Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cellular Material
2.3. Cell Cultures
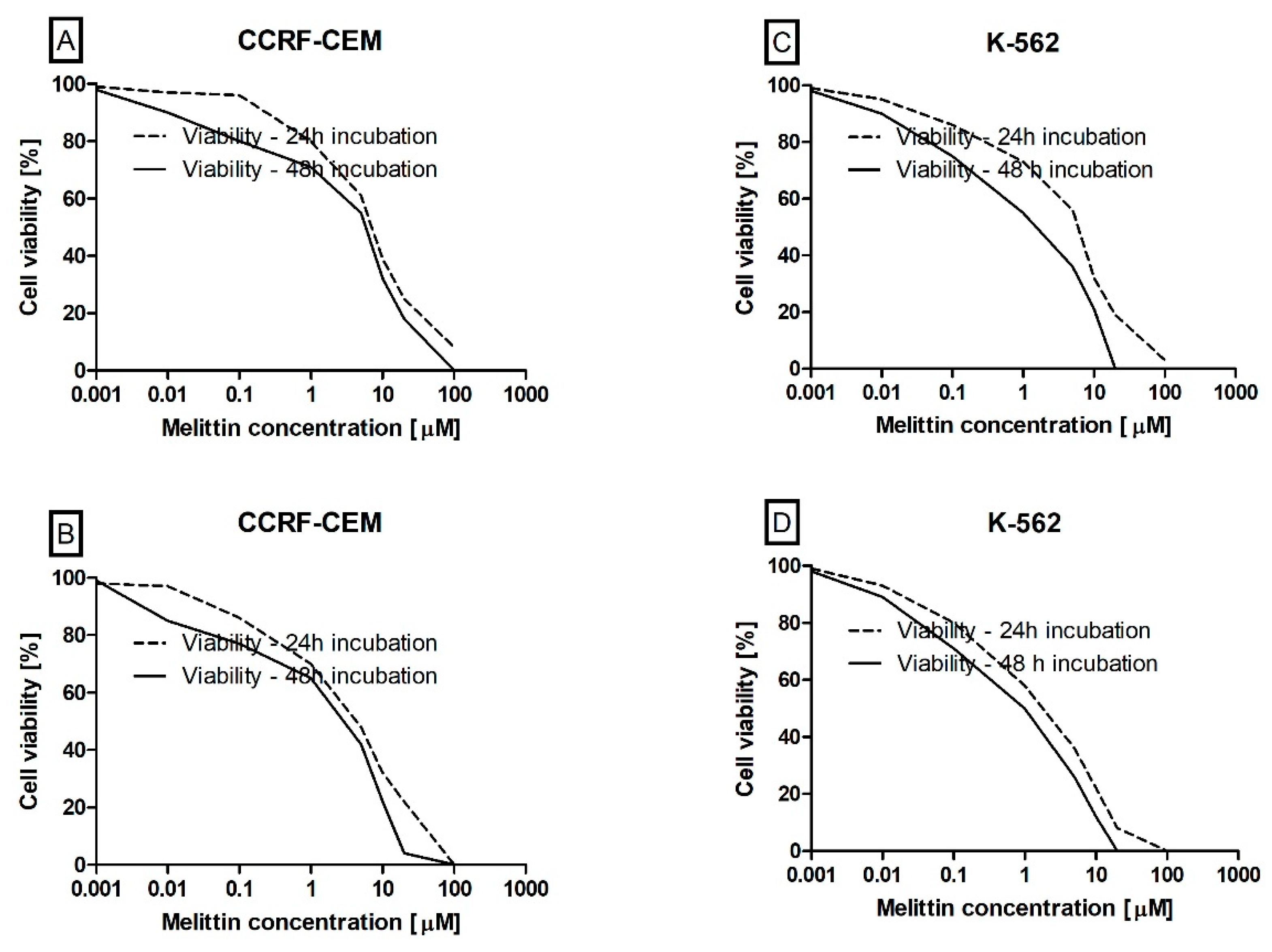
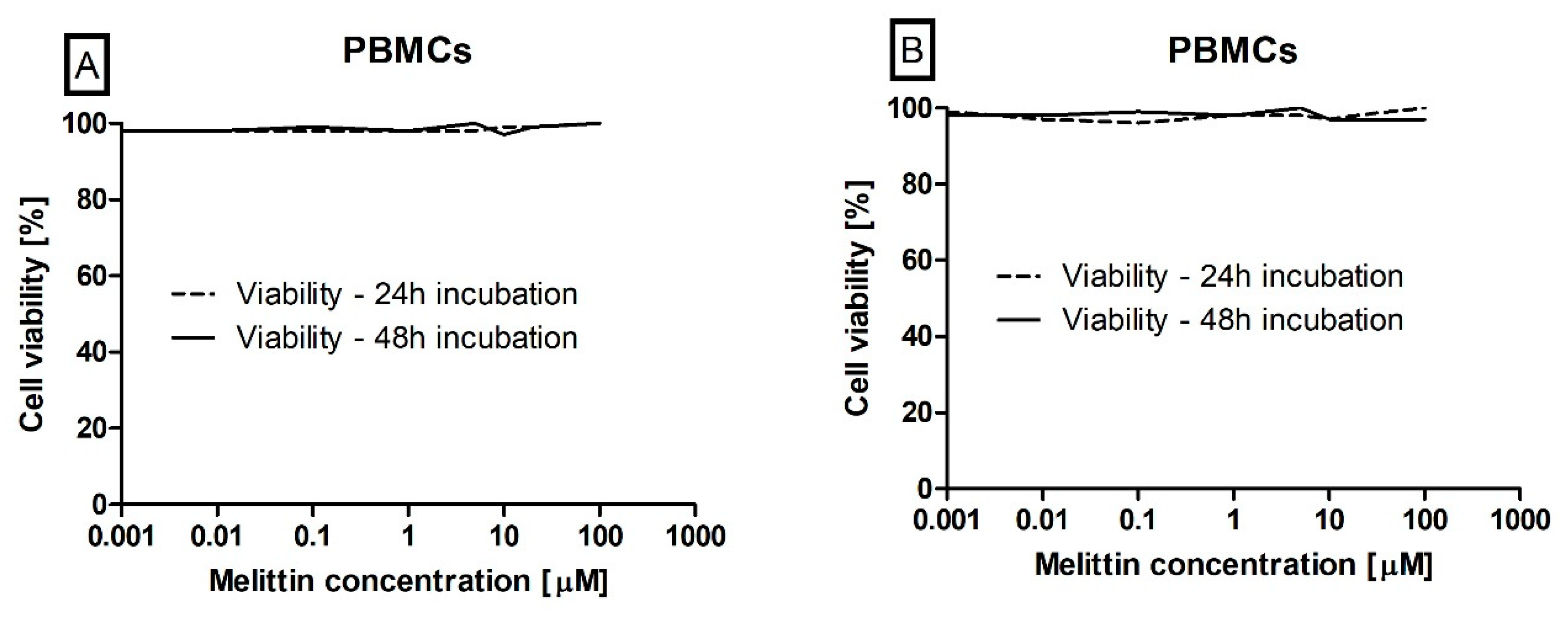
2.4. Cell Viability Determination
2.5. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP)
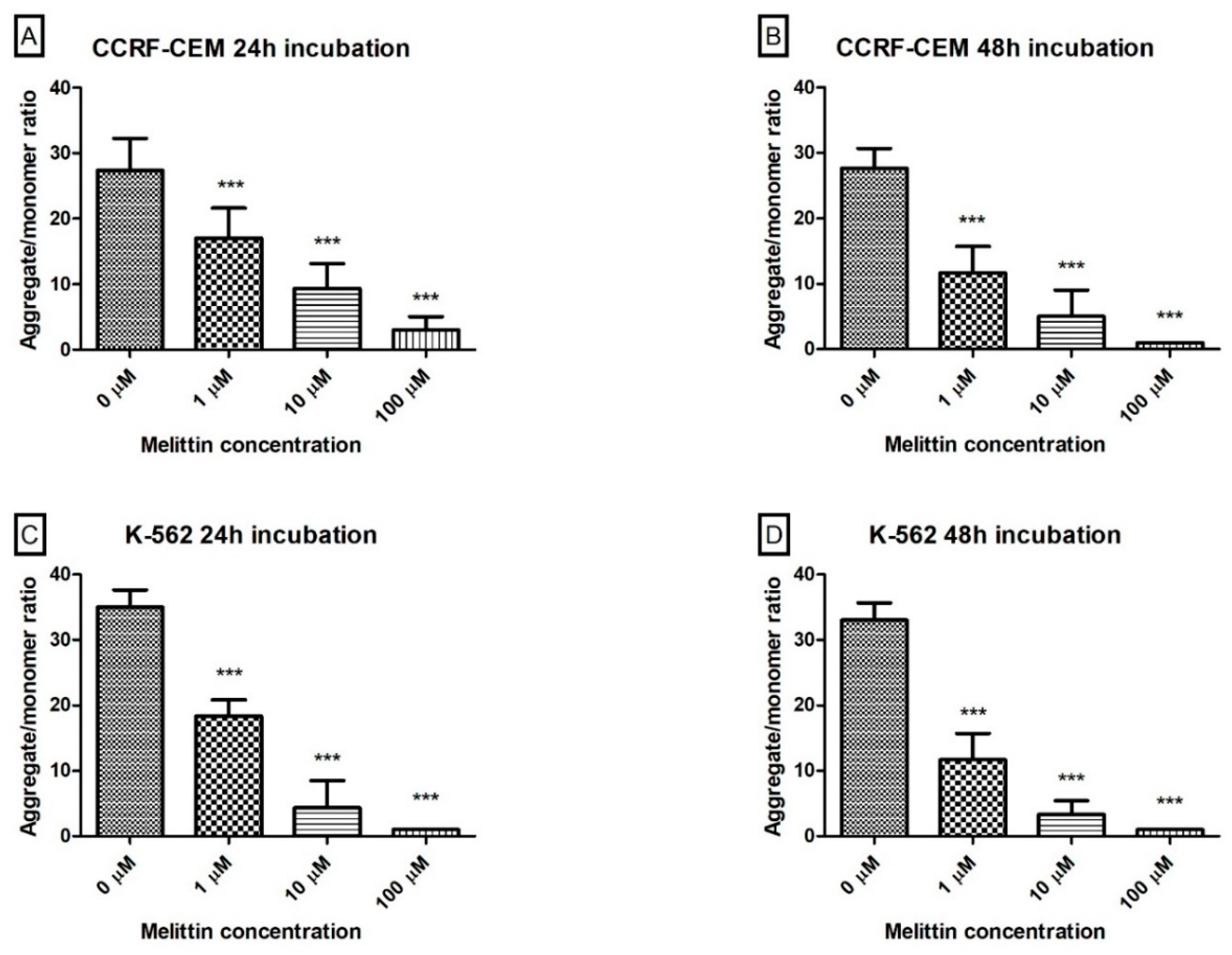
2.6. Apoptosis Assay—Anexin V Binding
2.7. Determining the Activity of Caspase-3/Caspase-7
2.8. Data Analysis
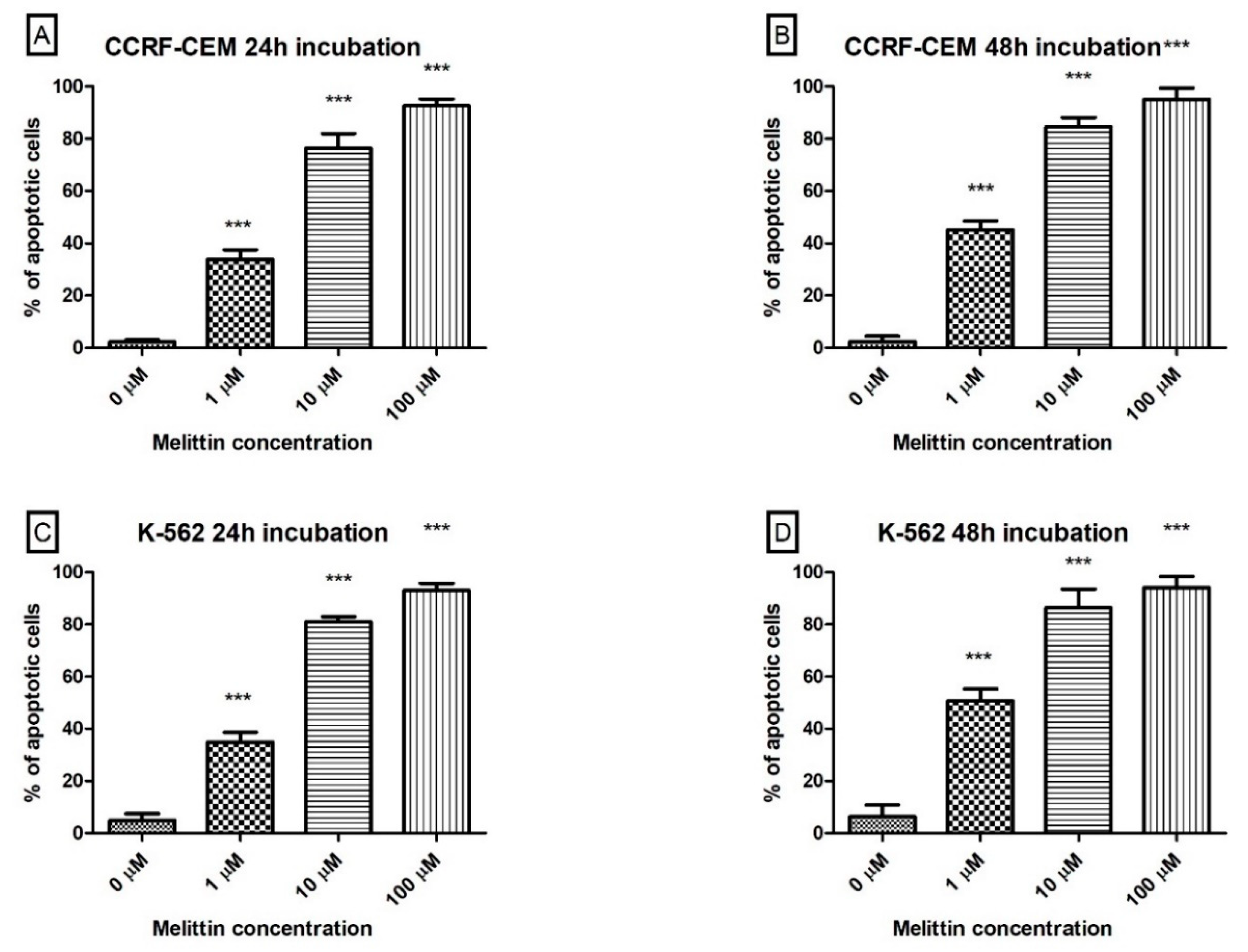
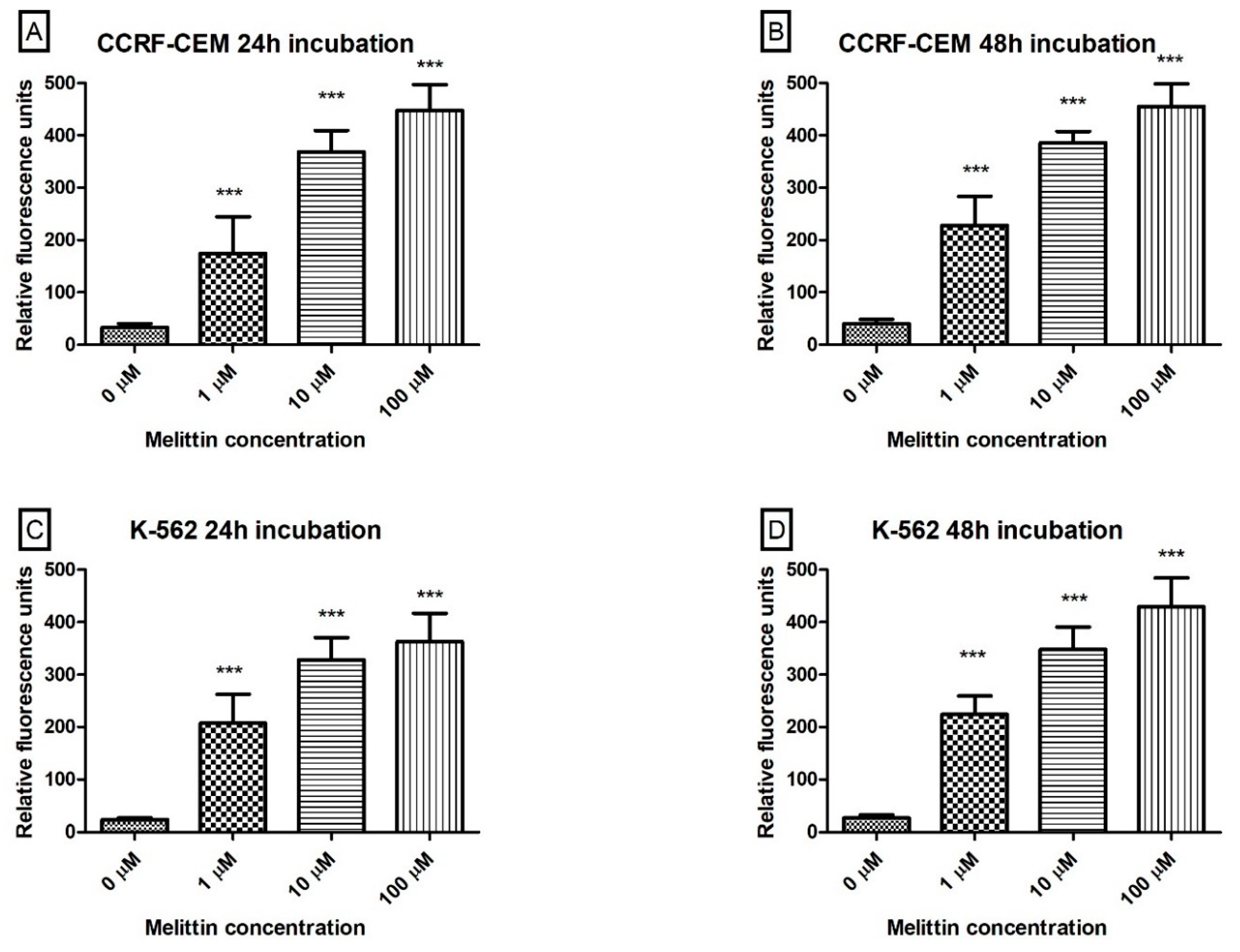
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wang, X.R.; Lin, L.T.; Xiao, L.Y.; Zhou, P.; Shi, G.X.; Liu, C.Z. Bee venom therapy: Potential mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Toxicon 2018, 148, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.J.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Song, H.S.; Lee, C.K.; Hong, J.T. Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis, pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its constituent compounds. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 115, 246–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ke, T.; He, C.; Cao, W.; Wei, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.X.; Wang, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.R.; et al. The anti-arthritic effects of synthetic melittin on the complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis model in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2010, 38, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Gendy, A.; Saber, M.; Daoud, E.; Abdel-Wahhab, K.; el-Rahman, E.; Hegaz, A. Role of bee Venom Acupuncture in improving pain and life quality in Egyptian Chronic Low Back Pain patients. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Rady, I.