On the Role of Abrupt Solar Wind Pressure Changes in Forbidden Energetic Electron Enhancements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Data
2.1. Data
2.2. A Catalog of FEE Events
2.3. Case Selection Criteria for FEE and Solar Wind Coupling Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Case on 31 March 2001
3.2. Case on 9 November 2004
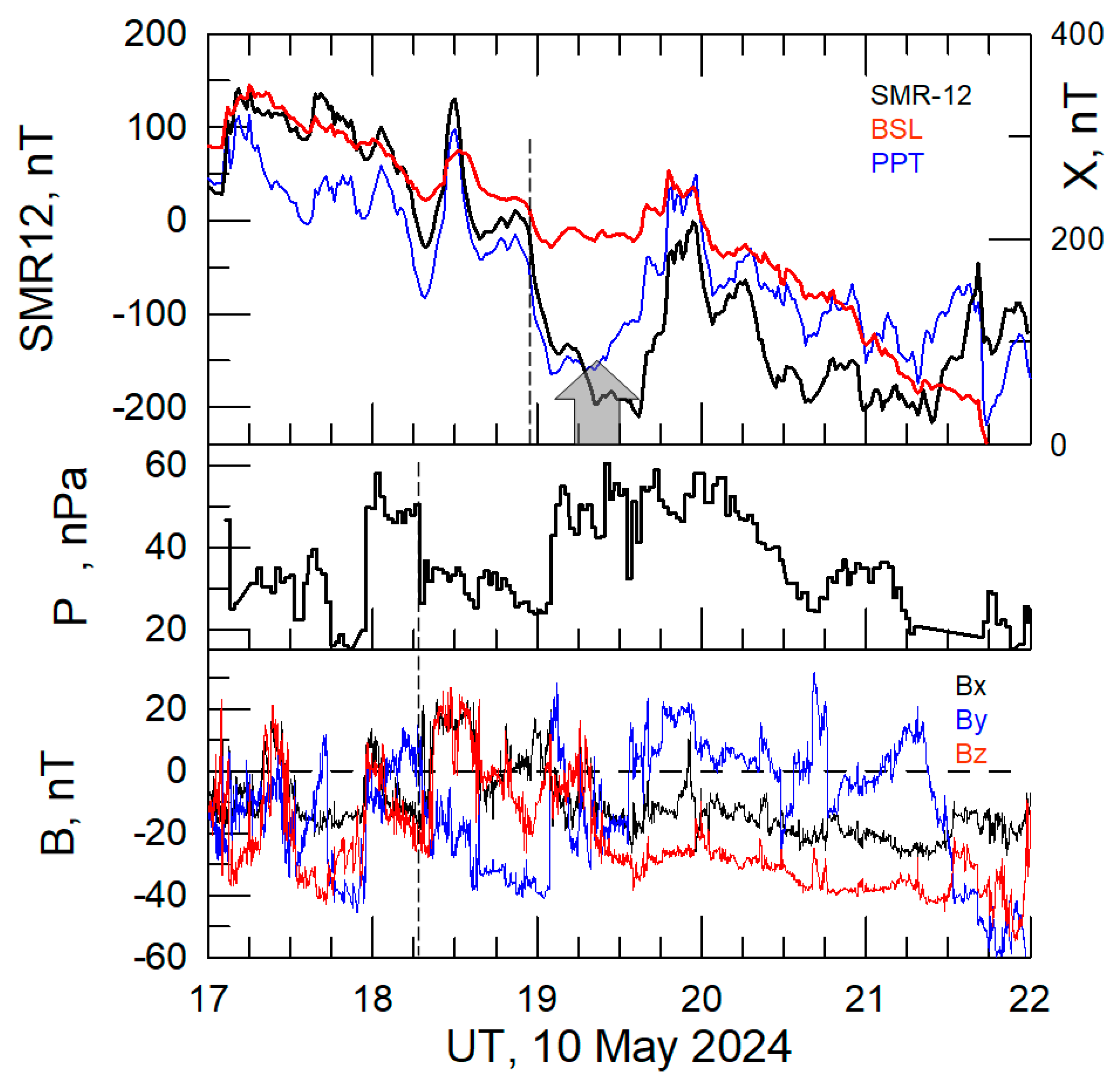
3.3. Case on 10 May 2024
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The occurrence of the FEE increases does not show any preference for any phase (early/maximum in main and recovery phases) of the super storms that confirms the results of previous studies.
- No FEE enhancements were observed during SSC/SI of the super storms.
- The FEE enhancement in each super storm was found to be associated with the abrupt change of the solar wind pressure.
- It was revealed that the sign of the solar wind pressure jump determines the local time sector in which injections can occur: the nighttime FEE injection is observed under a positive jump, and vice versa.
- The increases in the fluxes of the energetic quasi-trapped electrons occur within 20 min after the impact of a pressure jump.
