A Progress Report on Laser Resonance Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Approach
- No neutralization of the thermalized fusion products is required. The ions can be manipulated and guided with high efficiency by electric fields;
- No further ionization of the ions is required. Only one laser is needed for spectroscopy;
- No radiation detection is required as in fluorescence spectroscopy. The sensitivity does not depend on the solid angle coverage of the detectors;
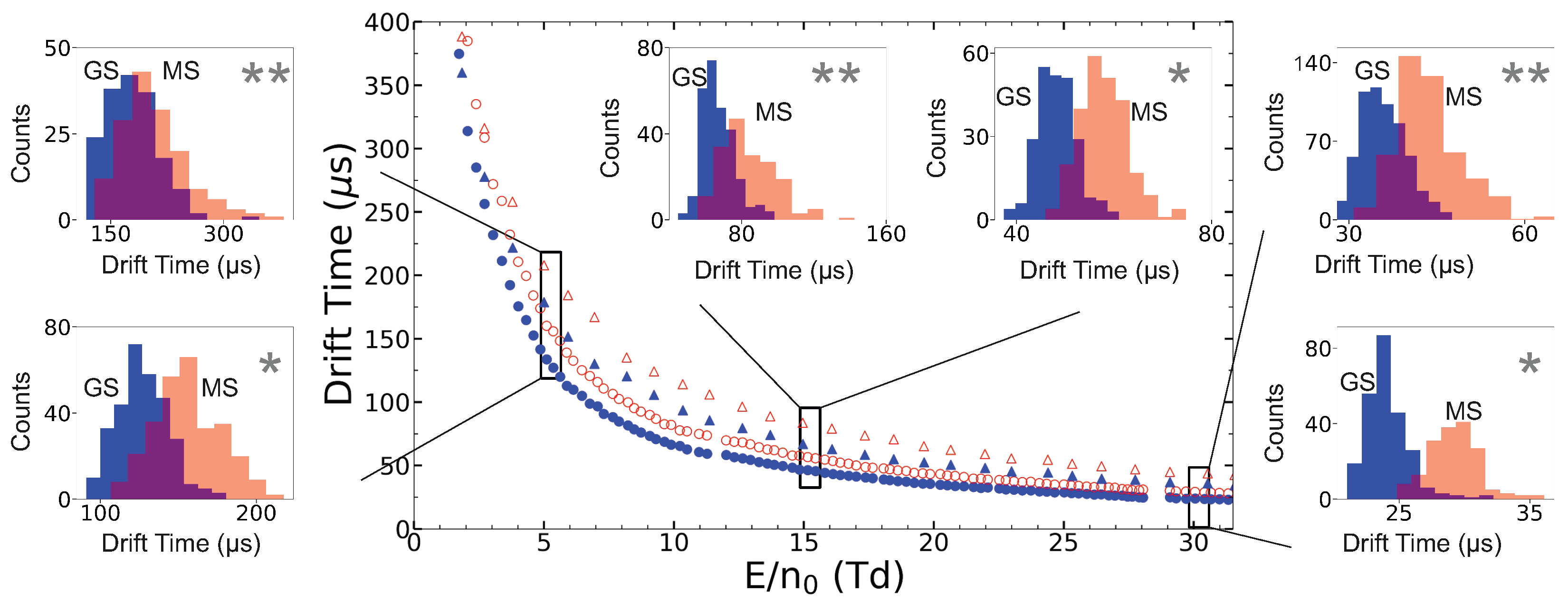
- A mass filter is a useful option at low ion production rates, but is not mandatory to suppress molecular sidebands or even isobars of different electronic configurations, as the drift itself provides the required ion discrimination.
