Bakkenolides and Caffeoylquinic Acids from the Aerial Portion of Petasites japonicus and Their Bacterial Neuraminidase Inhibition Ability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Extraction and Isolation
2.3.1. Bakkenolide B (1)
2.3.2. Bakkenolide D (2)
2.3.3. 1,5-di-O-Caffeoylquinic Acid (3)
2.3.4. 5-O-Caffeoylquinic Acid (4)
2.4. Bacterial Neuraminidase Inhibition Assay and Kinetics
2.5. Molecular Docking
2.6. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
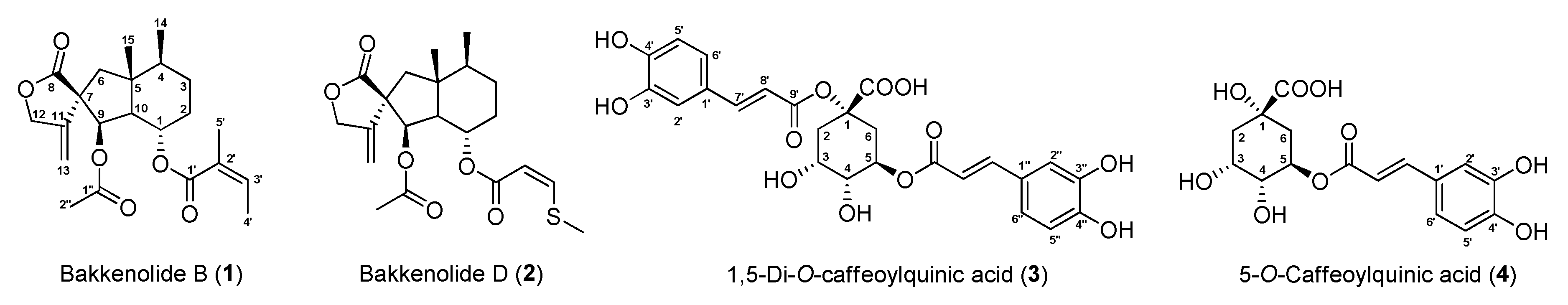
3.1. Isolation of Inhibitors from P. japonicus
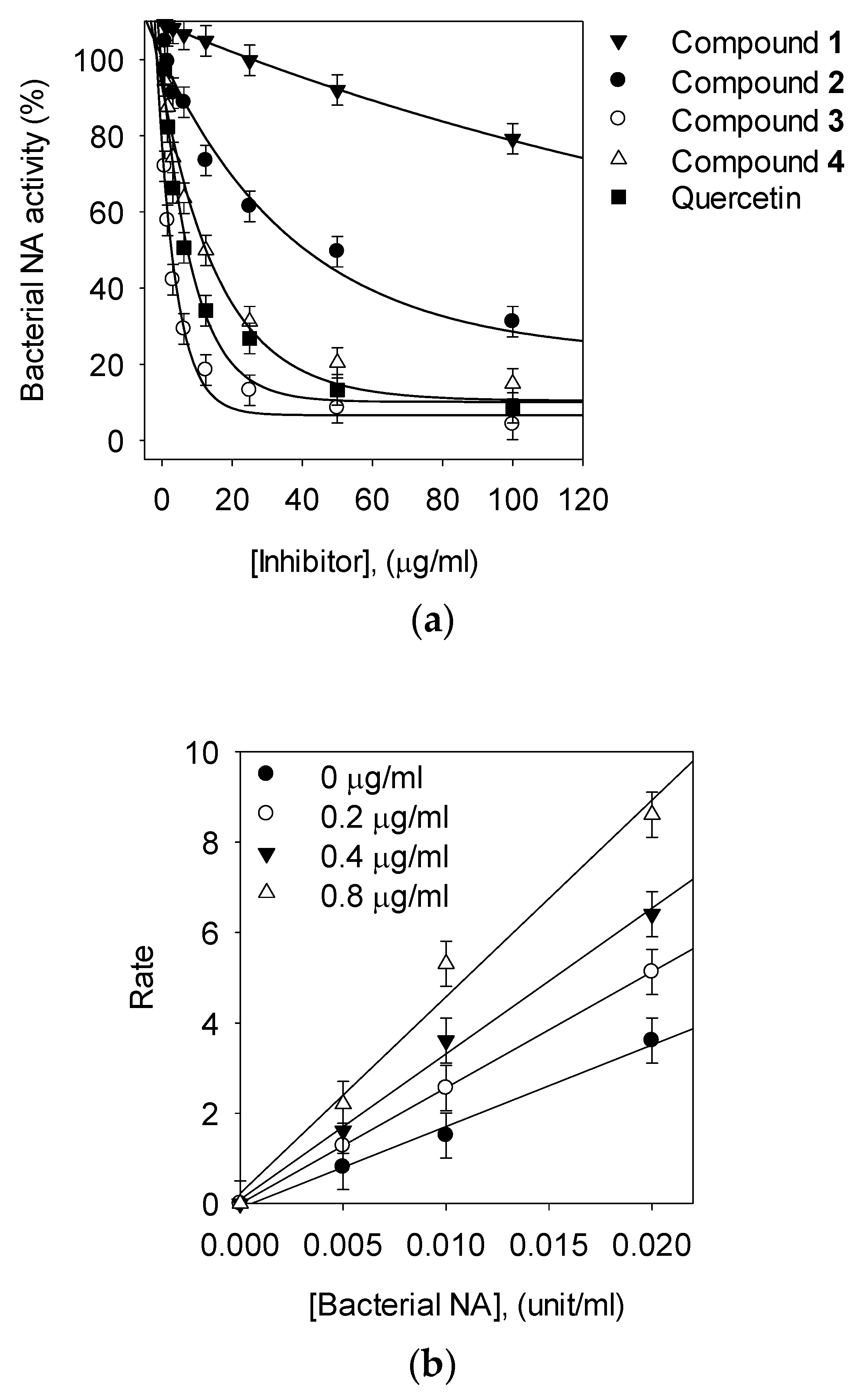
3.2. Bacterial Neuraminidase Inhibitory Activities
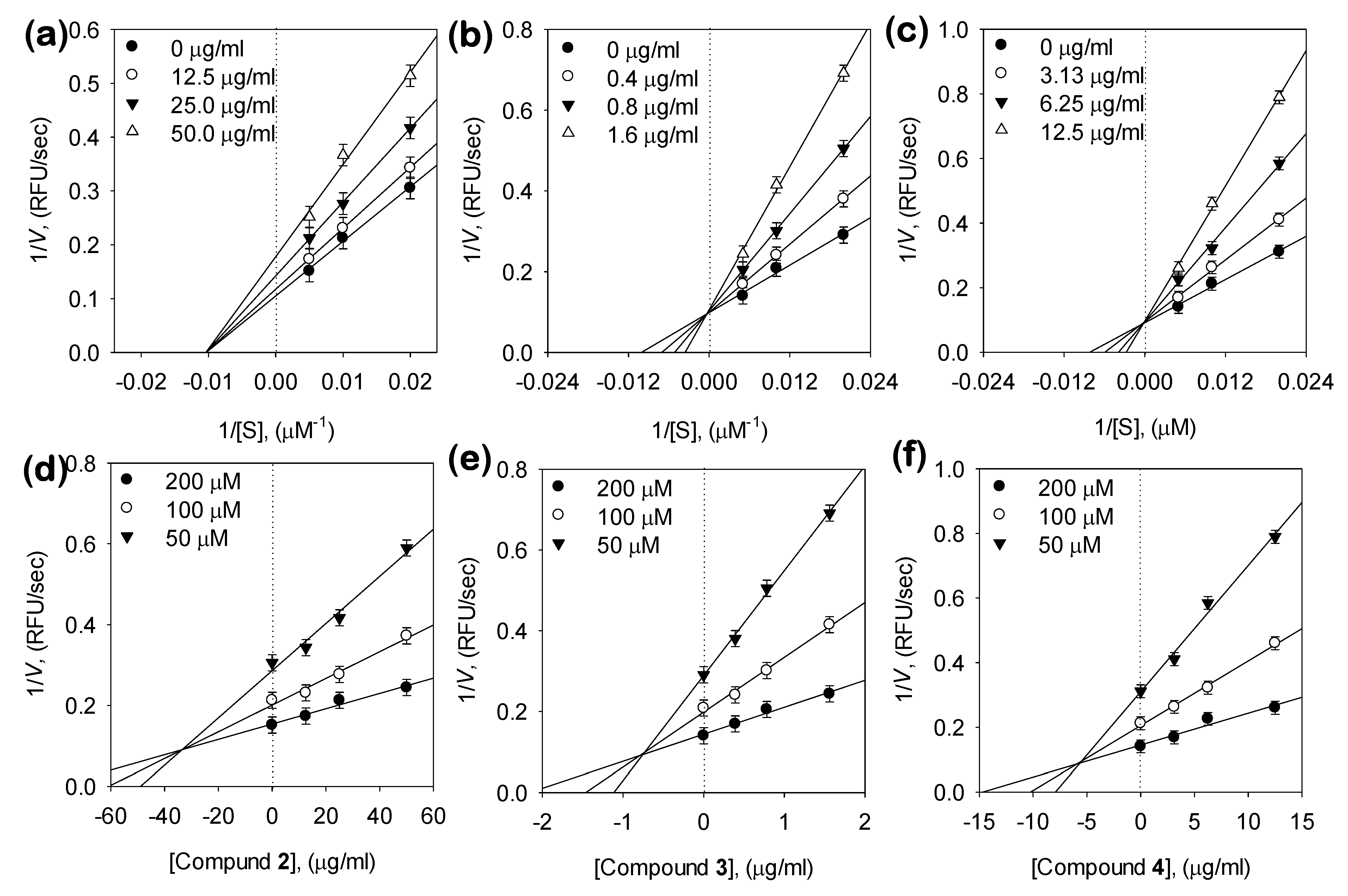
3.3. Kinetic Analysis of Inhibitors on NA
3.4. Molecular Docking Study of the Inhibition of NA by Inhibitors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angata, T.; Varki, A. Chemical diversity in the sialic acids and related α-keto acids: An evolutionary perspective. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 439–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Honma, K.; Douglas, C.I.; Sharma, A.; Stafford, G.P. Role of sialidase in glycoprotein utilization by Tannerella forsythia. Microbiology 2011, 157, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, R. Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, M.; Lu, Q.; Qing, G.; Sun, T. Sialic Acid-Targeted Biointerface Materials and Bio-Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrosovich, M.N.; Matrosovich, T.Y.; Gray, T.; Roberts, N.A.; Klenk, H.-D. Human and avian influenza viruses target different cell types in cultures of human airway epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101, 4620–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, E.; Preti, A.; Venerando, B.; Borsani, G. Recent development in mammalian sialidase molecular biology. Neurochem. Res. 2002, 27, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varki, N.M.; Varki, A. Diversity in cell surface sialic acid presentations: Implications for biology and disease. Lab. Investig. 2007, 87, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, J.C.; Kawasaki, N. Sialidase inhibitors DAMPen sepsis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.-Y.; Chen, X.; King, S.; Cavassani, K.A.