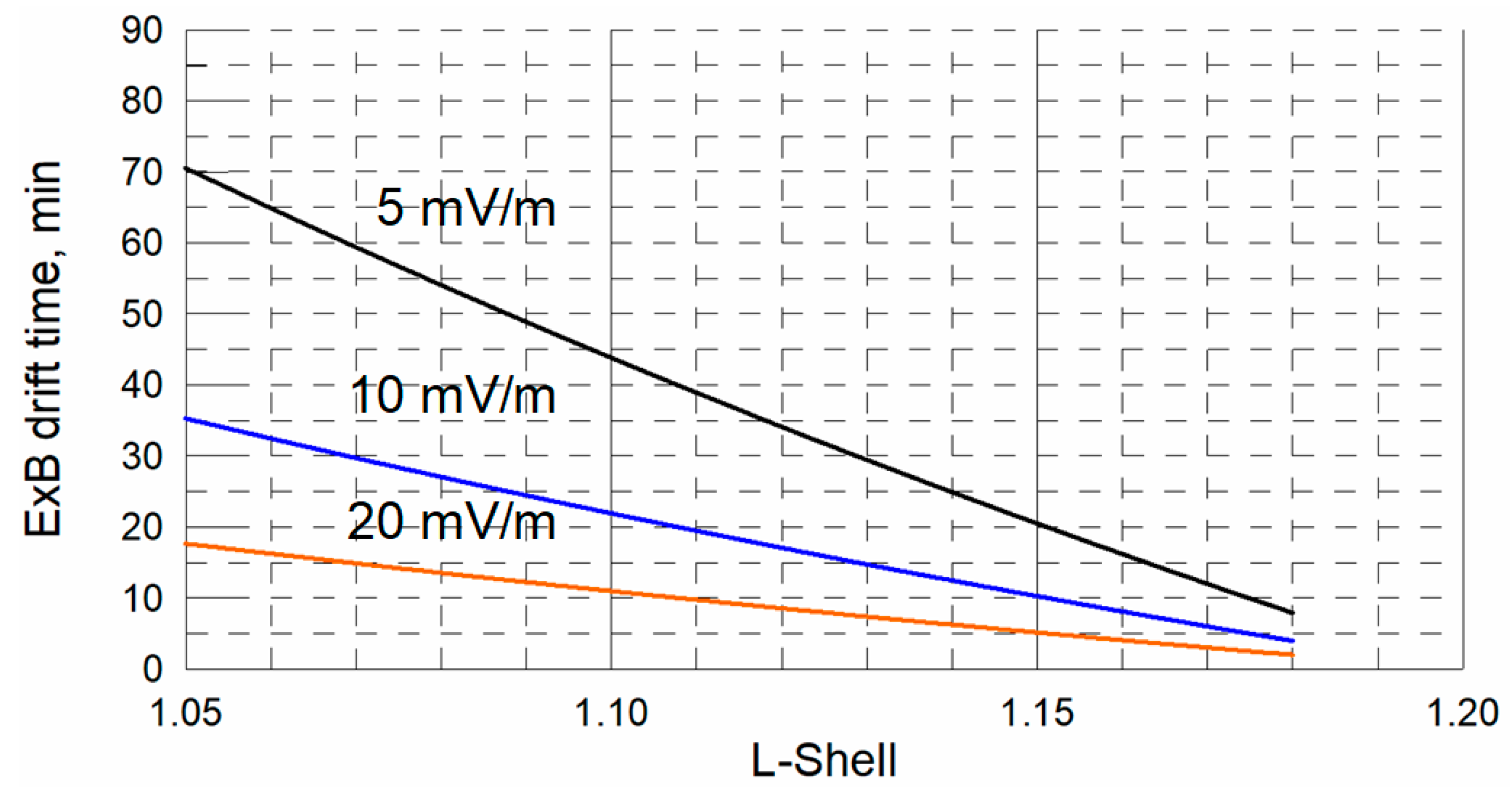
- The results substantiate the conclusion about the action of the electric drift mechanism. The dynamics of FEE injection with a characteristic time of ~20 min is required for an electric field of about 10 mV/m in order to move electrons from the L-shell 1.2 to 1.1. The nature of the electric field is rather inductive (transient), because a sharp pressure jump causes a geomagnetic field to change rapidly over time, and IMF conditions for penetration of the enhanced large-scale convection field are inconsistent with either daytime or nighttime first injections.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suvorova, A.V.; Tsai, L.C.; Dmitriev, A.V. On relation between mid-latitude ionospheric ionization and quasi-trapped energetic electrons during 15 December 2006 magnetic storm. Planet. Space Sci. 2012, 60, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Tsai, L.C.; Kunitsyn, V.E.; Andreeva, E.S.; Nesterov, I.A.; Lazutin, L.L. TEC evidence for near-equatorial energy deposition by 30 keV electrons in the topside ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 4672–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.V. Radiation aspects of geomagnetic storm impact below the radiation belt. In Cyclonic and Geomagnetic Storms: Predicting Factors, Formation and Environmental Impacts; Banks, V.P., Ed.; NOVA Science Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 19–76. [Google Scholar]
- Suvorova, A.V. Solar-cycle variations of forbidden energetic electrons enhancements. Universe 2023, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.V. Conditions for the occurrence of intense fluxes of energetic electrons at L < 1.2 associated with solar activity and solar wind parameters. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2024, 10, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, A.V. Flux enhancements of >30 keV electrons at low drift shells L < 1.2 during last solar cycles. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 12274–12287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, A.V.; Huang, C.M.; Matsumoto, H.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Kunitsyn, V.E.; Andreeva, E.S.; Nesterov, I.A.; Tsai, L.-C. Low-latitude ionospheric effects of energetic electrons during a recurrent magnetic storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 9283–9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Parkhomov, V.A. Energetic electron enhancements under the radiation belt (L < 1.2) during a non-storm interval on 1 August 2008. Ann. Geophys. 