Non-Canonical Dark Energy Parameter Evolution in a Canonical Quintessence Cosmology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Flat Minimally Coupled Quintessence
3. The Mathematical Properties of the LHQ Universe
3.1. Friedmann Constraints
3.2. Mathematical Properties, Equations, and Functions
3.2.1. The Dark Energy Scalar Constants and Current Values
3.2.2. The Time Derivative of the Scalar
3.2.3. The HI Potential Constants and M
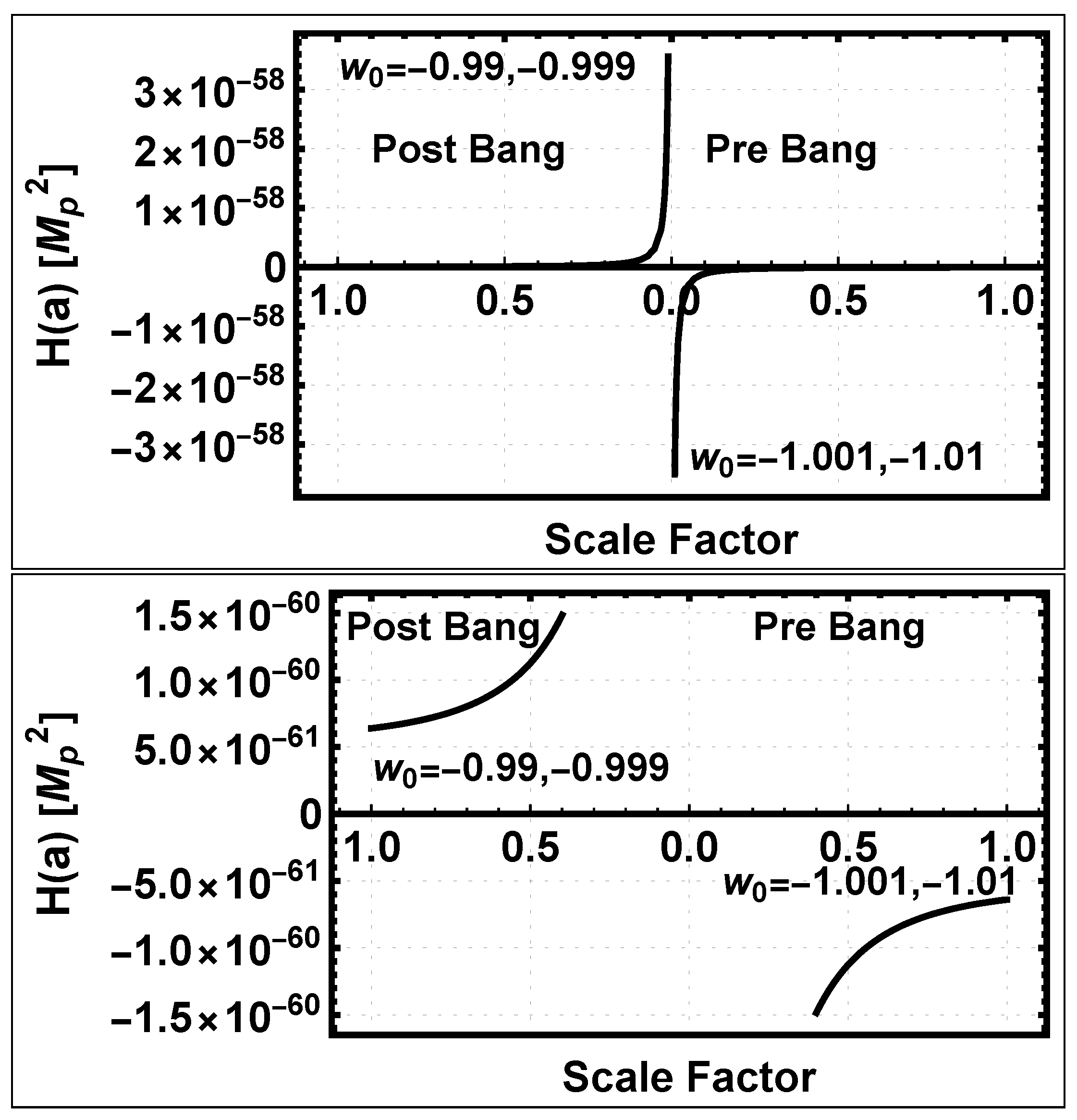
3.2.4. The Hubble Parameter
3.2.5. The Time Derivative of the Hubble Parameter
3.2.6. The Kinetic Term X
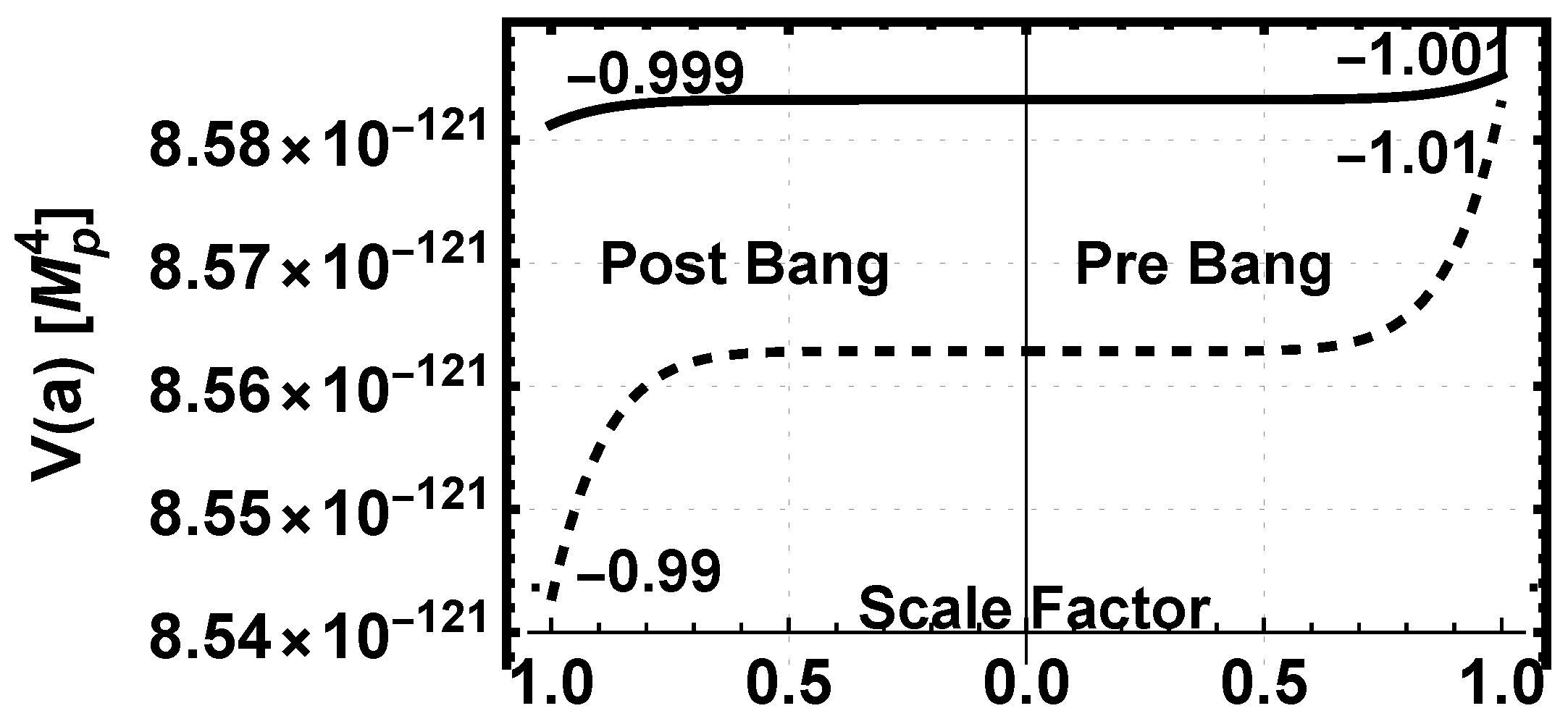
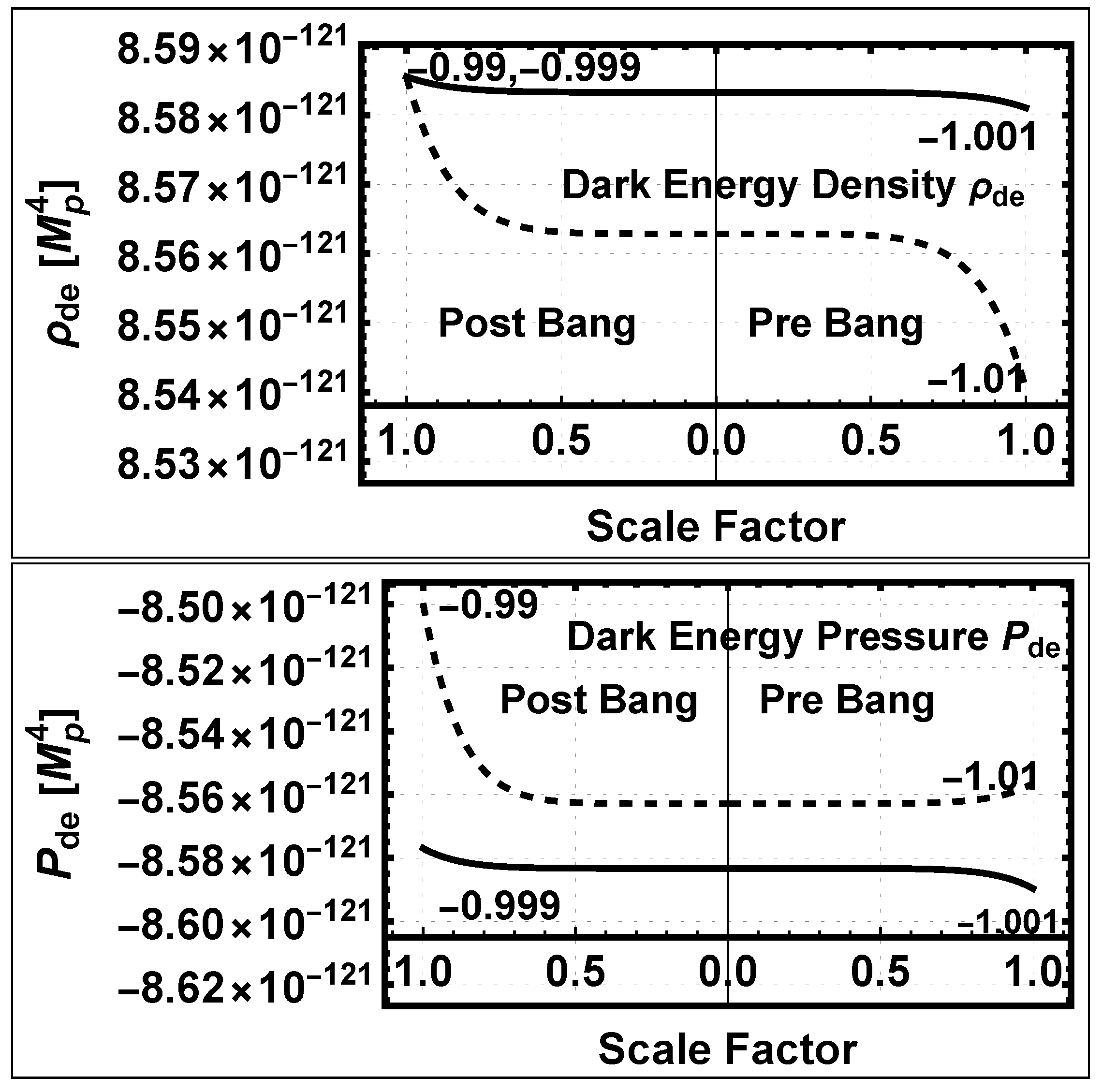
3.2.7. The Dark Energy Density and Pressure
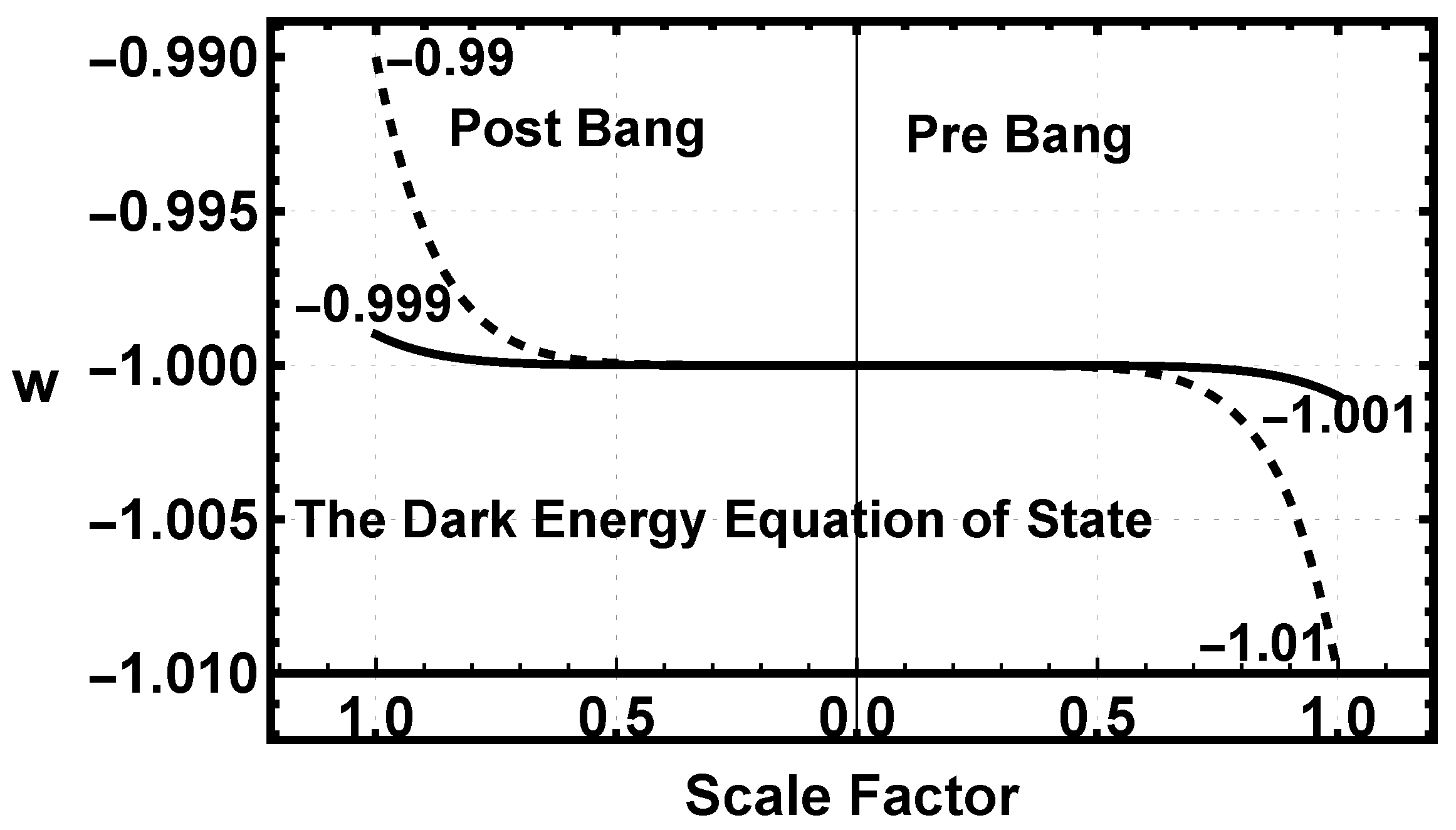
3.2.8. The Dark Energy Equation of State
4. Boundary Conditions
5. The Physical Properties of the LHQ Universe
5.1. The Physical Properties of the Pre-Bang Epoch
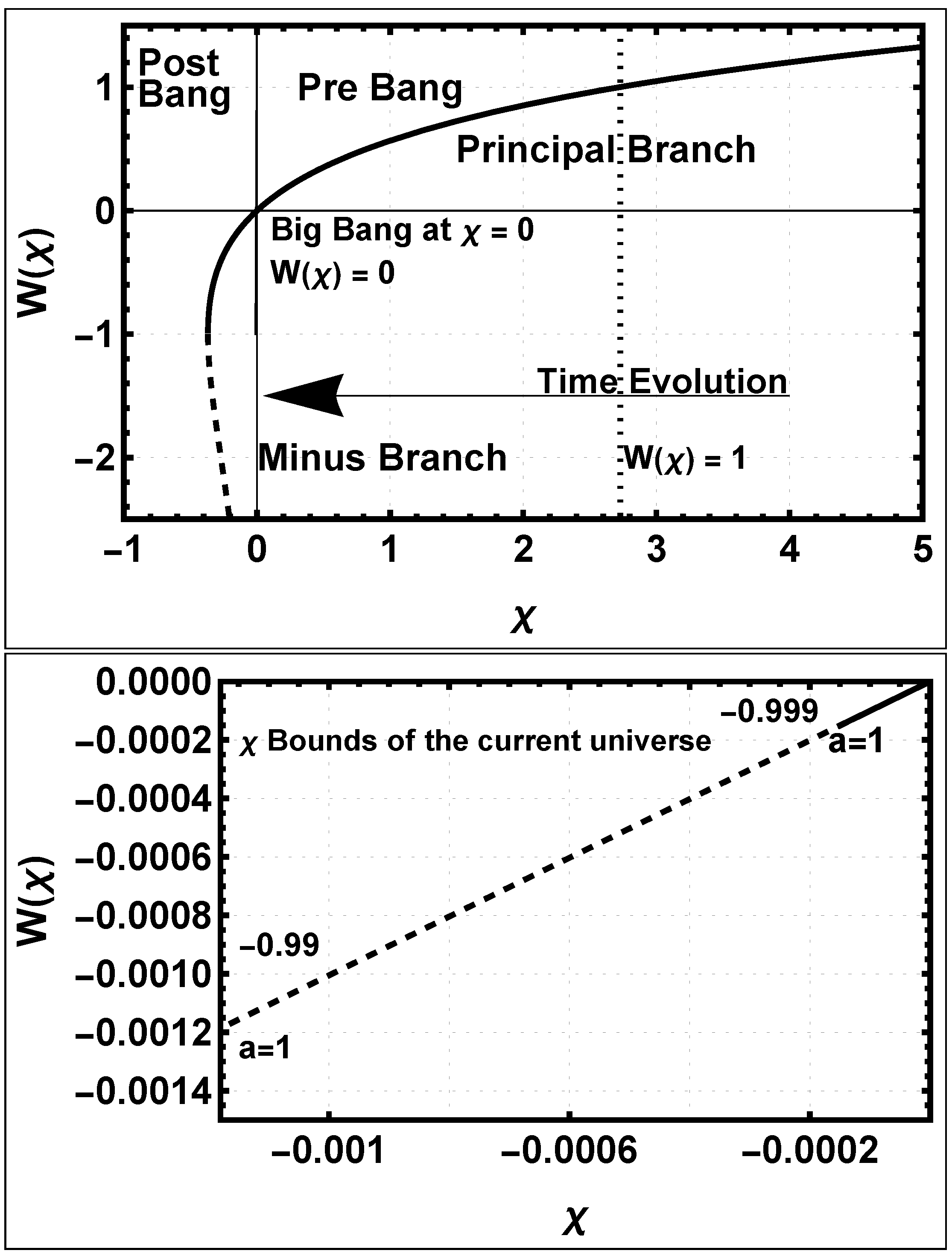
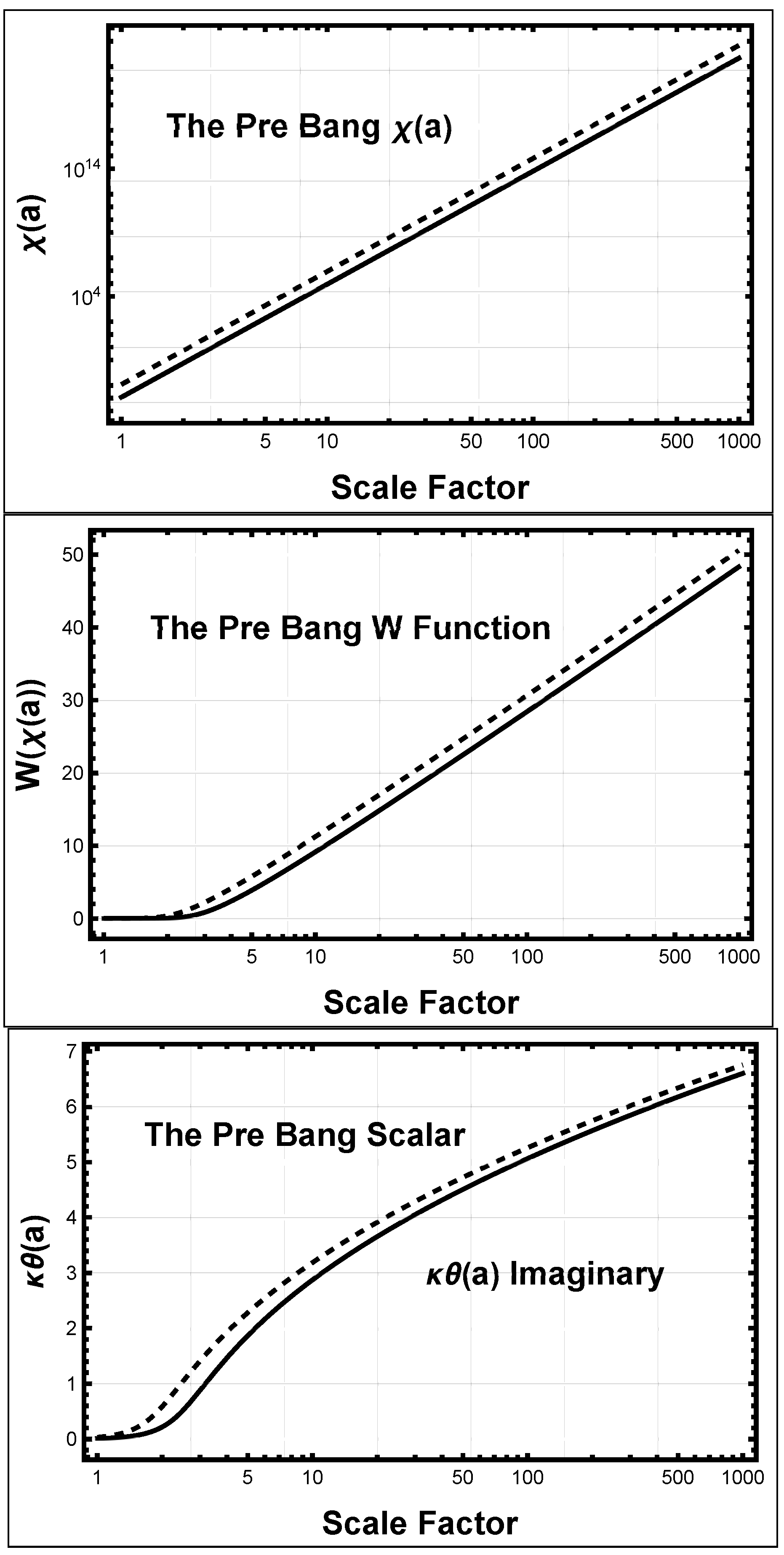
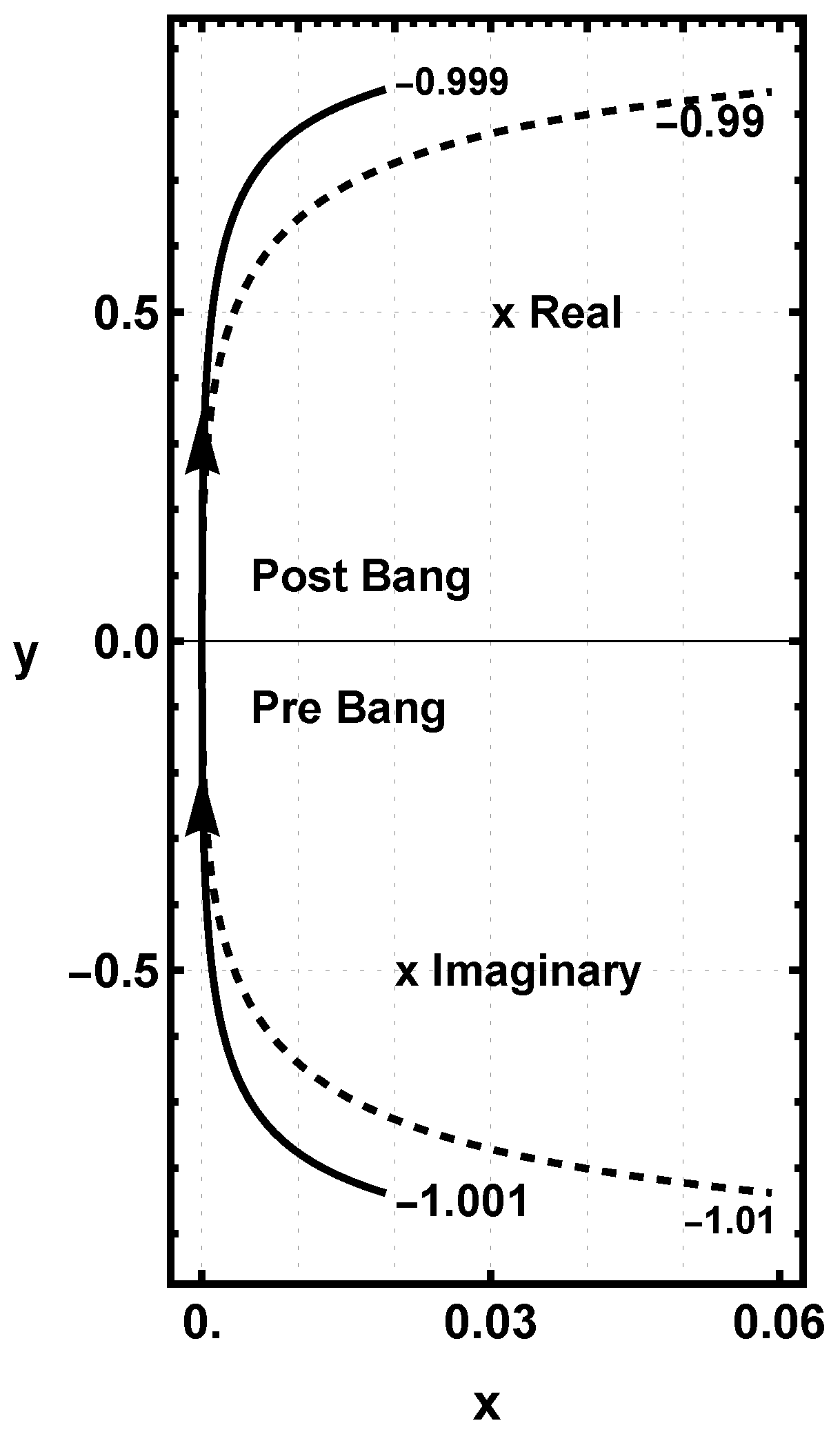
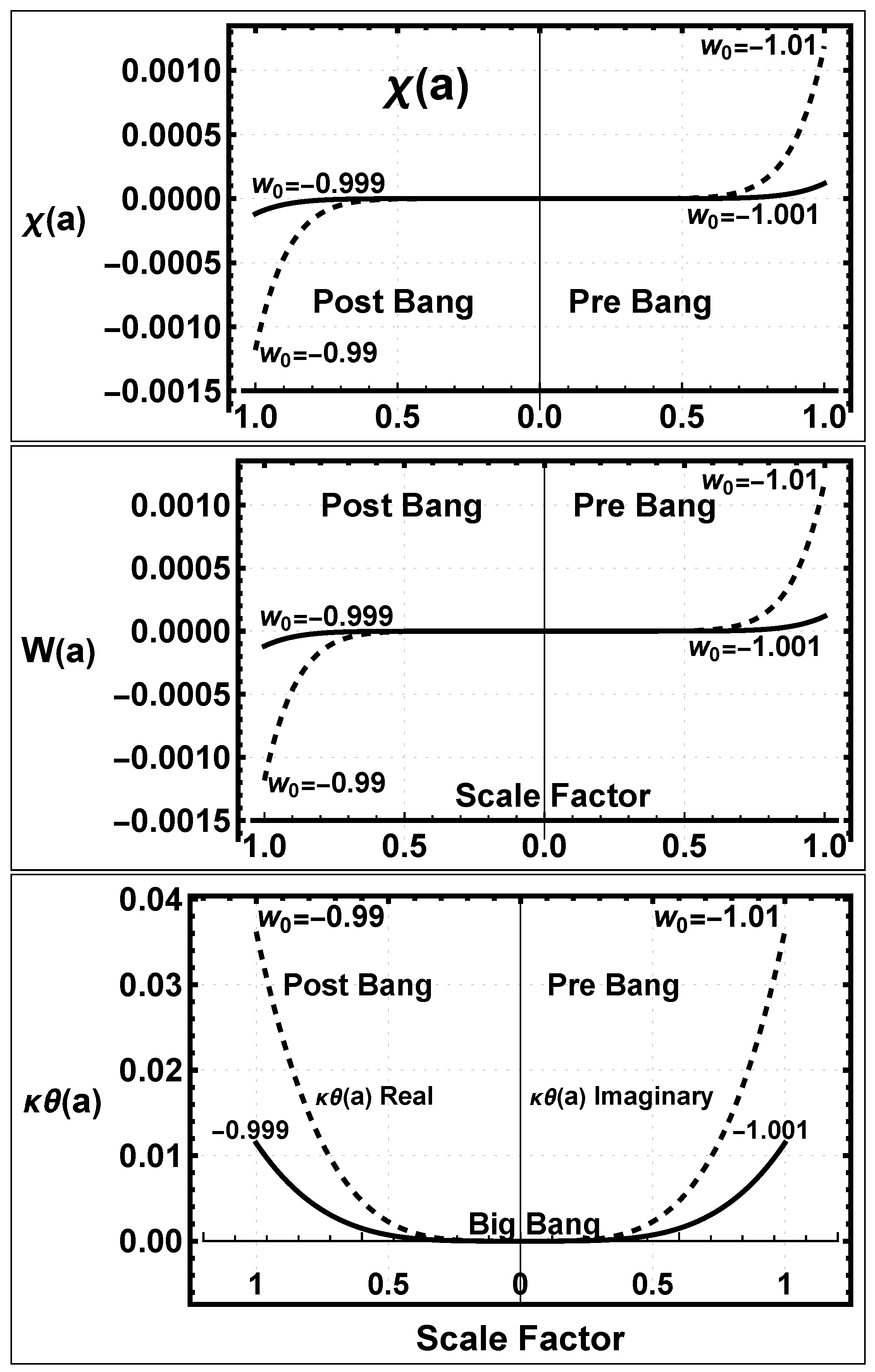
5.1.1. Chi, the W Function, and the Scalar
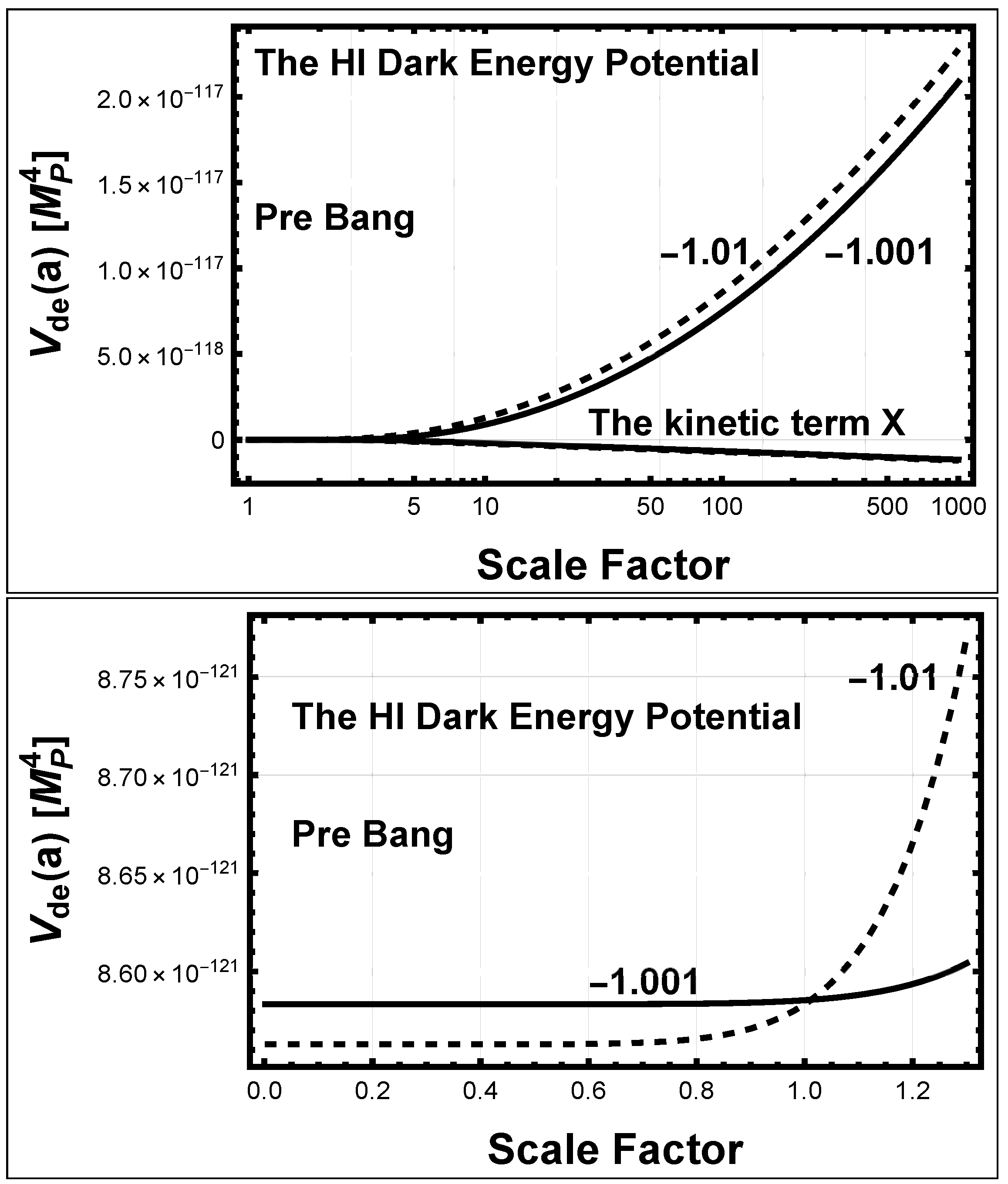
5.1.2. The HI Potential
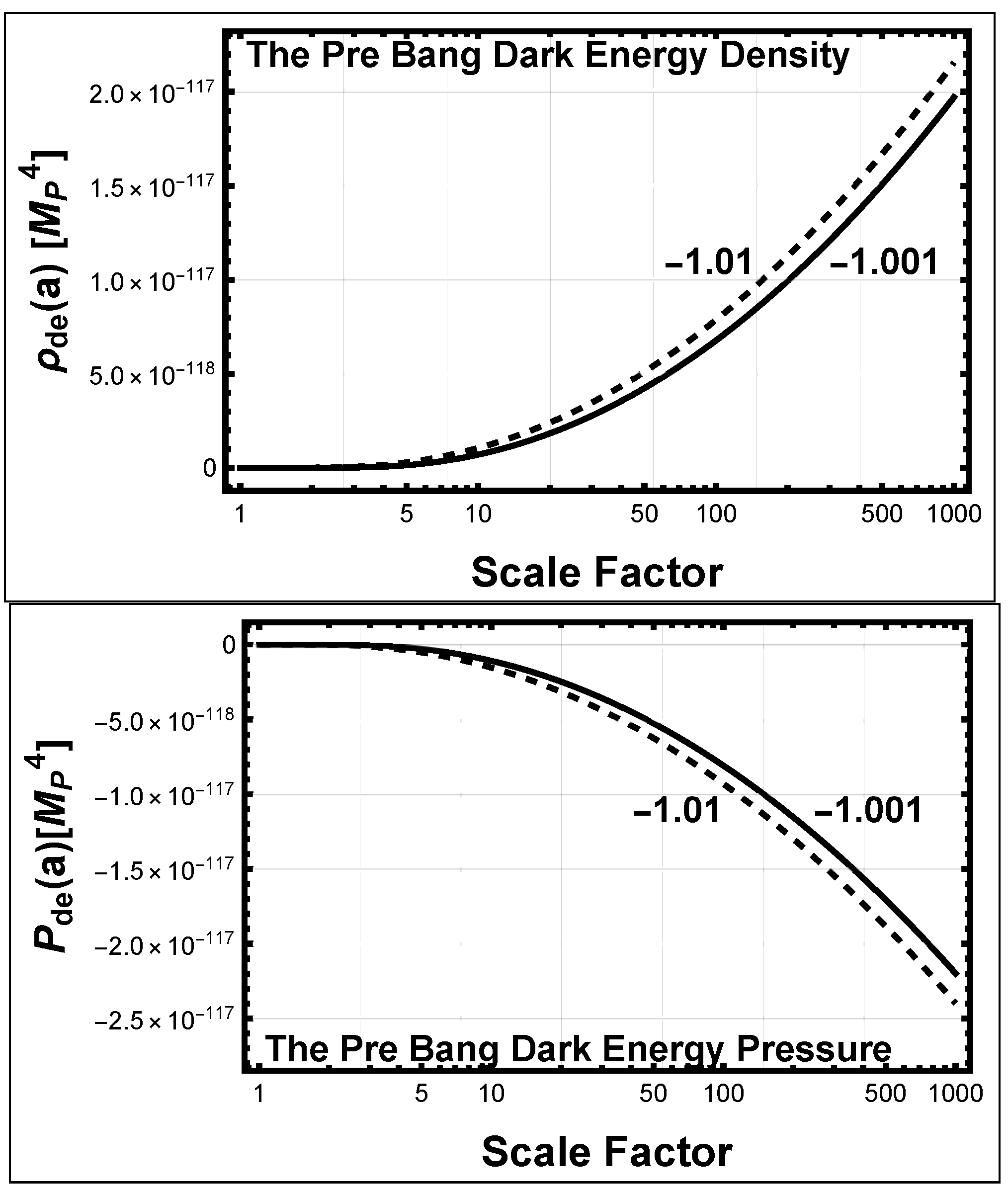
5.1.3. The Dark Energy Density and Pressure
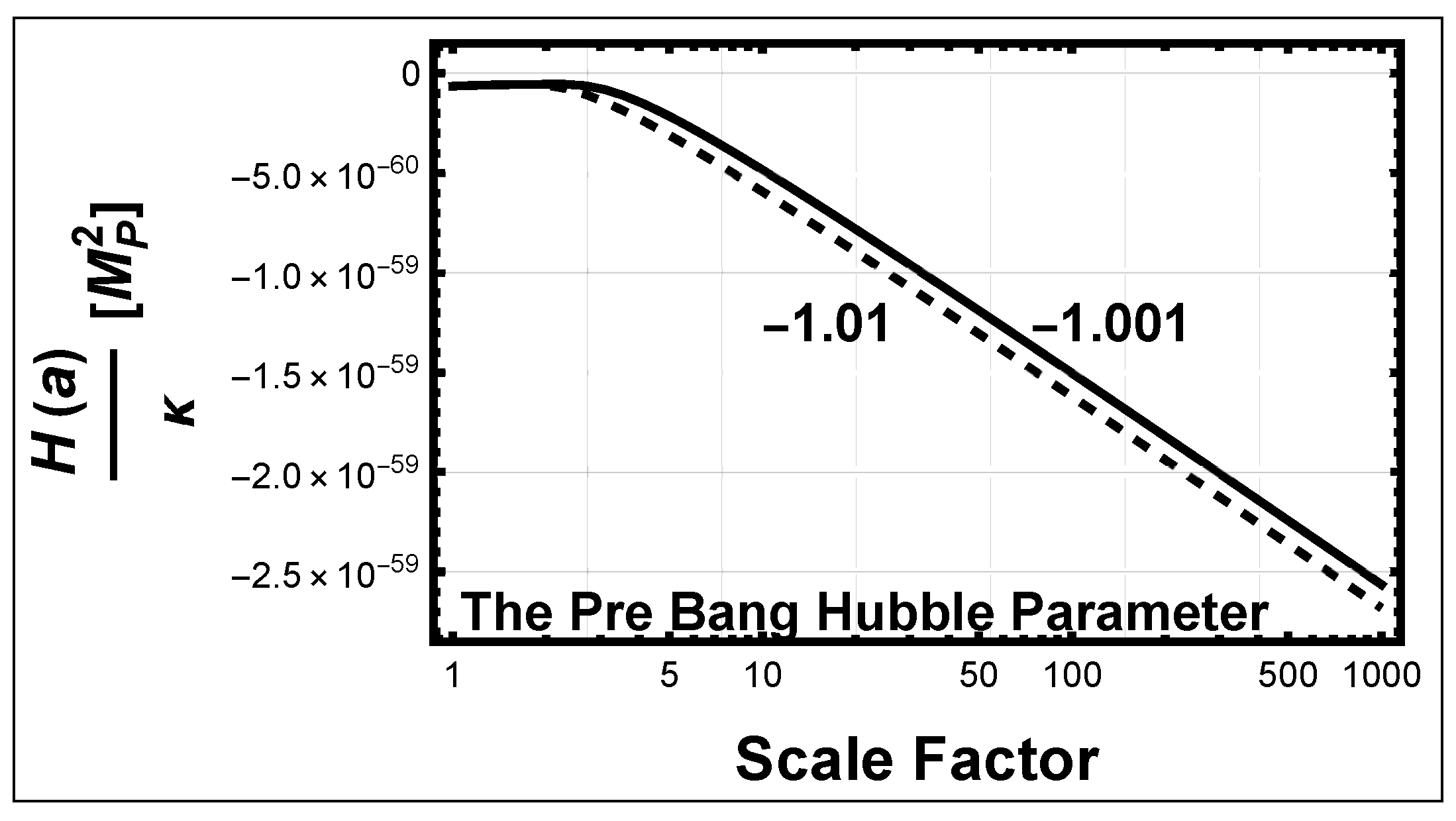
