Citrus sudachi Peel Extract Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Promotes the Differentiation of Keratinocytes through Inhibition of the EGFR–ERK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Aqueous Extract of Citrus Sudachi Peel
2.2. Phenolic Compound Evaluation by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.3. Cell Culture and Induction of Differentiation
2.4. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Assay
2.5. Proliferation Assay
2.6. Immunoblot Analysis
2.7. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.9. Reverse-Transcription Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
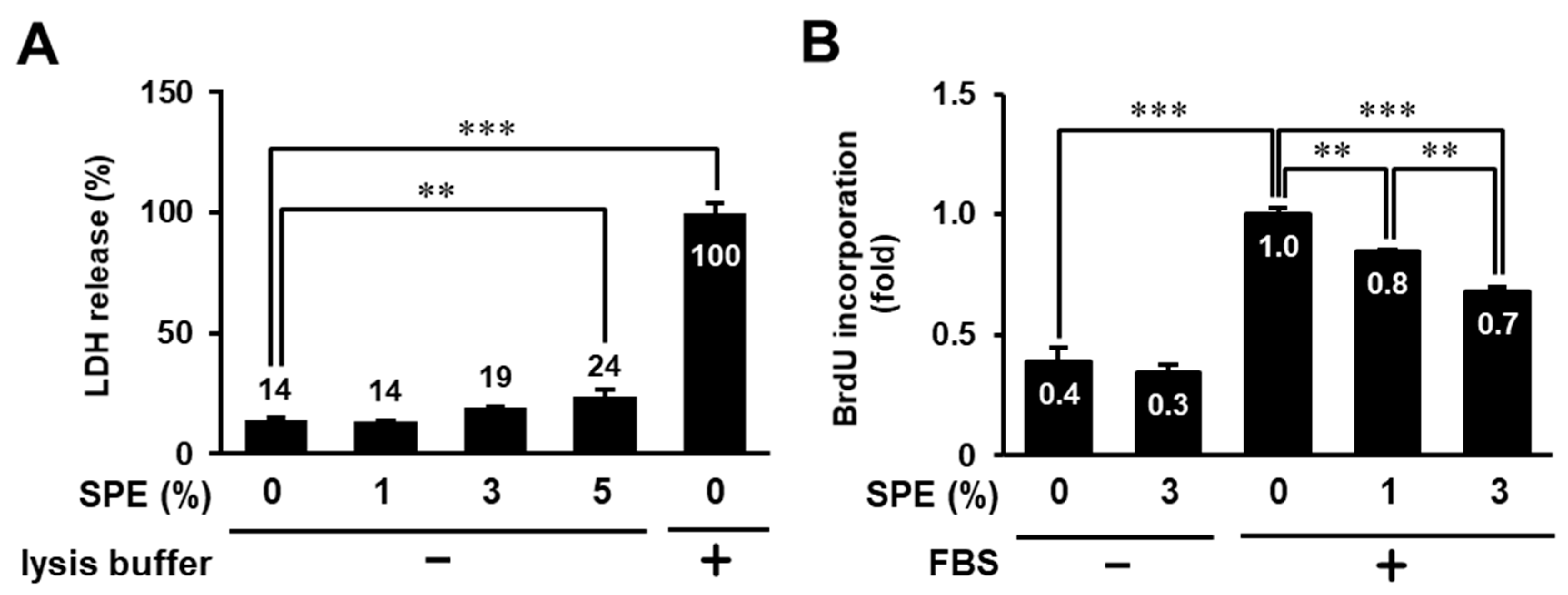
3.1. Toxicity Evaluation of Citrus sudachi Peel Extract (SPE) on HaCaT Cells
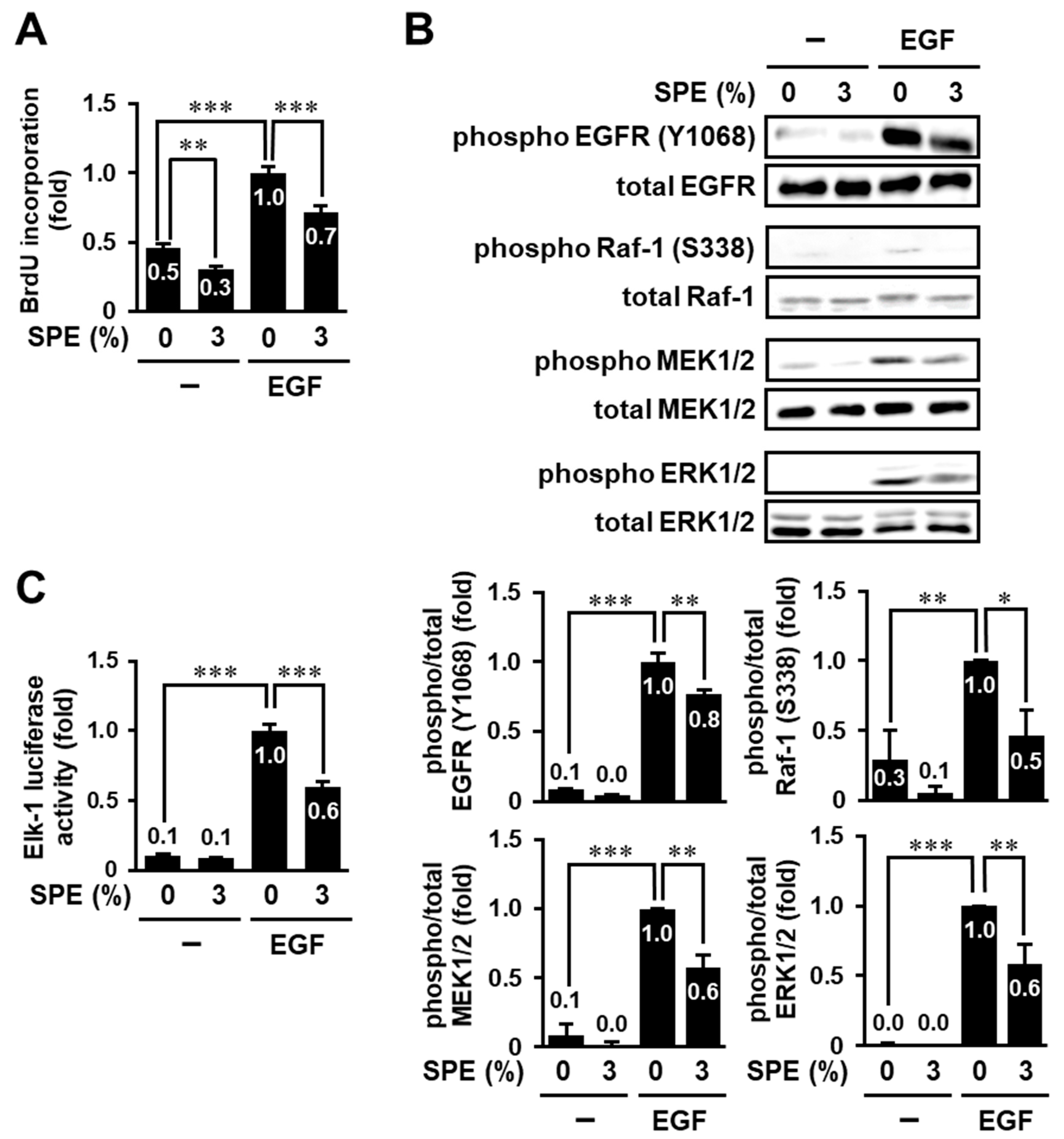
3.2. SPE Suppresses Cell Proliferation and the EGF Receptor–ERK Pathway in HaCaT Cells
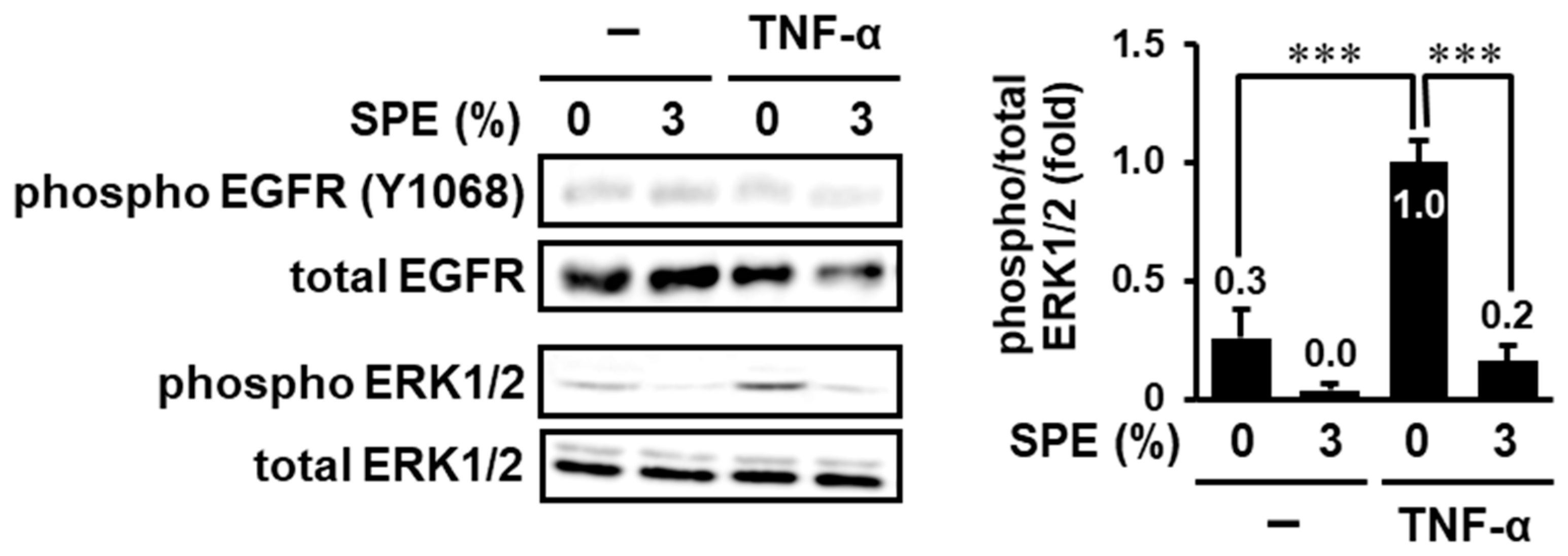
3.3. SPE Suppresses TNF-α-Induced EGFR-Independent ERK1/2 Activation
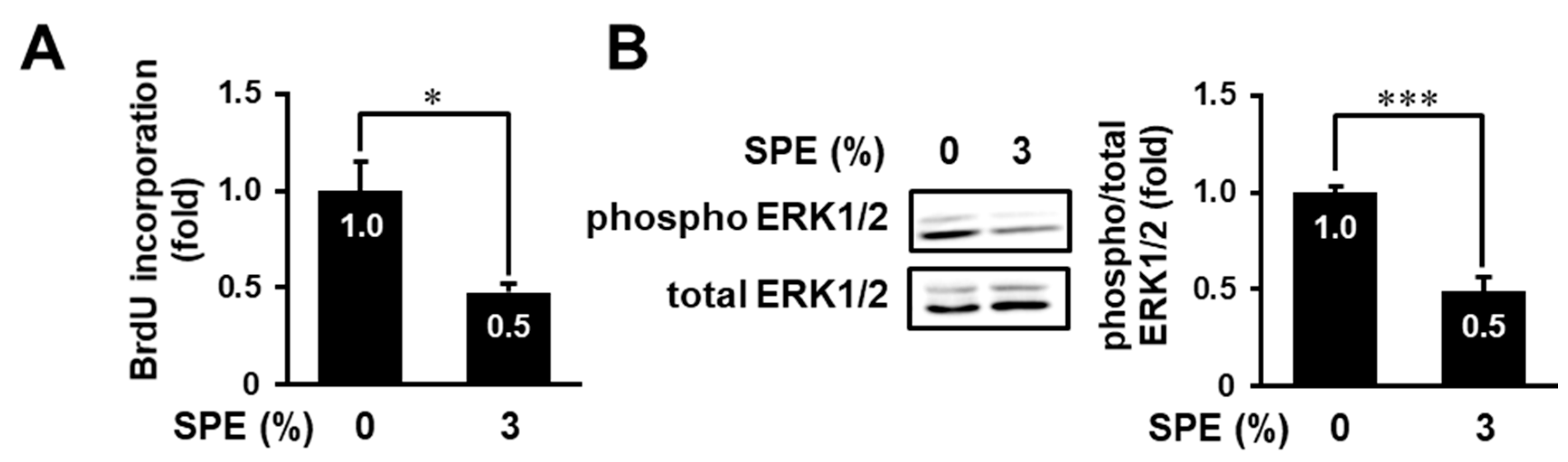
3.4. SPE Suppresses Cell Proliferation and the ERK Pathway in Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes
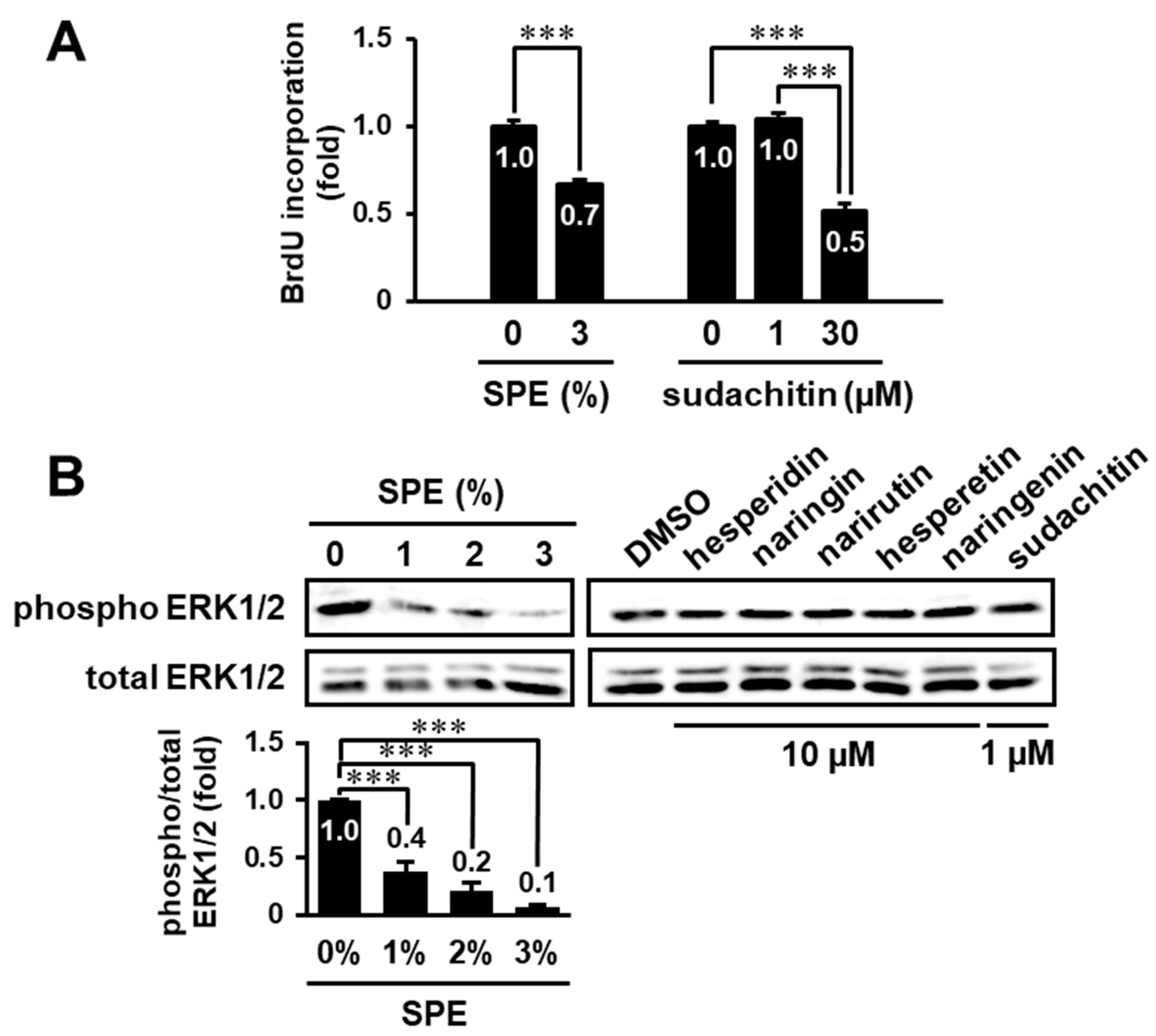
3.5. Search for Biologically Active Compound(s) in the Extract of C. sudachi Peel
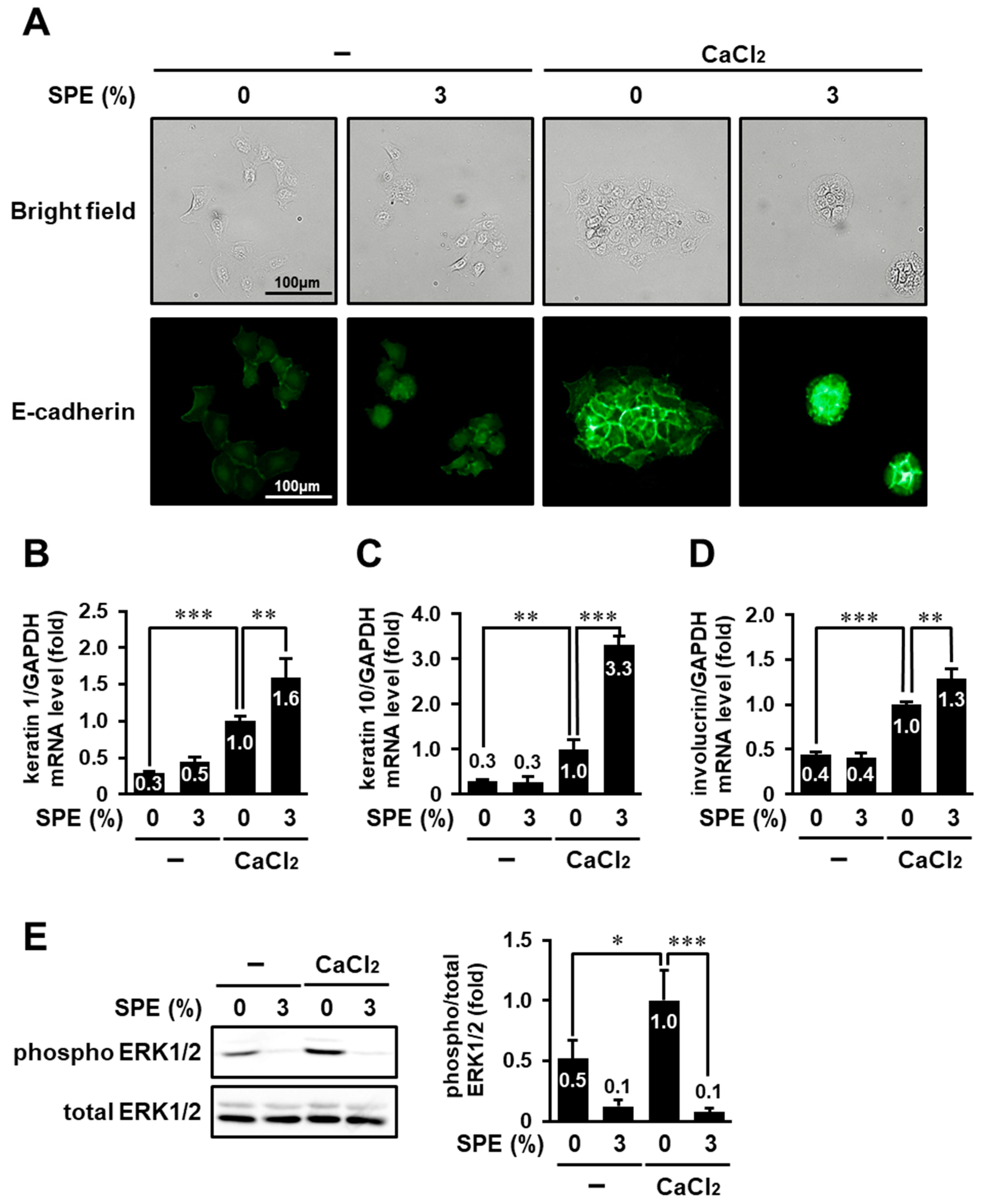
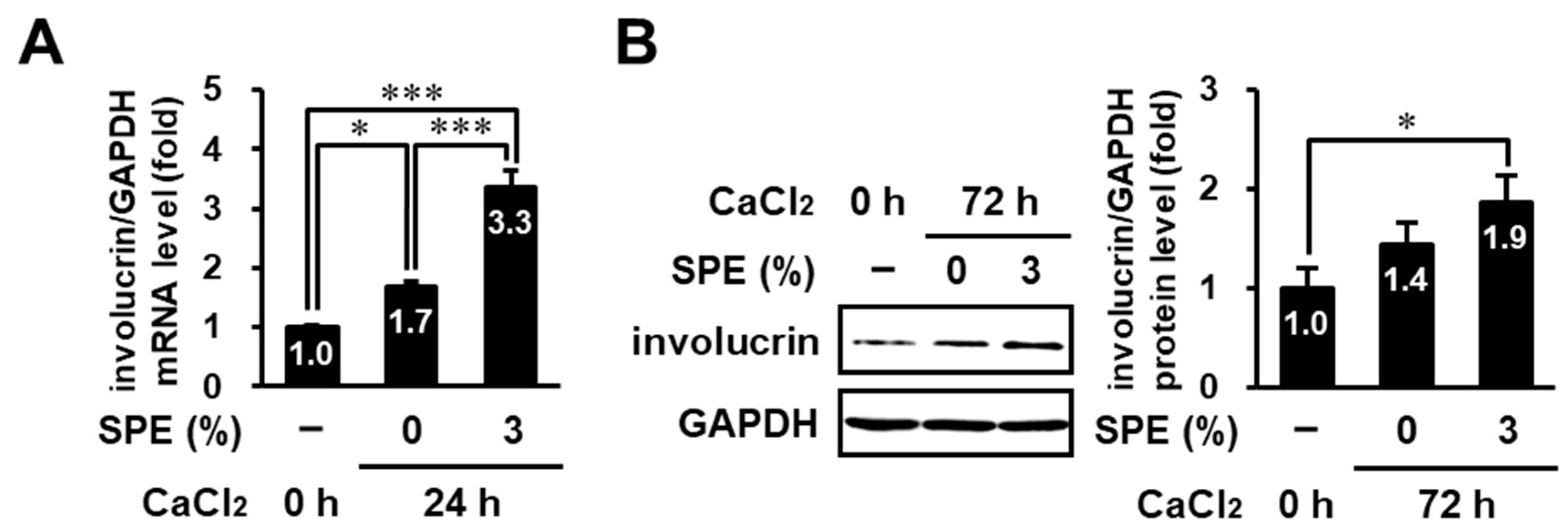
3.6. SPE Potentiates Calcium-Induced Keratinocyte Differentiation of HaCaT Cells
3.7. SPE Enhances Calcium-Induced Differentiation in Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chambers, E.S.; Vukmanovic-Stejic, M. Skin barrier immunity and ageing. Immunology 2019, 160, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goleva, E.; Berdyshev, E.; Leung, D.Y. Epithelial barrier repair and prevention of allergy. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, E.; Sato, Y.; Minagawa, A.; Okuyama, R. Pathogenesis of psoriasis and development of treatment. J. Dermatol. 