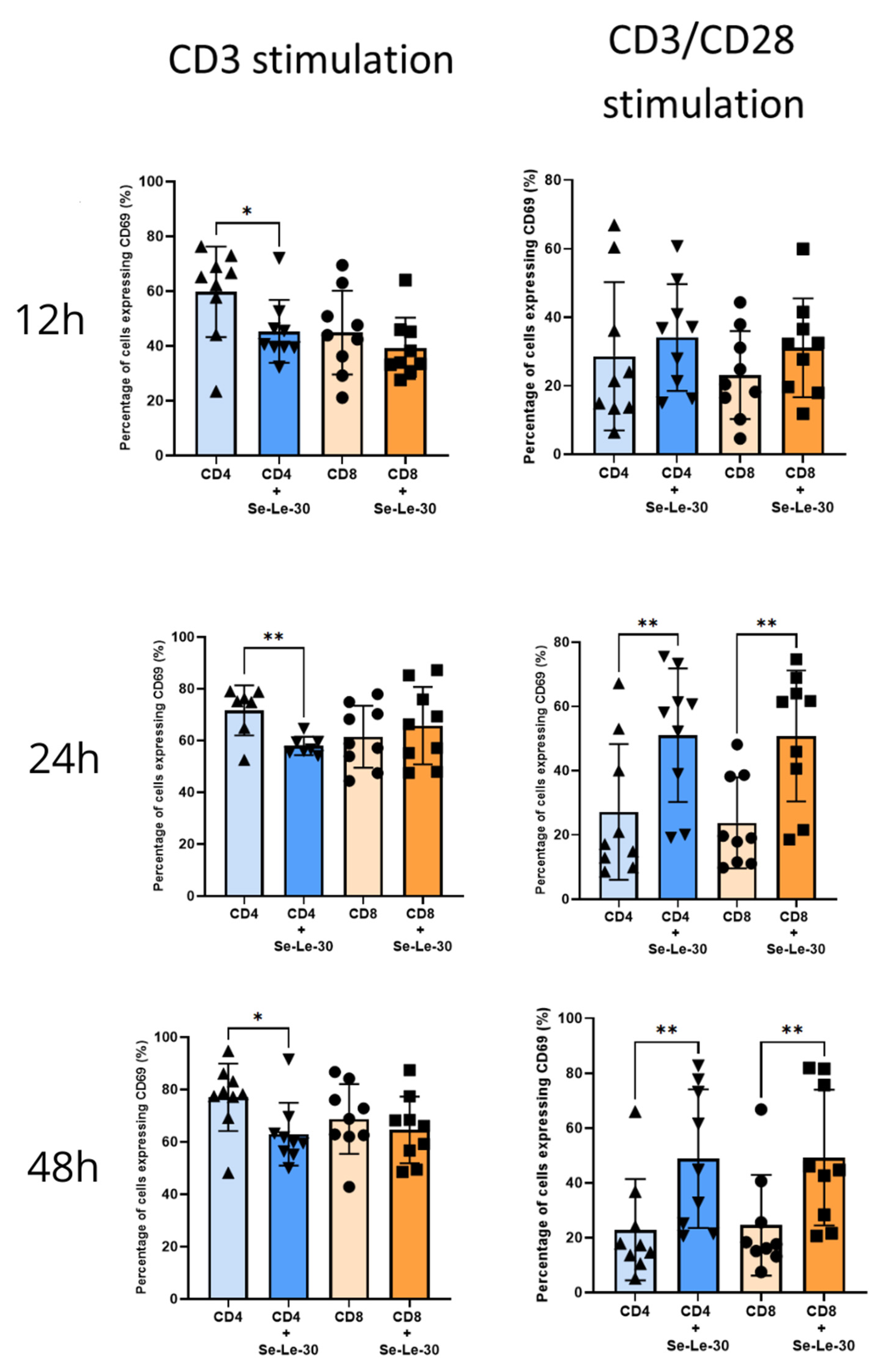
3.2. Effects of Se-Le-30 on Human CD4+ and CD8 + T Cells Activation
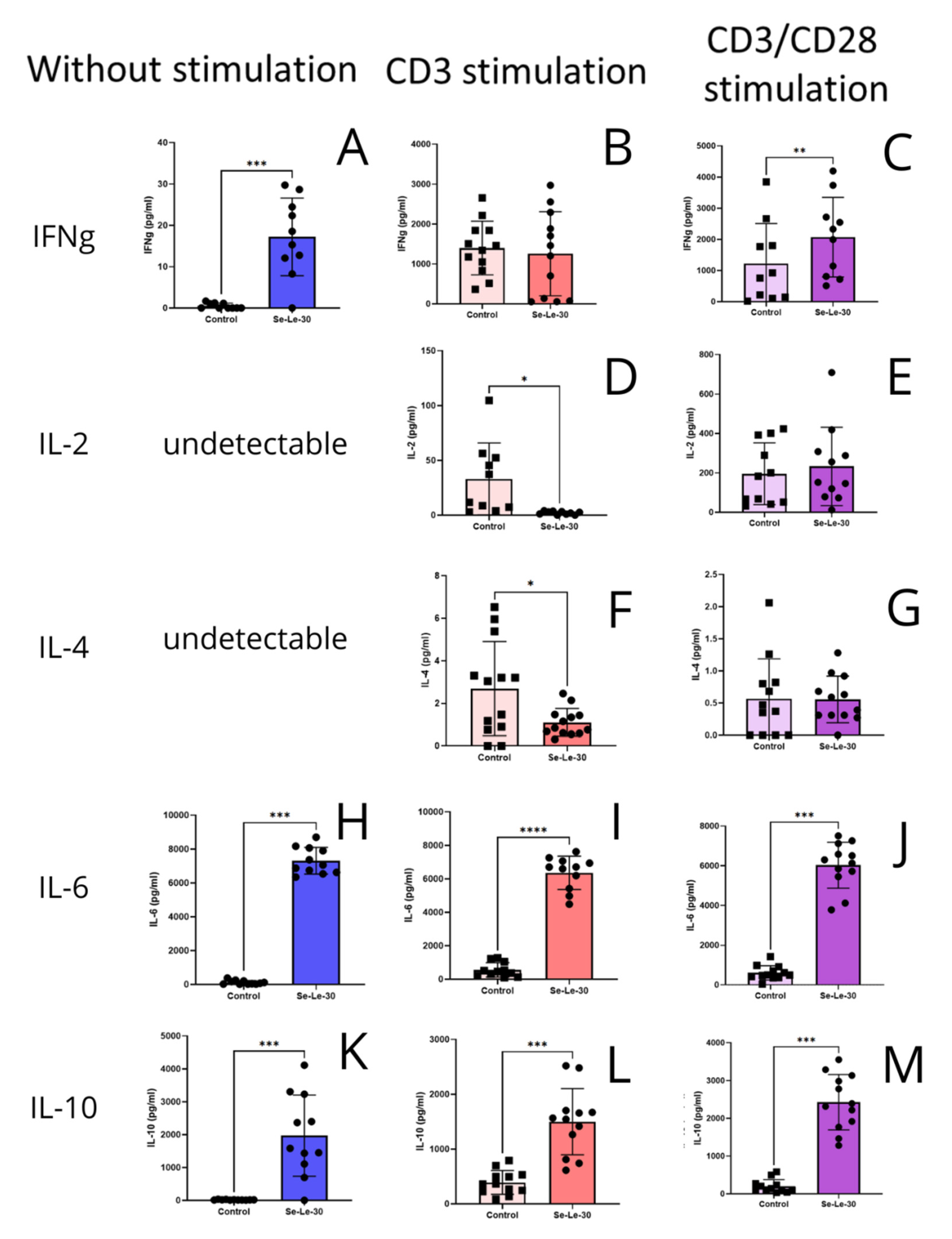
3.3. Effects of Se-Le-30 on Cytokines Production by PBMCs
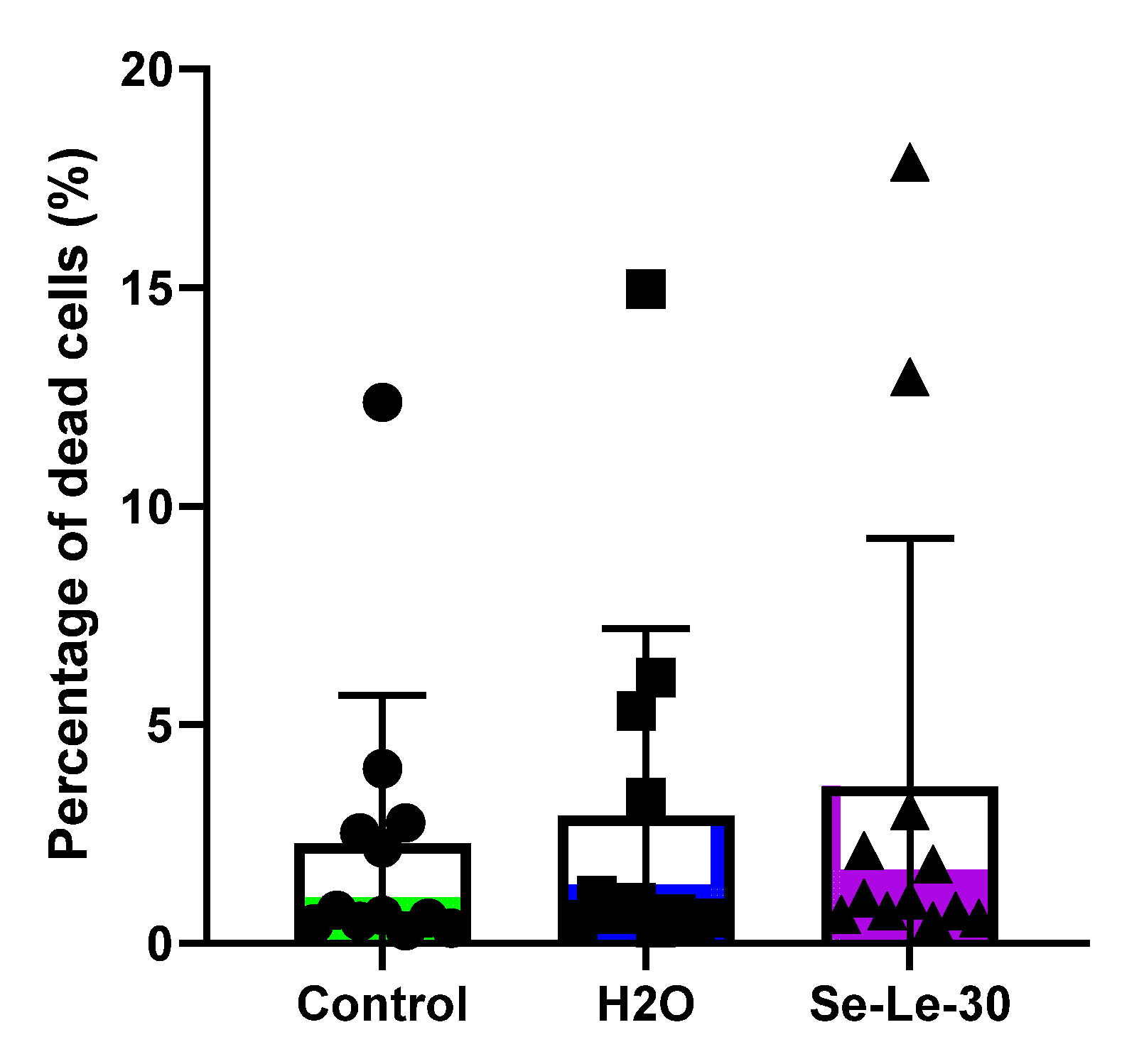
3.4. Effect of Se-Le-30 on Human CD3+ T Cells Viability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bisen, P.S.; Baghel, R.K.; Sanodiya, B.S.; Thakur, G.S.; Prasad, G.B. Lentinus edodes: A macrofungus with pharmacological activities. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, K.; Wang, C.; Chen, B.; Kang, M.; Wang, M.; Liu, K.; Wang, M. Recent advances in polysaccharides from Lentinus edodes (Berk.): Isolation, structures and bioactivities. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steimbach, L.; Borgmann, A.V.; Gomar, G.G.; Hoffmann, L.V.; Rutckeviski, R.; de Andrade, D.P.; Smiderle, F.R. Fungal beta-glucans as adjuvants for treating cancer patients—A systematic review of clinical trials. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3104–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassopoulou, M.; Yannakoulia, M.; Pletsa, V.; Zervakis, G.I.; Kyriacou, A. Effects of fungal beta-glucans on health - a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3366–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Huang, X.; Hu, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Fang, Q.; Dong, N.; Li, M.; Tang, W. Comparison of immunomodulatory effects of three polysaccharide fractions from Lentinula edodes water extracts. J. Functl. Foods 2020, 66, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Zeng, F. Correlation between antitumor activity, molecular weight, and conformation of lentinan. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.C.; Chan, W.K.; Sze, D.M. The effects of beta-glucan on human immune and cancer cells. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco Castro, E.; Calder, P.C.; Roche, H.M. beta-1,3/1,6-Glucans and Immunity: State of the Art and Future Directions. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e1901071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, T.C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Chao, A.L.; Chang, C.A. Use of statistical methods to find the polysaccharide structural characteristics and the relationships between monosaccharide composition ratio and macrophage stimulatory activity of regionally different strains of Lentinula edodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 584, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willment, J.A.; Marshall, A.S.; Reid, D.M.; Williams, D.L.; Wong, S.Y.; Gordon, S.; Brown, G.D. The