Expression Profile and Prognostic Significance of EPHB3 in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. DNA Isolation
2.3. Microsatellite Instability (MSI) Analysis
2.4. DNA Methylation Analysis
2.5. KRAS/BRAF Mutation Analysis
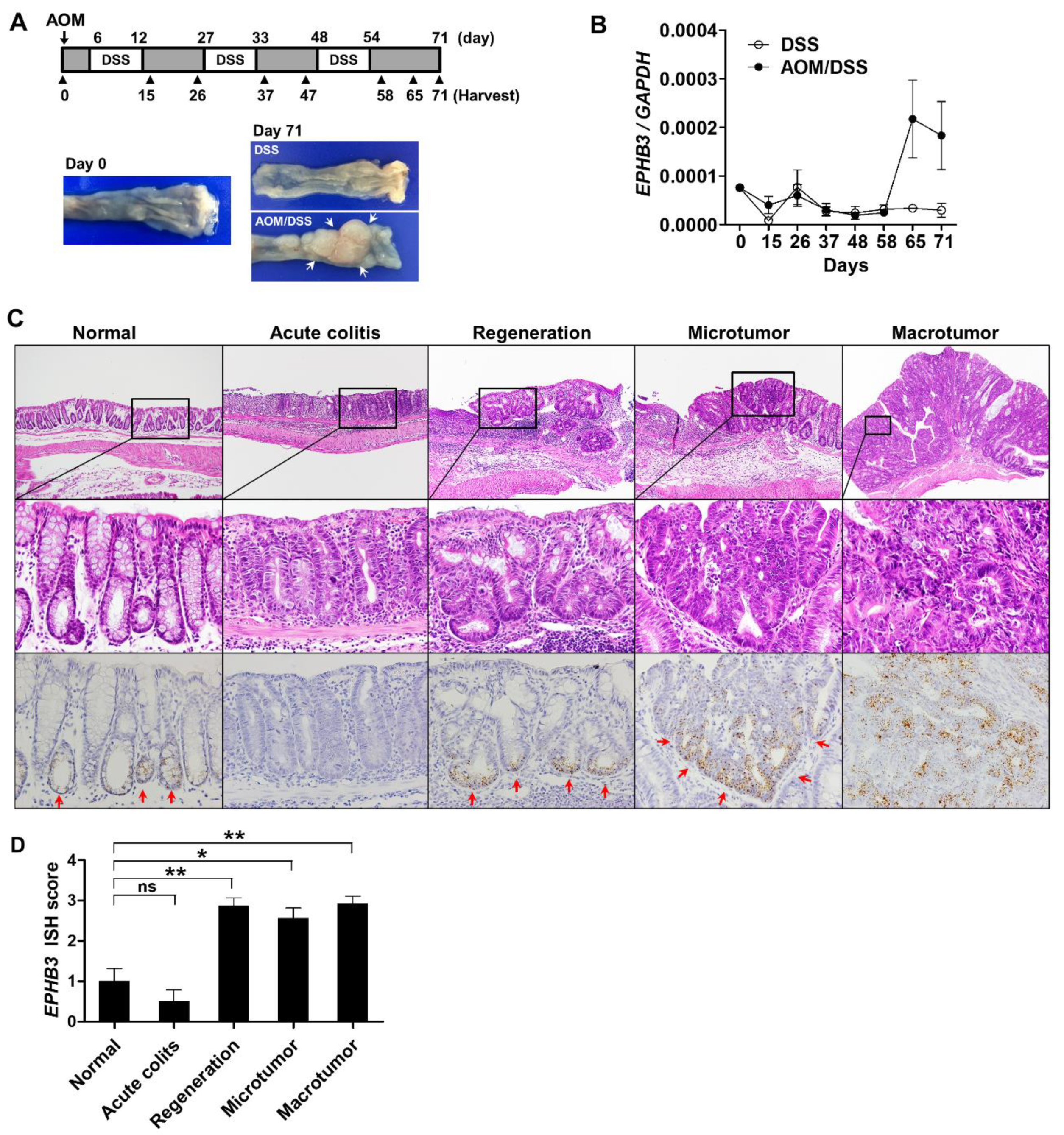
2.6. Mice and Induction of CAC
2.7. Tissue Microarray (TMA) Construction
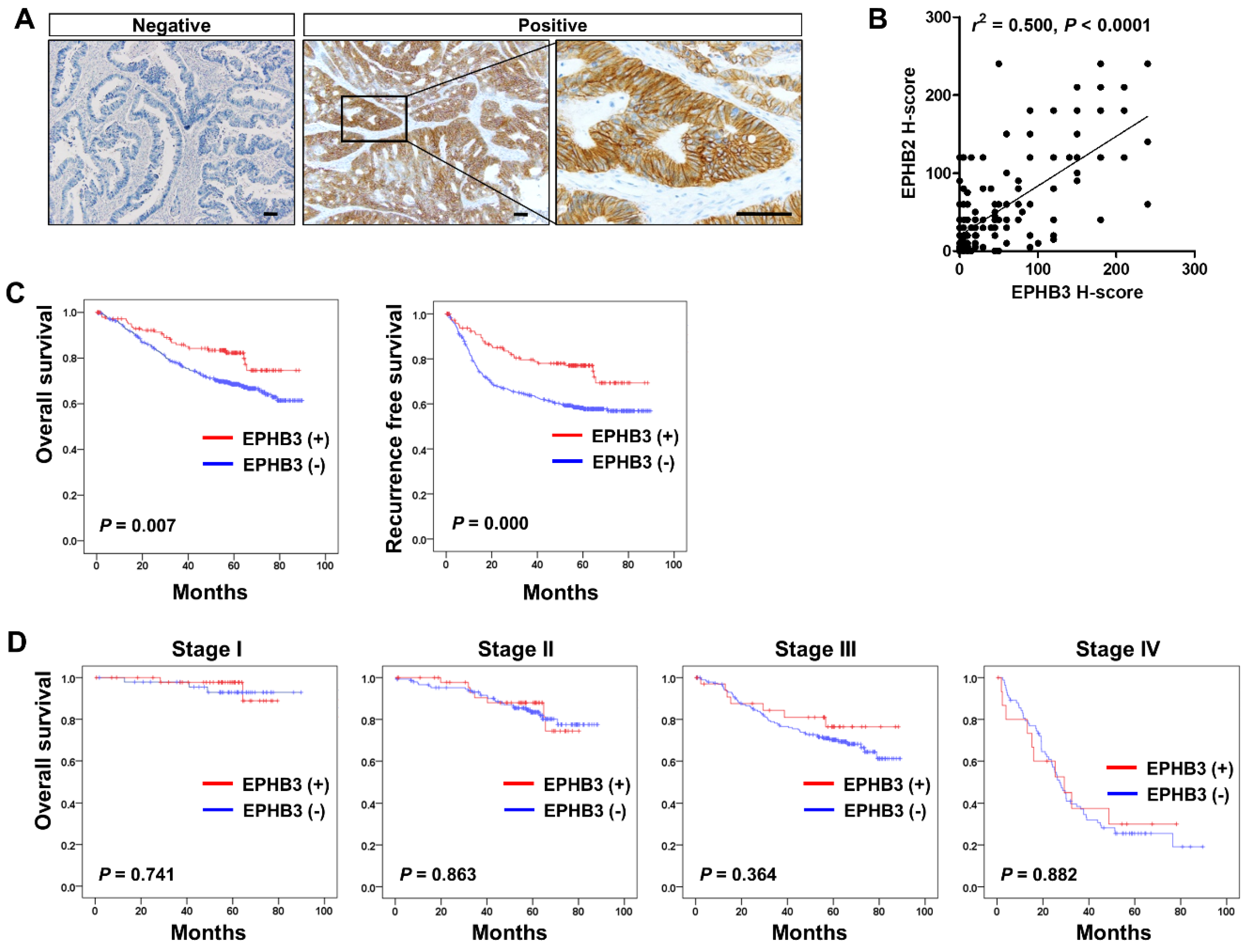
2.8. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Evaluation
2.9. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
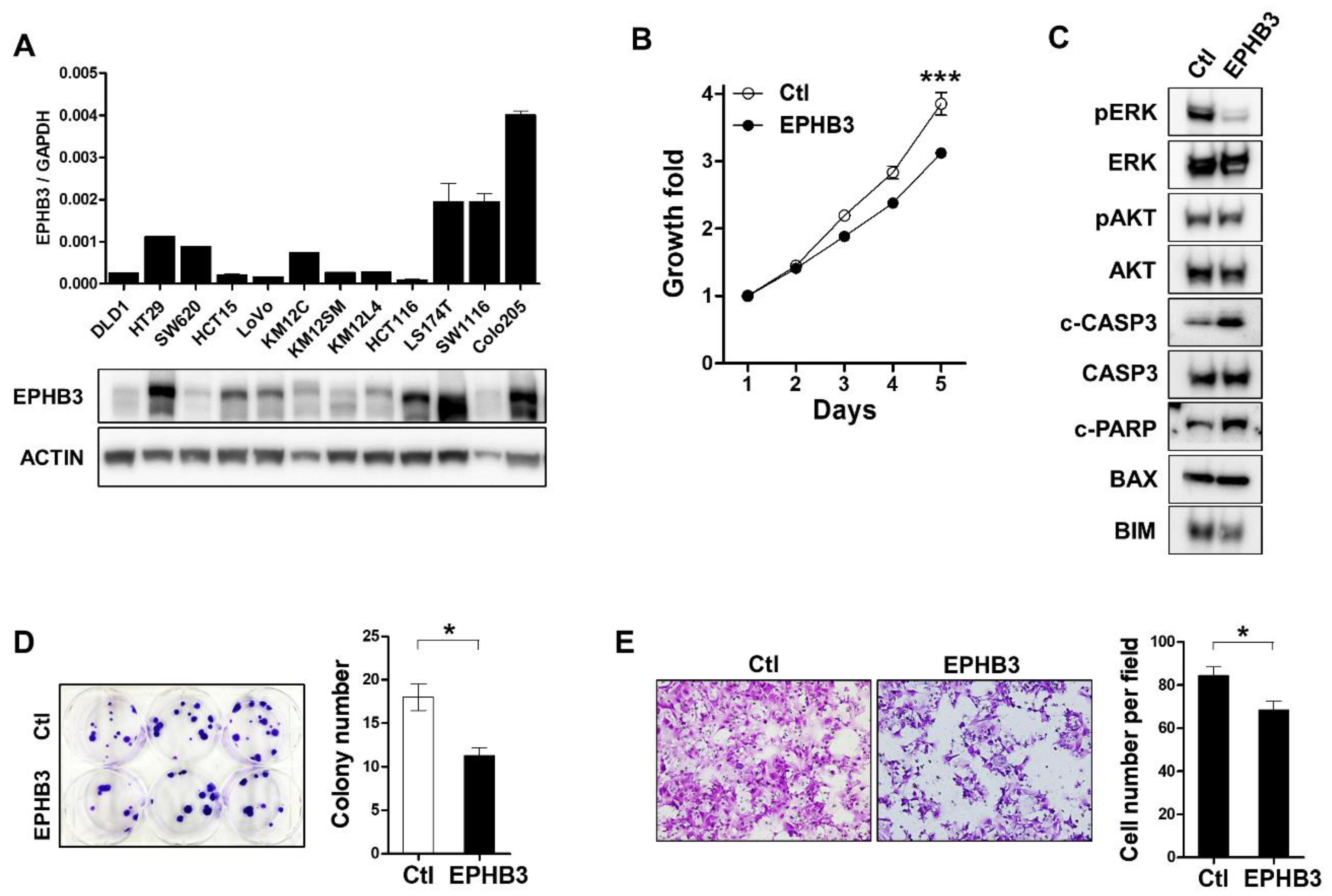
2.10. Colon Cancer Cell Lines
2.11. Antibodies
2.12. Western Blot Analysis
2.13. Transfection of EPHB3 and siRNA
2.14. Proliferation Assay and Colony Formation Assay
2.15. Migration Assay
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
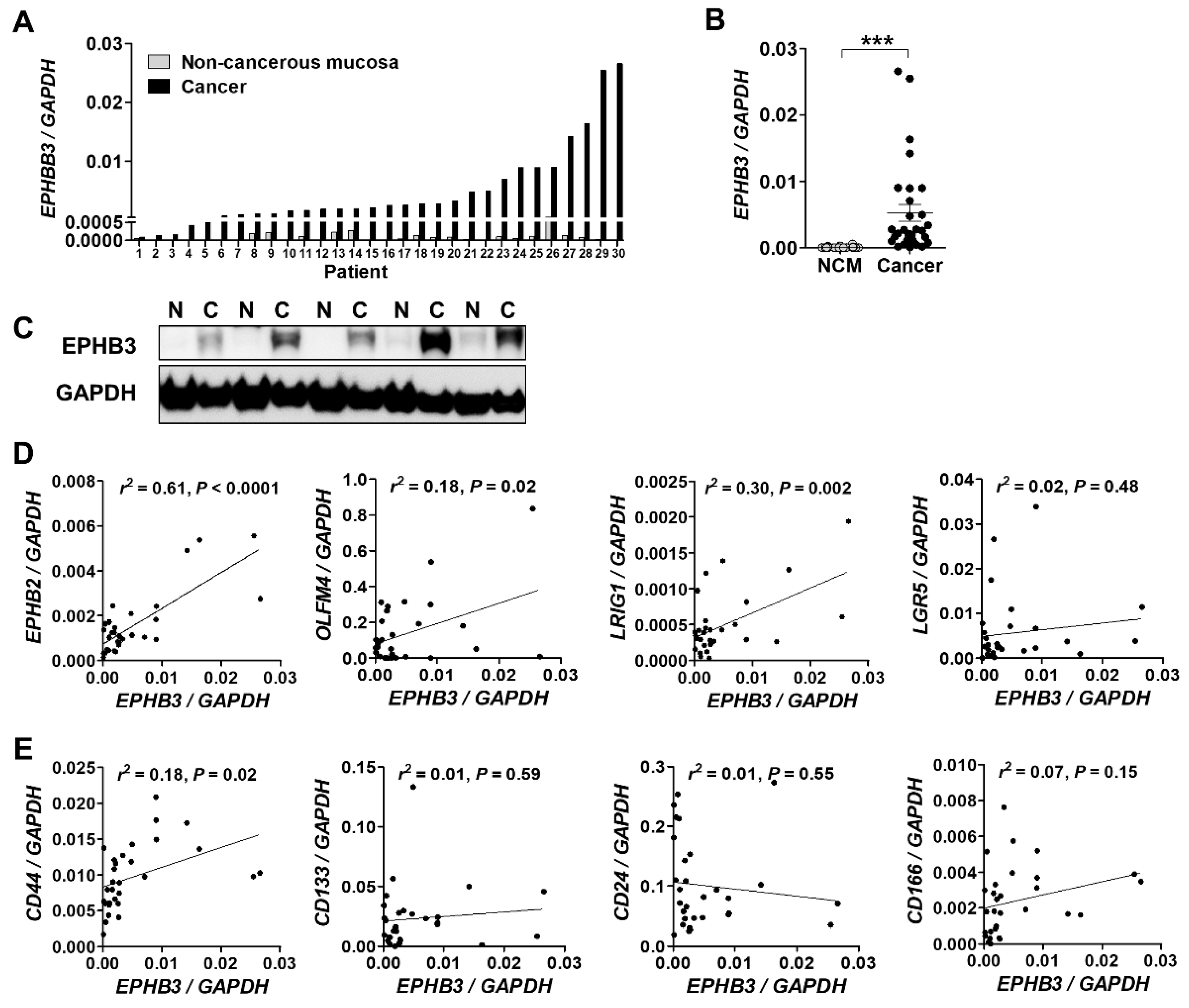
3.1. EPHB3 Expression in Human Colorectal Cancers and its Correlation with Stem Cell-Related Markers
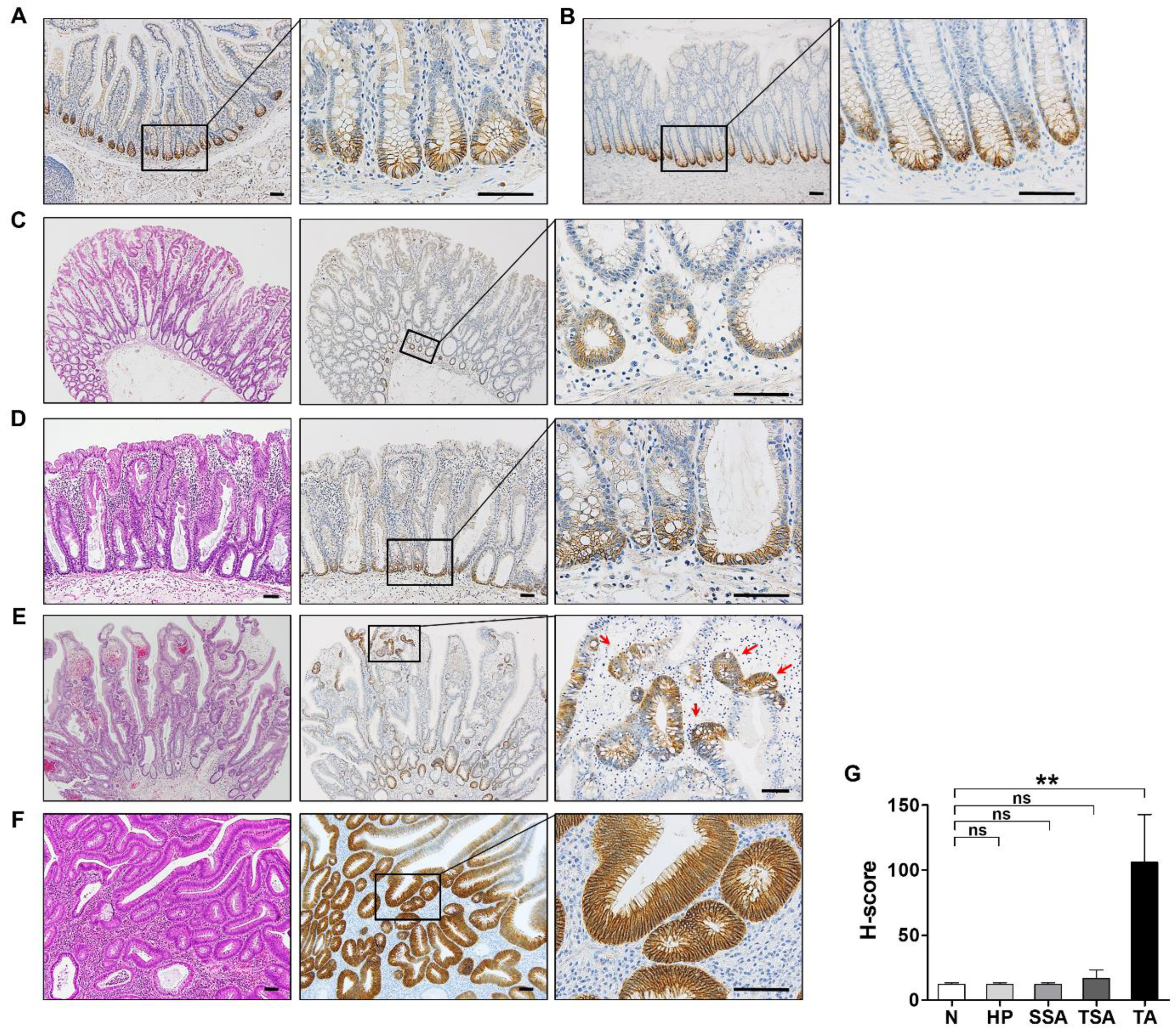
3.2. EPHB3 Expression in Colorectal Precancerous Lesions
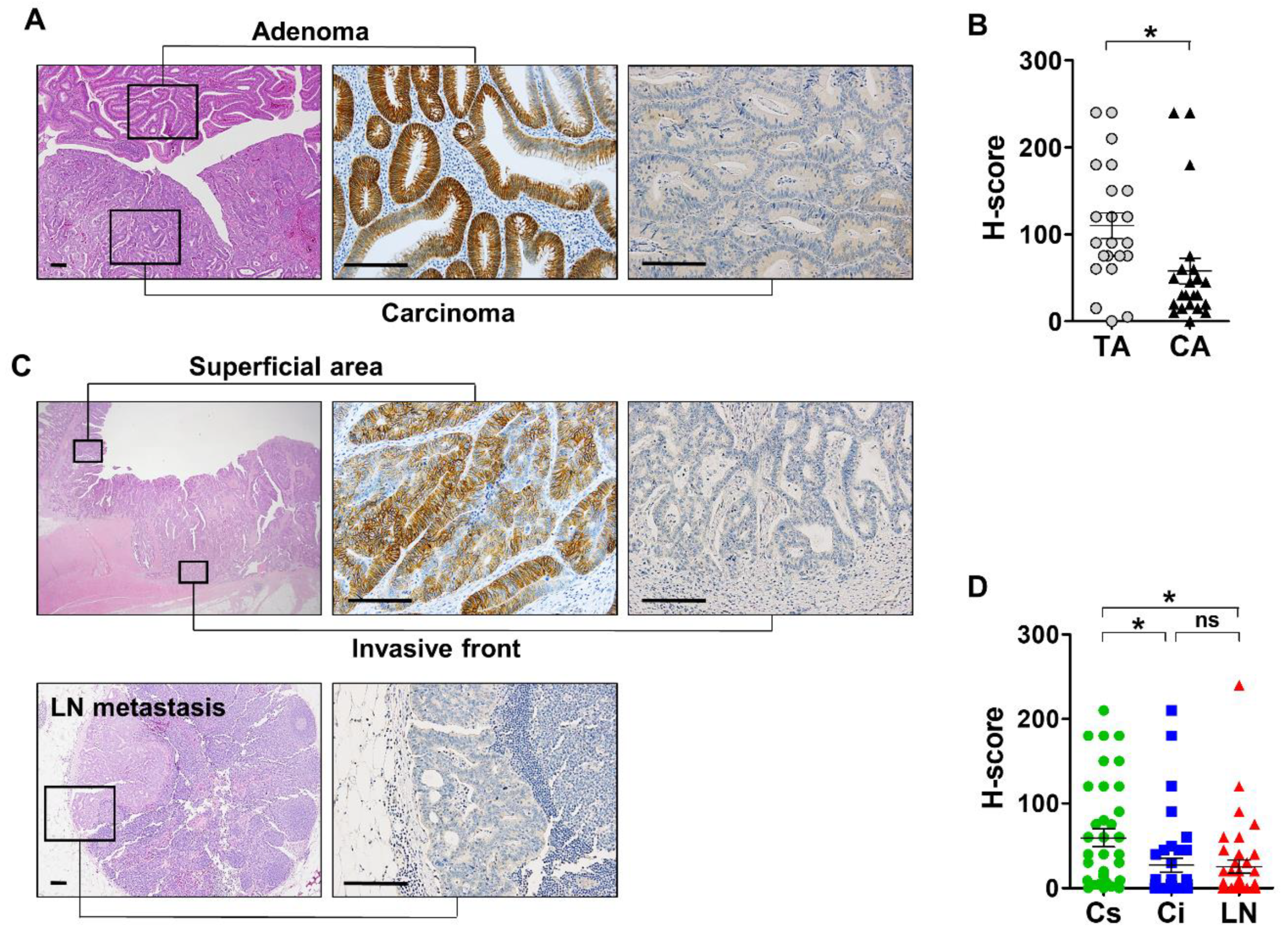
3.3. Expression Profile of EPHB3 During CRC Progression
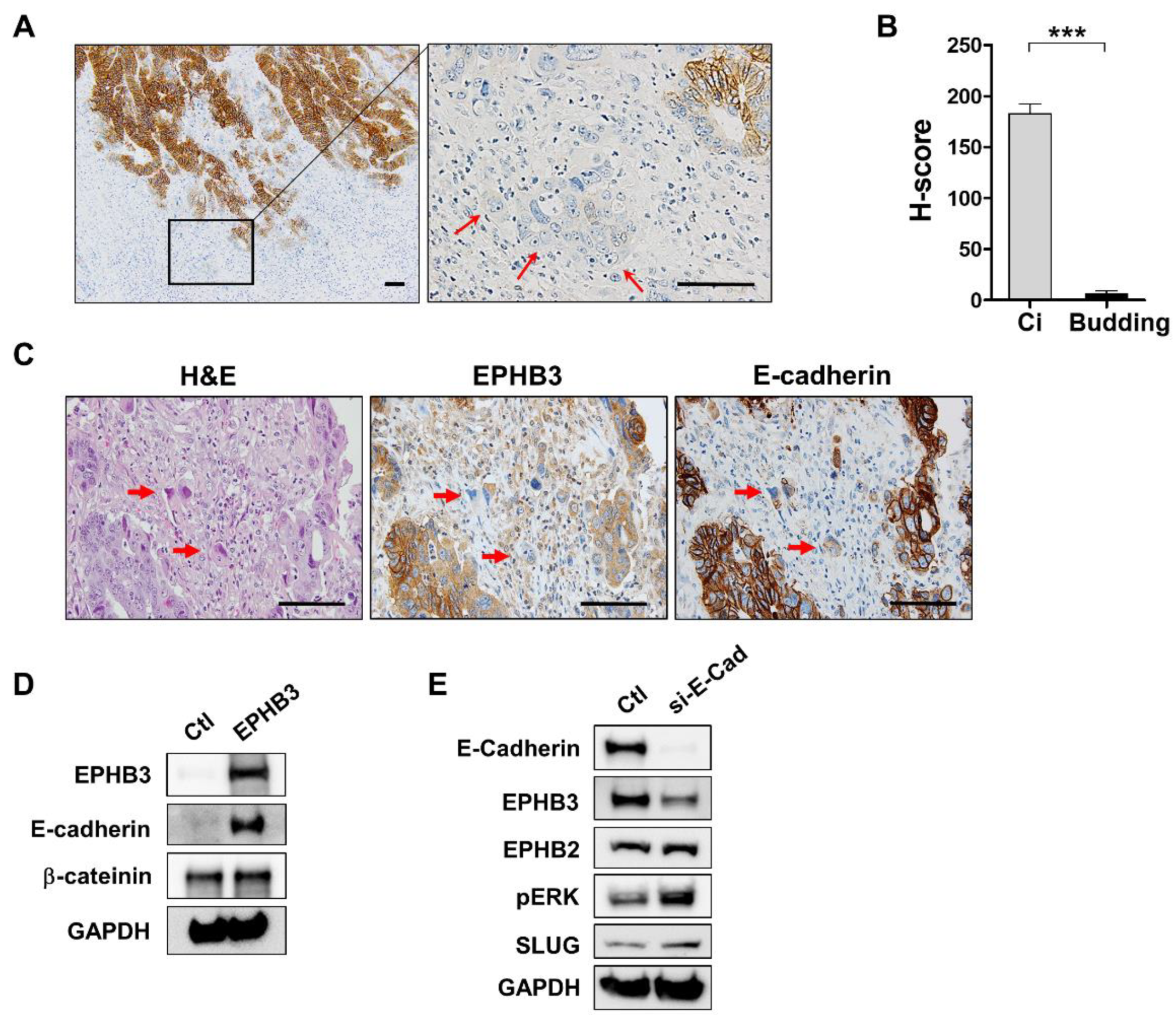
3.4. Decline of EPHB3 Expression in Budding Cancer Cells at the Invasive Front
3.5. EPHB3 Expression in CACs
3.6. Clinico-Pathological and Prognostic Significance of EPHB3 Expression in CRCs
3.7. Effects of EPHB3 Expression on the Growth and Migration of CRC Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasquale, E.B.J. Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: Bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaught, D.; Brantley-Sieders, D.M.; Chen, J. Eph receptors in breast cancer: Roles in tumor promotion and tumor suppression. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genander, M.; Frisén, J. Ephrins and Eph receptors in stem cells and cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullander, K.; Klein, R. Mechanisms and functions of Eph and ephrin signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquale, E.B. Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cell 2008, 133, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisle, J.E.; Mertens-Walker, I.; Rutkowski, R.; Herington, A.C.; Stephenson, S.-A. Eph receptors and their ligands: Promising molecular biomarkers and therapeutic targets in prostate cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1835, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E.; Henderson, J.T.; Beghtel, H.; Van den Born, M.M.; Sancho, E.; Huls, G.; Meeldijk, J.; Robertson, J.; Van de Wetering, M.; Pawson, T.; et al. β-Catenin and TCF mediate cell positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the expression of EphB/ephrinB. Cell 2002, 111, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E.; Bacani, J.; Begthel, H.; Jonkeer, S.; Gregorieff, A.; van de Born, M.; Malats, N.; Sancho, E.; Boon, E.; Pawson, T. EphB receptor activity suppresses colorectal cancer progression. Nature 2005, 435, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina, C.; Palomo-Ponce, S.; Iglesias, M.; Fernández-Masip, J.L.; Vivancos, A.; Whissell, G.; Huma, M.; Peiró, N.; Gallego, L.; Jonkheer, S. EphB–ephrin-B interactions suppress colorectal cancer progression by compartmentalizing tumor cells. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.