2017, 45, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, R.L.; Efimova, T.; Dashti, S.R.; Balasubramanian, S.; Deucher, A.; Crish, J.F.; Sturniolo, M.; Bone, F. Keratinocyte Survival, Differentiation, and Death: Many Roads Lead to Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2002, 7, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; López, J.M. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Pan, W.; Liu, S.; Shen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Sun, L.; Han, J.; Zheng, W.; Peng, W. DUSP1/MKP-1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis in keratinocytes through the ERK/Elk-1/Egr-1 signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2019, 223, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Goebeler, M.; Posern, G.; Feller, S.M.; Seitz, C.S.; Bröcker, E.-B.; Rapp, U.R.; Ludwig, S. Ras-independent Activation of the Raf/MEK/ERK Pathway upon Calcium-induced Differentiation of Keratinocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 41011–41017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Q. Activation of ERK-FAK Signaling Pathway and Enhancement of Cell Migration Involved in the Early Interaction Between Oral Keratinocytes and Candida albicans. Mycopathologia 2008, 167, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Li, C.; Luo, S.; Liu-Smith, F.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, N.; Lai, B.; Lei, T.; Wang, Q.; et al. Yes-Associated Protein Contributes to the Development of Human Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Activation of RAS. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zema, D.; Calabrò, P.; Folino, A.; Tamburino, V.; Zappia, G.; Zimbone, S. Valorisation of citrus processing waste: A review. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 252–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Takaishi, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Tsuchiya, K.; Shibata, H.; Higuti, T. Chemical Constituents from the Peels of Citrussudachi. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Schluesener, H. Health-promoting effects of the citrus flavanone hesperidin. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 57, 613–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Mitani, M.; Minatogawa, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Nakamoto, M.; Shuto, E.; Nii, Y.; Sakai, T. Extracts of Citrus sudachi peel attenuate body weight gain in C57BL/6 nice fed a high-fat diet. J. Med. Investig. 2017, 64, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Miyamoto, L.; Aihara, H.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, N.; Tsuchihashi, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Tamaki, T.; Kashiwada, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; et al. Methanol extraction fraction from Citrus Sudachi peel exerts lipid reducing effects in cultured cells. J. Med. Investig. 2018, 65, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, P.; Petrussevska, R.T.; Breitkreutz, D.; Hornung, J.; Markham, A.; E Fusenig, N. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 106, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S.; Yuasa, K. Sudachitin, a polymethoxyflavone from Citrus sudachi, induces apoptosis via the regulation of MAPK pathways in human keratinocyte HaCaT cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 519, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, S.; Hirose, S.; Nishitani, M.; Yoshida, I.; Tsukayama, M.; Tsuji, A.; Yuasa, K. Citrus peel polymethoxyflavones, sudachitin and nobiletin, induce distinct cellular responses in human keratinocyte HaCaT cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 2064–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltenberger, B.; Avula, B.; Ganzera, M.; Khan, I.; Stuppner, H.; Khan, S. Transport of sennosides and sennidines from Cassia angustifolia and Cassia senna across Caco-2 monolayers—An in vitro model for intestinal absorption. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, Q.; Tan, X.; Meng, L.; Wei, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C. Astilbin decreases proliferation and improves differentiation in HaCaT keratinocytes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyrieux, A.F.; Wilson, V.G. In vitro culture conditions to study keratinocyte differentiation using the HaCaT cell line. Cytotechnology 2007, 54, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, D.W.; Brunton, V.G.; Parkinson, E.; Frame, M.C. E-Cadherin at the Cell Periphery Is a Determinant of Keratinocyte Differentiation in Vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 269, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charest, J.L.; Jennings, J.M.; King, W.P.; Kowalczyk, A.P.; García, A.J. Cadherin-Mediated Cell–Cell Contact Regulates Keratinocyte Differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebaby, W.N.; Mroueh, M.A.; Boukamp, P.; Taleb, R.I.; Bodman-Smith, K.; El-Sibai, M.; Daher, C.F. Wild carrot pentane-based fractions suppress proliferation of human HaCaT keratinocytes and protect against chemically-induced skin cancer. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singkhorn, S.; Tantisira, M.H.; Tanasawet, S.; Hutamekalin, P.; Wongtawatchai, T.; Sukketsiri, W. Induction of keratinocyte migration by ECa 233 is mediated through FAK/Akt, ERK, and p38 MAPK signaling. Phytotherapy Res. 2018, 32, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, T.; Ohba, M.; Ohmori, T. Molecular-Targeted Therapies for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Resistance Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S.; Nagao, T.; Ingólfsson, H.I.; Maxfield, F.R.; Andersen, O.S.; Kopelovich, L.; Weinstein, I.B. The Inhibitory Effect of (-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate on Activation of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Is Associated with Altered Lipid Order in HT29 Colon Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6493–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziv, E.; Rotem, C.; Miodovnik, M.; Ravid, A.; Koren, R. Two modes of ERK activation by TNF in keratinocytes: Different cellular outcomes and bi-directional modulation by vitamin D. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Shin, M.S.; Singhirunnusorn, P.; Suzuki, S.; Kawanishi, M.; Koizumi, K.; Saiki, I.; Sakurai, H. TAK1-Mediated Serine/Threonine Phosphorylation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor via p38/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase: NF-κB-Independent Survival Pathways in Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 5529–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, G.; Davis, R.J. TNF and MAP kinase signalling pathways. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karoulia, Z.; Gavathiotis, E.; Poulikakos, P.I. New perspectives for targeting RAF kinase in human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 676–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.E.; Lee, S.H. Skin Barrier and Calcium. Ann. Dermatol. 2018, 30, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacouture, M.E. Mechanisms of cutaneous toxicities to EGFR inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, V.; Mandinova, A.; Guinea-Viniegra, J.; Hu, B.; Lefort, K.; Lambertini, C.; Neel, V.; Dummer, R.; Wagner, E.F.; Dotto, G.P. EGFR signalling as a negative regulator of Notch1 gene transcription and function in proliferating keratinocytes and cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasonen-Seppänen, S.; Karvinen, S.; Törrönen, K.; Hyttinen, J.M.; Jokela, T.; Lammi, M.J.; Tammi, M.I.; Tammi, R. EGF Upregulates, Whereas TGF-β Downregulates, the Hyaluronan Synthases Has2 and Has3 in Organotypic Keratinocyte Cultures: Correlations with Epidermal Proliferation and Differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, R.M.; Simpson, C.L.; Johnson, J.L.; Koetsier, J.L.; Dubash, A.D.; Najor, N.A.; Sarig, O.; Sprecher, E.; Green, K.J. Desmoglein-1/Erbin interaction suppresses ERK activation to support epidermal differentiation. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1556–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, H.; Zeng, K. Recent advances on the roles of epidermal growth factor receptor in psoriasis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 520–528. [Google Scholar]