human beta-glucan receptor is widely expressed and functionally equivalent to murine Dectin-1 on primary cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akramiene, D.; Kondrotas, A.; Didziapetriene, J.; Kevelaitis, E. Effects of beta-glucans on the immune system. Medicina 2007, 43, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, G.D.; Vetvicka, V.; Yan, J.; Xia, Y.; Vetvickova, J. Therapeutic intervention with complement and beta-glucan in cancer. Immunopharmacology 1999, 42, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.D.; Gordon, S. Immune recognition of fungal beta-glucans. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, B.P.; Vetvicka, V.; Pitman, M.; Goldman, R.C.; Ross, G.D. Analysis of the sugar specificity and molecular location of the beta-glucan-binding lectin site of complement receptor type 3 (CD11b/CD18). J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Zheng, L.; Chen, L.; Luo, N.; Yang, W.; Qu, X.; Liu, M.; Cheng, Z. Lipopolysaccharide activated TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway of fibroblasts from uterine fibroids. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10014–10025. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wan, J.; Lei, N.; Yao, X.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Tao, N.; et al. Polysaccharides From Lentinus Edodes Inhibits Lymphangiogenesis via the Toll-Like Receptor 4/JNK Pathway of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 547683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y. Toll-like receptor 4-related immunostimulatory polysaccharides: Primary structure, activity relationships, and possible interaction models. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wismar, R.; Brix, S.; Laerke, H.N.; Frokiaer, H. Comparative analysis of a large panel of non-starch polysaccharides reveals structures with selective regulatory properties in dendritic cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, J.W.; Lindermuth, J.; Fish, P.A.; Palace, G.P.; Stevenson, T.T.; DeMong, D.E. A novel carbohydrate-glycosphingolipid interaction between a beta-(1-3)-glucan immunomodulator, PGG-glucan, and lactosylceramide of human leukocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 22014–22020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewska, M.; Gorska, S.; Lapienis, G.; Kaleta, B.; Gorska, S.; Kaszowska, M.; Dawidowski, M.; Gamian, A.; Zagozdzon, R.; Gorski, A.; et al. Identification of the Primary Structure of Selenium-Containing Polysaccharides Selectively Inhibiting T-Cell Proliferation. Molecules 2021, 26, 5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, P.J.; Boise, L.H.; Green, J.M.; Thompson, C.B. CD28 costimulation prevents cell death during primary T cell activation. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 636–642. [Google Scholar]
