The Homologous Components of Flagellar Type III Protein Apparatus Have Acquired a Novel Function to Control Twitching Motility in a Non-Flagellated Biocontrol Bacterium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids and Culture Conditions
2.2. Genetic Manipulation
2.3. Twitching Motility Assay
2.4. Immunoblotting
3. Results
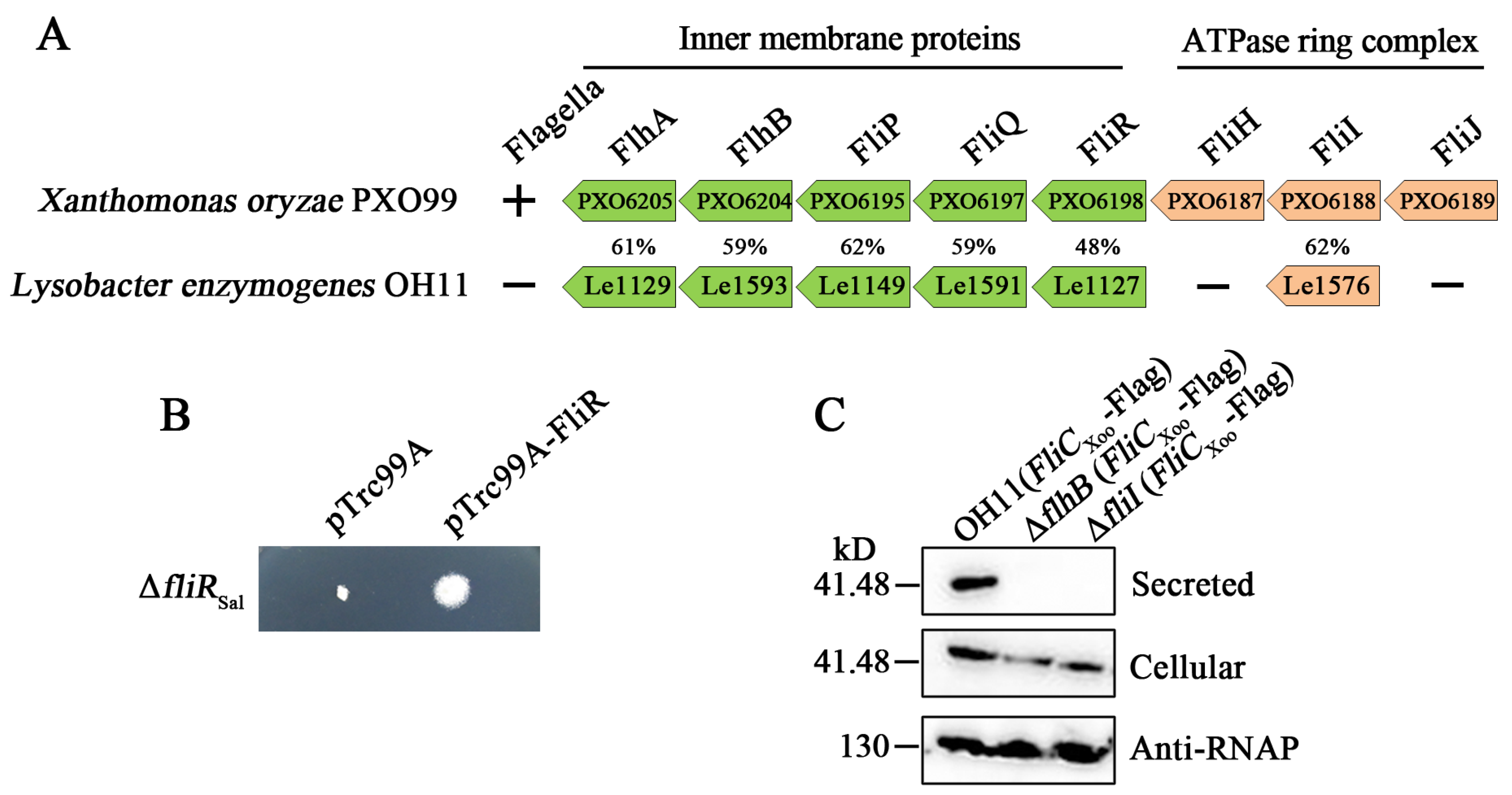
3.1. The Non-Flagellated L. enzymogenes OH11 Encodes FT3SS-Like Genes
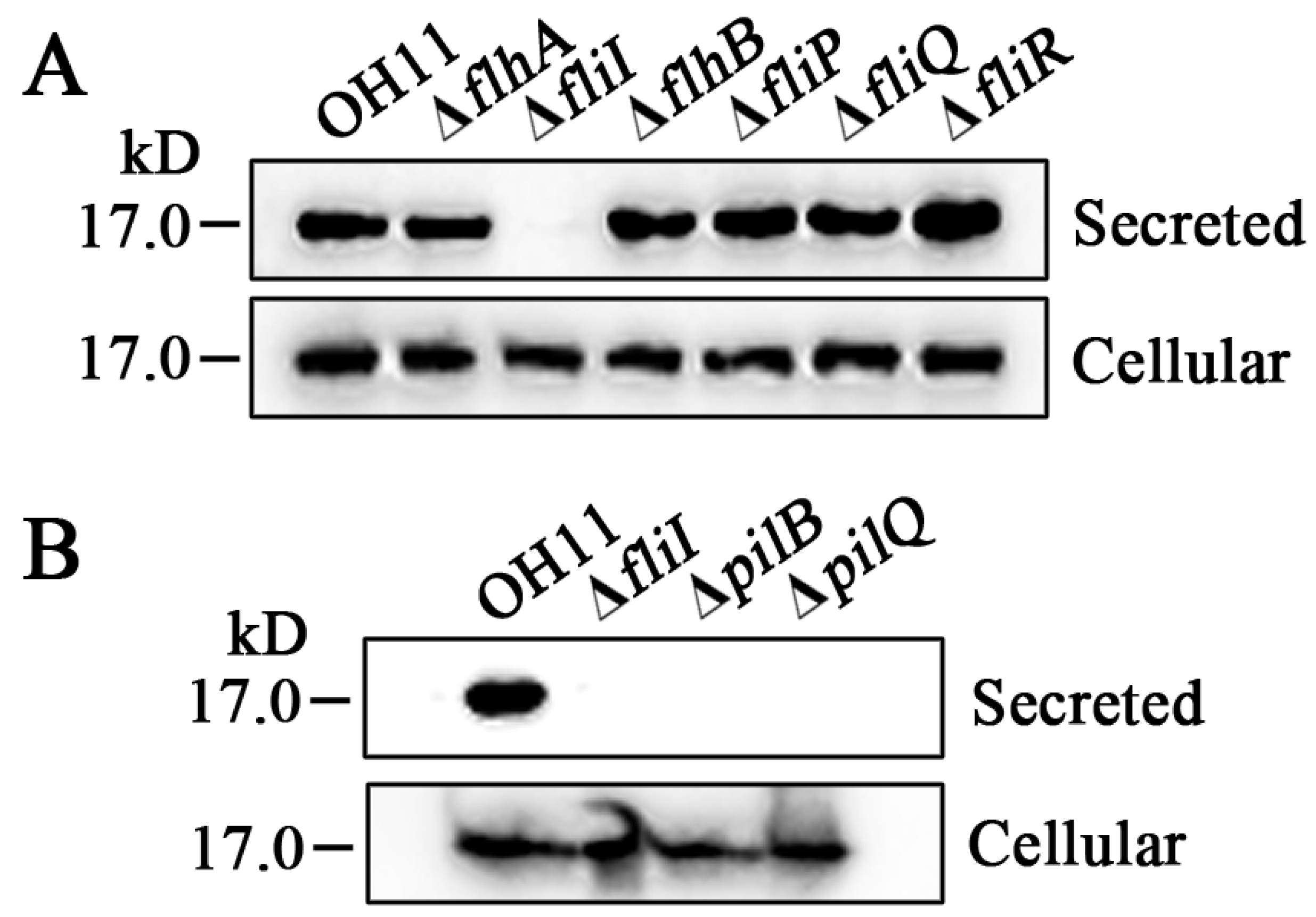
3.2. Several FT3SS-Like Genes in the Non-Flagellated L. enzymogenes OH11 Play Novel Functions to Affect Twitching Motility
3.3. The FliI Homolog Affects PilA Secretion in L. enzymogenes OH11
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christensen, P.; Cook, F.D. Lysobacter, a New Genus of Nonfruiting, Gliding Bacteria with a High Base Ratio. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1978, 28, 367–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, D.Y.; Reedy, R.M.; Palumbo, J.D.; Zhou, J.-M.; Yuen, G.Y. A clp Gene Homologue Belonging to the Crp Gene Family Globally Regulates Lytic Enzyme Production, Antimicrobial Activity, and Biological Control Activity Expressed by Lysobacterenzymogenes Strain C3. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wright, S.; Shen, Y.-M.; Du, L. Bioactive natural products from Lysobacter. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panthee, S.; Hamamoto, H.; Paudel, A.; Sekimizu, K. Lysobacter species: a potential source of novel antibiotics. Arch. Microbiol. 2016, 198, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruijn, I.; Cheng, X.; De Jager, V.; Expósito, R.G.; Watrous, J.D.; Patel, N.; Postma, J.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Kobayashi, D.Y.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Comparative genomics and metabolic profiling of the genus Lysobacter. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Qian, G.L.; Chen, Y.; Du, L.C.; Liu, F.Q.; Yuen, G.Y. PilG is involved in the regulation of twitching motility and antifungal antibiotic biosynthesis in the biological control agent Lysobacterenzymogenes. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Qian, G.; Liu, F. Type IV pilus biogenesis genes and their roles in biofilm formation in the biological control agent Lysobacterenzymogenes OH11. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 102, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, P.R. Robustness analysis of the E.coli chemosensory system to perturbations in chemoattractant concentrations. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Porter, S.L.; Wadhams, G.H.; Armitage, J.P. Signal processing in complex chemotaxis pathways. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 9, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumura, T.; Makino, F.; Dietsche, T.; Kinoshita, M.; Kato, T.; Wagner, S.; Namba, K.; Imada, K.; Minamino, T. Assembly and stoichiometry of the core structure of the bacterial flagellar type III export gate complex. PLoS Boil. 2017, 15, e2002281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H. Role of Flagella in the Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Minamino, T. Flagella-Driven Motility of Bacteria. Biomoecules 2019, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamino, T. Protein export through the bacterial flagellar type III export pathway. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2014, 1843, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamino, T.; Namba, K. Distinct roles of the FliI ATPase and proton motive force in bacterial flagellar protein export. Nature 2008, 451, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamino, T.; Morimoto, Y.V.; Kinoshita, M.; Aldridge, P.D.; Namba, K. The bacterial flagellar protein export apparatus processively transports flagellar proteins even with extremely infrequent ATP hydrolysis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamino, T.; Morimoto, Y.V.; Hara, N.; Namba, K. An energy transduction mechanism used in bacterial flagellar type III protein export. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepold, A.; Armitage, J.P. Type III secretion systems: the bacterial flagellum and the injectisome. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2015, 370, 20150020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietsche, T.; Mebrhatu, M.T.; Brunner, M.J.; Abrusci, P.; Yan, J.; Franz-Wachtel, M.; Schärfe, C.; Zilkenat, S.; Grin, I.; Galán, J.E.; et al. Structural and Functional Characterization of the Bacterial Type III Secretion Export Apparatus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1006071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.V.; Kami-Ike, N.; Miyata, T.; Kawamoto, A.; Kato, T.; Namba, K.; Minamino, T. High-Resolution pH Imaging of Living Bacterial Cells To Detect Local pH Differences. mBio 2016, 7, e01911–e01916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlen, L.; Abrusci, P.; Johnson, S.; Gault, J.; Deme, J.; Caesar, J.; Dietsche, T.; Mebrhatu, M.T.; Ganief, T.; Macek, B.; et al. Structure of the Core of the Type Three Secretion System Export Apparatus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Boil. 2018, 25, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Shi, K.; Portaliou, A.; Rossi, P.; Economou, A.; Kalodimos, C.G. Structures of chaperone-substrate complexes docked onto the export gate in a type III secretion system. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, F.D.; Renault, T.T.; Peters, B.; Dietsche, T.; Galvez, E.; Guse, A.; Freier, K.; Charpentier, E.; Strowig, T.; Franz-Wachtel, M.; et al. A flagellum-specific chaperone facilitates assembly of the core type III export apparatus of the bacterial flagellum. PLoS Boil. 2017, 15, e2002267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamino, T. Hierarchical protein export mechanism of the bacterial flagellar type III protein export apparatus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Baidya, A.K.; Pal, R.R.; Mamou, G.; Gatt, Y.E.; Margalit, H.; Rosenshine, I.; Ben-Yehuda, S. A Ubiquitous Platform for Bacterial Nanotube Biogenesis. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, F.; He, Y.-W.; Du, L.; Venturi, V.; Fan, J.; Hu, B.; Liu, F. Lysobacterenzymogenes Uses Two Distinct Cell-Cell Signaling Systems for Differential Regulation of Secondary-Metabolite Biosynthesis and Colony Morphology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6604–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, G.; Xu, F.; Venturi, V.; Du, L.; Liu, F. Roles of a solo LuxR in the biological control agent Lysobacterenzymogenes strain OH11. Phytopathology 2014, 104, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, M.G. Application of a time-delay neural network to promoter annotation in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Comput Chem. 2001, 26, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.R.; Mecsas, J. Bacterial Secretion Systems: An Overview. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-H.; So, B.-H.; Wang, J.-C.; Song, E.-S.; Park, Y.-J.; Lee, B.-M.; Kang, H.-W. Functional analysis of pilQ gene in Xanthomanasoryzaepv. oryzae, bacterial blight pathogen of rice. J. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.M.; Bernstein, H.D.; Information, P.E.K.F.C. Surface-Exposed Lipoproteins: An Emerging Secretion Phenomenon in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvaux, M.; Candela, T.; Serror, P. Surfaceome and Proteosurfaceome in Parietal Monoderm Bacteria: Focus on Protein Cell-Surface Display. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imada, K.; Minamino, T.; Tahara, A.; Namba, K. Structural similarity between the flagellar type III ATPase FliI and F1-ATPase subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imada, K.; Minamino, T.; Uchida, Y.; Kinoshita, M.; Namba, K. Insight into the flagella type III export revealed by the complex structure of the type III ATPase and its regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3633–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazetani, K.-I.; Minamino, T.; Miyata, T.; Kato, T.; Namba, K. ATP-induced FliIhexamerization facilitates bacterial flagellar protein export. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Rettberǵ, L.A.; Treuner-Lanǵe, A.; Iwasa, J.; Søǵaard-Andersen, L.; Jensen, G.J. Architecture of the type Iva pilus machine. Science 2016, 351, aad2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razia, M.; Raja, K.R.; Padmanaban, K.; Sivaramakrishnan, S.; Chellapandi, P. A phylogenetic approach for assigning function of hypothetical proteins in Photorhabdus luminescens Subsp. laumondii TT01 genome. J. Comput. Sci. Syst. Biol. 2010, 3, 021–029. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, C.K.; Rusch, D.B.; Brun, Y.V. Flagellar Mutants Have Reduced Pilus Synthesis in Caulobactercrescentus. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00031-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fulano, A.M.; Shen, D.; Kinoshita, M.; Chou, S.-H.; Qian, G. The Homologous Components of Flagellar Type III Protein Apparatus Have Acquired a Novel Function to Control Twitching Motility in a Non-Flagellated Biocontrol Bacterium. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050733
Fulano AM, Shen D, Kinoshita M, Chou S-H, Qian G. The Homologous Components of Flagellar Type III Protein Apparatus Have Acquired a Novel Function to Control Twitching Motility in a Non-Flagellated Biocontrol Bacterium. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(5):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050733
Chicago/Turabian StyleFulano, Alex M., Danyu Shen, Miki Kinoshita, Shan-Ho Chou, and Guoliang Qian. 2020. "The Homologous Components of Flagellar Type III Protein Apparatus Have Acquired a Novel Function to Control Twitching Motility in a Non-Flagellated Biocontrol Bacterium" Biomolecules 10, no. 5: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050733
APA StyleFulano, A. M., Shen, D., Kinoshita, M., Chou, S.-H., & Qian, G. (2020). The Homologous Components of Flagellar Type III Protein Apparatus Have Acquired a Novel Function to Control Twitching Motility in a Non-Flagellated Biocontrol Bacterium. Biomolecules, 10(5), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050733






