Cannabidiol: A Potential New Alternative for the Treatment of Anxiety, Depression, and Psychotic Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Introduction to the Phytocannabinoid Cannabidiol: Chemical Structure, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Profile
2.1. Overview of CBD Chemical Structure
2.2. Overview of CBD Pharmacological Profile
2.2.1. Pharmacokinetics
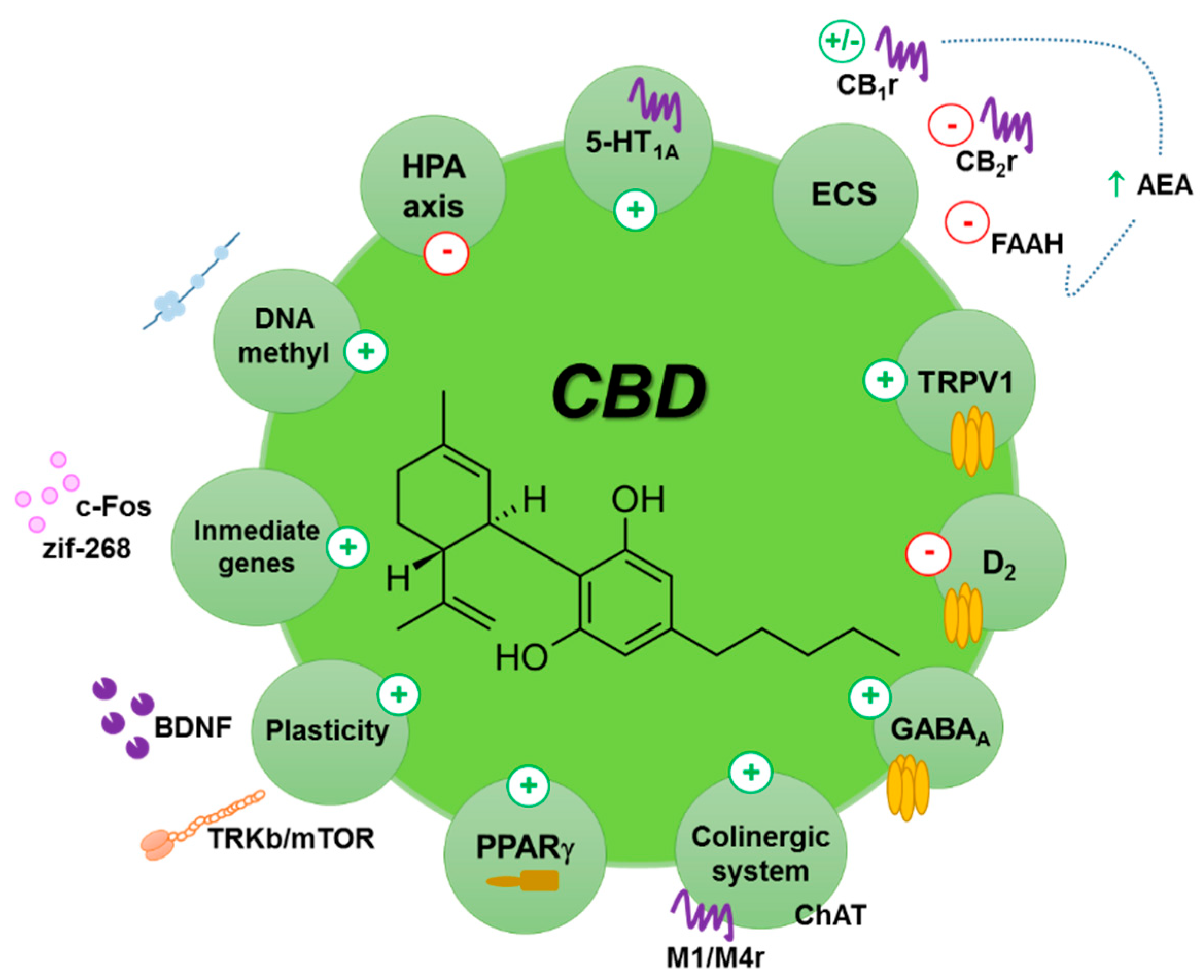
2.2.2. Pharmacodynamics
3. Role of CBD on Anxiety and Depressive Disorders: Animal and Human Studies
3.1. Current Scenario
3.2. Results from Animal Studies
3.3. Results from Clinical Studies
3.3.1. Clinical Studies Focused on Anxiety Disorders
3.3.2. Clinical Studies Focused on Stress-Related Disorders: PTSD
3.3.3. Clinical Studies Focused on Depressive Disorders
4. Role of CBD on Schizophrenia
4.1. Current Scenario
4.2. Results from Animal Studies
4.3. Results from Clinical Studies
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Depression in Europe: Facts and Figures. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/noncommunicable-diseases/mental-health/news/news/2012/10/depression-in-europe/depression-in-europe-facts-and-figures (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Whiteford, H.; Ferrari, A.J.; Degenhardt, L.; Feigin, V.; Vos, T. Chapter 2 Global burden of mental, neurological and substance use disorder: An analysis from the global burden of disease study 2010. In Mental, Neurological, and Substance Use Disorders: Disease Control Priorities, 3rd ed.; Patel, V., Laxminarayan, R., Medina-Mora, M.L., Dua, T., Chisholm, D., Eds.; The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Mental Health Policies and Programmes in the Workplace; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dome, P.; Rihmer, Z.; Gonda, X. Suicide Risk in Bipolar Disorder: A Brief Review. Medicina 2019, 55, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsenault-Lapierre, G.; Kim, C.; Turecki, G. Psychiatric diagnoses in 3275 suicides: A meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2004, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, J.T.; Carson, A.J.; Sharpe, M.; Lawrie, S.M. Psychological autopsy studies of suicide: A systematic review. Psychol. Med. 2003, 33, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The WHO Special Initiative for Mental Health (2019–2023): Universal Health Coverage for Mental Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Newson, J.J.; Hunter, D.; Thiagarajan, T.C. The Heterogeneity of Mental Health Assessment. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroney, M. An update on current treatment strategies and emerging agents for the management of schizophrenia. Am. J. Manag. Care 2020, 26, S55–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, M.J.; Vaccarino, S.R.; McInerney, S.J. Procognitive Effects of Antidepressants and Other Therapeutic Agents in Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2020, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Shan, W. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments for major depressive disorder in adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 281, 112595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Vieira, R. Tracking the impact of translational research in psychiatry: State of the art and perspectives. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.T.; Yang, K.C.; Lin, W.C. Glutamatergic Dysfunction and Glutamatergic Compounds for Major Psychiatric Disorders: Evidence From Clinical Neuroimaging Studies. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averill, L.A.; Purohit, P.; Averill, C.L.; Boesl, M.A.; Krystal, J.H.; Abdallah, C.G. Glutamate dysregulation and glutamatergic therapeutics for PTSD: Evidence from human studies. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 649, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reus, G.Z.; de Moura, A.B.; Silva, R.H.; Resende, W.R.; Quevedo, J. Resilience Dysregulation in Major Depressive Disorder: Focus on Glutamatergic Imbalance and Microglial Activation. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogaca, M.V.; Duman, R.S. Cortical GABAergic Dysfunction in Stress and Depression: New Insights for Therapeutic Interventions. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luscher, B.; Shen, Q.; Sahir, N. The GABAergic deficit hypothesis of major depressive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, J.C.; Vinkers, C.H.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E.; Marsman, A. GABAergic Mechanisms in Schizophrenia: Linking Postmortem and In Vivo Studies. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Ballinger, M.D.; Pletnikov, M.V.; Wong, D.F.; Kamiya, A. Endocannabinoid system: Potential novel targets for treatment of schizophrenia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 53, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, F.; Garcia-Gutierrez, M.S.; Jurado-Barba, R.; Rubio, G.; Gasparyan, A.; Austrich-Olivares, A.; Manzanares, J. Endocannabinoid System Components as Potential Biomarkers in Psychiatry. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, M.E.; Grant, C.W.; Gowin, J.L.; Ramchandani, V.A.; Le Foll, B. Endocannabinoid signaling in psychiatric disorders: A review of positron emission tomography studies. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.T.; Hill, M.N.; Lee, F.S. Developmental regulation of fear learning and anxiety behavior by endocannabinoids. Genes Brain Behav. 2016, 15, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, E.J.; Singh, J.B.; Fedgchin, M.; Cooper, K.; Lim, P.; Shelton, R.C.; Thase, M.E.; Winokur, A.; Van Nueten, L.; Manji, H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Intranasal Esketamine Adjunctive to Oral Antidepressant Therapy in Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedgchin, M.; Trivedi, M.; Daly, E.J.; Melkote, R.; Lane, R.; Lim, P.; Vitagliano, D.; Blier, P.; Fava, M.; Liebowitz, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Fixed-Dose Esketamine Nasal Spray Combined With a New Oral Antidepressant in Treatment-Resistant Depression: Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Controlled Study (TRANSFORM-1). Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Sci. J. Coll. Int. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, E.J.; Trivedi, M.H.; Janik, A.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Lane, R.; Lim, P.; Duca, A.R.; Hough, D.; et al. Efficacy of Esketamine Nasal Spray Plus Oral Antidepressant Treatment for Relapse Prevention in Patients With Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertwee, R.G. The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinghorn, A.D.; Falk, H.; Gibbons, S.; Kobayashi, J. Phytocannbinoids: Unraveling the Complex Chemistry and Pharmacology of Cannabis Sativa; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gaoni, Y.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation, structure, and partial synthesis of an active constituent of hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1646–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Hunt, M.; Clark, J.H. Structure of cannabidiol, a product isolated from the Marihuana extract of Minnesota Wild Hemp. I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940, 62, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Shvo, Y.; Hashish, I. The structure of cannabidiol. Tetrahedron 1963, 19, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, S. Cannabidiol (CBD) and its analogs: A review of their effects on inflammation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlebnik, N.E.; Cheer, J.F. Beyond the CB1 Receptor: Is Cannabidiol the Answer for Disorders of Motivation? Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 39, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusar-Poli, P.; Crippa, J.A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Borgwardt, S.J.; Allen, P.; Martin-Santos, R.; Seal, M.; Surguladze, S.A.; O’Carrol, C.; Atakan, Z.; et al. Distinct effects of {delta}9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol on neural activation during emotional processing. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winton-Brown, T.T.; Allen, P.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Borgwardt, S.J.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Crippa, J.A.; Seal, M.L.; Martin-Santos, R.; Ffytche, D.; Zuardi, A.W.; et al. Modulation of auditory and visual processing by delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol: An FMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Santos, R.; Crippa, J.A.; Batalla, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Atakan, Z.; Borgwardt, S.; Allen, P.; Seal, M.; Langohr, K.; Farre, M.; et al. Acute effects of a single, oral dose of d9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) administration in healthy volunteers. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 4966–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, L.A.; Burton, P.; Sorge, R.E.; Yakiwchuk, C.; Mechoulam, R. Effect of low doses of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol on the extinction of cocaine-induced and amphetamine-induced conditioned place preference learning in rats. Psychopharmacology 2004, 175, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vann, R.E.; Gamage, T.F.; Warner, J.A.; Marshall, E.M.; Taylor, N.L.; Martin, B.R.; Wiley, J.L. Divergent effects of cannabidiol on the discriminative stimulus and place conditioning effects of Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008, 94, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viudez-Martinez, A.; Garcia-Gutierrez, M.S.; Medrano-Relinque, J.; Navarron, C.M.; Navarrete, F.; Manzanares, J. Cannabidiol does not display drug abuse potential in mice behavior. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisanti, S.; Malfitano, A.M.; Ciaglia, E.; Lamberti, A.; Ranieri, R.; Cuomo, G.; Abate, M.; Faggiana, G.; Proto, M.C.; Fiore, D.; et al. Cannabidiol: State of the art and new challenges for therapeutic applications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 175, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviello, G.; Romano, B.; Borrelli, F.; Capasso, R.; Gallo, L.; Piscitelli, F.; Di Marzo, V.; Izzo, A.A. Chemopreventive effect of the non-psychotropic phytocannabinoid cannabidiol on experimental colon cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Remessy, A.B.; Al-Shabrawey, M.; Khalifa, Y.; Tsai, N.T.; Caldwell, R.B.; Liou, G.I. Neuroprotective and blood-retinal barrier-preserving effects of cannabidiol in experimental diabetes. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaus, P.W.; Wagner, J.G.; Harkema, J.R.; Kaminski, N.E.; Kaplan, B.L. Cannabidiol (CBD) enhances lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced pulmonary inflammation in C57BL/6 mice. J. Immunotoxicol. 2013, 10, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y.; McKeage, K.; Scott, L.J. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol/cannabidiol (Sativex(R)): A review of its use in patients with moderate to severe spasticity due to multiple sclerosis. Drugs 2014, 74, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devinsky, O.; Patel, A.D.; Cross, J.H.; Villanueva, V.; Wirrell, E.C.; Privitera, M.; Greenwood, S.M.; Roberts, C.; Checketts, D.; VanLandingham, K.E.; et al. Effect of Cannabidiol on Drop Seizures in the Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Moreno, A.M.; Reigada, D.; Ramirez, B.G.; Mechoulam, R.; Innamorato, N.; Cuadrado, A.; de Ceballos, M.L. Cannabidiol and other cannabinoids reduce microglial activation in vitro and in vivo: Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 79, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuvone, T.; Esposito, G.; De Filippis, D.; Scuderi, C.; Steardo, L. Cannabidiol: A promising drug for neurodegenerative disorders? CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2009, 15, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozela, E.; Lev, N.; Kaushansky, N.; Eilam, R.; Rimmerman, N.; Levy, R.; Ben-Nun, A.; Juknat, A.; Vogel, Z. Cannabidiol inhibits pathogenic T cells, decreases spinal microglial activation and ameliorates multiple sclerosis-like disease in C57BL/6 mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, M.; Benitez, S.U.; Cartarozzi, L.P.; Del Bel, E.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Oliveira, A.L. Neuroprotection and reduction of glial reaction by cannabidiol treatment after sciatic nerve transection in neonatal rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 38, 3424–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mello Schier, A.R.; de Oliveira Ribeiro, N.P.; Coutinho, D.S.; Machado, S.; Arias-Carrion, O.; Crippa, J.A.; Zuardi, A.W.; Nardi, A.E.; Silva, A.C. Antidepressant-like and anxiolytic-like effects of cannabidiol: A chemical compound of Cannabis sativa. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessing, E.M.; Steenkamp, M.M.; Manzanares, J.; Marmar, C.R. Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Anxiety Disorders. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2015, 12, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseger, T.A.; Bossong, M.G. A systematic review of the antipsychotic properties of cannabidiol in humans. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 162, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huestis, M.A. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of the plant cannabinoids, delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and cannabinol. Handb. Exp. Pharm. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawksworth, G.M.K. Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics of Cannabinoids; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, S.A.; Stone, N.L.; Yates, A.S.; O’Sullivan, S.E. A Systematic Review on the Pharmacokinetics of Cannabidiol in Humans. Front. Pharm. 2018, 9, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devinsky, O.; Cilio, M.R.; Cross, H.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J.; French, J.; Hill, C.; Katz, R.; Di Marzo, V.; Jutras-Aswad, D.; Notcutt, W.G.; et al. Cannabidiol: Pharmacology and potential therapeutic role in epilepsy and other neuropsychiatric disorders. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.S. The Utility of Cannabidiol in the Treatment of Refractory Epilepsy. Clin. Pharm. 2017, 101, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, A.; Lindgren, J.E.; Andersson, S.; Agurell, S.; Gillespie, H.; Hollister, L.E. Single dose kinetics of cannabidiol in man. Cannabinoids Chem. Pharmacol. Ther. Asp. 1984, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, D.J.; Samara, E.; Mechoulam, R. Comparative metabolism of cannabidiol in dog, rat and man. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 40, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujvary, I.; Hanus, L. Human Metabolites of Cannabidiol: A Review on Their Formation, Biological Activity, and Relevance in Therapy. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Yamaori, S.; Takeda, S.; Yamamoto, I.; Watanabe, K. Identification of cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for metabolism of cannabidiol by human liver microsomes. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, G.W.; Robson, P.J. A Phase I, Open Label, Four-Way Crossover Study to Compare the Pharmacokinetic Profiles of a Single Dose of 20 mg of a Cannabis Based Medicine Extract (CBME) Administered on 3 Different Areas of the Buccal Mucosa and to Investigate the Pharmacokinetics of CBME per Oral in Healthy Male and Female Volunteers (GWPK0112). J. Cannabis Ther. 2004, 3, 79–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamaschi, M.M.; Queiroz, R.H.; Zuardi, A.W.; Crippa, J.A. Safety and side effects of cannabidiol, a Cannabis sativa constituent. Curr. Drug Saf. 2011, 6, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuardi, A.W.; Morais, S.L.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Mechoulam, R. Antipsychotic effect of cannabidiol. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1995, 56, 485–486. [Google Scholar]
- Ibeas Bih, C.; Chen, T.; Nunn, A.V.; Bazelot, M.; Dallas, M.; Whalley, B.J. Molecular Targets of Cannabidiol in Neurological Disorders. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2015, 12, 699–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Baillie, G.L.; Phillips, A.M.; Razdan, R.K.; Ross, R.A.; Pertwee, R.G. Cannabidiol displays unexpectedly high potency as an antagonist of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Peters, M.; Murillo-Rodriguez, E.; Hanus, L.O. Cannabidiol—Recent advances. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 1678–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, A.A.; Borrelli, F.; Capasso, R.; Di Marzo, V.; Mechoulam, R. Non-psychotropic plant cannabinoids: New therapeutic opportunities from an ancient herb. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPartland, J.M.; Duncan, M.; Di Marzo, V.; Pertwee, R.G. Are cannabidiol and Delta(9) -tetrahydrocannabivarin negative modulators of the endocannabinoid system? A systematic review. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Bagher, A.M.; Kelly, M.E.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. Cannabidiol is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4790–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, C.A.J.; da Silva, T.R.; Raymundi, A.M.; de Souza, C.P.; Hiroaki-Sato, V.A.; Kato, L.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Andreatini, R.; Takahashi, R.N.; Bertoglio, L.J. Cannabidiol disrupts the consolidation of specific and generalized fear memories via dorsal hippocampus CB1 and CB2 receptors. Neuropharmacology 2017, 125, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Ligresti, A.; Moriello, A.S.; Allara, M.; Bisogno, T.; Petrosino, S.; Stott, C.G.; Di Marzo, V. Effects of cannabinoids and cannabinoid-enriched Cannabis extracts on TRP channels and endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1479–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, L.S.; Ryberg, E.; Sims, N.A.; Ridge, S.A.; Mackie, K.; Greasley, P.J.; Ross, R.A.; Rogers, M.J. The putative cannabinoid receptor GPR55 affects osteoclast function in vitro and bone mass in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16511–16516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylantyev, S.; Jensen, T.P.; Ross, R.A.; Rusakov, D.A. Cannabinoid- and lysophosphatidylinositol-sensitive receptor GPR55 boosts neurotransmitter release at central synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5193–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylantyev, S.J.T.; Ross, R.A.; Rusakov, D.A. The enigmatic receptor GPR55 potentiates neurotransmitter release at central synapses. In Proceedings of the Neuroscience Meeting Planner Washington, DC: Society for Neuroscience Online: Program, Washington, DC, USA, 12–16 November 2011. Program 653.01, Poster B28. [Google Scholar]