- Turlo, J.; Gutkowska, B.; Herold, F. Effect of selenium enrichment on antioxidant activities and chemical composition of Lentinula edodes (Berk.) Pegl. mycelial extracts. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turło, J.; Gutkowska, B.; Herold, F.; Gajzlerska, W.; Dawidowski, M.; Dorociak, A.; Zobel, A. Biological Availability and Preliminary Selenium Speciation in Selenium-Enriched Mycelium ofLentinula edodes (Berk.). Food Biotechnol. 2011, 25, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorska-Jakubowska, S.; Klimaszewska, M.; Podsadni, P.; Kaleta, B.; Zagozdzon, R.; Gorska, S.; Gamian, A.; Straczek, T.; Kapusta, C.; Cieslak, M.; et al. Selenium-Containing Exopolysaccharides Isolated from the Culture Medium of Lentinula edodes: Structure and Biological Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, G.; Hamuro, J.; Maeda, Y.Y.; Arai, Y.; Fukuoka, F. Fractionation and purification of the polysaccharides with marked antitumor activity, especially lentinan, from Lentinus edodes (Berk.) Sing. (an edible mushroom). Cancer Res. 1970, 30, 2776–2781. [Google Scholar]
- Kaleta, B.; Roszczyk, A.; Zych, M.; Kniotek, M.; Zagożdżon, R.; Klimaszewska, M.; Malinowska, E.; Pac, M.; Turło, J. Selective Biological Effects of Selenium-Enriched Polysaccharide (Se-Le-30) Isolated from Lentinula edodes Mycelium on Human Immune Cells. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Amaro, R.; Cortes, J.R.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; Martin, P. Is CD69 an effective brake to control inflammatory diseases? Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleta, B.; Gorski, A.; Zagozdzon, R.; Cieslak, M.; Kazmierczak-Baranska, J.; Nawrot, B.; Klimaszewska, M.; Malinowska, E.; Gorska, S.; Turlo, J. Selenium-containing polysaccharides from Lentinula edodes-Biological activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.E.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Ma, L.J.; Xie, G.M. Immunomodulatory Effect of Lentinan on Aberrant T Subsets and Cytokines Profile in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Stanilka, J.M.; Rowe, C.A.; Esteves, E.A.; Nieves, C., Jr.; Spaiser, S.J.; Christman, M.C.; Langkamp-Henken, B.; Percival, S.S. Consuming Lentinula edodes (Shiitake) Mushrooms Daily Improves Human Immunity: A Randomized Dietary Intervention in Healthy Young Adults. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2015, 34, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembron-Lacny, A.; Gajewski, M.; Naczk, M.; Siatkowski, I. Effect of shiitake (Lentinus edodes) extract on antioxidant and inflammatory response to prolonged eccentric exercise. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 64, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanigawa, K.; Ito, Y.; Sakai, M.; Kobayashi, Y. Evaluation of quality of life and immune function in cancer patients receiving combined immunotherapy and oral administration of lentinula edodes mycelia extract. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 2012, 39, 1779–1781. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Paik, D.J.; Kwon, D.Y.; Park, Y. Dietary supplementation with rice bran fermented with Lentinus edodes increases interferon-gamma activity without causing adverse effects: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, B.W. Supplementation with active hexose correlated compound increases survival following infectious challenge in mice. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Fujii, H.; Walshe, T. Effects of active hexose correlated compound on frequency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells producing interferon-gamma and/or tumor necrosis factor-alpha in healthy adults. Hum. Immunol. 2010, 71, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, B.E.; Beli, E.; Duriancik, D.M.; Gardner, E.M. Short-term supplementation with active hexose correlated compound improves the antibody response to influenza B vaccine. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, D.; Shetty, S.A.; Lopez-Plaza, B.; Gomez-Candela, C.; Smidt, H.; Marin, F.R.; Soler-Rivas, C. Modulation of human intestinal microbiota in a clinical trial by consumption of a beta-D-glucan-enriched extract obtained from Lentinula edodes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 3249–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaullier, J.M.; Sleboda, J.; Ofjord, E.S.; Ulvestad, E.; Nurminiemi, M.; Moe, C.; Tor, A.; Gudmundsen, O. Supplementation with a soluble beta-glucan exported from Shiitake medicinal mushroom, Lentinus edodes (Berk.) singer mycelium: A crossover, placebo-controlled study in healthy elderly. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms. 2011, 13, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Sun, S.; Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Boraschi, D.; Qu, D. beta-Glucan oligosaccharide enhances CD8(+) T cells immune response induced by a DNA vaccine encoding hepatitis B virus core antigen. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 10, 645213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Lee, H.T.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.J.; Yoon, J.W. A Bioprocessed Polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes Mycelia Cultures with Turmeric Protects Chicks from a Lethal Challenge of Salmonella Gallinarum. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, E.; Skavland, J.; Mujic, M.; Bruserud, O.; Gjertsen, B.T. Lentinan: Hematopoietic, immunological, and efficacy studies in a syngeneic model of acute myeloid leukemia. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.L.; Rice, P.J.; Graves, B.; Ensley, H.E.; Yu, H.; Brown, G.D.; Gordon, S.; Monteiro, M.A.; Papp-Szabo, E.; Lowman, D.W.; et al. Differential high-affinity interaction of dectin-1 with natural or synthetic glucans is dependent upon primary structure and is influenced by polymer chain length and side-chain branching. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Martinez, P.; Bergon-Gutierrez, M.; Del Fresno, C. Dectin-1 Signaling Update: New Perspectives for Trained Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 812148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Hansch, G.M.; Stegmaier, S.; Denefleh, B.; Hug, F.; Schoels, M. The complement receptor 3, CR3 (CD11b/CD18), on T lymphocytes: Activation-dependent up-regulation and regulatory function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, S.; Větvička, V.; Ross, G.D. CR3 (CD11b/CD18) expressed by cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells is upregulated in a manner similar to neutrophil CR3 following stimulation with various activating agents. J. Clin. Immunol. 1993, 13, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberg, H.H.; Juricke, M.; Kabelitz, D.; Wesch, D. Regulation of T cell activation by TLR ligands. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flo, T.H.; Halaas, O.; Torp, S.; Ryan, L.; Lien, E.; Dybdahl, B.; Sundan, A.; Espevik, T. Differential expression of Toll-like receptor 2 in human cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 69, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komai-Koma, M.; Jones, L.; Ogg, G.S.; Xu, D.; Liew, F.Y. TLR2 is expressed on activated T cells as a costimulatory receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3029–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabelitz, D. Expression and function of Toll-like receptors in T lymphocytes. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, V.; Rothenfusser, S.; Britsch, S.; Krug, A.; Jahrsdorfer, B.; Giese, T.; Endres, S.; Hartmann, G. Quantitative expression of toll-like receptor 1-10 mRNA in cellular subsets of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and sensitivity to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 4531–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin-Zhorov, A.; Cohen, I.R. Signaling via TLR2 and TLR4 Directly Down-Regulates T Cell Effector Functions: The Regulatory Face of Danger Signals. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, Y.; Funami, K.; Kikkawa, S.; Taniguchi, M.; Nishiguchi, M.; Fukumori, Y.; Seya, T.; Matsumoto, M. Surface-expressed TLR6 participates in the recognition of diacylated lipopeptide and peptidoglycan in human cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Sun, T.; Yu, X.H.; Yang, Y.X.; Yeo, A.E. The effects of TLR activation on T-cell development and differentiation. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 836485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakshull, E.; Brunke-Reese, D.; Lindermuth, J.; Fisette, L.; Nathans, R.S.; Crowley, J.J.; Tufts, J.C.; Zimmerman, J.; Mackin, W.; Adams, D.S. PGG-glucan, a soluble beta-(1,3)-glucan, enhances the oxidative burst response, microbicidal activity, and activates an NF-kappa B-like factor in human PMN: Evidence for a glycosphingolipid beta-(1,3)-glucan receptor. Immunopharmacology 1999, 41, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, P.Y.; Evans, S.E.; Kottom, T.J.; Standing, J.E.; Pagano, R.E.; Limper, A.H. Pneumocystis carinii cell wall beta-glucan induces release of macrophage inflammatory protein-2 from alveolar epithelial cells via a lactosylceramide-mediated mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibundgut-Landmann, S.; Osorio, F.; Brown, G.D.; Reis e Sousa, C. Stimulation of dendritic cells via the dectin-1/Syk pathway allows priming of cytotoxic T-cell responses. Blood 2008, 112, 4971–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Gupta, S.; Agrawal, A. Human dendritic cells activated via dectin-1 are efficient at priming Th17, cytotoxic CD8 T and B cell responses. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.K.; Melnick, S.J.; Ramachandran, R.; Escalon, E.; Ramachandran, C. Mechanism of macrophage activation by (1,4)-alpha-D-glucan isolated from Tinospora cordifolia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 1815–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Ryu, H.S.; Park, H.G.; Kim, Y.O.