2019, 37, 1223–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cladis, J.B. Resonance acceleration of particles in the inner radiation belt. In Radiation Trapped in the Earth’s Magnetic Field; McCormac, B.M., Ed.; D. Reidel: Hingham, MA, USA, 1966; p. 112. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, O.; Pinto, R.C.A.; Gonzalez, W.D.; Gonzalez, A.L.C. About the origin of peaks in the spectrum of inner belt electrons. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudela, K.; Matisin, J.; Shuiskaya, F.K.; Akentieva, O.S.; Romantsova, T.V.; Venkatesan, D. Inner zone electron peaks observed by the “Active” satellite. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 8681–8683. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, T.; Evans, D.S. Energetic electrons observed by NOAA-6 over Japan (L = 1.3) at the time of geomagnetic storm on February 8–9, 1986. In Proceedings of Research Institute of Atmospheric; Nagoya University: Nagoya, Japan, 1989; Volume 36, pp. 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y.; Nishino, M.; Iwata, A. Magnetic storm-related energetic electrons and magnetospheric electric fields penetrating into the low-latitude magnetosphere (L ~ 1.5). Planet. Space Sci. 1990, 38, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Tadokoro, H.; Tsuchiya, F.; Miyoshi, Y.; Misawa, H.; Morioka, A.; Evans, D.S. Electron flux enhancement in the inner radiation belt during moderate magnetic storms. Ann. Geophys. 2007, 25, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.-J.; Selesnick, R.S.; Blake, J.B. Formation of the inner electron radiation belt by enhanced large-scale electric fields. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 8508–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selesnick, R.S.; Su, Y.-J.; Blake, J.B. Control of the innermost electron radiation belt by large-scale electric fields. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 8417–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selesnick, R.S.; Su, Y.-J.; Sauvaud, J.-A. Energetic electrons below the inner radiation belt. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 5421–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, L.R.; Williams, D.J. Quantitative Aspects of Magnetospheric Physics; D. Reidel Pub. Co.: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C.; Fejer, B.G.; Gonzales, C.A. An explanation for anomalous equatorial ionospheric electric fields associated with a northward turning of the interplanetary magnetic field. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1979, 6, 301–304. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, D.E.; Wygant, J.R. Dependence of the large-scale, inner magnetospheric electric field on geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1998, 103, 14959–14964. [Google Scholar]