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, X.; Cao, H.; Yu, H.; Qu, J.; Fang, D. Preserving Sialic Acid-dependent Pattern Recognition by CD24-Siglec G Interaction for Therapy of Polybacterial Sepsis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soong, G.; Muir, A.; Gomez, M.I.; Waks, J.; Reddy, B.; Planet, P.; Singh, P.K.; Kaneko, Y.; Wolfgang, M.C.; Hsiao, Y.S.; et al. Bacterial neuraminidase facilitates mucosal infection by participating in biofilm production. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.S.; Kim, D.W.; Curtis-Long, M.J.; Lee, B.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kang, J.E.; Park, K.H. Potent inhibition of bacterial neuraminidase activity by pterocarpans isolated from the roots of Lespedeza bicolor. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 6100–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, H.; Tanaka, J.; Yamada, E.; Morikawa, T.; Kasajima, N.; Yoshikawa, M. Anti type I allergic property of Japanese butterbur extract and its mast cell degranulation inhibitory ingredients. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2915–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Jin, D.-Q.; Xie, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y. Isolation, characterization, and neuroprotective activities of sesquiterpenes from Petasites japonicus. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.-L.; Gao, G.-L.; Luo, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Zhang, M.; Feng, J. A new neuroprotective bakkenolide from the rhizome of Peatasites tatewakianus. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydın, A.A.; Letzel, T. Simultaneous investigation of sesquiterpenes, pyrrolizidine alkaloids and N-oxides in Butterbur (Petasites hybridus) with an offline 2D-combination of HPLC-UV and LC-MMI-ToF-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 85, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, P.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, C.-G.; Jiang, X.-J.; Li, X.-M.; Yang, W.-Q.; Li, R.-T.; Wang, F. New sesquiterpenoids from Petasites japonicus and Petasites tricholobus. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 23, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitilertdecha, P.; Guy, R.H.; Rowan, M.G. Characterisation of polyphenolic compounds in Clerodendrum petasites S. Moore and their potential for topical delivery through the skin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ji, F.; Cao, X.; Ma, J.; Ohizumi, Y.; Lee, D.; Guo, Y. Sesquiterpenoids from an edible plant Petasites japonicus and their promoting effects on neurite outgrowth. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 22, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaoita, Y.; Kikuchi, M. Petasiphenone, a phenolic compound from rhizomes ofPetasites japonicus. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 1773–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-W.; Lee, K.-P.; Kim, J.-M.; Kang, S.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, J.-M.; Moon, H.R.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, Y.-G.; Im, D.-S. Petatewalide B, a novel compound from Petasites japonicus with anti-allergic activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 178, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-G.; Jeong, S.-H.; Cho, J.-H. Antimutagenic and anticarcinogenic effect of methanol extracts of Petasites japonicus Maxim leaves. J. Vet. Sci. 2010, 11, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, K.-P.; Kang, S.; Park, S.-J.; Choi, Y.-W.; Lee, Y.-G.; Im, D.-S. Anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects of bakkenolide B isolated from Petasites japonicus leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Li, R.-P.; Guo, M.-L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, N.; Ma, Y.-L. Bakkenolides from Petasites tricholobus and their neuroprotective effects related to antioxidant activities. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Jeong, M.; Park, S.; Ryu, S.M.; Lee, J.; Song, Z.; Guo, Y.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, D.; Jang, D.S. Chemical Constituents of the Leaves of Butterbur (Petasites japonicus) and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ryu, Y.B.; Curtis-Long, M.J.; Yuk, H.J.; Cho, J.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, K.D.; Lee, W.S.; Park, K.H. Flavanones and rotenoids from the roots of Amorpha fruticosa L. that inhibit bacterial neuraminidase. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, C.; Fan, S. Caffeoylquinic Acids from the Aerial Parts of Chrysanthemum coronarium L. Plants 2017, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wray, V.; Tsevegsuren, N.