Abstract
The human small RNA miR-4443 is functionally involved in several types of cancer and in the biology of the immune system, downstream of insulin and leptin signaling. Next generation sequencing evidence and structural prediction suggest that miR-4443 is not produced via the canonical Drosha–Exportin 5–Dicer pathway of microRNA biogenesis. We tested this hypothesis by using qRT-PCR to measure miR-4443 and other microRNA levels in HCT-116 cells with Drosha, Exportin 5, and Dicer knockouts, as well as in the parental cell line. Neither of the knockouts decreased miR-4443 levels, while the levels of canonical microRNAs (miR-21 and let-7f-5p) were dramatically reduced. Previously published Ago2-RIP-Seq data suggest a limited incorporation of miR-4443 into RISC, in agreement with the functional studies. The miR-4443 locus shows conservation in primates but not in other mammals, while its seed region appears in additional microRNAs. Our results suggest that miR-4443 is a Drosha, Exportin 5, and Dicer-independent, non-canonical small RNA produced by a yet unknown biogenesis pathway.
Keywords:
noncoding RNA; microRNA; biogenesis; Drosha; Dicer; Exportin; microprocessor; non-canonical; leptin; insulin 1. Introduction
The human small RNA miR-4443 (miRbase accession MI0016786, http://www.mirbase.org/cgi-bin/mirna_entry.pl?acc=MI0016786) is functionally involved in several types of cancer and in the biology of the immune system. We previously reported that in cultured colon cancer cells, miR-4443 was upregulated by leptin and insulin in a MEK1/2-dependent manner, decreased invasion and proliferation, and directly downregulated pro-metastatic NCOA1 and TRAF4. Insulin and/or leptin resistance (e.g., in obesity) may neutralize this tumor-suppressive pathway, increasing the risk of developing cancer [1]. Supporting this notion, the miR-4443 locus is frequently deleted in cancers based on TCGA data; and a tumor suppressor role for miR-4443 was also reported in other cancer types, i.e., osteosarcoma [2], hepatocellular carcinoma [3], ovarian cancer [4], and glioblastoma [5]. On the other hand, miR-4443 was shown to promote the resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells, as well as metastatic breast cancer cells, to the chemotherapeutic agent epirubicin [6,7]; and its elevated levels in plasma were suggested as a biomarker of glial tumors [8]. In addition to its function in cancer cells, miR-4443 was reported to regulate the behavior of immune cells, i.e., CD4+ T cells in the context of Graves’ Disease [9] as well as mast cells, notably via microvesicles secreted from T cells [10]. Finally, a recent study reported that transfection with anti-miR-4443 oligos modified the response of differentiated neuronal cells (SH-SY5Y) to oxidative stress [11]. miR-4443 differs from most human microRNAs in the following aspects (summarized in Figure 1):

Figure 1.
Indirect evidence for non-canonical biogenesis of miR-4443. Adapted from miRbase (http://www.mirbase.org/cgi-bin/mirna_entry.pl?acc=MI0016786), with let-7f-5p and miR-21 included for comparison. (A) The predicted stem-loop structure of pre-miR-4443 compared with the structures of pre-let-7f-5p and pre-miR-21. Mature microRNA sequences are shown in gray. (B) The deep sequencing evidence for mature miR-4443, compared with let-7f-5p and miR-21. Note the short (17 nt) mature sequence, short terminal loop, and lack of evidence for passenger strand for miR-4443.
(a) The most common isoform of the mature sequence is only 17 nucleotides long. In comparison, the median length of mature human microRNAs is 22 nucleotides. A prior study of microRNA length distribution found that 60.7% of the cancer-associated human microRNAs analyzed were 22 nucleotides long, while 99.4% fell within the 22 ± 2 nucleotide bracket [12];
(b) The predicted terminal loop of pre-miR-4443 is only four nucleotides long. It is well known that the size and structural flexibility of the microRNA precursor terminal loop are important for both Drosha and Dicer-mediated processing [13,14], and to a lesser degree for Exportin 5 binding [15];
(c) Deep sequencing evidence from ~23 K reads shows only the 5′ mature miR-4443 product and no passenger strand product from pre-miR-4443.