- Maynard, N.C.; Aggson, T.L.; Heppner, J.P. The plasmaspheric electric field as measured by ISEE 1. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 3681–3990. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, T.; Hashimoto, K.K. Transmission of the electric fields to the low latitude ionosphere in the magnetosphere-ionosphere current circuit. Geosci. Lett. 2016, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-S. Continuous penetration of the interplanetary electric field to the equatorial ionosphere over eight hours during intense geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, A11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, A.; Vichare, G. Characteristics of penetration electric fields to th equatorial ionosphere during southward and northward IMF turnings. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 4696–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.; Vichare, G. Variable responses of equatorial ionosphere during undershielding and overshielding conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 1328–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califf, S.; Li, X.; Blum, L.; Jaynes, A.; Schiller, Q.; Zhao, H.; Malaspina, D.; Hartinger, M.; Wolf, R.A.; Rowland, D.E.; et al. THEMIS measurements of quasi-static electric fields in the inner magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 9939–9951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califf, S.; Li, X.; Wolf, R.A.; Zhao, H.; Jaynes, A.N.; Wilder, F.D.; Malaspina, D.M.; Redmon, R. Large-amplitude electric fields in the inner magnetosphere: Van Allen Probes observations of subauroral polarization streams. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 5294–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califf, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Kellerman, A.; Sarris, T.E.; Jaynes, A.; Malaspina, D.M. The role of the convection electric field in filling the slot region between the inner and outer radiation belts. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 5294–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, H.; Schmidt, R. Pc4-5 pulsations in the electric field at geostationary orbit (GEOS 2) triggered by sudden storm commencements. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 6626–6632. [Google Scholar]
