XIAP’s Profile in Human Cancer
Abstract
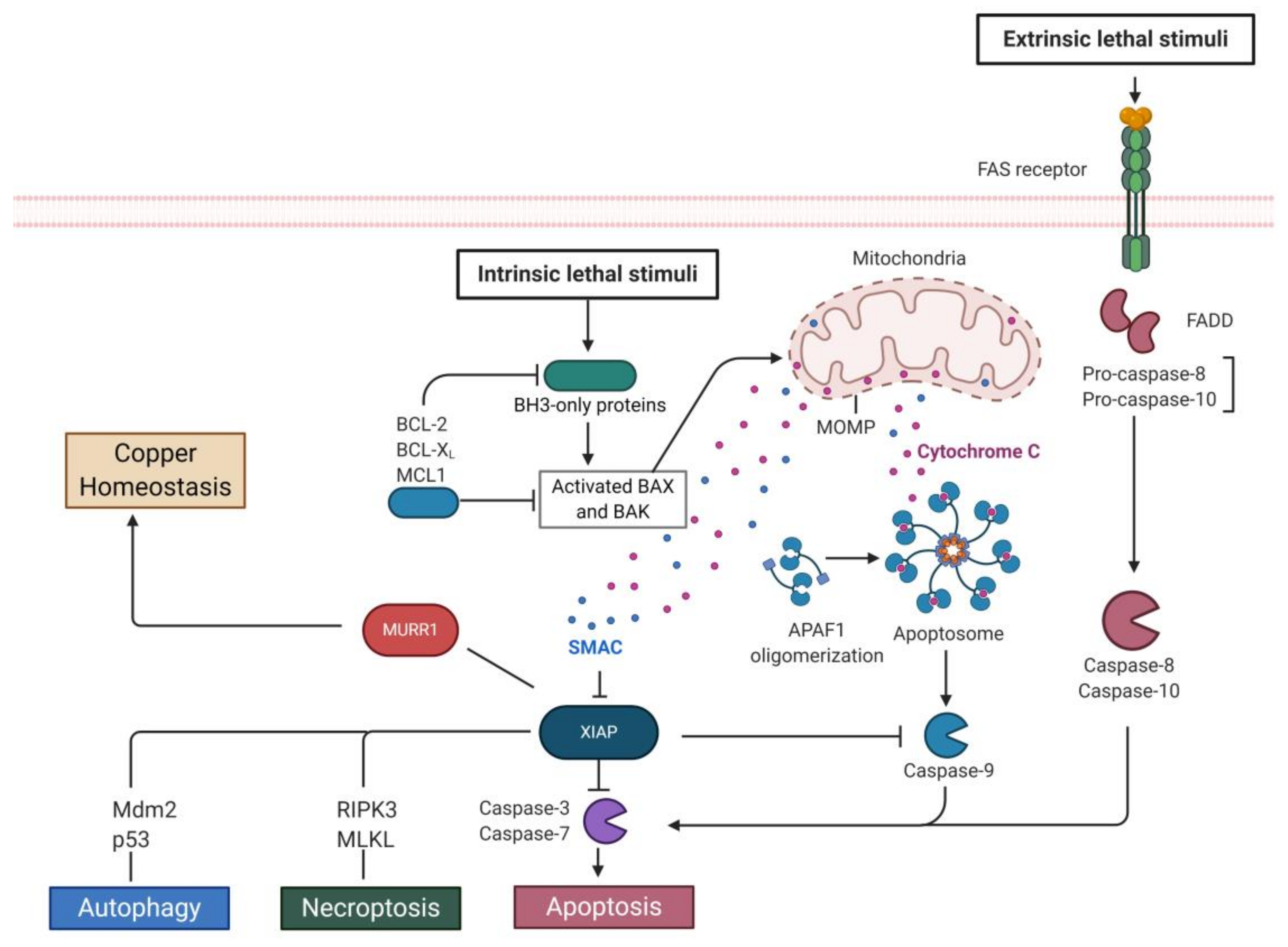
1. Introduction
2. XIAP and Cellular Functions
3. XIAP and Cancer
3.1. Bladder Cancer
3.2. Breast Cancer
3.3. Lung Cancer
3.4. Colon Cancer
3.5. Other Cancers
4. XIAP: A Potential Anti-Tumor Target
4.1. Inhibitors or Antagonists of XIAP
4.2. XIAP Promotes Cellular Resistance to Cancer Therapy
4.3. Novel Drug Development by Targeting XIAP
5. XIAP and Non-Coding RNA
5.1. Long Non-Coding RNA
5.2. Micro RNA
5.3. Circular RNA
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duckett, C.S.; Nava, V.E.; Gedrich, R.W.; Clem, R.J.; Van Dongen, J.L.; Gilfillan, M.C.; Shiels, H.; Hardwick, J.M.; Thompson, C.B. A conserved family of cellular genes related to the baculovirus iap gene and encoding apoptosis inhibitors. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2685–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProtKB-Q6PIA0 (Q6PIA0_HUMAN). Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q6PIA0//URL (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Duckett, C.S.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Tomaselli, K.J.; Thompson, C.B.; Armstrong, R.C. Human IAP-like protein regulates programmed cell death downstream of Bcl-xL and cytochrome c. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, P.; Roy, N.; Tamai, K.; Lefebvre, C.; Baird, S.; Cherton-Horvat, G.; Farahani, R.; McLean, M.; Ikeda, J.E.; MacKenzie, A.; et al. Suppression of apoptosis in mammalian cells by NAIP and a related family of IAP genes. Nature 1996, 379, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Cai, M.; Gunasekera, A.H.; Meadows, R.P.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, W.; Xu, N.; Ng, S.C.; et al. NMR structure and mutagenesis of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein XIAP. Nature 1999, 401, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Park, Y.C.; Rich, R.L.; Segal, D.; Myszka, D.G.; Wu, H. Structural basis of caspase inhibition by XIAP: Differential roles of the linker versus the BIR domain. Cell 2001, 104, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, Y.; Kleffmann, T.; Linke, K.; Condon, S.M.; Hinds, M.G.; Day, C.L. Regulation of ubiquitin transfer by XIAP, a dimeric RING E3 ligase. Biochem. J. 2013, 450, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schile, A.J.; García-Fernández, M.; Steller, H. Regulation of apoptosis by XIAP ubiquitin-ligase activity. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 2256–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, M.K.; Hui, S.K.; Yang, Y.; Yin, S.T.; Hu, H.Y.; Zou, B.; Wong, B.C.; Sze, K.H. Structural analysis of the UBA domain of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein reveals different surfaces for ubiquitin-binding and self-association. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polykretis, P.; Luchinat, E.; Bonucci, A.; Giachetti, A.; Graewert, M.A.; Svergun, D.I.; Banci, L. Conformational characterization of full-length X-chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) through an integrated approach. IUCrJ 2019, 6, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Lin, S.C.; Huang, Y.; Kang, Y.J.; Rich, R.; Lo, Y.C.; Myszka, D.; Han, J.; Wu, H. XIAP induces NF-kappaB activation via the BIR1/TAB1 interaction and BIR1 dimerization. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nakabayashi, Y.; Nakata, K.; Reed, J.C.; Takahashi, R. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) inhibits caspase-3 and -7 in distinct modes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 27058–27063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Hua, X.; Yang, R.; Jin, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Tian, Z.; Huang, M.; Jiang, G.; Huang, H.; et al. XIAP Interaction with E2F1 and Sp1 via its BIR2 and BIR3 domains specific activated MMP2 to promote bladder cancer invasion. Oncogenesis 2019, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Jang, M.; Park, Y.K.; Kang, S.; Bae, K.H.; Cho, S.; Lee, C.K.; Park, B.C.; Chi, S.W.; Park, S.G. Molecular interaction between HAX-1 and XIAP inhibits apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Ji, C.; Zhang, J.Z.H. Molecular basis of SMAC-XIAP binding and the effect of electrostatic polarization. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Rich, R.L.; Myszka, D.G.; Wu, H. Requirement of both the second and third BIR domains for the relief of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)-mediated caspase inhibition by Smac. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 49517–49522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, B.; Gottfried, Y.; Edison, N.; Shekhtman, A.; Lev, T.; Glaser, F.; Larisch, S. ARTS binds to a distinct domain in XIAP-BIR3 and promotes apoptosis by a mechanism that is different from other IAP-antagonists. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Luo, W.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.R.; Huang, C. E3 ligase activity of XIAP RING domain is required for XIAP-mediated cancer cell migration, but not for its RhoGDI binding activity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveraux, Q.L.; Takahashi, R.; Salvesen, G.S.; Reed, J.C. X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death proteases. Nature 1997, 388, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawen, A. Apoptosis-an introduction. Bioessays 2003, 25, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrez-Daloz, L.; Dupoux, A.; Cartier, J. XIAPs: More than just inhibitors of apoptosis proteins. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Huang, Y.; Lo, Y.C.; Lu, M.; Wu, H. Crystal structure of the BIR1 domain of XIAP in two crystal forms. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyrd-Hansen, M.; Darding, M.; Miasari, M.; Santoro, M.M.; Zender, L.; Xue, W.; Tenev, T.; da Fonseca, P.C.; Zvelebil, M.; Bujnicki, J.M. XIAPs contain an evolutionarily conserved ubiquitin-binding domain that regulates NF-kappaB as well as cell survival and oncogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasula, S.M.; Hegde, R.; Saleh, A.; Datta, P.; Shiozaki, E.; Chai, J.; Lee, R.A.; Robbins, P.D.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Shi, Y.; et al. A conserved XIAP-interaction motif in caspase-9 and Smac/DIABLO regulates caspase activity and apoptosis. Nature 2001, 410, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicki, S.; Gurzeler, U.; Wei-Lynn Wong, W.; Jost, P.J.; Bachmann, D.; Kaufmann, T. Loss of XIAP facilitates switch to TNFα-induced necroptosis in mouse neutrophils. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Y.; Kim, H.; Zhang, C.L.; Meng, X.L.; Wu, Z.S. Clinical significance of autophagic protein LC3 levels and its correlation with XIAP expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, Z.; Mei, Y.; Wu, M. XIAP inhibits autophagy via XIAP-Mdm2-p53 signalling. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2204–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalaoui, N.; Vaux, D.L. Recent advances in understanding inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. F1000Research 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.M.; Polykretis, P.; Luchinat, E.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.N.; Zuo, H.H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.L.; Ye, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Solution structure and interaction with copper in vitro and in living cells of the first BIR domain of XIAP. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ewing, P.M.; Laursen, W.J.; Tripp, V.T.; Singh, S.; Splan, K.E. Copper-binding properties of the BIR2 and BIR3 domains of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 140, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, E.; Ganesh, L.; Dick, R.D.; van De Sluis, B.; Wilkinson, J.C.; Klomp, L.W.; Wijmenga, C.; Brewer, G.J.; Nabel, G.J.; Duckett, C.S. A novel role for XIAP in copper homeostasis through regulation of MURR1. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, I.; Kornblau, S.M.; Segall, H.; Krajewski, S.; Welsh, K.; Kitada, S.; Scudiero, D.A.; Tudor, G.; Qui, Y.H.; Monks, A.; et al. Expression and prognostic significance of IAP-family genes in human cancers and myeloid leukemias. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, D.; Dalela, D.; Rath, S.K.; Goel, M.M.; Bhatt, M.L. Evaluation of urinary XIAP as a diagnostic biomarker of carcinoma of urinary bladder. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 8243–8248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zeng, X.; Jiang, G.; Liao, X.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Jin, H.; Zhu, J.; Sun, H.; Wu, X.R.; et al. XIAP BIR domain suppresses miR-200a expression and subsequently promotes EGFR protein translation and anchorage-independent growth of bladder cancer cell. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Huang, C.; Liao, X.; Li, J.; Wu, X.R.; Zeng, F.; Huang, C. The RING domain in the anti-apoptotic protein XIAP stabilizes c-Myc protein and preserves anchorage-independent growth of bladder cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 5935–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Xu, J.; Guo, X.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Peng, M.; Zhu, J.; Tian, Z.; Wu, X.R.; Tang, M.S.; et al. XIAP RING domain mediates miR-4295 expression and subsequently inhibiting p63α protein translation and promoting transformation of bladder epithelial cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jin, H.; Xu, J.; Gu, J.; Li, X.; Xie, Q.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Tian, Z.; Jiang, G.; et al. XIAP overexpression promotes bladder cancer invasion in vitro and lung metastasis in vivo via enhancing nucleolin-mediated Rho-GDIβ mRNA stability. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 2040–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, R.; Hua, X.; Huang, M.; Tian, Z.; Li, J.; Lam, H.Y.; Jiang, G.; Cohen, M.; Huang, C. lncRNA SNHG1 Promotes Basal Bladder Cancer Invasion via Interaction with PP2A Catalytic Subunit and Induction of Autophagy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, F.M.; Owens, T.W.; Tanianis-Hughes, J.; Clarke, R.B.; Brennan, K.; Bundred, N.J.; Streuli, C.H. Targeting inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in combination with ErbB antagonists in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ji, R.; Gu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B. Prognostic value of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein for invasive ductal breast cancer with triple-negative phenotype. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Iizumi, Y.; Goi, W.; Sowa, Y.; Taguchi, T.; Sakai, T. Ribosomal protein S3 regulates XIAP expression independently of the NF-κB pathway in breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 3205–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.K.; Brown, M.C.; Geradts, J.; Bao, X.; Robinson, T.J.; Jolly, M.K.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Palmer, G.M.; Gromeier, M.; Levine, H.; et al. XIAP Regulation by MNK Links MAPK and NFκB Signaling to Determine an Aggressive Breast Cancer Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1726–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, X.N.; Yuan, X.D.; Wu, W.Y.; Lobie, P.E.; Wu, Z. XIAP facilitates breast and colon carcinoma growth via promotion of p62 depletion through ubiquitination-dependent proteasomal degradation. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1448–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.B.; Li, Q.H.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Li, K. MiR-142 inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting XIAP. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 7430–7437. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.K.; Lee, J.M.; Kang, S.H.; Jeon, S.H.; Kim, C.M.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, N.K.; Kim, J.K. The novel microRNA hsa-miR-CHA1 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in human lung cancer by targeting XIAP. Lung Cancer 2019, 132, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augeri, D.J.; Langenfeld, E.; Castle, M.; Gilleran, J.A.; Langenfeld, J. Inhibition of BMP and of TGFβ receptors downregulates expression of XIAP and TAK1 leading to lung cancer cell death. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Yoshino, H.; Kazama, Y.; Kashiwakura, I. Involvement of caspase‑8 in apoptosis enhancement by cotreatment with retinoic acid‑inducible gene‑I‑like receptor agonist and ionizing radiation in human non‑small cell lung cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 5286–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Yue, J.R.; Dong, B.R. Abnormal expression of caspase8, bcl-2 and cytochrome C in drug resistant lung cancer cell. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2005, 36, 786–788. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.Y.; Feng, X.J.; Chen, Z.L.; Jiang, L.; Shen, A.Z. Xanthatin mediates G2/M cell cycle arrest, autophagy and apoptosis via ROS/XIAP signaling in human colon cancer cells. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 2616–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, K.L.; Agarwal, E.; Chowdhury, S.; Luo, J.; Brattain, M.G.; Black, J.D.; Wang, J. TGFβ/Smad3 regulates proliferation and apoptosis through IRS-1 inhibition in colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Luo, W.; Huang, C.; Chen, J. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) lacking RING domain localizes to the nuclear and promotes cancer cell anchorage-independent growth by targeting the E2F1/Cyclin E axis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7126–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Zhu, F.; Duan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cai, H. HtrA1 resensitizes multidrug-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting XIAP. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 70, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Talmon, G.; Wang, J. MicroRNA-587 antagonizes 5-FU-induced apoptosis and confers drug resistance by regulating PPP2R1B expression in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Rong, J.; Yu, Y. Circular RNA circ0005276 promotes the proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells by interacting with FUS to transcriptionally activate XIAP. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Zeng, W.; Wan, C.; Duan, S.; Jiang, S. microRNA-137 promotes apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells via the regulation of XIAP. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Mao, H.; Shen, L.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, P. MiR-519d represses ovarian cancer cell proliferation and enhances cisplatin-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro by targeting XIAP. Onco Targets Ther. 2014, 7, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Zhai, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S. MicroRNA-149 suppresses the proliferation and increases the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by targeting X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7328–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.P.; Han, T.; Li, Y.X.; Long, X.Y.; Li, W.Z. Simultaneous silencing of XIAP and survivin causes partial mesenchymal-epithelial transition of human pancreatic cancer cells via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Jo, M.J.; Yun, H.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, B.R.; Kim, J.L.; Park, S.H.; Na, Y.J.; Jeong, Y.A.; Kim, B.G.; et al. Cannabidiol promotes apoptosis via regulation of XIAP/Smac in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazhang, Y.; Jaliani, H.Z.; Imani, M.; Dariushnejad, H. Synergism between NF-kappa B inhibitor, celastrol, and XIAP inhibitor, embelin, in an acute myeloid leukemia cell line, HL-60. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper, E.C.; Bergsma, A.J.; Pijnappel, W.W.M.P.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Opportunities and challenges for antisense oligonucleotide therapies. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, E.; Jodrell, D.; Connolly, K.; Danson, S.; Jolivet, J.; Durkin, J.; Morris, S.; Jowle, D.; Ward, T.; Cummings, J.; et al. Phase I trial of AEG35156 administered as a 7-day and 3-day continuous intravenous infusion in patients with advanced refractory cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S. Smac Mimetics to Therapeutically Target IAP Proteins in Cancer. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 330, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Smith, D.C.; Wang, S. Small-molecule SMAC mimetics as new cancer therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraei, R.; Soleimani, M.; Movassaghpour Akbari, A.A.; Farshdousti Hagh, M.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Solali, S. The role of XIAP in resistance to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in Leukemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, C.; Li, R.H.; Chen, C.; Liu, H. Study on the Relationship Between XIAP Gene and Resistance of Taxol in Ovarian Cancer. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2018, 49, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan, L.; Kehoe, J.; Fay, J.; Bacon, O.; Lindner, A.U.; Kay, E.W.; Deasy, J.; McNamara, D.A.; Prehn, J.H. High levels of X-linked Inhibitor-of-Apoptosis Protein (XIAP) are indicative of radio chemotherapy resistance in rectal cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, G.H.; Wu, Y.M.; Wang, H.S.; Wang, H.F.; Zhang, G.; Lu, L.L.; Li, Z.Q.; Chan, K.Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. AP-1 confers resistance to anti-cancer therapy by activating XIAP. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 14124–14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, X. Cisplatin induces expression of drug resistance-related genes through c-jun N-terminal kinase pathway in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, J.M.; Brinkmann, K.; Yazdanpanah, B.; Haubert, D.; Pongratz, C.; Coutelle, O.; Krönke, M.; Kashkar, H. Elevated XIAP expression alone does not confer chemoresistance. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Bai, L.; Sun, H.; Nikolovska-Coleska, Z.; McEachern, D.; Qiu, S.; Miller, R.S.; Yi, H.; Shangary, S.; Sun, Y.; et al. SM-164: A novel, bivalent Smac mimetic that induces apoptosis and tumor regression by concurrent removal of the blockade of cIAP-1/2 and XIAP. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9384–9393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, A.Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y. Smac-mimetic compound SM-164 induces radiosensitization in breast cancer cells through activation of caspases and induction of apoptosis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, D.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; He, Z.; Chen, F.; Che, X.; Song, X. Expression of the IAP protein family acts cooperatively to predict prognosis in human bladder cancer patients. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.; Singh, P.; Kalha, B.; Singh, O.; Pal, R. Gonadotropin-mediated chemoresistance: Delineation of molecular pathways and targets. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.K.; Sauer, S.J.; Nath, S.; Robinson, T.J.; Morse, M.A.; Devi, G.R. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein mediates tumor cell resistance to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmer, A.D.; Dalili, S.; Batey, R.A.; Riedl, S.J. Targeting XIAP for the treatment of malignancy. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamanini, E.; Buck, I.M.; Chessari, G.; Chiarparin, E.; Day, J.E.H.; Frederickson, M.; Griffiths-Jones, C.M.; Hearn, K.; Heightman, T.D.; Iqbal, A.; et al. Discovery of a Potent Nonpeptidomimetic, Small-Molecule Antagonist of Cellular Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein 1 (cIAP1) and X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (XIAP). J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4611–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, G.A.; Lewis, E.J.; Ahn, J.S.; Johnson, C.N.; Lyons, J.F.; Martins, V.; Munck, J.M.; Rich, S.J.; Smyth, T.; Thompson, N.T.; et al. ASTX660, a Novel Non-peptidomimetic Antagonist of cIAP1/2 and XIAP, Potently Induces TNFα-Dependent Apoptosis in Cancer Cell Lines and Inhibits Tumor Growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, M.; Zhou, X. The role of long noncoding RNAs in gene expression regulation. In Gene Expression Profiling in Cancer; Vlachakis, D., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Li, X.D.