Abstract
In this paper, we calibrate the luminosity relation of gamma−ray bursts (GRBs) by employing artificial neural networks (ANNs) to analyze the Pantheon+ sample of type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) in a manner independent of cosmological assumptions. The A219 GRB dataset is used to calibrate the Amati relation (-) at low redshift with the ANN framework, facilitating the construction of the Hubble diagram at higher redshifts. Cosmological models are constrained with GRBs at high redshift and the latest observational Hubble data (OHD) via the Markov chain Monte Carlo numerical approach. For the Chevallier−Polarski−Linder (CPL) model within a flat universe, we obtain , , , and at the 1 − confidence level, which indicates a preference for dark energy with potential redshift evolution (). These findings using ANNs align closely with those derived from GRBs calibrated using Gaussian processes (GPs).
1. Introduction
Gamma−ray bursts (GRBs) can serve as cosmic probes by leveraging luminosity relations to explore the universe’s expansion history at redshifts far beyond Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. To address the circularity problem, Ref. [10] proposed a model−independent method to calibrate seven GRB luminosity relations utilizing SNe Ia at low redshifts. In [11], the authors used observational Hubble data (OHD) obtained via the cosmic chronometers (CC) method to calibrate the Amati relation, which connects the spectral peak energy to the isotropic equivalent radiated energy [12]. Therefore, GRB data can be used to constrain cosmological models at high redshift by using the standard Hubble diagram method [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Other local data have also been used to calibrate GRBs, e.g., mock data of gravitational waves (GWs) [24], quasars [25,26], and angular diameter distances of galaxy clusters [27]. In addition, Ref. [28] proposed the simultaneous fitting method, which constrains the coefficients of the relationship and the parameters of the cosmological model simultaneously to alleviate the circularity problem. It has been found that the Amati relation parameters are almost identical in all cosmological models by the simultaneous fitting method with a dataset of 118 GRBs (the A118 sample) from the total 220 GRBs (the A220 sample) [29,30,31,32,33]. Recent works on the luminosity relations of GRBs and their applications for cosmology can be found in [34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]; see [43,44] for reviews.
Similar to the interpolation method used in [10] and the Bézier parametric used in [11], GRBs can be calibrated from local data using iterative procedures [45], polynomial fitting [46], local regression [15,47], cosmography methods [48,49], the Padé approximation method [50], or a two−step method [51,52]. Recently, Gaussian processes (GPs) [53] have been used in GRB cosmological studies [54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61]. However, in GP analysis it is typically assumed that the errors in observational data follow a Gaussian distribution [53], which may pose a substantial limitation when reconstructing functions from data; furthermore, the results can be affected by the choice of the kernel functions, with many different available kernel functions [62,63]. The application of machine learning (ML) techniques has revolutionized data analysis in cosmology, offering robust tools for reconstructing complex astrophysical relationships and constraining cosmological parameters. In [64], the authors explored three ML treatments (linear regression, neural network, random forest) to alleviate the circularity problem with the Amati relation. In [65], machine learning algorithms were deployed to measure through regression analysis, finding that Support Vector Machine (SVM) exhibited the best performance in terms of bias−variance tradeoff in most cases, showing itself to be a competitive cross−check to GP. In [66], the authors utilized high−performance KNN (K-Nearest Neighbors) and RF (Random Forest) machine learning algorithms based on the Pantheon+ dataset [67] and the A219 sample [32,55] to calibrate the Amati relation in a model−independent manner and construct the Hubble diagram. By combining high−redshift data and observational Hubble data to constrain cosmological models, their results are consistent with those calibrated by Gaussian processes, providing a new pathway for precise cosmological studies.
Moreover, ANNs excel in modeling nonlinear correlations without requiring predefined functional forms, which can be used for cosmology at high redshifts [68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75]. In the context of GRBs, ANN−based approaches can provide a powerful framework for calibrating empirical luminosity relations. In [76], the authors used a novel deep learning framework to reconstruct the cosmic distance ladder with a GRB sample, while [77] employed neural networks to calibrate the Dainotti relations1 from the Pantheon+ sample of SNe Ia. In [80], an ANN framework was employed based on observational Hubble data (OHD) from cosmic chronometers, reconstructing in a model−independent way for relation calibration. Considering the physical correlations in the data, the authors introduced the covariance matrix and Kullback−Leibler (KL) divergence into the loss function, then used the A219 [32,55] and J220 samples [81,82] to select the optimal ANN model for calibrating the Amati relation.
Recent advances have incorporated machine learning approaches such as ANNs in combination with Bayesian neural networks (BNNs) to enhance the precision and reliability of these calibrations while quantifying uncertainties in a cosmology−independent manner [83,84,85]. In this study, we employ a hybrid ANN+BNN framework to calibrate the Amati relation. We utilize the Pantheon+ sample of SNe Ia to construct a high−redshift Hubble diagram and derive constraints on cosmological parameters in a flat universe, offering insights into the evolution of dark energy.
2. Reconstructing the Apparent Magnitude Redshift Relation from Pantheon+ Data
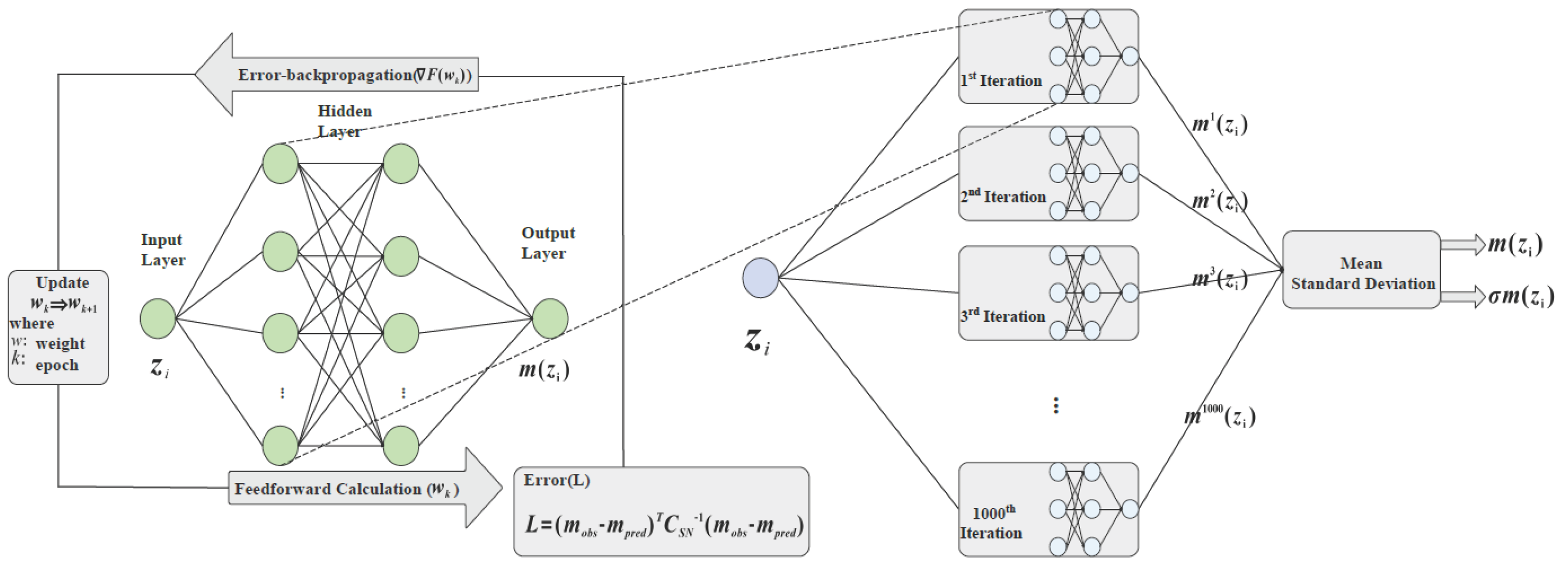
We explore the apparent magnitude−redshift relation using a hybrid model that integrates artificial (ANN) and Bayesian (BNN) neural networks. The ANN component models the relationship between redshift and apparent magnitude, while the BNN quantifies predictive uncertainties, accounting for the covariance errors inherent in the SNe Ia observations. Through backpropagation [86], the network iteratively refines its weights to minimize the loss function2, ensuring robust predictions. While ANNs excel in capturing complex patterns, they lack inherent uncertainty quantification. To address this, we employ a BNN approach, utilizing dropout to approximate Bayesian inference [87,88]. The ANN with dropout is run for 1000 iterations, producing a distribution of predicted magnitudes for each redshift. The mean of these predictions serves as the final , with the standard deviation providing the uncertainty . The ANN processes redshift inputs to generate corresponding apparent magnitudes , as illustrated in Figure 1.