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Rady, M.; Mukhtar, H. Melittin, a major peptide component of bee venom, and its conjugates in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2017, 402, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, W.H.; Gwon, M.G.; Gu, H.M.; Jeon, M.J.; Han, S.M.; Pak, S.C.; Lee, C.K.; Park, I.S.; et al. Therapeutic effects of bee venom and its major component, melittin, on atopic dermatitis in vivo and in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 4310–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreil, G. Structure and Multistep Activation of the Precursors of Peptides from Honeybee Venom Glands and Frog Skin. Curr. Top. Cell. Regul. 1984, 24, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Brewczyński, Z.; Anczyk, E.; Kasznica-Kocot, J.; Hom, A.; Dąbkowska, B.; Muszyńska-Graca, M.; Pypno, B.; Skiba, M.; Złotkowska, R. Znajomość biologii błonkówek ze szczególnym uwzględnieniem immunochemii ich jadów ma istotne znaczenie we współczesnej medycynie środowiskowej. Medycyna Środowiskowa 2010, 13, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger, T.C.; Eisenberg, D. The structure of melittin. II. Interpretation of the structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 6016–6022. [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger, T.C.; Weissman, L.; Eisenberg, D. The structure of melittin in the form I crystals and its implication for melittin’s lytic and surface activities. Biophys. J. 1982, 37, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuraman, H.; Chattopadhyay, A. Melittin: A membrane-active peptide with diverse functions. Biosci. Rep. 2007, 27, 189–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othon, C.M.; Kwon, O.H.; Lin, M.M.; Zewail, A.H. Solvation in protein (un)folding of melittin tetramer-monomer transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12593–12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perekalin, D.S.; Novikov, V.V.; Pavlov, A.A.; Ivanov, I.A.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Kopylov, A.N.; Volkov, D.S.; Seregina, I.F.; Bolshov, M.A.; Kudinov, A.R. Selective ruthenium labeling of the tryptophan residue in the bee venom Peptide melittin. Chemistry 2015, 21, 4923–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hait, W.N.; Grais, L.; Benz, C.; Cadman, E.C. Inhibition of growth of leukemic cells by inhibitors of calmodulin: Phenothiazines and melittin. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1985, 14, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Khalil, S.R.; Awad, A.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y. Combined cytogenotoxic effects of bee venom and bleomycin on rat lymphocytes: An in vitro study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 173903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumanov, K.; Momchilova, A.; Wolf, C. Bimodal regulatory effect of melittin and phospholipase A2-activating protein on human type II secretory phospholipase A2. Cell Boil. Int. 2003, 27, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, J.F.; Shipman, W.H.; Cole, L.J. Antibacterial action of melittin, a polypeptide from bee venom. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1968, 127, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Z. Melittin exerts an antitumor effect on non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3581–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, K.K.; Cho, H.J.; Chung, I.K.; Min, K.S.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.G.; Yeo, J.H.; Chang, Y.C. Melittin suppresses PMA-induced tumor cell invasion by inhibiting NF-kappaB and AP-1-dependent MMP-9 expression. Mol. Cells 2010, 29, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.H.; Choi, M.S.; Kwak, D.H.; Oh, K.W.; Yoon, D.Y.; Han, S.B.; Song, H.S.; Song, M.J.; Hong, J.T. Anti-cancer effect of bee venom in prostate cancer cells through activation of caspase pathway via inactivation of NF-κB. Prostate 2011, 71, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.; Park, M.H.; Kollipara, P.S.; An, B.J.; Song, H.S.; Han, S.B.; Kim, J.H.; Song, M.J.; Hong, J.T. Anti-cancer effect of bee venom toxin and melittin in ovarian cancer cells through induction of death receptors and inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.L.; Ke, Y.Q.; Xu, R.X.; Peng, P. Melittin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of malignant human glioma cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2007, 27, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Gu, W.