- Wygant, J.; Mozer, F.; Temerin, M.; Blake, J.; Maynard, N.; Singer, H.; Smiddy, M. Large amplitude electric and magnetic field signatures in the inner magnetosphere during injection of 15 MeV electron drift echoes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-H.; Cattell, C.A.; Lee, D.; Takahashi, K.; Yumoto, K.; Shiokawa, K.; Mozer, F.S.; Andre, M. Magnetospheric responses to sudden and quasiperiodic solar wind variations. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozelova, T.V.; Lazutin, L.; Kozelov, B. Energetic particle bursts before the main substorm injection. Adv. Space Res. 2002, 30, 1805–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Shinbori, A.; Nishimura, Y.; Ono, T.; Kumamoto, A.; Oya, H. Electrodynamics in the duskside inner magnetosphere and plasmasphere during a super magnetic storm on March 13–15, 1989. Earth Planets Space 2005, 57, 643–659. [Google Scholar]
- Shinbori, A.; Ono, T.; Iizima, M.; Kumamoto, A.; Nishimura, Y. Enhancements of magnetospheric convection electric field associated with sudden commencements in the inner magnetosphere and plasmasphere regions. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 38, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Shinbori, A.; Ono, T.; Iizima, M.; Kumamoto, A. Storm-time electric field distribution in the inner magnetosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L22102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, R.; Rowland, D.; Freudenreich, H.; Bromund, K.; Le, G.; Acuña, M.; Klenzing, J.; Liebrecht, C.; Martin, S.; Burke, W.J.; et al. Observations of DC electric fields in the low-latitude ionosphere and their variations with local time, longitude, and plasma density during extreme solar minimum. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A12324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, R.; Uribe, P.; Fourre, R.; Kujawski, J.; Maynard, N.; Acuña, M.; Rowland, D.; Freudenreich, H.; Bromund, K.; Martin, S.; et al. The vector electric field investigation (VEFI) on the C/NOFS satellite. Space Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, R.; Daldorff, L.K.S.; Liemohn, M.W.; Toth, G.; Chan, A.A. Calculating the inductive electric field in the terrestrial magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 5391–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ilie, R.; Liemohn, M.W.; Toth, G. The role of inductive electric fields shaping the morphology, asymmetry, and energy content of the storm-ring current. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2025, 130, 5391–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.S.; Greer, M.S. Polar Orbiting Environmental Satellite Space Environment Monitor: 2. Instrument Descriptions and Archive Data Documentation; Technical Report; Space Environment Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dmitriev, A.V.; Suvorova, A.V.; Veselovsky, I.S. Statistical characteristics of the heliospheric plasma and magnetic field at the Earth’s orbit during four solar cycles 20–23. In Handbook on Solar Wind: Effects, Dynamics and Interactions; Johannson, H.E., Ed.; NOVA Science Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 81–144. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, R.K.; McPherron, R.L.; Russell, C.T. An empirical relationship between interplanetary conditions and Dst. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 4204–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, A.; Dmitriev, A.; Chao, J.-K.; Thomsen, M.; Yang, Y.-H. Necessary conditions for the geosynchronous magnetopause crossings. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, A01206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, A.V.; Suvorova, A.V.; Chao, J.-K.; Wang, C.B.; Rastaetter, L.; Panasyuk, M.I.; Lazutin, L.L.; Kovtyukh, A.S.; Veselovsky, I.S.; Myagkova, I.N. Anomalous dynamics of the extremely compressed magnetosphere during 21 January 2005 magnetic storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 877–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, S.; Themens, D.R. The probability of the May 2024 geomagnetic superstorms. Space Weather 2025, 23, e2024SW004113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurutani, B.T.; Kamide, Y.; Arballo, J.; Gonzalez, W.; Lepping, R. Interplanetary causes of great and superintense magnetic storms. Phys. Chem. Earth 1999, 24, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhina, G.S.; Tsurutani, B.T. Geomagnetic storms: Hystorical perspective to modern view. Geosci. Lett. 2016, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpua, E.; Koskinen, H.E.J.; Pulkkinen, T.I. Coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions in interplanetary space. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2017, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerloev, J.W. The SuperMAG data processing technique. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, A09213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, P.T.; Gjerloev, J.W. SuperMAG-based partial ring current indices. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, A05215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, A.; Chao, J.-K.; Thomsen, M.; Suvorova, A. Geosynchronous magnetopause crossings on 29–31 October 2003. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, A08209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlaga, L.; Sittler, E.; Mariani, F.; Schwenn, R. Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock: Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 6673–6684. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, L.A.; Shi, J.; Alves, L.R.; Resende, L.C.A.; Vieira, L.E.A.; Costa, J.E.R.; Marchezi, J.P.; Agapitov, O.V.; Sibeck, D.G.; dos Santos, A.M.; et al. Space weather effects over SAMA during the extreme geomagnetic storm on May 10–11, 2024: Disturbances of the neutral and ionized atmosphere. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2025, 12, 1550635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurutani, B.T.; Hajra, R.; Echer, E.; Gjerloev, J.W. Extremely intense (SML ≤ −2500 nT) substorms: Isolated events that are externally triggered? In Annales Geophysicae; Copernicus GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2015; Volume 33, pp. 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, Q.-G.; Yue, C.; Fu, S.-Y. Shock induced strong substorms and super substorms: Preconditions and associated oxygen ion dynamics. Space Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchuk, R.A.; Mishin, V.V.; Penskikh, Y.V.; Klibanova, Y.Y.; Mikhalev, A.V. Geomagnetic disturbances and midlatitude airglow during the 20 December 2015 magnetic storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2025, 130, e2025JA033979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, R.; Tsurutani, B.T.; Lakhina, G.S.; Lu, Q.; Du, A. Interplanetary Causes and Impacts of the 2024 May Superstorm on the Geosphere: An Overview. Astrophys. J. 2024, 974, id264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.S.; Yeh, H.C. Satellite observations of electric fields in the South Atlantic anomaly region during the July 2000 magnetic storm. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, A03305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.A.; Shi, J.; Resende, L.C.A.; Agapitov, O.V.; Alves, L.R.; Batista, I.S.; Arras, C.; Vieira, L.E.; Deggeroni, V.; Marchezi, J.P.; et al. The role of the inner radiation belt dynamic in the generation of auroral-type sporadic E-layers over South American Magnetic Anomaly. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2022, 9, 970308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, J.B.; Kolasinski, W.A.; Fillius, R.W.; Millen, E.G. Injection of electrons and protons with energies of tens of MeV into L < 3 on March 24, 1991. Geopys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 821–824. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Roth, I.; Temerin, M.; Wygant, J.R.; Hudson, M.K.; Blake, J.B. Simulation of the prompt energization and transport of radiation belt particles during the March 24, 1991 SSC. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 2423–2426. [Google Scholar]
