Analysis and Identification of Bioactive Compounds of Cannabinoids in Silico for Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and methods
2.1. Protein and Ligand Preparation
2.2. In Silico Molecular Docking
2.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.4. MMPBSA Calculations
2.5. Prediction of ADMET Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Docking of Major Cannabinoids with the RBD-ACE2 Complex of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV
3.2. Root Mean Square Deviations
3.3. Cluster Analysis
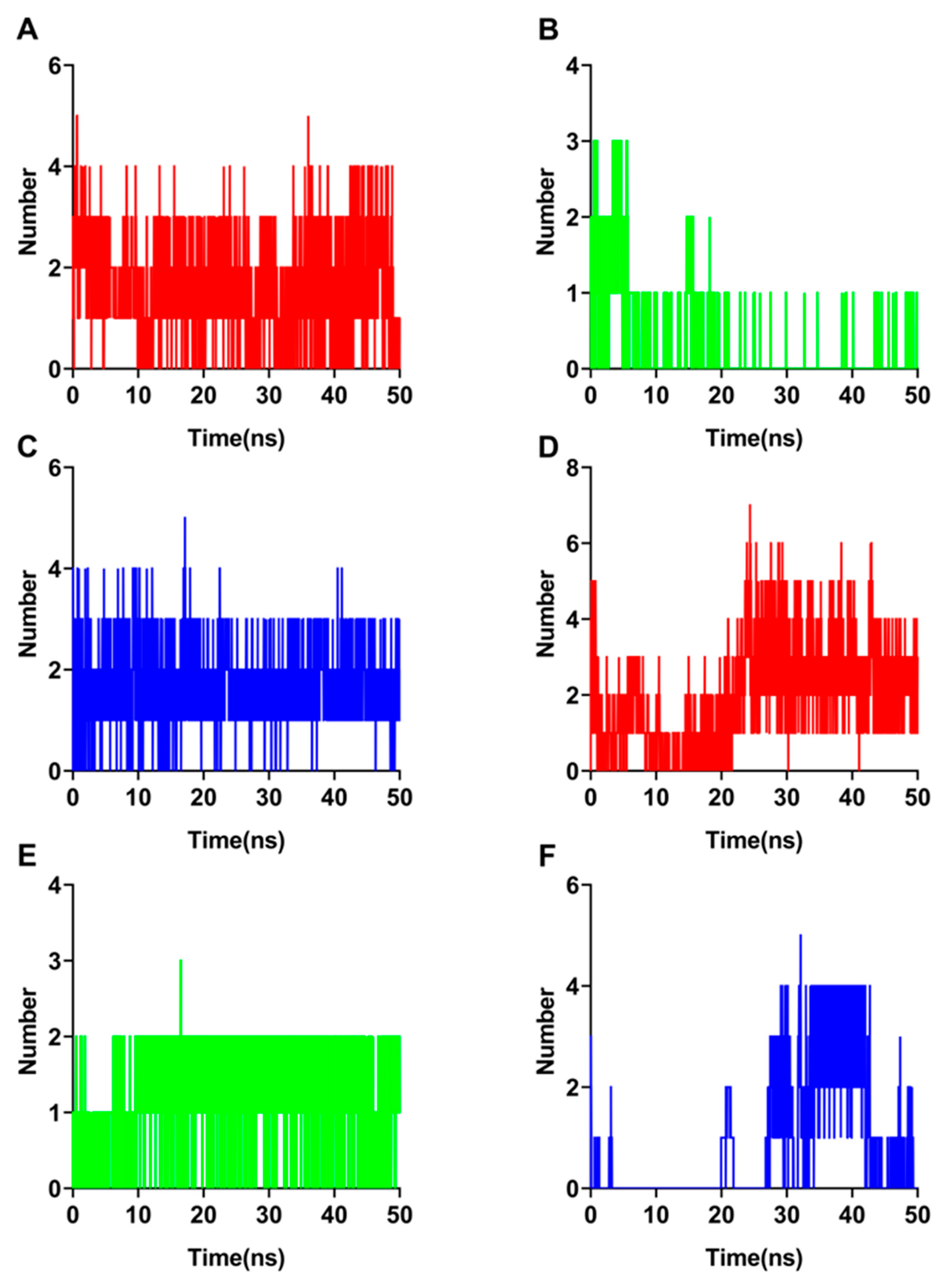
3.4. Hydrogen Bond and MMPBSA Analysis
3.5. A Potential Mechanism of Cannabinoids Inhibited SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV
3.6. ADMET Properties Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- COVID-19 Excess Mortality Collaborators. Estimating excess mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic analysis of COVID-19-related mortality, 2020–2021. Lancet 2022, 10334, 1513–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Belouzard, S.; Chu, V.C.; Whittaker, G.R. Activation of the SARS coronavirus spike protein via sequential proteolytic cleavage at two distinct sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5871–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Gui, M.; Wang, X.; Xiang, Y. Cryo-EM structure of the SARS coronavirus spike glycoprotein in complex with its host cell receptor ACE2. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Molina-Molina, M.; Abdul-Hafez, A.; Uhal, V.; Xaubet, A.; Uhal, B.D. Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 is protective but downregulated in human and experimental lung fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L178–L185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, C.A.; Rolain, J.M.; Raoult, D. ACE2 receptor polymorphism: Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 3, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, G.J.; Esshaki, D.J.; Thomas, W.D., Jr.; Ambrosino, D.M. Amino acids 270 to 510 of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein are required for interaction with receptor. J. Virol. 2004, 9, 4552–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry de-pends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.M.; Su, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, X.; Jin, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, F.; et al. Structure-based design of antiviral drug candidates targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Science 2020, 368, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.A.; Shetty, N.P. Structure-based screening of natural product libraries in search of potential antiviral drug-leads as first-line treatment to COVID-19 infection. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 165, 105497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, B.L.; de Oliveira, N.C.; Ritter, M.R.; Tonin, F.S.; Melo, E.B.; Sanches, A.C.C.; Fernandez-Llimos, F.; Petruco, M.V.; de Mello, J.C.P.; Chierrito, D.; et al. The naturally-derived alkaloids as a potential treatment for COVID-19: A scoping review. Phytother. Res. 2022, 7, 2686–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyebi, G.A.; Ogunro, O.B.; Adegunloye, A.P.; Ogunyemi, O.M.; Afolabi, S.O. Potential inhibitors of coronavirus 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro): An in silico screening of alkaloids and terpenoids from African medicinal plants. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 9, 3396–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawan, M.M.A.K.; Halder, S.K.; Hasan, M.A. Luteolin and abyssinone II as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2: An in silico molecular modeling approach in battling the COVID-19 outbreak. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2021, 45, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafò, F.; Donati, E.; Brindani, N.; Ottonello, G.; Armirotti, A.; De Vivo, M. Quercetin and luteolin are single-digit micromolar inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrack, D.M.; Deogratias, G.; Kiruri, L.W.; Onoka, I.; Vianney, J.M.; Swai, H.; Nyandoro, S.S. Luteolin: A blocker of SARS-CoV-2 cell entry based on relaxed complex scheme, molecular dynamics simulation, and metadynamics. J. Mol. Model. 