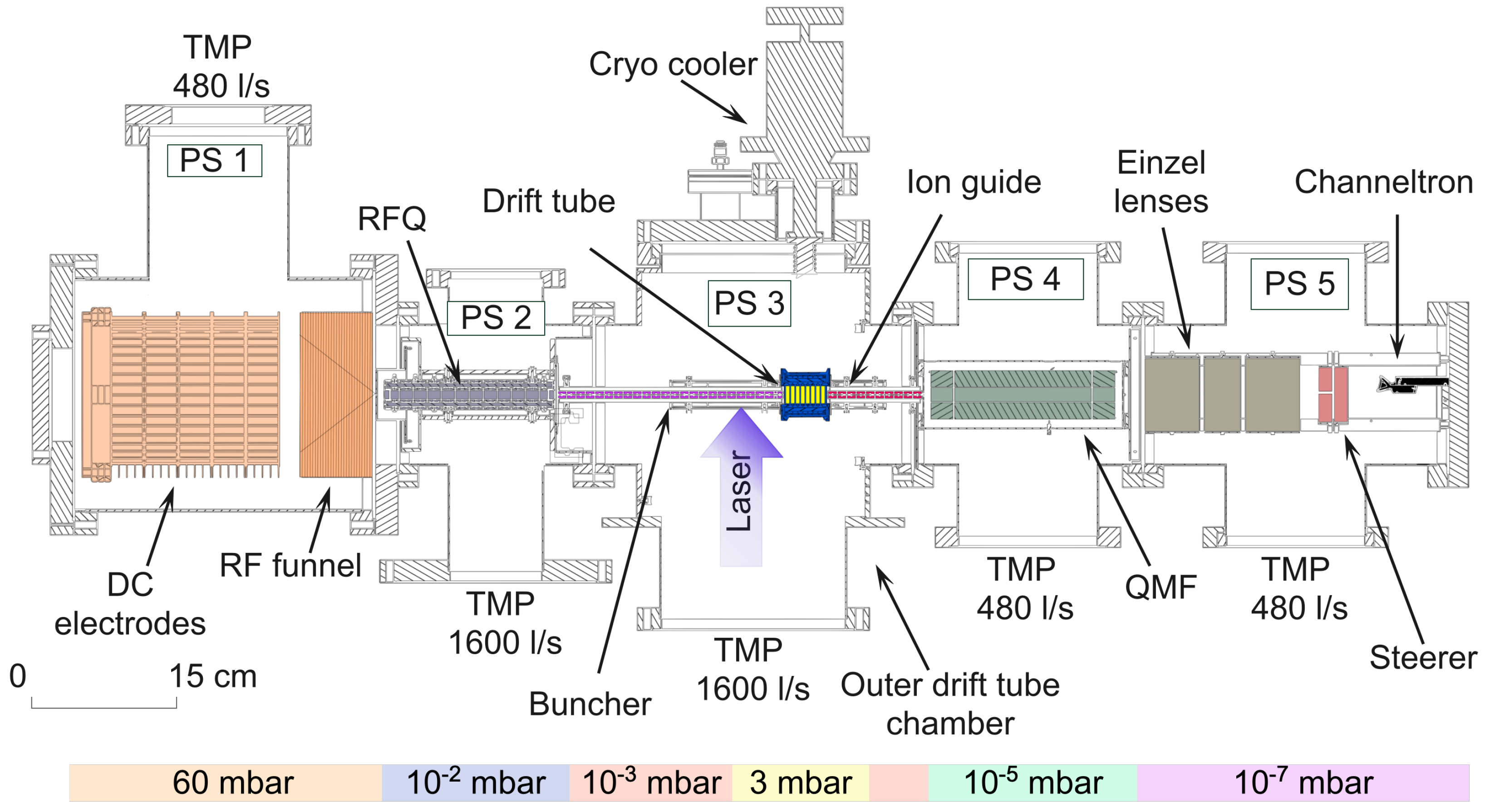
2.1. The LRC Apparatus
2.2. The Laser System
2.3. The Drift Tube Outer Chamber
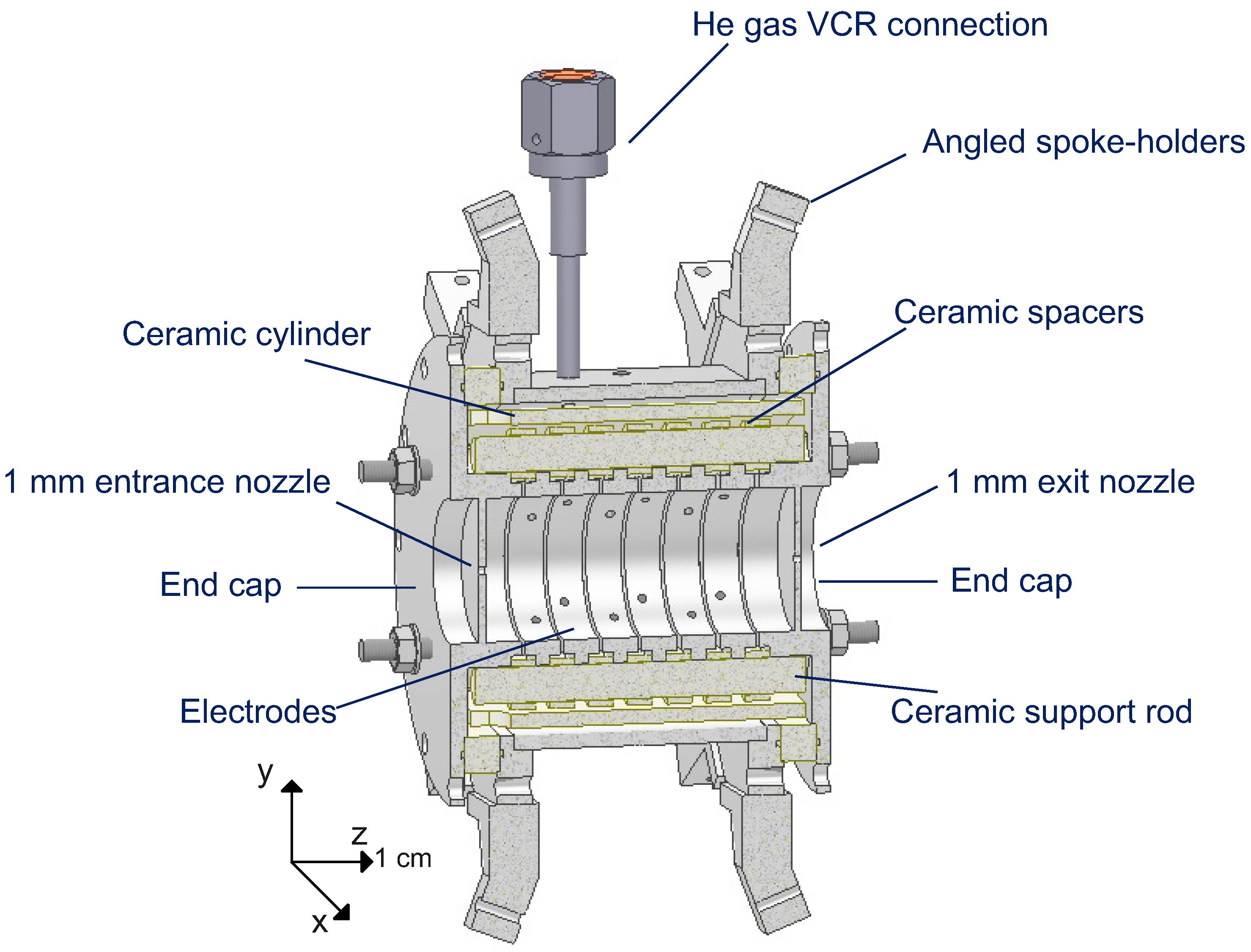
2.4. The Drift Tube Inner Chamber
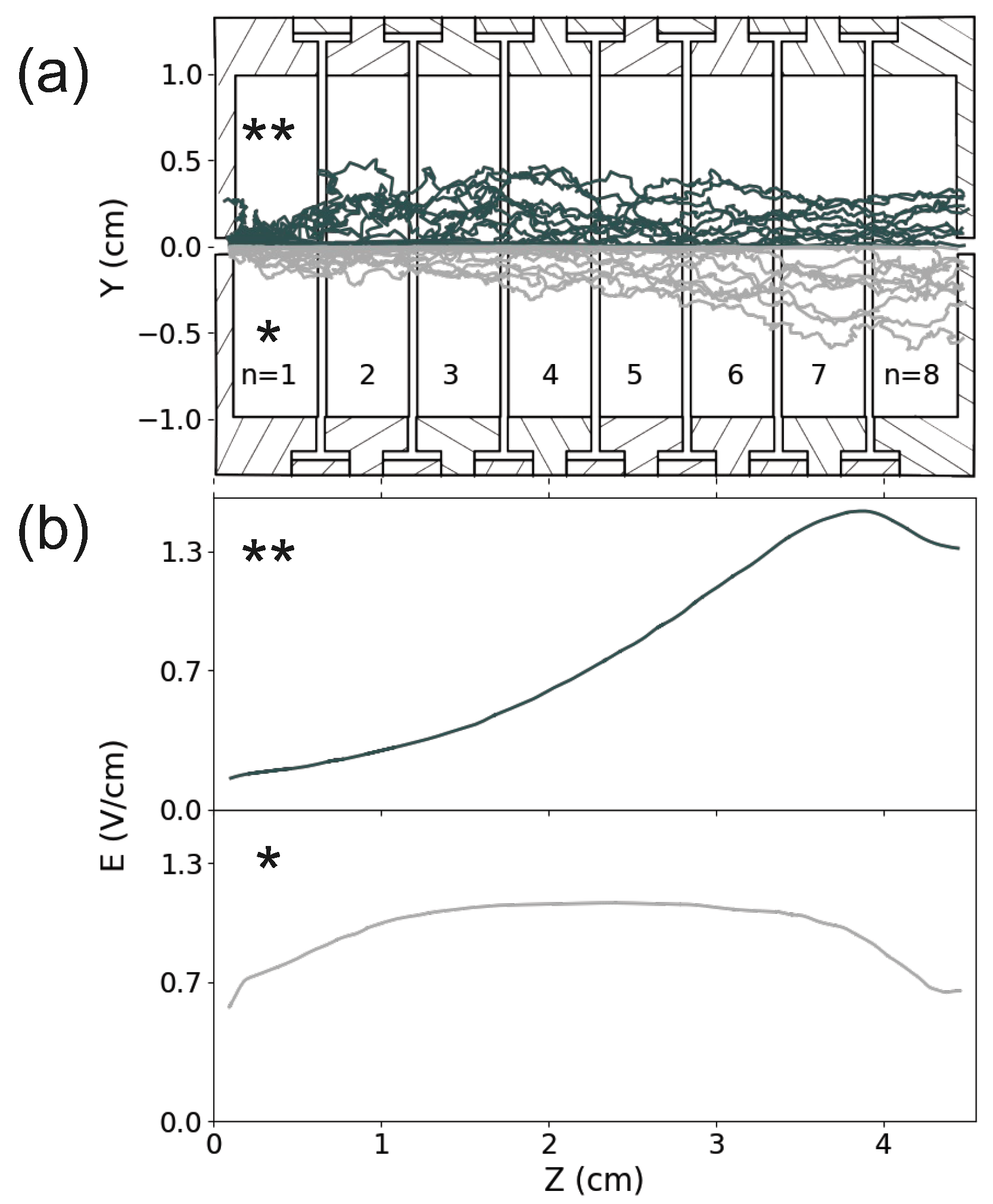
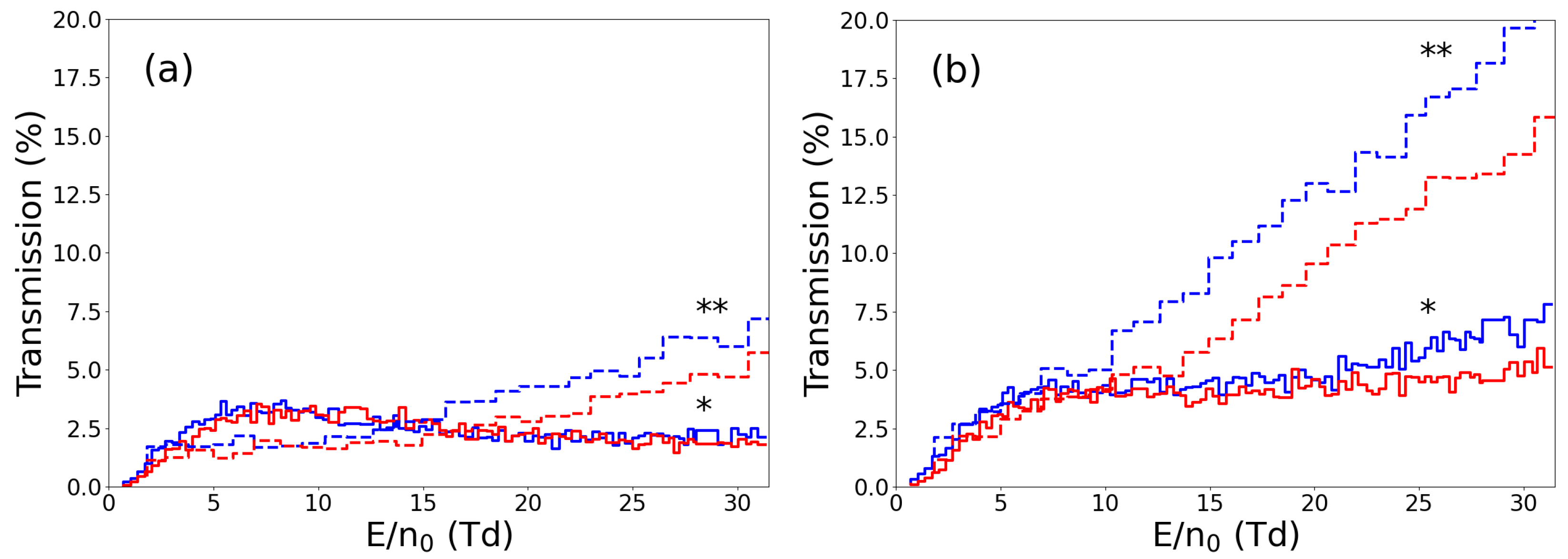
3. Ion Drift Simulations
Results
4. Current Status and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LRC | Laser Resonance Chromatography |
| SHE | Super Heavy Elements |
| PS | Pressure Section |
| SDS | Statistical Diffusion Simulation |
| VD | Viscous Damping |
References
- Giuliani, S.A.; Matheson, Z.; Nazarewicz, W.; Olsen, E.; Reinhard, P.G.; Sadhukhan, J.; Schuetrumpf, B.; Schunck, N.; Schwerdtfeger, P. Colloquium: Superheavy elements: Oganesson and beyond. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2019, 91, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarewicz, W. The limits of nuclear mass and charge. Nat. Phys. 2018, 14, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düllmann, C.E. Studying chemical properties of the heaviest elements: One atom at a time. Nucl. Phys. News 2017, 27, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakushev, A.; Gates, J.M.; Türler, A.; Schädel, M.; Düllmann, C.E.; Ackermann, D.; Andersson, L.L.; Block, M.; Brüchle, W.; Dvorak, J.; et al. Superheavy element flerovium (element 114) is a volatile metal. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, R.; Aksenov, N.; Albin, Y.V.; Belozerov, A.; Bozhikov, G.; Chepigin, V.; Dmitriev, S.; Dressler, R.; Gäggeler, H.; Gorshkov, V.; et al. Indication for a volatile element 114. Rca-Radiochim. Acta 2010, 98, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakushev, A.; Lens, L.; Düllmann, C.E.; Block, M.; Brand, H.; Calverley, T.; Dasgupta, M.; Di Nitto, A.; Götz, M.; Götz, S.; et al. First study on nihonium (Nh, element 113) chemistry at TASCA. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 753738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.K.; Sato, N.; Asai, M.; Tsukada, K.; Toyoshima, A.; Ooe, K.; Miyashita, S.; Schädel, M.; Kaneya, Y.; Nagame, Y.; et al. First successful ionization of Lr (Z = 103) by a surface-ionization technique. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 023304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.; Giacoppo, F.; Heßberger, F.P.; Raeder, S. Recent progress in experiments on the heaviest nuclides at SHIP. Riv. Nuovo C 2022, 45, 279–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, R.; Barzakh, A.; Bastin, B.; Beerwerth, R.; Block, M.; Creemers, P.; Grawe, H.; de Groote, R.; Delahaye, P.; Fléchard, X.; et al. Towards high-resolution laser ionization spectroscopy of the heaviest elements in supersonic gas jet