Cerevisterol Alleviates Inflammation via Suppression of MAPK/NF-κB/AP-1 and Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Cascade
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Measurement
2.3. Measurement of NO, PGE2, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6
2.4. Intracellular ROS Measurement
2.5. Transfection and Luciferase Assays for NF-kB and AP-1
2.6. Transfection of Small interfering RNA (siRNA)
2.7. Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
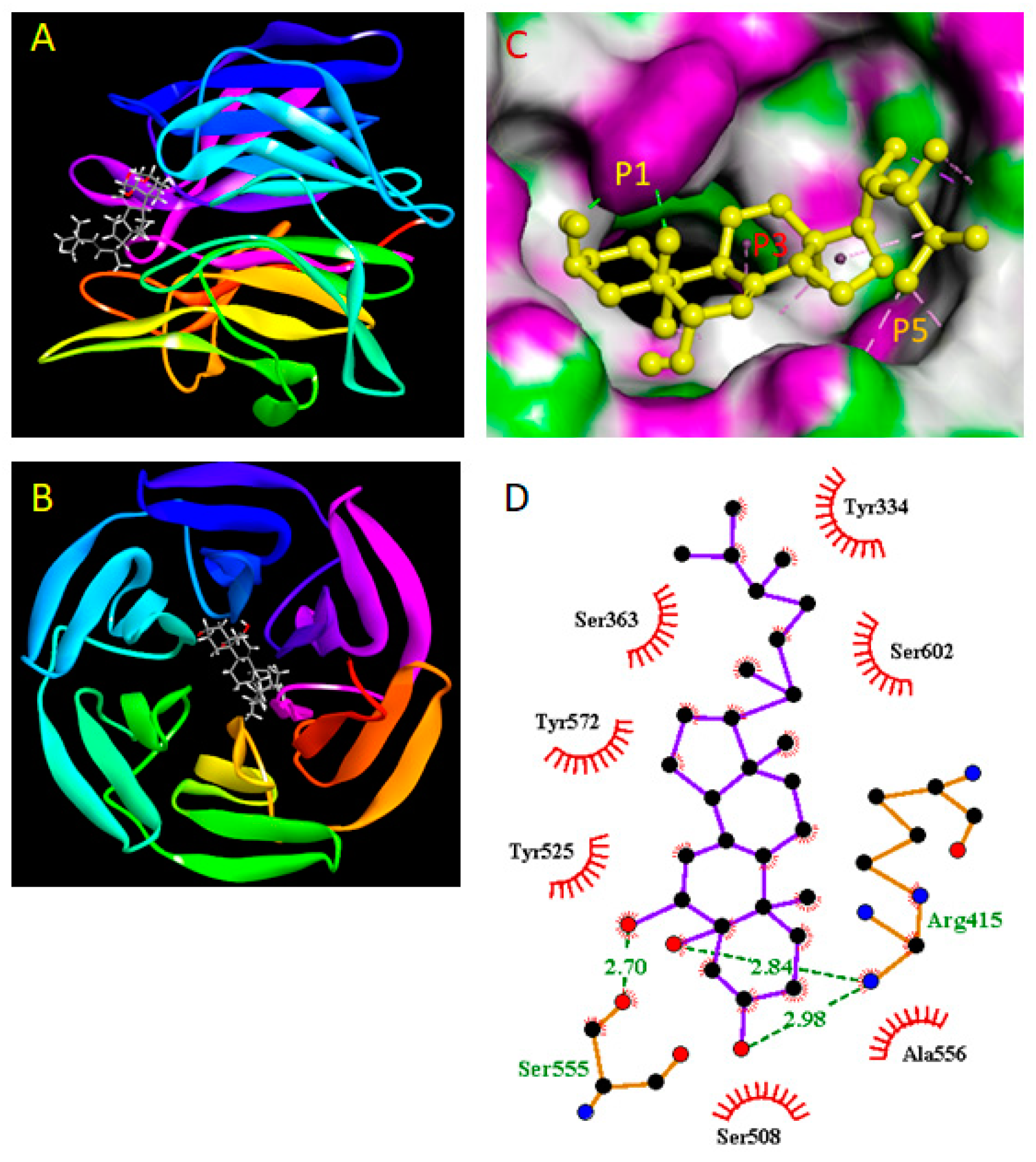
2.9. Molecular Docking Study
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
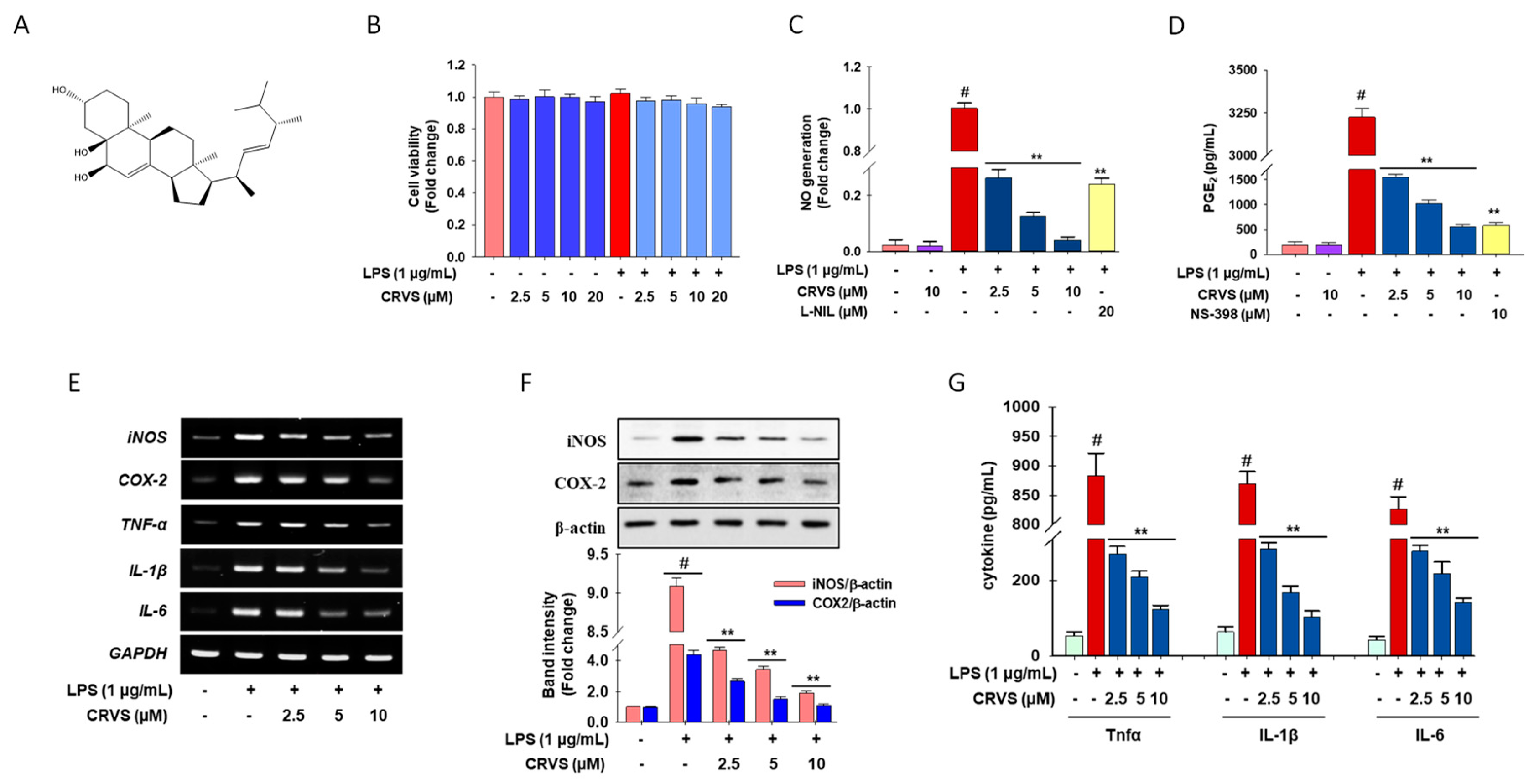
3.1. Effects of CVRS on Cell Viability, Inflammatory Mediators, and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages
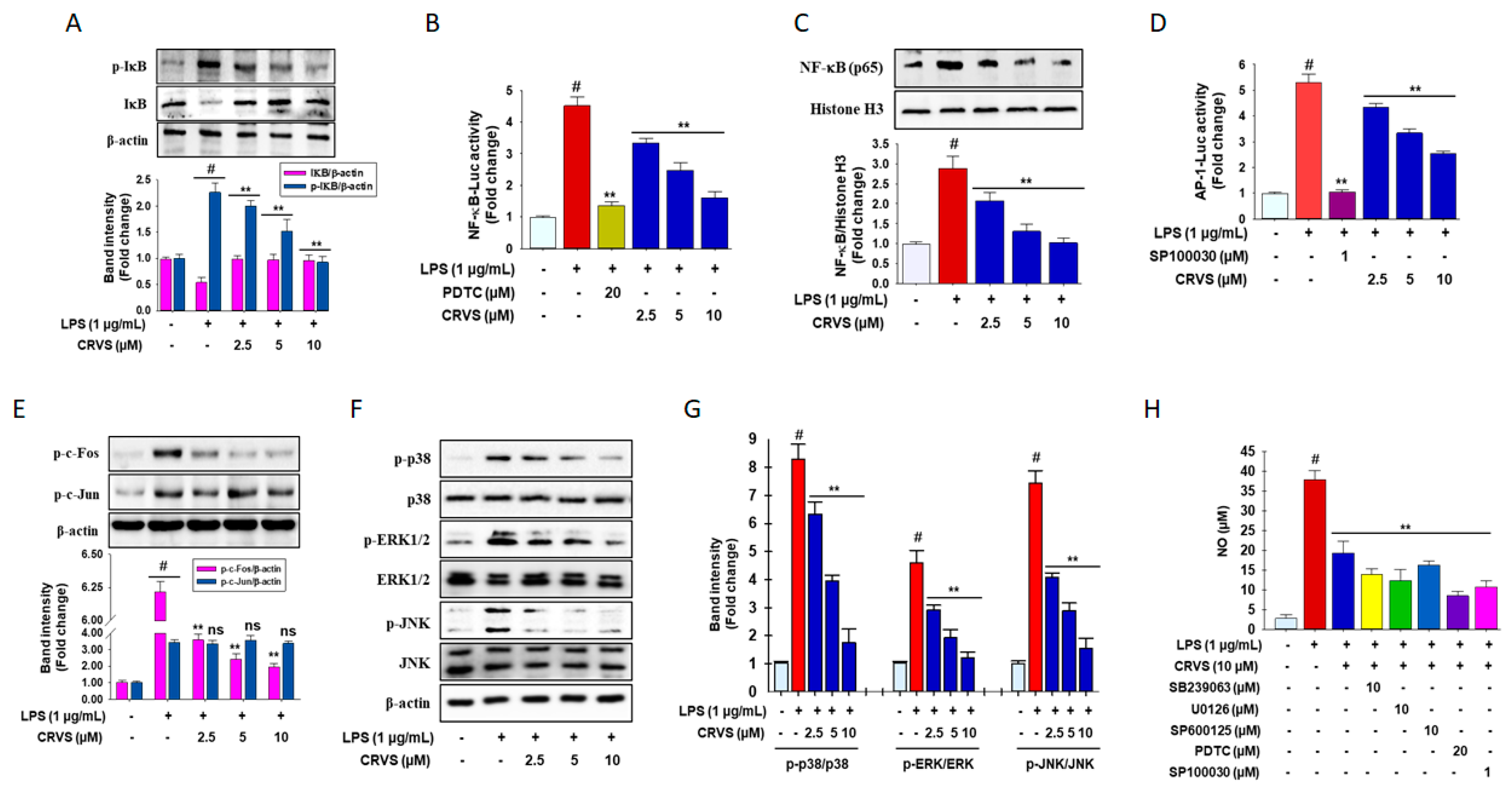
3.2. Inhibition of NF-κB and AP-1 signaling by CRVS in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages
3.3. CRVS Inhibits MAPK Phosphorylation in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages
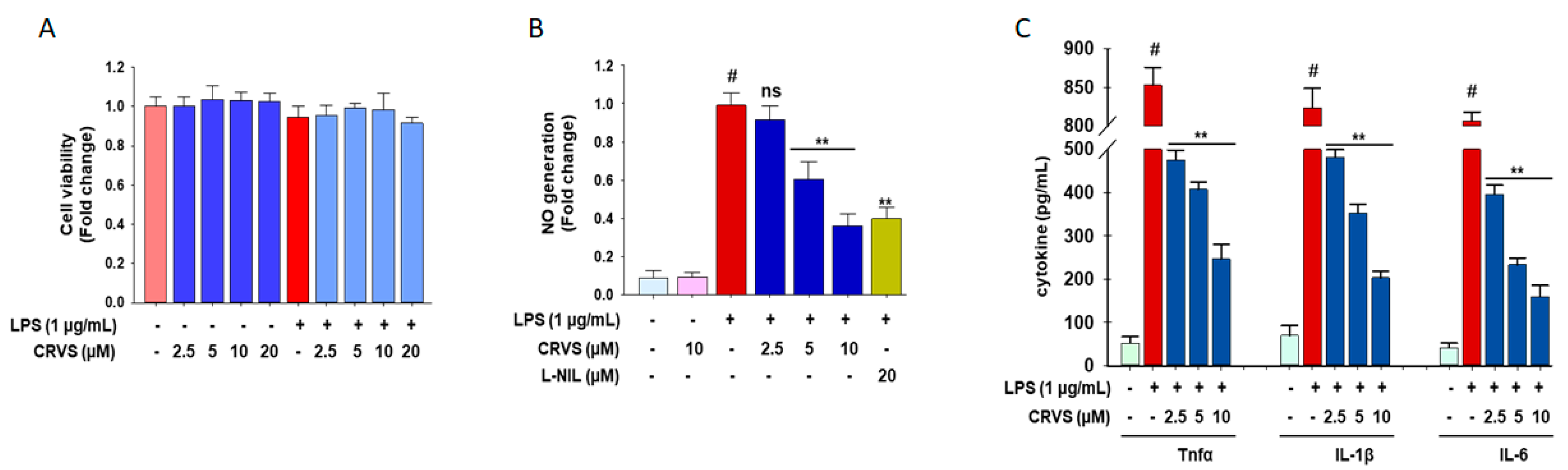
3.4. CRVS Suppresses the Production of NO and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Stimulated Murine Peritoneal Macrophages
3.5. Effects of CRVS on ROS Generation and HO-1 Expression in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Cells
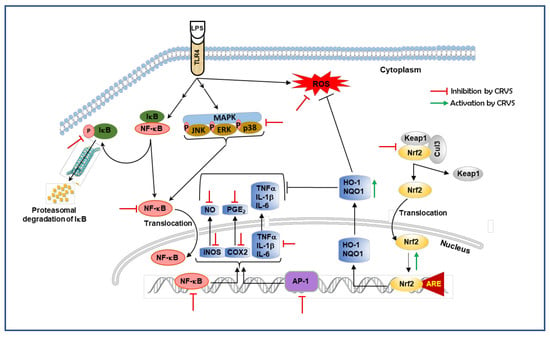
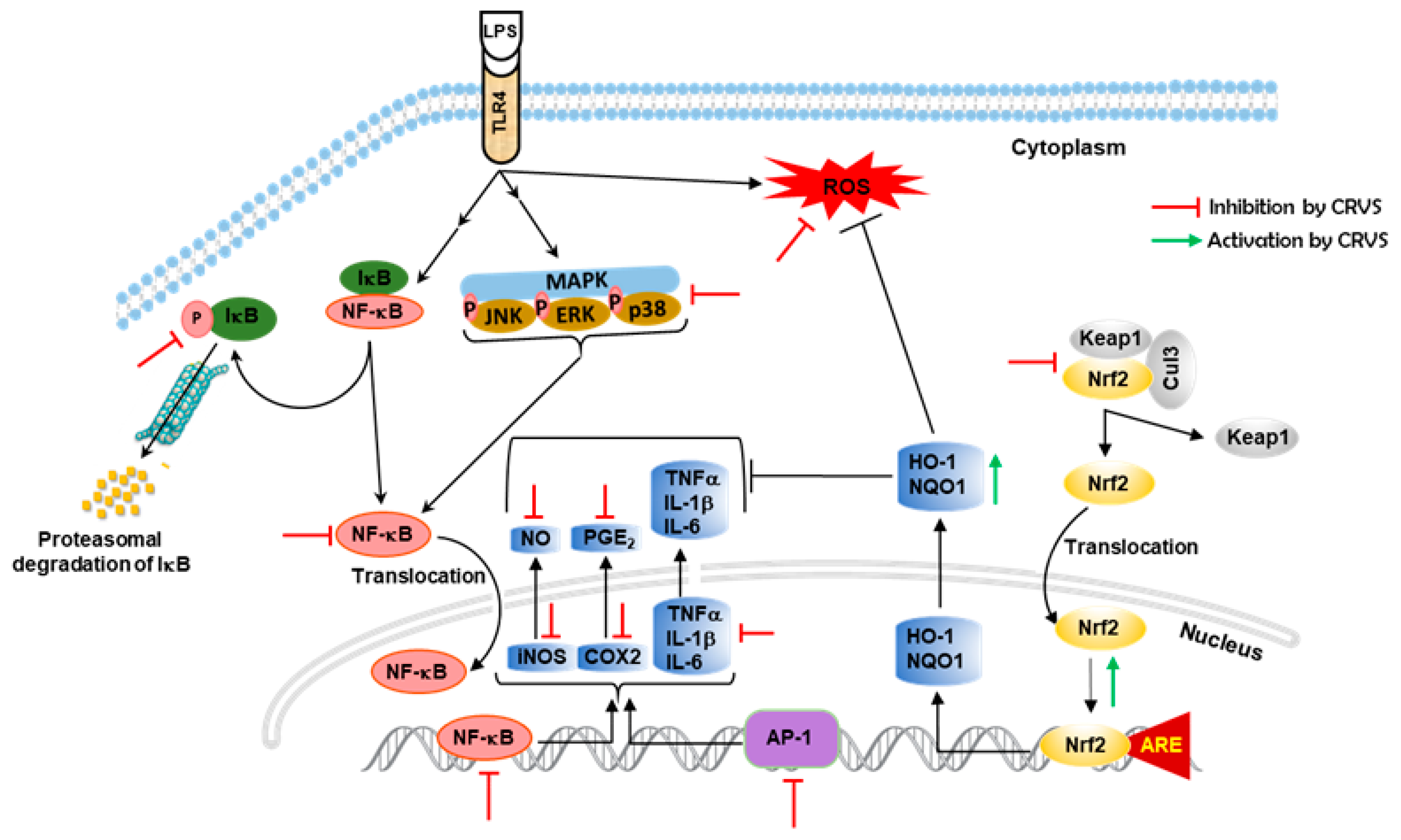