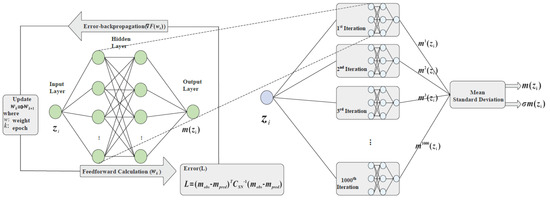
Figure 1.
Architecture of the ANN+BNN framework for fitting Pantheon+ SNe Ia apparent magnitudes . The left panel depicts the ANN structure, which maps the redshift to . The right panel shows the BNN simulation, where the ANN with dropout is executed over 1000 iterations for a given . The mean of these predictions provides , while the standard deviation yields the uncertainty .
Effective model performance depends on well−tuned hyperparameters, including the batch size, number and structure of hidden layers, activation function, and dropout rate, which together mitigate overfitting and enhance generalization ability [89]. We performed a grid search across 360 combinations, as summarized in Table 1, selecting the configuration with the lowest loss. This configuration consisted of a batch size of 16, one hidden layer with 512 units, a Tanh activation function, and a dropout rate of 0.1.

Table 1.
Candidate hyperparameters for the ANN+BNN framework used to model Pantheon+ SNe Ia apparent magnitudes . Optimal values determined via grid search are highlighted in bold.
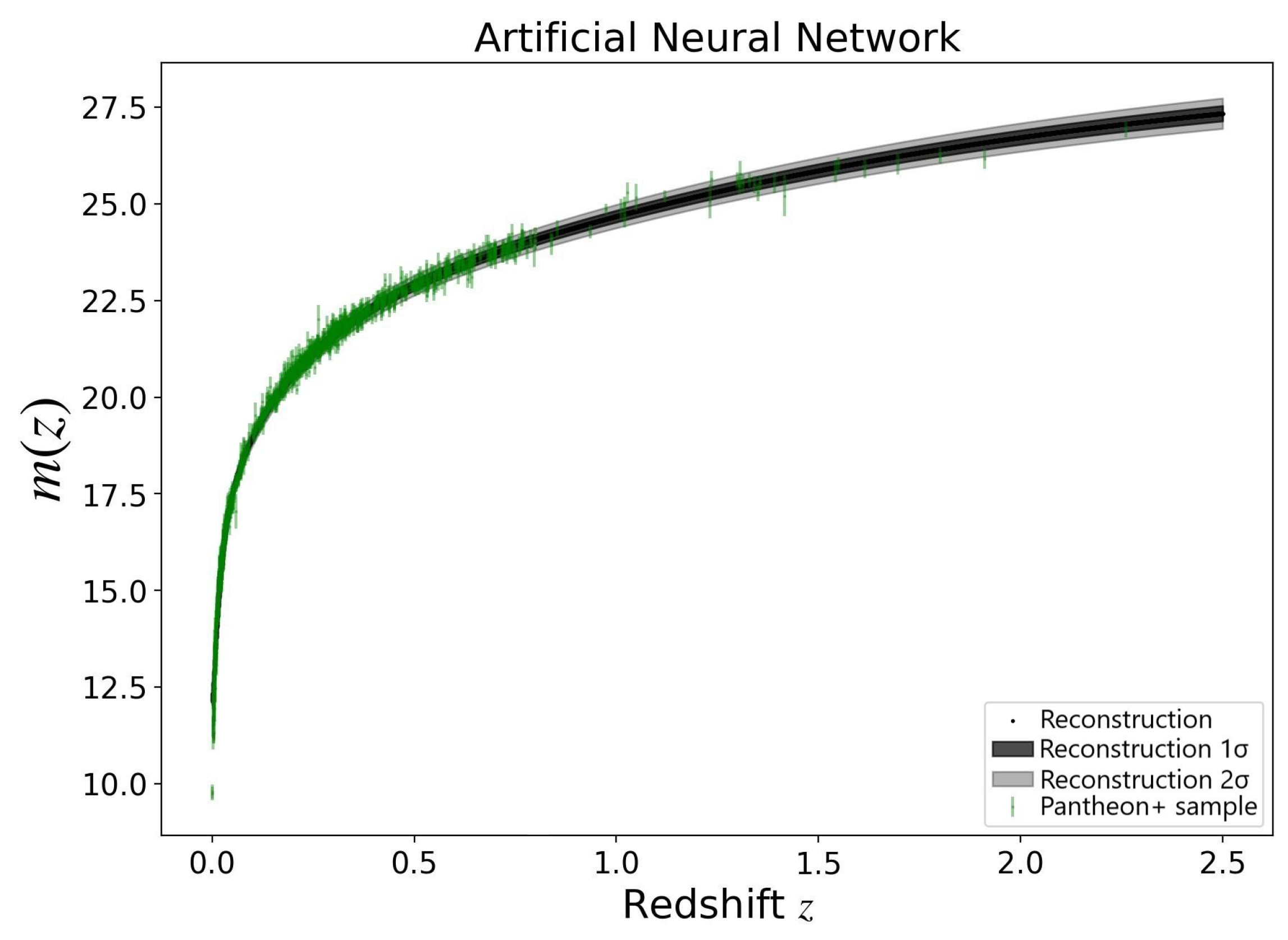
The ANN+BNN reconstruction for fitting Pantheon+ SNe Ia apparent magnitudes are shown in Figure 2. In this work, we utilize the A219 sample [55]3, which is divided into a low−redshift subset (, 79 GRBs) for calibration and a high-redshift subset (, 182 GRBs) for cosmological analysis.
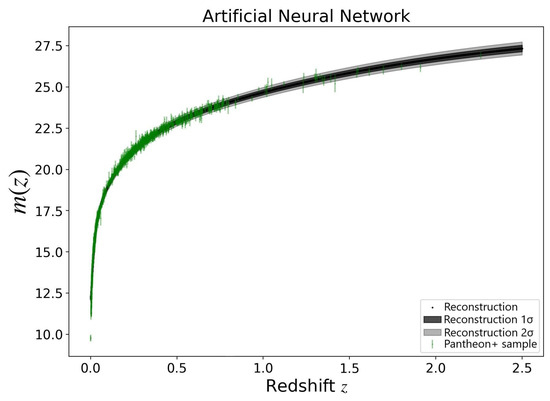
Figure 2.
Reconstruction of the relation between the apparent magnitude and the redshift from the Pantheon+ dataset using the proposed ANN+BNN. Green dots indicate Pantheon+ data points with 1 error bars. The black line represents the reconstructed central value, with shaded regions denoting 1 and 2 uncertainties.
3. Calibration of Amati Relation
The Amati relation linking the spectral peak energy () to the isotropic equivalent radiated energy () is formulated as follows:
where , , and a and b are free parameters. These quantities are defined as with as the luminosity distance, as the bolometric fluence, and as the observed spectral peak energy. The apparent magnitude m can be used to calibrate the relations between X-ray luminosity () and ultraviolet luminosity () of quasars without assuming a prior absolute magnitude of SNe Ia4 by introducing a new coefficient as a free parameter [90]. Furthermore, the Amati relation can be reformulated in terms of apparent magnitude m and a new coefficient as a free parameter [66]: where and . This permits calibration directly from observed GRB data using the apparent magnitude of SN Ia reconstructed at a redshift of GRBs at the same redshift.
We implement Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) fitting via the emcee package [91]. Parameters are fitted using the likelihood method of [92]5, which can avoid bias in variable selection [93,94]. We also used the GP method for comparison, which was done via the GaPP package with a squared exponential covariance function [53]. Results for the low-redshift A219 sample () are presented in Table 2. We find that the ANN+BNN results align with those obtained by GP with the A219 sample () [56] at 1 uncertainties, confirming the efficacy of machine learning approaches. We also find that the quality of the uncertainty estimates produced here are not well−calibrated; the value of the intrinsic scatter obtained by our method in this case is slightly larger than other values obtained in the literature. It should be noted that the KL divergence, which considers the physical meaning represented by the reconstruction data with their uncertainties and the covariance matrix of data, should be introduced into the loss function in order to correct potential miscalibrations [80]. Actually, given the critical role of uncertainty quantification in astrophysical inference, ensuring that ANNs produce reliable calibrated uncertainties is essential for their robust application in cosmology.

