Abstract
In this manuscript, we present our calculations of detailed electron-impact single ionization cross-sections for tungsten ions, spanning charge states W− W. The level-to-level distorted-wave method implemented in the flexible atomic code (FAC) was used for calculation. Comparison between the present level-to-level distorted wave treatment and previous configuration-averaged calculations has been performed for the W ion, and we explore the possible reason for the difference observed between two calculations. We demonstrate the importance of radiative damping on the total electron-impact ionization cross-section for the W ion. Present calculations provide missing cross-sections for W− W. The data obtained are expected to be useful for modeling plasmas for fusion applications, especially for the ITER community.
PACS:
34.50.Fa; 34.80.Dp; 32.80.Aa
1. Introduction
Tungsten is used as the plasma facing divertor plates because of its favorable temperature and material properties [1,2]. Since the divertor is a plasma-facing component, tungsten will be sputtered into the plasma and become an impurity. The presence of tungsten ions in the plasma provides an important source of radiative loss, and thus, accurate data on the atomic structure and rates for different plasma excitation and decay processes are essential for modeling fusion plasmas. To understand its behavior, various reliable atomic data are required for detailed collisional–radiative (CR) modeling. Spectroscopic data in tungsten ions have been studied using a number of different theoretical and experimental methods [3,4,5,6]. Therefore, to properly understand the effect of tungsten as a plasma impurity on plasma performance, a detailed understanding of atomic processes and the atomic structure of tungsten in all charged states is definitely required. In plasma fusion, electron-impact single ionization (EISI) is an essential atomic collision process, so reliable data are essential for spectral modeling and analysis.