expansion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laatiaoui, M.; Lauth, W.; Backe, H.; Block, M.; Ackermann, D.; Cheal, B.; Chhetri, P.; Düllmann, C.E.; Van Duppen, P.; Even, J.; et al. Atom-at-a-time laser resonance ionization spectroscopy of nobelium. Nature 2016, 538, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laatiaoui, M.; Buchachenko, A.A.; Viehland, L.A. Laser Resonance Chromatography of Superheavy Elements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backe, H.; Lauth, W.; Block, M.; Laatiaoui, M. Prospects for laser spectroscopy, ion chemistry and mobility measurements of superheavy elements in buffer-gas traps. Nucl. Phys. A 2015, 944, 492–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laatiaoui, M.; Backe, H.; Habs, D.; Kunz, P.; Lauth, W.; Sewtz, M. Low-field mobilities of rare-earth metals. Eur. Phys. J. D 2012, 66, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumbach, J. Ion mobility spectrometry in scientific literature and in the International Journal for Ion Mobility Spectrometry (1998–2007). Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spectrom. 2008, 11, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, E.A.; McDaniel, E.W. Transport Properties of Ions in Gases; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Kemper, P.R.; Bowers, M.T. State-selected mobilities of atomic cobalt ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, P.R.; Bowers, M.T. Electronic-state chromatography: Application to first-row transition-metal ions. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 5134–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iceman, C.; Rue, C.; Moision, R.M.; Chatterjee, B.K.; Armentrout, P.B. Ion mobility studies of electronically excited states of atomic transition metal cations: Development of an ion mobility source for guided ion beam experiments. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 18, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.; Alsharaeh, E.; Mabrouki, R.; Momoh, P.; Xie, E.; El-Shall, M.S. Ion mobility of ground and excited states of laser-generated transition metal cations. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 1112–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manard, M.J.; Kemper, P.R. Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry: The design of a new high-resolution mobility instrument with applications toward electronic-state characterization of first-row transition metal cations. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 402, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manard, M.J.; Kemper, P.R. Characterizing the electronic states of the second-row transitionmetal cations using high-resolution ion mobility mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 407, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manard, M.J.; Kemper, P.R. An experimental investigation into the reduced mobilities of lanthanide cations using high-resolution ion mobility mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 423, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, J.E.; Dakin, J.T. Absolute transition probabilities in Sc I and Sc II. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1989, 6, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramida, A.; Ralchenko, Y.; Reader, J. NIST Atomic Spectra Database (Ver. 5.7.1); National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Manard, M.J.; Kemper, P.R. Reduced mobilities of lanthanide cations measured using high-resolution ion mobility mass spectrometry with comparisons between experiment and theory. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 412, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinet, P.; Palmeri, P.; Biémont, E.; McCurdy, M.M.; Rieger, G.; Pinnington, E.H.; Wickliffe, M.E.; Lawler, J.E. Experimental and theoretical radiative lifetimes, branching fractions and oscillator strengths in Lu II. Mon. Not. Royal Astron. Soc. 1999, 307, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin. Lutetium Ion Spectroscopy. Bachelor’s Thesis, Department of Physics, National University of Singapore, Singapore, 2014.