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Phenolic compounds from the Mongolian medicinal plant Scorzonera radiata. Z. Für Nat. C 2012, 67, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-S.; Kao, M.-S.; Wu, P.-L.; LIN, F.-W.; Shi, L.-S.; Liou, M.-J.; Li, C.-Y. The bakkenolides from the root of Petasites formosanus and their cytotoxicity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]

| Compound | Bacterial Neuraminidase (Clostridium Perfringerns) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 a (μM) | Type of Inhibition | Kib (μM) | |
| Bakkenolide B (1) | >200 | NT c | NT |
| Bakkenolide D (2) | 80.1 ± 1.8 | Noncompetitive | 82.7 ± 0.4 |
| 1,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (3, 1,5-COQ) | 2.3 ± 0.4 | Competitive | 1.4 ± 0.05 |
| 5-O-Caffeoylquinic acid (4, 5-COQ) | 22.6 ± 0.6 | Competitive | 16.1 ± 0.5 |
| Quercetin | 21.8 ± 0.7 | NT | NT |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, H.S.; Shin, K.-C.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Ban, Y.J.; Oh, Y.J.; Cho, H.J.; Oh, D.-K.; Kim, D.W. Bakkenolides and Caffeoylquinic Acids from the Aerial Portion of Petasites japonicus and Their Bacterial Neuraminidase Inhibition Ability. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060888
Woo HS, Shin K-C, Kim JY, Kim Y-S, Ban YJ, Oh YJ, Cho HJ, Oh D-K, Kim DW. Bakkenolides and Caffeoylquinic Acids from the Aerial Portion of Petasites japonicus and Their Bacterial Neuraminidase Inhibition Ability. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(6):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060888
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Hyun Sim, Kyung-Chul Shin, Jeong Yoon Kim, Yeong-Su Kim, Young Jun Ban, Yu Jin Oh, Hae Jin Cho, Deok-Kun Oh, and Dae Wook Kim. 2020. "Bakkenolides and Caffeoylquinic Acids from the Aerial Portion of Petasites japonicus and Their Bacterial Neuraminidase Inhibition Ability" Biomolecules 10, no. 6: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060888
APA StyleWoo, H. S., Shin, K.-C., Kim, J. Y., Kim, Y.-S., Ban, Y. J., Oh, Y. J., Cho, H. J., Oh, D.-K., & Kim, D. W. (2020). Bakkenolides and Caffeoylquinic Acids from the Aerial Portion of Petasites japonicus and Their Bacterial Neuraminidase Inhibition Ability. Biomolecules, 10(6), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060888