Combined, these properties exclude miR-4443 from stringent microRNA annotation criteria, e.g., the MirGeneDB database [16] (http://mirgenedb.org/) and suggest that miR-4443 is not a product of the canonical Drosha–Exportin 5–Dicer microRNA biogenesis pathway.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Cell Culture
The following HCT-116 parental strain and knockout strains, originally developed and described by the lab of Narry Kim [17], were obtained from the Korean Collection for Type Cultures (KCTC, Jeollabuk-do, Korea) in January 2019, and kept frozen in liquid nitrogen until use. These included Drosha knockout (KO) clone #40, Exportin 5 KO clones #19 and #19-1, and Dicer KO clones #43 and #45. Cells were cultured based on ATCC recommendations. Culture media and fetal bovine serum were obtained from Biological Industries (Israel). All strains were grown in triplicates in Greiner Bio-One (Kremsmünster, Austria) Cellstar 6-well tissue culture plates until reaching ~80% confluence.
2.2. RNA Isolation
Isolation of total RNA (including miRNAs) was carried out using the Qiagen (Venlo, Netherlands) miRNeasy Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA concentration was assessed using a Thermo-Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA) NanoDrop 8000 Spectrophotometer. All RNA samples had an OD260/280 of ≥1.8. A total of 1 μg of RNA from each sample was used for qRT-PCR.
2.3. qRT-PCR
Reverse transcription, primer design, and quantitative PCR were performed using SYBR Green chemistry (iTaq SYBR Master Mix, BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA) and DNA primers (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Primer extension was used for miRNA quantification as previously described [1,18,19]. This qRT-PCR method is highly accurate and reproducible [18,19], and was chosen over hydrolysis probe chemistry due to its lower cost. The sequence of the RT-primer was 5′-CAGGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTVN-3′, where V is A, C and G and N is A, C, G, and T. qPCR primer sequences are provided in Table 1. All primers were tested for efficiency (by serial dilutions) and specificity (by melting peak analysis). RT was performed on an Applied Biosystems ABI-9600 (Thermo-Fisher Scientific) with reagents from New England Biolabs (Ipswich, MA, USA) as previously described [1]. qPCR was performed in technical quadruplicates on an Applied Biosystems ABI-7900HT Sequence Detection System (Thermo-Fisher Scientific) equipped with a 384-well block. Data were analyzed using the SDS 2.3 software (Applied Biosystems, Thermo-Fisher Scientific) and Microsoft Excel. Relative quantification and the ΔCq method were used.

Table 1.
qPCR primers used (see [1,18,19]).
2.4. Bioinformatics and Online Datasets
Raw read files from Krell et al. [20] were obtained from the European Nucleotide Archive, projects PRJEB3396 and PRJEB3157 for PAR-CLIP-seq of AGO2 binding sites and AGO-RIP-seq data, respectively. MiR-4443 locus conservation was assessed using NCBI BLAST [21], human reference genome release GRCh38, and the NCBI genome browser. For seed region comparison, microRNA sequences were retrieved from miRBase, release 22.1 [22], and scanned for identification of all miRNAs with the same seed sequence (UGGAGG) at positions 2–7.
2.5. Statistics
For statistical tests, Student’s t-test was used.
