Secretory Leucoprotease Inhibitor (SLPI) Promotes Survival during Acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection by Suppression of Inflammation Rather Than Microbial Killing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. SLPI-Deficient Mice Are Highly Susceptible to Pulmonary Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection
3.2. Endogenous SLPI Is Involved in Controlling LPS-Induced Lung Inflammation
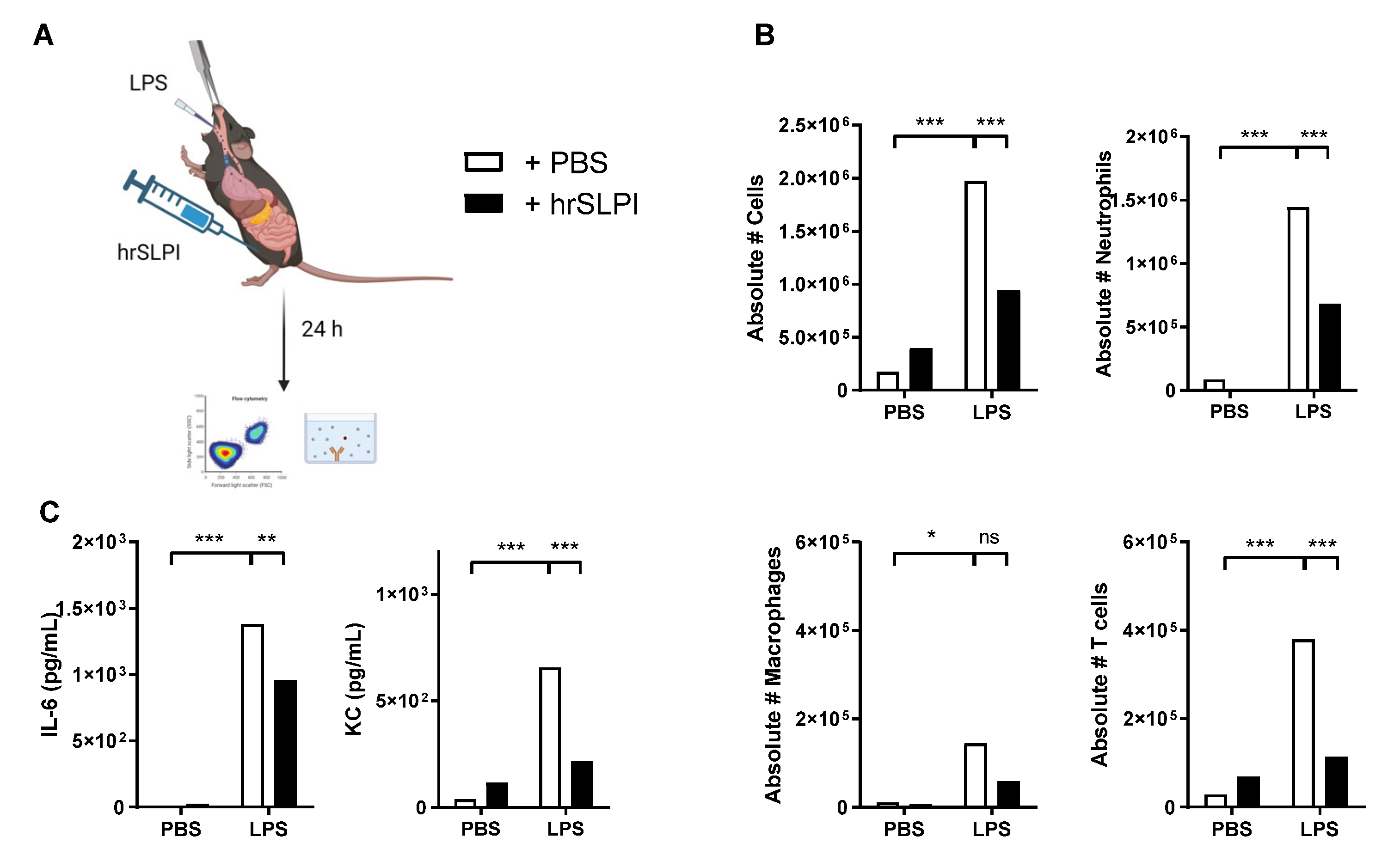
3.3. Administration of hrSLPI Decreases LPS-Induced Lung Inflammation
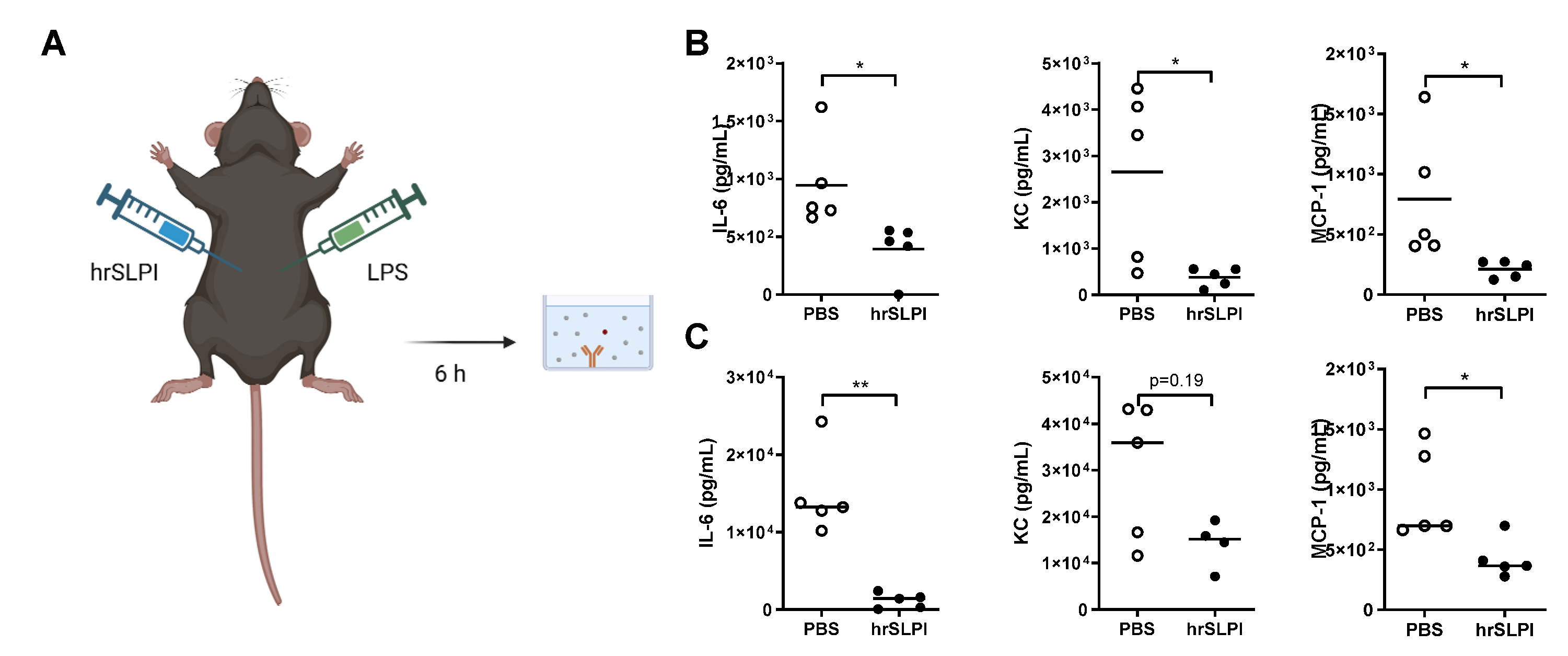
3.4. Administration of hrSLPI Decreases LPS-Induced Systemic Inflammation
3.5. hrSLPI Interferes with the NFκB and MAPK Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Codagnone, M.; Cianci, E.; Lamolinara, A.; Mari, V.C.; Nespoli, A.; Isopi, E.; Mattoscio, D.; Arita, M.; Bragonzi, A.; Iezzi, M.; et al. Resolvin D1 enhances the resolution of lung inflammation caused by long-term Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbier, F.; Andremont, A.; Wolff, M.; Bouadma, L. Hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia: Recent advances in epidemiology and management. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2013, 19, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.K.; Kazmierczak, B.I. Inflammation: A Double-Edged Sword in the Response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. J. Innate Immun. 2017, 9, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewicz, A.; Richter, K.; Zakrzewicz, D.; Siebers, K.; Damm, J.; Agné, A.; Hecker, A.; McIntosh, J.M.; Chamulitrat, W.; Krasteva-Christ, G.; et al. SLPI Inhibits ATP-Mediated Maturation of IL-1β in Human Monocytic Leukocytes: A Novel Function of an Old Player. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taggart, C.C.; Cryan, S.-A.; Weldon, S.; Gibbons, A.; Greene, C.M.; Kelly, E.; Low, T.B.; O’neill, S.J.; McElvaney, N.G. Secretory leucoprotease inhibitor binds to NF-kappaB binding sites in monocytes and inhibits p65 binding. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Water, R.; Willems, L.N.A.; van Muijen, G.N.P.; Franken, C.; Fransen, J.A.; Dijkman, J.H.; Kramps, J.A. Ultrastructural localization of bronchial antileukoprotease in central and peripheral human airways by a gold-labeling technique using monoclonal antibodies. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1986, 133, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.Y.; Nathan, C.; Radzioch, D.; Ding, A. Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor: A macrophage product induced by and antagonistic to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Cell 1997, 88, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sallenave, J.M.; Har, M.S.-T.; Cox, G.; Chignard, M.; Gauldie, J. Secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor is a major leukocyte elastase inhibitor in human neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1997, 61, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsom, J.N.; van der Marel, A.P.J.; van Berkel, L.A.; van Helvoort, J.M.L.M.; Simons-Oosterhuis, Y.; Jansen, W.; Greuter, M.; Nelissen, R.L.H.; Meeuwisse, C.M.L.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E.S.; et al. Secretory Leukoprotease Inhibitor in Mucosal Lymph Node Dendritic Cells Regulates the Threshold for Mucosal Tolerance. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 6588–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kammouni, W.; Figarella, C.; Baeza, N.; Marchand, S.; Merten, M.D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide induces CF-like alteration of protein secretion by human tracheal gland cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 241, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wetering, S.; Van Der Linden, A.C.; Van Sterkenburg, M.A.J.A.; De Boer, W.I.; Kuijpers, A.L.A.; Schalkwijk, J.; Hiemstra, P.S. Regulation of SLPI and elafin release from bronchial epithelial cells by neutrophil defensins. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 278, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saitoh, H.; Masuda, T.; Shimura, S.; Fushimi, T.; Shirato, K. Secretion and gene expression of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor by human airway submucosal glands. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 280, L79–L87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, J.B.; van Sterkenburg, M.A.; Rabe, K.F.; Schalkwijk, J.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Datson, N.A. Transcriptional response of bronchial epithelial cells to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Identification of early mediators of host defense. Physiol. Genom. 2005, 21, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, A.; Thieblemont, N.; Zhu, J.; Jin, F.; Zhang, J.; Wright, S. Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor interferes with uptake of lipopolysaccharide by macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4485–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiedow, O.; Harder, J.; Bartels, J.; Streit, V.; Christophers, E. Antileukoprotease in human skin: An antibiotic peptide constitutively produced by keratinocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 248, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, P.S.; Maassen, R.J.; Stolk, J.; Heinzel-Wieland, R.; Steffens, G.J.; Dijkman, J.H. Antibacterial activity of antileukoprotease. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 4520–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Si-Tahar, M.; Merlin, D.; Sitaraman, S.; Madara, J.L. Constitutive and regulated secretion of secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor by human intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomee, J.F.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Heinzel-Wieland, R.; Kauffman, H.F. Antileukoprotease: An endogenous protein in the innate mucosal defense against fungi. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiemstra, P.S.; Van Watering, S.; Stolk, J. Neutrophil serine proteinases and defensins in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Effects on pulmonary epithelium. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernie-King, B.A.; Seilly, D.J.; Davies, A.; Lachmann, P.J. Streptococcal inhibitor of complement inhibits two additional components of the mucosal innate immune system: Secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor and lysozyme. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4908–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugteren, S.; Samsom, J.N. Secretory Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor (SLPI) in mucosal tissues: Protects against inflammation, but promotes cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 59, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, J.; Sun, D.; Ding, A. Suppression of macrophage responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) is independent of its anti-protease function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2005, 1745, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, A.; Mori, Y.; Hagiwara, K.; Suzuki, T.; Sakakibara, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Igarashi, T.; Ebina, M.; Abe, T.; Miyazaki, J.; et al. Increased susceptibility to LPS-induced endotoxin shock in secretory leukoprotease inhibitor (SLPI)-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulligan, M.S.; Lentsch, A.B.; Huber-Lang, M.; Guo, R.-F.; Sarma, V.; Wright, C.D.; Ulich, T.R.; Ward, P.A. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Mutant Forms of Secretory Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentsch, A.B.; Jordan, J.A.; Czermak, B.J.; Diehl, K.M.; Younkin, E.M.; Sarma, V.; Ward, P.A. Inhibition of NF-κB activation and augmentation of IκBβ by secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor during lung inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gipson, T.S.; Bless, N.M.; Shanley, T.P.; Crouch, L.D.; Bleavins, M.R.; Younkin, E.M.; Sarma, V.; Gibbs, D.F.; Tefera, W.; McConnell, P.C.; et al. Regulatory effects of endogenous protease inhibitors in acute lung inflammatory injury. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 3653–3662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taggart, C.C.; Greene, C.M.; McElvaney, N.G.; O’Neill, S. Secretory leucoprotease inhibitor prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced IκBα degradation without affecting phosphorylation or ubiquitination. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33648–33653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greene, C.M.; McElvaney, N.G.; O’Neill, S.J.O.; Taggart, C.C. Secretory leucoprotease inhibitor impairs toll-like receptor 2- and 4-mediated responses in monocytic Cells. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 3684–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McElvaney, N.G.; Nakamura, H.; Birrer, P.; Hébert, C.A.; Wong, W.L.; Alphonso, M.; Baker, J.B.; Catalano, M.A.; Crystal, R.G. Modulation of airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis: In vivo suppression of interleukin-8 levels on the respiratory epithelial surface by aerosolization of recombinant secretory leukoprotease inhibitor. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greene, C.M.; McElvaney, N.G. Proteases and antiproteases in chronic neutrophilic lung disease—Relevance to drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolphus, A.; Stolk, J.; Dijkman, J.H.; Kramps, J.A. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary emphysema by intratracheally instilled recombinant secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 147, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElvaney, N.G.; Doujaiji, B.; Moan, M.J.; Burnham, M.R.; Wu, M.C.; Crystal, R.G. Pharmacokinetics of recombinant secretory leukoprotease inhibitor aerosolized to normals and individuals with cystic fibrosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 148, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, J.; Saiga, H.; Sato, S.; Okuyama, M.; Kayama, H.; Kuwata, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Nishida, T.; Sawa, Y.; Akira, S.; et al. Potent Antimycobacterial Activity of Mouse Secretory Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4032–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, A.; Glasgow, A.; Small, D.; Carlile, S.; McCrudden, M.; McLean, D.; Brown, R.; Doherty, D.; Lundy, F.T.; Hamid, U.I.; et al. Characterisation of eppin function: Expression and activity in the lung. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1601937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bivas-Benita, M.; Zwier, R.; Junginger, H.E.; Borchard, G. Non-invasive pulmonary aerosol delivery in mice by the endotracheal route. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 61, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camper, N.; Glasgow, A.M.A.; Osbourn, M.; Quinn, D.J.; Small, D.M.; McLean, D.T.; Lundy, F.T.; Elborn, J.S.; McNally, P.; Ingram, R.J.; et al. A secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor variant with improved activity against lung infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Humphries, F.; Bergin, R.; Jackson, R.; Delagic, N.; Wang, B.; Yang, S.; Dubois, A.V.; Ingram, R.J.; Moynagh, P.N. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Pellino2 mediates priming of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payne, J.E.; Dubois, A.V.; Ingram, R.J.; Weldon, S.; Taggart, C.C.; Elborn, J.S.; Tunney, M.M. Activity of innate antimicrobial peptides and ivacaftor against clinical cystic fibrosis respiratory pathogens. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sallenave, J.M.; Shulmann, J.; Crossley, J.; Jordana, M.; Gauldie, J. Regulation of secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor (SLPI) and elastase-specific inhibitor (ESI/elafin) in human airway epithelial cells by cytokines and neutrophilic enzymes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1994, 11, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbinante-Nissen, J.M.; Simpson, L.G.; Leikauf, G.D. Neutrophil elastase increases secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor transcript levels in airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, L286–L292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grobmyer, S.R.; Barie, P.S.; Nathan, C.F.; Fuortes, M.; Lin, E.; Lowry, S.F.; Wright, C.D.; Weyant, M.J.; Hydo, L.; Reeves, F.; et al. Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor, an inhibitor of neutrophil activation, is elevated in serum in human sepsis and experimental endotoxemia. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallenave, J.M.; Donnelly, S.C.; Grant, I.S.; Robertson, C.; Gauldie, J.; Haslett, C. Secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor is preferentially increased in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 13, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoumakidou, M.; Bouloukaki, I.; Thimaki, K.; Tzanakis, N.; Siafakas, N.M. Innate immunity proteins in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Exp. Lung Res. 2010, 36, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollander, C.; Sitkauskiene, B.; Sakalauskas, R.; Westin, U.; Janciauskiene, S.M. Serum and bronchial lavage fluid concentrations of IL-8, SLPI, sCD14 and sICAM-1 in patients with COPD and asthma. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gompertz, S.; Bayley, D.L.; Hill, S.L.; Stockley, R.A. Relationship between airway inflammation and the frequency of exacerbations in patients with smoking related COPD. Thorax 2001, 56, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kikuchi, T.; Abe, T.; Hoshi, S.; Matsubara, N.; Tominaga, Y.; Satoh, K.; Nukiwa, T. Structure of the murine secretory leukoprotease inhibitor (Slpi) gene and chromosomal localization of the human and murine SLPI genes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1998, 19, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, C.D.; Kennedy, J.A.; Zitnik, R.J.; Kashem, M.A. Inhibition of murine neutrophil serine proteinases by human and murine secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 254, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, R.; Thuraisingam, T.; Camateros, P.; Kanagaratham, C.; Xu, Y.Z.; Henri, J.; Yang, J.; He, G.; Ding, A.; Radzioch, D. Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor plays an important role in the regulation of allergic asthma in mice. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4433–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, X.Y.; Zeng, L.; Jin, W.; Thompson, J.; Mizel, D.E.; Lei, K.; Billinghurst, R.C.; Poole, A.R.; Wahl, S.M. Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor suppresses the inflammation and joint damage of bacterial cell wall-induced arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozaka, S.; Sonoda, A.; Ariki, S.; Kamiyama, N.; Hidano, S.; Sachi, N.; Ito, K.; Kudo, Y.; Minata, M.; Saechue, B.; et al. Protease inhibitory activity of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor ameliorates murine experimental colitis by protecting the intestinal epithelial barrier. Genes Cells 2021, 26, 807–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osbourn, M.; Rodgers, A.M.; Dubois, A.V.; Small, D.M.; Humphries, F.; Delagic, N.; Moynagh, P.N.; Weldon, S.; Taggart, C.C.; Ingram, R.J. Secretory Leucoprotease Inhibitor (SLPI) Promotes Survival during Acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection by Suppression of Inflammation Rather Than Microbial Killing. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121728
Osbourn M, Rodgers AM, Dubois AV, Small DM, Humphries F, Delagic N, Moynagh PN, Weldon S, Taggart CC, Ingram RJ. Secretory Leucoprotease Inhibitor (SLPI) Promotes Survival during Acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection by Suppression of Inflammation Rather Than Microbial Killing. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(12):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121728
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsbourn, Megan, Aoife M. Rodgers, Alice V. Dubois, Donna M. Small, Fiachra Humphries, Nezira Delagic, Paul N. Moynagh, Sinéad Weldon, Clifford C. Taggart, and Rebecca J. Ingram. 2022. "Secretory Leucoprotease Inhibitor (SLPI) Promotes Survival during Acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection by Suppression of Inflammation Rather Than Microbial Killing" Biomolecules 12, no. 12: 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121728
APA StyleOsbourn, M., Rodgers, A. M., Dubois, A. V., Small, D. M., Humphries, F., Delagic, N., Moynagh, P. N., Weldon, S., Taggart, C. C., & Ingram, R. J. (2022). Secretory Leucoprotease Inhibitor (SLPI) Promotes Survival during Acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection by Suppression of Inflammation Rather Than Microbial Killing. Biomolecules, 12(12), 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121728