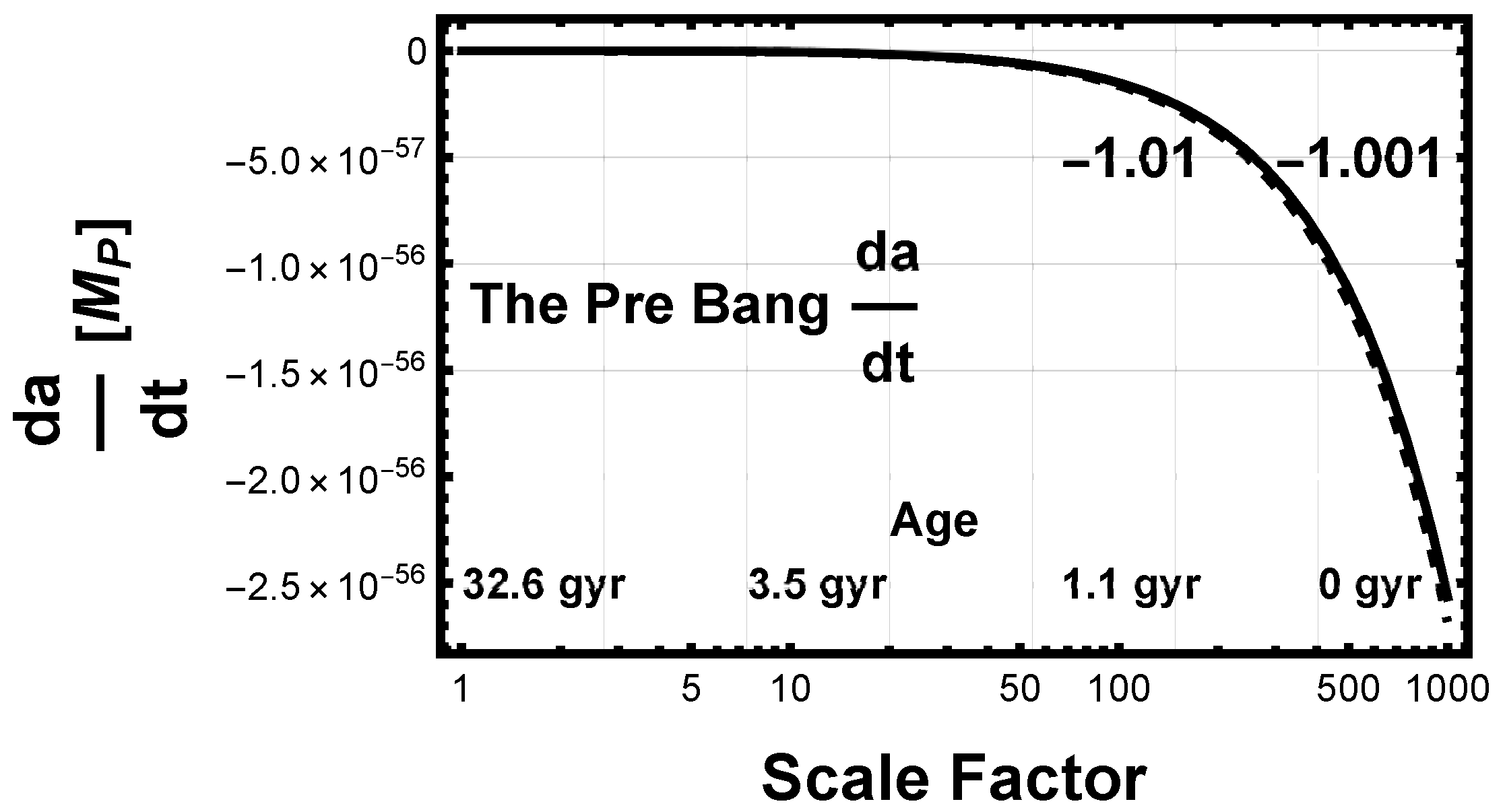
5.1.4. The Hubble Parameter
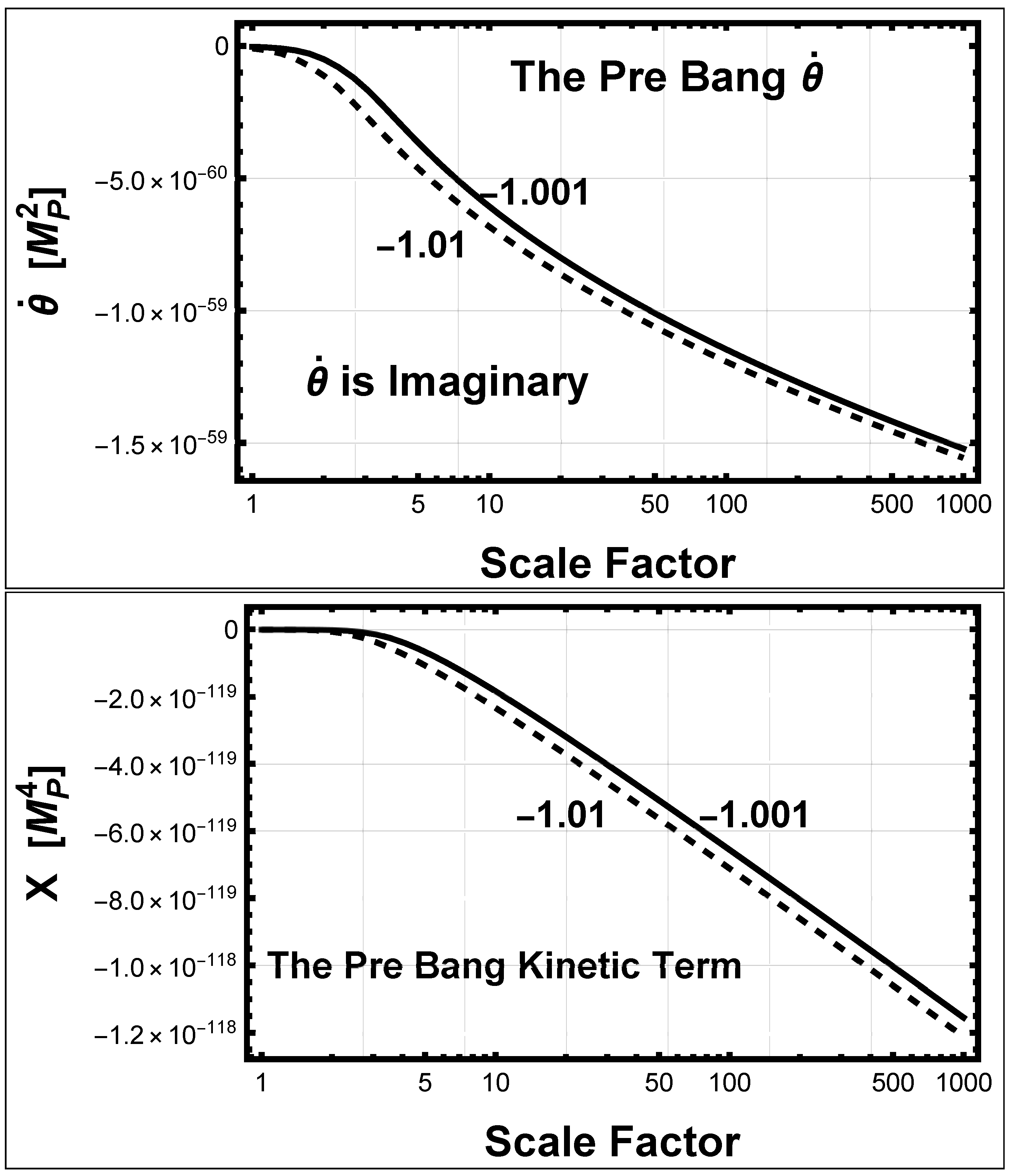
5.1.5. The Time Derivative of the Scalar and the Kinetic Term
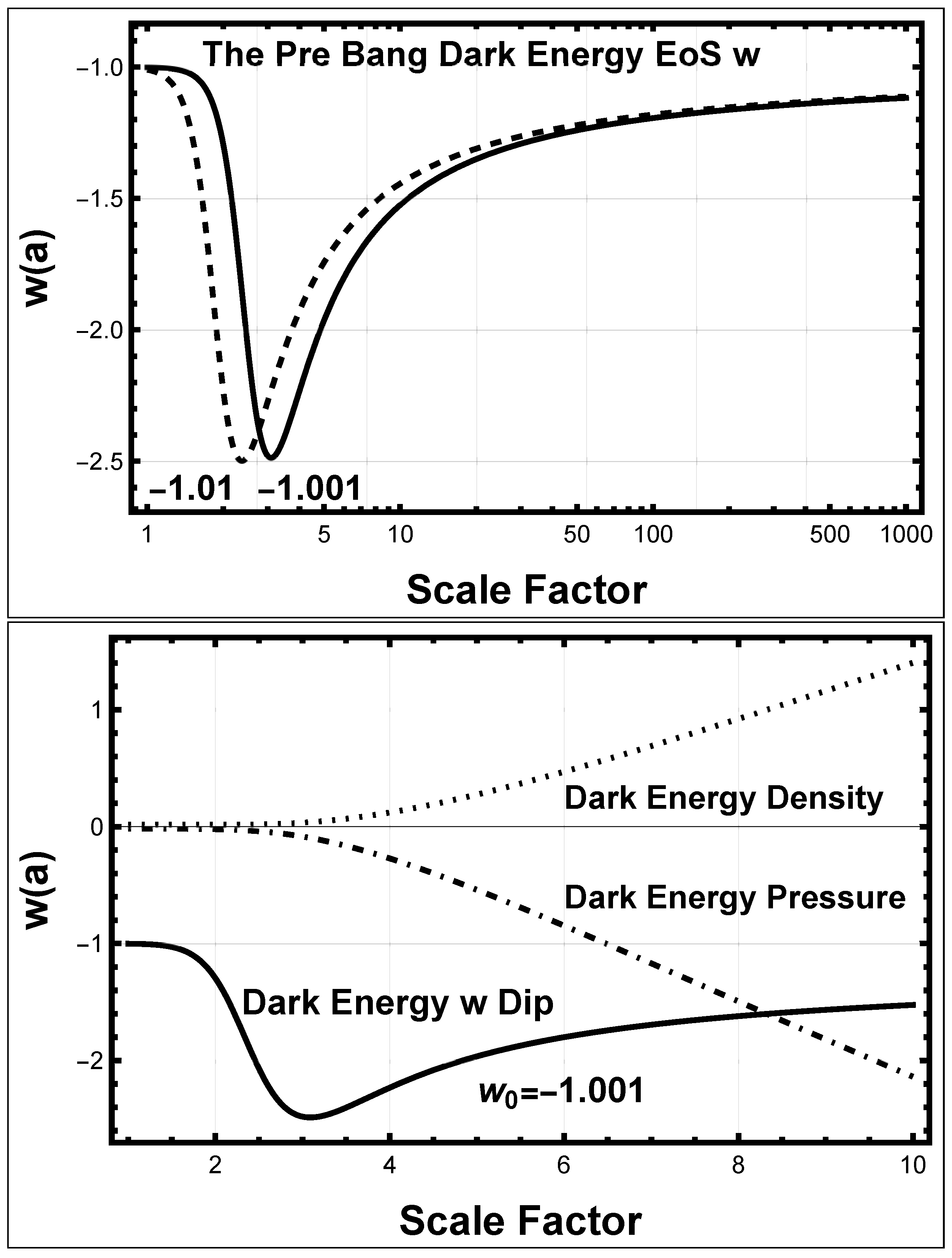
5.1.6. The Dark Energy Equation of State
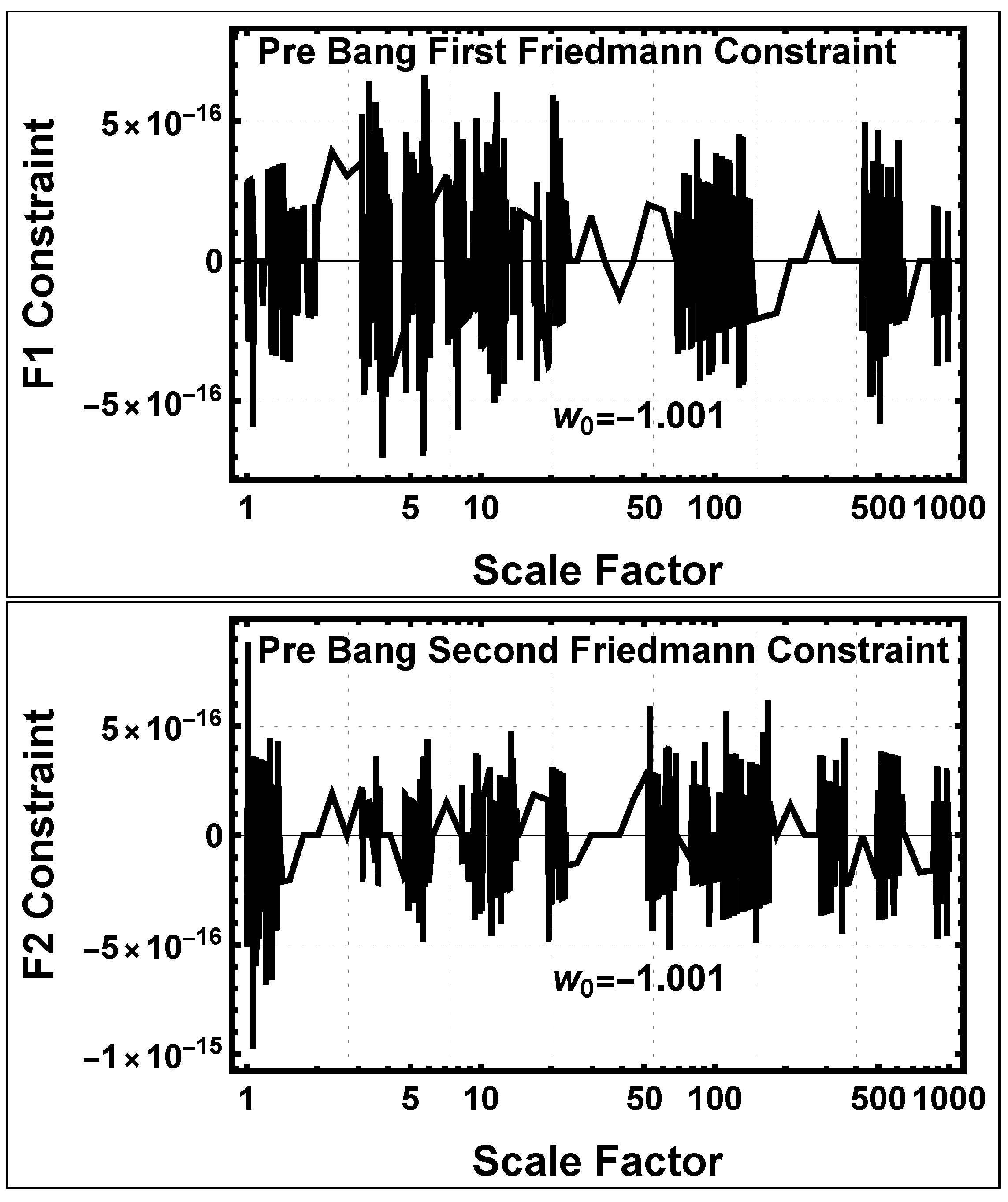
5.1.7. Friedmann Constraints in the Pre-Bang Era
5.1.8. Pre-Bang Chronology
5.1.9. Still a Quintessence Cosmology
5.2. The Physical Properties of the Transition Zone
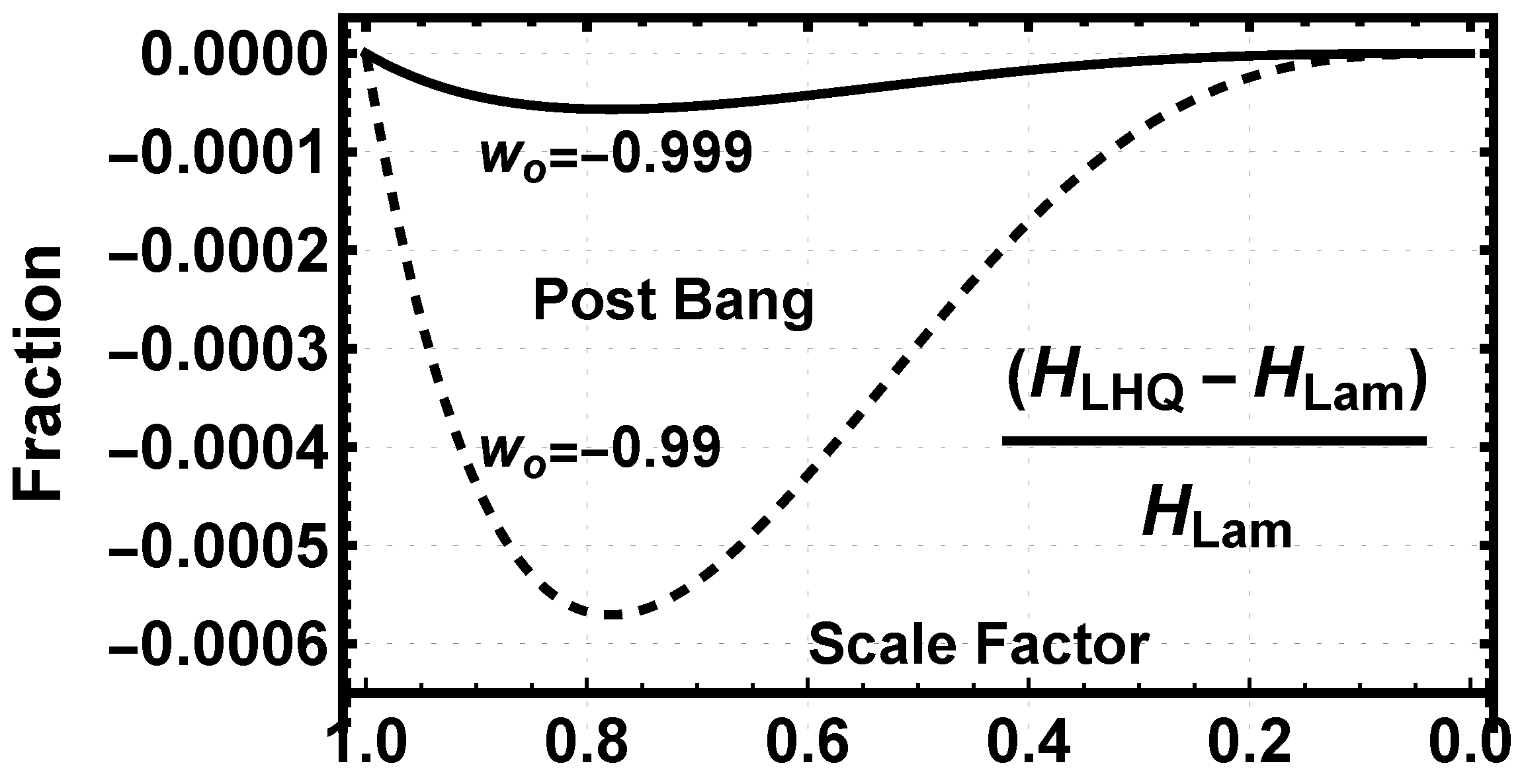
5.2.1. Expansion-Normalized Variable Examination of the Transition Zone
5.2.2. , the Lambert W Function, and the Scalar
5.2.3. The HI Dark Energy Potential
5.2.4. The Hubble Parameter
5.2.5. The Time Derivative of the Scalar and the Kinetic Term
5.2.6. The Dark Energy Density and Pressure
5.2.7. The Dark Energy Equation of State
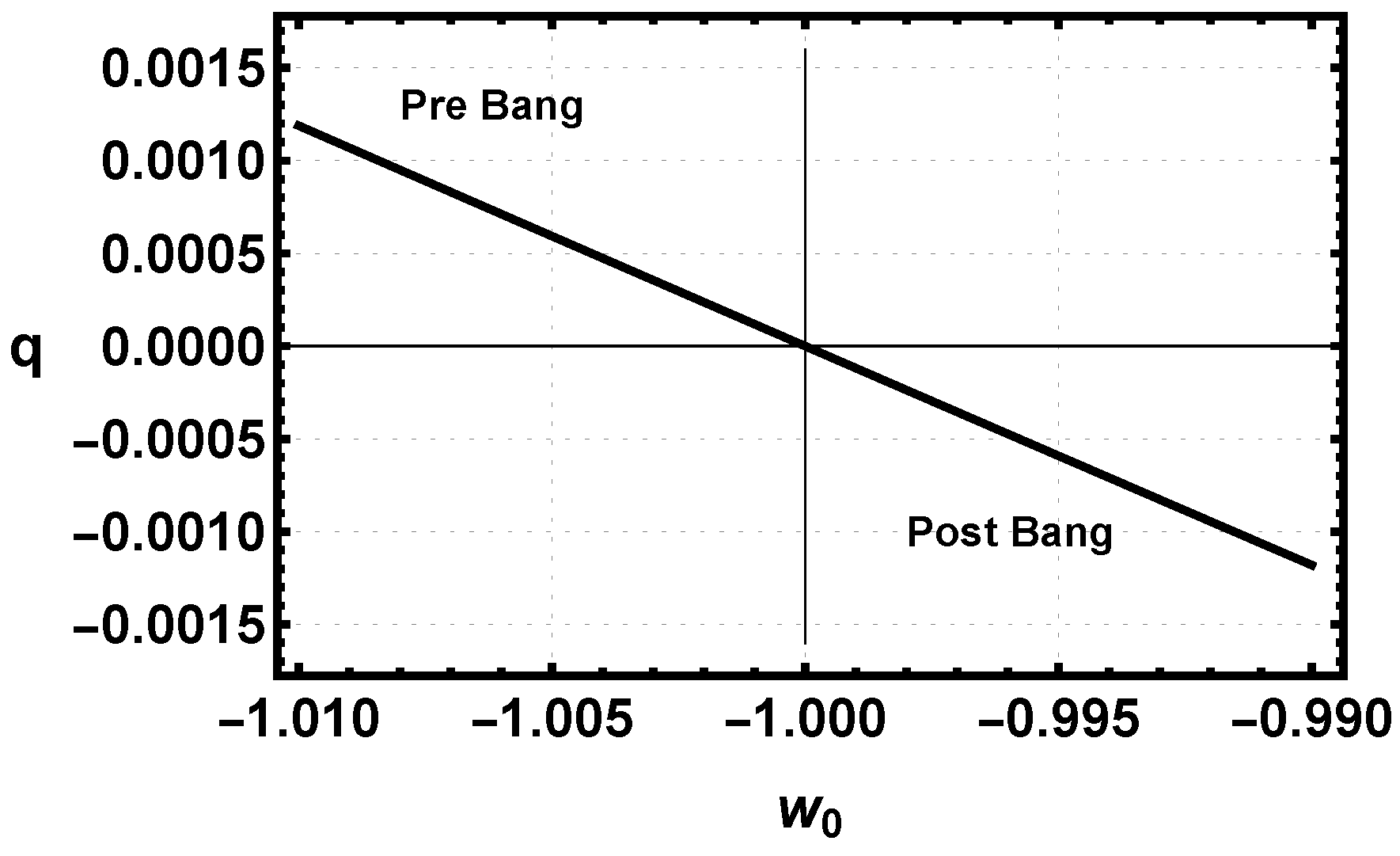
5.2.8. Friedmann Constraints in the Transition Zone
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ratra, B.; Peebles, P. Cosmological consequences of a rolling homogeneous scalar field. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 37, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, P.; Ratra, B. Cosmology with a time-variable cosmological ‘constant’. Astrophys. J. 1988, 325, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.I. Evolution