Experimentally, for EISI data for tungsten, the cross-beams technique has been used in W ions in charge states [7]. Single and double electron-impact ionization (EII) cross-sections for W− W [8], W [9] and W [10] have been measured employing the electron–ion crossed-beams method. Theoretically, various simulation codes generally adopted the semi-empirical formulas, such as Lotz expression [7]. In 2005, Loch et al. [11] calculated the electron collision ionization cross-sections of tungsten ions using a configuration-average distorted wave (CADW) method. To check the accuracy, Loch et al. assessed the influence of the radiative damping (RD) effect and compared their CADW calculated excitation–autoionization cross-section with that obtained using the level-to-level distorted wave (LLDW) method. They found that RD will considerably reduce the contribution of excitation–autoionization. The agreement between LLDW and CADW is within 15% for electron energies larger than 5 keV, while the discrepancies are larger in the low energy region and cause some channels to be closed in the CADW approximation. W [12], W and W [13] have been calculated by Jin ey al. using two different theory methods, i.e., the subconfiguration averaged distorted-wave (SCADW) method and the more involved LLDW method. Zhang and Kwon reported their theoretical calculation for W by using the LLDW method [14]. In their calculation for W and W by Zhang et al. [15], they found that the present calculated results are larger than the experimental measurement when all channels’ contributions are included, especially at the peak position. They also found that some important excitation autoionization (EA) channels are not included into previous theoretical calculation [16]. Theoretical and experimental studies on the W were subsequently reported by Jonauskas et al. [17]; they found that the metastable states and contributed greatly to the total cross-section. Jonauskas et al. reported their calculated EII data for W [18] and W [19]. The EII cross-section for the W atom and W ions have been calculated in the distorted wave approximation [20]. Chen et al. performed an LLDW approximation calculation for W with special attention to the contributions from metastable