Multi-Configuration Dirac–Hartree–Fock Calculations of Pr9+ and Nd10+: Configuration Resolution and Probing Fine-Structure Constant Variation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
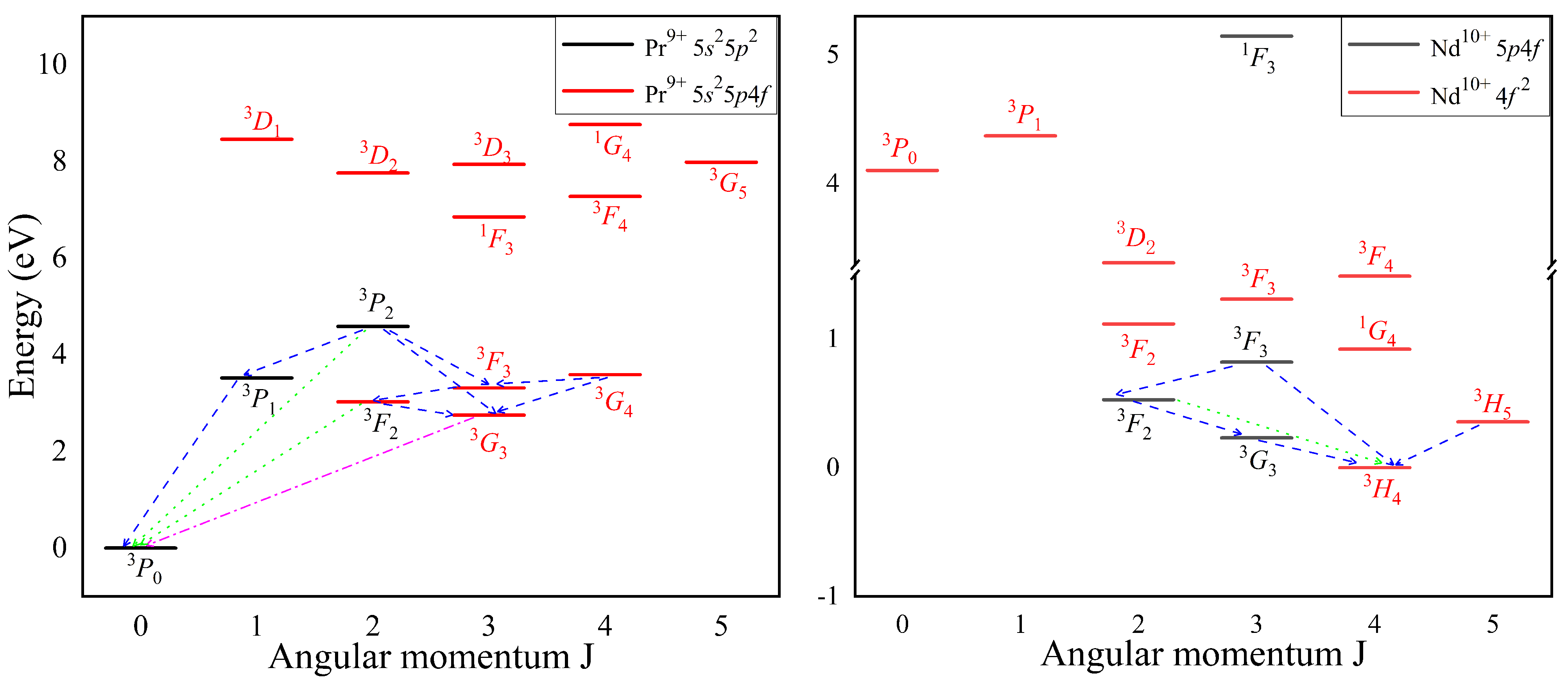
2.1. Energy Levels of and Ions
2.2. Transition Properties
2.3. Hyperfine Interaction Constant and Landé g Factor
2.4. Sensitivity of Clock Transitions
3. Theory and Methods
3.1. Multi-Configuration Dirac–Hartree–Fock Method
3.2. Electron Correlation Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bekker, H.; Hensel, C.; Daniel, A.; Windberger, A.; Pfeifer, T.; Crespo López-Urrutia, J.R. Laboratory precision measurements of optical emissions from coronal iron. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 062514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaft, I.; Borneis, S.; Engel, T.; Fricke, B.; Grieser, R.; Huber, G.; Kühl, T.; Marx, D.; Neumann, R.; Schröder, S.; et al. Precision Laser Spectroscopy of the Ground State Hyperfine Splitting of Hydrogenlike 209Bi82+. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 2425–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seelig, P.; Borneis, S.; Dax, A.; Engel, T.; Faber, S.; Gerlach, M.; Holbrow, C.; Huber, G.; Kühl, T.; Marx, D.; et al. Ground State Hyperfine Splitting of Hydrogenlike 207Pb81+ by Laser Excitation of a Bunched Ion Beam in the GSI Experimental Storage Ring. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 4824–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, J.; Andelkovic, Z.; Brandau, C.; Dax, A.; Geithner, W.; Geppert, C.; Gorges, C.; Hammen, M.; Hannen, V.; Kaufmann, S.; et al. High precision hyperfine measurements in Bismuth challenge bound-state strong-field QED. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derevianko, A.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V. Highly Charged Ions as a Basis of Optical Atomic Clockwork of Exceptional Accuracy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 180801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.Y.; Zhang, T.X.; Guan, H.; Lu, Q.F.; Xiao, J.; Chen, S.L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, C.B.; Zou, Y.M.; et al. Probing multiple electric-dipole-forbidden optical transitions in highly charged nickel ions. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 022804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berengut, J.C.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V. Enhanced Laboratory Sensitivity to Variation of the Fine-Structure Constant using Highly Charged Ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 120801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, S. Hydrogenlike Highly Charged Ions for Tests of the Time Independence of Fundamental Constants. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 180801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Dolde, J.; Ming Lim, H.; Ranabhat, N.; Kolkowitz, S. Differential clock comparisons with a multiplexed optical lattice clock. Nature 2022, 602, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, D.K.; Sahoo, B.K. Highly charged W13+, Ir16+, and Pt17+ ions as promising optical clock candidates for probing variations of the fine-structure constant. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 032504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berengut, J.C.