The 3D Direct Simulation Monte Carlo Study of Europa’s Gas Plume
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Description
2.2. A Parametric Study of the Gas Production Rate and Gas Bulk Velocity
3. Results
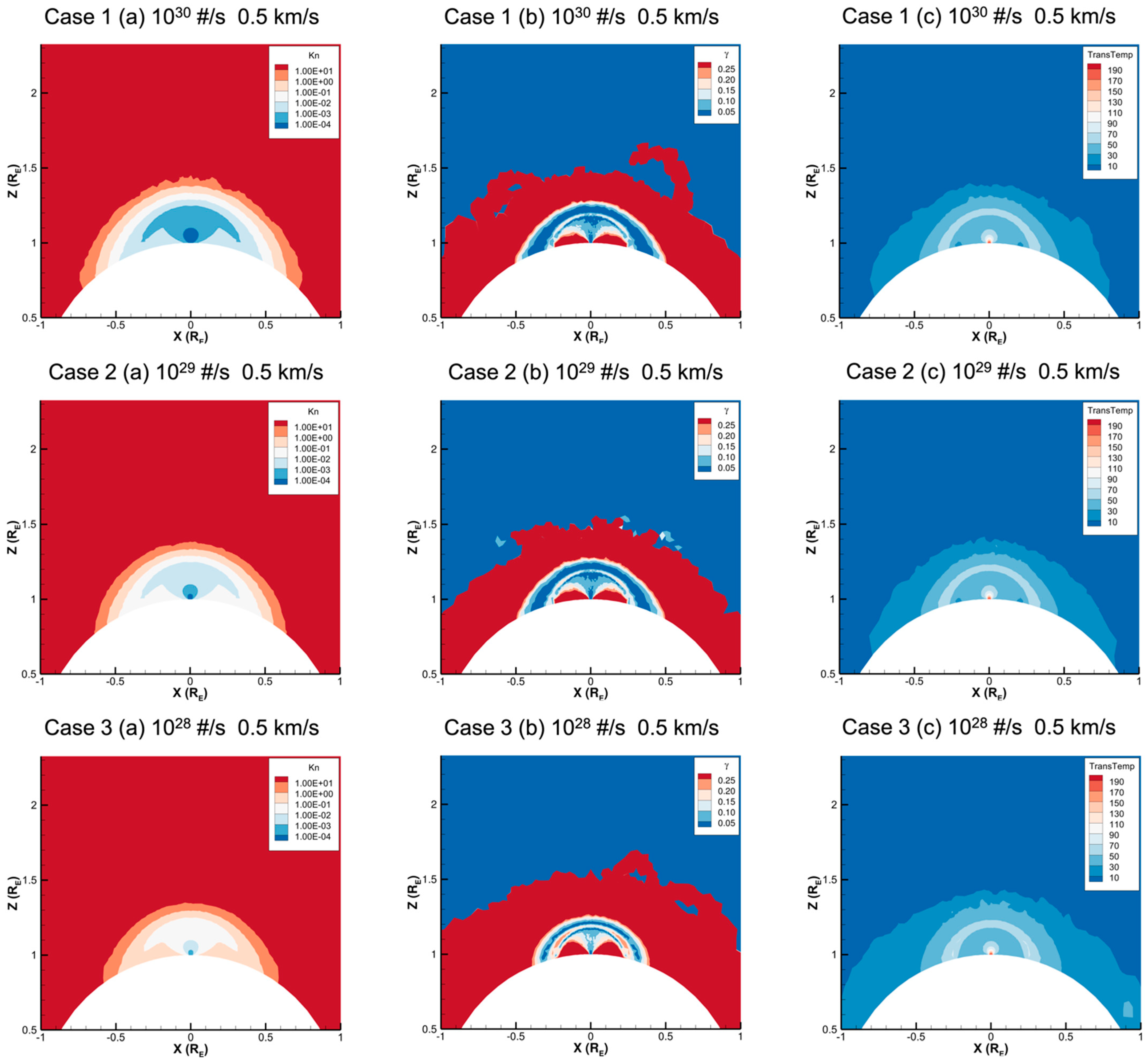
3.1. Knudsen Number, Gas Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium
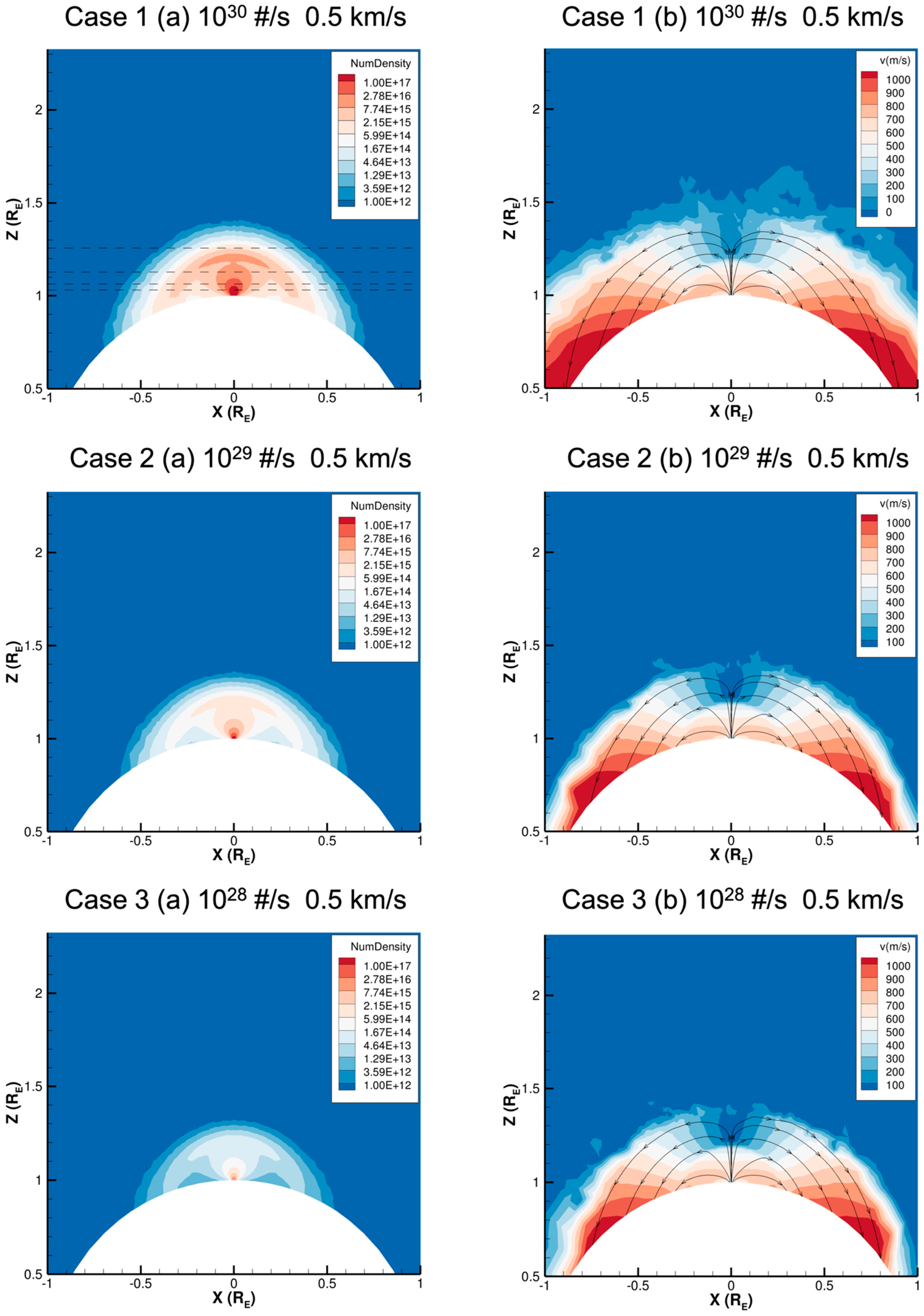
3.2. Gas Number Density and Velocity Distributions
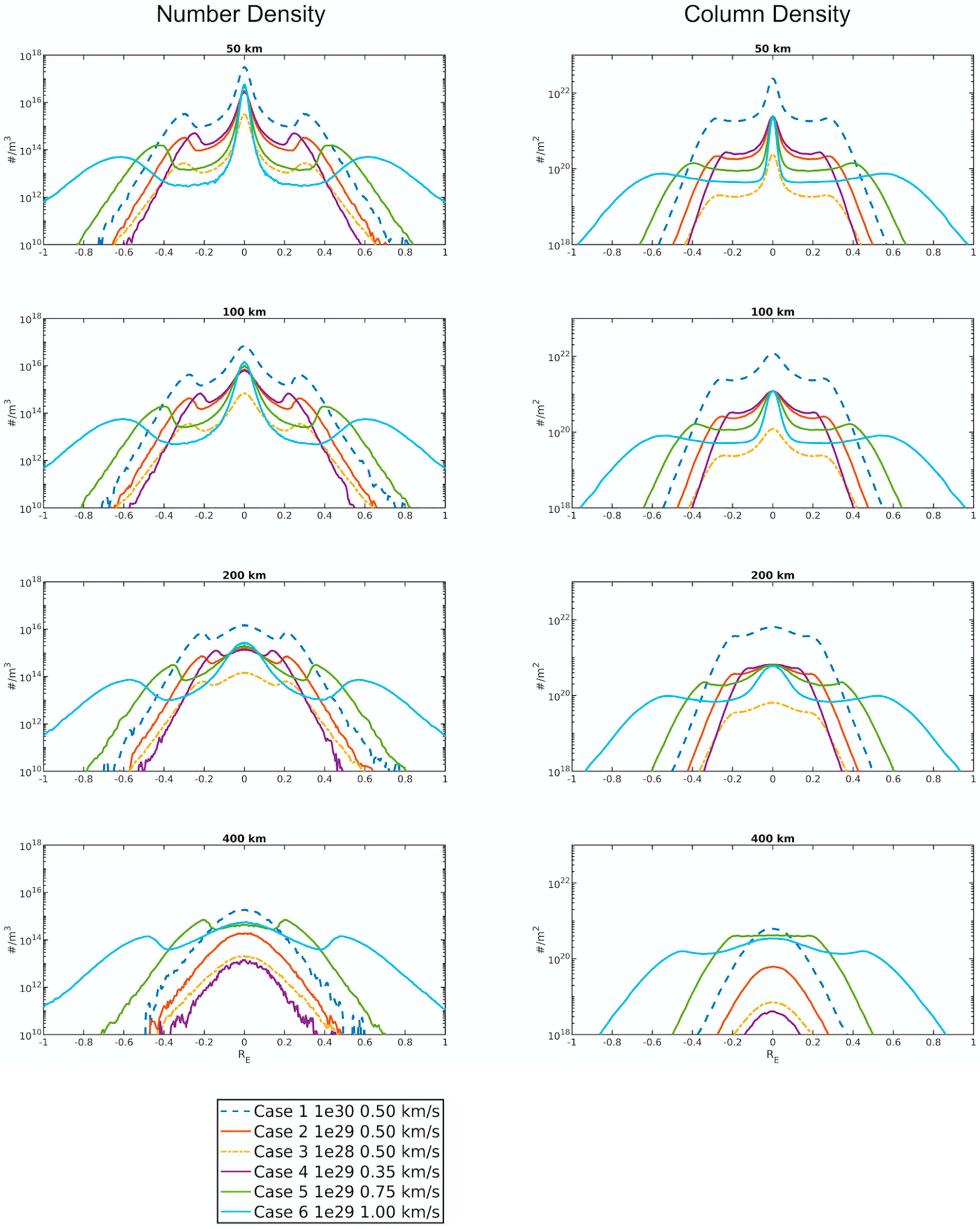
3.3. Column Density
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The gas kinetic temperature rapidly dropped to below 100 K during initial expansion in the low-altitude region (i.e., <100 km) due to the fact of adiabatic cooling;
- Mostly, the central parts of the plumes with large production rates of 1029 s−1 and 1030 s−1 were in thermal equilibrium and near continuum conditions;
- The gas acceleration near the surface (within an altitude of ~100 km) was a combined effect of gas collision and adiabatic cooling. At a higher altitude, the plume velocity distribution was governed by Europa’s large gravity. The plume simulated from the DSMC modeling (i.e., gas collision considered) was, therefore, generally much larger than the one computed from purely ballistic motion. For example, while the purely ballistic motion of the initial velocity of 0.75 km s−1 could arrive at a maximum altitude of only ~210 km, a similar altitude could be reached by the DSMC modeled plume with the initial velocity of 0.35 km s−1;
- The projection effect could be significant; therefore, it would be not an easy task to trace back a plume to its exact source region on Europa’s surface from the observed 2D images/maps without further supporting information.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, J.D.; Schubert, G.; Jacobson, R.A.; Lau, E.L.; Moore, W.B.; Sjogren, W.L. Europa’s Differentiated Internal Structure: Inferences from Four Galileo Encounters. Science 1998, 281, 2019–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, M.H.; Belton, M.J.; Chapman, C.R.; Davies, M.E.; Geissler, P.; Greenberg, R.; McEwen, A.S.; Tufts, B.R.; Greeley, R.; Sullian, R.; et al. Evidence for a subsurface ocean on Europa. Nature 1998, 391, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, R.; Geissler, P.; Hoppa, G.; Tufts, B.R. Tidal-tectonic processes and their implications for the character of Europa’s icy crust. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelson, M.G.; Khurana, K.K.; Russell, C.T.; Volwerk, M.; Walker, R.J.; Zimmer, C. Galileo magnetometer measurements: A stronger case for a subsurface ocean at Europa. Science 2000, 289, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, L.J.; Saur, J.; Retherford, K.D.; Strobel, D.F.; Feldman, P.D.; McGrath, M.A.; Nimmo, F. Transient Water Vapor at Europa’s South Pole. Science 2014, 343, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giono, G.; Roth, L.; Ivchenko, N.; Saur, J.; Retherford, K.; Schlegel, S.; Ackland, M.; Strobel, D. An Analysis of the Statistics and Systematics of Limb Anomaly Detections in HST/STIS Transit Images of Europa. Astron. J. 2020, 159, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, W.B.; Hand, K.P.; McGrath, M.A.; Bergeron, E.; Cracraft, M.; Deustua, S.E. Probing for Evidence of Plumes on Europa with HST/STIS. Astrophys. J. 2016, 829, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, W.B.; Schmidt, B.E.; McGrath, M.; Hand, K.P.; Spencer, J.R.; Cracraft, M.; E Deustua, S. Active Cryovolcanism on Europa? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 839, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganini, L.; Villanueva, G.L.; Roth, L.; Mandell, A.M.; Hurford, T.A.; Retherford, K.D.; Mumma, M.J. A measurement of water vapour amid a largely quiescent environment on Europa. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, H.; Liuzzo, L.; Simon, S. Plasma Interaction Signatures of Plumes at Europa. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 125, e2019JA027346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huybrighs, H.L.F.; Roussos, E.; Blöcker, A.; Krupp, N.; Futaana, Y.; Barabash, S.; Hadid, L.Z.; Holmberg, M.K.G.; Lomax, O.; Witasse, O. An active plume eruption on Europa during Galileo Flyby E26 as indicated by energetic proton depletions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Kurth, W.; Kivelson, M.; Khurana, K.K.; Kurth, W.S. Evidence of a plume on Europa from Galileo magnetic and plasma wave signatures. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, L.J.; Saur, J.; Retherford, K.D.; Strobel, D.F.; Feldman, P.D.; McGrath, M.A.; Spencer, J.R.; Blöcker, A.; Ivchenko, N. Europas far ultraviolet oxygen aurora from a comprehensive set of HST observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 2143–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, W.B.; Richter, M.; deWitt, C.; Montiel, E.; Dello Russo, N.; Grunsfeld, J.M.; McGrath, M.A.; Weaver, H.; Hand, K.P.; Bergeron, E.; et al. A Search for Water Vapor Plumes on Europa using SOFIA. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 871, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagents, S.A.; Greeley, R.; Sullivan, R.J.; Pappalardo, R.T.; Prockter, L.M.; Galileo SSI Team. Cryomagmatic mechanisms for the formation of Rhadamanthys Linea, triple band margins, and other low albedo features on Europa. Icarus 2000, 144, 54–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, L.C.; Barnouin, O.S.; Prockter, L.M.; Patterson, G.W. Constraints on the detection of cryovolcanic plumes on Europa. Planet. Space Sci. 2013, 86, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, L.; Hedman, M. Characterizing deposits emplaced by cryovolcanic plumes on Europa. Icarus 2020, 343, 113667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southworth, B.S.; Kempf, S.; Schmidt, J. Modeling Europa’s dust plumes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10541–10548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Brilliantov, N.; Spahn, F.; Kempf, S. Slow dust in Enceladus’ plume from condensation and wall collisions in Tiger Stripe fractures. Nature 2008, 451, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teolis, B.D.; Wyrick, D.Y.; Bouquet, A.; Magee, B.A.; Waite, J.H. Plume and surface feature structure and compositional effects on Europa’s global exosphere: Preliminary Europa mission predictions. Icarus 2017, 284, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorburger, A.; Wurz, P. Modeling of possible plume mechanisms on Europa. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2021JA029690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, L.; Retherford, K.D.; Saur, J.; Strobel, D.F.; Feldman, P.D.; McGrath, A.M.; Nimmo, F. Orbital apocenter is not a sufficient condition for HST/STIS detection of Europa’s water vapor aurora. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5123–E5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, G.A. Molecular Gas Dynamics and the Direction Simulation of Gas Flows; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, D.B.; Hedman, M.; Manga, M.; Perry, M.; Spitale, J.; Teolis, B. Enceladus plume dynamics: From surface to space. In Enceladus and the Icy Moons of Saturn; Schenk, P.M., Clark, R.N., Howett, C.J.A., Verbiscer, A.J., Waite, J.H., Eds.; University of Arizona: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2018; pp. 175–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, I.