Table 2.
Best−fitting parameters (, b, ) for the Amati relation in the A219 GRB sample at (79 GRBs) by ANN and GaPP methods along with the likelihood [92].
4. The GRB Hubble Diagram and Constraints on DE Models
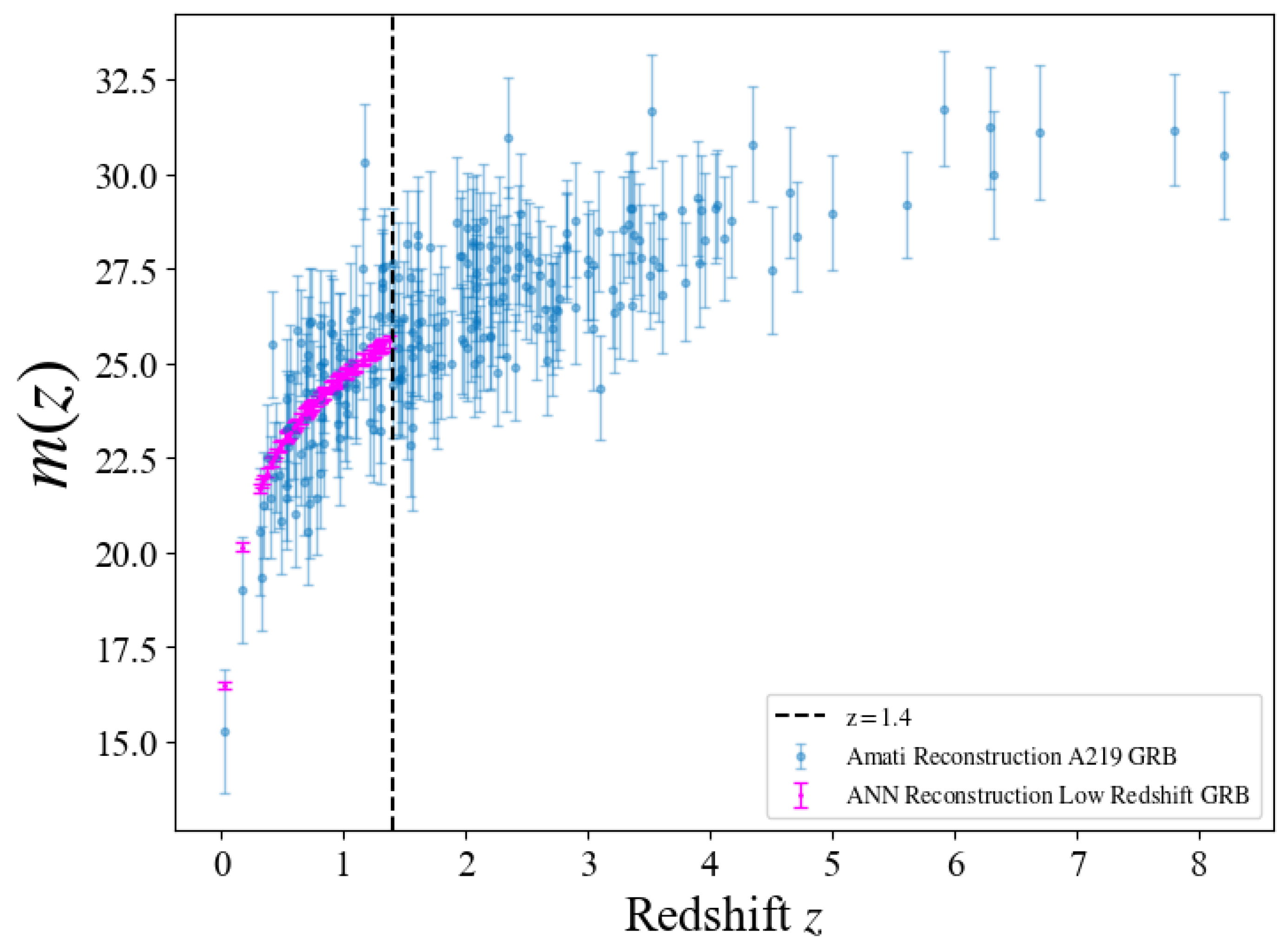
Assuming that the low−redshift calibration extends to higher redshifts, we construct the GRB Hubble diagram for . While the redshift dependence of GRB relations remains debated [15,25,32,39,40,82,84,95,96,97,98], we apply the calibrated Amati relation, noting that evolutionary effects warrant further scrutiny. By extrapolating the calibrated from the low−redshift GRBs to the high−redshift results using the ANN+BNN, we can obtain GRB Hubble diagram. The diagram combines low−redshift () and high−redshift () GRBs is shown in Figure 36. To investigate dark energy (DE) properties, we leverage the high−redshift GRB Hubble diagram from the A219 sample to constrain the cosmological parameters in various DE models. We consider two flat models: the CDM model with a constant equation of state (EoS) , and the Chevallier−Polarski−Linder (CPL) model [99,100] with a redshift−dependent EoS: 7.
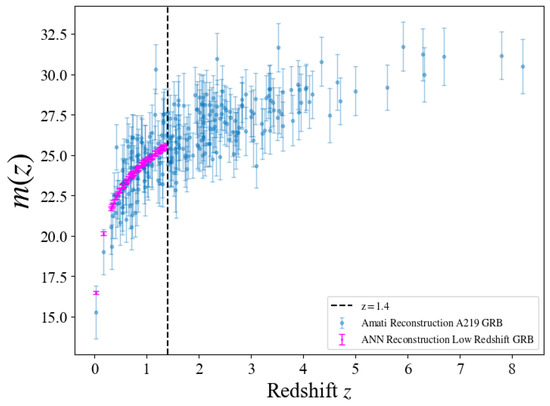
Figure 3.
GRB Hubble diagram for the A219 dataset. Purple points denote GRBs at derived from Pantheon+ using the proposed ANN+BNN. Blue points denote GRBs with the Amati relation calibrated using the likelihood method [92], including low−redshift () and high−redshift () GRBs.
We fit the cosmological parameters by minimizing the statistic, incorporating the GRB covariance matrix . The function for GRBs is defined as follows:
where is the residual vector between observed apparent magnitudes and theoretical magnitudes , and is calculated for cosmological parameters P. The theoretical magnitude is provided by
where is the unanchored luminosity distance, , , and is the Hubble constant.