-T.; Chang, K.-J.; Ting, C.-H.; Shen, H.-C.; Li, H.; Hsieh, F.-J. Over-expression of EphB3 enhances cell–cell contacts and suppresses tumor growth in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Z.; Huang, J.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.J.P.; Research, O. Receptor tyrosine kinase EphB3: A prognostic indicator in colorectal carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.-D.; Li, G.; Feng, Y.-X.; Zhao, J.-S.; Li, J.-J.; Sun, Z.-J.; Shi, S.; Deng, Y.-Z.; Xu, J.-F.; Zhu, Y.-Q. EphB3 is overexpressed in non–small-cell lung cancer and promotes tumor metastasis by enhancing cell survival and migration. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ji, X.D.; Gao, H.; Zhao, J.S.; Xu, J.F.; Sun, Z.J.; Deng, Y.Z.; Shi, S.; Feng, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.Q.; et al. EphB3 suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis via a PP2A/RACK1/Akt signalling complex. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubb, A.M.; Zhong, F.; Bheddah, S.; Grabsch, H.I.; Frantz, G.D.; Mueller, W.; Kavi, V.; Quirke, P.; Polakis, P.; Koeppen, H. EphB2 is a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5181–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.G.; Kim, H.S.; Chang, W.Y.; Bae, J.M.; Kang, G.H. Prognostic Significance of EPHB2 Expression in Colorectal Cancer Progression. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2018, 52, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.L.; Zhang, J.; Yuen, S.T.; Tsui, W.Y.; Chan, A.S.; Ho, C.; Ji, J.; Leung, S.Y.; Chen, X. Reduced expression of EphB2 that parallels invasion and metastasis in colorectal tumours. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.-J.; Rhee, Y.-Y.; Oh, S.; Cho, N.-Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, G.H. Expression status of wild-type HSP110 correlates with HSP110 T 17 deletion size and patient prognosis in microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, C.; Kim, W.H.; Maeng, Y.H.; Jang, B.G. Expression profile of intestinal stem cell markers in colitis-associated carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.G.; Kim, H.S.; Chang, W.Y.; Bae, J.M.; Kim, W.H.; Kang, G.H. Expression Profile of LGR5 and Its Prognostic Significance in Colorectal Cancer Progression. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 2236–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, M.; Mousavi, E.; Arab-Bafrani, Z.; Sahebkar, A.J.J.o.c.p. The most reliable surface marker for the identification of colorectal cancer stem-like cells: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 8192–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, B.; Schaeffer, D.F.; Riddell, R.H.; Kirsch, R.J. Tumor budding in colorectal carcinoma: Time to take notice. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogler, G.J. Chronic ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashiro, M. Ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Maiello, M.R.; D’Alessio, A.; Pergameno, M.; Normanno, N.J. The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT signalling pathways: Role in cancer pathogenesis and implications for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin. Their Tar. 2012, 16, S17–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jägle, S.; Rönsch, K.; Timme, S.; Andrlová, H.; Bertrand, M.; Jäger, M.; Proske, A.; Schrempp, M.; Yousaf, A.; Michoel, T. Silencing of the EPHB3 tumor-suppressor gene in human colorectal cancer through decommissioning of a transcriptional enhancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 111, 4886–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jass, J.R. HNPCC and sporadic MSI-H colorectal cancer: A review of the morphological similarities and differences. Fam. cancer 2004, 3, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.-p.; Wang, W.-y.; Ma, P.; Shuai, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wang, Y.-f.; Li, W.; Xia, R.; Chen, W.-m.; Zhang, E.-B. Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes carcinogenesis by epigenetically silencing EphB3 through EZH2 and LSD1, and predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5020–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; He, J.; Wang, Y.-f.; Fan, Y.; Fang, N.; Qian, J.; Xu, T.-p.; Guo, R.-h. EZH2-mediated epigenetic suppression of EphB3 inhibits gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis by affecting E-cadherin and vimentin expression. Gene 2019, 686, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prall, F. Tumour budding in colorectal carcinoma. Histopahtology 2007, 50, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönsch, K.; Jägle, S.; Rose, K.; Seidl, M.; Baumgartner, F.; Freihen, V.; Yousaf, A.; Metzger, E.; Lassmann, S.; Schüle, R. SNAIL1 combines competitive displacement of ASCL2 and epigenetic mechanisms to rapidly silence the EPHB3 tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.; Sugai, T.; Eizuka, M.; Tsuchida, K.; Sugimoto, R.; Mue, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Osakabe, M.; Uesugi, N.; Ishida, K. Tumor budding at the invasive front of colorectal cancer may not be associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 60, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total (%) | EPHB3 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative (%) | Positive (%) | |||
| Patients | 610 (100) | 463 (76) | 147 (24) | |
| Age | ||||
| ≥60 | 345 (57) | 254 (74) | 91 (26) | 0.152 † |
| <60 | 265 (43) | 209 (79) | 56 (21) | |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 240 (39) | 178 (74) | 62 (26) | 0.439 † |
| Male | 370 (61) | 285 (77) | 85 (23) | |
| Location | ||||
| Proximal | 161 (26) | 115 (71) | 46 (29) | 0.133 † |
| Distal | 449 (74) | 348 (78) | 101 (22) | |
| Differentiation | ||||
| WD | 46 (8) | 26 (57) | 20 (44) | 0.002 # |
| MD | 544 (89) | 419 (77) | 125 (23) | |
| PD | 20 (3) | 18 (90) | 2 (10) | |
| Mucin | ||||
| Absent | 539 (88) | 416 (77) | 123 (28) | 0.042 # |
| Present | 71 (12) | 47 (66) | 24 (34) | |
| TIL > 8 | ||||
| Negative | 462 (76) | 369 (80) | 93 (20) | <0.001 † |
| Positive | 148 (24) | 94 (64) | 54 (37) | |
| Lymphatic invasion | ||||
| Negative | 341 (56) | 232 (68) | 109 (32) | <0.001 † |
| Positive | 269 (44) | 231 (86) | 38 (14) | |
| Venous invasion | ||||
| Negative | 526 (86) | 389 (74) | 137 (26) | 0.004 † |
| Positive | 84 (14) | 74 (88) | 10 (12) | |
| TNM_7th | ||||
| I | 95 (156) | 46 (48) | 49 (52) | <0.001 # |
| II | 197 (32) | 149 (76) | 48 (24) | |
| III | 221 (36) | 187 (85) | 34 (15) | |
| IV | 97 (16) | 81 (84) | 16 (16) | |