states [21]. Modeling must to be able to provide accurate data to help in diagnostic and control system design. Due to the importance of EISI data for tungsten, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) hosted two meetings on recommended data for tungsten ions in 2021. Participants agreed that it is important to improve the accuracy of atomic data for tungsten and its ions [22].
Given this scenario, there is a critical need for accurate EISI cross-section data. We calculated the EISI cross-sections for W−W ions. The main aim is to benchmark the theoretical work of Loch et al. [11] and provide new EISI data to the database.
2. Methods
Based on previous research, we can divide the EISI process into DI and EA processes [23]. So, the total cross-section for electron-impact single ionization from level i to j can be expressed as the sum of the direct ionization (DI) cross-section and excitation–auto-ionization (EA) cross-sections,
here, is the incident electron energy, is the direct ionization cross-section, is the electron-impact excitation cross-section to the intermediate level k of the initial ion, and is the autoionization branching ratio from level k to the final level j, as determined by equation,
where is the radiative decay rate of ion from k to m while is the autoionization rate from k of to any level n of .
The DI cross-section at the incident electron energy is determined by the following equation [24],
where and are the kinetic momentum of the incident electron and the statistical weight of the initial state, respectively. is the collision strength.
The EA cross-section at the incident electron energy, , can be expressed as [24],
here, is the collision strength.
3. Results
3.1. W
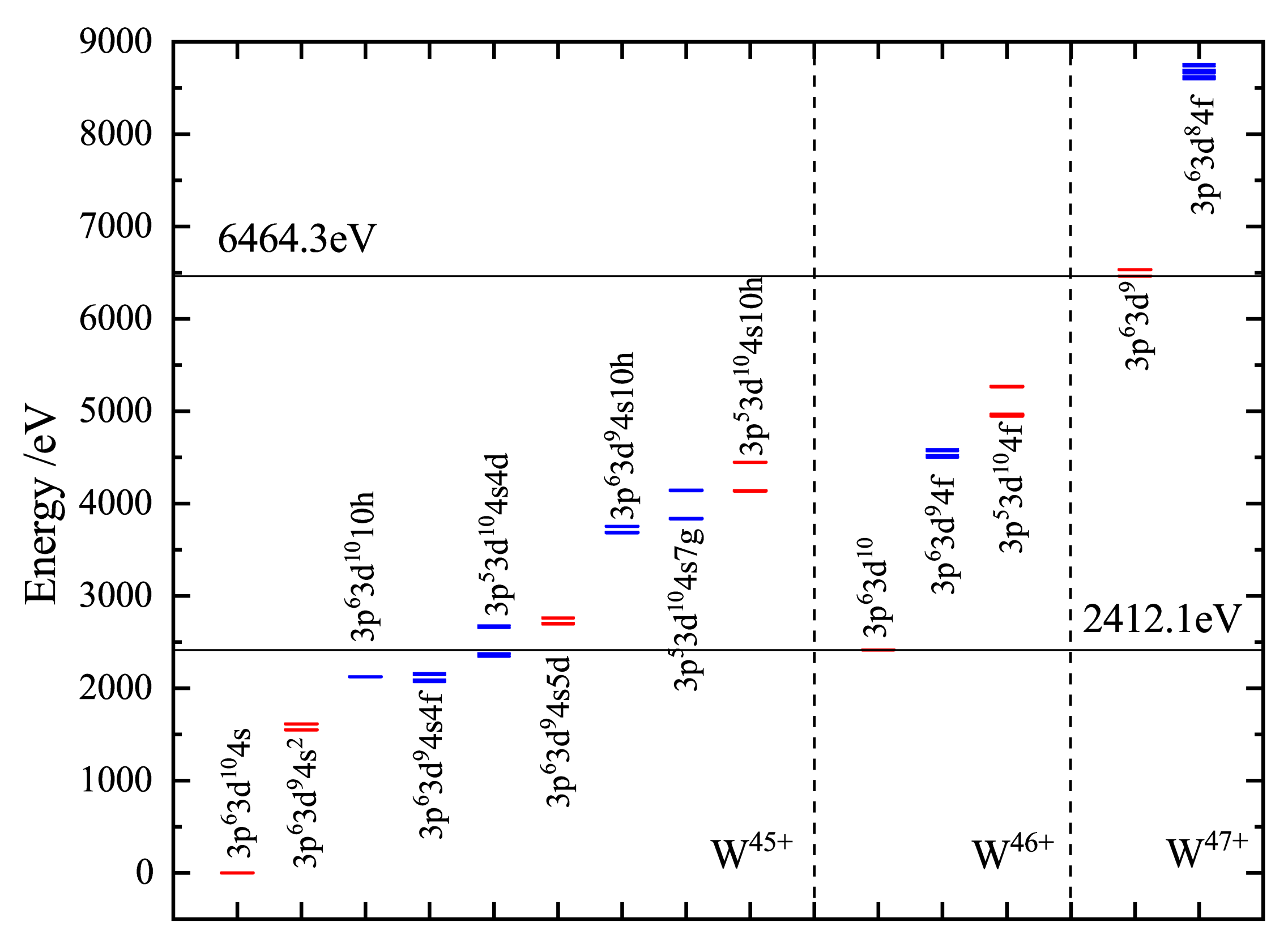
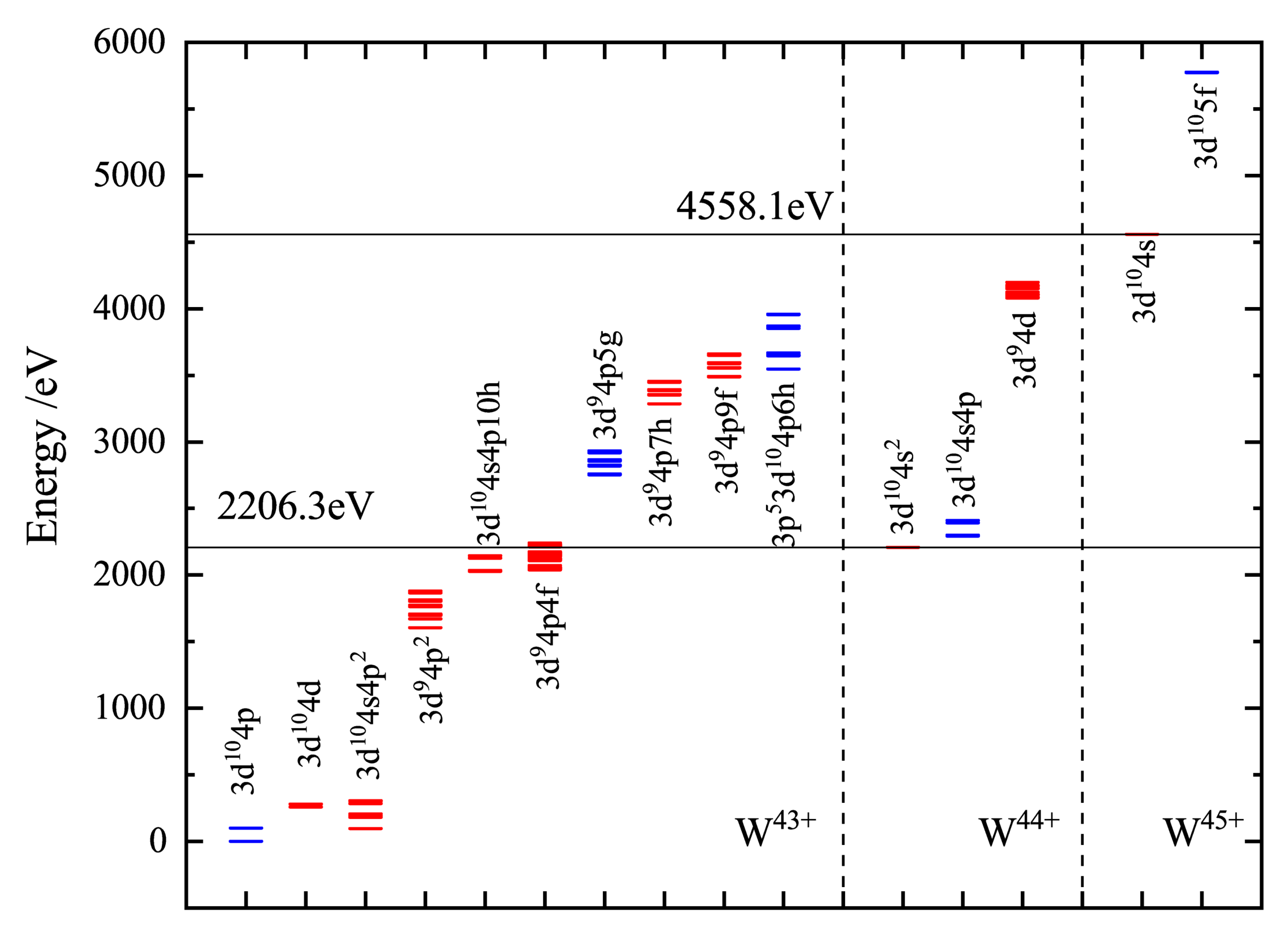
Among the tungsten ions spanning charge states W−W, W is especially interested by the fusion research community because it has a closed shell with one active 4s electron (ground state of W is ). Figure 1 shows the level energies of the lowest energy configurations and the double ionization threshold of the W ion.
