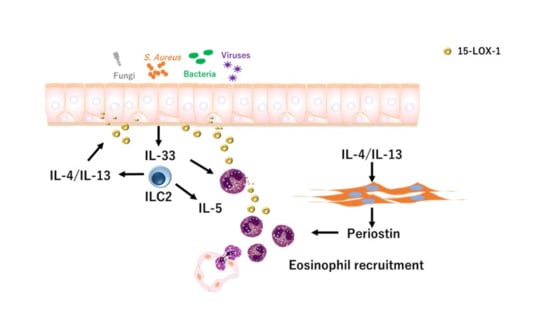
Enhanced 15-Lipoxygenase 1 Production is Related to Periostin Expression and Eosinophil Recruitment in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment and Clinical Sample Collection
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
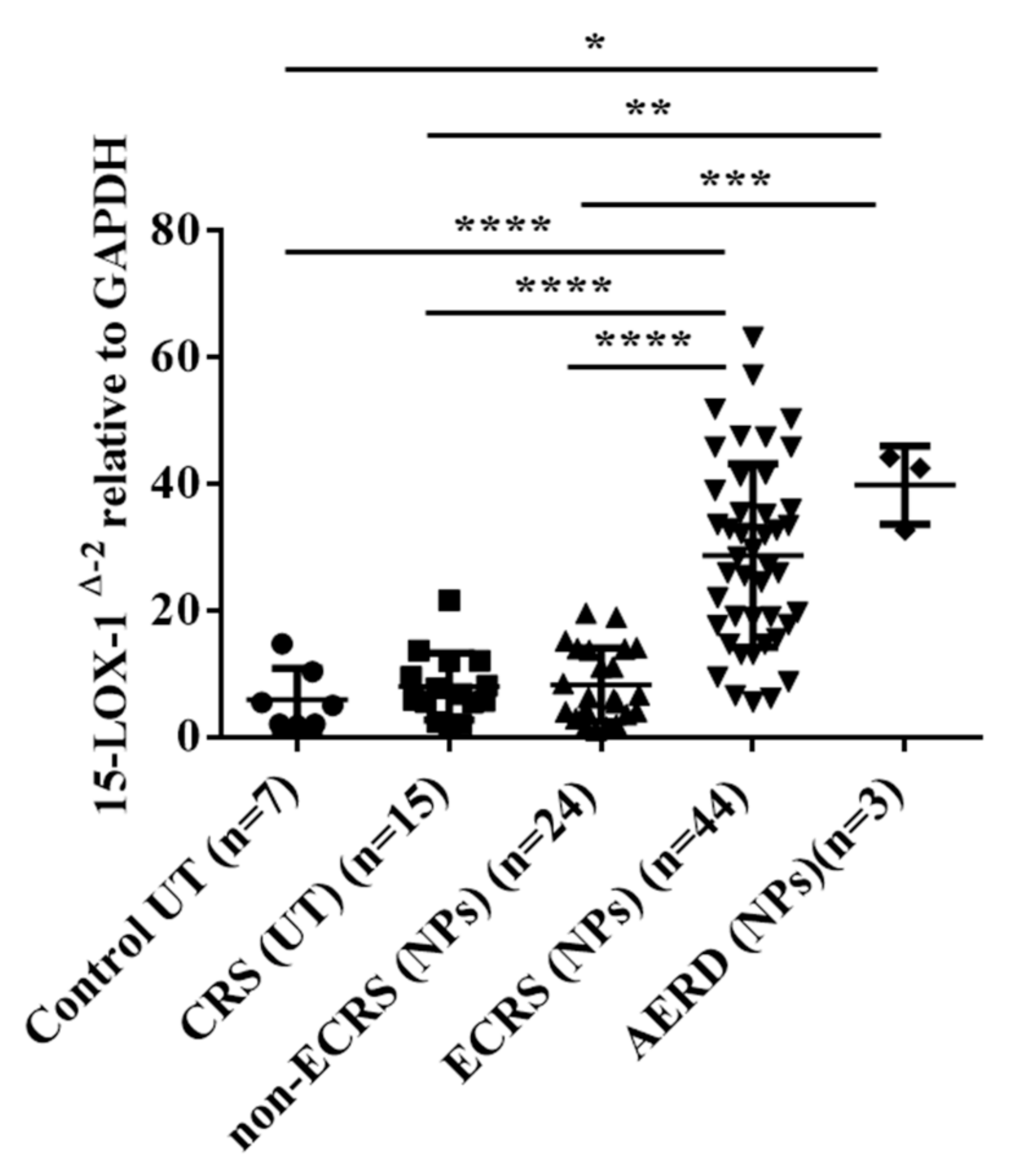
3.1. 15-LOX-1 mRNA Expression was Upregulated in NP Tissues from the ECRS Patients but not Those from the Non-ECRS Patients
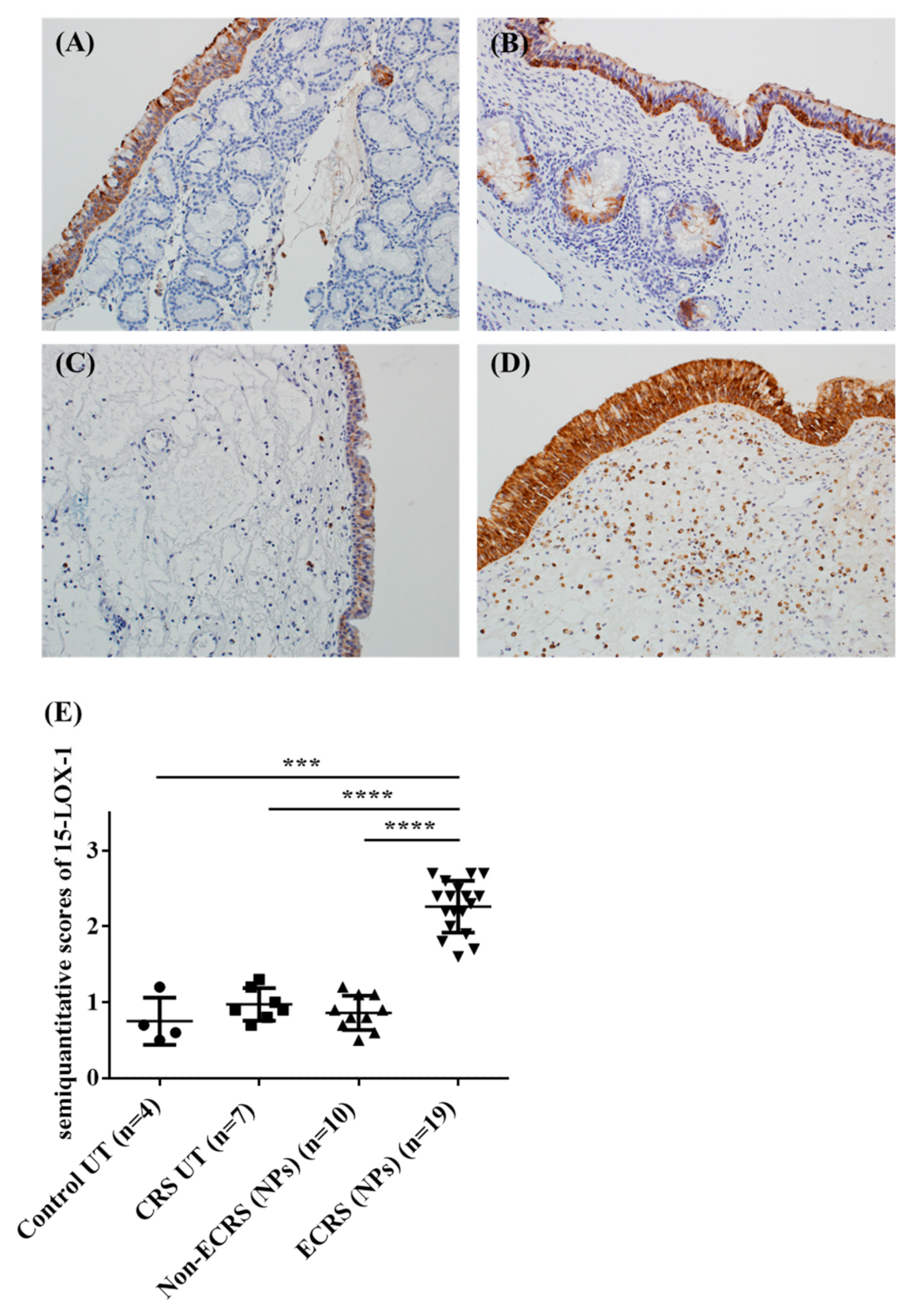
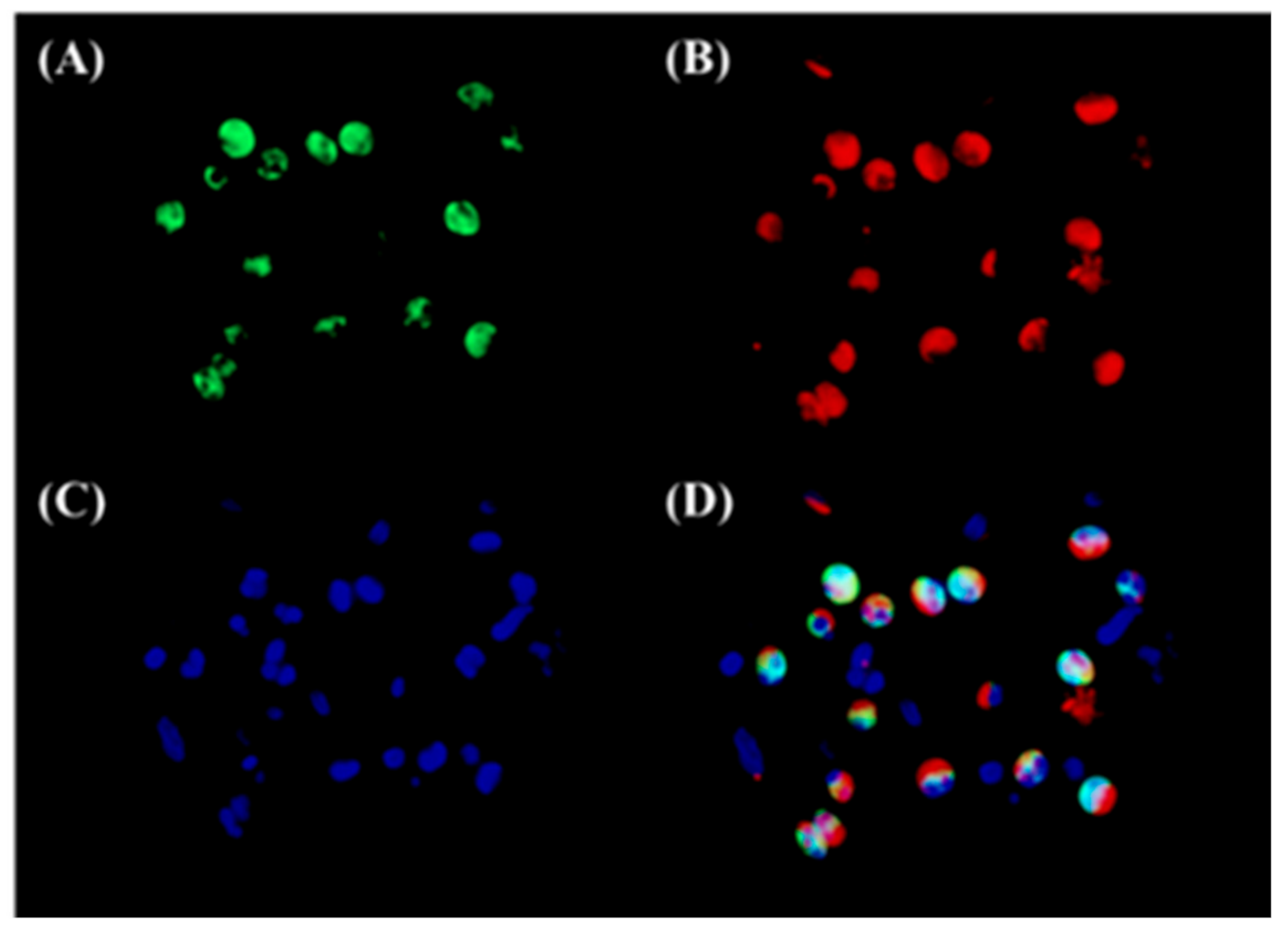
3.2. Both Epithelial Cells and Eosinophils Expressed 15-LOX-1 in Sinonasal Tissues
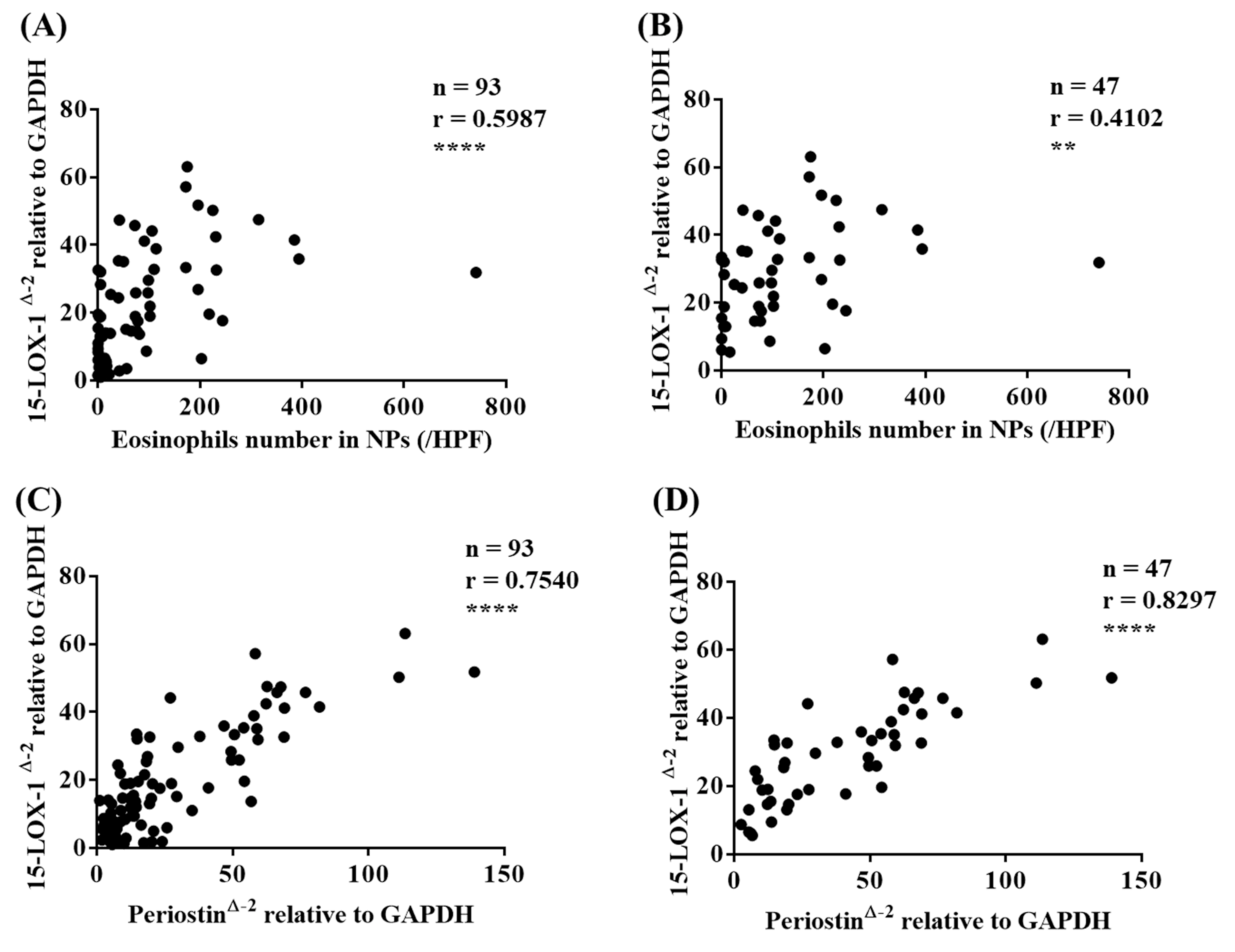
3.3. 15-LOX-1 mRNA Expression was Correlated with Eosinophilic Inflammation in Nasal Tissues
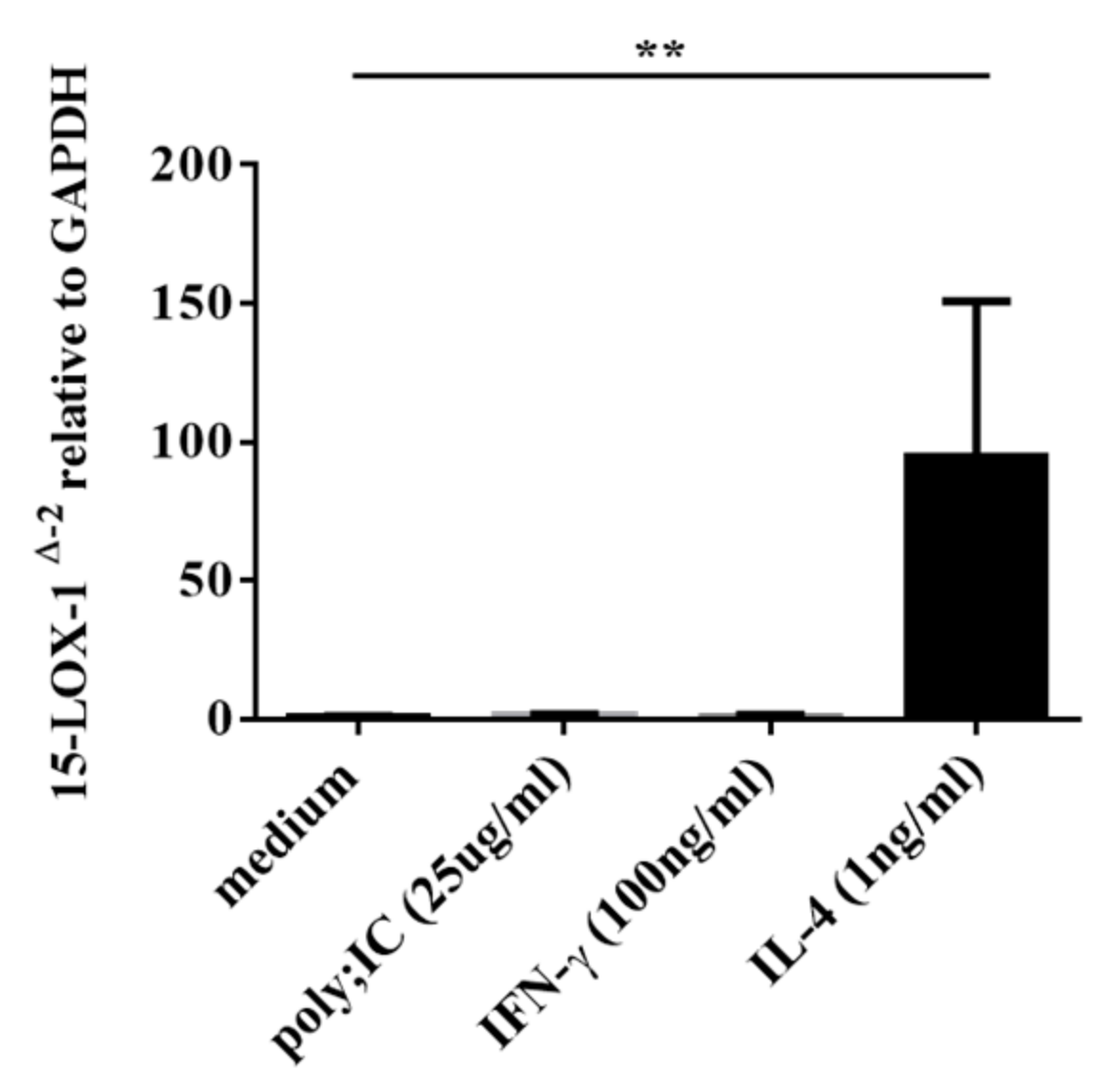
3.4. IL-4, but not IFN-γ nor poly(I:C), Induced 15-LOX-1 from NHBE Cells
3.5. IL-33 Induced 15-LOX-1 from Eol-1 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhattacharyya, N. Incremental Health Care Utilization and Expenditures for Chronic Rhinosinusitis in the United States. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2011, 120, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, E.O.; Hamilos, D.L.; Hadley, J.A.; Lanza, D.C.; Marple, B.F.; Nicklas, R.A.; Bachert, C.; Baraniuk, J.; Baroody, F.M.; Benninger, M.S.; et al. Rhinosinusitis: Establishing definitions for clinical research and patient care. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 155–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, R.C.; Conley, D.B.; Walsh, W.; Chandra, R.; Kato, A.; Tripathi-Peters, A.; Grammer, L.C.; Schleimer, R.P. Perspectives on the Etiology of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: An Immune Barrier Hypothesis. Am. J. Rhinol. 2008, 22, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.C.; Chandra, R.K.; Tan, B.K.; Zirkle, W.; Conley, D.B.; Grammer, L.C.; Kern, R.C.; Schleimer, R.P.; Peters, A.T. Association between Severity of Asthma and Degree of Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2011, 25, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, D.; Newson, R.; Lotvall, J.; Hastan, D.; Tomassen, P.; Keil, T.; Gjomarkaj, M.; Forsberg, B.; Gunnbjornsdottir, M.; Minov, J.; et al. Asthma in adults and its association with chronic rhinosinusitis: The GA2LEN survey in Europe. Allergy 2012, 67, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, M.R.; Stevens, W.W.; Li, N.; Bose, S.; Grammer, L.C.; Kern, R.C.; Tan, B.K.; Conley, D.B.; Smith, S.S.; Welch, K.