Effect of Substrate Reduction Therapy in Comparison to Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Immune Aspects and Bone Involvement in Gaucher Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagral, A. Gaucher disease. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2014, 4, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goker-Alpan, O. Therapeutic approaches to bone pathology in Gaucher disease: Past, present and future. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 104, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; McDonald, J.M. Disorders of bone remodeling. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Dar, H.Y.; Mishra, P.K. Immunoporosis: Immunology of Osteoporosis-Role of T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzetti, M.; Rucci, N. Updates on Osteoimmunology: What’s New on the Cross-Talk Between Bone and Immune System. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, P.K.; Liu, J.; Yang, M.; Nottoli, T.; McGrath, J.; Jain, D.; Zhang, K.; Keutzer, J.; Chuang, W.L.; Mehal, W.Z.; et al. Glucocerebrosidase gene-deficient mouse recapitulates Gaucher disease displaying cellular and molecular dysregulation beyond the macrophage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19473–19478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, J.M.; Rozenfeld, P. Pathogenesis of Bone Alterations in Gaucher Disease: The Role of Immune System. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 192761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.K.; Grabowski, G.A. Immunological cells and functions in Gaucher disease. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2013, 18, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, L.; Arosa, F.A.; Lacerda, R.; Cabeda, J.; Porto, G.; Amaral, O.; Fortuna, A.; Pinto, R.; Oliveira, P.; McLaren, C.E.; et al. T cell numbers relate to bone involvement in Gaucher disease. Blood Cellsmolecules Dis. 1999, 25, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, G.J.; Kostakis, P.; Vincent, C.; Farrugia, A.N.; Houchins, J.P.; Findlay, D.M.; Evdokiou, A.; Zannettino, A.C. RANK Expression as a cell surface marker of human osteoclast precursors in peripheral blood, bone marrow, and giant cell tumors of bone. J. Bone Miner. Res.: Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibbrandt, A.; Penninger, J.M. Novel functions of RANK(L) signaling in the immune system. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 658, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzmann, M.N. Bone and the Immune System. Toxicol. Pathol. 