-L.; Su, C.-C.; Ip, W.-H.; Wei, C.-E.; Wu, J.-S.; Lo, M.-C.; Liao, Y.; Thomas, N. Transport and Distribution of Hydroxyl Radicals and Oxygen Atoms from H2O Photodissociation in the Inner Coma of–Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Earth Moon Planets 2016, 117, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, I.-L.; Rubin, M.; Wu, J.-S.; Ip, W.-H. DSMC Simulation of Europa’s Gas Plume. EPSC 2019, 13, EPSC-DPS2019-575-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tenishev, V.; Combi, M.R.; Rubin, M. Numerical simulation of dust in a cometary coma: Application to comet 67p/churyumov-gerasimenko. Astrophys. J. 2011, 732, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, S.K.; Li, Z.; Goldstein, D.B.; Varghese, P.L.; Levin, D.A.; Trafton, L.M. Constraining the Enceladus plume using numerical simulation and Cassini data. Icarus 2017, 281, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, V.V.; Rodionovc, A.V.; Lukianov, G.A.; Crifo, J.F. Monte-Carlo and multifluid modelling of the circumnuclear dust coma II. Aspherical-homogeneous, and spherical-inhomogeneous nuclei. Icarus 2009, 201, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Goldstein, D.B.; Varghese, P.L.; Trafton, L.; Moore, C.; Miki, K. Numerical modeling of ionian volcanic plumes with entrained particulates. Icarus 2004, 172, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.J.; Goldstein, D.B.; Vargheseet, P.L.; Traftion, L.M. DSMC simulation of Europa water vapor plumes. Icarus 2016, 277, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasset, O.; Dougherty, M.K.; Coustenis, A.; Bunce, E.J.; Erd, C.; Titov, D.; Bunce, E.J.; Erd, C.; Titov, D.; Blanc, M.; et al. JUpiter ICy moons Explorer (JUICE): An ESA mission to orbit Ganymede and to characterise the Jupiter system. Planet. Space Sci. 2013, 78, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.B.; Pappalardo, R.T. Europa clipper mission concept: Exploring Jupiter’s ocean moon. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2014, 95, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercignani, C. The Boltzmann Equation and Its Application; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cave, H.M.; Tseng, K.-C.; Wu, J.-S.; Jermy, M.C.; Huang, J.-C.; Krumdieck, S.P. Implementation of unsteady sampling procedures for the parallel direct simulation Monte Carlo method. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazy, Y. The surface temperature of Europa. Helion 2019, 5, e01908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, M.-C.; Su, C.-C.; Wu, J.-S.; Tseng, K.C. Modelling Rarefied Hypersonic Reactive Flows Using the Direct Simulation Monte Carlo Method. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2015, 18, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-C.; Tseng, K.-C.; Cave, H.M.; Wu, J.-S.; Lian, Y.-Y.; Kuo, T.-C.; Jermy, M.C. Implementation of a Transient Adaptive Sub-Cell Module for the Parallel DSMC Code Using Unstructured Grids. Comput. Fluids 2010, 39, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-S.; Tseng, K.-C.; Wu, F.-Y. Parallel three-dimensional DSMC method using mesh refinement and variable time-step scheme. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2004, 162, 166–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finklenburg, S.; Thomas, N.; Su, C.-C.; Wu, J.-S. The spatial distribution of water in the inner coma of Comet 9P/Tempel 1: Comparison between models and observations. Icarus 2014, 236, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, I.-L.; Ip, W.-H.; Su, C.-C.; Wu, J.-S.; Lee, J.-C.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Liao, Y.; Thomas, N.; Sierks, H.; Barbieri, C.; et al. Gas outflow and dust transport of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. MNRAS 2016, 462, S533–S546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Marschall, R.; Su, C.-C.; Wu, J.-S.; Lai, I.-L.; Pinzon, O.; Thomas, N. Water vapor deposition from the inner gas coma onto the nucleus of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Planet. Space Sci. 2018, 157, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschall, R.; Su, C.-C.; Liao, Y.; Thomas, N.; Altwegg, K.; Sierks, H.; Ip, W.-H.; Keller, H.U.; Knollenberg, J.; Kührt, E. Modelling observations of the inner gas and dust coma of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko usingROSINA/COPS and OSIRIS data: First results. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 589, A90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, S.K.; Chapman, T.A.; Goldstein, D.B.; Varghese, P.L.; Trafton, L.M. On understanding the physics of the Enceladus south polar plume via numerical simulation. Icarus 2015, 253, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchetti, A.; Plainaki, C.; Cremonese, G.; Milillo, A.; Cassidy, T.; Jia, X.; Shematovich, V. Loss rates of Europa’s tenuous atmosphere. Planet. Space Sci. 2016, 130, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagents, S.A. Considerations for effusive cryovolcanism on Europa: The post-Galileo perspective. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porco, C.; Helfenstein, P.; Thomas, P.C. How the geysers, tidal stresses, and thermal emission across the south polarterrain of Enceladus are related. Astron. J. 2014, 148, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitale, J.N.; Porco, C.C. Association of the jets of Enceladus with the warmest regions on its south-polar fractures. Nature 2007, 449, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.R.; Pearl, J.C.; Segura, M.; Mamoutkine, A.; Romani, P.; Buratti, B.J.; Hendrix, A.R.; Spilker, L.J.; Lopes, R.M.C. Cassini encounters Enceladus: Background and the discovery of a south polar hot spot. Science 2006, 311, 1401–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Hill, T.W.; Teolis, B.D.; Magee, B.A.; Waite, J.H. The water vapor plumes of Enceladus. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, A10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.J.; Esposito, L.W.; Stewart, A.I.F.; Meinke, B.; Wallis, B.; Colwell, J.E.; Hendrix, A.R.; Larsen, K.; Pryor, W.; Tian, F. Water vapour jets inside the plume of gas leaving Enceladus. Nature 2008, 456, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.J.; Esposito, L.W.; Hendrix, A.R.; Stewart, A.I.F.; Lewis, B.R.; Colwell, J.E.; Hendrix, A.R.; West, R.A.; Waite, J.H.; Teolis, B.; et al. The composition and structure of the Enceladus plume. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L11202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.J.; Esposito, L.W.; Hendrix, A.R. Ultraviolet observation of Enceladus’ plume in transit across Saturn, compared to Europa. Icarus 2019, 330, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, K.P.; Carlson, R.W. Europa’s surface color suggests an ocean rich with sodium chloride. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligier, N.; Poulet, F.; Carter, J.; Brunetto, R.; Gourgeot, F. Vlt/sinfoni observations of europa: New insights into the surface composition. Astron. J. 2016, 151, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, P.M. The Search for Europa’s Plumes: No Surface Patterns or Changes 1979–2007? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 892, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumbo, S.K.; Brown, M.E.; Hand, K.P. H2O2 within Chaos Terrain on Europa’s Leading Hemisphere. Astron. J. 2019, 158, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdis, J.R.; Gudipati, M.S.; Murphy, J.R.; Chanover, N.J. Europa’s surface water ice crystallinity: Discrepancy between observations and thermophysical and particle flux modeling. Icarus 2020, 341, 113660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgacem, I.; Schmidt, F.; Jonniaux, G. Regional study of Europa’s photometry. Icarus 2020, 338, 113525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.B.; McCord, T.B. Amorphous and crystalline ice on the Galilean satellites: A balance between thermal and radiolytic processes. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, E01012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | Case 6 | Case 7 * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas Production Rate (H2O s−1) | 1 × 1030 | 1 × 1029 | 1 × 1028 | 1 × 1029 | 1 × 1029 | 1 × 1029 | 1 × 1026 |
| Gas Bulk Velocity (km s−1) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.35 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 0.35 |
| Gas Temperature (K) | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 |
| Mach Number | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 2.2 | 0.8 |
| Simulated Plume Height (km) | ~350 | ~350 | ~350 | ~250 | ~500 | ~800 | - ** |
| Simulated Plume Width (km) *** | ~80 | ~80 | ~80 | ~90 | ~50 | ~50 | - ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseng, W.-L.; Lai, I.-L.; Ip, W.-H.; Hsu, H.-W.; Wu, J.-S. The 3D Direct Simulation Monte Carlo Study of Europa’s Gas Plume. Universe 2022, 8, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8050261
Tseng W-L, Lai I-L, Ip W-H, Hsu H-W, Wu J-S. The 3D Direct Simulation Monte Carlo Study of Europa’s Gas Plume. Universe. 2022; 8(5):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8050261
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseng, Wei-Ling, Ian-Lin Lai, Wing-Huen Ip, Hsiang-Wen Hsu, and Jong-Shinn Wu. 2022. "The 3D Direct Simulation Monte Carlo Study of Europa’s Gas Plume" Universe 8, no. 5: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8050261
APA StyleTseng, W.-L., Lai, I.-L., Ip, W.-H., Hsu, H.-W., & Wu, J.-S. (2022). The 3D Direct Simulation Monte Carlo Study of Europa’s Gas Plume. Universe, 8(5), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8050261