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis without Nasal Polyps in an Academic Setting. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassen, P.; Vandeplas, G.; Van Zele, T.; Cardell, L.-O.; Arebro, J.; Olze, H.; Förster-Ruhrmann, U.; Kowalski, M.L.; Olszewska-Ziąber, A.; Holtappels, G.; et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1449–1456.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleimer, R.P. Immunopathogenesis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyposis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2017, 12, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.W.; Ocampo, C.J.; Berdnikovs, S.; Sakashita, M.; Mahdavinia, M.; Suh, L.; Takabayashi, T.; Norton, J.E.; Hulse, K.E.; Conley, D.B.; et al. Cytokines in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Role in Eosinophilia and Aspirin-exacerbated Respiratory Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.K.; Klingler, A.I.; Poposki, J.A.; Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Suh, L.A.; Norton, J.; Carter, R.G.; Hulse, K.E.; Harris, K.E.; et al. Heterogeneous inflammatory patterns in chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps in Chicago, Illinois. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 699–703.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.-T.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, P.-F.; Guo, L.-J. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in East Asians. World J. Clin. Cases 2014, 2, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katotomichelakis, M.; Tantilipikorn, P.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Feng, L.; Van Zele, T.; Muangsomboon, S.; Jareonchasri, P.; Bunnag, C.; Danielides, V.; et al. Inflammatory Patterns in Upper Airway Disease in the Same Geographical Area may Change over Time. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2013, 27, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gevaert, E.; Lou, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Bachert, C.; Zhang, N. Chronic rhinosinusitis in Asia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujieda, S.; Imoto, Y.; Kato, Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Tokunaga, T.; Tsutsumiuchi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Kidoguchi, M.; Takabayashi, T. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, T.; Sakashita, M.; Haruna, T.; Asaka, D.; Takeno, S.; Ikeda, H.; Nakayama, T.; Seki, N.; Ito, S.; Murata, J.; et al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: The JESREC Study. Allergy 2015, 70, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelavkar, U.P.; Badr, K.F. Effects of mutant p53 expression on human 15-lipoxygenase-promoter activity and murine 12/15-lipoxygenase gene expression: Evidence that 15-lipoxygenase is a mutator gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4378–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltenmark, S.; Gautam, N.; Brunnström, A.; Griffiths, W.; Backman, L.; Edenius, C.; Lindbom, L.; Björkholm, M.; Claesson, H.-E. Eoxins are proinflammatory arachidonic acid metabolites produced via the 15-lipoxygenase-1 pathway in human eosinophils and mast cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunnström, Å.; Tryselius, Y.; Feltenmark, S.; Andersson, E.; Leksell, H.; James, A.; Mannervik, B.; Dahlén, B.; Claesson, H.-E. On the biosynthesis of 15-HETE and eoxin C4 by human airway epithelial cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015, 121, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.; Daham, K.; Backman, L.; Brunnström, Å.; Tingvall, T.; Kumlin, M.; Edenius, C.; Dahlen, S.E.; Dahlén, B.; Claesson, H.-E. The Influence of Aspirin on Release of Eoxin C4, Leukotriene C4 and 15-HETE, in Eosinophilic Granulocytes Isolated from Patients with Asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 162, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zeng, M.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.; Trudeau, J.B.; Goldschmidt, E.; Moore, J.A.; Chu, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. 15-Lipoxygenase 1 in nasal polyps promotes CCL26/eotaxin 3 expression through extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1228–1241.