- Poddar, M.K.; Dewey, W.L. Effects of cannabinoids on catecholamine uptake and release in hypothalamic and striatal synaptosomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1980, 214, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfo, P.; Silveirinha, V.; dos Santos-Rodrigues, A.; Venance, L.; Ledent, C.; Takahashi, R.N.; Cunha, R.A.; Kofalvi, A. Cannabinoids inhibit the synaptic uptake of adenosine and dopamine in the rat and mouse striatum. Eur. J. Pharm. 2011, 655, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaysse, P.J.; Gardner, E.L.; Zukin, R.S. Modulation of rat brain opioid receptors by cannabinoids. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1987, 241, 534–539. [Google Scholar]
- Kathmann, M.; Flau, K.; Redmer, A.; Trankle, C.; Schlicker, E. Cannabidiol is an allosteric modulator at mu- and delta-opioid receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2006, 372, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, P. Cannabidiol is a partial agonist at dopamine D2High receptors, predicting its antipsychotic clinical dose. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, E.M.; Bolognini, D.; Limebeer, C.L.; Cascio, M.G.; Anavi-Goffer, S.; Fletcher, P.J.; Mechoulam, R.; Pertwee, R.G.; Parker, L.A. Cannabidiol, a non-psychotropic component of cannabis, attenuates vomiting and nausea-like behaviour via indirect agonism of 5-HT(1A) somatodendritic autoreceptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 2620–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, E.B.; Burnett, A.; Hall, B.; Parker, K.K. Agonistic properties of cannabidiol at 5-HT1a receptors. Neurochem. Res. 2005, 30, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Heather, A.; Church, A.C.; Lucey, J.V. Core Psychiatry, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, M.J.; Luoto, S.; Krams, I.; Karlsson, H. Depression subtyping based on evolutionary psychiatry: Proximate mechanisms and ultimate functions. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, J.C.; Schmidt, S.L. DSM-5 Criteria and Depression Severity: Implications for Clinical Practice. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragones, E.; Pinol, J.L.; Labad, A. Comorbidity of major depression with other common mental disorders in primary care patients. Aten Primaria 2009, 41, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.; McGuffin, P.; Farmer, A.E. The classification of depression: Are we still confused? Br. J. Psychiatry 2008, 192, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiller, J.W. Depression and anxiety. Med. J. Aust. 2013, 199, S28–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Takeshima, N.; Hayasaka, Y.; Tajika, A.; Watanabe, N.; Streiner, D.; Furukawa, T.A. Antidepressants plus benzodiazepines for adults with major depression. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 6, CD001026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, R.H. Buspirone: Back to the Future. J. Psychosoc. Nurs. Ment. Health Serv. 2015, 53, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NHS Psychological Therapies Service. Generalized Anxiety Disorder in Adults-Treatment. Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/generalised-anxiety-disorder/treatment (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Machmutow, K.; Meister, R.; Jansen, A.; Kriston, L.; Watzke, B.; Harter, M.C.; Liebherz, S. Comparative effectiveness of continuation and maintenance treatments for persistent depressive disorder in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 5, CD012855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Faucett, J.; Lichtenberg, P.; Kirsch, I.; Brown, W.A. A systematic review of comparative efficacy of treatments and controls for depression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, A.; D’Avanzo, B.; Parabiaghi, A. Couple therapy for depression. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 6, CD004188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, N.G.S.; Tufik, S. Comparative effects between cannabidiol and diazepam on neophobia, food intake and conflict behavior. Res. Commun. Psychol. Psychiatry Behav. 1981, 6, 251–266. [Google Scholar]
- Zuardi, A.W.; Karniol, I.G. Effects on variable-interval performance in rats of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol, separately and in combination. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1983, 16, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, F.S.; Chiaretti, T.M.; Graeff, F.G.; Zuardi, A.W. Antianxiety effect of cannabidiol in the elevated plus-maze. Psychopharmacology 1990, 100, 558–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Green, M.R.; Martin, B.R. Pharmacological characterization of cannabinoids in the elevated plus maze. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990, 253, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, V.; Levin, R.; Peres, F.F.; Niigaki, S.T.; Calzavara, M.B.; Zuardi, A.W.; Hallak, J.E.; Crippa, J.A.; Abilio, V.C. Cannabidiol exhibits anxiolytic but not antipsychotic property evaluated in the social interaction test. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 41, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resstel, L.B.; Tavares, R.F.; Lisboa, S.F.; Joca, S.R.; Correa, F.M.; Guimaraes, F.S. 5-HT1A receptors are involved in the cannabidiol-induced attenuation of behavioural and cardiovascular responses to acute restraint stress in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 156, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viudez-Martinez, A.; Garcia-Gutierrez, M.S.; Manzanares, J. Cannabidiol regulates the expression of hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis-related genes in response to acute restraint stress. J. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 32, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.A.; Aguiar, D.C.; Guimaraes, F.S. Anxiolytic-like effect of cannabidiol in the rat Vogel conflict test. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 30, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardo, M.; Casarotto, P.C.; Gomes, F.V.; Guimaraes, F.S. Cannabidiol reverses the mCPP-induced increase in marble-burying behavior. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 28, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casarotto, P.C.; Gomes, F.V.; Resstel, L.B.; Guimaraes, F.S. Cannabidiol inhibitory effect on marble-burying behaviour: Involvement of CB1 receptors. Behav. Pharm. 2010, 21, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, S.M.; Arnold, J.C. Neural correlates of interactions between cannabidiol and Delta(9) -tetrahydrocannabinol in mice: Implications for medical cannabis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, S.M.; Zhou, C.; Clarke, D.J.; Chohan, T.W.; Bahceci, D.; Arnold, J.C. Interactions between cannabidiol and Delta(9)-THC following acute and repeated dosing: Rebound hyperactivity, sensorimotor gating and epigenetic and neuroadaptive changes in the mesolimbic pathway. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 27, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, A.J.; Fogaca, M.V.; Sartim, A.G.; Pereira, V.S.; Wegener, G.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Joca, S.R.L. Cannabidiol Induces Rapid and Sustained Antidepressant-Like Effects Through Increased BDNF Signaling and Synaptogenesis in the Prefrontal Cortex. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, Z.; Farkas, S.; Albert, A.; Ferencz, E.; Vancea, S.; Urkon, M.; Kolcsar, M. Effects of Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment in the Rat Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Model of Depression. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, C.A.; Gazarini, L.; Takahashi, R.N.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Bertoglio, L.J. On disruption of fear memory by reconsolidation blockade: Evidence from cannabidiol treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 2132–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shbiro, L.; Hen-Shoval, D.; Hazut, N.; Rapps, K.; Dar, S.; Zalsman, G.; Mechoulam, R.; Weller, A.; Shoval, G. Effects of cannabidiol in males and females in two different rat models of depression. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 201, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reus, G.Z.; Stringari, R.B.; Ribeiro, K.F.; Luft, T.; Abelaira, H.M.; Fries, G.R.; Aguiar, B.W.; Kapczinski, F.; Hallak, J.E.; Zuardi, A.W.; et al. Administration of cannabidiol and imipramine induces antidepressant-like effects in the forced swimming test and increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in the rat amygdala. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2011, 23, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.C.; Guimaraes, F.S. Involvement of 5HT1A receptors in the anxiolytic-like effects of cannabidiol injected into the dorsolateral periaqueductal gray of rats. Psychopharmacology 2008, 199, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paula Soares, V.; Campos, A.C.; Bortoli, V.C.; Zangrossi, H., Jr.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Zuardi, A.W. Intra-dorsal periaqueductal gray administration of cannabidiol blocks panic-like response by activating 5-HT1A receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 213, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.V.; Alves, F.H.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Correa, F.M.; Resstel, L.B.; Crestani, C.C. Cannabidiol administration into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis alters cardiovascular responses induced by acute restraint stress through 5-HT(1)A receptor. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granjeiro, E.M.; Gomes, F.V.