- Flisiak, I.; Szterling-Jaworowska, M.; Baran, A.; Rogalska-Taranta, M. Effect of psoriasis activity on epidermal growth factor (EGF) and the concentration of soluble EGF receptor in serum and plaque scales. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 39, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commandeur, S.; van Drongelen, V.; de Gruijl, F.R.; el Ghalbzouri, A. Epidermal growth factor receptor activation and inhibition in 3D in vitro models of normal skin and human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 2120–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, P.; Gonzalez, S. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Molecular bases for EGFR-targeted therapy. Pathol. Res. Pr. 2011, 207, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, M.; Xu, S.; Bu, W.; Zhang, M.; Gu, H.; Chen, X. Is Ras a potential target in treatment against cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma? J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3373–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Viros, A.; Milagre, C.; Trunzer, K.; Bollag, G.; Spleiss, O.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Kong, X.; Koya, R.C.; Flaherty, K.T.; et al. RAS mutations in cutaneous squamous-cell carcinomas in patients treated with BRAF inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, X.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, M.; Zhai, C.; Liu, Z.; Di, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. Hesperidin inhibits keratinocyte proliferation and imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis via the IRS-1/ERK1/2 pathway. Life Sci. 2019, 219, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.-C.; Wu, H.; Li, P.-B.; Xie, L.-M.; Luo, Y.-L.; Shen, J.-G.; Su, W.