Reduced Local Response to Corticosteroids in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Asthma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Preparation
2.2. Corticosteroid Sensitivity
2.3. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.5. In-Cell Western Assay
2.6. Cell lysis, Immunoprecipitation, and Western Blotting
2.7. Phosphatase Activity
2.8. RNA Interference
2.9. Transfection
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
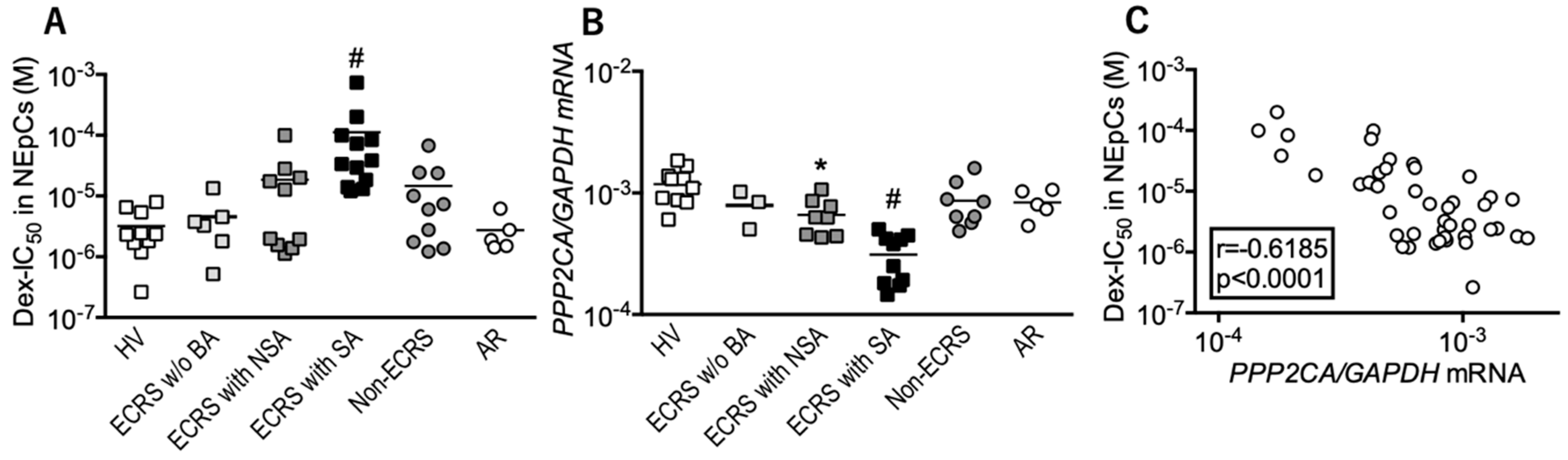
3.1. Local Responses to Corticosteroid are Reduced in ECRS Patients with Asthma
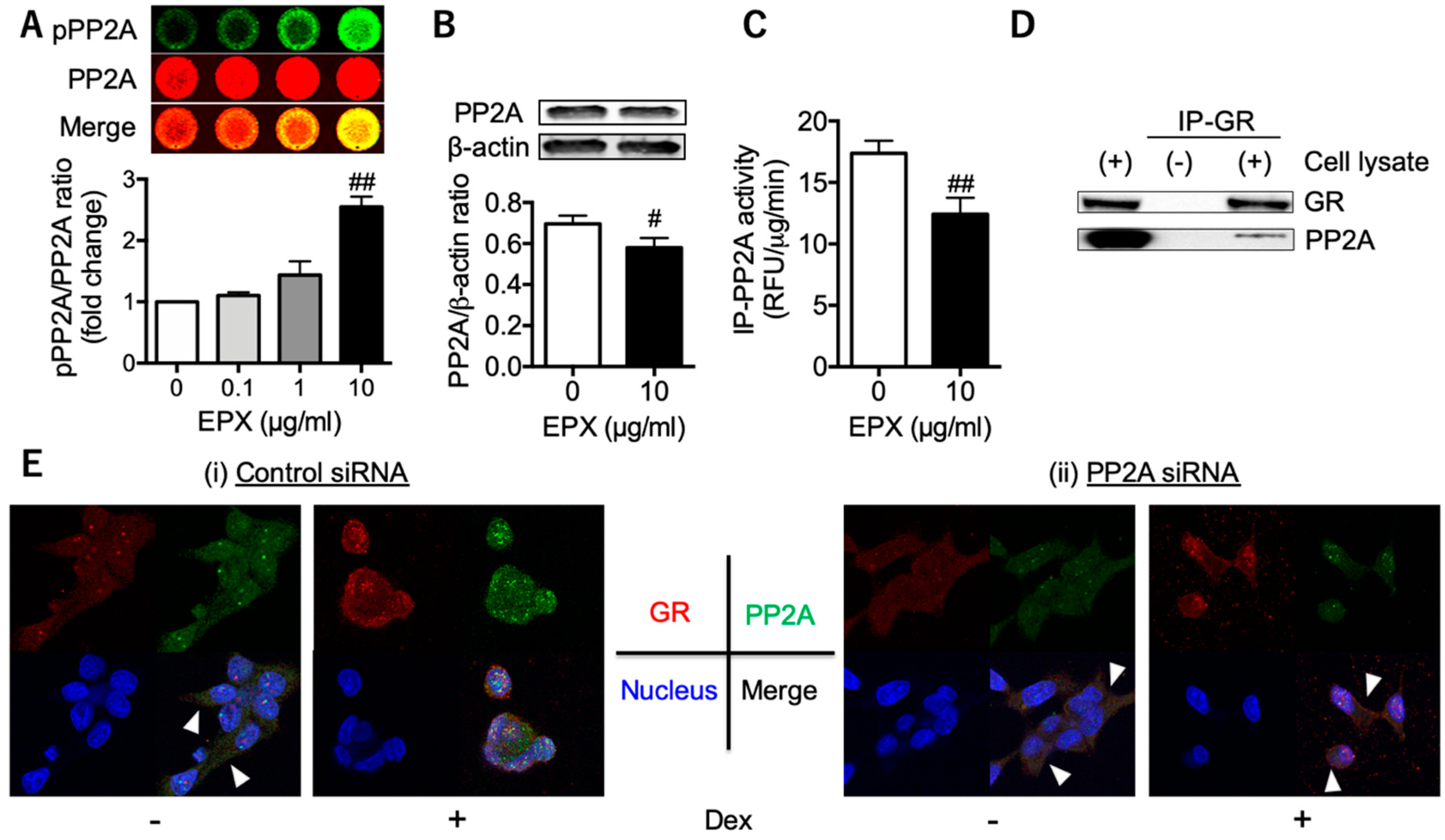
3.2. Decreased PP2A in Eosinophilic Inflammation Leads to Reduced GR Nuclear Translocation
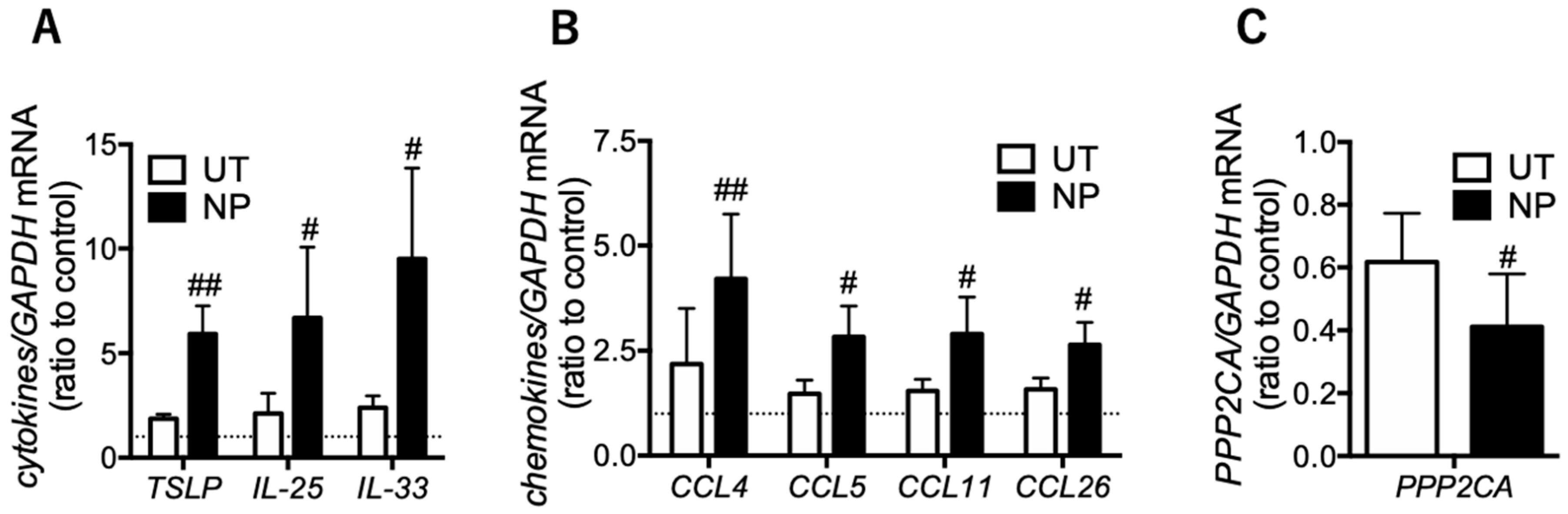
3.3. Eosinophilic Inflammatory Mediators are Increased in the Epithelial Cells of Nasal Polyps
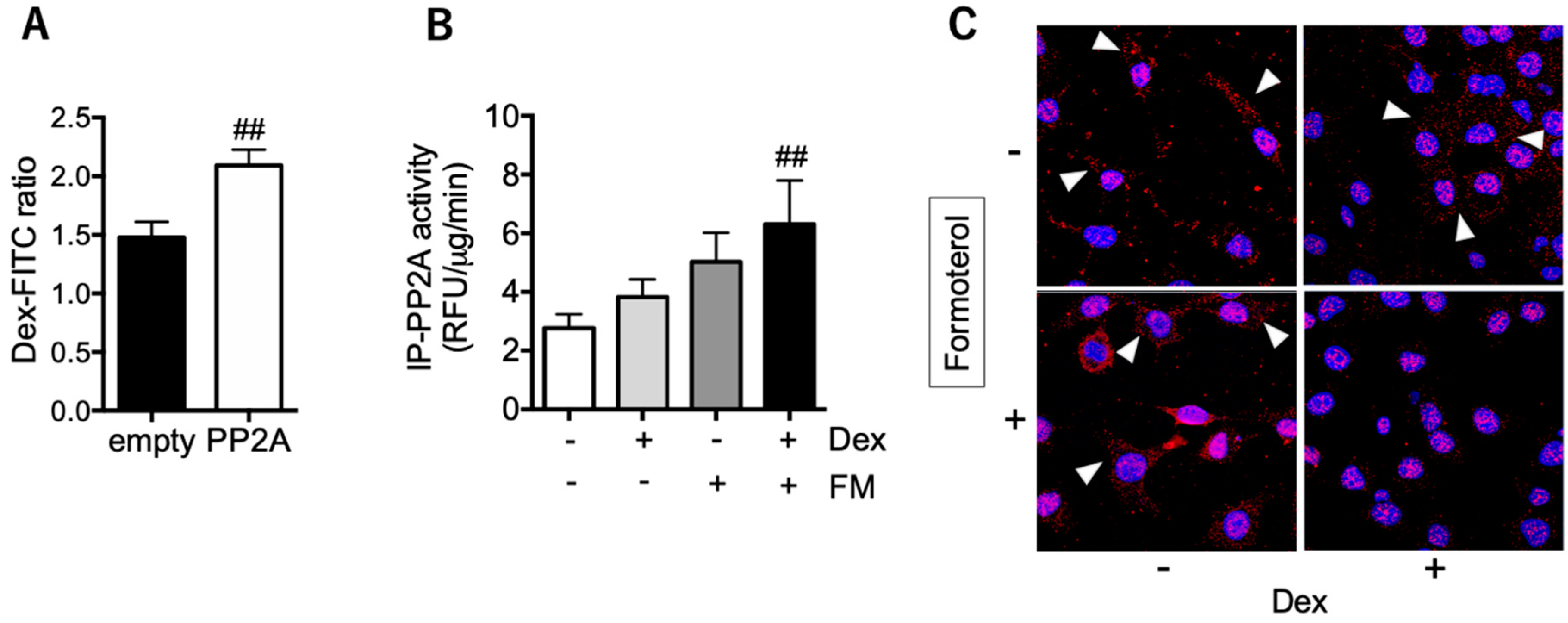
3.4. PP2A may Present a Promising Therapeutic Target for Tocal Corticosteroid Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ishidoya, J.; Sakuma, Y.; Tsukuda, M. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan. Allergol. Int. 2010, 59, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Bo, M.; Holtappels, G.; Zheng, M.; Lou, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Bachert, C. Diversity of TH cytokine profiles in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: A multicenter study in Europe, Asia, and Oceania. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Hirota, T.; Kamijo, A.; Ishii, H.; Hatsushika, K.; Fujieda, S.; Ishitoya, J.; Masuyama, K.; Tamari, M. Lung functions of Japanese patients with chronic rhinosinusitis who underwent endoscopic sinus surgery. Allergol. Int. 2014, 63, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Asako, M.; Kanda, A.; Tomoda, K.; Yasuba, H. A novel therapeutic use of HFA-BDP metereddose inhaler for asthmatic patients with rhinosinusitis: Case series. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2014, 52, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Asako, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Yasuba, H.; Tomoda, K.; Kanda, A. Replacement of SFC-DPI with SFC-MDI exhaled through the nose improves eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in patients with bronchial asthma. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2017, 55, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Yasuba, H.; Asako, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Takano, H.; Tomoda, K.; Kanda, A.; Iwai, H. HFA-BDP Metered-Dose Inhaler Exhaled Through the Nose Improves Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Bronchial Asthma: A Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Study. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, T.; Sakashita, M.; Haruna, T.; Asaka, D.; Takeno, S.; Ikeda, H.; Nakayama, T.; Seki, N.; Ito, S.; Murata, J.; et al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: The JESREC Study. Allergy 2015, 70, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milara, J.; Peiro, T.; Armengot, M.; Frias, S.; Morell, A.; Serrano, A.; Cortijo, J. Mucin 1 downregulation associates with corticosteroid resistance in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, O.S.; Ito, K.; Maneechotesuwan, K.; Ito, M.; Johnson, M.; Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M. Glucocorticoid receptor nuclear translocation in airway cells after inhaled combination therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2005, 172, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mercado, N.; Barnes, P.J.; Ito, K. Defects of protein phosphatase 2A causes corticosteroid insensitivity in severe asthma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ito, K.; Kanda, A.; Tomoda, K.; Miller-Larsson, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Mercado, N. Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-RR regulates corticosteroid sensitivity. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ito, K.; Kanda, A.; Tomoda, K.; Mercado, N.; Barnes, P.J. Impaired Dual-Specificity Protein Phosphatase DUSP4 Reduces Corticosteroid Sensitivity. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 91, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terna, E.; Luukkainen, A.; Seppala, M.; Renkonen, R.; Huhtala, H.; Tommola, S.; Paavonen, T.; Kauppi, P.; Tynninen, O.; Jeskanen, L.; et al. The expression of cancerous inhibitor protein phosphatase 2A in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016, 136, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Corticosteroid resistance in patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licona-Limon, P.; Kim, L.K.; Palm, N.W.; Flavell, R.A. TH2, allergy and group 2 innate lymphoid cells. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Konno, Y.; Kanda, A.; Yamada, Y.; Yasuba, H.; Sakata, Y.; Fukuchi, M.; Tomoda, K.; Iwai, H.; Ueki, S. Critical role of CCL4 in eosinophil recruitment into the airway. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, B.L.; Siciliano, S.J.; DeMartino, J.A.; Malkowitz, L.; Sirotina, A.; Springer, M.S. Cloning, expression, and characterization of the human eosinophil eotaxin receptor. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provost, V.; Larose, M.C.; Langlois, A.; Rola-Pleszczynski, M.; Flamand, N.; Laviolette, M. CCL26/eotaxin-3 is more effective to induce the migration of eosinophils of asthmatics than CCL11/eotaxin-1 and CCL24/eotaxin-2. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raport, C.J.; Gosling, J.; Schweickart, V.L.; Gray, P.W.; Charo, I.F. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel human CC chemokine receptor (CCR5) for RANTES, MIP-1beta, and MIP-1alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17161–17166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, T.N.; Power, C.A.; Shaw, J.P.; Proudfoot, A.E. Chemokine blockers—Therapeutics in the making? Trends. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 27, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, C.A.; Rana, B.M.J.; Cousins, D.J. Differential expression of functional chemokine receptors on human blood and lung group 2 innate lymphoid cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, Y.; Kanda, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Van Bui, D.; Suzuki, K.; Sawada, S.; Baba, K.; Yagi, M.; Asako, M.; Okazaki, H.; et al. Increased CD69 expression on activated eosinophils in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis correlates with clinical findings. Allergol. Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, M.K.; Brashler, J.R.; Stout, B.K.; Johnson, H.G.; Sanders, M.E.; Lin, A.H.; Gorman, R.R.; Bienkowski, M.J.; Ishizaka, T. Activation of human eosinophils by platelet-derived growth factor. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1992, 97, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, A.T.; Ludowyke, R.I.; Verrills, N.M. Mast cell function: Regulation of degranulation by serine/threonine phosphatases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 112, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Parsons, S.; Brautigan, D.L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of protein phosphatase 2A in response to growth stimulation and v-src transformation of fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 7957–7962. [Google Scholar]
- Wera, S.; Hemmings, B.A. Serine/threonine protein phosphatases. Biochem. J. 1995, 311, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mercado, N.; Miller-Larsson, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Ito, K. Increased corticosteroid sensitivity by a long acting beta2 agonist formoterol via beta2 adrenoceptor independent protein phosphatase 2A activation. Pulm. Pharm. 