- Visentin, G.; Laatiaoui, M.; Viehland, L.A.; Buchachenko, A.A. Mobility of the Singly-Charged Lanthanide and Actinide Cations: Trends and Perspectives. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, E.V.; Berengut, J.C.; Laatiaoui, M.; Eliav, E.; Borschevsky, A. High-precision ab initio calculations of the spectrum of Lr+. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 062505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanantoanina, H.; Borschevsky, A.; Block, M.; Laatiaoui, M. Electronic Structure of Lr+ (Z = 103) from Ab Initio Calculations. Atoms 2022, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanantoanina, H.; Borschevsky, A.; Block, M.; Laatiaoui, M. State specific mobility of Lr+ ion in He. Phys. Rev. A 2022. Manuscript in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Buchachenko, A.A.; Visentin, G.; Viehland, L.A. Gaseous transport properties of the ground and excited Cr, Co and Ni cations in He: Ab initio study of electronic state chromatography. J. Chem. Phys. 2022, in press. [CrossRef]
- Ramanantoanina, H.; Borschevsky, A.; Block, M.; Laatiaoui, M. Electronic structure of Rf+(Z=104) from ab initio calculations. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 104, 022813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumayr, J.B.; Beck, L.; Habs, D.; Heinz, S.; Szerypo, J.; Thirolf, P.G.; Varentsov, V.; Voit, F.; Ackermann, D.; Beck, D.; et al. The ion-catcher device for SHIPTRAP. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2006, 244, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific-Instrument-Services. SIMION 8.0. Available online: https://simion.com/ (accessed on 9 July 2022).
- Appelhans, A.D.; Dahl, D.A. SIMION ion optics simulations at atmospheric pressure. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 244, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, C.L.; Trimpin, S. Ion Mobility Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry: Theory and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, S.; Fisher, E.; Lian, L.; Schulz, R.; Armentrout, P. State-specific reactions of Fe+ (6D, 4F) with O2 and c-C2H4O: D∘ 0 (Fe+-O) and effects of collisional relaxation. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 3159–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, P.; Ackermann, D.; Backe, H.; Block, M.; Cheal, B.; Düllmann, C.E.; Even, J.; Ferrer, R.; Giacoppo, F.; Götz, S.; et al. Impact of buffer gas quenching on the 1S0→1P1 ground-state atomic transition in nobelium. Eur. Phys. J. D 2017, 71, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ion | Ground State | State to Be Probed | Metastable State | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Config. | Config. | Config. | ||||||
| (cm) | (cm/Vs) | (cm) | (cm) | (cm/Vs) | ||||
| Sc | aD | 0 | 22.5 | zD | 27,917.78 | aF | 4802.87 | 18.5 |
| Lu | S | 0 | 16.8 | P | 28,503.16 | D | 11,796.24 | 19.5 |
| Lr | S | 0 | 16.8 | P | 31,540 | D | 20,846 | 19.4 |
| Electrode # | Unfocused beam Voltage (V) | Focused beam Voltage (V) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | * | ** | ||||
| 1 | + | 0 | + | 0 | ||
| 2 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 3 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 4 | 0 | |||||
| 5 | 0 | 3 | ||||
| 6 | 0 | 7 | ||||
| 7 | 0 | 12 | ||||
| 8 | 0 | 24 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero Romero, E.; Block, M.; Jana, B.; Kim, E.; Nothhelfer, S.; Raeder, S.; Ramanantoanina, H.; Rickert, E.; Schneider, J.; Sikora, P.; et al. A Progress Report on Laser Resonance Chromatography. Atoms 2022, 10, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms10030087
Romero Romero E, Block M, Jana B, Kim E, Nothhelfer S, Raeder S, Ramanantoanina H, Rickert E, Schneider J, Sikora P, et al. A Progress Report on Laser Resonance Chromatography. Atoms. 2022; 10(3):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms10030087
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero Romero, Elisa, Michael Block, Biswajit Jana, Eunkang Kim, Steven Nothhelfer, Sebastian Raeder, Harry Ramanantoanina, Elisabeth Rickert, Jonas Schneider, Philipp Sikora, and et al. 2022. "A Progress Report on Laser Resonance Chromatography" Atoms 10, no. 3: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms10030087
APA StyleRomero Romero, E., Block, M., Jana, B., Kim, E., Nothhelfer, S., Raeder, S., Ramanantoanina, H., Rickert, E., Schneider, J., Sikora, P., & Laatiaoui, M. (2022). A Progress Report on Laser Resonance Chromatography. Atoms, 10(3), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms10030087