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.Q.; Han, K.Q.; Ling, C.Q. Growth arrest and apoptosis of the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line BEL-7402 induced by melittin. Onkologie 2006, 29, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.M.; Bian, E.B.; Li, J. Melittin restores PTEN expression by down-regulating HDAC2 in human hepatocelluar carcinoma HepG2 cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yu, M.; He, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wang, F.; Song, C.; Sun, S.; Ling, C.; Xu, Z. Melittin prevents liver cancer cell metastasis through inhibition of the Rac1-dependent pathway. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Choi, Y.; Shin, J.M.; Cho, H.J.; Kang, J.H.; Park, K.K.; Choe, J.Y.; Bae, Y.S.; Han, S.M.; Kim, C.H.; et al. Melittin suppresses EGF-induced cell motility and invasion by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Jeong, Y.J.; Cho, H.J.; Park, K.K.; Chung, I.K.; Lee, I.K.; Kwak, J.Y.; Chang, H.W.; Kim, C.H.; Moon, S.K.; et al. Melittin suppresses HIF-1α/VEGF expression through inhibition of ERK and mTOR/p70S6K pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Zhu, Z.A.; Hao, Y.Q.; Dai, K.R.; Zhang, C. Effect of melittin on apoptosis and necrosis of U2 OS cells. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 2004, 2, 208–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.C.; Wu, C.C.; Hsieh, H.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, S.L. Honeybee venom induces calcium-dependent but caspase-independent apoptotic cell death in human melanoma A2058 cells. Toxicon 2008, 52, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, M.; Aydin, C.; Savci, V. Cardiovascular effect of peripheral injected melittin in normotensive conscious rats: Mediation of the central cholinergic system. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2009, 81, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, D.J.; Ha, S.J.; Song, H.S.; Lim, Y.; Yun, Y.P.; Lee, J.W.; Moon, D.C.; Park, Y.H.; Park, B.S.; Song, M.J.; et al. Melittin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through induction of apoptosis via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB and Akt activation and enhancement of apoptotic protein expression. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 317, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijak, M.; Synowiec, E.; Sitarek, P.; Sliwiński, T.; Saluk-Bijak, J. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Flavonolignans in Different Cellular Models. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitarek, P.; Synowiec, E.; Kowalczyk, T.; Śliwiński, T.; Skała, E. An In Vitro Estimation of the Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Root Extract from. Molecules 2018, 23, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijak, M.; Kolodziejczyk-Czepas, J.; Ponczek, M.B.; Saluk, J.; Nowak, P. Protective effects of grape seed extract against oxidative and nitrative damage of plasma proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbikowska, H.M.; Antosik, A.; Szejk, M.; Bijak, M.; Olejnik, A.K.; Saluk, J.; Nowak, P. Does quercetin protect human red blood cell membranes against γ-irradiation? Redox Rep. 2014, 19, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijak, M.; Saluk, J.; Antosik, A.; Ponczek, M.B.; Zbikowska, H.M.; Borowiecka, M.; Nowak, P. Aronia melanocarpa as a protector against nitration of fibrinogen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 55, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.H.; Jeha, S. New therapeutic strategies for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartledge Wolf, D.M.; Langhans, S.A. Moving Myeloid Leukemia Drug Discovery Into the Third Dimension. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwilliger, T.; Abdul-Hay, M. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2017 update. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, E.; O’Brien, S.; Konopleva, M.; Kantarjian, H. New insights into the pathophysiology and therapy of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 2015, 121, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flis, S.; Chojnacki, T. Chronic myelogenous leukemia, a still unsolved problem: Pitfalls and new therapeutic possibilities. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2018 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śladowska, K.; Handzlik, J.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Mazur, L. In vitro cytotoxic activity evaluation of phenytoin derivatives against human leukemia cells. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 54, 553–559. [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi, L.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Andrews, D.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; et al. Essential versus accessory aspects of cell death: Recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watala, C.; Gwoździński, K. Melittin-induced alterations in dynamic properties of human red blood cell membranes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1992, 82, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panina, S.B.; Baran, N.; Brasil da Costa, F.H.; Konopleva, M.; Kirienko, N.V. A mechanism for increased sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia to mitotoxic drugs. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.D.; Schirm, D.K.; Felices, M.; Miller, J.S.; Eckfeldt, C.E. Dinaciclib enhances natural killer cell cytotoxicity against acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2448–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Fang, F.; Li, B. Anti-Tumor Effects of Melittin and Its Potential Applications in Clinic. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.T.; Cheng, H.H.; Huang, C.J.; Chang, H.C.; Chi, C.C.; Su, H.H.; Hsu, S.S.; Wang, J.L.; Chen, I.S.; Liu, S.I.; et al. Phospholipase A2-independent Ca2+ entry and subsequent apoptosis induced by melittin in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.S.; Jang, B.H.; Jo, Y.S.; Kim, S.J.; Eom, T.I.; Kim, M.C.; Ko, H.J.; Sim, S.S. The effect of acteoside on intracellular Ca(2+) mobilization and phospholipase C activity in RBL-2H3 cells stimulated by melittin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratton, D.L.; Fadok, V.A.; Richter, D.A.; Kailey, J.M.; Guthrie, L.A.; Henson, P.M. Appearance of phosphatidylserine on apoptotic cells requires calcium-mediated nonspecific flip-flop and is enhanced by loss of the aminophospholipid translocase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 26159–26165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, J.P.; Blaecke, A.; Lecoanet-Henchoz, S.; Jeannin, P.; Herbault, N.; Caron, G.; Moine, V.; Bonnefoy, J.Y. Annexin V used for measuring apoptosis in the early events of cellular cytotoxicity. Cytometry 1999, 37, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synowiec, E.; Hoser, G.; Wojcik, K.; Pawlowska, E.; Skorski, T.; Błasiak, J. UV Differentially Induces Oxidative Stress, DNA Damage and Apoptosis in BCR-ABL1-Positive Cells Sensitive and Resistant to Imatinib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18111–18128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, C.M.; Singh, A.T.K. Apoptosis: A Target for Anticancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, J.D.; Grubb, D.R.; Lawen, A. The mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsi(m)) in apoptosis; an update. Apoptosis 2003, 8, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.G. Melittin triggers apoptosis in Candida albicans through the reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondria/caspase-dependent pathway. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 355, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| The Biological Effect of Melittin | Reference |
|---|---|
| Inhibits clonogenicity and growth in leukemic cells of humans and mice | [15] |
| Activates of secretory phospholipase A2 | [17] |