To enhance constraints, we incorporate 32 OHD measurements, including 31 Hubble parameter data points at [101,102,103,104,105,106] and one additional point at [107]8. The OHD is
where for 15 correlated measurements [101,102,103], is the inverse covariance matrix [109], and for 17 uncorrelated measurements. The theoretical Hubble parameter is . The total is
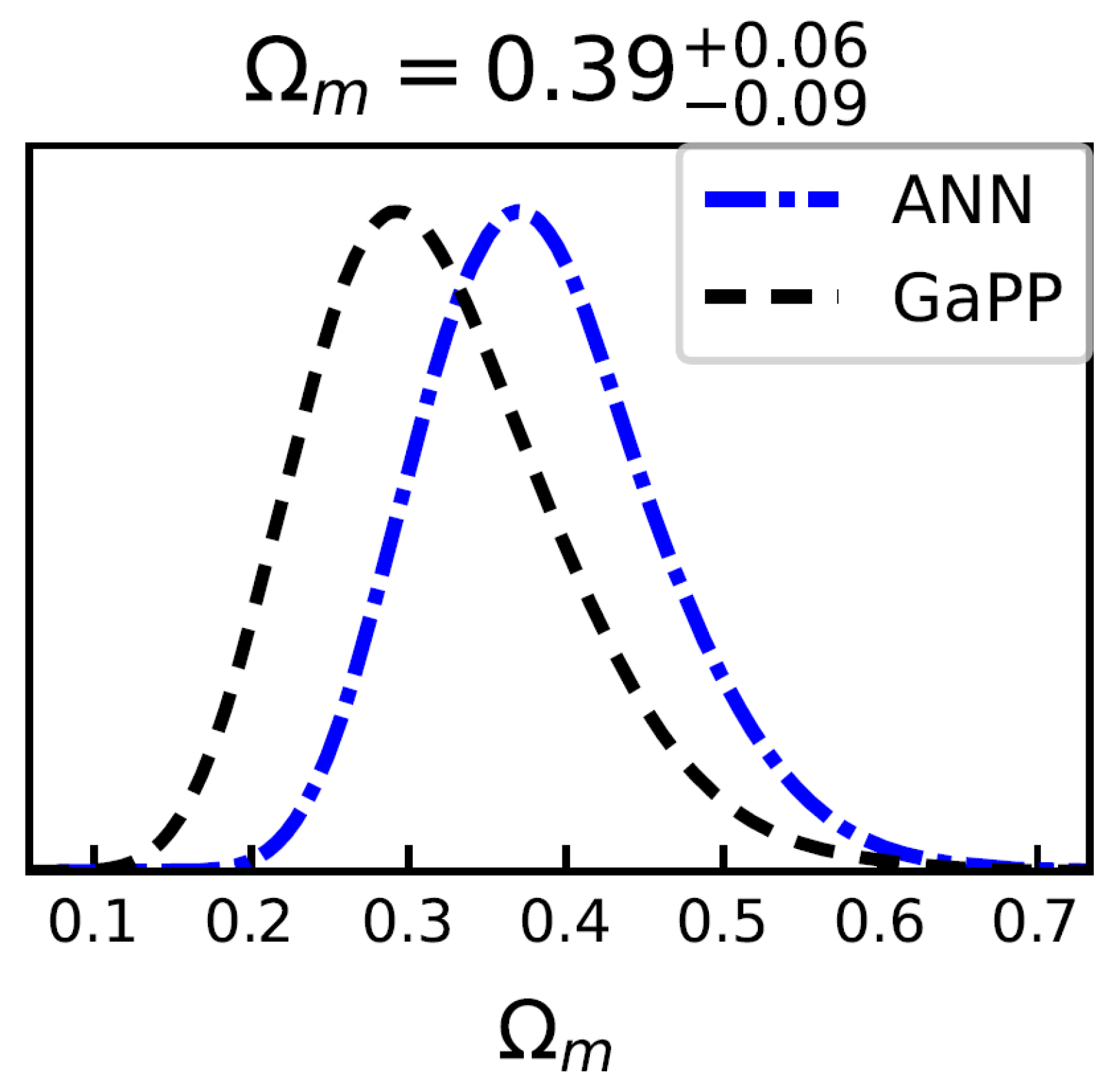
We perform MCMC fitting to constrain the DE models. Constraints using 140 GRBs at are shown in Figure 4 (for the CDM model) and Figure 5 (for the CPL model); and joint constraints using 140 GRBs at and 32 OHD are presented in Figure 6 (for CDM model) and Figure 7 (for CPL model), which are summarized in Table 3. We find that the inclusion of OHD in the joint constraints can tighten the constraints significantly. The results for the CPL model at the 1 confidence level favor a possible DE evolution (). We find that the ANN+BNN results are consistent with those obtained by GaPP, while showing slight differences. Compared to the fitting results from CMB data based on the CDM model at very high redshift ( = 67.36 km s−1, = 0.315) [110] and SNe Ia at very low redshift ( = 74.3 km s−1, = 0.298) [67], we find that the value with GRBs at and OHD at favors the one from the Planck observations and that the value of our results for the flat CDM model is consistent with the CMB observations at the 1 confidence level.
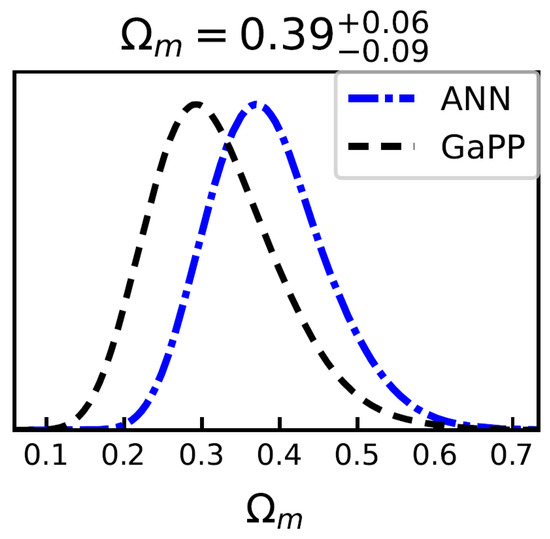
Figure 4.
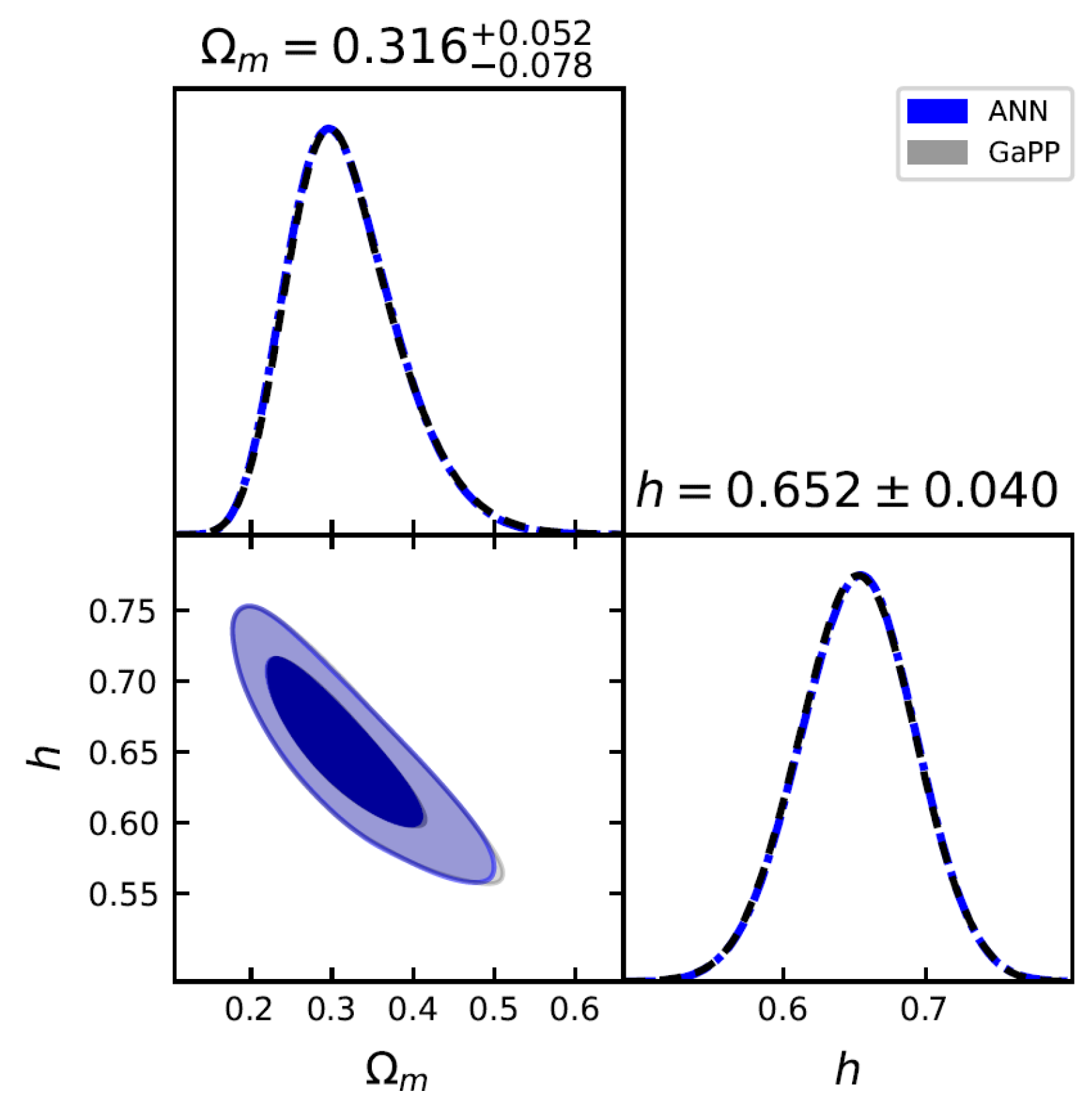
Constraints on for the flat CDM model using 140 GRBs () by ANN and GaPP methods, with fixed at 70 km/s/Mpc.