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.B.; Xue, Y.X.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, Y.H. CRNDE affects the malignant biological characteristics of human glioma stem cells by negatively regulating miR-186. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25339–25355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, D.; Bai, Z.G.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.T. The long noncoding RNA XIAP-AS1 promotes XIAP transcription by XIAP-AS1 interacting with Sp1 in gastric cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yu, Y.; Tan, S. Long non-coding XIAP-AS1 regulates cell proliferation, invasion and cell cycle in colon cancer. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yan, H.; Tao, S.Q.; Wang, X.N.; Mou, L.; Chen, P.; Cheng, X.W.; Wu, W.Y.; Wu, Z.S. XIAP 3′-untranslated region as a ceRNA promotes FSCN1 function in inducing the progression of breast cancer by binding endogenous miR-29a-5p. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Xue, L.; Mo, L.; Zhang, D.; Guo, X.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Peng, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhong, M.; et al. Downregulation of miR-200c stabilizes XIAP mRNA and contributes to invasion and lung metastasis of bladder cancer. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2019, 13, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouHaidar, M.G.; Venkataraman, S.; Golshani, A.; Liu, B.; Ahmad, T. Novel coding, translation, and gene expression of a replicating covalently closed circular RNA of 220 nt. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14542–14547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.P.; Li, X.M.; Liu, C.; Liu, B.H.; Shan, K.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Yan, B. Identification and Characterization of Circular RNAs as a New Class of Putative Biomarkers in Diabetes Retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 6500–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Chen, W.M.; Wang, Z.H.; Wei, T.N.; Chen, Z.Z.; Wu, W.B. CircPAN3 mediates drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia through the miR-153-5p/miR-183-5p-XIAP axis. Exp. Hematol. 2019, 70, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Domain | Binding Substrates | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| BIR1 | TAB1, BIR1 | [10,11] |
| linker-BIR2 | Caspase-3/7, E2F1, HAX-1, SMAC | [12,18,19,20] |
| BIR3 | Caspase-9, Sp1, ARTS, HAX-1, SMAC, BIR3 | [18,19,20,21,22] |
| UBA | Ubiquitin, UBA | [9] |
| RING | Multiple protein substrates and plays E3 ligase activity | [10,23] |
| Drug | Stage | Group and Reference |
|---|---|---|
| AEG35156/GEM640 | Phase1–2 complicated | Aegera Therapeutics, Inc. |
| ASTX660 | Phase 1–2 recruiting | Astex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
| ASTX727 | Phase 2 | Astex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
| AT-406/Debio 1143 | Phase 1 complicated | Debiopharm International SA. |
| LCL-161 | Phase 2 complicated | Novartis Pharmaceuticals. |
| GDC-0152 | Phase 1 terminated | Genentech, Inc. |
| TL32711/Birinipant | Phase 1–2 complicated | TetraLogic Pharmaceuticals. |
| HGS1029 | Phase 1 complicated | Human Genome Sciences Inc. |
| SM-164 | Preclinic | [71,72] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, H.; Costa, M. XIAP’s Profile in Human Cancer. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111493
Tu H, Costa M. XIAP’s Profile in Human Cancer. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(11):1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111493
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Huailu, and Max Costa. 2020. "XIAP’s Profile in Human Cancer" Biomolecules 10, no. 11: 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111493
APA StyleTu, H., & Costa, M. (2020). XIAP’s Profile in Human Cancer. Biomolecules, 10(11), 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111493