| β-catenin | ||||
| No nuclear stain | 225 (37) | 172 (76) | 53 (24) | 0.845 † |
| Nuclear stain | 385 (63) | 291 (76) | 94 (24) | |
| Characteristics | Total (%) | EPHB3 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative (%) | Positive (%) | |||
| Patients | 610 (100) | 463 (76) | 147 (24) | |
| CIMP | ||||
| Negative and Low | 570 (93) | 429 (75) | 141 (25) | 0.185 † |
| High | 40 (7) | 34 (85) | 6 (15) | |
| MSI | ||||
| Negative and Low | 559 (92) | 434 (78) | 125 (22) | 0.002 † |
| High | 51 (8) | 29 (57) | 22 (43) | |
| Total (%) | EPHB3 | p-Value | ||
| Negative (%) | Positive (%) | |||
| Patients | 590 (100) | 447 (76) | 143 (24) | |
| KRAS | ||||
| Wt | 432 (73) | 329 (76) | 103 (24) | 0.745 † |
| Mt | 158 (27) | 118 (75) | 40 (25) | |
| Total (%) | EPHB3 | p-Value | ||
| Negative (%) | Positive (%) | |||
| Patients | 605 (100) | 458 (76) | 147 (24) | |
| BRAF | ||||
| Wt | 572 (95) | 430 (75) | 142 (25) | 0.296 † |
| Mt | 33 (5) | 28 (85) | 5 (15) | |
| Variables | Category | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value a | ||
| Age | >60/<60 | 1.271 | 1.008–1.602 | 0.043 | 1.668 | 1.215–2.288 | 0.002 |
| Gender | Female/male | 0.974 | 0.774–1.227 | 0.825 | |||
| Site | Distal/proximal | 0.7 | 0.549–0.894 | 0.004 | 0.742 | 0.526–1.047 | 0.090 |
| Differentiation | Poor/moderate/well | 3.31 | 2.280–4.805 | 0.000 | 1.366 | 0.807–2.311 | 0.245 |
| Lymphatic invasion | Positive/negative | 2.917 | 2.309–3.685 | 0.000 | 1.122 | 0.810–1.554 | 0.489 |
| Venous invasion | Positive/negative | 3.202 | 2.487–4.123 | 0.000 | 1.845 | 1.306–2.607 | 0.001 |
| TIL > 8 | Positive/negative | 0.682 | 0.465–1.001 | 0.050 | 0.735 | 0.495–1.090 | 0.126 |