3. Results and Discussion
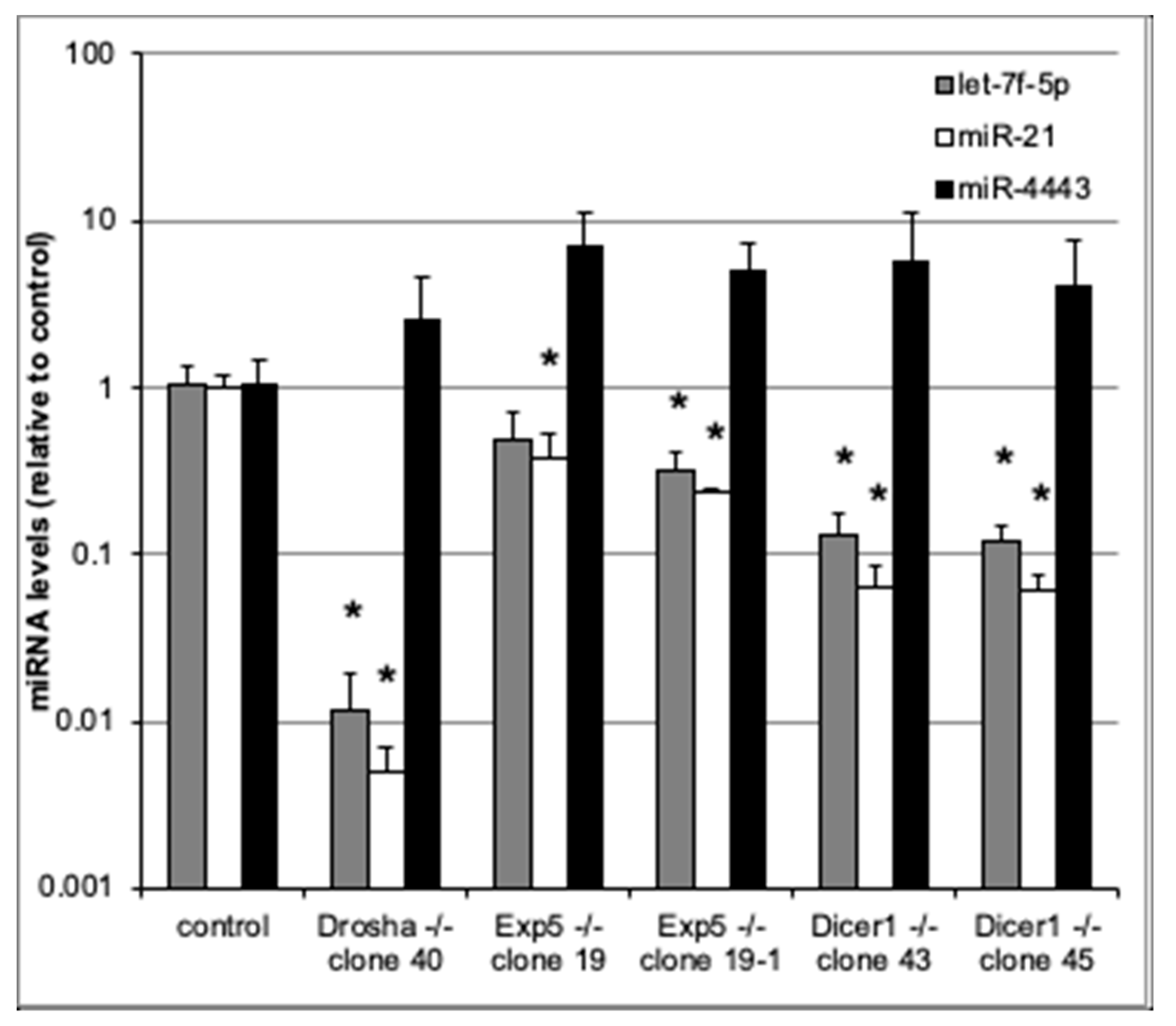
To assess whether miR-4443 biogenesis is canonical, we used qRT-PCR to measure miR-4443 levels in cultured HCT-116 colon cancer cell lines with Drosha, Exportin 5, and Dicer knockouts [17], as well as in the parental cell line. We also measured the levels of two canonical microRNAs, miR-21 and let-7f-5p, in the same cells. As expected, the levels of both canonical microRNAs (miR-21 and let-7f-5p) were dramatically reduced in the knockout lines (Figure 2). Thus, Drosha, Exportin 5, and Dicer knockouts caused ~100×, ~3× and ~10× decreases, respectively, in the levels of both miR-21 and let-7f-5p. All these decreases (except for the decrease in let-7f-5p in one of the Exportin 5 KO lines) were statistically significant (p < 0.05). In contrast, neither of the knockouts decreased miR-4443 levels (Figure 2). Indeed, miR-4443 levels were between 2× and 7× higher in the knockout lines than in the parental line, although this difference was not statistically significant and may have resulted from differences in total small RNA quantity between the samples.