2017, 45, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, L.L.; Mohan, D. Gaucher disease and its treatment options. Ann. Pharmacother. 2013, 47, 1182–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrow, J.; Scott, C.R. Long-term treatment outcomes in Gaucher disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, S19–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goker-Alpan, O. Optimal therapy in Gaucher disease. Clin. Risk Manag 2010, 6, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van Rossum, A.; Holsopple, M. Enzyme Replacement or Substrate Reduction? A Review of Gaucher Disease Treatment Options. Hosp. Pharm. 2016, 51, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimran, A.; Elstein, D. Management of Gaucher disease: Enzyme replacement therapy. Pediatric Endocrinol. Rev.: Per 2014, 12, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Limgala, R.P.; Ioanou, C.; Plassmeyer, M.; Ryherd, M.; Kozhaya, L.; Austin, L.; Abidoglu, C.; Unutmaz, D.; Alpan, O.; Goker-Alpan, O. Time of Initiating Enzyme Replacement Therapy Affects Immune Abnormalities and Disease Severity in Patients with Gaucher Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonder, S.U.; Limgala, R.P.; Ivanova, M.M.; Ioanou, C.; Plassmeyer, M.; Marti, G.E.; Alpan, O.; Goker-Alpan, O. Persistent immune alterations and comorbidities in splenectomized patients with Gaucher disease. Blood Cellsmolecules Dis. 2016, 59, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Breemen, M.J.; de Fost, M.; Voerman, J.S.; Laman, J.D.; Boot, R.G.; Maas, M.; Hollak, C.E.; Aerts, J.M.; Rezaee, F. Increased plasma macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha and MIP-1beta levels in type 1 Gaucher disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1772, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, P.K.; Deegan, P.; Vellodi, A.; Cole, J.A.; Yeh, M.; Weinreb, N.J. Timing of initiation of enzyme replacement therapy after diagnosis of type 1 Gaucher disease: Effect on incidence of avascular necrosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 147, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dussen, L.; Biegstraaten, M.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; Hollak, C.E. Modelling Gaucher disease progression: Long-term enzyme replacement therapy reduces the incidence of splenectomy and bone complications. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, N.; Taylor, J.; Cox, T.; Yee, J.; vom Dahl, S. A benchmark analysis of the achievement of therapeutic goals for type 1 Gaucher disease patients treated with imiglucerase. Am. J. Hematol. 2008, 83, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smid, B.E.; Ferraz, M.J.; Verhoek, M.; Mirzaian, M.; Wisse, P.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Hollak, C.E.; Aerts, J.M. Biochemical response to substrate reduction therapy versus enzyme replacement therapy in Gaucher disease type 1 patients. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2016, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceravolo, F.; Grisolia, M.; Sestito, S.; Falvo, F.; Moricca, M.T.; Concolino, D. Combination therapy in a patient with chronic neuronopathic Gaucher disease: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, D.; Patterson, M.A. Combined miglustat and enzyme replacement therapy in two patients with type 1 Gaucher disease: Two case reports. J. Med. Case Rep. 2018, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gravallese, E.M. Osteopontin: A bridge between bone and the immune system. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


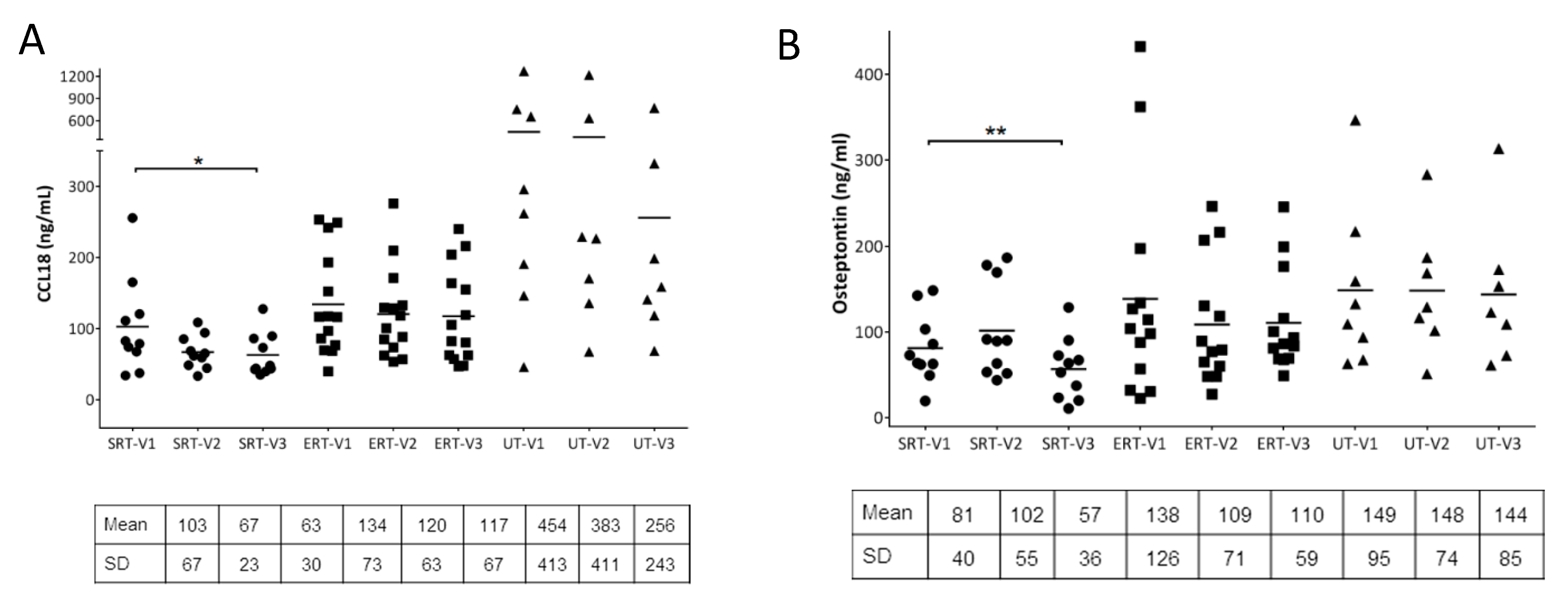
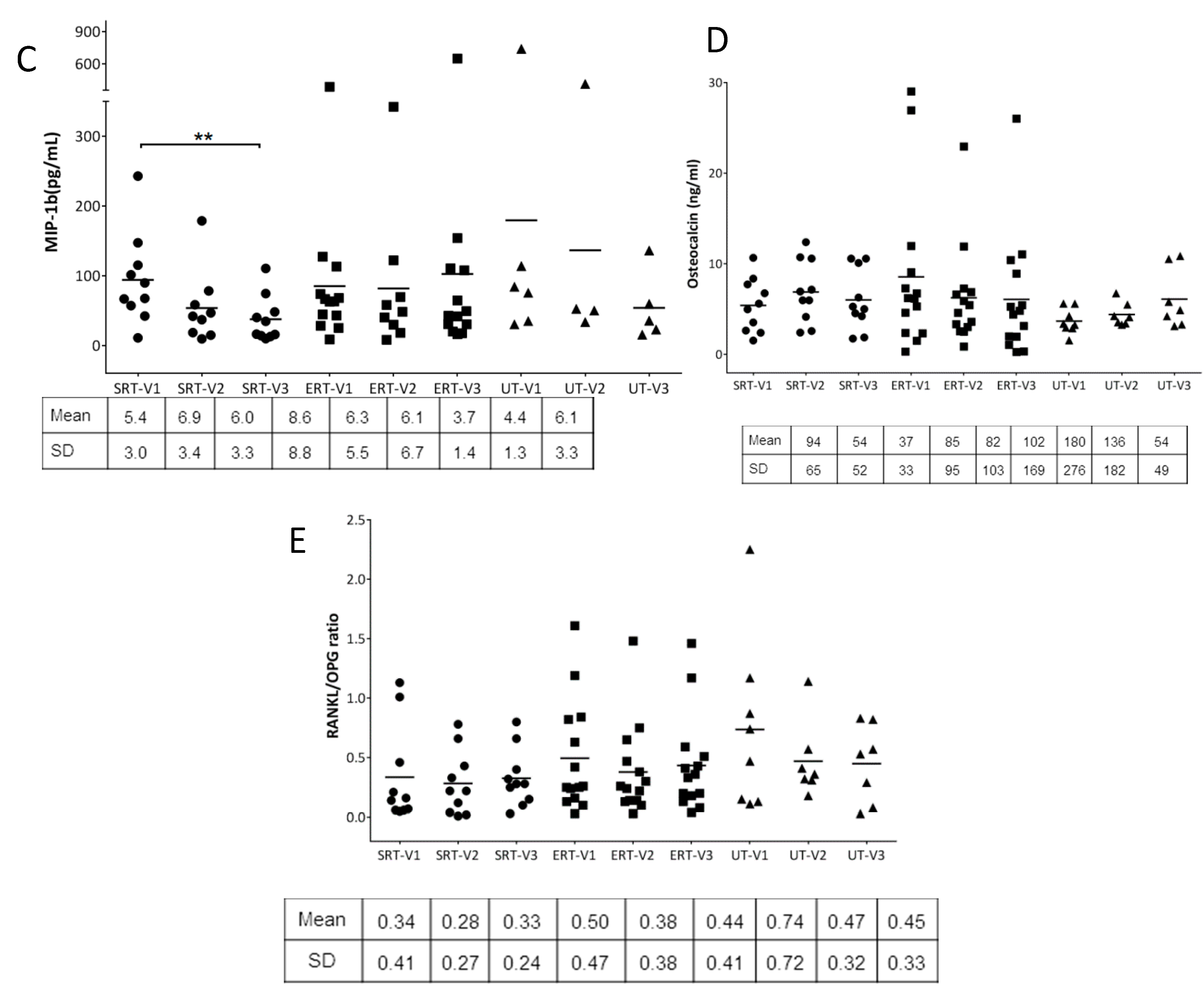
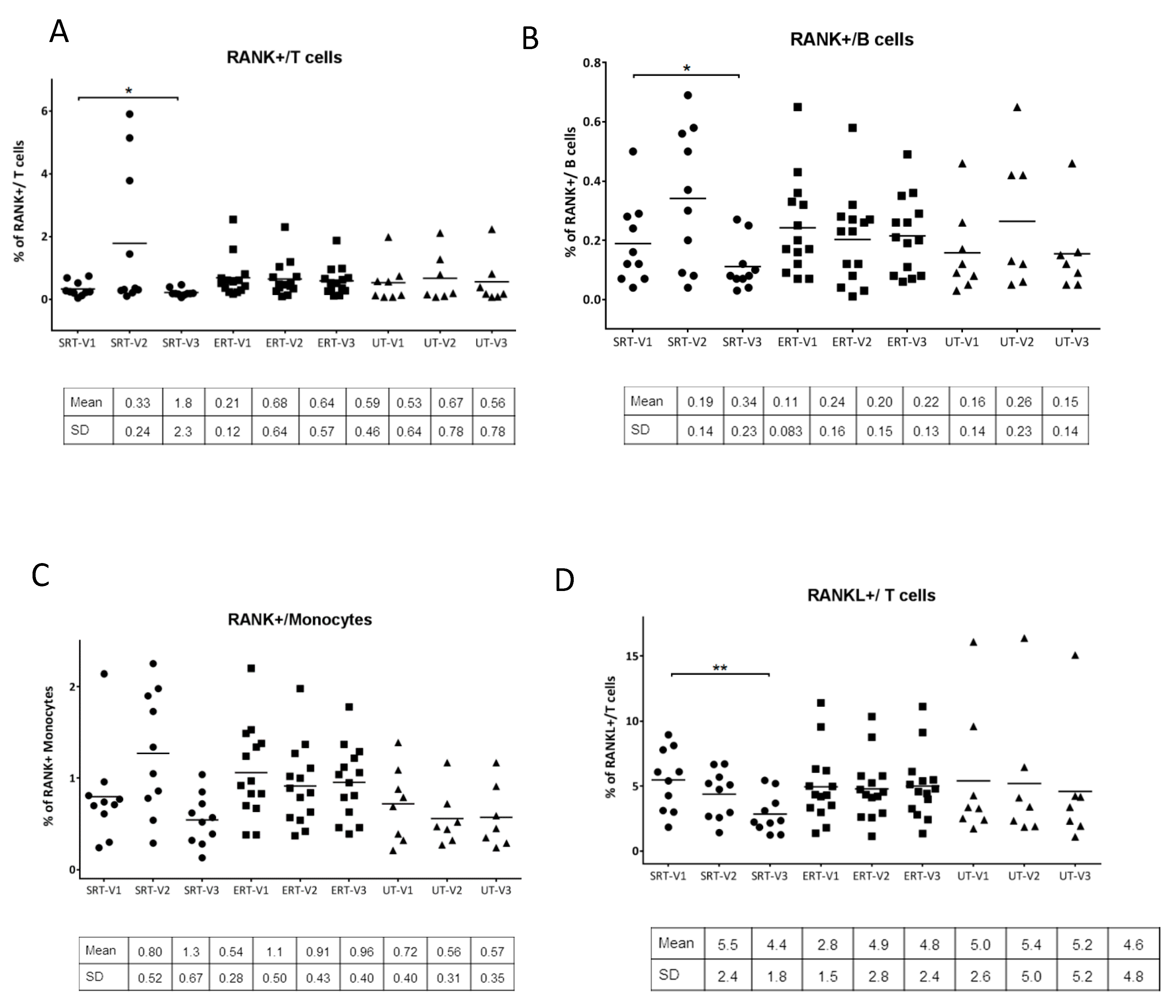
| ID | Gender | Age (Years) | Genotype | Initial Visit | Follow-Up Visit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRT-01 | F | 50 | N370S/N370S | ERT ¶ | SRT |
| SRT-02 | M | 59 | N370S/N370S | ERT * | SRT |
| SRT-03 | F | 46 | N370S/N370S | ERT * | SRT |
| SRT-04 | F | 57 | N370S/N370S | ERT * | SRT |
| SRT-05 | F | 35 | N370S/R463C | ERT * | SRT |
| SRT-06 | F | 37 | N370S/R463C | ERT * | SRT |
| SRT-07 | F | 24 | N370S/L444P | ERT * | SRT |
| SRT-08 | F | 62 | N370S/R463C | ERT * | SRT |
| SRT-09 | F | 52 | 1448C/L444P | ERT ¶ | SRT |
| SRT-10 | F | 47 | N370S/N370S | ERT ¶ | SRT |
| ERT-01 | F | 34 | N370S/L444P | ERT ¶ | ERT ¶ |
| ERT-02 | F | 35 | N370S/R120Q | ERT ¶ | ERT ¶ |
| ERT-03 | F | 45 | N370S/N370S | ERT ¶ | ERT ¶ |
| ERT-04 | F | 61 | N370S/L444P | ERT ¶ | ERT ¶ |
| ERT-05 | F | 20 | L444P/L444P | ERT * | ERT * |
| ERT-06 | M | 18 | L444P/L444P | ERT * | ERT * |
| ERT-07 | F | 10 | L444P/L444P | ERT * | ERT * |
| ERT-08 | F | 27 | N370S/L444P | ERT * | ERT * |
| ERT-09 | F | 42 | N370S/L444P | ERT * | ERT * |
| ERT-10 | M | 50 | N370S/L444P | ERT ¶ | ERT ¶ |
| ERT-11 | M | 76 | N370S/N370S | ERT * | ERT * |
| ERT-12 | M | 14 | L444P/L444P | ERT * | ERT * |
| ERT-13 | F | 40 | L444P/R463C | ERT ¶ | ERT ¶ |
| ERT-14 | F | 23 | N370S/W381X | ERT ¶ | ERT ¶ |