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Correa, F.M.; Resstel, L.B. Effects of intracisternal administration of cannabidiol on the cardiovascular and behavioral responses to acute restraint stress. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 99, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogaca, M.V.; Campos, A.C.; Coelho, L.D.; Duman, R.S.; Guimaraes, F.S. The anxiolytic effects of cannabidiol in chronically stressed mice are mediated by the endocannabinoid system: Role of neurogenesis and dendritic remodeling. Neuropharmacology 2018, 135, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourt, R.M.; Pamplona, F.A.; Takahashi, R.N. Facilitation of contextual fear memory extinction and anti-anxiogenic effects of AM404 and cannabidiol in conditioned rats. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 18, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, J.I.; Resstel, L.B.; Guimaraes, F.S. Involvement of the prelimbic prefrontal cortex on cannabidiol-induced attenuation of contextual conditioned fear in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 207, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Monte, F.H.; Souza, R.R.; Bitencourt, R.M.; Kroon, J.A.; Takahashi, R.N. Infusion of cannabidiol into infralimbic cortex facilitates fear extinction via CB1 receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 250, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymundi, A.M.; da Silva, T.R.; Zampronio, A.R.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Bertoglio, L.J.; Stern, C.A.J. A time-dependent contribution of hippocampal CB1, CB2 and PPARgamma receptors to cannabidiol-induced disruption of fear memory consolidation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartim, A.G.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Joca, S.R. Antidepressant-like effect of cannabidiol injection into the ventral medial prefrontal cortex-Possible involvement of 5-HT1A and CB1 receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 303, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bis-Humbert, C.; Garcia-Cabrerizo, R.; Garcia-Fuster, M.J. Decreased sensitivity in adolescent versus adult rats to the antidepressant-like effects of cannabidiol. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElBatsh, M.M.; Assareh, N.; Marsden, C.A.; Kendall, D.A. Anxiogenic-like effects of chronic cannabidiol administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 2012, 221, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoval, G.; Shbiro, L.; Hershkovitz, L.; Hazut, N.; Zalsman, G.; Mechoulam, R.; Weller, A. Prohedonic Effect of Cannabidiol in a Rat Model of Depression. Neuropsychobiology 2016, 73, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, H.; Chaves, Y.C.; Waltrick, A.P.F.; Jesus, C.H.A.; Genaro, K.; Crippa, J.A.; da Cunha, J.M.; Zanoveli, J.M. Sub-chronic treatment with cannabidiol but not with URB597 induced a mild antidepressant-like effect in diabetic rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 682, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.E.; Chesworth, R.; Huang, X.F.; McGregor, I.S.; Arnold, J.C.; Karl, T. A behavioural comparison of acute and chronic Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol in C57BL/6JArc mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Sci. J. Coll. Int. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 13, 861–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assareh, N.; Gururajan, A.; Zhou, C.; Luo, J.L.; Kevin, R.C.; Arnold, J.C. Cannabidiol disrupts conditioned fear expression and cannabidiolic acid reduces trauma-induced anxiety-related behaviour in mice. Behav. Pharm. 2020, 31, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten, C.R.; Zhang, Y.; Boehm, S.L., Jr. Acute Cannabinoids Produce Robust Anxiety-Like and Locomotor Effects in Mice, but Long-Term Consequences Are Age- and Sex-Dependent. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparyan, A.N.F.; Manzanares, J. Effects of cannabidiol plus sertraline on behavioural and gene expression alterations in a long-lasting animal model of post-traumatic stress disorder. Authorea 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, E.M.; Ott, F.W.; Muller, M.; Silcher, B.; Sichler, M.E.; Low, M.J.; Wagner, J.M.; Bouter, Y. Prolonged Cannabidiol Treatment Lacks on Detrimental Effects on Memory, Motor Performance and Anxiety in C57BL/6J Mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.A.; Bick-Sander, A.; Fabel, K.; Leal-Galicia, P.; Tauber, S.; Ramirez-Rodriguez, G.; Muller, A.; Melnik, A.; Waltinger, T.P.; Ullrich, O.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor CB1 mediates baseline and activity-induced survival of new neurons in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Cell Commun. Signal 2010, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linge, R.; Jimenez-Sanchez, L.; Campa, L.; Pilar-Cuellar, F.; Vidal, R.; Pazos, A.; Adell, A.; Diaz, A. Cannabidiol induces rapid-acting antidepressant-like effects and enhances cortical 5-HT/glutamate neurotransmission: Role of 5-HT1A receptors. Neuropharmacology 2016, 103, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavon, A.P.; Bonato, J.M.; Milani, H.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Weffort de Oliveira, R.M. Influence of single and repeated cannabidiol administration on emotional behavior and markers of cell proliferation and neurogenesis in non-stressed mice. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 64, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Chang, T.; Du, Y.; Yu, C.; Tan, X.; Li, X. Pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous cannabidiol and its antidepressant-like effects in chronic mild stress mouse model. Env. Toxicol. Pharm. 2019, 70, 103202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, A.J.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Joca, S.R.L. CBD modulates DNA methylation in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of mice exposed to forced swim. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 388, 112627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, A.J.; Crestani, C.C.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Joca, S.R.L. Antidepressant-like effect induced by Cannabidiol is dependent on brain serotonin levels. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 86, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanelati, T.V.; Biojone, C.; Moreira, F.A.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Joca, S.R. Antidepressant-like effects of cannabidiol in mice: Possible involvement of 5-HT1A receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Alfy, A.T.; Ivey, K.; Robinson, K.; Ahmed, S.; Radwan, M.; Slade, D.; Khan, I.; ElSohly, M.; Ross, S. Antidepressant-like effect of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and other cannabinoids isolated from Cannabis sativa L. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 95, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogaca, M.V.; Reis, F.M.; Campos, A.C.; Guimaraes, F.S. Effects of intra-prelimbic prefrontal cortex injection of cannabidiol on anxiety-like behavior: Involvement of 5HT1A receptors and previous stressful experience. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resstel, L.B.; Joca, S.R.; Moreira, F.A.; Correa, F.M.; Guimaraes, F.S. Effects of cannabidiol and diazepam on behavioral and cardiovascular responses induced by contextual conditioned fear in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 172, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignoli, M.T.; Lopes-Aguiar, C.; Ruggiero, R.N.; Do Val da Silva, R.A.; Bueno-Junior, L.S.; Kandratavicius, L.; Peixoto-Santos, J.E.; Crippa, J.A.; Cecilio Hallak, J.E.; Zuardi, A.W.; et al. Selective post-training time window for memory consolidation interference of cannabidiol into the prefrontal cortex: Reduced dopaminergic modulation and immediate gene expression in limbic circuits. Neuroscience 2017, 350, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, C.; Loureiro, M.; Kramar, C.; Zunder, J.; Renard, J.; Rushlow, W.; Laviolette, S.R. Cannabidiol Modulates Fear Memory Formation Through Interactions with Serotonergic Transmission in the Mesolimbic System. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho, A.L.; Vila-Verde, C.; Fogaca, M.V.; Guimaraes, F.S. Effects of intra-infralimbic prefrontal cortex injections of cannabidiol in the modulation of emotional behaviors in rats: Contribution of 5HT(1)A receptors and stressful experiences. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 286, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shallcross, J.; Hamor, P.; Bechard, A.R.; Romano, M.; Knackstedt, L.; Schwendt, M. The Divergent Effects of CDPPB and Cannabidiol on Fear Extinction and Anxiety in a Predator Scent Stress Model of PTSD in Rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.C.; Ferreira, F.R.; Guimaraes, F.S. Cannabidiol blocks long-lasting behavioral consequences of predator threat stress: Possible involvement of 5HT1A receptors. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2012, 46, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardowschy, A.; Castiblanco-Urbina, M.A.; Uribe-Marino, A.; Biagioni, A.F.; Salgado-Rohner, C.J.; Crippa, J.A.; Coimbra, N.C. The role of 5-HT1A receptors in the anti-aversive effects of cannabidiol on panic attack-like behaviors evoked in the presence of the wild snake Epicrates cenchria crassus (Reptilia, Boidae). J. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 27, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P.; Muscat, R.; Papp, M. Chronic mild stress-induced anhedonia: A realistic animal model of depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1992, 16, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P. Validity, reliability and utility of the chronic mild stress model of depression: A 10-year review and evaluation. Psychopharmacology 1997, 134, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.C.; Ortega, Z.; Palazuelos, J.; Fogaca, M.V.; Aguiar, D.C.; Diaz-Alonso, J.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Vazquez-Villa, H.; Moreira, F.A.; Guzman, M.; et al. The anxiolytic effect of cannabidiol on chronically stressed mice depends on hippocampal neurogenesis: Involvement of the endocannabinoid system. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Sci. J. Coll. Int. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karniol, I.G.; Shirakawa, I.; Kasinski, N.; Pfeferman, A.; Carlini, E.A. Cannabidiol interferes with the effects of delta 9 - tetrahydrocannabinol in man. Eur. J. Pharm. 1974, 28, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuardi, A.W.; Shirakawa, I.; Finkelfarb, E.; Karniol, I.G. Action of cannabidiol on the anxiety and other effects produced by delta 9-THC in normal subjects. Psychopharmacology 1982, 76, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuardi, A.W.; Cosme, R.A.; Graeff, F.G.; Guimaraes, F.S. Effects of ipsapirone and cannabidiol on human experimental anxiety. J. Psychopharmacol. 1993, 7, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crippa, J.A.; Zuardi, A.W.; Garrido, G.E.; Wichert-Ana, L.; Guarnieri, R.; Ferrari, L.; Azevedo-Marques, P.M.; Hallak, J.E.; McGuire, P.K.; Filho Busatto, G. Effects of cannabidiol (CBD) on regional cerebral blood flow. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Borgwardt, S.; Martin-Santos, R.; Nosarti, C.; O’Carroll, C.; Allen, P.; Seal, M.L.; Fletcher, P.C.; Crippa, J.A.; et al. Modulation of mediotemporal and ventrostriatal function in humans by Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol: A neural basis for the effects of Cannabis sativa on learning and psychosis. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crippa, J.A.; Derenusson, G.N.; Ferrari, T.B.; Wichert-Ana, L.; Duran, F.L.; Martin-Santos, R.; Simoes, M.V.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Atakan, Z.; et al. Neural basis of anxiolytic effects of cannabidiol (CBD) in generalized social anxiety disorder: A preliminary report. J. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 25, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, M.M.; Queiroz, R.H.; Chagas, M.H.; de Oliveira, D.C.; De Martinis, B.S.; Kapczinski, F.; Quevedo, J.; Roesler, R.; Schroder, N.; Nardi, A.E.; et al. Cannabidiol reduces the anxiety induced by simulated public speaking in treatment-naive social phobia patients. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, S.; Lewis, N.; Lee, H.; Hughes, S. Cannabidiol in Anxiety and Sleep: A Large Case Series. Perm. J. 2019, 23, 18–041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundal, H.; Lister, R.; Evans, N.; Antley, A.; Englund, A.; Murray, R.M.; Freeman, D.; Morrison, P.D. The effects of cannabidiol on persecutory ideation and anxiety in a high trait paranoid group. J. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 32, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsop, D.J.; Copeland, J.; Lintzeris, N.; Dunlop, A.J.; Montebello, M.; Sadler, C.; Rivas, G.R.; Holland, R.M.; Muhleisen, P.; Norberg, M.M.; et al. Nabiximols as an agonist replacement therapy during cannabis withdrawal: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindocha, C.; Freeman, T.P.; Schafer, G.; Gardener, C.; Das, R.K.; Morgan, C.J.; Curran, H.V. Acute effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and their combination on facial emotion recognition: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in cannabis users. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurd, Y.L.; Spriggs, S.; Alishayev, J.; Winkel, G.; Gurgov, K.; Kudrich, C.; Oprescu, A.M.; Salsitz, E. Cannabidiol for the Reduction of Cue-Induced Craving and Anxiety in Drug-Abstinent Individuals With Heroin Use Disorder: A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusar-Poli, P.; Allen, P.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Crippa, J.A.; Mechelli, A.; Borgwardt, S.; Martin-Santos, R.; Seal, M.L.; O’Carrol, C.; Atakan, Z.; et al. Modulation of effective connectivity during emotional processing by Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Sci. J. Coll. Int. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 13, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elms, L.; Shannon, S.; Hughes, S.; Lewis, N. Cannabidiol in the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Case Series. J. Altern. Complement Med. 2019, 25, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beale, C.; Broyd, S.J.; Chye, Y.; Suo, C.; Schira, M.; Galettis, P.; Martin, J.H.; Yucel, M.; Solowij, N. Prolonged Cannabidiol Treatment Effects on Hippocampal Subfield Volumes in Current Cannabis Users. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2018, 3, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solowij, N.; Broyd, S.J.; Beale, C.; Prick, J.A.; Greenwood, L.M.; van Hell, H.; Suo, C.; Galettis, P.; Pai, N.; Fu, S.; et al. Therapeutic Effects of Prolonged Cannabidiol Treatment on Psychological Symptoms and Cognitive Function in Regular Cannabis Users: A Pragmatic Open-Label Clinical Trial. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2018, 3, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, J.A.; Hallak, J.E.; Machado-de-Sousa, J.P.; Queiroz, R.H.; Bergamaschi, M.; Chagas, M.H.; Zuardi, A.W. Cannabidiol for the treatment of cannabis withdrawal syndrome: A case report. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, S. NCT02548559. Sublingual Cannabidiol for Anxiety. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02548559 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Gruber, S.; Mclean Hospital. NTC04286594. A Clinical Trial of a Hemp-Derived Cannabidiol Product for Anxiety. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04286594 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- McMaster University. NCT03549819. Cannabidiol for the Treatment of Anxiety Disorders: An 8-Week Pilot Study. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03549819 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- CB2 Insights. NCT04267679. Cannabidiol for Anxiety. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04267679 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- University of Texas at Austin. NCT04197102. Use of CBD Oil in the Treatment of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04197102 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). NCT03248167. Cannabidiol as a Treatment for AUD Comorbid with PTSD. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03248167 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies. NCT02759185. Study of Four Different Potencies of Smoked Marijuana in 76 Veterans with PTSD. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02759185 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Portenoy, R.K.; Ganae-Motan, E.D.; Allende, S.; Yanagihara, R.; Shaiova, L.; Weinstein, S.; McQuade, R.; Wright, S.; Fallon, M.T. Nabiximols for opioid-treated cancer patients with poorly-controlled chronic pain: A randomized, placebo-controlled, graded-dose trial. J. Pain Off. J. Am. Pain Soc. 2012, 13, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corroon, J.; Phillips, J.A. A Cross-Sectional Study of Cannabidiol Users. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2018, 3, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul; University of Sao Paulo. NCT03310593. Cannabidiol as an Adjunctive Treatment for Bipolar Depression. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03310593 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association (APA): Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen, N.C. Symptoms, signs, and diagnosis of schizophrenia. Lancet 1995, 346, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, T.M.; Nordentoft, M.; Mortensen, P.B. Excess early mortality in schizophrenia. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2014, 10, 425–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.S.; Winter van Rossum, I.; Leucht, S.; McGuire, P.; Lewis, S.W.; Leboyer, M.; Arango, C.; Dazzan, P.; Drake, R.; Heres, S.; et al. Amisulpride and olanzapine followed by open-label treatment with clozapine in first-episode schizophrenia and schizophreniform disorder (OPTiMiSE): A three-phase switching study. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maric, N.P.; Jovicic, M.J.; Mihaljevic, M.; Miljevic, C. Improving Current Treatments for Schizophrenia. Drug Dev. Res. 2016, 77, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuardi, A.W.; Crippa, J.A.; Hallak, J.E.; Moreira, F.A.; Guimaraes, F.S. Cannabidiol, a Cannabis sativa constituent, as an antipsychotic drug. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2006, 39, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.A.; Watson, D.J.; Fone, K.C. Animal models of schizophrenia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1162–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiana, S.; Watanabe, A.; Yamasaki, Y.; Amada, N.; Kikuchi, T.; Stott, C.; Riedel, G. MK-801-induced deficits in social recognition in rats: Reversal by aripiprazole, but not olanzapine, risperidone, or cannabidiol. Behav. Pharm. 