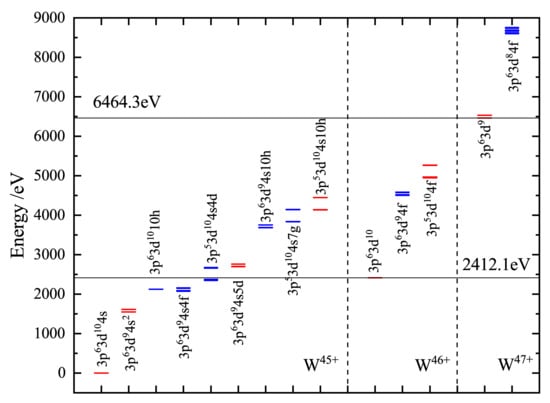
Figure 1.
Energy levels of the major configurations of W, W, and W ions that we calculated relevant to this study. Even configurations are shown in red; odd configurations are shown in blue. Horizontal lines: the thresholds for single and double ionization of W.
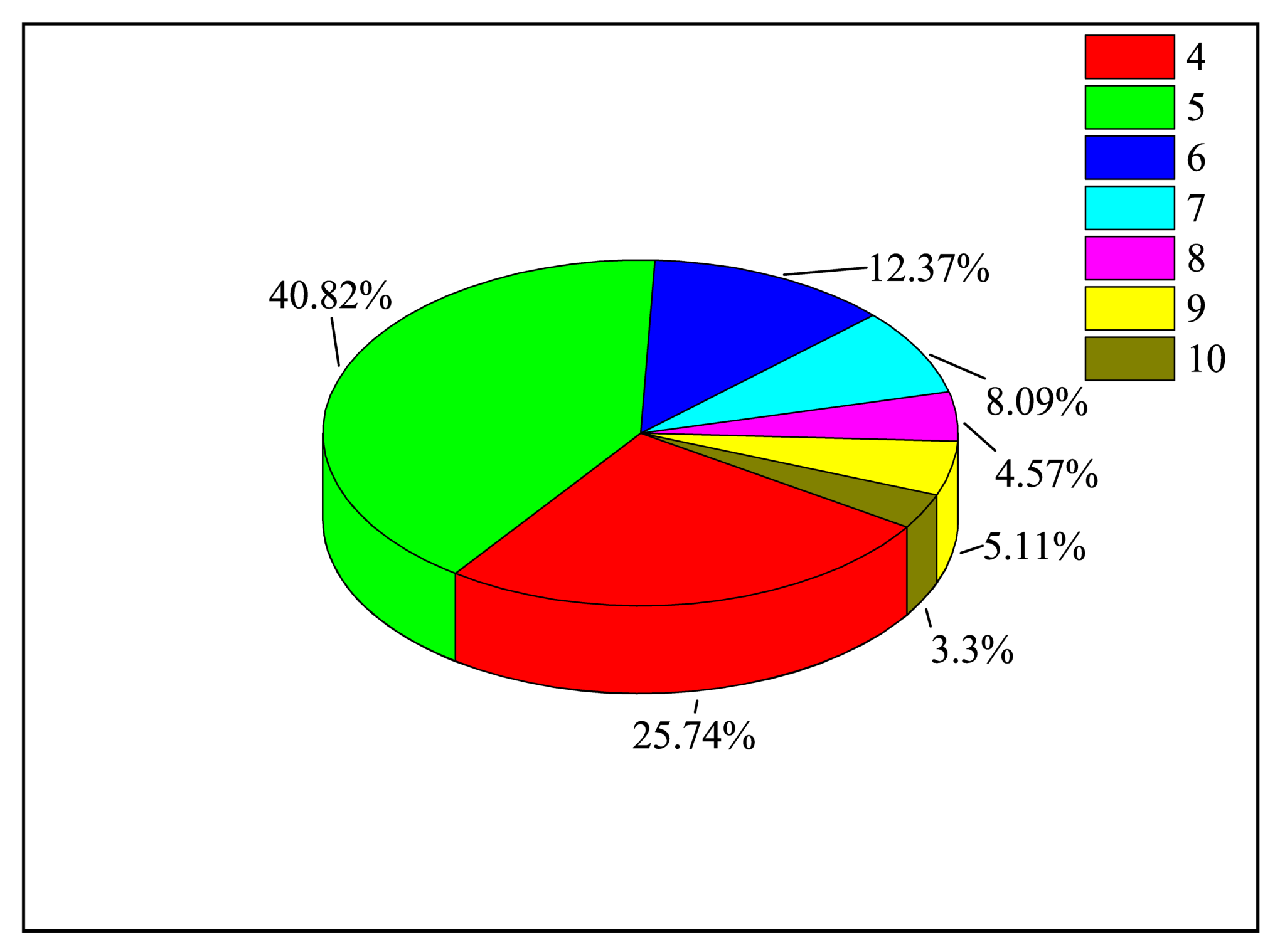
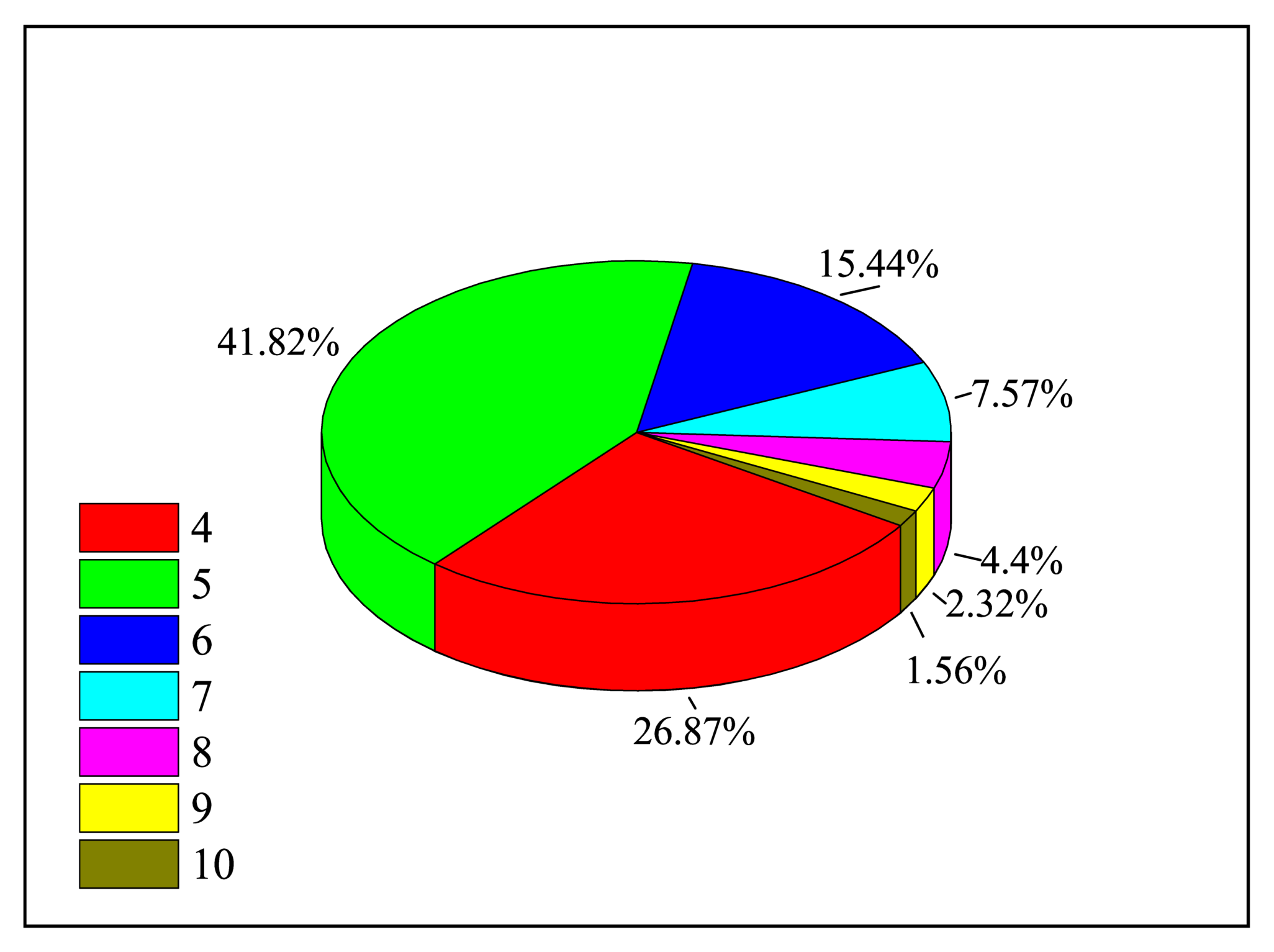
Our analysis of the DI channels includes ionization from the 4s, 3d and 3p shells of the ground configuration levels. When it comes to EA channels, the convergence of the ionization cross-sections must be considered in the calculation. So, we calculated the proportion of (n = 4 − 10) levels in the total cross-section during EA and presented in Figure 2. We can see in Figure 2 that contributes up to 40.82%, and the proportion of the is 3.3%, so we ignored the contributions of higher . The EA cross-sections are investigated for the excited configurations,
here, n ≤ 10 and l ≤ 6. These excitation channels can undergo autoionization (AI) or radiative decay (RD) via:
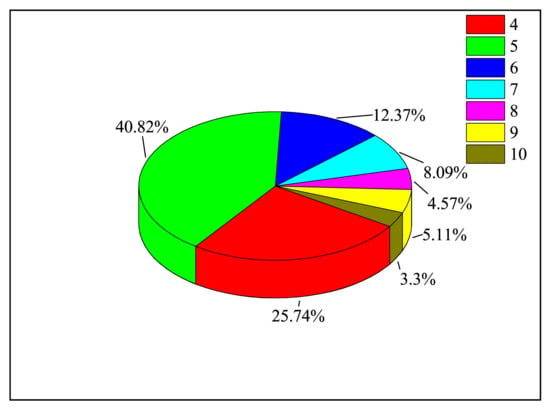
Figure 2.
The proportions of nl (n = 4 − 10) energy levels to the total cross-section in EA processes of the ground state W.
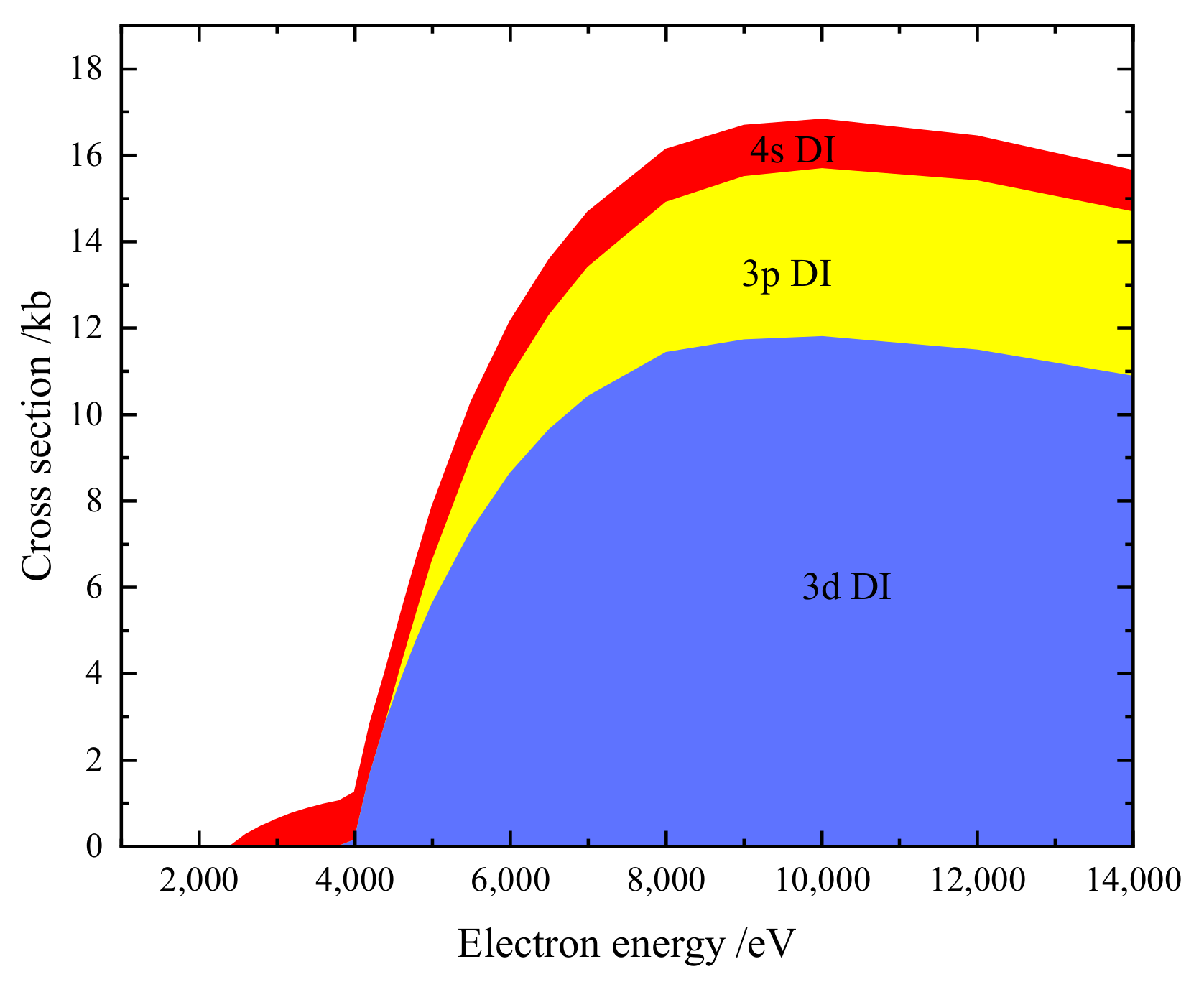
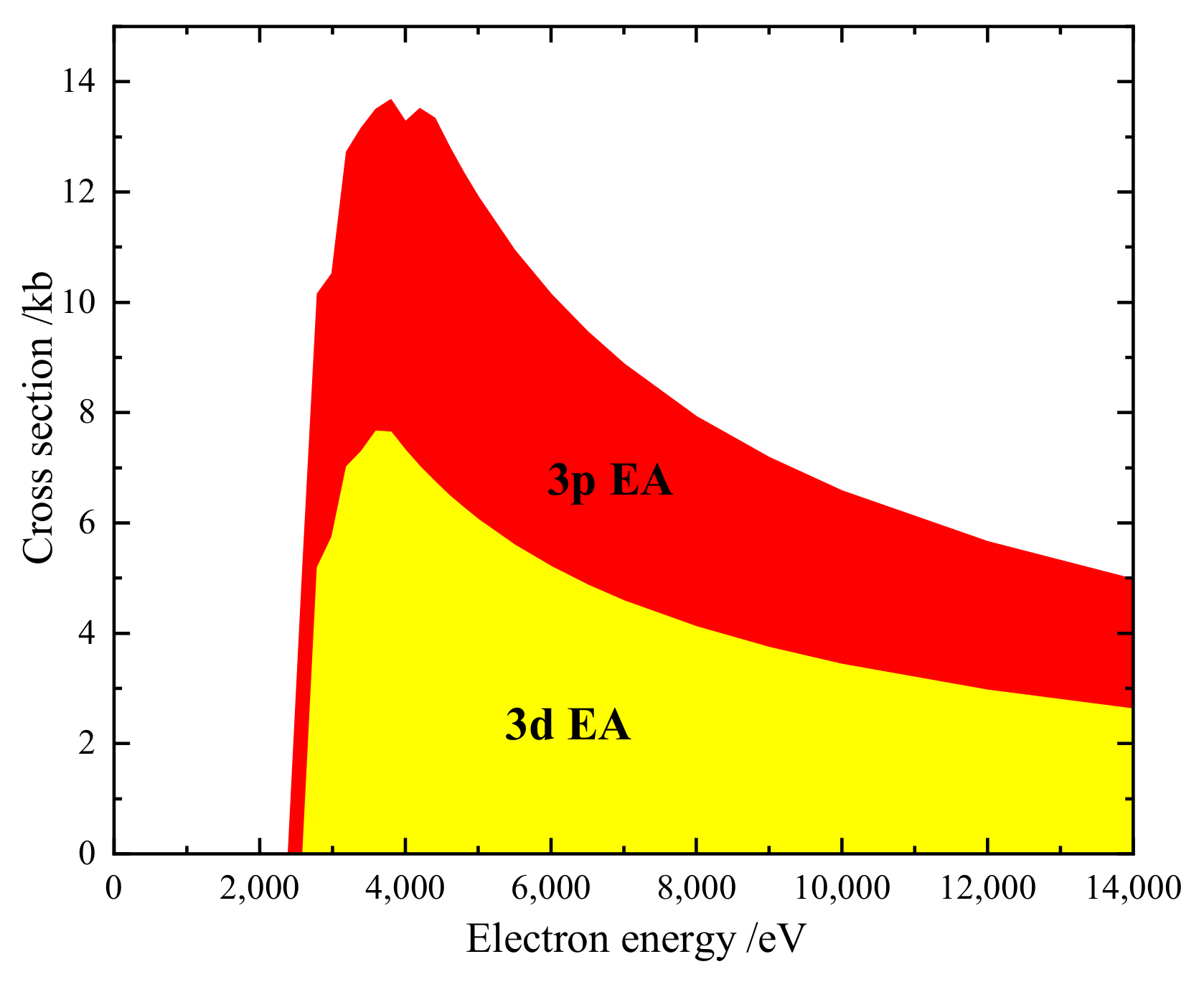
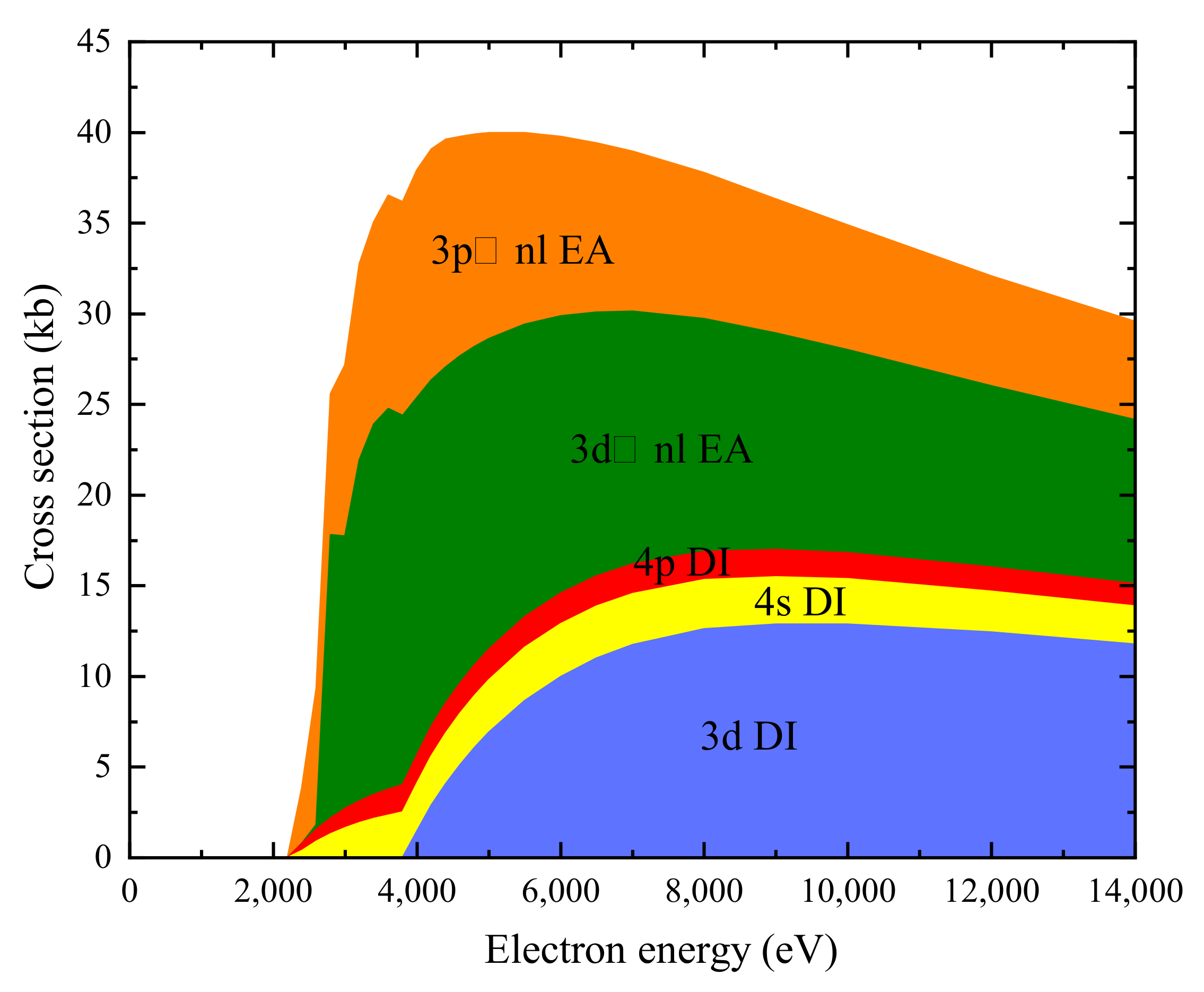
We have separately studied the contribution from DI and EA processes. Figure 3 shows our calculated DI cross-section of W. The and DI cross-section is dominant when the electron energy is above 4 keV. Figure 4 shows our calculated EA cross-section for W. All the levels of the and included in the EA calculation lie below the double ionization limit. According to Figure 1, the contribution of the and subshell should be taken into account.
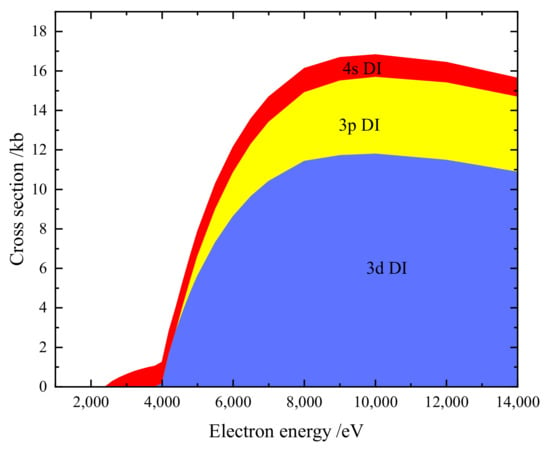
Figure 3.
Accumulated DI cross-sections of ground state W. The shadow areas show contributions from different subshells (1.0 kb = 10 cm).
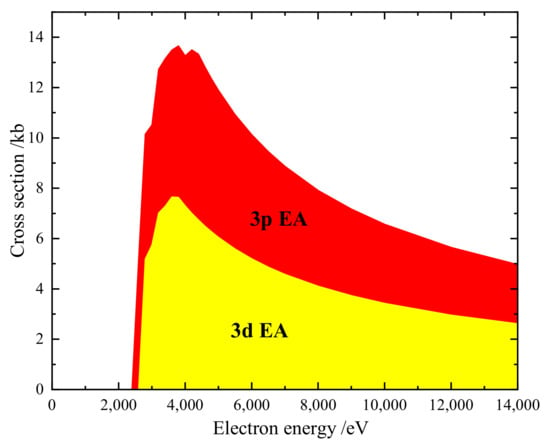
Figure 4.
Accumulated EA cross-sections of ground state W. The shadow areas show contributions from different subshells (1.0 kb = 10 cm).