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V.; Ong, A. Optical Transitions in Highly Charged Californium Ions with High Sensitivity to Variation of the Fine-Structure Constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 070802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V. Highly charged ions for atomic clocks and search for variation of the fine structure constant. Hyperfine Interact. 2015, 236, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothwell, T.; Kennedy, C.J.; Aeppli, A.; Kedar, D.; Robinson, J.M.; Oelker, E.; Staron, A.; Ye, J. Resolving the gravitational redshift across a millimetre-scale atomic sample. Nature 2022, 602, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitaki, A.; Huang, J.; Van Tilburg, K. Searching for dilaton dark matter with atomic clocks. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudin, V.I.; Taichenachev, A.V.; Derevianko, A. Magnetic-Dipole Transitions in Highly Charged Ions as a Basis of Ultraprecise Optical Clocks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 233003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dailey, C.; Bradley, C.; Jackson Kimball, D.F.; Sulai, I.A.; Pustelny, S.; Wickenbrock, A.; Derevianko, A. Quantum sensor networks as exotic field telescopes for multi-messenger astronomy. Nat. Astron. 2020, 5, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludlow, A.D.; Boyd, M.M.; Ye, J.; Peik, E.; Schmidt, P.O. Optical atomic clocks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 637–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, L.; Yao, Z.; Cladé, P.; Guellati-Khélifa, S. Determination of the fine-structure constant with an accuracy of 81 parts per trillion. Nature 2020, 588, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godun, R.M.; Nisbet-Jones, P.B.R.; Jones, J.M.; King, S.A.; Johnson, L.A.M.; Margolis, H.S.; Szymaniec, K.; Lea, S.N.; Bongs, K.; Gill, P. Frequency Ratio of Two Optical Clock Transitions in 171Yb+ and Constraints on the Time Variation of Fundamental Constants. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 210801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, C.C.; Chen, Z.B.; Sun, Y.; Shen, X.Z.; Hu, F.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.L. Hyperfine structure and 2s-2p transition in C-like Fe, Co and Ni. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2019, 230, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunefeld, S.J.; Roberts, B.M.; Ginges, J.S.M. Correlation trends in the hyperfine structure for Rb, Cs, and Fr, and high-accuracy predictions for hyperfine constants. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 042506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronova, M.S.; Budker, D.; DeMille, D.; Kimball, D.F.J.; Derevianko, A.; Clark, C.W. Search for new physics with atoms and molecules. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2018, 90, 025008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, F.; Suzuki, C.; Murakami, I.; Kato, D.; Tamura, N.; Nakamura, N. Z-dependent crossing of excited-state energy levels in highly charged galliumlike lanthanide atomic ions. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 105, 032802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenband, T.; Hume, D.B.; Schmidt, P.O.; Chou, C.W.; Brusch, A.; Lorini, L.; Oskay, W.H.; Drullinger, R.E.; Fortier, T.M.; Stalnaker, J.E.; et al. Frequency Ratio of Al+ and Hg+ Single-Ion Optical Clocks; Metrology at the 17th Decimal Place. Science 2008, 319, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, S.M.; Chen, J.S.; Hankin, A.M.; Clements, E.R.; Chou, C.w.; Wineland, D.J.; Hume, D.B.; Leibrandt, D.R. 27Al+ quantum-logic clock with a systematic uncertainty below 10-18. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 033201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Hume, D.; Koelemeij, J.; Wineland, D.; Rosenband, T. Frequency Comparison of Two High-Accuracy Al+ Optical Clocks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 070802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.W.; Hume, D.B.; Rosenband, T.; Wineland, D.J. Optical Clocks and Relativity. Science 2010, 329, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.M.; Sahoo, B.K.; Suo, B.B. Highly charged ion (HCI) clocks: Frontier candidates for testing variation of fine-structure constant. Front. Phys. 2023, 11, 1104848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.m.; Sahoo, B.K. Energy-level-crossing study of forbidden transitions in highly charged ions with (n=4,5)d6 and (n=4,5)d8 configurations for making optical clocks. Phys. Rev. A 2024, 109, 023106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.S.; Bonczyk, P.A.; Javan, A. Observation of Hyperfine Level Crossing in Stimulated Emission. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1969, 22, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloy, K.; Dzuba, V.A.; Brewer, S.M. Quadruply Ionized Barium as a Candidate for a High-Accuracy Optical Clock. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 173002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekker, H.; Borschevsky, A.; Harman, Z.; Keitel, C.H.; Pfeifer, T.; Schmidt, P.O.; Crespo López-Urrutia, J.R.; Berengut, J.C. Detection of the 5p – 4f orbital crossing and its optical clock transition in Pr9+. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsev, S.G.; Safronova, U.I.; Safronova, M.S.; Schmidt, P.O.; Bondarev, A.I.; Kozlov, M.G.; Tupitsyn, I.I.; Cheung, C. Optical clocks based on the Cf15+ and Cf17+ ions. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 102, 012802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Pan, D.; Chen, S.; Arora, B.; Guan, H.; Gao, K.; Chen, J. Atomic Structure of Nd9+ for Highly Charged Ion Clocks. Atoms 2022, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronova, M.S.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V.; Safronova, U.I.; Porsev, S.G.; Kozlov, M.G. Highly Charged Ions for Atomic Clocks, Quantum Information, and Search for α variation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 030801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzuba, V.A.; Safronova, M.S.; Safronova, U.I.; Flambaum, V.V. Actinide ions for testing the spatial α-variation hypothesis. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 92, 060502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berengut, J.C.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V.; Ong, A. Electron-Hole Transitions in Multiply Charged Ions for Precision Laser Spectroscopy and Searching for Variations in α. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 210802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsev, S.G.; Ludlow, A.D.; Boyd, M.M.; Ye, J. Determination of Sr properties for a high-accuracy optical clock. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 78, 032508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lu, Z.; Liang, X.; He, K.; He, Y.; Ji, X. Optical Frequency Transfer on the Order of 10-19 Fractional Frequency Instability over a 64 m Free-Space Link. Photonics 2024, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.A.; Spieß, L.J.; Micke, P.; Wilzewski, A.; Leopold, T.; Benkler, E.; Lange, R.; Huntemann, N.; Surzhykov, A.; Yerokhin, V.A.; et al. An optical atomic clock based on a highly charged ion. Nature 2022, 611, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Keitel, C.H.; Harman, Z. Ultrastable and ultra-accurate clock transitions in open-shell highly charged ions. Commun. Phys. 2025, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, X.P.; Wen, W.Q.; Lu, Q.F.; Yan, C.L.; Xu, G.Q.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Z.K.; Wang, H.B.; Chen, D.Y.; et al. Spectral calibration for electron beam ion trap and precision measurement of M1 transition wavelength in Ar13+. Acta Phys. Sin. 2022, 71, 033201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronova, M.S.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V.; Safronova, U.I.; Porsev, S.G.; Kozlov, M.G. Atomic properties of Cd-like and Sn-like ions for the development of frequency standards and search for the variation of the fine-structure constant. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 052509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berengut, J.C.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V.; Ong, A. Highly charged ions with E1,M1, and E2 transitions within laser range. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 022517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, M.G.; Safronova, M.S.; Crespo López-Urrutia, J.R.; Schmidt, P.O. Highly charged ions: Optical clocks and applications in fundamental physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2018, 90, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, C.; Shi, T.; Huang, Y.; Gao, K.; Guan, H. Precision measurement of M1 optical clock transition in Ni12+. Phys. Rev. Res. 2024, 6, 013030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, S.; Nakajima, T.; Safronova, M.S.; Safronova, U.I.; Nakamura, N. Visible transitions in Ag-like and Cd-like lanthanide ions. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 062506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.F.; Verdebout, S.; Godefroid, M.; Rynkun, P.; Jönsson, P.; Gaigalas, G. Toward Calculations with Spectroscopic Accuracy: The 2s22p 2P3/2 - 2s2p24P5/2 Excitation Energy in Boron. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1310.2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsev, S.G.; Cheung, C.; Safronova, M.S.; Bekker, H.; Rehbehn, N.H.; López-Urrutia, J.R.C.; Brewer, S.M. Pr10+ as a candidate for a high-accuracy optical clock for tests of fundamental physics. Phys. Rev. A 2024, 110, 042823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, N. Table of nuclear magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole moments. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2005, 90, 75–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Chang, H. Theoretical calculations on Landé g-factors and quadratic Zeeman shift coefficients of nsnp 3P0 clock states in Mg and Cd optical lattice clocks. Chin. Phys. B 2023, 32, 013101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Dong, C.; Ding, X. Precision investigations of clock transitions and metastable lifetimes in highly charged Te-like ions. Phys. Lett. A 2024, 522, 129805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhi, D.E.; Nasr, S.B.; Manai, S.; Jelassi, H. Multiconfiguration Dirac–Hartree–Fock energy levels, weighted oscillator strengths, transitions probabilities, lifetimes, hyperfine interaction constants, Landé g-factors and isotope shifts of O VII. Results Phys. 2021, 23, 103960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, B.B.; Wu, L.; Jiang, J. The Landé g factors of highly charged Sn47+ and Bi80+ ions. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 055406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.P.; Indelicato, P.; Parente, F.; Sampaio, J.M.; Santos, J.P. Ground-state Landé g factors for selected ions along the boron isoelectronic sequence. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 042504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntemann, N.; Sanner, C.; Lipphardt, B.; Tamm, C.; Peik, E. Single-Ion Atomic Clock with 3×10-18 Systematic Uncertainty. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilles, J.; Fritzsche, S.; Spieß, L.J.; Schmidt, P.O.; Surzhykov, A. Quadratic Zeeman and Electric Quadrupole Shifts in Highly Charged Ions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.05687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.T.; Childs, W.J. Ab initio calculation of 4fN6s2 hyperfine structure in neutral rare-earth atoms. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 31, 2775–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flambaum, V.V.; Dzuba, V.A. Search for variation of the fundamental constants in atomic, molecular, and nuclear spectra. Can. J. Phys. 2009, 87, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allehabi, S.O.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V. Atomic clocks highly sensitive to the variation of the fine-structure constant based on Hf II, Hf IV, and W VI ions. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 106, 032807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allehabi, S.O.; Brewer, S.M.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V.; Beloy, K. High-accuracy optical clocks based on group-16-like highly charged ions. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 106, 043101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P.; He, X.; Froese Fischer, C.; Grant, I. The Grasp2K relativistic atomic structure package. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2007, 177, 597–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P.; Gaigalas, G.; Bieroń, J.; Fischer, C.F.; Grant, I. New version: Grasp2K relativistic atomic structure package. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2013, 184, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P.; Gaigalas, G.; Fischer, C.F.; Bieroń, J.; Grant, I.P.; Brage, T.; Ekman, J.; Godefroid, M.; Grumer, J.; Li, J.; et al. GRASP Manual for Users. Atoms 2023, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.F.; Godefroid, M.; Brage, T.; Jönsson, P.; Gaigalas, G. Advanced multiconfiguration methods for complex atoms: I. Energies and wave functions. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2016, 49, 182004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, I.P. Relativistic Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules: Theory and Computation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Ding, X.; Cao, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Xue, Y.; Yu, D.; Dong, C. Energy levels and radiative transition properties of the 2s2p double K-shell vacancy state in He-like ions. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2023, 154, 101602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Xue, Y.; Yu, D.; Dong, C.; Ding, X. The influence of relativistic, Breit interaction, and QED effects on the 1s22p2 and 2s2p3 energy levels of Be-like (4≤Z≤74) isoelectronic sequence. Eur. Phys. J. D 2023, 77, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ion | Ref [32] | Config (Term) | Coulomb | Breit | QED | Final | AMBiT [32] | FSCC [32] | CI + all Order [43] | Expt [32] | Diff (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pr9+ | [3] | [3] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [3] | [3] | 22,848 | −642 | −11 | 22,195 (4) | 21,368 | 22,248 | 21,055 (840) | 22,101.36 (5) | 0.42 | |