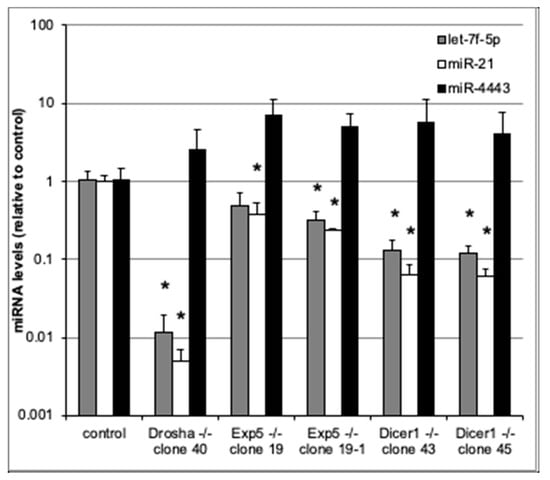
Figure 2.
qRT-PCR for miR-4443, let7f-5p, and miR-21 in cultured HCT-116 cells with knockouts of Drosha, Exportin 5, or Dicer genes and controls. The levels of each microRNA relative to control are shown. Note logarithmic scale of vertical axis. Bars: st. dev. from biological triplicates. * p < 0.05 (t test).
As these results raised the possibility that miR-4443 is not an actual microRNA (functionally defined by its association with RISC proteins), we examined the evidence of its association with Argonaute 2 (Ago2) in published Ago2-RIP-Seq datasets. Utilizing the raw data from a study by Krell et al. [20], notably also performed in HCT-116 cells, we identified the core sequence of miR-4443 (TGGAGGCGTGGGTT) in both input and Ago2-RIP-Seq reads, as well as in the PAR-CLIP reads. The frequency of this sequence was low (~1/105 of total reads, and ~1/103 compared to common microRNAs like miR-21) in both the input and the Ago2-RIP-Seq data, which does not necessarily indicate weak binding to Ago2 due to the low overall cytoplasmic levels of this RNA (e.g., Figure 1B).
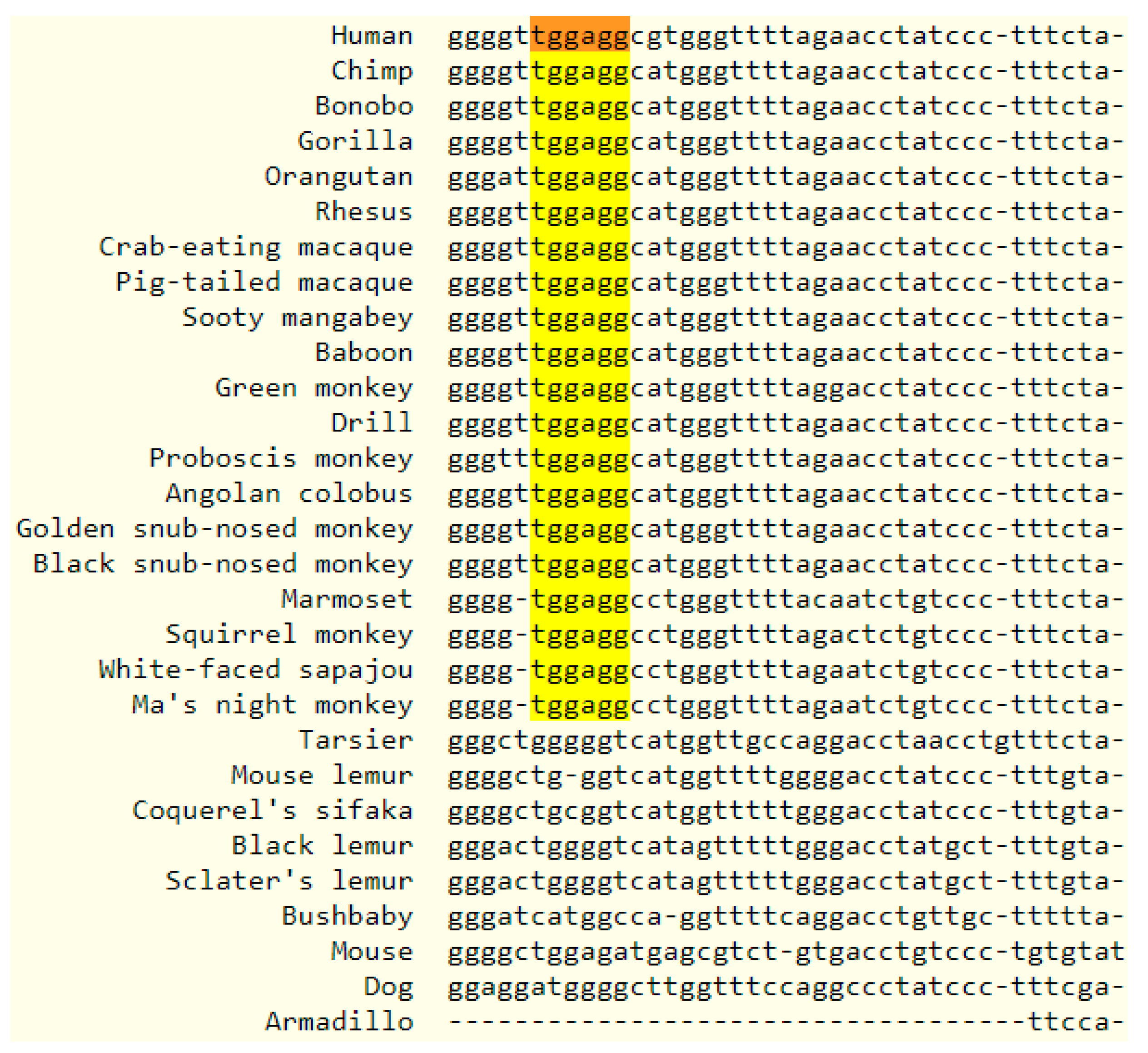
To assess the cross-species conservation of miR-4443, we examined the conservation of the human miR-4443 genome locus. Additionally, we searched for other annotated microRNAs with the same seed region as miR-4443, defined as a contiguous string of at least six nucleotides beginning at position two [23]. While no significant cross-vertebrate or cross-mammal conservation was observed for the miR-4443 locus, it was conserved in primates (Figure 3), albeit the similar sequences in other primates were not annotated as microRNAs. An identical seed sequence was identified in additional microRNAs of human, mouse, rat, and bovine origin, as well as in non-mammalian sequences (Table 2). While seed homology is not an indicator of miR-4443′s relatedness to other microRNAs (due to the high probability of a chance match), it does suggest that this RNA is likely to share a set of targets with other microRNAs.

Figure 3.
Multiple alignment output showing the human mir-4443 locus and similar loci in 27 primates and 3 other mammals. The identical 6-nucleotide seed region is highlighted.

Table 2.
Animal miRbase-annotated microRNAs sharing a 6-nucleotide seed (in bold) with miR-4443.