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjansson, R.P.; Benonisdottir, S.; Davidsson, O.B.; Oddsson, A.; Tragante, V.; Sigurdsson, J.K.; Stefansdottir, L.; Palsson, S.; Jensson, B.O.; Arthur, J.G.; et al. A loss-of-function variant in ALOX15 protects against nasal polyps and chronic rhinosinusitis. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, W.W.; Staudacher, A.G.; Hulse, K.E.; Carter, R.G.; Winter, D.R.; Kato, A.; Suh, L.; Norton, J.E.; Huang, J.H.; Peters, A.T.; et al. Activation of the 15-lipoxygenase pathway in aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takabayashi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Susuki, D.; Yoshida, K.; Tomita, K.; Sakashita, M.; Imoto, Y.; Kato, Y.; Narita, N.; Nakayama, T.; et al. Increased expression of L-plastin in nasal polyp of patients with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-exacerbated respiratory disease. Allergy 2019, 74, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, G.; Arima, K.; Kanaji, T.; Toda, S.; Tanaka, H.; Shoji, S.; McKenzie, A.N.; Nagai, H.; Hotokebuchi, T.; Izuhara, K. Periostin: A novel component of subepithelial fibrosis of bronchial asthma downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 signals. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuhara, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Ohta, S.; Ono, J.; Arima, K.; Ogawa, M. Recent developments regarding periostin in bronchial asthma. Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuhara, K.; Nunomura, S.; Nanri, Y.; Ono, J.; Takai, M.; Kawaguchi, A. Periostin: An emerging biomarker for allergic diseases. Allergy 2019, 74, 2116–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, T.; Noguchi, E.; Haruna, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Yoshida, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Okano, M.; Yoshida, N.; Haruna, S.; Sakuma, Y.; et al. Periostin as a novel biomarker for postoperative recurrence of chronic rhinosinitis with nasal polyps. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Takemura, M.; Yokota, M.; Fukumitsu, K.; Takeda, N.; Ichikawa, H.; Uemura, T.; Takakuwa, O.; Ohkubo, H.; et al. Serum Periostin as a Biomarker for Comorbid Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Patients with Asthma. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017, 14, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an Interleukin-1-like Cytokine that Signals via the IL-1 Receptor-Related Protein ST2 and Induces T Helper Type 2-Associated Cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.E.; Smith, D.E. The IL-1 family: Regulators of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, F.Y.; Pitman, N.I.; McInnes, I.B. Disease-associated functions of IL-33: The new kid in the IL-1 family. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werder, R.B.; Zhang, V.; Lynch, J.P.; Snape, N.; Upham, J.W.; Spann, K.; Phipps, S. Chronic IL-33 expression predisposes to virus-induced asthma exacerbations by increasing type 2 inflammation and dampening antiviral immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1607–1619.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.L.; Fakhri, S.; Citardi, M.J.; Porter, P.C.; Corry, D.B.; Kheradmand, F.; Liu, Y.-J.; Luong, A. IL-33–Responsive Innate Lymphoid Cells Are an Important Source of IL-13 in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-K.; Jin, H.R.; Eun, K.M.; Mo, J.-H.; Cho, S.H.; Oh, S.; Cho, D.; Kim, D.W. The role of interleukin-33 in chronic rhinosinusitis. Thorax 2016, 72, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, E.P.; Kariyawasam, H.H.; Rana, B.M.; Durham, S.R.; McKenzie, A.N.; Powell, N.; Orban, N.; Lennartz-Walker, M.; Hopkins, C.; Ying, S.; et al. IL-25/IL-33–responsive T H 2 cells characterize nasal polyps with a default T H 17 signature in nasal mucosa. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufelberger, A.R.; Nordengrün, M.; Braun, H.; Maes, T.; De Grove, K.; Holtappels, G.; O’Brien, C.; Provoost, S.; Hammad, H.; Goncalves, A.; et al. The IL-33/ST2 axis is crucial in type 2 airway responses induced by Staphylococcus aureus –derived serine protease–like protein D. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 549–559.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudacher, A.G.; Peters, A.T.; Kato, A.; Stevens, W.W. Use of endotypes, phenotypes, and inflammatory markers to guide treatment decisions in chronic rhinosinusitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 124, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Zhang, N.; Hellings, P.W.; Bousquet, J. Endotype-driven care pathways in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardell, L.