| [3] | [3] | 24,993 | −607 | −4 | 24,382 (3) | 23,845 | 24,525 | 23,845 (710) | 24,494.00 (5) | 0.46 | |
| [3] | [3] | 27,644 | −917 | −8 | 26,720 (3) | 26,372 | 27,575 | 26,182 (820) | 27,287.09 (5) | 2.12 | |
| [3] | [3] | 28,753 | −412 | 45 | 28,386 (2) | 27,789 | 28,526 | 28,440 (900) | 28,561.06 (6) | 0.62 | |
| [3] | [3] | 29,897 | −949 | −8 | 28,940 (3) | 28,369 | 29,482 | 28,474 (320) | 29,230.87 (6) | 1.01 | |
| [3] | [3] | 37,467 | −513 | 42 | 36,997 (1) | 35,550 | 35,980 | 35,935 (380) | 36,407.48 (6) | 1.59 | |
| [3] | [1] | 56,305 | −1072 | 36 | 55,269 (9) | 54,852 | 55,737 | 54,404 (820) | 55,662.43 (5) | 0.71 | |
| [3] | [3] | 59,898 | −1254 | 37 | 58,681 (10) | 58,469 | 59,393 | 59,184.84 (5) | 0.86 | ||
| [3] | [3] | 63,547 | −1005 | 45 | 62,587 (17) | 61,325 | 62,380 | 62,182.14 (2) | 0.65 | ||
| [3] | [3] | 65,312 | −1317 | 36 | 64,031 (11) | 62,788 | 64,214 | 63,924.17 (6) | 0.17 | ||
| [3] | [3] | 69,229 | −1048 | 66 | 68,217 (10) | 66,429 | 67,925 | 67,309.3 (1) | 1.36 | ||
| Nd10+ | [3] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| [3] | 978 | 881 | 13 | 1872 (1) | 1062 (1300) | ||||||
| [3] | 3185 | −310 | 2 | 2877 (1) | 3059 (210) | ||||||
| [3] | 3535 | 718 | 13 | 4265 (2) | 4550 (1100) | ||||||
| [3] | 6180 | 427 | 15 | 6621 (1) | 6738 (1320) | ||||||
| [1] | 7276 | 153 | 10 | 7437 (2) |
| Rate | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ion | Upper | Lower | Type | MCDHF | Expt [32] | AMBiT [32] | FSCC [32] | CI + all Order [43] | (nm) | MCDHF | Ref. [43] | MCDHF | Ref. [43] |
| M3 | 2.75 | 2.74 | 2.65 | 2.76 | 2.71 | 451 | 4.32 [−15] | 2.00 [−15] | 2.32 [+14] | 4.99 [+14] | |||
| E2 | 3.02 | 3.04 | 2.96 | 3.04 | 3.00 | 410 | 3.43 [−02] | 8.64 [−01] | 2.3 [+01] | 5.18 [+01] | |||
| M1 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 4573 | 9.12 [−03] | 7.92 [−03] | |||||
| M1 | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 4278 | 1.54 [−01] | 2.12 [−01] | 6.49 [+00] | 4.72 [+00] | |||
| M1 | 3.52 | 3.54 * | 3.45 | 3.54 | 3.53 | 352 | 3.38 [+02] | 3.36 [+02] | 2.94 [−03] | 2.98 [−03] | |||
| M1 | 0.84 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 1483 | 3.34 [+00] | 4.32 [+00] | 2.93 [−01] | 2.27 [−01] | |||
| M1 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.29 | 1483 | 7.04 [−02] | 7.39 [−02] | |||||
| E2 | 4.59 | 4.51 | 4.41 | 4.46 | 4.49 | 270 | 4.91 [+00] | 4.85 [+00] | 7.70 [−02] | 8.38 [−02] | |||
| M1 | 1.84 | 1.77 | 1.76 | 1.70 | 1.78 | 675 | 7.28 [−01] | 7.46 [−01] | |||||
| M1 | 1.27 | 1.13 | 1.14 | 1.04 | 1.14 | 973 | 3.40 [+00] | 4.16 [+00] | |||||
| M1 | 1.07 | 1.22 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 1161 | 3.91 [+00] | 2.20 [+00] | |||||
| M3 | 3.26 | 3.20 * | 3.20 | 3.27 | 380 | 9.63 [−14] | 1.14 [−02] | ||||||
| M1 | 4.21 | 4.17 * | 4.16 | 4.20 | 295 | 8.75 [+01] | |||||||
| M1 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 5347 | 1.41 [−04] | 1.96 [−05] | 7.10 [+03] | 5.09 [+04] | ||||||
| M1 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 3475 | 6.09 [−01] | 7.26 [−01] | 1.64 [+00] | 1.38 [+00] | ||||||