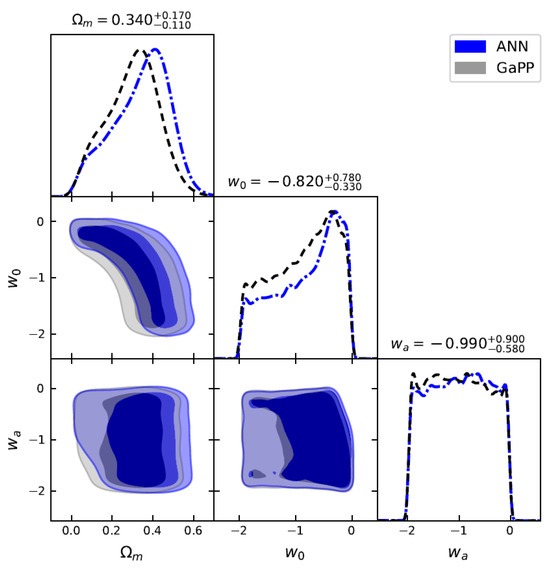
Figure 5.
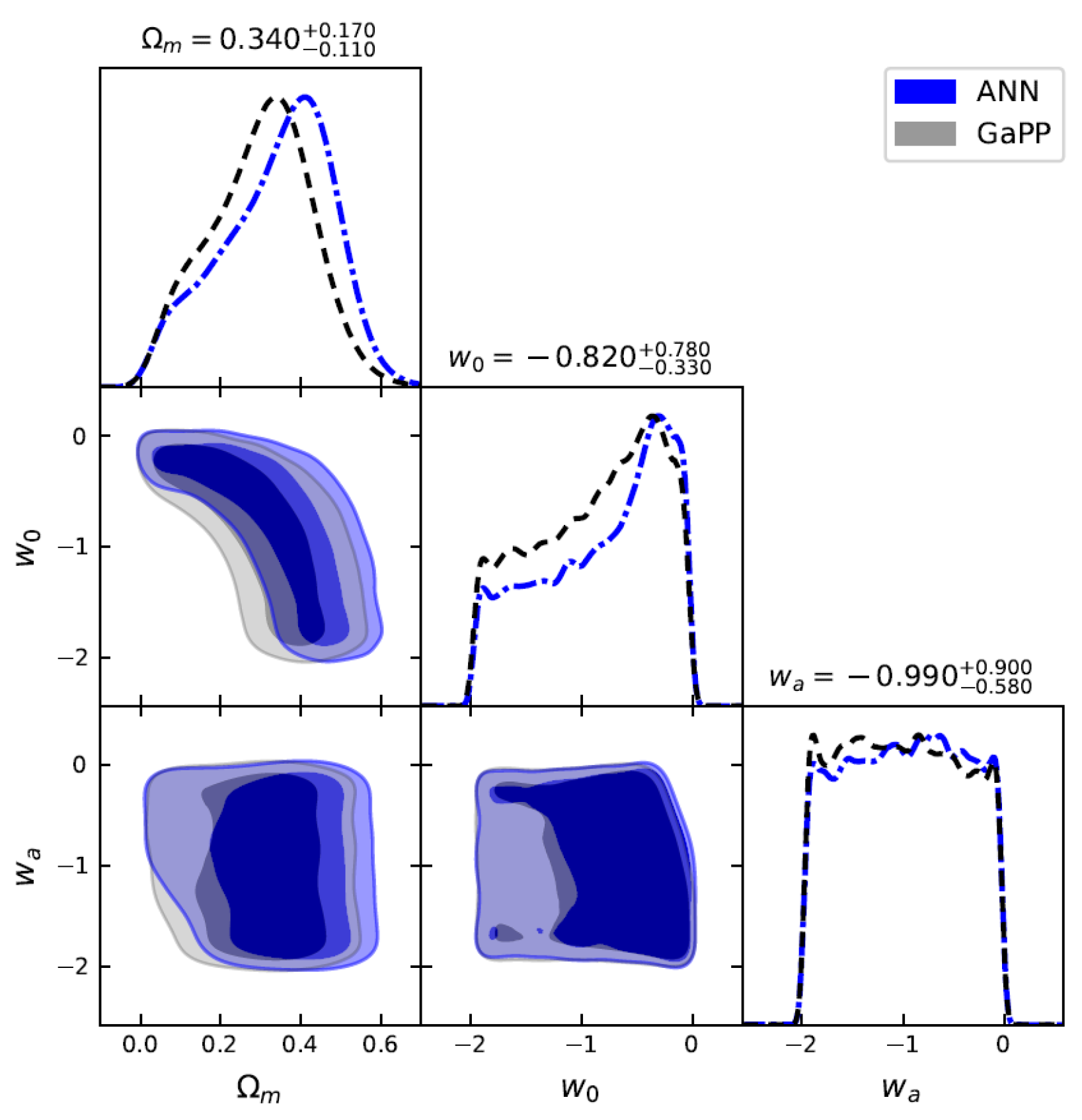
Constraints on , , and for the flat CPL model using 140 GRBs () by ANN and GaPP methods, with fixed at 70 km/s/Mpc.
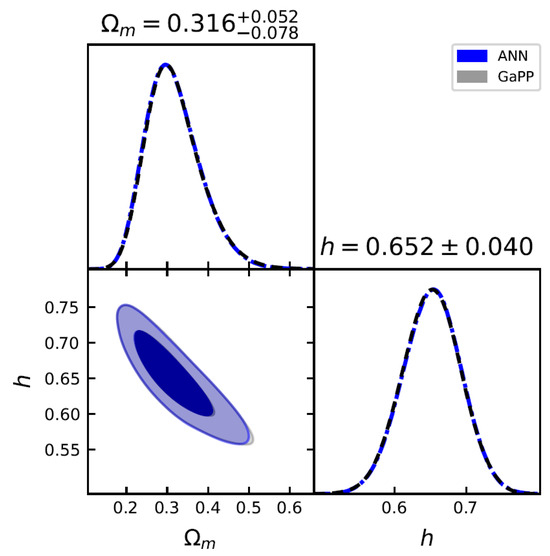
Figure 6.
Joint constraints on and h for the flat CDM model using 140 GRBs () + 32 OHD by the ANN and GaPP methods.
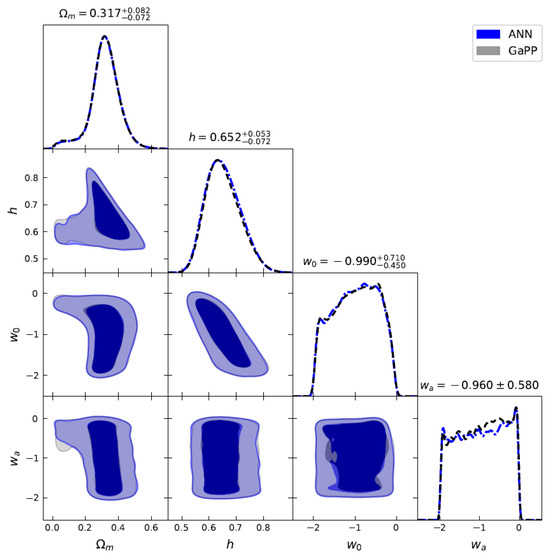
Figure 7.