2021, 8, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Breemen, R.B.; Muchiri, R.N.; Bates, T.A.; Weinstein, J.B.; Leier, H.C.; Farley, S.; Tafesse, F.G. Cannabinoids Block Cellular Entry of SARS-CoV-2 and the Emerging Variants. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, V.; Park, J.G.; Cho, K.H.; Choi, P.; Kim, T.; Ham, J.; Lee, J. Assessment of antiviral potencies of cannabinoids against SARS-CoV-2 using computational and in vitro approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicman, A.; Pędzińska-Betiuk, A.; Kozłowska, H. The potential of cannabinoids and inhibitors of endocannabinoid degradation in respiratory diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 911, 174560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.C.; Yang, D.; Nicolaescu, V.; Best, T.J.; Ohtsuki, T.; Chen, S.N.; Friesen, J.B.; Drayman, N.; Mohamed, A.; Dann, C.; et al. Cannabidiol Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Promotes the Host Innate Immune Response. bioRxiv 2021, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.; Kumar, B.V.; Singh, R.; Rajendran, V.; Purohit, R.; Kumar, S. An in-silico evaluation of different bioactive molecules of tea for their inhibition potency against non structural protein-15 of SARS-CoV-2. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, B.; Peng, W.; Du, S.; Chen, B.; Feng, Y.; Hu, X.; Lai, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.W.; Fang, P.; et al. Oridonin Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 by Targeting Its 3C-Like Protease. Small Sci. 2022, 13, 2100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Olotu, F.A.; Dev, S.; Pannipara, M.; Soliman, M.E.; Carradori, S.; Mathew, B. Natural products database screening for the discovery of naturally occurring SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein blockers. ChemistrySelect 2020, 42, 13309–13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Sarkar, A.; Maulik, U. Molecular docking study of potential phytochemicals and their effects on the complex of SARS-CoV2 spike protein and human ACE2. Sci. Rep. 2020, 1, 17699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaji, D.; Yamamoto, S.; Saito, R.; Suzuki, R.; Nakamura, S.; Kurita, N. Proposal of novel natural inhibitors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 main protease: Molecular docking and ab initio fragment molecular orbital calculations. Biophys. Chem. 2021, 275, 106608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.S.; Kumar, A.; Shankar, R.; Sharma, U. In silico approach for identifying natural lead molecules against SARS-CoV-2. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2021, 106, 107916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Sindhu, J.; Thakur, S.; Rana, A.; Sharma, G.; Mayank, P.R. Recent efforts for drug identification from phytochemicals against SARS-CoV-2: Exploration of the chemical space to identify druggable leads. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Sun, D.; Rajashankar, K.R.; Qian, Z.; Holmes, K.V.; Li, F. Crystal structure of mouse coronavirus receptor-binding domain complexed with its murine receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 26, 10696–10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linciano, P.; Citti, C.; Russo, F.; Tolomeo, F.; Laganà, A.; Capriotti, A.L.; Luongo, L.; Iannotta, M.; Belardo, C.; Maione, S.; et al. Identification of a new cannabidiol n-hexyl homolog in a medicinal cannabis variety with an antinociceptive activity in mice: Cannabidihexol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülck, T.; Møller, B.L. Phytocannabinoids: Origins and Biosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 985–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanabus, J.; Bryła, M.; Roszko, M.; Modrzewska, M.; Pierzgalski, A. Cannabinoids—Characteristics and Potential for Use in Food Production. Molecules 2021, 26, 6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Autodock4 and Auto-DockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 16, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, D.; de Groot, B.L. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and Autodock/Vina. J. Comput. -Aided Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.; Berk, H.; Erik, L. GROMACS 2022.1 Source code (2022.1). Zenodo 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. MD Simulations of the P53 oncoprotein structure: The effect of the Arg273→His mutation on the DNA binding domain. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A Linear Constraint Solver for Molecular Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S.; Valdés-Tresanco, M.E.; Valiente, P.A.; Moreno, E. MMPBSA: A New Tool to Perform End-State Free Energy Calculations with GROMACS. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 6281–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Chakraborty, A.; Biswas, A.; Chowdhuri, S. Identification of polyphenols from Broussonetia papyrifera as SARS CoV-2 main protease inhibitors using in silico docking and molecular dynamics simulation approaches. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 17, 6747–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, G.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; Hsieh, C.; Yin, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, A.; et al. ADMETlab 2.0: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W5–W14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, A.K.; Mishra, N. In silico validation of coumarin derivatives as potential inhibitors against main protease, NSP10/NSP16-Methyltransferase, phosphatase and endoribonuclease of SARS CoV-2. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 18, 7306–7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kwon, E.B.; Kim, B.; Chung, H.S.; Choi, G.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, J.G. Mulberry Component Kuwanon C Exerts Potent Therapeutic Efficacy In Vitro against COVID-19 by Blocking the SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 RBD:ACE2 Receptor Interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 20, 12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, K.; Jokinen, E.M.; Kurkinen, S.T.; Pentikäinen, O.T. Screening of Natural Products Targeting SARS-CoV-2-ACE2 Receptor Interface—A MixMD Based HTVS Pipeline. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 589769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelinger, G.; Merfort, I.; Schempp, C.M. Anti-Oxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergic Activities of Luteolin. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paland, N.; Pechkovsky, A.; Aswad, M.; Hamza, H.; Popov, T.; Shahar, E.; Louria-Hayon, I. The Immunopathology of COVID-19 and the Cannabis Paradigm. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 631233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Goel, N.; Abhinav, N.; Varma, T.; Achari, A.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Kamal, I.M.; Chakrabarti, S.; Ravichandiran, V.; Reddy, A.M.; et al. Virtual screening of natural products inspired in-house library to discover potential lead molecules against the SARS-CoV-2 main protease. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Liang, H.; Deng, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Hou, C. Analysis and Identification of Bioactive Compounds of Cannabinoids in Silico for Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121729
Chen C, Liang H, Deng Y, Yang X, Li X, Hou C. Analysis and Identification of Bioactive Compounds of Cannabinoids in Silico for Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(12):1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121729
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chenxiao, Hao Liang, Yanchun Deng, Xiushi Yang, Xiaoming Li, and Chunsheng Hou. 2022. "Analysis and Identification of Bioactive Compounds of Cannabinoids in Silico for Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV" Biomolecules 12, no. 12: 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121729
APA StyleChen, C., Liang, H., Deng, Y., Yang, X., Li, X., & Hou, C. (2022). Analysis and Identification of Bioactive Compounds of Cannabinoids in Silico for Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. Biomolecules, 12(12), 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121729