-O.; Stjärne, P.; Jonstam, K.; Bachert, C. Endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: Impact on management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Tan, B.K.; Klingler, A.I.; Poposki, J.A.; Hulse, K.E.; Grammer, L.C.; Welch, K.C.; Smith, S.S.; Conley, D.B.; et al. Associations Between Inflammatory Endotypes and Clinical Presentations in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 2812–2820.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Minami, Y.; Etling, E.; Coleman, J.M.; Lauder, S.N.; Tyrrell, V.; Aldrovandi, M.; O’Donnell, V.; Claesson, H.-E.; Kagan, V.; et al. Preferential Generation of 15-HETE-PE Induced by IL-13 Regulates Goblet Cell Differentiation in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archambault, A.-S.; Turcotte, C.; Martin, C.; Provost, V.; LaRose, M.-C.; Laprise, C.; Chakir, J.; Bissonnette, É.; LaViolette, M.; Bossé, Y.; et al. Comparison of eight 15-lipoxygenase (LO) inhibitors on the biosynthesis of 15-LO metabolites by human neutrophils and eosinophils. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Chen, D.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Chen, L. The Role of Periostin in the Occurrence and Progression of Eosinophilic Chronic Sinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chackerian, A.A.; Oldham, E.R.; Murphy, E.E.; Schmitz, J.; Pflanz, S.; Kastelein, R.A. IL-1 Receptor Accessory Protein and ST2 Comprise the IL-33 Receptor Complex. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2551–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.; Salter, B.; Oliveria, J.P.; El Gammal, A.I.; Tworek, D.; Smith, S.G.; Sehmi, R.; Gauvreau, G.M.; Byrne, P.M.O.A. IL-33 and Its Receptor ST2 after Inhaled Allergen Challenge in Allergic Asthmatics. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 176, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzaki, H.; Iijima, K.; Kobayashi, T.; O’Grady, S.M.; Kita, H. The Danger Signal, Extracellular ATP, Is a Sensor for an Airborne Allergen and Triggers IL-33 Release and Innate Th2-Type Responses. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4375–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysko, O.; Teufelberger, A.; Van Nevel, S.; Krysko, D.V.; Bachert, C. Protease/antiprotease network in allergy: The role of Staphylococcus aureus protease-like proteins. Allergy 2019, 74, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Kariya, S.; Higaki, T.; Haruna, T.; Matsushita, O.; Noda, Y.; Makihara, S.; Kanai, K.; Noyama, Y.; et al. Cellular Responses to Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Allergol. Int. 2014, 63, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Zhang, N.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Krysko, O.; Van Crombruggen, K.; Braun, H.; Johnston, S.L.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Zhang, L.; et al. Staphylococcus aureusInduces a Mucosal Type 2 Immune Response via Epithelial Cell–derived Cytokines. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, T.W.; Ramakrishnan, V.R.; Suh, J.D. The Role of Staphylococcus aureus in Patients with Chronic Sinusitis and Nasal Polyposis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljkovic, D.; Bassiouni, A.; Cooksley, C.; Ou, J.; Hauben, E.; Wormald, P.-J.; Vreugde, S. Association between Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells enrichment, nasal polyps and allergy in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Allergy 2014, 69, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poposki, J.A.; Klingler, A.I.; Tan, B.K.; Soroosh, P.; Banie, H.; Lewis, G.; Hulse, K.E.; Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Grammer, L.C.; et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells are elevated and activated in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2017, 5, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Han, J.K.; Desrosiers, M.; Hellings, P.W.; Amin, N.; E Lee, S.; Mullol, J.; Greos, L.S.; Bosso, J.V.; Laidlaw, T.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): Results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials. Lancet 2019, 394, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Gevaert, P.; Hellings, P. Biotherapeutics in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with and without Nasal Polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 1512–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Subjects | Control UT (n = 7) | CRS (UT) (n = 15) | Non-ECRS (NPs) (n = 24) | ECRS (NPs) (n = 7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, male/female | 6/1 | 9/6 | 18/6 | 35/13 |