-W. Naringin attenuates EGF-induced MUC5AC secretion in A549 cells by suppressing the cooperative activities of MAPKs-AP-1 and IKKs-IκB-NF-κB signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 690, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.D. Hesperetin Inhibits Vascular Formation by Suppressing of the PI3K/AKT, ERK, and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathways. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 19, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Gu, H.; Ye, Y.; Lin, B.; Sun, L.; Deng, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Protective effects of hesperidin against oxidative stress of tert-butyl hydroperoxide in human hepatocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2980–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-I.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Park, K.; Kim, W.-J.; Moon, S.-K. Requirement for Ras/Raf/ERK pathway in naringin-induced G1-cell-cycle arrest via p21WAF1 expression. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Liu, K.-C.; Chiou, Y.-L. Melanogenesis of murine melanoma cells induced by hesperetin, a Citrus hydrolysate-derived flavonoid. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Slambrouck, S.; Parmar, V.S.; Sharma, S.K.; de Bondt, B.; Foré, F.; Coopman, P.; Vanhoecke, B.W.; Boterberg, T.; Depypere, H.T.; Leclercq, G.; et al. Tangeretin inhibits extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Hou, W.-C.; Shen, S.-C.; Juan, S.-H.; Ko, C.-H.; Wang, L.-M.; Chen, Y.-C. Quercetin inhibition of tumor invasion via suppressing PKC /ERK/AP-1-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation in breast carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound | Concentration in Aqueous Extract (µM) | Concentration of SPE Containing 30% BG (µM) | Concentration in 3% SPE (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| hesperidin | 426 | 298 | 8.95 |
| naringin | 279 | 195 | 5.85 |
| narirutin | 286 | 200 | 6.01 |