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Teng, H.; Fang, T.; Xiao, J. Agrimonolide from Agrimonia pilosa suppresses inflammatory responses through down-regulation of COX-2/iNOS and inactivation of NF-κB in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankhong, S.; Iawsipo, P.; Srisook, E.; Srisook, K. 4-methoxycinnamyl p-coumarate isolated from Etlingera pavieana rhizomes inhibits inflammatory response via suppression of NF-κB, Akt and AP-1 signaling in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Phytomedicine 2019, 54, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.Y.; Ju, J.M.; Mo, L.H.; Ma, L.; Hu, W.H.; You, R.R.; Chen, X.Q.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Qiu, S.Q.; et al. Anti-inflammation action of xanthones from Swertia chirayita by regulating COX-2/NF-κB/MAPKs/Akt signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transd. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Kim, M.S.; Le, M.Q.; Song, Y.S.; Bak, Y.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.R.; Yoon, D.Y. Fargesin exerts anti-inflammatory effects in THP-1 monocytes by suppressing PKC-dependent AP-1 and NF-κB signaling. Phytomedicine 2017, 24, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.B.; Ju, M.K.; Kwon, Y.G.; Lee, S.H. Protopine attenuates inflammation stimulated by carrageenan and LPS via the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gai, Y.N.; Li, B.B.; Huang, L.L. Andalucin from Artemisia lannta suppresses the neuroinflammation via the promotion of Nrf2-mediated HO-1 levels by blocking the p65-p300 interaction in LPS-activated BV2 microglia. Phytomedicine 2018, 51, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.M.; Zhang, W.Y.; Li, R.J.; Guo, C.; Wei, S.S.; Tian, X.M.; Luo, J.; Kong, L.Y. Anti-inflammatory activity of Khayandirobilide A from Khaya senegalensis via NF-kB, AP-1 and p38 MAPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 and BV-2 cells. Phytomedicine 2018, 42, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Valerio, M.S.; Kirkwood, K.L. MAPK usage in periodontal disease progression. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 308943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Park, S.D.; Koh, Y.J.; Kim, D.I.; Lee, J.H. Aqueous extract of Dipsacus asperoides suppresses lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses by inhibiting the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 231, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.H.; Hsu, W.L.; Chen, T.H.; Chou, T.C. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1signaling pathway involves the anti-inflammatory activity of magnolol in Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, R.M.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Ramirez, A.M. Compounds derived from endophytes: a review of phytochemistry and pharmacology. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2992–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, N.S.; Sohrab, M.H.; Rana, M.S.; Hasan, C.M.; Jamshidi, S.; Rahman, K.M. Cytotoxic naphthoquinone and azaanthraquinone derivatives from an endophytic Fusarium solani. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilahur, G.; Ben-Aicha, S.; Diaz, E.; Badimon, L.; Padro, T. Phytosterols and inflammation. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Tay, D.; de Blanco, E.C. NF-κB inhibitory activity of compounds isolated from Cantharellus cibarius. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lee, S.H.; Jang, H.D.; Ma, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Antioxidant and anti-osteoporotic activities of aromatic compounds and sterols from Hericium erinaceum. Molecules 2017, 22, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Kornsakulkarn, J.; Srichomthong, K.; Feng, T.; Liu, J.K.; Isaka, M.; Thongpanchang, C. Antimicrobial anthraquinones from cultures of the ant pathogenic fungus Cordyceps morakotii BCC 56811. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.L.; Wang, S.C.; Suzuki, K.; Fang, S.H.; Chen, C.S.; Cheng, W.C.; Su, C.C.; Yeh, H.C.; Tu, H.P.; Liu, P.L.; et al. Bavachin attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory response and inhibits the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 152785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.B.; Ju, M.K.; Lee, S.H. DNA Protecting activities of Nymphaea nouchali (Burm. f) flower extract attenuate t-BHP-induced oxidative stress cell death through Nrf2-mmediated induction of heme oxygenase-1 expression by activating MAP-kinases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Computatl. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Lu, M.C.; You, Q.D. Discovery and development of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1. nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Keap1:Nrf2) protein-protein interaction inhibitors: achievements, challenges, and future directions. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 10837–10858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.; Shen, S.S.; Deng, X.; Shiu, H.T.; Siu, W.S.; Leung, P.C.; Ko, C.H.; Cheng, B.H. Dihydrofisetin exerts its anti-inflammatory effects associated with suppressing ERK/p38 MAPK and heme oxygenase-1 activation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and carrageenan-induced mice paw edema. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.E.; Jung, E.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Jung, D.H.; Ku, S.K.; Cho, I.J.; Kim, S.C. Hemistepsin A ameliorates acute inflammation in macrophages via inhibition of NF-κB and activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yang, L.; Wan, C.X.; Xia, Y.Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, M.H.; Wang, Z.D.; Li, Z.R.; Li, X.M.; Geng, Y.D.; et al. Anti-neuroinflammatory effect of sophoraflavanone G from Sophora alopecuroides in LPS-activated BV2 microglia by MAPK, JAK/STAT and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-W.; Mei, H.-C.; Su, Y.-W.; Fan, H.-T.; Chen, C.-C.; Tsai, Y.-C. Inhibitory effects of Pleurotus tuber-regium mycelia and bioactive constituents on LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 7, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Zhou, W.; Jin, C.; Jiang, Z.; Diao, S.; Jin, Z.; Li, G. Anti-inflammatory activities of the chemical constituents isolated from Trametes versicolor. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2422–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Meng, X.M.; Jiang, G.L.; Li, H.; Cao, Q.; Yu, S.C.; Lv, X.W.; Cheng, W.M. Effect of triterpene acids of Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. leaf and MAPK signal transduction pathway on inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in alveolar macrophage of chronic bronchitis rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2009, 37, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo-Choi, R.; Cheng, M.S.; Shik Kim, Y. Desoxyrhapontigenin up-regulates Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression in macrophages and inflammatory lung injury. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, J.; Chen, G.; Hu, K. 2019. Gambogic acid induces heme oxygenase-1 through Nrf2 signaling pathway and inhibits NF-κB and MAPK activation to reduce inflammation in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedruzzi, L.M.; Stockler-Pinto, M.B.; Leite, M., Jr.; Mafra, D. Nrf2-keap1 system versus NF-κB: the good and the evil in chronic kidney disease? Biochimie 2012, 94, 2461–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Jeong, W.S.; Hu, R.; Kong, A.N. Regulation of Nrf2, NF-κB, and AP-1 signaling pathways by chemopreventive agents. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2005, 7, 1648–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canning, P.; Sorrell, F.J.; Bullock, A.N. Structural basis of Keap1 interactions with Nrf2. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, M. Molecular basis of the Keap1-Nrf2 system. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alam, M.B.; Chowdhury, N.S.; Sohrab, M.H.; Rana, M.S.; Hasan, C.M.; Lee, S.-H. Cerevisterol Alleviates Inflammation via Suppression of MAPK/NF-κB/AP-1 and Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Cascade. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020199
Alam MB, Chowdhury NS, Sohrab MH, Rana MS, Hasan CM, Lee S-H. Cerevisterol Alleviates Inflammation via Suppression of MAPK/NF-κB/AP-1 and Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Cascade. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020199
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlam, Md Badrul, Nargis Sultana Chowdhury, Md Hossain Sohrab, Md Sohel Rana, Choudhury Mahmood Hasan, and Sang-Han Lee. 2020. "Cerevisterol Alleviates Inflammation via Suppression of MAPK/NF-κB/AP-1 and Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Cascade" Biomolecules 10, no. 2: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020199
APA StyleAlam, M. B., Chowdhury, N. S., Sohrab, M. H., Rana, M. S., Hasan, C. M., & Lee, S.-H. (2020). Cerevisterol Alleviates Inflammation via Suppression of MAPK/NF-κB/AP-1 and Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Cascade. Biomolecules, 10(2), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020199