| UT-01 | M | 27 | C677T/C677T | UT | SRT |
| UT-02 | F | 56 | N370S/N370S | UT | SRT |
| UT-03 | M | 38 | N370S/N370S | UT | SRT |
| UT-04 | M | 34 | N370S/N370S | UT | ERT ¶ |
| UT-05 | F | 36 | N370S/N370S | UT | UT |
| UT-06 | F | 32 | N370S/N370S | UT | UT |
| UT-07 | F | 61 | N370S/N370S | UT | UT |
| UT-08 | F | 58 | N370S/N370S | UT | UT |
| ID | Splenectomy | Bone Surgery | Bone Pain | Bone Marrow Infiltration | EM-Flask Deformity | Cystic/ Lytic Lesions | Pathologic Fractures | Osteo Penia | Osteo Porosis | AVN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRT-01 | No | No | Moderate | Moderate dark marrow | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| SRT-02 | No | No | Moderate | Patchy dark marrow | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| SRT-03 | No | No | Moderate | Patchy dark marrow | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| SRT-04 | No | No | Mild | Patchy dark marrow | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| SRT-05 | No | No | Mild | Mild symmetric dark marrow | No | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| SRT-06 | No | No | Mild | Mild symmetric dark marrow | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| SRT-07 | No | No | No | Patchy dark marrow | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| SRT-08 | Yes | Yes | Moderate | Extensive dark marrow | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| SRT-09 | Yes | Yes | Moderate | Mild symmetric dark marrow | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| SRT-10 | Yes | Yes | Severe | Marrow infarcts | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ERT-01 | No | No | No | Mild patchy dark marrow | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| ERT-02 | No | No | Moderate | Patchy, hypo intense marrow | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| ERT-03 | Yes | Yes | No | Heterogeneous dark marrow | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| ERT-04 | Yes | Yes | Moderate | Marrow infarcts/patchy dark | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ERT-05 | No | No | No | Patchy dark marrow | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| ERT-06 | No | No | No | Patchy dark marrow | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| ERT-07 | No | No | No | Patchy dark marrow | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| ERT-08 | No | No | No | Patchy dark marrow | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| ERT-09 | No | Yes | Moderate | Marrow infarcts | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| ERT-10 | No | No | No | Marrow infarcts | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ERT-11 | No | No | Moderate | Marrow infarcts | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ERT-12 | No | No | Moderate | Patchy dark marrow | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| ERT-13 | Yes | Yes | Severe | Marrow infarcts | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ERT-14 | No | No | Mild | Symmetric dark marrow | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| UT-01 | No | No | No | Patchy dark marrow | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| UT-02 | No | Yes | Moderate | Marrow infarcts/dark marrow | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| UT-03 | No | No | No | Confluent dark marrow | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| UT-04 | Yes | No | No | Patchy dark marrow | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| UT-05 | No | No | No | Symmetric dark marrow | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| UT-06 | No | No | No | Symmetric dark marrow | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| UT-07 | No | No | Moderate | Mild symmetric dark marrow | No | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| UT-08 | No | No | Mild | Patchy dark marrow | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Limgala, R.P.; Goker-Alpan, O. Effect of Substrate Reduction Therapy in Comparison to Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Immune Aspects and Bone Involvement in Gaucher Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040526
Limgala RP, Goker-Alpan O. Effect of Substrate Reduction Therapy in Comparison to Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Immune Aspects and Bone Involvement in Gaucher Disease. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(4):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040526
Chicago/Turabian StyleLimgala, Renuka P., and Ozlem Goker-Alpan. 2020. "Effect of Substrate Reduction Therapy in Comparison to Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Immune Aspects and Bone Involvement in Gaucher Disease" Biomolecules 10, no. 4: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040526
APA StyleLimgala, R. P., & Goker-Alpan, O. (2020). Effect of Substrate Reduction Therapy in Comparison to Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Immune Aspects and Bone Involvement in Gaucher Disease. Biomolecules, 10(4), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040526