2015, 26, 748–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, J.; Loureiro, M.; Rosen, L.G.; Zunder, J.; de Oliveira, C.; Schmid, S.; Rushlow, W.J.; Laviolette, S.R. Cannabidiol Counteracts Amphetamine-Induced Neuronal and Behavioral Sensitization of the Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway through a Novel mTOR/p70S6 Kinase Signaling Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 5160–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururajan, A.; Taylor, D.A.; Malone, D.T. Effect of cannabidiol in a MK-801-rodent model of aspects of schizophrenia. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 222, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururajan, A.; Taylor, D.A.; Malone, D.T. Cannabidiol and clozapine reverse MK-801-induced deficits in social interaction and hyperactivity in Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 1317–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, A.L.; Solowij, N.; Babic, I.; Huang, X.F.; Weston-Green, K. Improved Social Interaction, Recognition and Working Memory with Cannabidiol Treatment in a Prenatal Infection (poly I:C) Rat Model. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, A.L.; Solowij, N.; Babic, I.; Lum, J.S.; Newell, K.A.; Huang, X.F.; Weston-Green, K. Effect of cannabidiol on endocannabinoid, glutamatergic and GABAergic signalling markers in male offspring of a maternal immune activation (poly I:C) model relevant to schizophrenia. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 95, 109666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez Naranjo, C.; Osborne, A.L.; Weston-Green, K. Effect of cannabidiol on muscarinic neurotransmission in the pre-frontal cortex and hippocampus of the poly I:C rat model of schizophrenia. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 94, 109640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, T.; Ruda-Kucerova, J.; Iannotti, F.A.; D’Addario, C.; Di Marco, R.; Pekarik, V.; Drazanova, E.; Piscitelli, F.; Bari, M.; Babinska, Z.; et al. Peripubertal cannabidiol treatment rescues behavioral and neurochemical abnormalities in the MAM model of schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 2019, 146, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.V.; Issy, A.C.; Ferreira, F.R.; Viveros, M.P.; Del Bel, E.A.; Guimaraes, F.S. Cannabidiol Attenuates Sensorimotor Gating Disruption and Molecular Changes Induced by Chronic Antagonism of NMDA receptors in Mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Sci. J. Coll. Int. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.V.; Llorente, R.; Del Bel, E.A.; Viveros, M.P.; Lopez-Gallardo, M.; Guimaraes, F.S. Decreased glial reactivity could be involved in the antipsychotic-like effect of cannabidiol. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 164, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues da Silva, N.; Gomes, F.V.; Sonego, A.B.; Silva, N.R.D.; Guimaraes, F.S. Cannabidiol attenuates behavioral changes in a rodent model of schizophrenia through 5-HT1A, but not CB1 and CB2 receptors. Pharm. Res. 2020, 156, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peres, F.F.; Diana, M.C.; Suiama, M.A.; Justi, V.; Almeida, V.; Bressan, R.A.; Zuardi, A.W.; Hallak, J.E.; Crippa, J.A.; Abilio, V.C. Peripubertal treatment with cannabidiol prevents the emergence of psychosis in an animal model of schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2016, 172, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.A.; Guimaraes, F.S. Cannabidiol inhibits the hyperlocomotion induced by psychotomimetic drugs in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. 2005, 512, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrazzi, J.F.; Issy, A.C.; Gomes, F.V.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Del-Bel, E.A. Cannabidiol effects in the prepulse inhibition disruption induced by amphetamine. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 3057–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.E.; Malone, D.T.; Taylor, D.A. Cannabidiol reverses MK-801-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.E.; Chesworth, R.; Huang, X.F.; Wong, A.; Spiro, A.; McGregor, I.S.; Arnold, J.C.; Karl, T. Distinct neurobehavioural effects of cannabidiol in transmembrane domain neuregulin 1 mutant mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligresti, A.; Moriello, A.S.; Starowicz, K.; Matias, I.; Pisanti, S.; De Petrocellis, L.; Laezza, C.; Portella, G.; Bifulco, M.; Di Marzo, V. Antitumor activity of plant cannabinoids with emphasis on the effect of cannabidiol on human breast carcinoma. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leweke, F.M.; Piomelli, D.; Pahlisch, F.; Muhl, D.; Gerth, C.W.; Hoyer, C.; Klosterkotter, J.; Hellmich, M.; Koethe, D. Cannabidiol enhances anandamide signaling and alleviates psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saletti, P.G.; Tomaz, C. Cannabidiol effects on prepulse inhibition in nonhuman primates. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 30, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Vellani, V.; Schiano-Moriello, A.; Marini, P.; Magherini, P.C.; Orlando, P.; Di Marzo, V. Plant-derived cannabinoids modulate the activity of transient receptor potential channels of ankyrin type-1 and melastatin type-8. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corfas, G.; Roy, K.; Buxbaum, J.D. Neuregulin 1-erbB signaling and the molecular/cellular basis of schizophrenia. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Hashimotodani, Y.; Uchigashima, M.; Watanabe, M. Endocannabinoid-mediated control of synaptic transmission. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 309–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, T.; van Nieuwenhuijzen, P.S.; Devenish, S.O.; McGregor, I.S.; Arnold, J.C.; Chebib, M. The direct actions of cannabidiol and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol at GABAA receptors. Pharm. Res. 2017, 119, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretzsch, C.M.; Freyberg, J.; Voinescu, B.; Lythgoe, D.; Horder, J.; Mendez, M.A.; Wichers, R.; Ajram, L.; Ivin, G.; Heasman, M.; et al. Effects of cannabidiol on brain excitation and inhibition systems; a randomised placebo-controlled single dose trial during magnetic resonance spectroscopy in adults with and without autism spectrum disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.A.; Levitt, P. Schizophrenia as a disorder of neurodevelopment. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 25, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Morrison, P.D.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Martin-Santos, R.; Borgwardt, S.; Winton-Brown, T.; Nosarti, C.; CM, O.C.; Seal, M.; Allen, P.; et al. Opposite effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol on human brain function and psychopathology. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devane, W.A.; Hanus, L.; Breuer, A.; Pertwee, R.G.; Stevenson, L.A.; Griffin, G.; Gibson, D.; Mandelbaum, A.; Etinger, A.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 1992, 258, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitet, F.; Jeantaud, B.; Reibaud, M.; Imperato, A.; Dubroeucq, M.C. Complex pharmacology of natural cannabinoids: Evidence for partial agonist activity of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and antagonist activity of cannabidiol on rat brain cannabinoid receptors. Life Sci. 1998, 63, PL1–PL6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, D.L.; Nguyen, J.D.; Morgenson, D.; Taffe, M.A.; Ranganathan, M. Clinical and Preclinical Evidence for Functional Interactions of Cannabidiol and Delta(9)-Tetrahydrocannabinol. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bioque, M.; Garcia-Bueno, B.; Macdowell, K.S.; Meseguer, A.; Saiz, P.A.; Parellada, M.; Gonzalez-Pinto, A.; Rodriguez-Jimenez, R.; Lobo, A.; Leza, J.C.; et al. Peripheral endocannabinoid system dysregulation in first-episode psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, N.; De Petrocellis, L.; Orlando, P.; Daniele, F.; Fezza, F.; Di Marzo, V. Endocannabinoid signalling in the blood of patients with schizophrenia. Lipids Health Dis. 2003, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuardi, A.W.; Crippa, J.A.; Hallak, J.E.; Pinto, J.P.; Chagas, M.H.; Rodrigues, G.G.; Dursun, S.M.; Tumas, V. Cannabidiol for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson’s disease. J. Psychopharmacol. 2009, 23, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuardi, A.W.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Cunha, J.M. Effects of cannabidiol in animal models predictive of antipsychotic activity. Psychopharmacology 1991, 104, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, D.L.; Surti, T.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, S.; Niciu, M.; Pittman, B.; Schnakenberg Martin, A.M.; Thurnauer, H.; Davies, A.; D’Souza, D.C.; et al. The effects of cannabidiol (CBD) on cognition and symptoms in outpatients with chronic schizophrenia a randomized placebo controlled trial. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, P.; Robson, P.; Cubala, W.J.; Vasile, D.; Morrison, P.D.; Barron, R.; Taylor, A.; Wright, S. Cannabidiol (CBD) as an Adjunctive Therapy in Schizophrenia: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, A.; Wilson, R.; Blest-Hopley, G.; Annibale, L.; Colizzi, M.; Brammer, M.; Giampietro, V.; Bhattacharyya, S. Normalization of mediotemporal and prefrontal activity, and mediotemporal-striatal connectivity, may underlie antipsychotic effects of cannabidiol in psychosis. Psychol. Med. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Wilson, R.; Appiah-Kusi, E.; O’Neill, A.; Brammer, M.; Perez, J.; Murray, R.; Allen, P.; Bossong, M.G.; McGuire, P. Effect of Cannabidiol on Medial Temporal, Midbrain, and Striatal Dysfunction in People at Clinical High Risk of Psychosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.; Bossong, M.G.; Appiah-Kusi, E.; Petros, N.; Brammer, M.; Perez, J.; Allen, P.; McGuire, P.; Bhattacharyya, S. Cannabidiol attenuates insular dysfunction during motivational salience processing in subjects at clinical high risk for psychosis. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallak, J.E.; Machado-de-Sousa, J.P.; Crippa, J.A.; Sanches, R.F.; Trzesniak, C.; Chaves, C.; Bernardo, S.A.; Regalo, S.C.; Zuardi, A.W. Performance of schizophrenic patients in the Stroop Color Word Test and electrodermal responsiveness after acute administration of cannabidiol (CBD). Braz. J. Psychiatry 2010, 32, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard Pratt Health System; University of California, Los Angeles. NTC03883360. Effects of Cannabidiol on Psychiatric Symptons, Cognition, and Cannabis Consumption in Cannabis Users with Recent-Onset Psychosis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03883360 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Central Institute of Mental Health, Mannheim. NCT02926859. Enhancing Recovery in Early Schizophrenia. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02926859 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Cadenhead, K.; University of California, San Diego. NCT04411225. Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research. Effects of cannabidiol (CBD) versus Placebo as an Adjunct to Treatment in Early Psychosis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04411225 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Elsaid, S.; Kloiber, S.; Le Foll, B. Effects of cannabidiol (CBD) in neuropsychiatric disorders: A review of pre-clinical and clinical findings. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 167, 25–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.X.; Yang, L.K.; Shi, W.L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.M.; Guan, S.Y.; Zhao, M.G.; Yang, Q. The novel cannabinoid receptor GPR55 mediates anxiolytic-like effects in the medial orbital cortex of mice with acute stress. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, A.; Moghaddam, A.H.; Roohbakhsh, A. Central administration of GPR55 receptor agonist and antagonist modulates anxiety-related behaviors in rats. Fundam. Clin. Pharm. 2015, 29, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Values | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ko/w | 6–7 | [52] |
| Oral bioavailability | 6–19% | [53] |
| Cmax | 3 ± 3.1 μg/L | [55,56,61] |
| Tmax | 2.8 ± 1.3 h | [55,56,61] |
| Vd | 32 L/kg | [55,56,57] |
| t1/2 |
1.4–10.9 h (oromucosal spray) 2–5 h (oral chronic administration) 24 h (intravenously) 31 h (smoked) | [53,54] |
| Plasma clearance rate | 960–1500 mL/min | [53,54,55] |
| Strain | Doses and Route of Administration | Effect and Test | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wistar rats | 1 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Anxiolytic/SI | [99] |
| 2.5, 5, 10.0 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Anxiolytic/EPM | [97] | |
| 7–30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [107] | |
| 5 and 15 mg/kg, i.p.; acute | No effect/SI | [99] | |
| 1, 10, 20 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Anxiolytic/restraint stress | [100] | |
| 10 mg/kg; i.p.; acute 10 mg/kg; i.p.; 28 days | Anxiolytic/THC-induced conditioned emotional responses Anxiolytic/VCT Anxiolytic/CFC Antidepressant/CMS | [96,102,108] | |
| 20 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effect/EPM | [97] | |
| 3–30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | ↓ freezing behavior/CFC | [109] | |
| 30 mg/kg; p.o.; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [110] | |
| 30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute and chronic | Antidepressant/FST | [111] | |
| 100 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effect/GSP | [95] | |
| 30 nmol/μL; dlPAG; acute | Anxiolytic/EPM and VCT | [112] | |
| 30 and 60 nmol/μL; PAG; acute | Anxiolytic/ETMPanicolytic/ES dPAG | [113] | |
| 30 and 60 nmol/μL; BNST; acute | Anxiolytic/restraint stress | [114] | |
| 30 nmol/μL; intracisternal; acute | Anxiolytic/restraint stress | [115] | |
| 30 nmol/μL; PL; acute | Anxiolytic/EPM | [116] | |
| 2 μg/μL; icv and mPFC; acute | ↓ freezing behavior/CFC | [117] | |
| 15 or 30 nmol/μL; IL-PFC; acute | ↑ freezing behavior/CFC | [118] | |
| 30 nmol/μL; PL-PFC; acute | ↓ freezing behavior/CFC | [118] | |
| 0.4 μg; IL-PFC; 3 days | Improve extinction/CFC | [119] | |
| 10–30 pmol; dorsal HIP; acute | ↓ Memory consolidation/CFC | [120] | |
| 10 mg/kg; bilateral intra-PFC | ↓ Memory consolidation/CFC | [109] | |
| 10–60 nmol/side; intra-IL or intra-PL; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [121] | |
| Sprague-Dawley rats | 10 mg/kg; i.p.; 7 days 30 mg/kg; i.p.; 7 days | Antidepressant/FST | [122] |
| Lister-hooded rats | 10 mg/kg; i.p.; 14 days | ↑ Freezing behavior/CFC | [123] |
| Flinders Sensitive rats | 7–30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute 30 mg/kg; p.o.; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [107] [110] |
| Flinders Resistant rats | 7–30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [107] |
| Wistar Kyoto rats | 30 mg/kg; p.o.; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [110] |
| 30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Antidepressant/SP and OR | [124] | |
| Spontaneously Hypertensive rats | 1–60 mg/kg; i.p. | No effect/SI | [99] |
| DBT rats | 30 mg/kg; i.p.; sub-chronic | Antidepressant/FST | [125] |
| NGL rats | 0.3 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [125] |
| C57Bl/6J mice | 1 mg/kg; i.p.; acute 1 mg/kg; i.p.; 21 days | No effect/OF and EPM Anxiolytic/LDB | [126] |
| 1, 10 and 10 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effect/CFC | [127] | |
| 30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | ↓ freezing behavior/CFC | [127] | |
| 5, 10 or 20 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effect/EPM | [128] | |
| 10 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effect/OF No effect/THC-induced anxiety | [105,106] | |
| 15 mg/kg; i.p. (+ FLX, 3 mg/kg; i.p.); acute | Anxiolytic/MBT | [103] | |
| 20 mg/kg/day; i.p.; 3 weeks | Anxiolytic/PTSD model | [129] | |
| 20 mg/kg; i.p.; 6 weeks 20 mg/kg; i.p.; 3 weeks | No effect/LBD and OF Anxiogenic/EPM | [130] [128] | |
| 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Anxiolytic/MBT * * (even 7 days after its administration) | [104] | |
| 30 mg/kg; i.p.; chronic 30 mg/kg; i.p.; 14 days | Anxiolytic and antidepressant/CMS Antidepressant/CMS | [131] [116] | |
| 50 mg/kg; i.p.; 21 days | Anxiolytic/OF | [126] | |
| 50 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effect/OF and EPM | [126] | |
| 50 mg/kg; i.p.; acute 50 mg/kg; i.p.; 3 days and 10 mg/kg; 11 days | Anxiolytic/OF Antidepressant/SP | [132] | |
| ICR mice Swiss Albino | 0.5, 1, 2.5, 5, 10 and 50 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Anxiolytic/EPM | [98] |
| 0.01, 0.1 and 100 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effect/EPM | [98] | |
| 3 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Anxiolytic/EPM | [133] | |
| 10 or 30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effect/EPM | [133] | |
| 3, 10 or 30 mg/kg; i.p.; chronic | No effect/EPM | [133] | |
| 7–30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [107] | |
| 10 mg/kg; i.v.; 21 days 100 mg/kg; p.o.; 21 days | Antidepressant/CMS | [134] | |
| 0.7 mg/kg; i.p.; (plus 0.1 mg/kg; i.p. 5-AZAD or RG108) | Antidepressant/FST | [135] | |
| 7 mg/kg; i.p. (plus FLX 5 mg/kg; i.p. or DES 2.5 mg/kg; i.p.) | Antidepressant/FST | [136] | |
| 10 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [135] | |
| 30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [137] | |
| Swiss Webster mice | 2 and 100 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effect/FST | [138] |
| 200 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Antidepressant/FST | [138] | |
| DBA/2 mice | 2, 100 and 200 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effect/TST | [138] |
| Clinical Condition | Clinical Trial Design | Sample Size and Gender | Doses and Route of CBD Administration | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy volunteers | Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial | 40 M (N = 5/group) | 15–60 mg dissolved in ethanol and orange juice; p.o.; acute | ↓ THC-induced anxiety | [150] |
| Healthy volunteers | Double-blind randomized placebo- and diazepam-controlled trial | 8 (6 M/2 F) | 0.5 mg/kg; dissolved in ethanol and artificial lemon juice; p.o.; acute | ↓ THC-induced anxiety | [151] |
| Healthy volunteers | Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial | 40 (18 M/22 F) | 300 mg dissolved in corn oil and given in gelatin capsules; p.o.; acute | Stimulated public speaking test | [152] |
| Healthy volunteers | Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial | 10 M (N = 5/group) | 400 mg dissolved in corn oil and given in gelatin capsules; p.o.; acute | ↓ Subjective anxiety ↑ Mental sedation | [153] |
| Healthy volunteers (Cannabis sativa users) | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, repeated-measures within-subject vs. placebo | 15 M | 600 mg; gelatin capsules; p.o.; 3 separate sessions | No behavioral or regional brain activation | [154] |