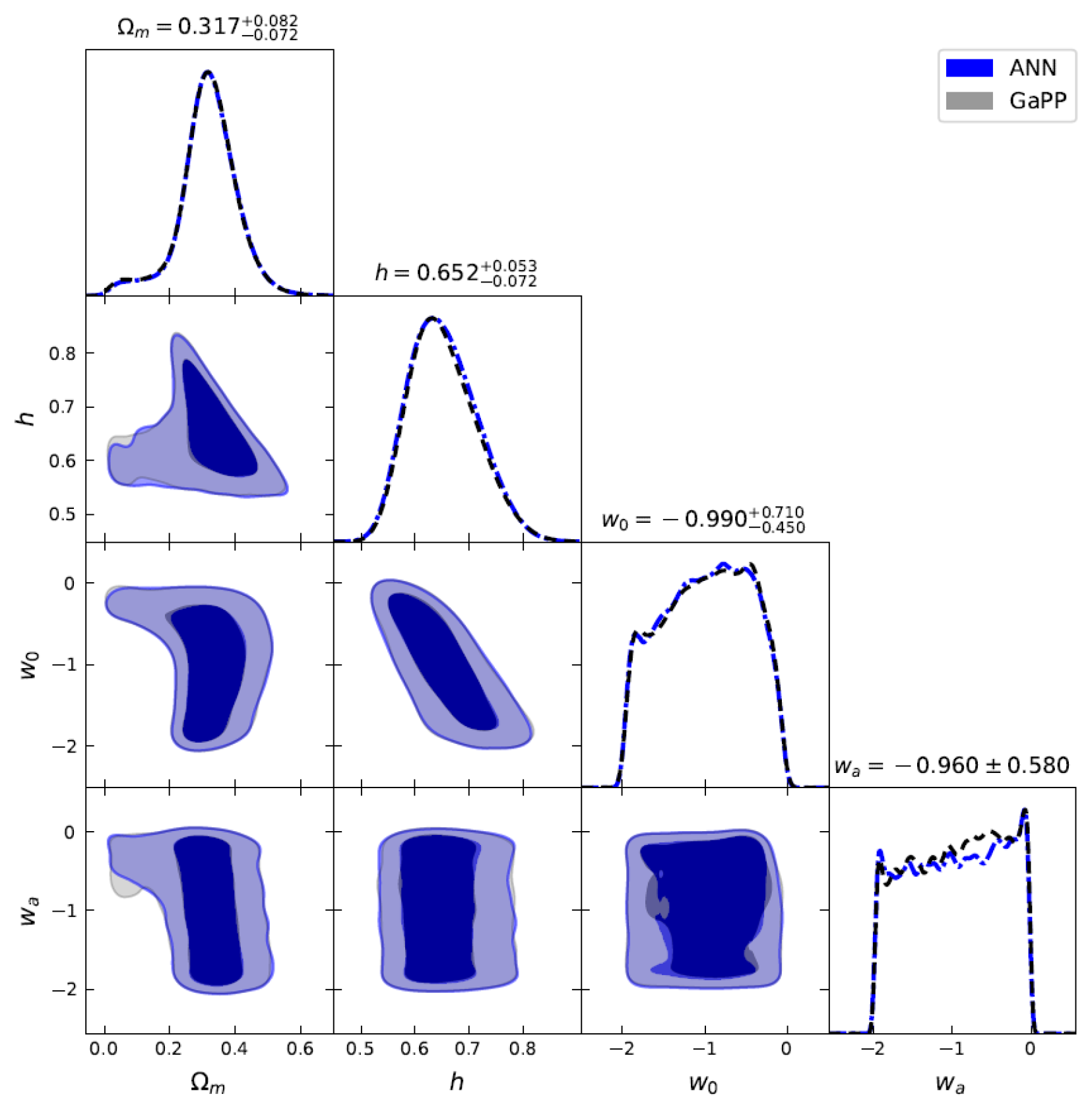
Joint constraints on , h, , and for the flat CPL model using 140 GRBs () + 32 OHD by the ANN and GaPP methods.

Table 3.
Constraints on cosmological parameters for flat CDM and CPL models by the ANN and GaPP methods with GRBs () only and GRBs () + OHD.
We also compare models using the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) and Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC). The values of and relative to the reference model (the CDM model) are given by: We find that the results of and indicate that the CDM model is favoured respect to the CPL model.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we use an ANN+BNN to calibrate the Amati relation from the Pantheon+ sample to obtain the GRB Hubble diagram with the A219 sample in a cosmology−independent way. Using the ANN method with GRBs at in the A219 sample and 32 OHD, we find that the results for the CPL model favor a possible DE evolution () at the 1 − confidence region. Compared to GP, which imposes strict Gaussian assumptions, ANN eliminates distributional constraints, enabling robust analysis of non−Gaussian observational datasets. Our results with GRBs at are consistent with previous analyses in [40,55,94] using GP methods.
We find that the calibration results of the slope in the Amati relation provided by Reichart method are close to the typical value (). The physical interpretation of the Amati relation can be provided by a model for the spectral formation of GRB prompt emission [111]. If the timescale of the GRB prompt emission and its shape for any burst is more or less the same, then proportional to is seen precisely. Frontera et al. [112] have concluded that the Yonetoku relation (the spectral peak energy to the isotropic bolometric luminosity ) is intrinsic to the emission process, and their results strongly support the reality of both the Amati and Yonetoku relations derived using time-averaged spectra.
Recently, Ref. [59] presented a sample of long GRBs from fifteen years of the Fermi−GBM catalogue with identified redshift, in which the GOLD sample contains 123 long GRBs at and the FULL sample contains 151 long GRBs with redshifts at . In [113], the authors analyzed 151 Fermi−observed long GRBs to simultaneously constrain the Amati correlation and cosmological parameters within six spatially flat and non−flat dark energy models. We expect that GRBs could be used to set tighter constraints on cosmological models by using the ANN approach with samples from recent Fermi data [59].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.H. and N.L.; methodology, B.Z.; software, X.L.; validation, Z.H., X.L. and B.Z.; formal analysis, B.Z.; data curation, Z.H., X.L. and B.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.H., B.Z. and N.L.; writing—review and editing, J.F., Y.L., P.W. and N.L.; supervision, N.L.; project administration, N.L.; funding acquisition, J.F., Y.L., P.W. and N.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was supported by the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Foundations (QKHJC—ZK[2021] Key 020, QKHJC—ZK[2024] General 443 and QKHPT ZSYS [2025] 004). Y. Liu was supported by the NSFC under Grant No. 12373063. P. Wu was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 12275080) and the Innovative Research Group of Hunan Province (Grant No. 2024JJ1006). J. Feng was supported by the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Foundations QKHJC—ZK[2022] General 311.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous referees for their helpful comments and constructive suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Notes
| 1 | The 2D Dainotti relation [78] is the correlation between the plateau luminosity and its end time in X-ray afterglows; the 3D Dainotti relation [79] is the correlation incorporating the peak prompt luminosity with the plateau end time and luminosity in the rest frame, achieving a small intrinsic scatter. |
| 2 | We incorporate the Pantheon+ covariance matrix into the loss function: where represents the difference between predicted and observed magnitudes. |
| 3 | The A219 sample is refined from the A220 sample [32] by removing the GRB051109A. |
| 4 | The distance module of SN Ia is related to the luminosity distance and the absolute magnitude (M); the value of M cannot be directly obtained using only the SN Ia sample, and as such M is treated as a free parameter. |
| 5 | Likelihood method of [92]: where and the intrinsic scatter is . |
| 6 | The uncertainty in the apparent magnitude is calculated as follows: where: and , with . |
| 7 | The luminosity distance in a flat universe is expressed as where , and are respectively the matter and DE density parameters, with for flat geometry. For the CDM model, and . |
| 8 | An alternative OHD point at is available [108], but due to unclear covariance with [107], we use only the latter, which accounts for a fraction of systematic uncertainty. |
References
- Dai, Z.; Liang, E.; Xu, D. Constraining ΩM and Dark Energy with Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2004, 612, L101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmani, C.; Ghisellini, G.; Ghirlanda, G.; Avila-Reese, V. A new method optimized to use gamma-ray bursts as cosmic rulers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 360, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirlanda, G.; Ghisellini, G.; Lazzati, D.; Firmani, C. Gamma-Ray Bursts: New Rulers to Measure the Universe. Astrophys. J. 2004, 613, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirlanda, G.; Ghisellini, G.; Firmani, C. Gamma-ray bursts as standard candles to constrain the cosmological parameters. New J. Phys. 2006, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.; Zhang, B. Calibration of gamma-ray burst luminosity indicators. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 369, L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, B.E. Gamma-Ray Burst Hubble Diagram to z = 4.5. Astrophys. J. 2003, 583, L67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, B.E. The Hubble Diagram to Redshift >6 from 69 Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2007, 660, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Dai, Z.G. Constraining the cosmological parameters and transition redshift with gamma-ray bursts and supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 368, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Dai, Z.; Liang, E. Can Gamma-Ray Bursts Be Used to Measure Cosmology? A Further Analysis. Astrophys. J. 2005, 633, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Xiao, W.K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.N. A Cosmology-Independent Calibration of Gamma-Ray Burst Luminosity Relations and the Hubble Diagram. Astrophys. J. 2008, 685, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, L.; D’Agostino, R.; Luongo, O.; Muccino, M.; Tantalo, M. Addressing the circularity problem in the Ep-Eiso correlation of gamma-ray bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 486, L46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, L.; Frontera, F.; Tavani, M.; in’t Zand, J.J.M.; Antonelli, A.; Costa, E.; Feroci, M.; Guidorzi, C.; Heise, J.; Masetti, N.; et al. Intrinsic spectra and energetics of BeppoSAX Gamma-Ray Bursts with known redshifts. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 390, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Izzo, L. Cosmography by gamma ray bursts. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 490, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Izzo, L. Cosmography by GRBs: Gamma Ray Bursts as possible distance indicators. Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 2009, 194, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demianski, M.; Piedipalumbo, E.; Sawant, D.; Amati, L. Cosmology with gamma-ray bursts. I. The Hubble diagram through the calibrated Ep,I-Eiso correlation. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 598, A112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demianski, M.; Piedipalumbo, E.; Sawant, D.; Amati, L. Cosmology with gamma-ray bursts. II. Cosmography challenges and cosmological scenarios for the accelerated Universe. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 598, A113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Wu, P.; Zhang, S.N. Constraints on cosmological models and reconstructing the acceleration history of the Universe with gamma-ray burst distance indicators. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 083518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Z.H. Constraints on the generalized Chaplygin gas model including gamma-ray bursts via a Markov Chain Monte Carlo approach. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 527, A11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, S.N. Reconstructing the cosmic expansion history up to redshift z = 6.29 with the calibrated gamma-ray bursts. Eur. Phys. J. C 2009, 63, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H. Observational constraints on cosmological models with the updated long gamma-ray bursts. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 8, 020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, O.; Muccino, M. Intermediate redshift calibration of gamma-ray bursts and cosmic constraints in non-flat cosmology. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 518, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, A.; Cabrera, J.I.; Hidalgo, J.C. Improving sampling and calibration of gamma-ray bursts as distance indicators. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 467, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Wang, F.Y.; Cheng, K.S.; Dai, Z.G. Measuring dark energy with the Eiso-Ep correlation of gamma-ray bursts using model-independent methods. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 585, A68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, F.Y. Calibration of Gamma-Ray Burst Luminosity Correlations Using Gravitational Waves as Standard Sirens. Astrophys. J. 2019, 873, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zheng, X.