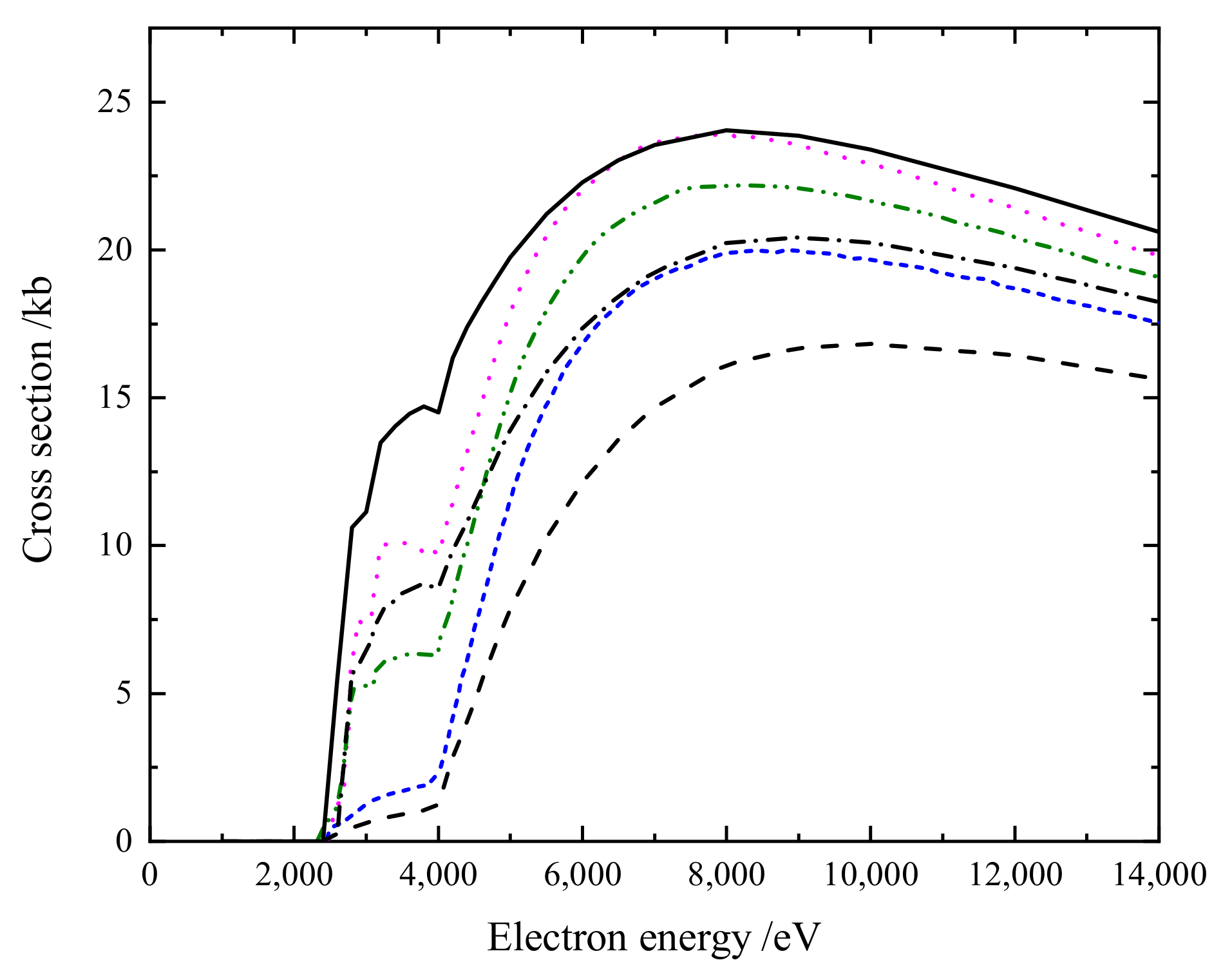
The only calculation available for W was performed by Loch et al. [11], who used a CADW distorted-wave method as well as a hybrid CADW DI + LLDW EA to obtain the total EISI cross-section. In Figure 5, we have plotted the calculation of Loch et al. along with our total LLDW calculated EISI cross-section. The shape of all three curves matches well from low electron energy down to the threshold; however, a large discrepancy in magnitude can be seen between our results and those of Loch et al. The reason behind these discrepancy could be that the DI cross-section in the two sets of data of Loch et al. were obtained using the semi-relativistic CADW method, while the present calculations were all performed within the fully relativistic LLDW approximation.
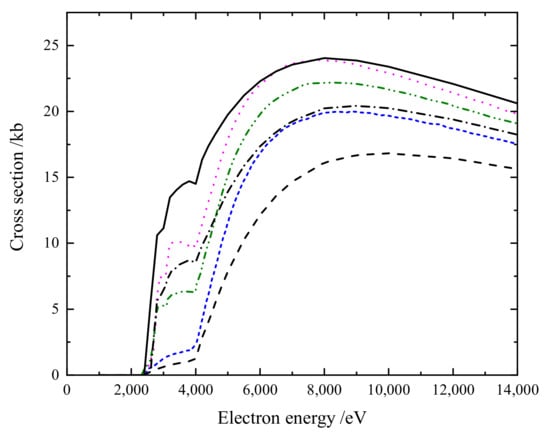
Figure 5.
The total electron-impact single ionization cross-section for W. The color curves are the calculated results of Loch et al. [11]. Blue dashed curve: CADW calculations for direct ionization. Green dot–dashed curve: CADW calculations for direct and indirect ionization with full branching. Magenta dot curve: CADW calculations for direct ionization and LLDW calculations for indirect ionization with full branching. Black dashed curve: LLDW calculations for direct ionization. Black dot–dashed curve: the total cross-section which contains 3d→ excitation cross-sections with full branching. Black solid curve: the total cross-section which contains 3d→ and 3p→ excitation cross-sections with full branching (1.0 kb = 10 cm).
3.2. W
W is another ion stage deserving special attention because it has a closed and shell with one active 4p electron (the ground state of W is ). The presence of a single 4p electron above a filled 4s subshell may lead to large and excitation cross-sections. Although the inclusion of autoionization branching considerably reduces the contribution of excitation–autoionization, the contributions from and are comparable to those of the DI. Figure 6 shows the level energies of the lowest energy configurations and double ionization threshold of the W ion.
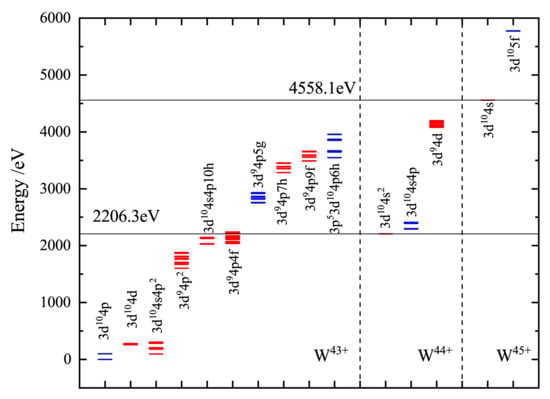
Figure 6.
Energy levels of the major configurations of W, W, and W ions that we calculated relevant to the present study. Even configurations are shown in red, odd configurations are shown in blue. Horizontal lines: the thresholds for single and double ionization of W.