| Mucin | Present/absent | 1.048 | 0.670–1.640 | 0.836 | |||
| Stage | IV/III/II/I | 3.476 | 2.974–4.064 | 0.000 | 2.758 | 2.228–3.414 | <0.001 |
| KRAS mutation | Present/absent | 1.05 | 0.745–1.480 | 0.779 | |||
| BRAF mutation | Present/absent | 1.307 | 0.709–2.409 | 0.390 | |||
| CIMP | High/low or negative | 1.964 | 1.205–3.201 | 0.007 | 0.735 | 0.495–1.090 | 0.423 |
| MSI | Unstable/stable | 0.865 | 0.481–1.554 | 0.627 | |||
| Nuclear β-catenin | Positive/negative | ||||||
| EPHB3 | Positive/negative | 0.568 | 0.374–0.862 | 0.008 | 0.832 | 0.541–1.278 | 0.400 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, B.G.; Kim, H.S.; Bae, J.M.; Kim, W.H.; Hyun, C.L.; Kang, G.H. Expression Profile and Prognostic Significance of EPHB3 in Colorectal Cancer. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040602
Jang BG, Kim HS, Bae JM, Kim WH, Hyun CL, Kang GH. Expression Profile and Prognostic Significance of EPHB3 in Colorectal Cancer. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(4):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040602
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Bo Gun, Hye Sung Kim, Jeong Mo Bae, Woo Ho Kim, Chang Lim Hyun, and Gyeong Hoon Kang. 2020. "Expression Profile and Prognostic Significance of EPHB3 in Colorectal Cancer" Biomolecules 10, no. 4: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040602
APA StyleJang, B. G., Kim, H. S., Bae, J. M., Kim, W. H., Hyun, C. L., & Kang, G. H. (2020). Expression Profile and Prognostic Significance of EPHB3 in Colorectal Cancer. Biomolecules, 10(4), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040602