-G.; Li, Z.-X.; Gao, H.; Zhu, Z.-H. Redshift evolution of the Amati relation: Calibrated results from the Hubble diagram of quasars at high redshifts. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 651, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, S.; Desai, S. Calibration of Luminosity Correlations of Gamma-Ray Bursts Using Quasars. Galaxies 2024, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowri, G.; Shantanu, D. Low redshift calibration of the Amati relation using galaxy clusters. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2022, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, L.; Guidorzi, C.; Frontera, F.; Della Valle, M.; Finelli, F.; Landi, F.; Montanari, E. Measuring the cosmological parameters with the Ep,i-Eiso correlation of gamma-ray bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Dainotti, M.; Ratra, B. Standardizing Platinum Dainotti-correlated gamma-ray bursts, and using them with standardized Amati-correlated gamma-ray bursts to constrain cosmological model parameters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 512, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Khadka, N.; Ratra, B. Standardizing Dainotti-correlated gamma-ray bursts, and using them with standardized Amati-correlated gamma-ray bursts to constrain cosmological model parameters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 510, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, N.; Ratra, B. Constraints on cosmological parameters from gamma-ray burst peak photon energy and bolometric fluence measurements and other data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 499, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, N.; Luongo, O.; Muccino, M.; Ratra, B. Do gamma-ray burst measurements provide a useful test of cosmological models? J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 09, 042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Ratra, B. Using lower redshift, non-CMB, data to constrain the Hubble constant and other cosmological parameters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 513, 5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgáin, E.O.; Sheikh-Jabbari, M.M.; Yin, L. Do high redshift QSOs and GRBs corroborate JWST? Phys. Dark Universe 2025, 49, 101975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favale, A.; Dainotti, M.G.; Gómez-Valent, A.; Migliaccio, M. Towards a new model-independent calibration of Gamma-Ray Bursts. J. High Energy Astrophys. 2024, 44, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, G.; Xu, L. Detection of gamma-ray burst Amati relation based on Hubble data set and Pantheon+ samples. Eur. Phys. J. C 2024, 84, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.P.; Wang, F.Y.; Dai, Z.G. Measuring cosmological parameters with a luminosity-time correlation of gamma-ray bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 507, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-L.; Yang, Y.-P.; Yi, S.-X.; Hu, J.-P.; Qu, Y.-K.; Wang, F.-Y. Standardizing the gamma-ray burst as a standard candle and applying it to cosmological probes: Constraints on the two-component dark energy model. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 689, A165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, F.; Liang, N.; Yuan, Z.; Yu, H.; Wu, P. The Improved Amati Correlations from Gaussian Copula. Astrophys. J. 2022, 931, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, N.; Xie, X.; Yuan, Z.; Yu, H.; Wu, P. Gamma-Ray Burst Constraints on Cosmological Models from the Improved Amati Correlation. Astrophys. J. 2022, 935, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliathanasis, A. Testing Non-Coincident f(Q)-gravity with DESI DR2 BAO and GRBs. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.11132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Li, J.-L.; Yi, S.-X.; Yang, Y.-P.; Hu, J.-P.; Qu, Y.-K.; Wang, F.-Y. Radio Plateaus in Gamma-Ray Burst Afterglows and Their Application in Cosmology. Astrophys. J. 2023, 958, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargiacchi, G.; Dainotti, M.G.; Hernandez, X. High-redshift cosmology by Gamma-Ray Bursts: An overview. New Astron. Rev. 2025, 100, 101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Huang, Y.-F.; Xu, F.; Kurban, A. The Observed Luminosity Correlations of Gamma-Ray Bursts and Their Applications. Galaxies 2025, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Zhang, S. Cosmology-Independent Distance Moduli of 42 Gamma-Ray Bursts between Redshift of 1.44 and 6.60. AIP Conf. Proc. 2008, 1065, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, Y.; Yonetoku, D.; Murakami, T.; Tanabe, S.; Tsutsui, R.; Nakamura, T. Gamma-ray bursts in 1.8 < z < 5.6 suggest that the time variation of the dark energy is small. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, V.F.; Capozziello, S.; Dainotti, M.G. An updated gamma-ray bursts Hubble diagram. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 400, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Izzo, L. A cosmographic calibration of the Ep,i-Eiso (Amati) relation for GRBs. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 519, A73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liang, N.; Zhu, Z.-H. Calibration of GRB Luminosity Relations with Cosmography. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2012, 21, 1250016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wei, H. Cosmological models and gamma-ray bursts calibrated by using Padé method. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2015, 47, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, L.; Muccino, M.; Zaninoni, E.; Amati, L.; Della Valle, M. New measurements of Ωm from gamma-ray bursts. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 582, A115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccino, M.; Izzo, L.; Luongo, O.; Boshkayev, K.; Amati, L.; Della Valle, M.; Pisani, G.B.; Zaninoni, E. Tracing Dark Energy History with Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seikel, M.; Clarkson, C.; Smith, M. Reconstruction of dark energy and expansion dynamics using Gaussian processes. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 6, 036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-L.; Yang, Y.-P.; Yi, S.-X.; Hu, J.-P.; Wang, F.-Y.; Qu, Y.-K. Constraints on the Cosmological Parameters with Three-Parameter Correlation of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2023, 953, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, N.; Li, Z.; Xie, X.; Wu, P. Calibrating Gamma-Ray Bursts by Using a Gaussian Process with Type Ia Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2022, 941, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Chang, B.; Xu, L. Cosmography via Gaussian process with gamma ray bursts. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2023, 9, 041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.-D.; Liang, N. Testing the Phenomenological Interacting Dark Energy Model with Gamma-Ray Bursts and Pantheon+ type Ia Supernovae. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 24, 125003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Z.; Li, X.L.; Liang, N. Constraining the emergent dark energy models with observational data at intermediate redshift. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2024, 369, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, N. Constraints from Fermi observations of long gamma-ray bursts on cosmological parameters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 533, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Nong, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, Z.; Liang, N. Constraints on cosmological models with gamma-ray bursts in cosmology-independent way. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2025, 20, 2450073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seikel, M.; Yahya, S.; Maartens, R.; Clarkson, C. Using H(z) data as a probe of the concordance model. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.-J.; Wu, X.-F. An Improved Method to Measure the Cosmic Curvature. Astrophys. J. 2017, 838, 160w. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, Z. Testing the fidelity of Gaussian processes for cosmography. Chin. Phys. 2019, 43, 035103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, O.; Muccino, M. Model-independent calibrations of gamma-ray bursts using machine learning. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 503, 4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengaly, C.; Dantas, M.A.; Casarini, L.; Alcaniz, J. Measuring the Hubble constant with cosmic chronometers: A machine learning approach. Eur. Phys. J. 2023, 83, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Nong, X.; Wang, G.; Wu, P.; Liang, N. Model-independent gamma-ray bursts constraints on cosmological models using machine learning. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2025, 370, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolnic, D.; Brout, D.; Carr, A.; Riess, A.G.; Davis, T.M.; Dwomoh, A.; Jones, D.O.; Ali, N.; Charvu, P.; Chen, R.; et al. The Pantheon+ Analysis: The Full Data Set and Light-curve Release. Astrophys. J. 2022, 938, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Zhang, T.J.; He, P.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J. Estimating Cosmological Parameters and Reconstructing Hubble Constant with Artificial Neural Networks: A Test with covariance matrix and mock H(z). arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.08369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dialektopoulos, K.; Said, J.L.; Mifsud, J.; Sultana, J.; Adami, K.Z. Neural network reconstruction of late-time cosmology and null tests. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2022, 2, 023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Valentino, E.; Levi Said, J.; Riess, A.; Pollo, A.; Poulin, V.; Gómez-Valent, A.; Weltman, A.; Palmese, A.; Huang, C.; van de Bruck, C.; et al. The CosmoVerse White Paper: Addressing observational tensions in cosmology with systematics and fundamental physics. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2405.19953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-Rivera, C.; Quintero, M.A.C.; Capozziello, S. A deep learning approach to cosmological dark energy models. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2020, 3, 008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Vargas, I.; Medel-Esquivel, R.; García-Salcedo, R.; Vázquez, J.A. Neural network reconstructions for the Hubble parameter, growth rate and distance modulus. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; He, P.; Zhang, T.-J. Constraining the Hubble Constant with a Simulated Full Covariance Matrix Using Neural Networks. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.11443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-J.; Ma, X.-J.; Li, S.-Y.; Xia, J.-Q. Reconstructing Functions and Estimating Parameters with Artificial Neural Networks: A Test with a Hubble Parameter and SNe Ia. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2020, 246, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Hu, Y.; Jiao, K.; Wang, H.F.; Xie, Y.B.; Yu, B.; Zhao, L.L.; Zhang, T.J. A Nonparametric Reconstruction of the Hubble Parameter H(z) Based on Radial Basis Function Neural Networks. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2024, 270, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Saha, S.; Mukherjee, P.; Garain, U.; Pal, S. LADDER: Revisiting the Cosmic Distance Ladder with Deep Learning Approaches and Exploring Its Applications. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2024, 273, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Dainotti, M.; Dialektopoulos, K.F.; Said, J.L.; Mifsud, J. Model-independent calibration of Gamma-Ray Bursts with neural networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.03773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainotti, M.G.; Cardone, V.F.; Capozziello, S. A time-luminosity correlation for γ-ray bursts in the X-rays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, L79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainotti, M.G.; Postnikov, S.; Hernandez, X.; Ostrowski, M. A Fundamental Plane for Long Gamma-Ray Bursts with X-Ray Plateaus. Astrophys. J. 2016, 825, L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Luo, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Liang, N. Gamma-ray bursts calibrated from the observational H(z) data in artificial neural network framework. J. High Energy Astrophys. 2025, 47, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Ratra, B. Testing the standardizability of, and deriving cosmological constraints from, a new Amati-correlated gamma-ray burst data compilation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 10, 093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.D.; Hu, J.P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, B.B.; Wang, F.Y. E iso-Ep correlation of gamma-ray bursts: Calibration and cosmological applications. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 516, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-Rivera, C.; Carvajal, M.; Zamora, C.; Hendry, M. Neural networks and standard cosmography with newly calibrated high redshift GRB observations. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2022, 4, 016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Li, X.; Lin, H.-N.; Liu, L. Model-independently Calibrating the Luminosity Correlations of Gamma-Ray Bursts Using Deep Learning. Astrophys. J. 2021, 907, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lin, H.-N.; Li, X.; Liu, L. Reconstructing the Hubble diagram of gamma-ray bursts using deep learning. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 509, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, Y.; Ghahramani, Z. Dropout as a Bayesian Approximation: Representing Model Uncertainty in Deep Learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1506.02142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, Y.; Ghahramani, Z. Dropout as a Bayesian Approximation: Appendix. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1506.02157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overftting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Nong, X.; Liang, N.; Wu, P. Constraints on cosmological models from quasars calibrated with type Ia supernova by a Gaussian process. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 530, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman-Mackey, D.; Hogg, D.W.; Lang, D.; Goodman, J. emcee: The MCMC Hammer. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2013, 125, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichart, D.E. Dust Extinction Curves and Lyα Forest Flux Deficits for Use in Modeling Gamma-Ray Burst Afterglows and All Other Extragalactic Point Sources. Astrophys. J. 2001, 553, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, L.; Della Valle, M. Measuring Cosmological Parameters with Gamma Ray Bursts. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 2013, 22, 1330028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liang, N. Testing dark energy models with gamma-ray bursts calibrated from the observational H(z) data through a Gaussian process. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 521, 4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demianski, M.; Piedipalumbo, E.; Sawant, D.; Amati, L. Prospects of high redshift constraints on dark energy models with the Ep,i-Eiso correlation in long gamma ray bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 506, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Rani, N.; Jain, D.; Mahajan, S.; Mukherjee, A. Gamma rays bursts: A viable cosmological probe? J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2023, 07, 021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.N.; Li, X.; Chang, Z. Model-independent distance calibration of high-redshift gamma-ray bursts and constrain on the ΛCDM model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 455, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-J.; Wei, J.-J.; Li, Z.-X.; Xia, J.-Q.; Zhu, Z.-H. Model-independent Constraints on Cosmic Curvature and Opacity. Astrophys. J. 2017, 847, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, M.; Polarski, D. Accelerating Universes with Scaling Dark Matter. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2001, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.V. Exploring the Expansion History of the Universe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 091301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Cimatti, A.; Jimenez, R.; Pozzetti, L.; Zamorani, G.; Bolzonella, M.; Dunlop, J.; Lamareille, F.; Mignoli, M.; Pearce, H.; et al. Improved constraints on the expansion rate of the Universe up to z ~1.1 from the spectroscopic evolution of cosmic chronometers. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M. Raising the bar: New constraints on the Hubble parameter with cosmic chronometers at z ~2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Pozzetti, L.; Cimatti, A.; Jimenez, R.; Maraston, C.; Verde, L.; Thomas, D.; Citro, A.; Tojeiro, R.; Wilkinson, D. A 6% measurement of the Hubble parameter at z~0.45: Direct evidence of the epoch of cosmic re-acceleration. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 2016, 014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratsimbazafy, A.L.; Loubser, S.I.; Crawford, S.M.; Cress, C.M.; Bassett, B.A.; Nichol, R.C.; Väisänen, P. Age-dating luminous red galaxies observed with the Southern African Large Telescope. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D.; Jimenez, R.; Verde, L.; Kamionkowski, M.; Starford, S.A. Cosmic chronometers: Constraining the equation of state of dark energy. I: H(z) measurements. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 2010, 008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T.; Sun, Y. Four new observational H(z) data from luminous red galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey data release seven. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 14, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Borghi, N.; Moresco, M.; Zhang, T.-J. New Observational H(z) Data from Full-spectrum Fitting of Cosmic Chronometers in the LEGA-C Survey. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2023, 265, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, N.; Moresco, M.; Cimatti, A. Toward a Better Understanding of Cosmic Chronometers: A New Measurement of H(z) at z∼0.7. Astrophys. J. 2022, 928, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Jimenez, R.; Verde, L.; Cimatti, A.; Pozzetti, L. Setting the Stage for Cosmic Chronometers. II. Impact of Stellar Population Synthesis Models Systematics and Full Covariance Matrix. Astrophys. J. 2020, 898, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghanim, N.; Akrami, Y.; Arroja, F.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; et al. Planck 2018 results. I. Overview and the cosmological legacy of Planck. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titarchuk, L.; Farinelli, R.; Frontera, F.; Amati, L. An Upscattering Spectral Formation Model for the Prompt Emission of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2012, 752, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, F.; Amati, L.; Guidorzi, C.; Landi, R.; in’t Zand, J. Broadband Time-resolved E p,i-L iso Correlation in Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2012, 754, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Ratra, B. Testing the consistency of new Amati-correlated gamma-ray burst dataset cosmological constraints with those from better-established cosmological data. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.08429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).