Our analysis of the DI channels includes ionization from the 4p, 4s and 3d shells of the ground configuration levels. The EA cross-sections are investigated for the excited configurations
These excitation channels can undergo AI or RD via
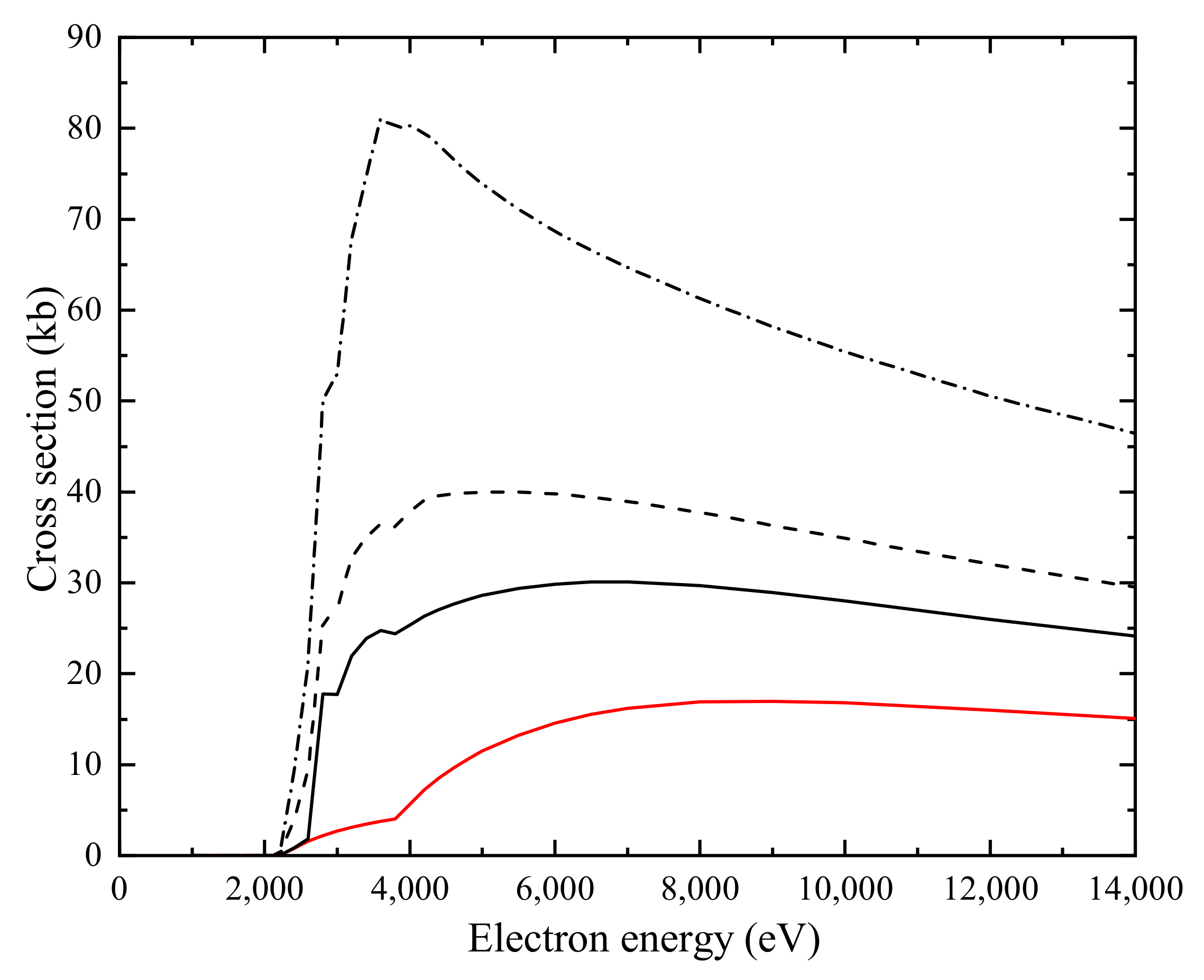
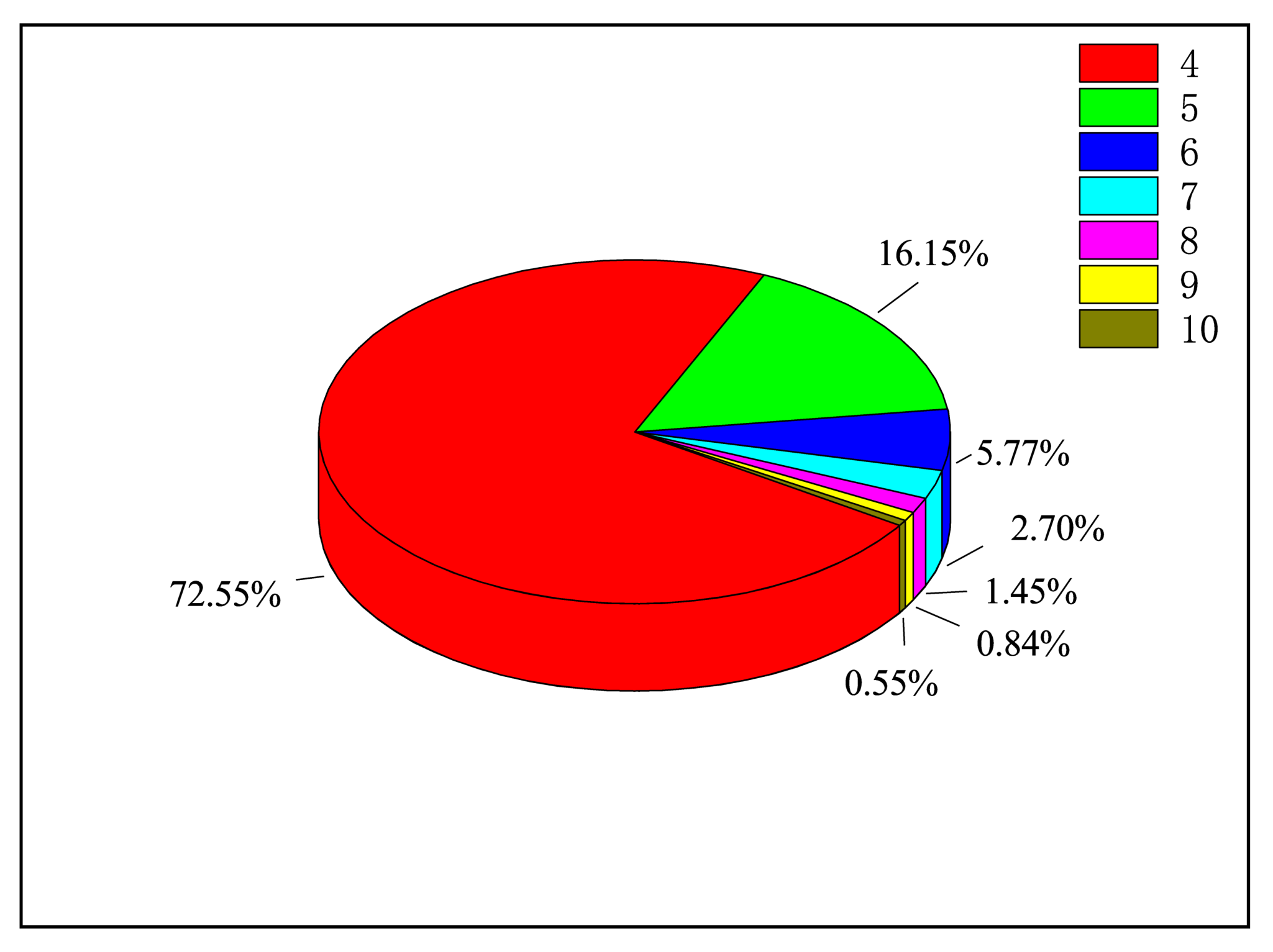
Again, we have separately studied the contribution from DI and EA processes in Figure 7. Apparently, the contributions from EA are comparable to those of the DI. Moreover, a plausible approximation was to set the autoionization branching ratios to 1, i.e., ignoring the effect of radiative damping. We checked the validy of this approximation in Figure 8, where we found that ignoring the effect of radiative damping will significantly overestimate the total EISI cross-section. We also plot the ratio of to the total EA cross-section at the electron energy 4200 eV in Figure 9.
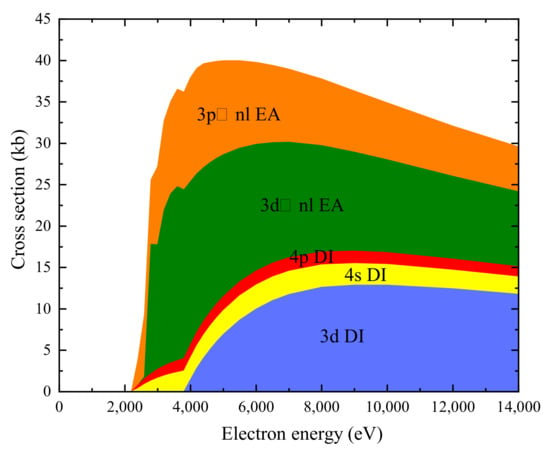
Figure 7.
Accumulated DI and EA cross-sections of ground state W. The shadow areas show contributions from different subshells (1.0 kb = 10 cm).
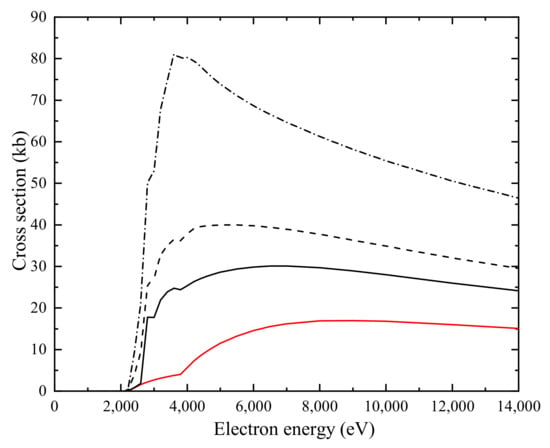
Figure 8.
The total electron-impact single ionization cross-section for W. Red solid curve: LLDW calculations for direct ionization. Black solid curve: the total cross-section which contains 3d→ excitation cross-sections with full branching. Black dashed curve: the total cross-section which contains 3d→ and 3p→ excitation cross-sections with full branching. Black dot–dashed curve: LLDW calculations for direct and indirect ionization with unit branching (1.0 kb = 10 cm).
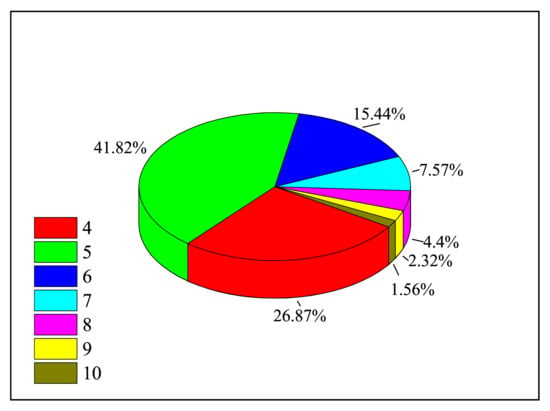
Figure 9.
The proportions of (n = 4 − 10) energy levels to the total cross-section in EA processes of the ground state W.
3.3. W, W−W
From W through to W and W, LLDW calculations were carried out with consideration of the effects of configuration interaction. For these ion stages, the influence of radiative decay may become greater than autoionization, and the branching ratio is then considerably less than 1. This reduces the contribution of excitation–autoionization. In this way, to obtain accurate cross-sections, we calculated the branching radios of each ion stage in Equation (2).