Although some researchers have suggested excluding non-canonical microRNAs from being considered microRNAs at all, many examples of these molecules are known, and some clearly have important biological functions. Most non-canonical microRNAs require Dicer for their final processing step [24]; however, there are notable exceptions. One well-known example is miR-451a, which is abundantly expressed in erythrocytes, plays an important role in erythropoiesis [25,26], and shows evolutionary conservation in vertebrates [27]. miR-451a biogenesis has been shown to be mediated by Argonaute 2, independent of Dicer but not of Drosha [25,27,28]. Another class of non-canonical microRNAs, named “simtrons”, which includes miR-1225 and miR-1228, also require Drosha but not Dicer or Exportin 5 for their processing [29]. Our results suggest that miR-4443 represents yet another type of small regulatory RNAs, independent of Drosha, Exportin 5, and Dicer, and produced by a hitherto unknown biogenesis pathway.
Despite this divergent biogenesis of miR-4443, we have found evidence of its binding to Argonaute 2. Additionally, a growing number of functional studies suggest that miR-4443 regulates the expression of target genes by binding the 3′ UTRs of their mRNA. Although more conclusive evidence of RISC incorporation of miR-4443 is necessary, existing evidence (in this and other studies) suggests that miR-4443 functions in RISC-mediated gene regulation. Its inclusion or exclusion from microRNA nomenclature is therefore subject to opinion of what constitutes a microRNA. Furthermore, it seems that, due to the several known non-canonically produced microRNAs, it is indeed more acceptable to draw the line based on function rather than on biogenesis.
4. Conclusions
Our results suggest that miR-4443 is a small regulatory RNA produced by a hitherto unknown biogenesis pathway. The physiologically and pathologically relevant functions of miR-4443 warrant a better understanding of this molecule, its upstream regulation, and downstream effectors. Further experiments are required to elucidate the biogenesis of miR-4443, and to address the question whether it is unique or indeed representative of a novel class of small regulatory RNAs.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Isana Veksler-Lublinsky from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev for the conservation analysis; Bastian Fromm from Stockholm University for his helpful suggestions; the group of Narry Kim from Seoul National University for making the KO cell lines available; Hila Yehuda from MIGAL for the technical support; and Tomer Revach, an intern from the “Galilium” program (Tel Hai), for his participation in conducting the experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Meerson, A.; Yehuda, H. Leptin and insulin up-regulate miR-4443 to suppress NCOA1 and TRAF4, and decrease the invasiveness of human colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Xu, J.; Lin, J.; Lin, R.; Chen, K.; Kong, J.; Shui, X. Long Noncoding RNA FEZF1-AS1 Promotes Osteosarcoma Progression by Regulating the miR-4443/NUPR1 Axis. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Gong, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, T.; Hu, J.; Hu, J.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, J. lncRNA FEZF1-AS1 contributes to cell proliferation, migration and invasion by sponging miR-4443 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 5614–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, S.O.; Reiisi, S. Downregulation of miR-4443 and miR-5195-3p in ovarian cancer tissue contributes to metastasis and tumorigenesis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2019, 299, 1453–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Wen, L.; Feng, J. lncRNA MNX1-AS1 Promotes Glioblastoma Progression Through Inhibition of miR-4443. Oncol. Res. 2019, 27, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qiao, B.; Fan, J. Overexpression of miR-4443 Promotes the Resistance of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Epirubicin by Targeting INPP4A and Regulating the Activation of JAK2/STAT3 Pathway. Pharmazie 2018, 73, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhong, S.; Lu, P.; Wang, D.; Zhou, S.; Yang, S.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. miR-4443 Participates in the Malignancy of Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusco, A.; Fadda, P.; Nigita, G.; Fassan, M.; Bottoni, A.; Gardiman, M.P.; Sacchi, D.; Calore, F.; Carosi, M.; Antenucci, A.; et al. Circulating Micrornas Predict Survival of Patients with Tumors of Glial Origin. E. Bio. Medicine 2018, 30, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, L.