| M1 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 4171 | 2.08 [−02] | 3.95 [−02] | 4.81 [+01] | 2.54 [+01] | ||||||
| E2 | 0.53 | 0.63 | 2345 | 1.13 [−05] | 1.94 [−05] | ||||||||
| M1 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 4243 | 2.02 [−01] | 1.53 [−01] | 4.79 [+00] | 3.92 [+00] | ||||||
| M1 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 1510 | 6.72 [−03] | 5.97 [−03] | ||||||||
| Hyperfine Constant (GHz) | Landé -Factor | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ion | Config | Level | AMBiT [32] | MCDHF | AMBiT [32] | Expt [32] | ||
| Pr9+ | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 3 | 7.631 | 7.771 | 0.075 | 0.857 | 0.853 | 0.875 (2) | ||
| 3 | −2.434 | −1.688 | 0.012 | 0.841 | 0.883 | 0.889 (5) | ||
| 3 | −3.572 | −3.857 | 0.119 | 1.138 | 1.145 | 1.136 (4) | ||
| 3 | −2.967 | −3.203 | −0.256 | 1.500 | 1.500 | 1.487 (3) | ||
| 3 | 5.343 | 5.692 | 0.190 | 1.122 | 1.115 | 1.130 (3) | ||
| 3 | 11.467 | 11.004 | −0.104 | 1.187 | 1.139 | 1.19 (1) | ||
| Nd10+ | 3 | 0.281 | −0.057 | 0.806 | ||||
| 3 | 1.637 | 0.063 | 0.854 | |||||
| 3 | 0.214 | 0.034 | 1.032 | |||||
| 3 | −0.645 | 0.069 | 0.774 | |||||
| 3 | −0.612 | 0.083 | 1.136 | |||||
| 1 | 0.680 | −0.078 | 1.109 | |||||
| Ion | Config | Level | (cm −1) | q | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 22,184.96 | 46,027 | 4.1 | ||
| 3 | 24,376.09 | 46,020 | 3.8 | ||
| 3 | 26,710.83 | 51,206 | 3.8 | ||
| Pr9+ | 3 | 28,380.26 | 36,608 | 2.6 | |
| 3 | 28,931.23 | 51,206 | 3.5 | ||
| 36,995.13 | 42,944 | 2.3 | |||
| 3 | 1871.53 | −79,197 | −84.6 | ||
| 3 | 4265.37 | −60,108 | −28.2 | ||
| 3 | 6621.39 | −76,526 | −23.1 | ||
| Nd10+ | 1 | 7437.39 | −43,269 | −11.6 | |
| 3 | 9011.82 | −27,591 | −6.1 |
| Energy (cm −1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| DF | 27,672.04 | 36,470.81 | 21,048.52 | 23,645.63 | 25,955.64 | 28,098.59 |
| AS1 | 28,346.58 | 36,989.53 | 21,895.37 | 24,144.97 | 26,437.06 | 28,669.28 |
| AS2 | 28,342.42 | 36,950.90 | 21,943.95 | 24,181.02 | 26,482.04 | 28,704.41 |
| AS3 | 28,354.15 | 36,985.37 | 22,117.35 | 24,318.77 | 26,646.55 | 28,872.52 |
| AS4 | 28,359.17 | 36,980.70 | 22,145.11 | 24,340.75 | 26,673.04 | 28,894.80 |
| AS5 | 28,380.26 | 36,995.13 | 22,184.96 | 24,374.09 | 26,710.83 | 28,931.23 |
| AS6 | 28,385.66 | 36,996.78 | 22,195.03 | 24,381.87 | 26,719.68 | 28,939.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Dong, C.; Ding, X. Multi-Configuration Dirac–Hartree–Fock Calculations of Pr9+ and Nd10+: Configuration Resolution and Probing Fine-Structure Constant Variation. Atoms 2025, 13, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13060054
Zhang S, Wu C, Dong C, Ding X. Multi-Configuration Dirac–Hartree–Fock Calculations of Pr9+ and Nd10+: Configuration Resolution and Probing Fine-Structure Constant Variation. Atoms. 2025; 13(6):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13060054
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Songya, Cunqiang Wu, Chenzhong Dong, and Xiaobin Ding. 2025. "Multi-Configuration Dirac–Hartree–Fock Calculations of Pr9+ and Nd10+: Configuration Resolution and Probing Fine-Structure Constant Variation" Atoms 13, no. 6: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13060054
APA StyleZhang, S., Wu, C., Dong, C., & Ding, X. (2025). Multi-Configuration Dirac–Hartree–Fock Calculations of Pr9+ and Nd10+: Configuration Resolution and Probing Fine-Structure Constant Variation. Atoms, 13(6), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13060054