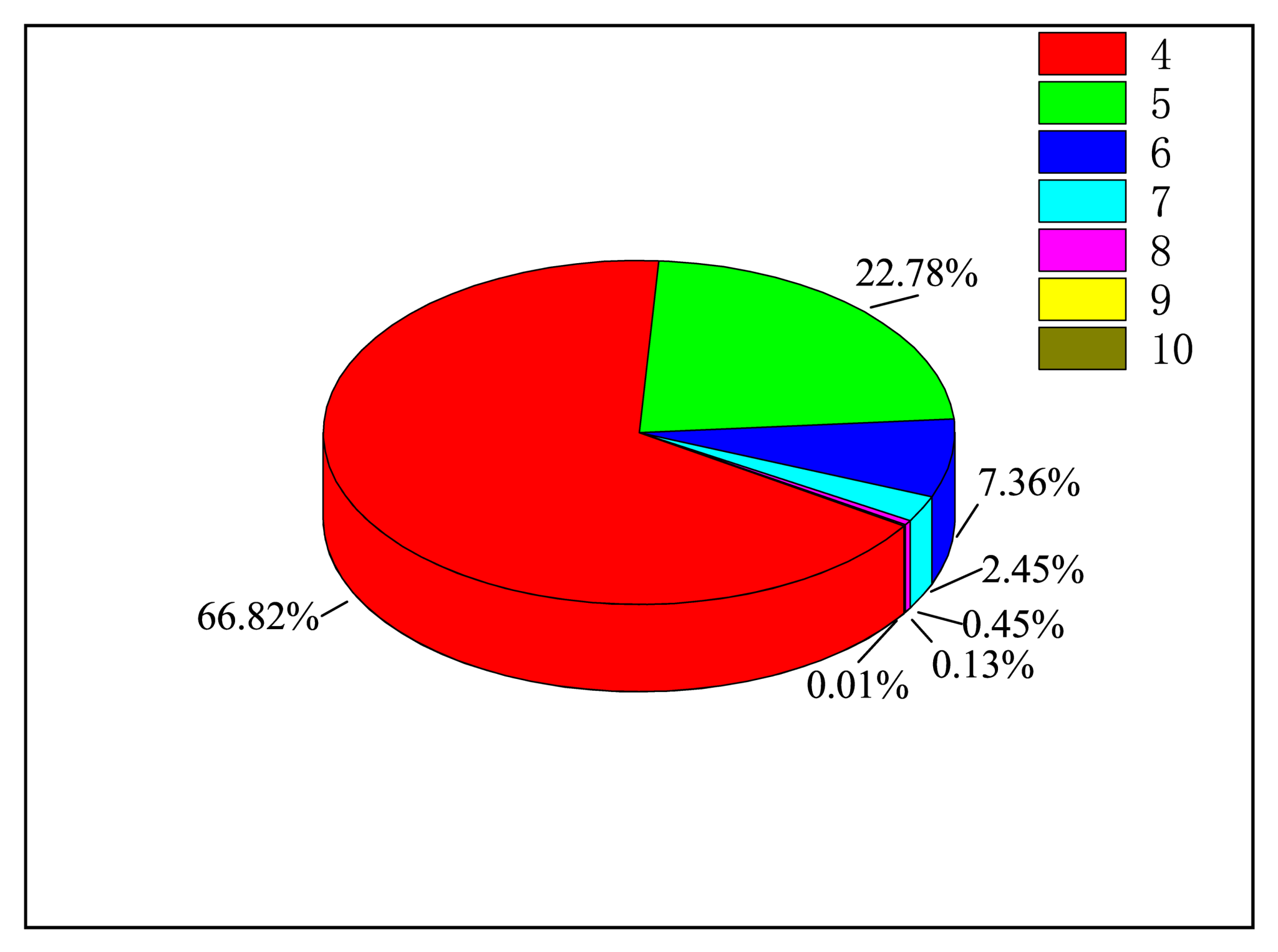
As for the EA cross-section of W−W and W, we give the ratios of of W and W to the total EA cross-section at peak energy as examples. In Figure 10 and Figure 11, we listed the ratios of different of W and W in turn, and we can find that the proportions of n = 10 in the total EA cross-section are both less than 5%. So, contributions from higher n were omitted in this work.
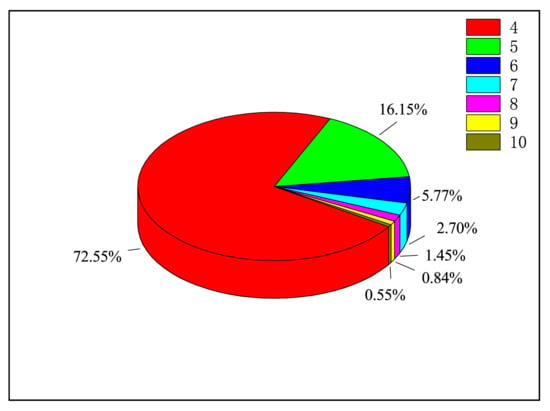
Figure 10.
The proportions of (n = 4 − 10) energy levels to the total cross-section in EA processes of the ground state W.
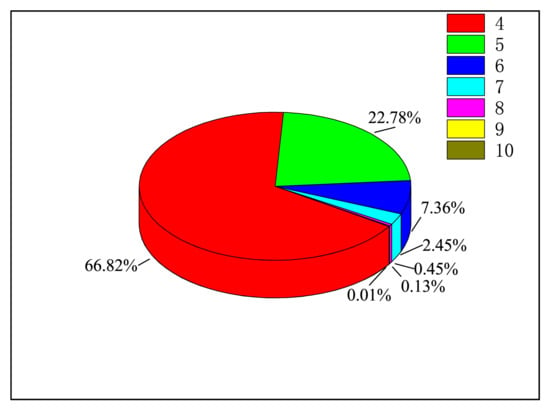
Figure 11.
The proportions of (n = 4 − 10) energy levels to the total cross-section in EA processes of the ground state W.
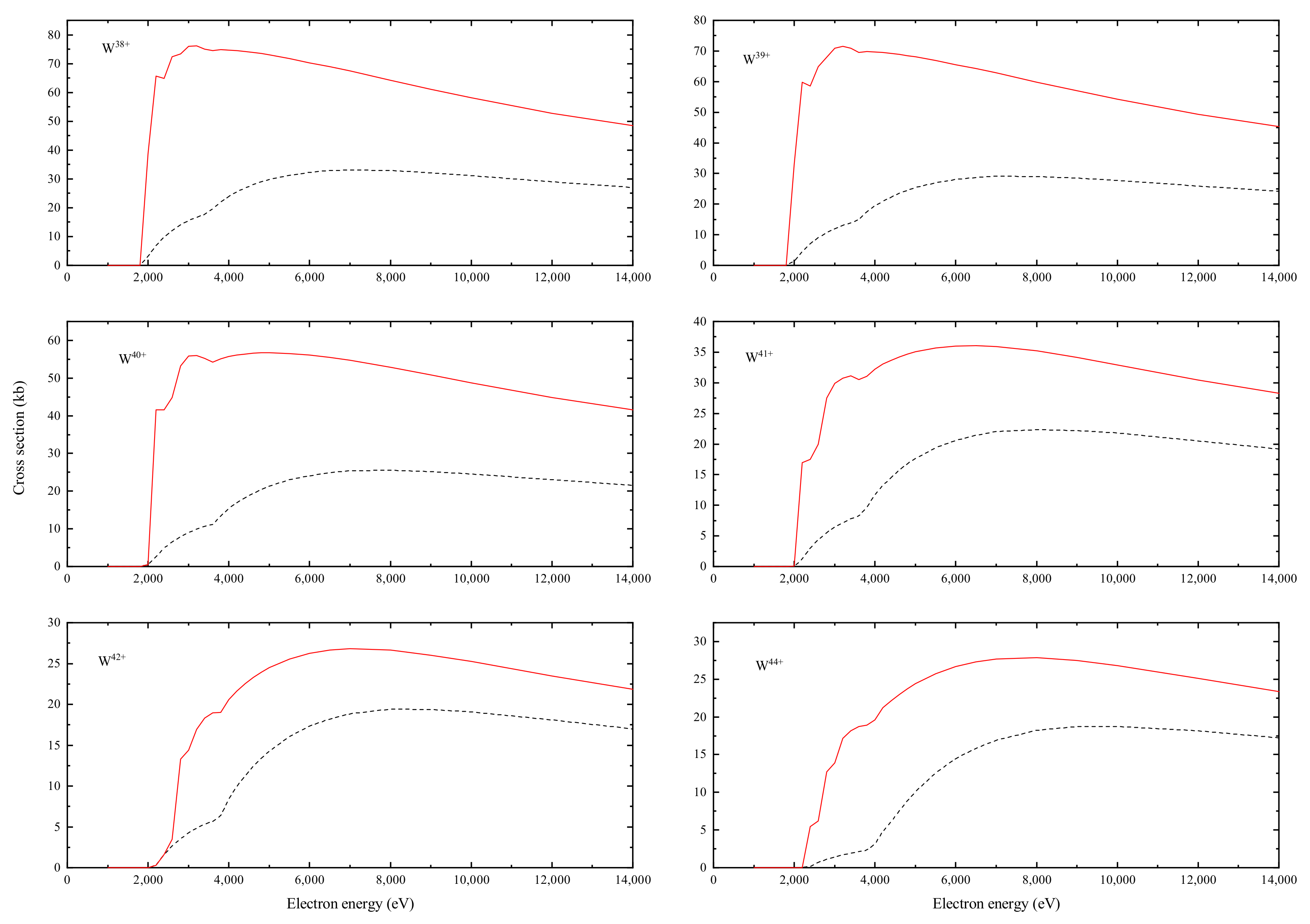
The EISI cross-sections for the ionic stages are presented in Figure 12, which illustrates that the contributions of excitation–autoionization gradually decrease when the ion stages become higher. We list the DI and EA cross-section contributions of W−W by subshells in Table 1. Table 2 lists the ionization potentials of W−W calculated in the present work and some available results from NIST. Our calculated ionization potentials for W ions differ from those calculated by NIST to within 0.2%. More details about the ionization potentials are shown in Table 3. Considering that we are calculating the EISI cross-sections, subshells above the single ionization threshold and below the double ionization threshold are needed. Based on the data of Table 3, we can determine the subshells involved in the excitation–autoionization contribution of the single ionization, and we also list the double ionization thresholds for these ions. Selected threshold excitation cross-sections for these ion stages are listed in Table 4.