| Demonstrates antibacterial activity against strain of Staphylococcus aureus (strain 80) resistant to penicillin | [18] |
| Inhibits invasion and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells induced by the epidermal growth factor | [19] |
| Inhibits human renal carcinoma invasion | [20] |
| Inhibits growth of human prostate cancer cells | [21] |
| Induces apoptotic cell death in ovarian cancer cells | [22] |
| Inhibits proliferation and induction of apoptosis in malignant human glioma cells. | [23] |
| Inhibits proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells | [24,25,26] |
| Inhibits breast cancer cell invasion and migration | [27] |
| Inhibits human cervical cancer progression and angiogenesis. | [28] |
| Inhibits proliferation of the osteosarcoma cells | [29] |
| Induces apoptosis in human melanoma cells | [30] |
| Exerts tachycardic effects by activating COX pathway | [31] |
| Increasing blood pressure and reversing hypotension in haemorrhagic shock | [32] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceremuga, M.; Stela, M.; Janik, E.; Gorniak, L.; Synowiec, E.; Sliwinski, T.; Sitarek, P.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M. Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020247
Ceremuga M, Stela M, Janik E, Gorniak L, Synowiec E, Sliwinski T, Sitarek P, Saluk-Bijak J, Bijak M. Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020247
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeremuga, Michal, Maksymilian Stela, Edyta Janik, Leslaw Gorniak, Ewelina Synowiec, Tomasz Sliwinski, Przemyslaw Sitarek, Joanna Saluk-Bijak, and Michal Bijak. 2020. "Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells" Biomolecules 10, no. 2: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020247
APA StyleCeremuga, M., Stela, M., Janik, E., Gorniak, L., Synowiec, E., Sliwinski, T., Sitarek, P., Saluk-Bijak, J., & Bijak, M. (2020). Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells. Biomolecules, 10(2), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020247