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, F.; Cui, B.; Lin, D.; Ning, G.; Wang, W.; et al. MicroRNA-4443 Causes CD4+ T Cells Dysfunction by Targeting TNFR-Associated Factor 4 in Graves’ Disease. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shefler, I.; Salamon, P.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Mor, A.; Hershko, A.Y.; Mekori, Y.A. MicroRNA-4443 regulates mast cell activation by T cell–derived microvesicles. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallarès-Albanell, J.; Zomeño-Abellán, M.T.; Escaramís, G.; Pantano, L.; Soriano, A.; Segura, M.F.; Martí, E. A High-Throughput Screening Identifies MicroRNA Inhibitors That Influence Neuronal Maintenance and/or Response to Oxidative Stress. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 17, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Du, R.; Edwards, A.; Flemington, E.K.; Zhang, K. The Sequence Structures of Human MicroRNA Molecules and Their Implications. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zeng, Y. The terminal loop region controls microRNA processing by Drosha and Dicer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 7689–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Wang, H.-W. Structure of precursor microRNA’s terminal loop regulates human Dicer’s dicing activity by switching DExH/D domain. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeng, Y.; Cullen, B.R. Structural requirements for pre-microRNA binding and nuclear export by Exportin 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 4776–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, B.; Billipp, T.; Peck, L.E.; Johansen, M.; Tarver, J.E.; King, B.L.; Newcomb, J.M.; Sempere, L.F.; Flatmark, K.; Hovig, E.; et al. A Uniform System for the Annotation of Vertebrate microRNA Genes and the Evolution of the Human microRNAome. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2015, 49, 213–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Kim, B.; Kim, V.N. Re-evaluation of the roles of DROSHA, Exportin 5, and DICER in microRNA biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1881–E1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcells, I.; Cirera, S.; Busk, P.K. Specific and sensitive quantitative RT-PCR of miRNAs with DNA primers. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busk, P.K. A tool for design of primers for microRNA-specific quantitative RT-qPCR. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krell, J.; Stebbing, J.; Carissimi, C.; Dabrowska, A.F.; Giorgio, A.; de Frampton, A.E.; Harding, V.; Fulci, V.; Macino, G.; Colombo, T.; et al. TP53 regulates miRNA association with AGO2 to remodel the miRNA–mRNA interaction network. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellwanger, D.C.; Büttner, F.A.; Mewes, H.-W.; Stümpflen, V. The sufficient minimal set of miRNA seed types. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfattah, A.M.; Park, C.; Choi, M.Y. Update on non-canonical microRNAs. Biomol. Concepts 2014, 5, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cifuentes, D.; Xue, H.; Taylor, D.W.; Patnode, H.; Mishima, Y.; Cheloufi, S.; Ma, E.; Mane, S.; Hannon, G.J.; Lawson, N.D.; et al. A Novel miRNA Processing Pathway Independent of Dicer Requires Argonaute2 Catalytic Activity. Science 2010, 328, 1694–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Tan, Y.S.; Cheng, W.-C.; Kingsbury, T.J.; Heimfeld, S.; Civin, C.I. MIR144 and MIR451 regulate human erythropoiesis via RAB14. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 168, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-S.; Maurin, T.; Robine, N.; Rasmussen, K.D.; Jeffrey, K.L.; Chandwani, R.; Papapetrou, E.P.; Sadelain, M.; O’Carroll, D.; Lai, E.C. Conserved vertebrate mir-451 provides a platform for Dicer-independent, Ago2-mediated microRNA biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15163–15168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheloufi, S.; Dos Santos, C.O.; Chong, M.M.W.; Hannon, G.J. A Dicer-independent miRNA biogenesis pathway that requires Ago catalysis. Nature 2010, 465, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, M.A.; Reich, A.A.; Duelli, D.M.; Hastings, M.L. Biogenesis of mammalian microRNAs by a non-canonical processing pathway. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4626–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).