| Mean ± SEM, Age, years | 52.7 ± 19.4 | 49.3 ± 18.0 | 50.5 ± 15.6 | 54.7 ± 13.6 |
| Asthma, yes/no | 2/5 | 2/13 | 1/23 | 22/26 #,††† |
| AERD, yes/no | 0/7 | 0/15 | 0/24 | 3/45 |
| Mean ± SEM Serum total IgE (IU/mL) | 287.6 ± 324.4 | 743.2 ± 1390.1 | 322.7 ± 447.0 | 532.3 ± 1328.5 |
| Mean ± SEM, Eosinophils in peripheral blood (%) | 2.6 ± 1.3 | 3.9 ± 2.5 | 2.9 ± 1.4 | 6.8 ± 4.7 **,#,††† |
| Mean ± SEM, Total number of Eosinophils in peripheral blood | 138.2 ± 57.1 | 228.9 ± 163.5 | 156.8 ± 102.2 | 420.1 ± 331.6 **,#,†††† |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imoto, Y.; Takabayashi, T.; Sakashita, M.; Kato, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Kidoguchi, M.; Koyama, K.; Adachi, N.; Kimura, Y.; Ogi, K.; et al. Enhanced 15-Lipoxygenase 1 Production is Related to Periostin Expression and Eosinophil Recruitment in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111568
Imoto Y, Takabayashi T, Sakashita M, Kato Y, Yoshida K, Kidoguchi M, Koyama K, Adachi N, Kimura Y, Ogi K, et al. Enhanced 15-Lipoxygenase 1 Production is Related to Periostin Expression and Eosinophil Recruitment in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(11):1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111568
Chicago/Turabian StyleImoto, Yoshimasa, Tetsuji Takabayashi, Masafumi Sakashita, Yukinori Kato, Kanako Yoshida, Masanori Kidoguchi, Keisuke Koyama, Naoto Adachi, Yukihiro Kimura, Kazuhiro Ogi, and et al. 2020. "Enhanced 15-Lipoxygenase 1 Production is Related to Periostin Expression and Eosinophil Recruitment in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis" Biomolecules 10, no. 11: 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111568
APA StyleImoto, Y., Takabayashi, T., Sakashita, M., Kato, Y., Yoshida, K., Kidoguchi, M., Koyama, K., Adachi, N., Kimura, Y., Ogi, K., Ito, Y., Kanno, M., Okamoto, M., Narita, N., & Fujieda, S. (2020). Enhanced 15-Lipoxygenase 1 Production is Related to Periostin Expression and Eosinophil Recruitment in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Biomolecules, 10(11), 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111568