| sudachitin | 22 | 15 | 0.46 |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5’ to 3’) | Reverse Primer (5’ to 3’) |
|---|---|---|
| keratin 1 | ATATGGGGGTGGTTATGGTCC | GTGACTTGATTTGCTCCCTTTCT |
| keratin 10 | TTGCTGAACAAAACCGCAAAG | GCCAGTTGGGACTGTAGTTCT |
| involucrin | ACTGAGGGCAGGGGAGAG | TCTGCCTCAGCCTTACTGTG |
| GAPDH | CAGCCTCAAGATCATCAGCA | CATCCACAGTCTTCTGGGTG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abe, S.; Ueno, M.; Nishitani, M.; Akamatsu, T.; Sato, T.; Shimoda, M.; Kanaoka, H.; Nii, Y.; Yamasaki, H.; Yuasa, K. Citrus sudachi Peel Extract Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Promotes the Differentiation of Keratinocytes through Inhibition of the EGFR–ERK Signaling Pathway. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101468
Abe S, Ueno M, Nishitani M, Akamatsu T, Sato T, Shimoda M, Kanaoka H, Nii Y, Yamasaki H, Yuasa K. Citrus sudachi Peel Extract Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Promotes the Differentiation of Keratinocytes through Inhibition of the EGFR–ERK Signaling Pathway. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(10):1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101468
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbe, Shogo, Misako Ueno, Mami Nishitani, Tetsuya Akamatsu, Takumi Sato, Marie Shimoda, Hiroki Kanaoka, Yoshitaka Nii, Hiroko Yamasaki, and Keizo Yuasa. 2020. "Citrus sudachi Peel Extract Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Promotes the Differentiation of Keratinocytes through Inhibition of the EGFR–ERK Signaling Pathway" Biomolecules 10, no. 10: 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101468
APA StyleAbe, S., Ueno, M., Nishitani, M., Akamatsu, T., Sato, T., Shimoda, M., Kanaoka, H., Nii, Y., Yamasaki, H., & Yuasa, K. (2020). Citrus sudachi Peel Extract Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Promotes the Differentiation of Keratinocytes through Inhibition of the EGFR–ERK Signaling Pathway. Biomolecules, 10(10), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101468