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, H.M.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.B. Induction of dendritic cell maturation by beta-glucan isolated from Sparassis crispa. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Ma, F.; Qin, Z.; Lei, N.; Tao, N. MPSSS impairs the immunosuppressive function of cancer-associated fibroblasts via the TLR4-NF-kappaB pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, T.C.; Hsu, F.M.; Chang, C.A.; Cheng, J.C. Branched alpha-(1,4) glucans from Lentinula edodes (L10) in combination with radiation enhance cytotoxic effect on human lung adenocarcinoma through the Toll-like receptor 4 mediated induction of THP-1 differentiation/activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11997–12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comer, J.; Bassette, M.; Burghart, R.; Loyd, M.; Ishiguro, S.; Azhagiya Singam, E.R.; Vergara-Jaque, A.; Nakashima, A.; Suzuki, K.; Geisbrecht, B.V.; et al. Beta-1,3 Oligoglucans Specifically Bind to Immune Receptor CD28 and May Enhance T Cell Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roszczyk, A.; Zych, M.; Zielniok, K.; Krata, N.; Turło, J.; Klimaszewska, M.; Zagożdżon, R.; Kaleta, B. The Effect of Novel Selenopolysaccharide Isolated from Lentinula edodes Mycelium on Human T Lymphocytes Activation, Proliferation, and Cytokines Synthesis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121900
Roszczyk A, Zych M, Zielniok K, Krata N, Turło J, Klimaszewska M, Zagożdżon R, Kaleta B. The Effect of Novel Selenopolysaccharide Isolated from Lentinula edodes Mycelium on Human T Lymphocytes Activation, Proliferation, and Cytokines Synthesis. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(12):1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121900
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoszczyk, Aleksander, Michał Zych, Katarzyna Zielniok, Natalia Krata, Jadwiga Turło, Marzenna Klimaszewska, Radosław Zagożdżon, and Beata Kaleta. 2022. "The Effect of Novel Selenopolysaccharide Isolated from Lentinula edodes Mycelium on Human T Lymphocytes Activation, Proliferation, and Cytokines Synthesis" Biomolecules 12, no. 12: 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121900
APA StyleRoszczyk, A., Zych, M., Zielniok, K., Krata, N., Turło, J., Klimaszewska, M., Zagożdżon, R., & Kaleta, B. (2022). The Effect of Novel Selenopolysaccharide Isolated from Lentinula edodes Mycelium on Human T Lymphocytes Activation, Proliferation, and Cytokines Synthesis. Biomolecules, 12(12), 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121900