- Dmitriev, A.V.; Lin, R.L.; Liu, S.-Q.; Suvorova, A.V. Model prediction of geosynchronous magnetopause crossings. Space Weather 2016, 14, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejosne, S.; Kunduri, B.S.; Mozer, F.S.; Turner, D.L. Energetic electron injections deep into the inner magnetosphere: A result of the subauroral polarization stream (SAPS) potential drop. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3811–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califf, S.; Zhao, H.; Gkioulidou, M.; Manweiler, J.W.; Mitchell, D.G.; Tian, S. Multi-event study on the connection between subauroral polarization streams and deep energetic particle injections in the inner magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2022, 127, e2021JA029895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Lin, D.; Wu, Q. Low-latitude zonal ion drifts and their relationship with subauroral polarization streams and auroral return flows during intense magnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2022, 126, e2021JA030001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
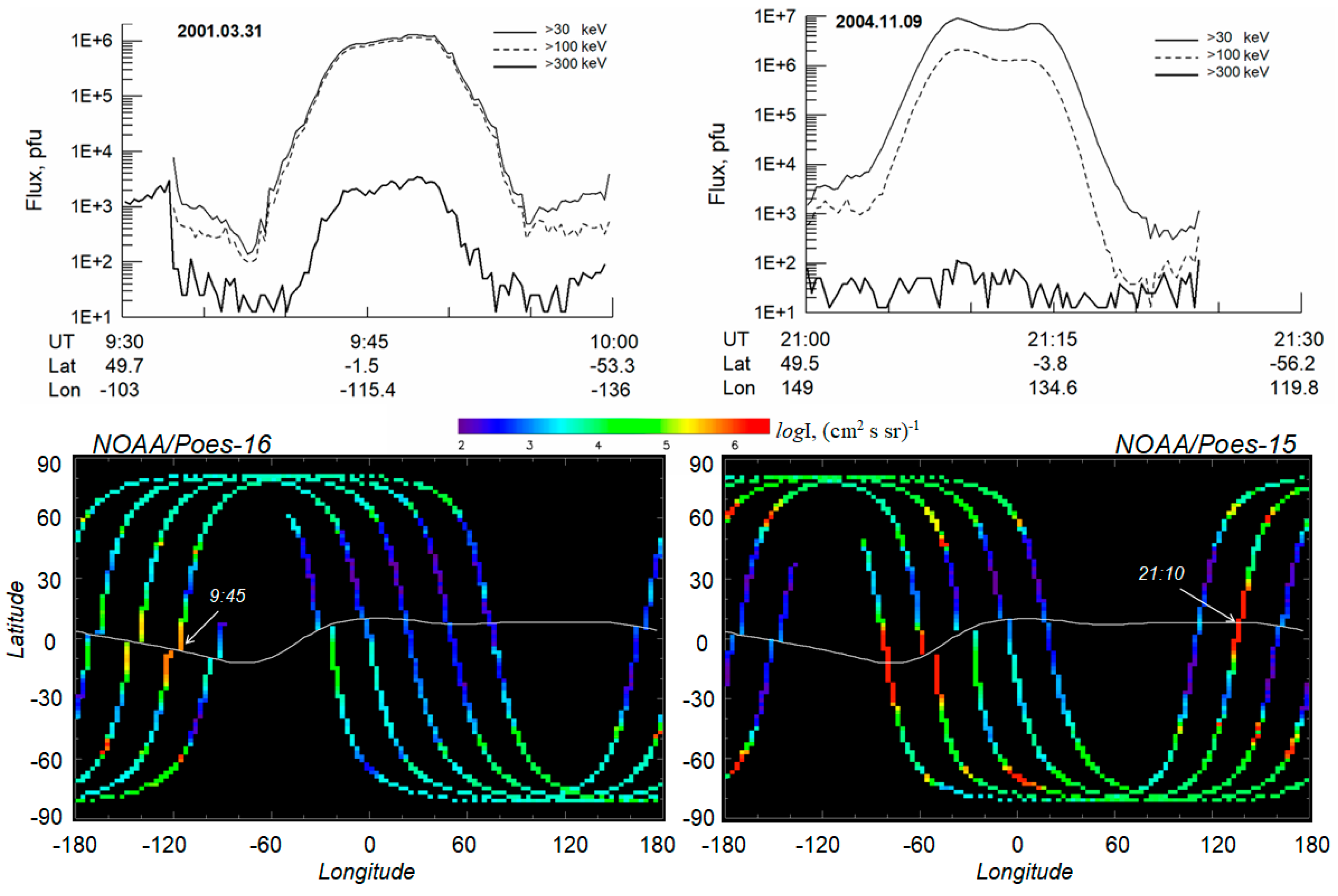
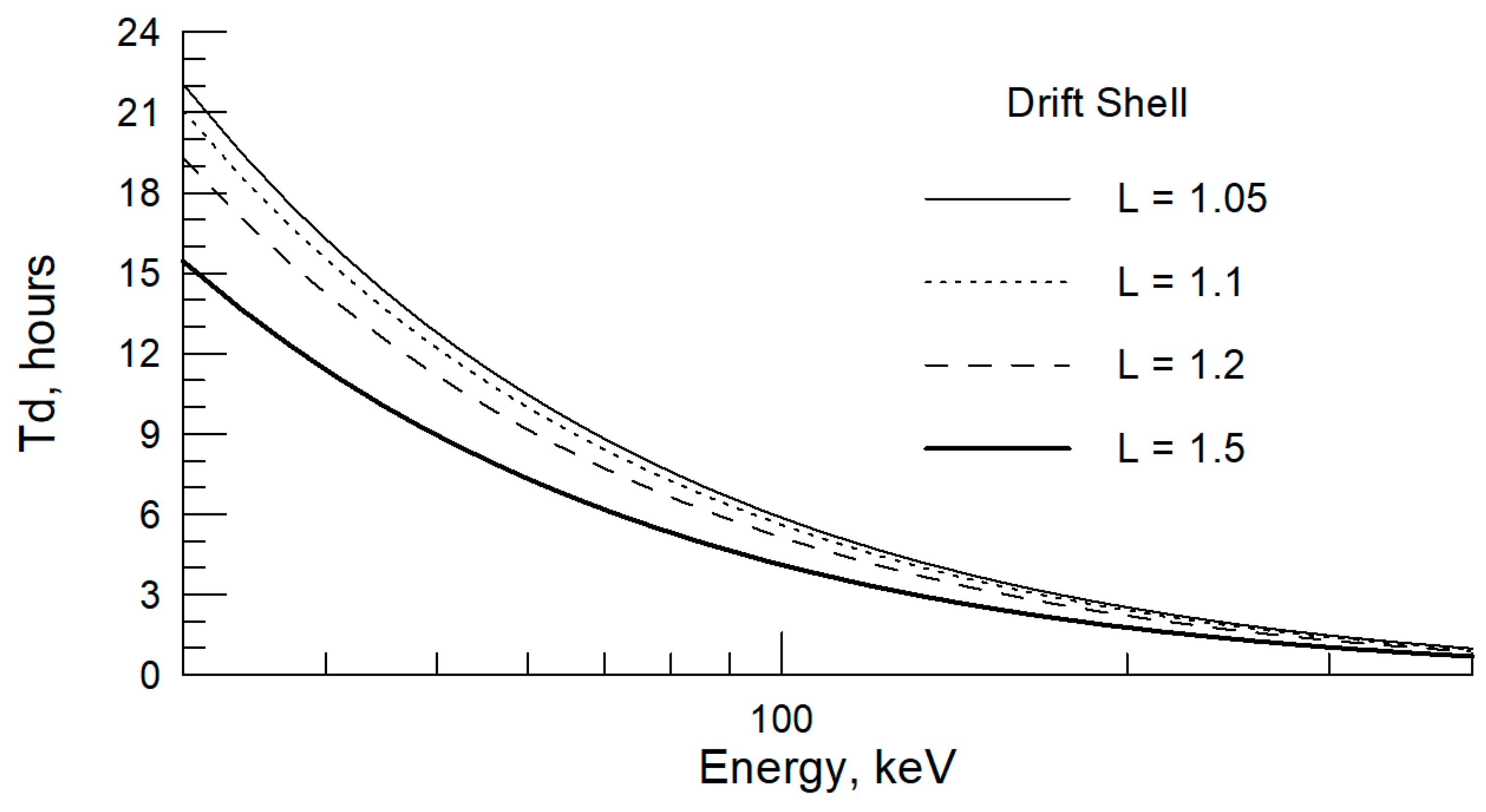
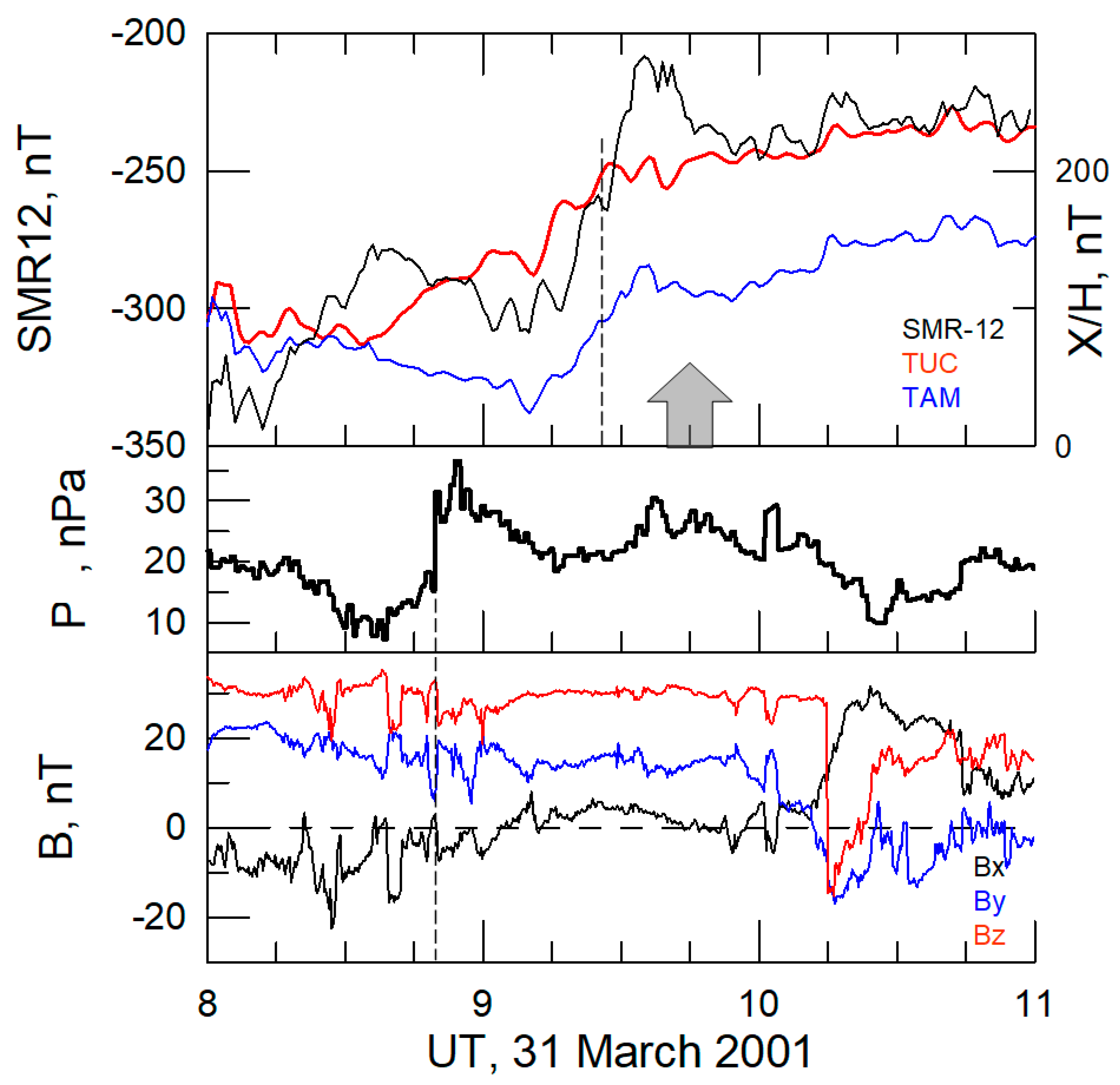
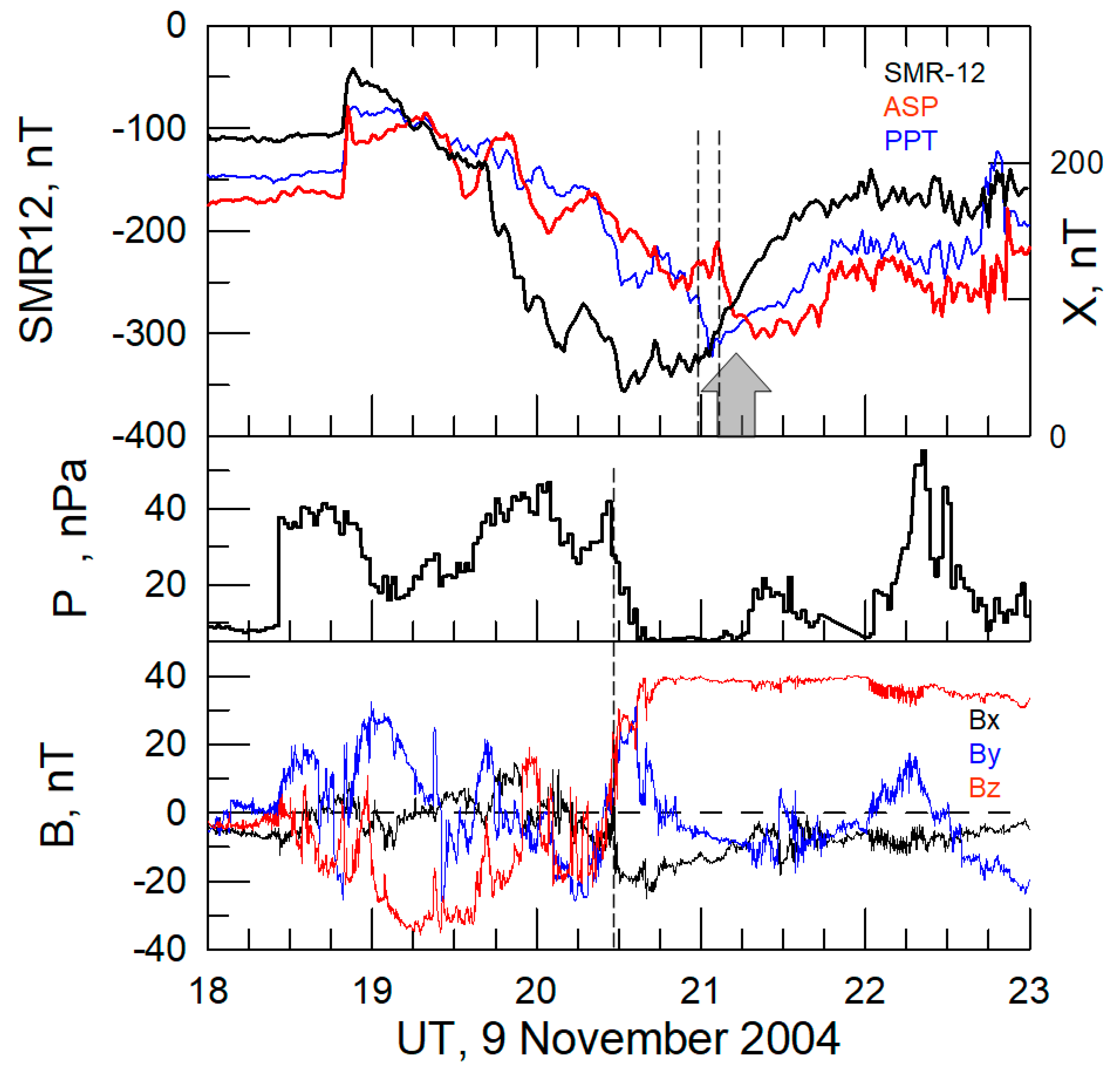
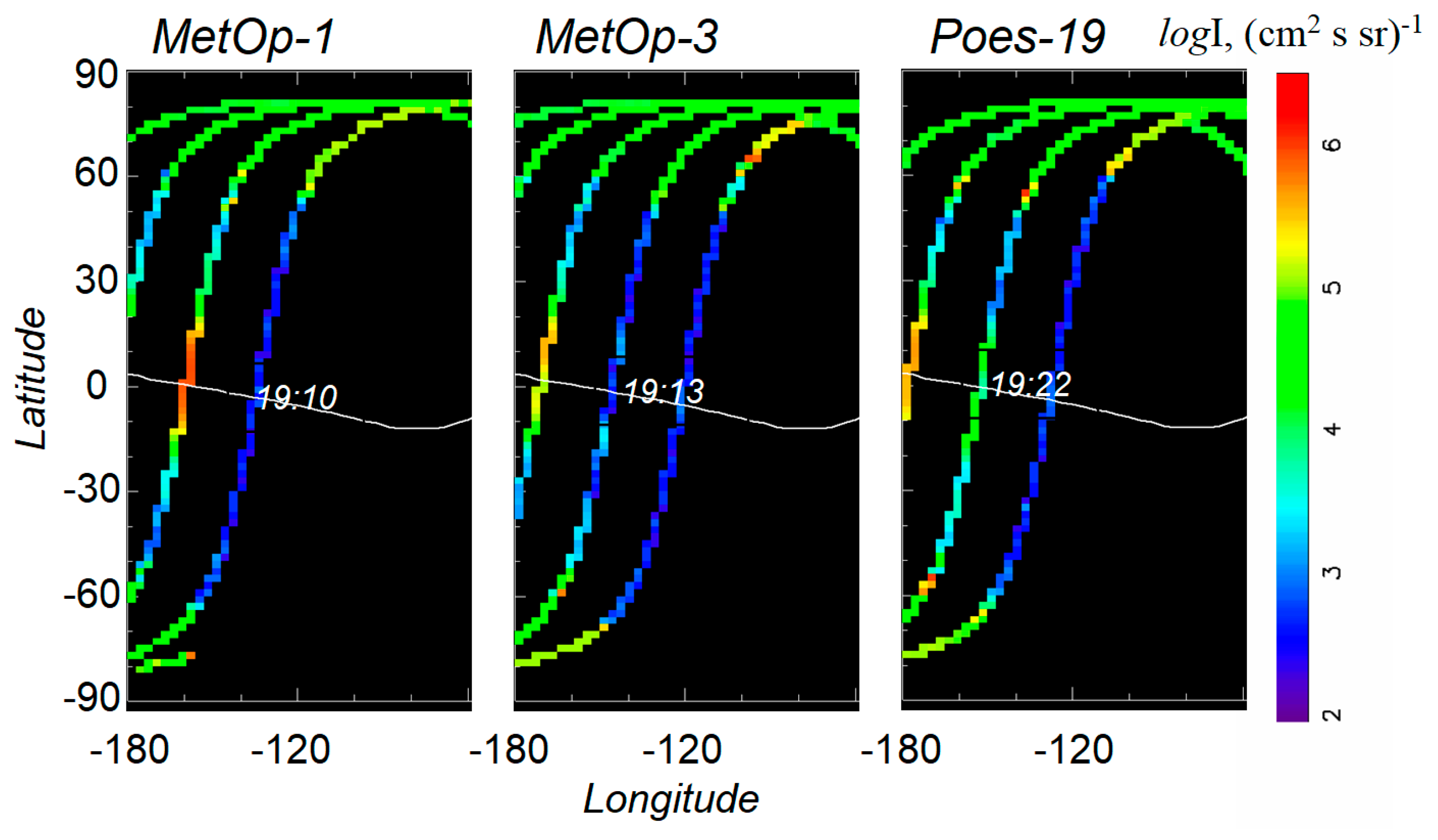
| Sat | LT | Time hh:mm | Longitude φ° | Je >40 keV | Je >130 keV | L-Shell | Comment (ACE or Wind Monitor Time) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31 March 2001 | |||||||
| P6 * | 2 | 09:45 | −120 | 1 × 106 | 1 × 106 | L ~ 1.12 | Δp > 0 (~8:50 UT), magnetic cloud, Bz > 0; early recovery phase |
| 9 November 2004 | |||||||
| P5 | 6 | 21:10 | 137 | 1 × 107 | 2 × 106 | L ~ 1.05 | Δp < 0 (20:30 UT), magnetic cloud, Bz northward turning; storm maximum |
| 10 May 2024 | |||||||
| P9 | 9 | 19:22 | −153 | 7 × 104 | 5 × 104 | L ~ 1.11 | Δp < 0 (~19:00 UT), interplanetary sheath, Bz > 0; storm main phase |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suvorova, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.V. On the Role of Abrupt Solar Wind Pressure Changes in Forbidden Energetic Electron Enhancements. Universe 2025, 11, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070226
Suvorova AV, Dmitriev AV. On the Role of Abrupt Solar Wind Pressure Changes in Forbidden Energetic Electron Enhancements. Universe. 2025; 11(7):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070226
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuvorova, Alla V., and Alexei V. Dmitriev. 2025. "On the Role of Abrupt Solar Wind Pressure Changes in Forbidden Energetic Electron Enhancements" Universe 11, no. 7: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070226
APA StyleSuvorova, A. V., & Dmitriev, A. V. (2025). On the Role of Abrupt Solar Wind Pressure Changes in Forbidden Energetic Electron Enhancements. Universe, 11(7), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070226