2012, 25, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokulsky, L.A.; Collison, A.M.; Nightingale, S.; Fevre, A.L.; Percival, E.; Starkey, M.R.; Hansbro, P.M.; Foster, P.S.; Mattes, J. TRAIL deficiency and PP2A activation with salmeterol ameliorates egg allergen-driven eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G998–G1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchwell, L.; Girkin, J.; Dun, M.D.; Morten, M.; Verrills, N.; Toop, H.D.; Morris, J.C.; Johnston, S.L.; Foster, P.S.; Collison, A.; et al. Salmeterol attenuates chemotactic responses in rhinovirus-induced exacerbation of allergic airways disease by modulating protein phosphatase 2A. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, Y.; Kanda, A.; Yun, Y.; Bui, D.V.; Suzuki, K.; Sawada, S.; Asako, M.; Iwai, H. Reduced Local Response to Corticosteroids in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Asthma. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020326
Kobayashi Y, Kanda A, Yun Y, Bui DV, Suzuki K, Sawada S, Asako M, Iwai H. Reduced Local Response to Corticosteroids in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Asthma. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020326
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Yoshiki, Akira Kanda, Yasutaka Yun, Dan Van Bui, Kensuke Suzuki, Shunsuke Sawada, Mikiya Asako, and Hiroshi Iwai. 2020. "Reduced Local Response to Corticosteroids in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Asthma" Biomolecules 10, no. 2: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020326
APA StyleKobayashi, Y., Kanda, A., Yun, Y., Bui, D. V., Suzuki, K., Sawada, S., Asako, M., & Iwai, H. (2020). Reduced Local Response to Corticosteroids in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Asthma. Biomolecules, 10(2), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020326