of Cosmological Parameters and Fundamental Constants in a Flat Quintessence Cosmology: A Dynamical Alternative to ΛCDM. Universe 2023, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olver, F.W.J.; Lozier, D.W.; Boisvert, R.F.; Clark, C.W. NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Chapter 4; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Adame, A.G.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Alexander, D.M.; Alvarez, M.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; Armengaud, E.; et al. DESI 2024 VI: Cosmological Constraints from the Measurements of Baryon Acoustic Oscillations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2024.03002v1. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, P.; Sen, A.A. Model-independent cosmological inference post DESI DR1 BAO measurements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.19178v1. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, N. Dynamical dark energy in the light of DESI 2024 data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.00634. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.D.; Hu, J.P.; Wang, F.Y. Uncorrelated estimations of H0 redshift evolution from DESI baryon acoustic oscillation observations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.02019v1. [Google Scholar]
- Orchard, L.; Cardenas, V.H. Probing Dark Energy Evolution Post-DESI 2024. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.05579v1. [Google Scholar]
- Pourojaghi, S.; Mlekjani, M.; Davari, Z. Cosmological constraints on dark energy parametrizations after DESI 2024: Persistent deviation from standard ΛCDM cosmology. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.09767v1. [Google Scholar]
- Giare, W.; Najafi, M.; Pan, S.; Di Valentino, E.; Firouzjaee, J.T. Robust Preference for Dynamical Dark Energy in DESI BAO and SN Measurements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.16689v1. [Google Scholar]
- Dinda, B.R.; Maartens, R. Model-agnostic assessment of dark energy after DESI DR1 BAO. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.17252v1. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwll, R.R. A phantom menace? Cosmological consequences of a dark energy component with super-negative equation of state. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 545, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M.; Hoffman, M.; Trodden, M. Can the dark energy equation-of-state parameter w be less than −1? Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 023509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, J.M.; Jeon, S.Y.; Moore, G.D. The phantom menaced: Constraints on low-energy effective ghosts. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 043543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, R.J. Phantom dark energy, cosmic doomsday, and the coincidence problem. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 063519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikman, A. Gravitational waves from inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 023525. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwick, K.J. The viability of phantom dark energy: A review. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 32, 1730025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barenboim, G.; Kinney, W.H.; Morse, M.J.P. Phantom Dirac-Born-Infeld dark energy. Phys. Rev. D. 2018, 98, 083531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, J.K.; Caldwell, R.; Steinhardt, P.J.; Armendariz-Picon, C.; Mukhanov, V. Measuring the speed of sound of quintessence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartle, J.B.; Hawking, S.W. Wave function of the universe. Phys. Rev. D 1983, 28, 2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.W. The quantum state of the universe. Nucl. Phys. B 1984, 239, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartle, J.B.; Hawking, S.W.; Hertog, T. Classical universes of the no-boundary quantum state. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 123537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartle, J.; Hertog, T. Anthropic bounds on Λ from the no-boundary quantum state. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 123516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.W. Singularities and the geometry of spacetime. Eur. Phys. J. H 2014, 39, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. Gravitational collapse and space-time singularities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1965, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. On gravitational collapse. Contemp. Phys. 1969, 1, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gravitational Collapse: The role of General Relativity. Riv. Del Nuovo Dimento Numero Speziale 1969, 1, 252–276.
- Gasperini, M.; Veneziano, G. Pre-big-bang in string cosmology. Astropart Phys. 1993, 1, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.; Ovrut, B.A.; Seiberg, N.; Steinhardt, P.J.; Turok, N. From big crunch to big bang. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 65, 086007-1–086007-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A.D. Eternally existing self-reproducing chaotic inflanationary universe. Phys. Lett. B 1986, 175, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, P.J.; Turok, N. Cosmic evolution in a cyclic universe. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 65, 126003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, P.J.; Turok, N. A cyclic model of the universe. Science 2002, 296, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Lu, Y.; Shen, Y.-G. Cyclic universe due to phantom and quintessence. Gen. Relativ. Gravity 2014, 46, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Veneziano, G. A model for the Big Bounce. J. Cosmol. Astroparit. Phys. 2004, 3, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde, S.; Bohmer, C.; Carloni, S.; Copeland, E.; Fang, W.; Tamanini, N. Dynamical systems applied to cosmology: Dark energy and modified gravity. Phys. Rep. 2018, 775–777, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.I. Beta function quintessence cosmological parameters and fundamental constants—I. Power and inverse power law dark energy potentials. MNRAS 2018, 477, 4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.I. Beta function quintessence cosmological parameters and fundamental constants—II. Exponential and logarithmic dark energy potentials. MNRAS 2019, 482, 5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| The Boundary Condition and Constant Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-Bang | Pre-Bang | |||
| 73 | 73 | |||
| −0.99 | −0.999 | −1.01 | −1.001 | |
| 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | |
| 8.58555 × | 8.56511 × | 8.54043 × | 8.56059 × | |
| 0.2999 | 0.2999 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 3.6783 × | 3.6783 × | 3.67952 × | 3.67952 × | |
| 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 1.22651 × | 1.22651 × | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| M | 1.01518 × | 1.01347 × | 1.01518 × | 1.01347 × |
| 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thompson, R.I. Non-Canonical Dark Energy Parameter Evolution in a Canonical Quintessence Cosmology. Universe 2024, 10, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10090356
Thompson RI. Non-Canonical Dark Energy Parameter Evolution in a Canonical Quintessence Cosmology. Universe. 2024; 10(9):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10090356
Chicago/Turabian StyleThompson, Rodger I. 2024. "Non-Canonical Dark Energy Parameter Evolution in a Canonical Quintessence Cosmology" Universe 10, no. 9: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10090356
APA StyleThompson, R. I. (2024). Non-Canonical Dark Energy Parameter Evolution in a Canonical Quintessence Cosmology. Universe, 10(9), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10090356