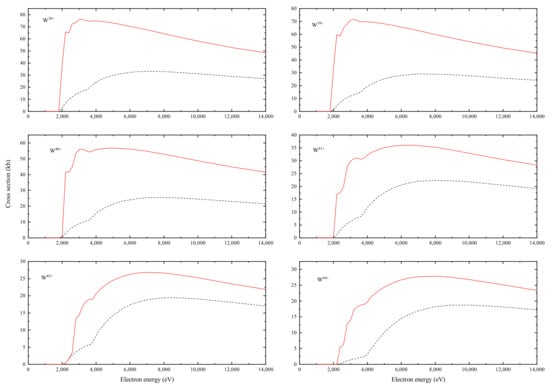
Figure 12.
The total electron-impact single ionization cross-section for W, W−W. Dot curve: cross-sections of direct ionization. Red sold curve: cross-sections of total ionization with full branching (1.0 kb = 10 cm).

Table 1.
Ground-state configurations for W ions and ionization contributions by subshell.

Table 2.
Ionization potentials for W ions.

Table 3.
Ionization potentials for W−W.

Table 4.
Selected threshold excitation cross-sections for W−W (1.0 Mb = 1.0 × 10 cm).
3.4. Fitting Coefficients
We have fitted the calculated total EISI cross-sections for convenience in plasma modeling using the following formula [26]
where (in eV) is the incident electron energy, (in eV) is the ionization potential and are the fitting coefficients. The fitted coefficients are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Fitting coefficients for total EI cross-section.
4. Summary
In this article, we report the first detailed LLDW calculation of the electron-impact single ionization cross-sections for tungsten ions, spanning charge states W−W. In order to obtain the total cross-section accurately, all the ionic stages were calculated considering the interaction of each configuration. Furthermore, the radiative damping was taken into account in the calculations of all autoionizing states, and it reduces the cross-sections depending on the levels considered. When the ion stage is increasing, radiation damping becomes important, and this reduces the excitation autoionization contribution. This was illustrated for W, where the inclusion of radiation damping was seen to reduce the large excitation–autoionization contributions. The present calculations provide missing cross-sections for W−W. The data obtained are expected to be useful for modeling plasmas for fusion applications that contain W impurities. Moreover, we expect that both present LLDW and previous CADW calculations could be benchmarked by the future devices, such as HIAF [27].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L.; investigation, R.B. and J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, R.B.; writing—review and editing, B.L. and R.B.; validation, X.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant No. 11404152 and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities Grant No. lzujbky-2017-94.
Data Availability Statement
Data in numerical form are available upon request. The fitted coefficients are available in the paper.
Acknowledgments
Suggestions for improving the text by Gerry O’Sullivan from University College Dublin are also gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Federici, G. Plasma wall interactions in ITER. Phys. Scr. 2006, T124, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, M.; Brezinsek, S.; Belo, P.; Beurskens, M.N.; Brix, M.; Clever, M.; Coenen, J.W.; Corrigan, C.; Eich, T.; Flanagan, J.; et al. Impact of carbon and tungsten as divertor materials on the scrape-off layer conditions in JET. Nucl. Fusion 2013, 53, 093016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pütterich, T.; Neu, R.; Dux, R.; Whiteford, A.; O’Mullane, M.; Summers, H. and the ASDEX Upgrade Team. Calculation and experimental test of the cooling factor of tungsten. Nucl. Fusion 2010, 50, 025012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pütterich, T.; Fable, E.; Dux, R.; O’Mullane, M.; Neu, R.; Siccinio, M. Determination of the tolerable impurity concentrations in a fusion reactor using a consistent set of cooling factors. Nucl. Fusion 2019, 55, 056013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A. Fusion-Related Ionization and Recombination Data for Tungsten Ions in Low to Moderately High Charge States. Atoms 2015, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pütterich, T.; Neu, R.; Dux, R.; Whiteford, A.D.; O’Mullane, M.G.; ASDEX Upgrade Team. Modelling of measured tungsten spectra from ASDEX Upgrade and predictions for ITER. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2008, 50, 085016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenke, M.; Aichele, K.; Harthiramani, D.; Hofmann, G.; Steidl, M.; Volpel, R.; Salzborn, E. Electron-impact single-ionization of singly and multiply charged tungsten ions. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 1995, 28, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schury, D.; Borovik, A., Jr.; Ebinger, B.; Jin, F.; Spruck, K.; Müller, A.; Schippers, S. Electron-impact single ionisation of Wq+ ions: Experiment and theory for 11 ≤ q ≤ 18. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2020, 53, 015201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, J.; Becker, A.; Spruck, K.; Hellhund, J.; Borovik, A., Jr.; Huber, K.; Schippers, S.; Müller, A. Electron-impact single and double ionization of W17+. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2011, 44, 165202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovik, B.A., Jr.; Ebinger; Schury, D.; Schippers, S.; Müller, A. Electron-impact single ionization of W19+ ions. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 012708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, S.D.; Ludlow, J.A.; Pindzola, M.S.; Whiteford, A.D.; Griffin, D.C. Electron-impact ionization of atomic ions in the W isonuclear sequence. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 052716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Borovik, A., Jr.; Ebinger, B.; Schippers, S. Electron-impact single ionisation of W14+ ions: Subconfiguration-average and level-to-level distorted wave calculations. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2020, 53, 075201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Borovik, A., Jr.; Ebinger, B.; Schippers, S. Hybrid subconfiguration-average and level-to-level distorted-wave treatment of electron-impact single ionisation of W15+ and W16+. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2020, 53, 175201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Kwon, D.H. Theoretical electron-impact ionization of W17+ forming W18+. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2014, 47, 075202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Xie, L.Y.; Jiang, J.; Wu, Z.W.; Dong, C.Z.; Shi, Y.L.; Qu, Y.Z. Electron-impact single ionizaiton for W4+ and W5+. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 053402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindzola, M.S.; Griffin, D.C. Electron-impact ionization of tungsten ions in the configuration-average distorted-wave approximation. Phys. Rev. A 1997, 56, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonauskas, V.; Kynienė, A.; Kučas, S.; Pakalka, S.; Masys, Š.; Prancikevičius, A.; Borovik, A., Jr.; Gharaibeh, M.F.; Schippers, S.; Müller, A. Electron-impact ionization of W5+. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 062701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kynienė, A.; Pakalka, S.; Masys, Š.; Jonauskas, V. Electron-impact ionization of W25+. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2016, 49, 185001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kynienė, A.; Merkelis, G.; Šukys, A.; Masys, Š.; Pakalka, S.; Kisielius, R.; Jonauskas, V. Maxwellian rate coefficients for electron-impact ionization of W26+. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2018, 51, 155202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D.; Murakami, I. Electron Impact Ionization Cross Sections of Tungsten Atoms and Tungsten Ions. Plasma Fusion Res. 2018, 13, 3401026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, B.W.; Chen, X.M. Contribution of the metastable states to electron-impact single ionization for W7+. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2022, 285, 108179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Meeting on the Collisional-Radiative Properties of Tungsten and Hydrogen in Edge Plasma of Fusion Devices, 29 March–1 April 2021, Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://amdis.iaea.org/meetings/tm-tungsten-hydrogen/ (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Badnell, N.R.; Pindzola, M.S. Resonance contributions to the electron-impact ionization of few-electron highly charged ions. Phys. Rev. A 1993, 47, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.F. The flexible atomic code. Can. J. Phys. 2008, 86, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramida, A.; Ralchenko, Y.; Reader, J.; NIST ASD Team. NIST Atomic Spectra Database (Version 5.9); National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2021. Available online: https://physics.nist.gov/asd (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Dipti; Das, T.; Bartschat, K.; Bray, I.; Fursa, D.V.; Zatsarinny, O.; Ballance, C.; Chung, H.K.; Ralchenko, Y. Recommended electron-impact excitation and ionization cross sections for Be I. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2019, 127–128, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Xiao, G.Q.; Xu, H.S.; Zhao, X.H.; Ma, X.W.; He, Y.; Ma, L.Z.; Gao, D.Q.; Meng, J.; Xu, Z.; et al. High Intensity heavy ion Accelerator Facility (HIAF) in China. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2013, 317, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).