| Healthy volunteers | Double-blind, repeated-measures vs. placebo | 16 M | 600 mg; opaque capsules; p.o.; 3 consecutive sessions | No psychotic symptoms, mental sedation, intellectual impairment or physical sedation | [35] |
| Treatment-naïve SAD patients | Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial | 10 M | 400 mg dissolved in corn oil and packed inside gelatin capsules; p.o.; acute | ↓ Subjective anxiety Changes in regional cerebral flow | [155] |
| Treatment-naïve SAD patients | Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial | 12 M | 600 mg dissolved in corn oil and packed inside gelatin capsules; p.o.; acute | ↓ Subjective anxiety ↓ Cognitive impairment | [156] |
| Psychiatric patients with primary concern of anxiety or poor sleep | Large retrospective case series (adjunct to usual treatment) | 47 anxiety (28 M/19 F) 25 poor sleep (16 M/9 F) | 25 mg/day to 50–75 mg/day; capsule; 1–3 months | ↓ Anxiety Improved sleep disturbances | [157] |
| Non-clinical volunteers with high paranoid traits | Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial | 32 (16 M/16 F) N = 8/group | 600 mg; hard gelatin capsule; p.o.; acute | ↑ Anxiety No effects persecutory ideation | [158] |
| Cannabis use disorder | Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial | 51 CBD N = 27 (18 M/9 F) Placebo N = 24 (21 M/3 F) | Nabiximols (CBD 2.5 mg plus THC 2.7 mg); 6 days | ↓ Anxiety ↓ Craving ↓ Depression | [159] |
| Volunteers selected for high and low frequency of cannabis use and schizotypy (males and females | Double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial | 48 LSS group N = 12 (9 M:3 F) LHS group N = 12 (7 M:5 F) HLS group N = 12 (11 M/1 F) HHS group N = 12 (7 M:5 F) | 16 mg, formulated in alcohol solution; vaporization | Improved emotional processing | [160] |
| Drug-abstinent patients with heroin user disorder | Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial | 42 CBD 400 mg N = 14 (12 M/2 F) CBD 800 mg N = 13 (11 M/2 F) Placebo N = 15 (12 M/3 F) | 400 (n = 14) or 800 mg (n = 13); once daily; oral solution Epidiolex; acute (1, 2 or 24 h) and Short-term administration (3 consecutive day) | ↓ Anxiety ↓ Craving ↓ Heart rate ↓ Salivary cortisol levels | [161] |
| Healthy volunteers | Double-blind, pseudo-randomized, placebo-controlled, repeated-measures, within-subject design | 15 M | 600 mg; capsules; p.o.; 3 consecutive sessions | Altered prefrontal-subcortical connectivity/response to fearful faces | [162] |
| PTSD | Open-label | 11 (8 F/3 M) | Flexible doses: starting at 25 to 48.64 mg/day; capsule or liquid spray; 8 weeks | ↓ PTSD severity | [163] |
| Regular cannabis users | Open-label | 18 (14 M/4 F) | 200 mg/day (99.5% pure crystalline of herbal origin); gelatin-coated capsules; 10 weeks | ↓ Depressive ↓ Psychotic symptoms | [164] |
| Regular cannabis users | Open-label | 20 (16 M/4 F) | 200 mg/day (99.5% pure crystalline of herbal origin); gelatin-coated capsules; 10 weeks | ↓ Depressive symptoms ↓ Psychotic symptoms ↑ Attentional switching ↑ Verbal learning ↑ Memory | [165] |
| Strain | Doses and Route of Administration | Effect and Test | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wistar rats | 5, 12 and 30 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | No effects on behavioral alterations induced by MK-801 | [184] |
| Sprague Dawley rats | 100 ng/0.5 µL, intra-NAcc; acute | Improve PPI and hyperlocomotion induced by AMPH | [185] |
| 3, 10 and 30 mg/kg, i.p.; acute | No effects on behavioral alterations induced by MK-801 | [186] | |
| 1 and 3 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | ↓ anxiety and hyperlocomotion induced by MK-801 | [187] | |
| 10 mg/kg; i.p.; 11 days | Anxiolytic and ↑ recognition and working memory induced by poly I:C given on GD15 | [188] | |
| Normalization of CB1r and glutamate decarboxylase alterations in the PFC and HIPP induced by poly I:C given on GD15 | [189] | ||
| Modulation of muscarinic M1/M4 receptors and choline acetyltransferase levels in PFC and HIPP/poly I:C on GD15 | [190] | ||
| 10 and 30 mg/kg; i.p.; 20 days | Normalization of social withdrawal and cognitive impairment induced by MAM on GD17 Normalization of CB1r alterations in PFC induced by MAM given on GD17 | [191] | |
| C57BL/6J mice | 1, 5, 10 and 50 mg/kg; i.p.; chronic | CBD (50 mg/kg) attenuated hyperlocomotion induced by DEXAMPH | [126] |
| 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg; i.p.; 21 days | Dose-dependent attenuation of MK-801-induced disruption in PPI | [192] | |
| 30 and 60 mg/kg; i.p.; 21 days | Improvement of anxiety and cognitive impairment induced by MK-801 | [193] | |
| 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg; i.p.; 1 week | Improvement of anxiety and cognitive impairment induced by MK-801 | [194] | |
| 1 mg/kg; i.p.; 30 days | Attenuation of motor hyperactivity on PND90 induced by poly I:C given on GD9 | [195] | |
| Swiss mice | 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | CBD (30 and 60 mg/kg) blocked AMPH-induced hyperlocomotion CBD (60 mg/kg) attenuated KET-induced hyperlocomotion | [196] |
| 15, 30 & 60 mg/kg; i.p. 60 nmol in 0.2 µL; intra-NAcc; acute | Attenuation of PPI alterations induced by AMPH | [197] | |
| 15 mg/kg; i.p.; acute | Modulation of PPI disruption induced by MK-801 | [198] | |
| Nrg1 HET mice | 1, 50 and 100 mg/kg; i.p.; 21 days | CBD (50 and 100 mg/kg) improved hyperlocomotion and anxiety No significant improvement in PPI | [199] |
| Clinical Condition | Clinical Trial Design | Sample Size and Gender | Doses and Route of Administration | Outcomes | Adverse Events | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic schizophrenia | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled | 36 CBD group N = 18 (12 M/6 F) Placebo group N = 18 (13 M:5 F) | 600 mg/day; p.o.; 6 weeks | No improvement in PANSS or MCCB scores | No movement alterations | [217] |
| Schizophrenia or a related psychotic disorder | Double-blind randomized, placebo-controlled | 88 CBD group N = 42 (28 M/14 F) Placebo group N = 44 (23 M/11 F) | 1000 mg/day; oral solution; p.o.; 6 weeks | ↓ Positive symptoms (PANSS) Improve cognitive performances (BACS) and overall functioning (GAF) | No prolactin or metabolic alterations; No weight gain; No liver alterations Mild GI events | [218] |
| Acute paranoid schizophrenia | Double-blind, randomized CBD vs. amisulpride | 39 CBD group N = 20 (15 M/5 F) Amisulpride group N = 19 (17 M/2 F) | 800 mg/day; p.o.; 4 weeks | ↓ PANSS scores (no difference compared to amisulpride) | Fewer extrapyramidal effects Less weight gain Lower prolactin increase | [201] |
| Psychosis in the early stages of illness | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled | 34 Psychosis group N = 15 (10 M:5 F) Healthy controls N = 19 (11 M:5 F) | 600 mg; gelatin capsules; p.o.; acute | Attenuation of a dysfunctional activation of mediotemporal and prefrontal cortex, and mediotemporal-striatal functional connectivity during verbal paired associate learning task | - | [219] |
| Patients at clinical high risk (CHR) of psychosis | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled | 52 Antipsychotic medication–naive participants at CHR of psychosis N = 33 (CBD group N = 16 (10 M/6 F) Placebo group N = 17 (7 M/10 F) Healthy controls N = 19 (11 M/8 F) | 600 mg; gelatin capsules; p.o.; acute | Improved right caudate, parahippocampal gyrus and midbrain region’s activation during verbal learning task | - | [220] |
| Patients at CHR of psychosis | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled | 52 Antipsychotic medication–naive participants at CHR of psychosis N = 33 (CBD group N = 16 (10 M/6 F) Placebo group N = 17 (7 M/10 F) Healthy controls N = 19 (11 M/8 F) | 600 mg; gelatin capsules; p.o.; acute | Attenuated the increased activation in left insula/parietal operculum, and reduced reaction time during monetary incentive delay task | - | [221] |
| Schizophrenia | Double-blind randomized, placebo-controlled | 28 CBD 600 mg group N = 9 (5 M/4 F) CBD 300mg group N = 9 (6 M/3 F) Placebo group N = 10 (7 M/3 F) | 300 or 600 mg; gelatin capsules; p.o.; acute | No effects were observed in SCWT and electrodermal responsiveness | - | [222] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Navarrete, F.; Gasparyan, A.; Austrich-Olivares, A.; Sala, F.; Manzanares, J. Cannabidiol: A Potential New Alternative for the Treatment of Anxiety, Depression, and Psychotic Disorders. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111575
García-Gutiérrez MS, Navarrete F, Gasparyan A, Austrich-Olivares A, Sala F, Manzanares J. Cannabidiol: A Potential New Alternative for the Treatment of Anxiety, Depression, and Psychotic Disorders. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(11):1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111575
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Gutiérrez, María S., Francisco Navarrete, Ani Gasparyan, Amaya Austrich-Olivares, Francisco Sala, and Jorge Manzanares. 2020. "Cannabidiol: A Potential New Alternative for the Treatment of Anxiety, Depression, and Psychotic Disorders" Biomolecules 10, no. 11: 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111575
APA StyleGarcía-Gutiérrez, M. S., Navarrete, F., Gasparyan, A., Austrich-Olivares, A., Sala, F., & Manzanares, J. (2020). Cannabidiol: A Potential New Alternative for the Treatment of Anxiety, Depression, and Psychotic Disorders. Biomolecules, 10(11), 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111575









